Random Weighting, Strong Tracking, and Unscented Kalman Filter for Soft Tissue Characterization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Nonlinear Hunt-Crossley Contact Model
3. Analysis of Unscented Kalman Filter
4. Random Weighting Strong Tracking Unscented Kalman Filter
4.1. Correction of Predicted State Covariance
4.2. Identification of Model Error
4.3. Algorithm
5. Performance Evaluation and Discussions
5.1. Initial State Estimation Error
5.2. Model Simplification Error
5.3. Local Modelling Error
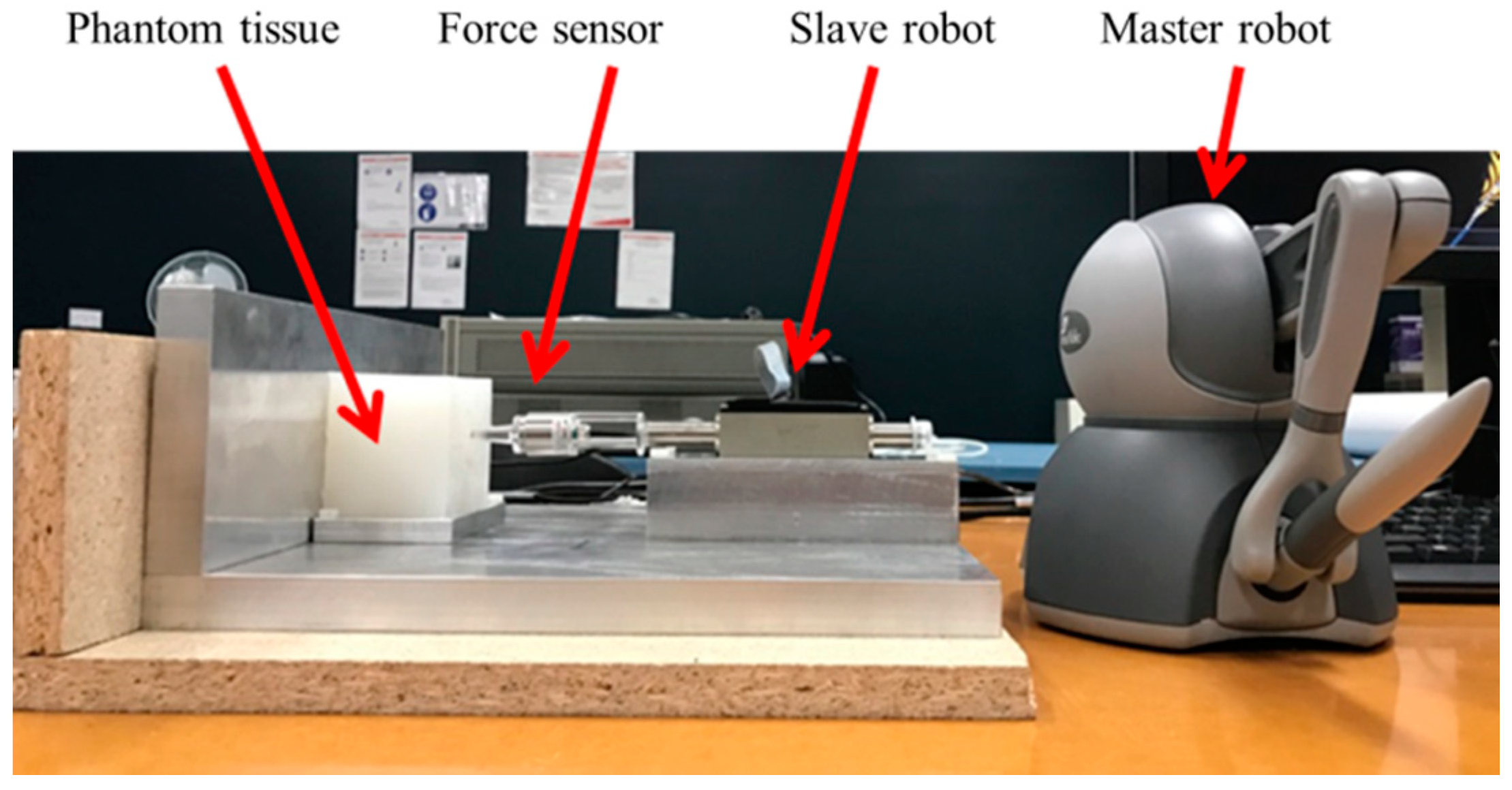
5.4. Robotic Indentation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Enayati, N.; De Momi, E.; Ferrigno, G. Haptics in Robot-Assisted Surgery: Challenges and Benefits. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 9, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunachalam, S.; Ansell, J. The use of simulation training for robotic-assisted surgery. J. Surg. Simul. 2017, 4, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhong, Y.; Gu, C. Deformable models for surgical simulation: A survey. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, B.; Sciavicco, L.; Villani, L.; Oriolo, G. Robotics-Modelling, Planning and Control. Advanced Textbooks in Control and Signal Processing Series; Springer: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell, J.C. IV. On the dynamical theory of gases. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1867, 157, 49–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbé, L.; Bayle, B.; de Mathelin, M.; Gangi, A. In vivo model estimation and haptic characterization of needle insertions. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2007, 26, 1283–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, A.; Albakri, A.; Liu, C.; Bascetta, L.; De Momi, E.; Poignet, P. Hunt-Crossley model based force control for minimally invasive robotic surgery. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2016, 29, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddadi, A.; Hashtrudi-Zaad, K. Real-time identification of Hunt–Crossley dynamic models of contact environments. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2012, 28, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diolaiti, N.; Melchiorri, C.; Stramigioli, S. Contact impedance estimation for robotic systems. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2005, 21, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Lamata, P.; Lee, J.; Moireau, P.; Chapelle, D.; Smith, N. Myocardial transversely isotropic material parameter estimation from in-silico measurements based on a reduced-order unscented Kalman filter. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 4, 1090–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarahmadian, M.; Zhong, Y.; Gu, C.; Shin, J. Soft tissue deformation estimation by spatio-temporal Kalman filter finite element method. Technol. Health Care 2018, 1–9, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jazwinski, A.H. Stochastic Processes and Filtering Theory; Courier Corporation: North Chelmsford, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Asadian, A.; Kermani, M.R.; Patel, R.V. A novel force modeling scheme for needle insertion using multiple Kalman filters. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2012, 61, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julier, S.J.; Uhlmann, J.K. New extension of the Kalman filter to nonlinear systems. In Proceedings of the Aerospace/Defense Sensing, Simulations and Controls, Orlando, FL, USA, 20–25 April 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Hu, G.; Zhong, Y. Windowing and random weighting-based adaptive unscented Kalman filter. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2015, 29, 201–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Abolhassani, N.; Jung, S.; Okamura, A.M.; Judkins, T.N. Augmented reality and haptic interfaces for robot-assisted surgery. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2012, 8, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SHIN, J.; Zhong, Y.; Smith, J.; Gu, C. A New Parameter Estimation Method For Online Soft Tissue Characterization. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 2016, 16, 1640019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Lv, H.; Wu, J. In-flight initial alignment for small UAV MEMS-based navigation via adaptive unscented Kalman filtering approach. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2017, 61, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Schwarz, K. Adaptive Kalman filtering for INS/GPS. J. Geodesy 1999, 73, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jwo, D.-J.; Weng, T.-P. An adaptive sensor fusion method with applications in integrated navigation. J. Navig. 2008, 61, 705–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wei, W.; Zhong, Y.; Subic, A. Sage windowing and random weighting adaptive filtering method for kinematic model error. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2015, 51, 1488–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.-B.; Li, S.-Y. Autonomous navigation filtering algorithm for spacecraft based on strong tracking UKF. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2011, 33, 2485–2491. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J. A strong tracking nonlinear robust filter for eye tracking. J. Control Theory Appl. 2010, 8, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.Y.; Choi, W.S. Robust positioning technique in low-cost DR/GPS for land navigation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2006, 55, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, K.; Crossley, F. Coefficient of restitution interpreted as damping in vibroimpact. J. Appl. Mech. 1975, 42, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kailath, T. An innovations approach to least-squares estimation—Part I: Linear filtering in additive white noise. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1968, 13, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalanobis, P.C. On the generalized distance in statistics. Proc. Natl. Inst. Sci. 1936, 2, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Arras, K.O.; Tomatis, N.; Jensen, B.T.; Siegwart, R. Multisensor on-the-fly localization: Precision and reliability for applications. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2001, 34, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, J.M.; Jiménez-Valverde, A.; Hortal, J. The uncertain nature of absences and their importance in species distribution modelling. Ecography 2010, 33, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, J.L.; Vavalle, N.A.; Kasting, K.E.; Long, B.; Tanaka, M.L.; Sanger, P.A.; Schnell, K.; Conner-Kerr, T.A. Use of Silicone Materials to Simulate Tissue Biomechanics as Related to Deep Tissue Injury. Adv. Skin Wound Care 2015, 28, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Errors (mN) | UKF | RWSTUKF |
|---|---|---|
| Mean error | 16.8818 | 1.8092 |
| Max error | 74.2650 | 13.8870 |
| RMSE | 30.2395 | 2.9133 |
| Errors (mN) | UKF | RWSTUKF |
|---|---|---|
| Mean error | 0.4068 | 0.0897 |
| Max error | 1.4844 | 0.3039 |
| RMSE | 0.5394 | 0.1063 |
| Errors (mN) | UKF | RWSTUKF |
|---|---|---|
| Mean error | 0.9531 | 0.6911 |
| Max error | 6.7853 | 2.5880 |
| RMSE | 1.4200 | 0.8590 |
| Errors (N) | UKF | RWSTUKF |
|---|---|---|
| Mean error | 0.4131 | 0.2624 |
| Max error | 9.6501 | 3.3760 |
| RMSE | 0.9332 | 0.5088 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, J.; Zhong, Y.; Oetomo, D.; Gu, C. Random Weighting, Strong Tracking, and Unscented Kalman Filter for Soft Tissue Characterization. Sensors 2018, 18, 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051650
Shin J, Zhong Y, Oetomo D, Gu C. Random Weighting, Strong Tracking, and Unscented Kalman Filter for Soft Tissue Characterization. Sensors. 2018; 18(5):1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051650
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Jaehyun, Yongmin Zhong, Denny Oetomo, and Chengfan Gu. 2018. "Random Weighting, Strong Tracking, and Unscented Kalman Filter for Soft Tissue Characterization" Sensors 18, no. 5: 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051650
APA StyleShin, J., Zhong, Y., Oetomo, D., & Gu, C. (2018). Random Weighting, Strong Tracking, and Unscented Kalman Filter for Soft Tissue Characterization. Sensors, 18(5), 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051650






