EFPC: An Environmentally Friendly Power Control Scheme for Underwater Sensor Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Impact of Anthropogenic Noise on Marine Mammals
| Criterion | Criterion Definition | Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| Level A | PTS (injury) conservatively based on TTS | 180 dB re µPa a |
| Level B | Behavioral disruption for impulsive noise | 160 dB re µPa a |
3. EFPC Power Control Scheme
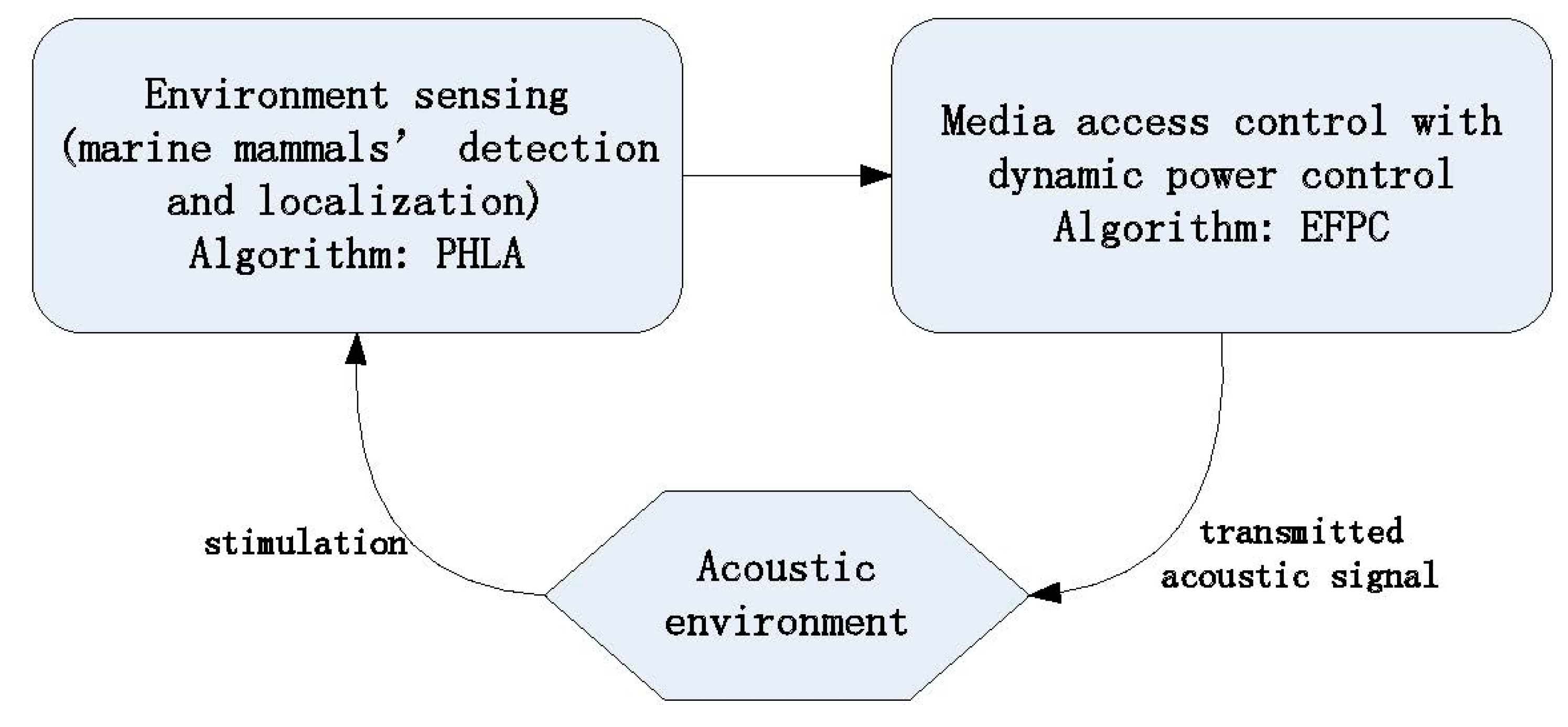
3.1. Power Control Scheme Overview
3.2. Environmentally Friendly Power Control Scheme
3.2.1. EF-MAC

3.2.2. Power Control Algorithm: EFPC
Exclusive Mode
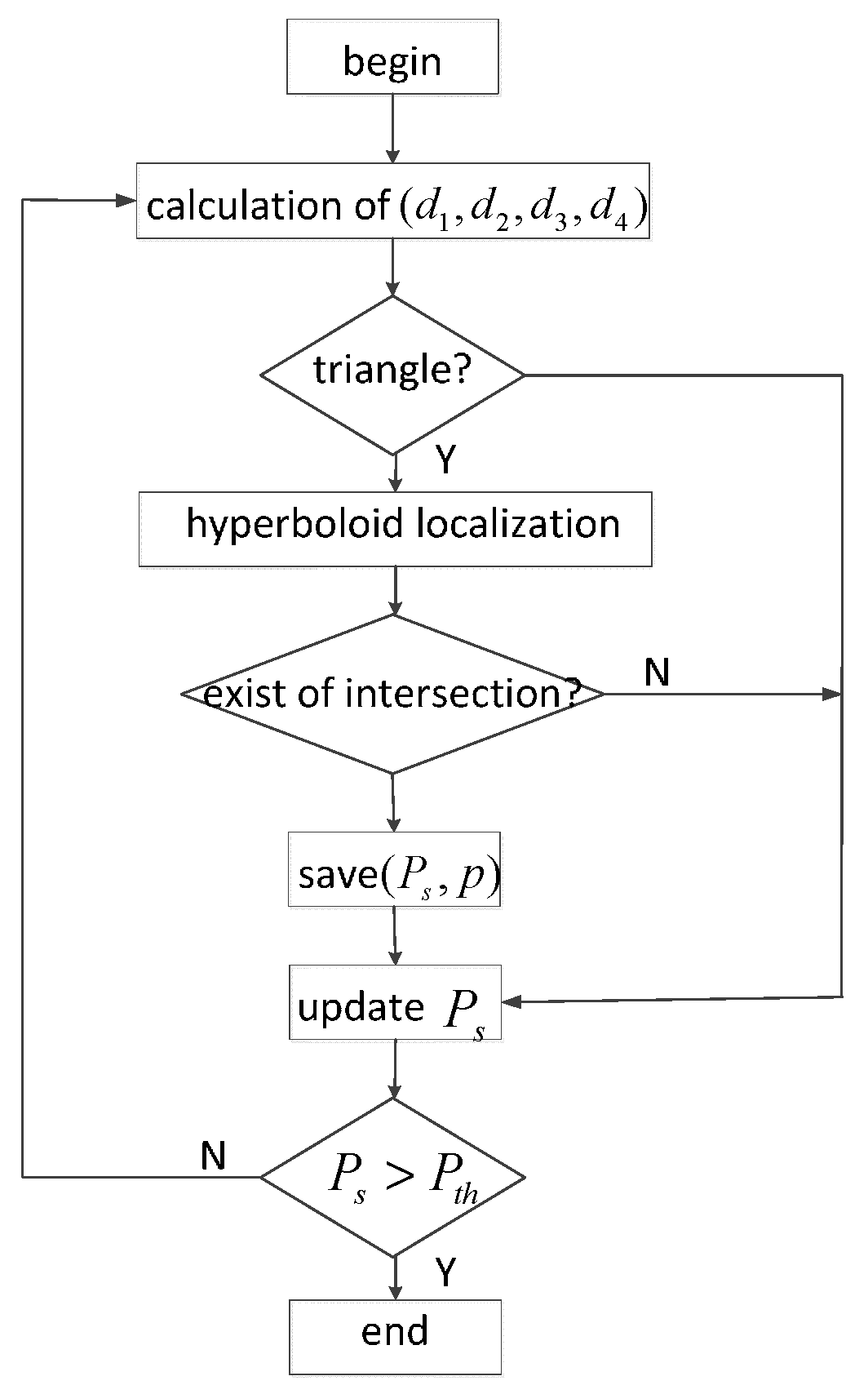
3.3. PHLA: Passive Hyperboloid Localization Algorithm

- Only one and a corresponding position exist. This value can be concluded as the position of the target;
- None of exists. This may result from the blind area in hyperboloid localization, which will be discussed later. The PHLA algorithm failure;
- More than one exists. Then a best qualified node is selected based on Equations (17)–(21).
4. Evaluation
| Maximum Transmission Range | 3000 m |
|---|---|
| Simulation time | 104 s |
| Full power | 40 W |


4.1. PHLA Evaluation

4.1.1. Success Rate of Localization
| Velocity | v1 | v2 | v3 | v4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 m/s | 0.918 (0.893) | 0.897 (0.889) | 0.917 (0.891) | 0.917 (0.890) |
| 10 m/s | 0.901 (0.878) | 0.899 (0.873) | 0.889 (0.875) | 0.897 (0.876) |
| 15 m/s | 0.896 (0.873) | 0.875 (0.860) | 0.897 (0.858) | 0.893 (0.851) |
| 20 m/s | 0.916 (0.884) | 0.879 (0.861) | 0.907 (0.870) | 0.870 (0.862) |
| Deployment | Average Success Rate of Localization |
|---|---|
| Scenario 1 | 89.8% |
| Scenario 2 | 87.4% |

4.1.2. Accuracy of PHLA Localization Algorithm

4.2. EFPC Evaluation
| v1 | (1, 0, 0) |
|---|---|
| v2 | (2 ,0, 0) |
| v3 | (0, 1, 0) |
| v4 | (0, 2, 0) |



5. Conclusions and Future Work
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akyildiz, I.F.; Pompili, D.; Melodia, T. Underwater acoustic sensor networks: Research challenges. Ad Hoc Netw. 2005, 3, 257–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.-H.; Kong, J.; Gerla, M.; Zhou, S. Challenges: Building scalable mobile underwater wireless sensor networks for aquatic applications. IEEE Netw. 2006, 20, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Chitre, M.; Shahabudeen, S.; Stojanovic, M. Underwater acoustic communications and networking: Recent advances and future challenges. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 2008, 42, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovic, M. Underwater Acoustic Communication—For the Wiley Encyclopedia of Electrical and Electronics Engineering. Avaible online: http://millitsa.coe.neu.edu/sites/millitsa.coe.neu.edu/files/ency3_0.pdf (accessed on 4 November 2015).
- Partan, J.; Kurose, J.; Levine, B.N. Spatial Reuse in Underwater Acoustic Networks Using RTS/CTS Mac Protocols. Available online: http://forensics.umass.edu/pubs/Partan.UM-CS-2010-045.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2015).
- Singh, S.; Raghavendra, C.S. PAMAS—Power aware multi-access protocol with signalling for ad hoc networks. ACM SIGCOMM Comp. Commun. Rev. 1998, 28, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Katz, R.H.; Krishnamurthy, S.V.; Dao, S.K. Distributed power control in ad-hoc wireless networks. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, San Diego, CA, USA, 30 September–3 October 2001; pp. 59–66.
- Muqattash, A.; Krunz, M. POWMAC: A single-channel power-control protocol for throughput enhancement in wireless ad hoc networks. IEEE J Sel Area Comm. 2005, 23, 1067–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.S.; Lim, H.; Hou, J.C. Improving spatial reuse through tuning transmit power, carrier sense threshold, and data rate in multihop wireless networks. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 23–26 September 2006; pp. 366–377.
- Jornet, J.; Stojanovic, M. Distributed power control for underwater acoustic networks. In Proceedings of MTS/IEEE OCEANS Conference, Kobe, Japan, 8–11 April 2008; pp. 1–7.
- Rodoplu, V.; Park, M.K. An energy-efficient MAC protocol for underwater wireless acoustic networks. In Proceedings of MTS/IEEE OCEANS conference, Washington, WA, USA, 18–23 September 2005; pp. 1198–1203.
- Zhou, Z.; Zhou, S.; Cui, J.-H.; Cui, S. Energy-efficient cooperative communication based on power control and selective single-relay in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2008, 7, 3066–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Mo, H.; Cui, J.-H.; Jin, Z. UPC-MAC: A power control mac protocol for underwater sensor networks. In Wireless Algorithms, Systems, and Applications; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 377–390. [Google Scholar]
- Stojanovic, M. On the relationship between capacity and distance in an underwater acoustic communication channel. ACM SIGMOBILE Mob. Comput. Commun. Rev. 2007, 11, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Pu, L.; Zuba, M.; Peng, Z.; Cui, J.-H. Challenges and opportunities of underwater cognitive acoustic networks. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. 2014, 2, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doksæter, L. Behavioural Effects of Naval Sonars on Fish and Cetaceans. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, A.J.; Soto, N.A.; Baldwin, A.L.; Bateson, M.; Beale, C.; Clark, C.; Deak, T.; Edwards, T.; Godinho, A.; Fernandes, A.; et al. Do marine mammals experience stress related to anthropogenic noise? Int. J. Comp. Psychol. 2007, 20, 274–316. [Google Scholar]
- Jepson, P.D.; Arbelo, M.; Deaville, R.; Patterson, I.A.P.; Castro, P.; Baker, J.R.; Degollada, E.; Ross, H.M.; Herráez, P.; Pocknell, A.M.; et al. Gas-bubble lesions in stranded cetaceans. Nature 2003, 425, 575–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchner, H.; Aichner, R.; Stenglein, J.; Teutsch, H.; Kellermann, K. Simultaneous localization of multiple sound sources using blind adaptive MIMO filtering. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 18–23 March 2005; pp. iii/97–iii100.
- Dmochowski, J.P.; Benesty, J.; Affes, S. Broadband MUSIC: Opportunities and challenges for multiple source localization. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics, Hamilton, ON, Canada, 21–24 October 2007; pp. 18–21.
- Southall, B.L.; Bowles, A.E.; Ellison, W.T.; Finneran, J.J.; Gentry, R.L.; Greene, J.R.C.; Kastak, P.; Ketten, D.; Miller, J.; Nachtigall, P.; et al. Marine mammal noise-exposure criteria: Initial scientific recommendations. Bioacoustics 2008, 17, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, V.; Seah, W.; Choo, Y.S.; Ee, H.V. Localization in underwater sensor networks: Survey and challenges. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM International Workshop on Underwater Networks, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 25 September 2006; pp. 33–40.
- Syed, A.; Heidemann, J. Time synchronization for high latency acoustic networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Communications, Barcelona, Spain, 23–29 April 2006; pp. 1–12.
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Zuba, M.; Peng, Z.; Cui, J.-H.; Zhou, S. JSL: Joint time synchronization and localization design with stratification compensation in mobile underwater sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 9th Annual IEEE Communications Society Conference on Sensor, Mesh and Ad Hoc Communications and Networks, Seoul, Korea, 18–21 June 2012; pp. 317–325.
- Molins, M.; Stojanovic, M. Slotted FAMA: A MAC protocol for underwater acoustic networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE OCEANS 2006-Asia Pacific Conference, Singapore, 16–19 May 2007; pp. 1–7.
- Saraydar, C.U.; Mandayam, N.B.; Goodman, D.J. Efficient power control via pricing in wireless data networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2002, 50, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.F.; Zorzi, M. Modeling the underwater acoustic channel in NS-2. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Performance Evaluation Methodologies and Tools, Nantes, France, 22–27 October 2007; p. 18.
- Challa, R.N.; Shamsunder, S. 3-D spherical localization of multiple non-Gaussian sources using cumulants. In Proceedings of Statistical Signal and Array Processing, Corfu, Greece, 24–26 June 1996; pp. 101–104.
- Chan, Y.T.; Ho, K.C. A simple and efficient estimator for hyperbolic location. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1994, 42, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güvenç, İ.; Chong, C.C. A survey on TOA based wireless localization and NLOS mitigation techniques. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2009, 11, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.; Frunzke, T.; Dressler, F. Adaptive distance estimation and localization in WSN using RSSI measures. In Proceedings of the 10th Euromicro Conference Digital System Design Architectures, Methods and Tools, Lubeck, Germany, 29–31 August 2007; pp. 471–478.
- Janik, V.M. Source levels and the estimated active space of bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) whistles in the Moray Firth, Scotland. J. Comparative Physiol. A 2000, 186, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schusterman, R.J. Low false-alarm rates in signal detection by marine mammals. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1974, 55, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, Sl.; Sturtivant, C. Dolphin whistle classification for determining group identities. Signal Process. 2002, 82, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brekhovskikh, L.M.; Lysanov, Y.P. Fundamentals of Ocean Acoustics; Springer-Verlag New York: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sozer, E.M.; Stojanovic, M.; Proakis, J.G. Underwater acoustic networks. IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 2000, 25, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellakula, A.K. Acoustic Source Localization Using Time Delay Estimation. M.Sc. Thesis, Supercomputer Education and Research Centre, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, India, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, P.; Zhou, Z.; Peng, Z.; Yan, H.; Hu, T.; Cui, J.-H.; Shi, Z.; Fei, Y.; Zhou, S. Aqua-Sim: An NS-2 based simulator for underwater sensor networks. In Proceedings of the Biloxi-Marine Technology for Our Future: Global and Local Challenges, Biloxi, MS, USA, 26–29 October 2009; pp. 1–7.
- Yan, H.; Zhou, S.; Shi, Z.J.; Li, B. A DSP implementation of OFDM acoustic modem. In Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Underwater Networks, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14 September 2007; pp. 89–92.
- Cui, J.H.; Zhou, S.; Shi, Z.; O’Donnell, J.; Peng, Z.; Gerla, M.; Baschek, B.; Roy, S.; Arabshahi, P.; Zhang, X. Ocean-TUNE: A community ocean testbed for underwater wireless networks. In Proceedings of the 7th ACM International Conference on Underwater Networks and Systems, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 5–6 November 2012; p. 17.
- Guerra, F.; Casari, P.; Zorzi, M. World Ocean Simulation System (WOSS): A simulation tool for underwater networks with realistic propagation modeling. In Proceedings of the 4th ACM International Workshop on UnderWater Networks, Berkeley, CA, USA, 25 November 2009; p. 4.
- General Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans. Available Online: www.gebco.net (accessed on 4 November 2015).
- National Geophysical Data Center, Seafloor Surficial Sediment Descriptions. Available Online: www.ngdc.noaa.gov/mgg/geology/deck41.html (accessed on 25 June 2015).
- Rohr, J.J.; Fish, F.E.; Gilpatrick, J.W. Maximum swim speeds of captive and free-ranging delphinids: Critical Analysis of extraordinary performance. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2002, 18, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Q.; Su, Y.; Jin, Z.; Yao, G. EFPC: An Environmentally Friendly Power Control Scheme for Underwater Sensor Networks. Sensors 2015, 15, 29107-29128. https://doi.org/10.3390/s151129107
Yang Q, Su Y, Jin Z, Yao G. EFPC: An Environmentally Friendly Power Control Scheme for Underwater Sensor Networks. Sensors. 2015; 15(11):29107-29128. https://doi.org/10.3390/s151129107
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Qiuling, Yishan Su, Zhigang Jin, and Guidan Yao. 2015. "EFPC: An Environmentally Friendly Power Control Scheme for Underwater Sensor Networks" Sensors 15, no. 11: 29107-29128. https://doi.org/10.3390/s151129107
APA StyleYang, Q., Su, Y., Jin, Z., & Yao, G. (2015). EFPC: An Environmentally Friendly Power Control Scheme for Underwater Sensor Networks. Sensors, 15(11), 29107-29128. https://doi.org/10.3390/s151129107






