Adaptive Linear Quadratic Attitude Tracking Control of a Quadrotor UAV Based on IMU Sensor Data Fusion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. System Dynamics and Problem Definition
2.1. Quadrotor UAV Dynamics
2.1.1. Attitude Model
2.1.2. Yaw Model
2.1.3. Altitude Model
2.2. Problem Statement
- Given the IMU sensor measurements of the attitude angles, design a data fusion algorithm based on (i) Kalman filtering and, for comparative analysis purposes, (ii) complementary filtering, in order to cancel the IMU sensor noise effects and produce accurate attitude state estimates;
- Design the control units to generate the command signals , , , for feeding the pulse width modulation (PWM) generator that generates the motor control input signal , per the diagram in Figure 1: (a) design an infinite-horizon ALQT controller to generate the optimal attitude control signal so that tracks its desired trajectory , minimizing the predefined quadratic performance optimal tracking and energy consumption cost functionwhere Q and R are positive constant weighting terms andis the attitude tracking error; (b) design a P yaw controller to generate and a PID altitude controller to generate ;
- Combining the designs in 1 and 2, above, real-time implement and experimentally validate the overall control scheme.
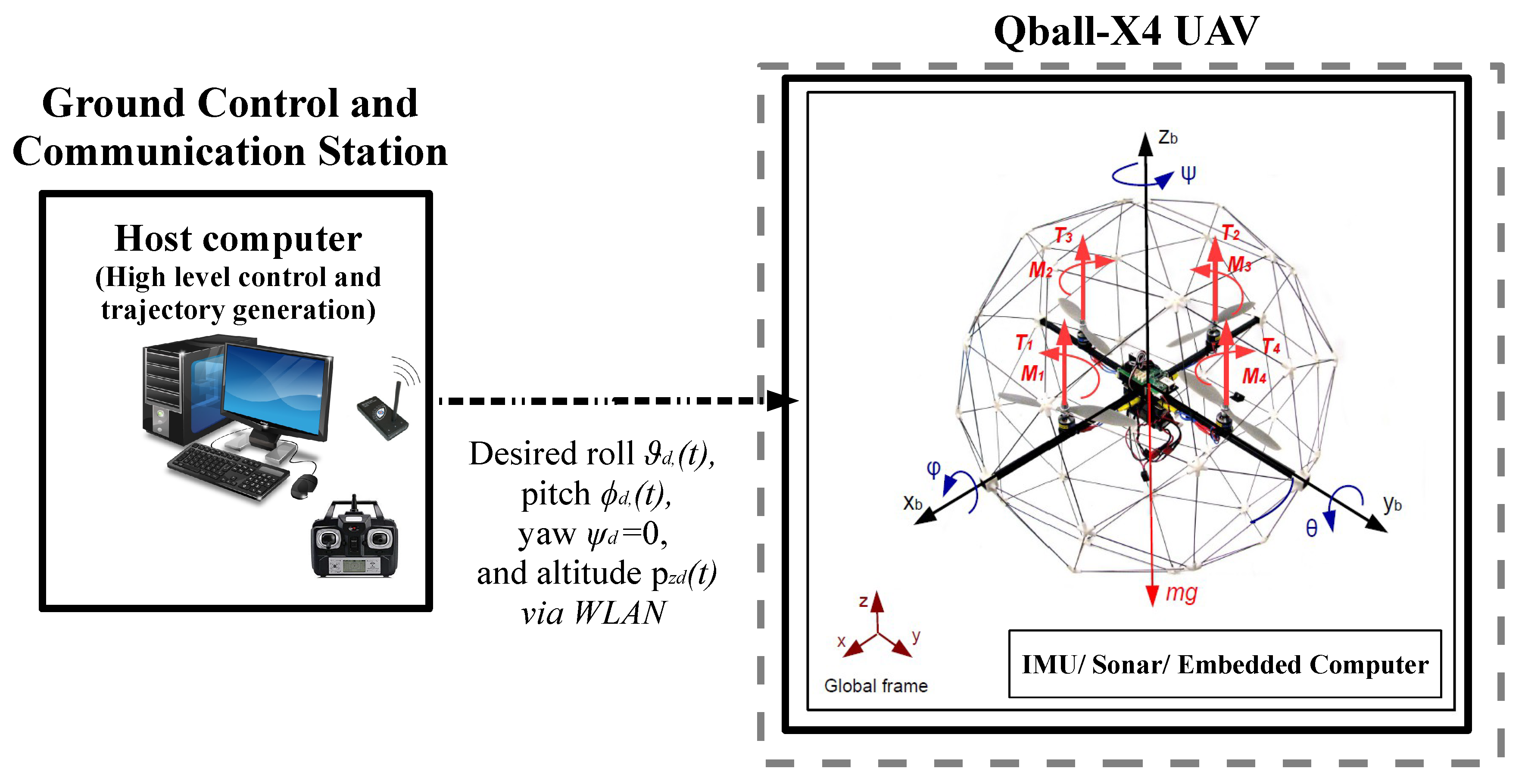
2.3. Control Approach
3. IMU Sensor Data Fusion
3.1. Attitude Determination from IMU Sensors
3.2. Attitude Estimation Using a Kalman Filter
3.3. Attitude Estimation by a Complementary Filter
4. Adaptive Optimal Attitude Tracking Control Design
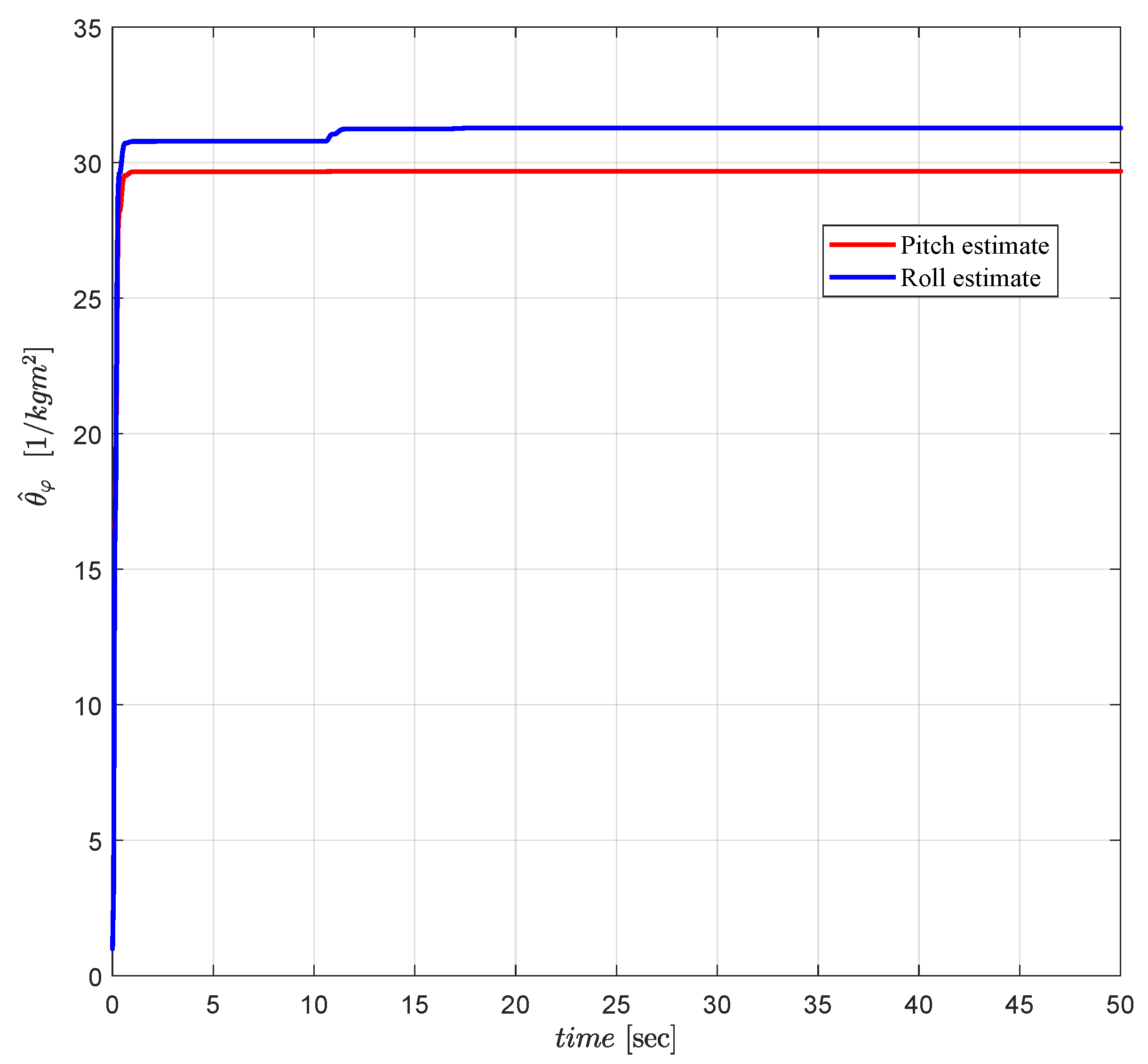
4.1. Adaptive Parameter Identification Scheme
4.2. Generic Linear Quadratic Tracking Control Design
4.3. Adaptive Linear Quadratic Tracking (ALQT) Control Design
5. Yaw and Altitude Control
5.1. Yaw Control
5.2. Altitude Control
6. Experimental Tests and Comparative Simulations
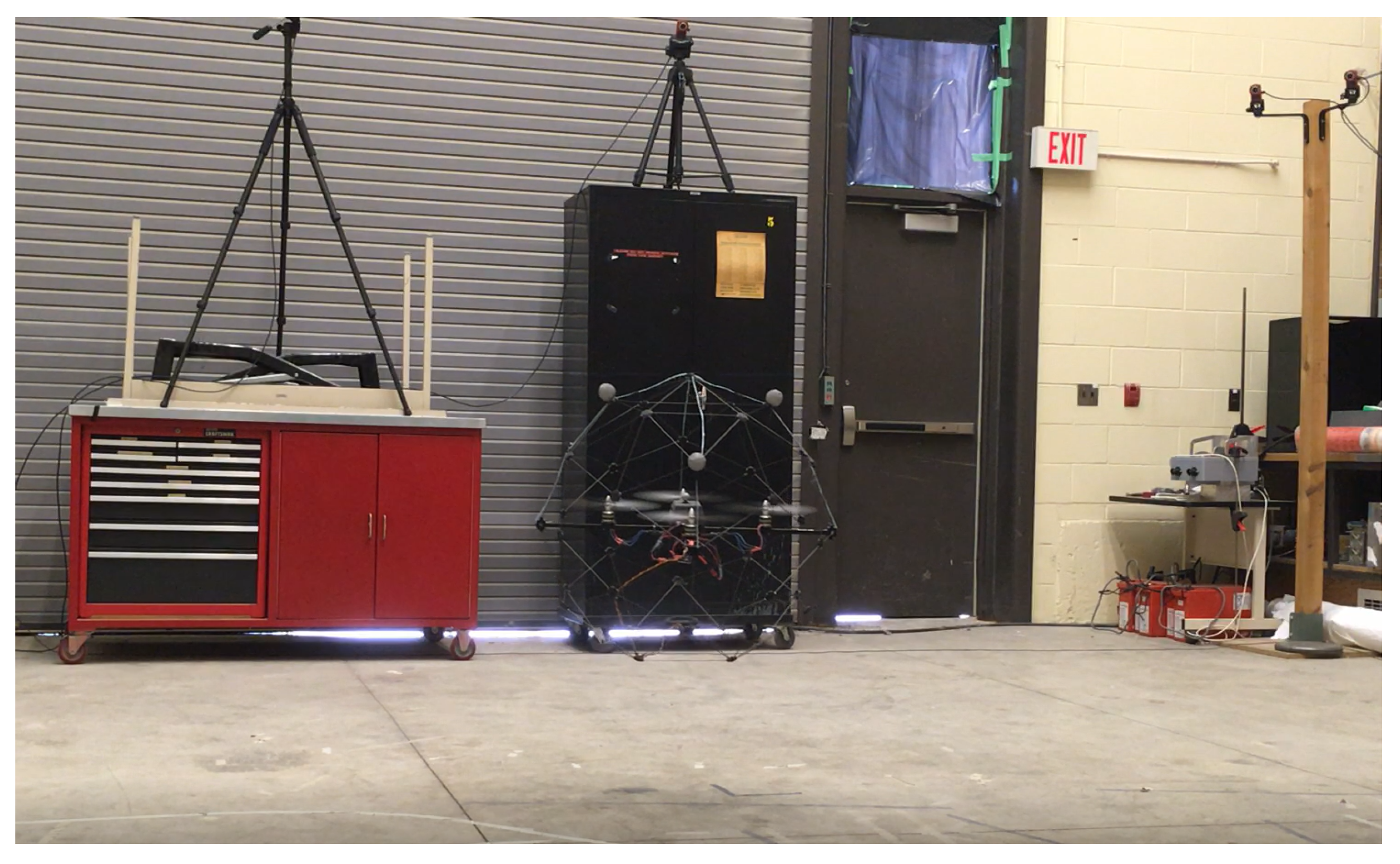
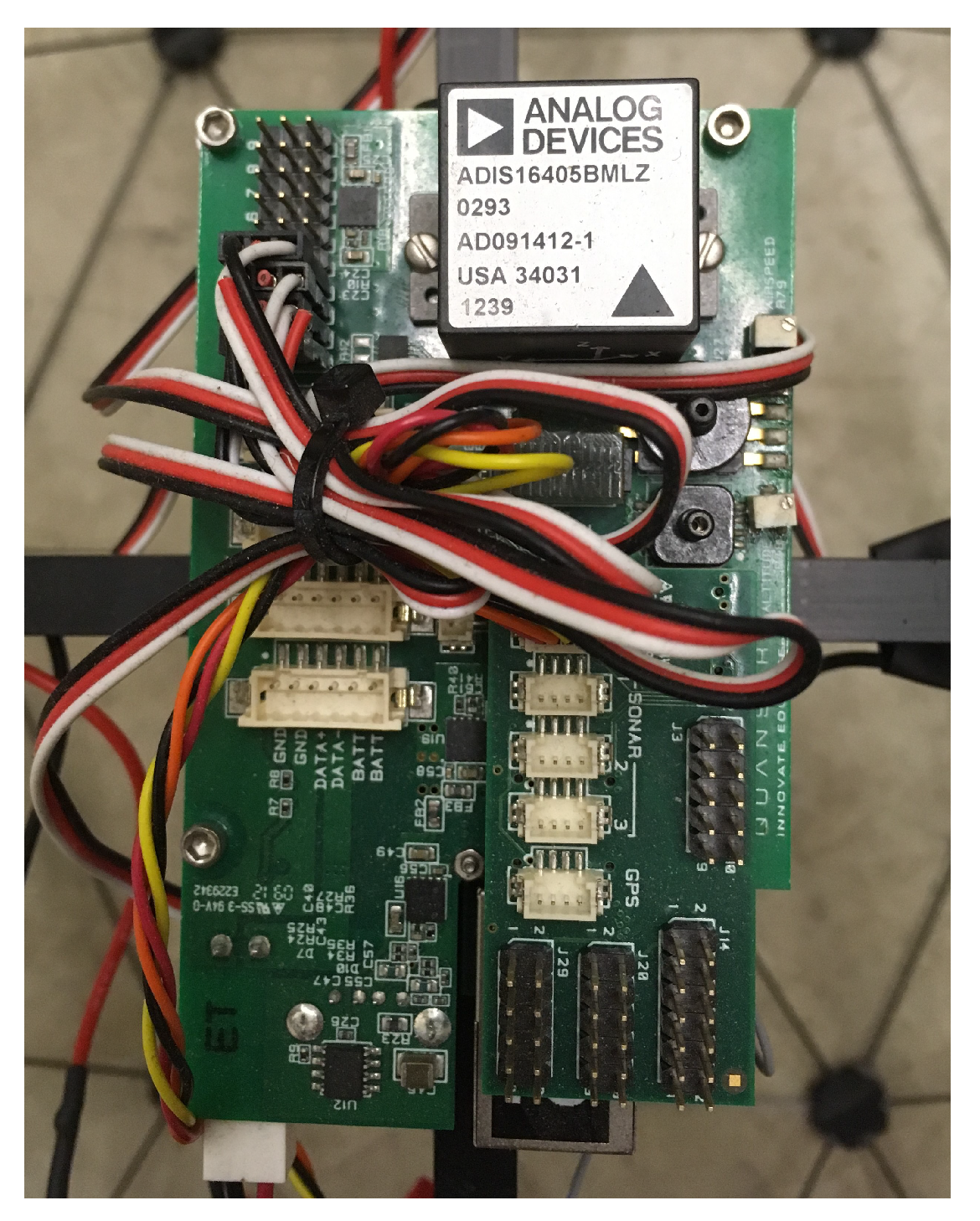
6.1. Test Platform
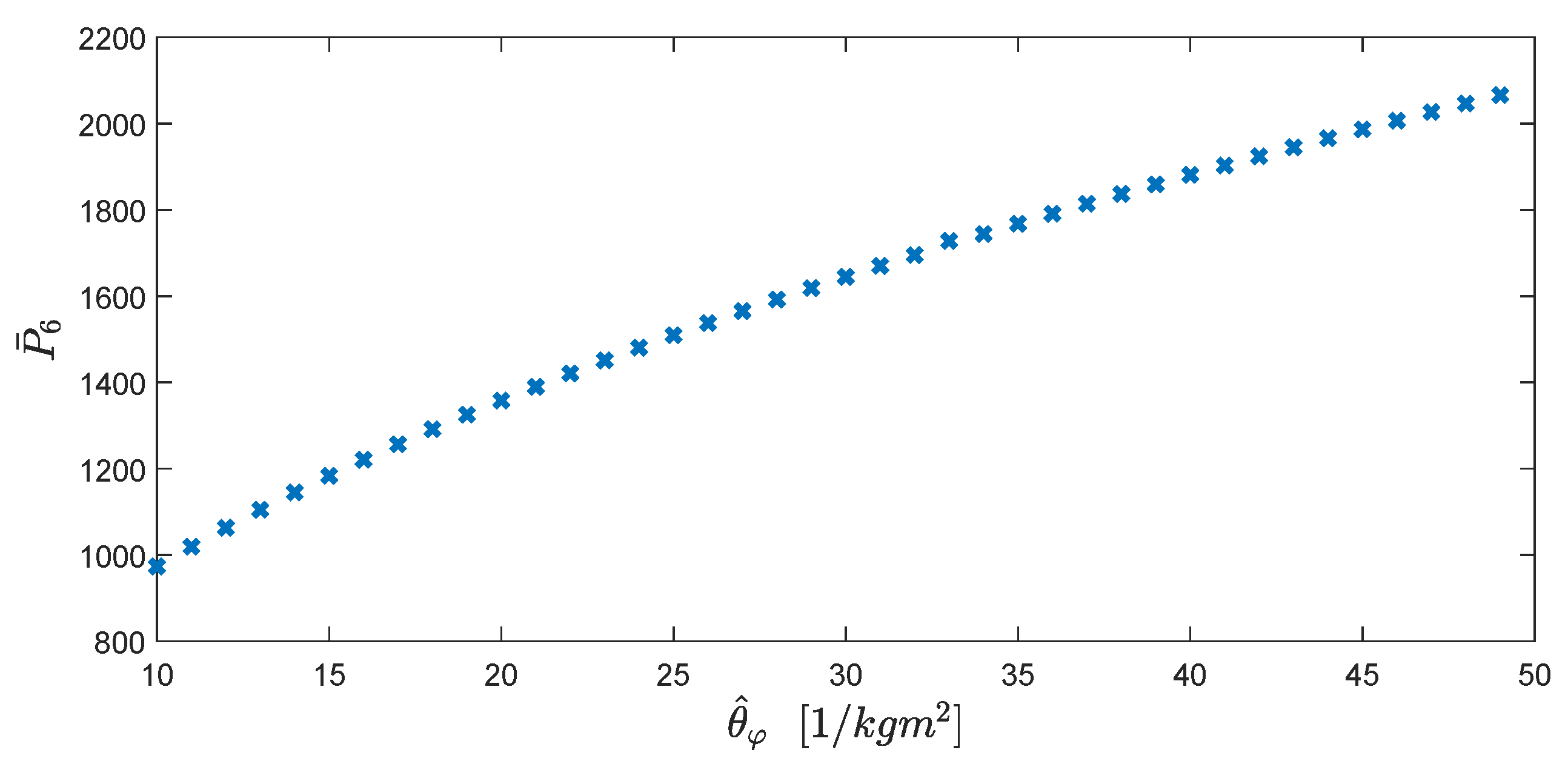
6.2. Control Design Specifications and Online Calculation of Control Parameters
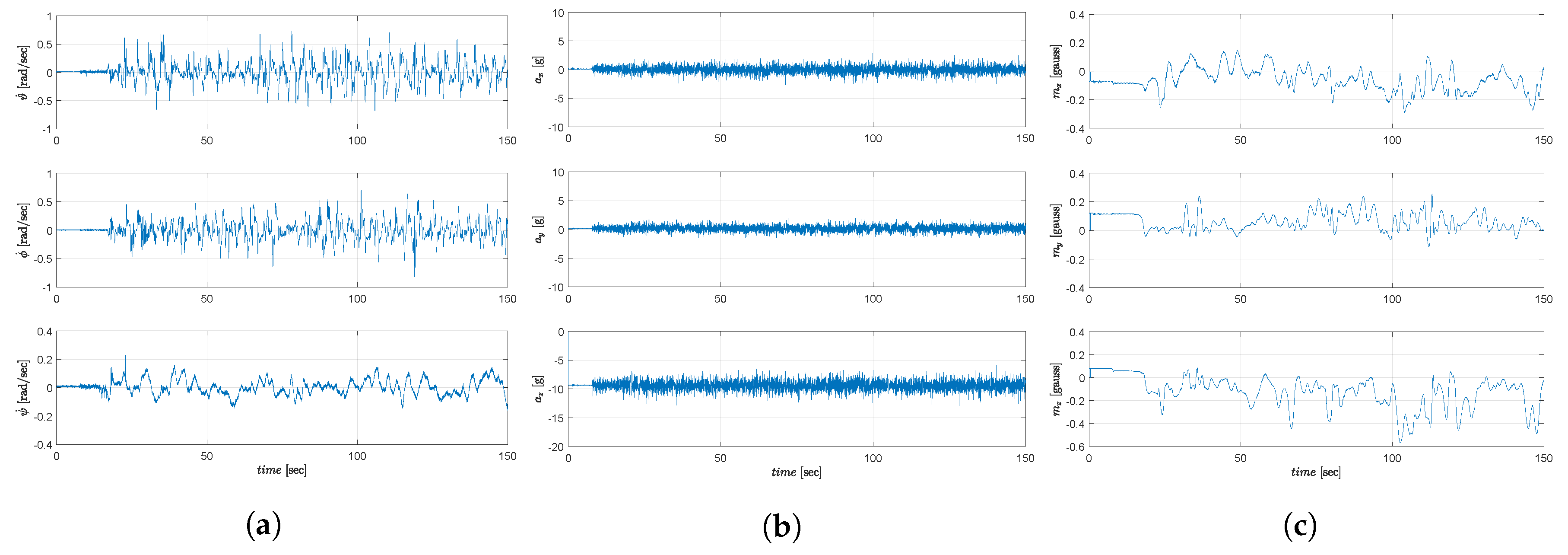
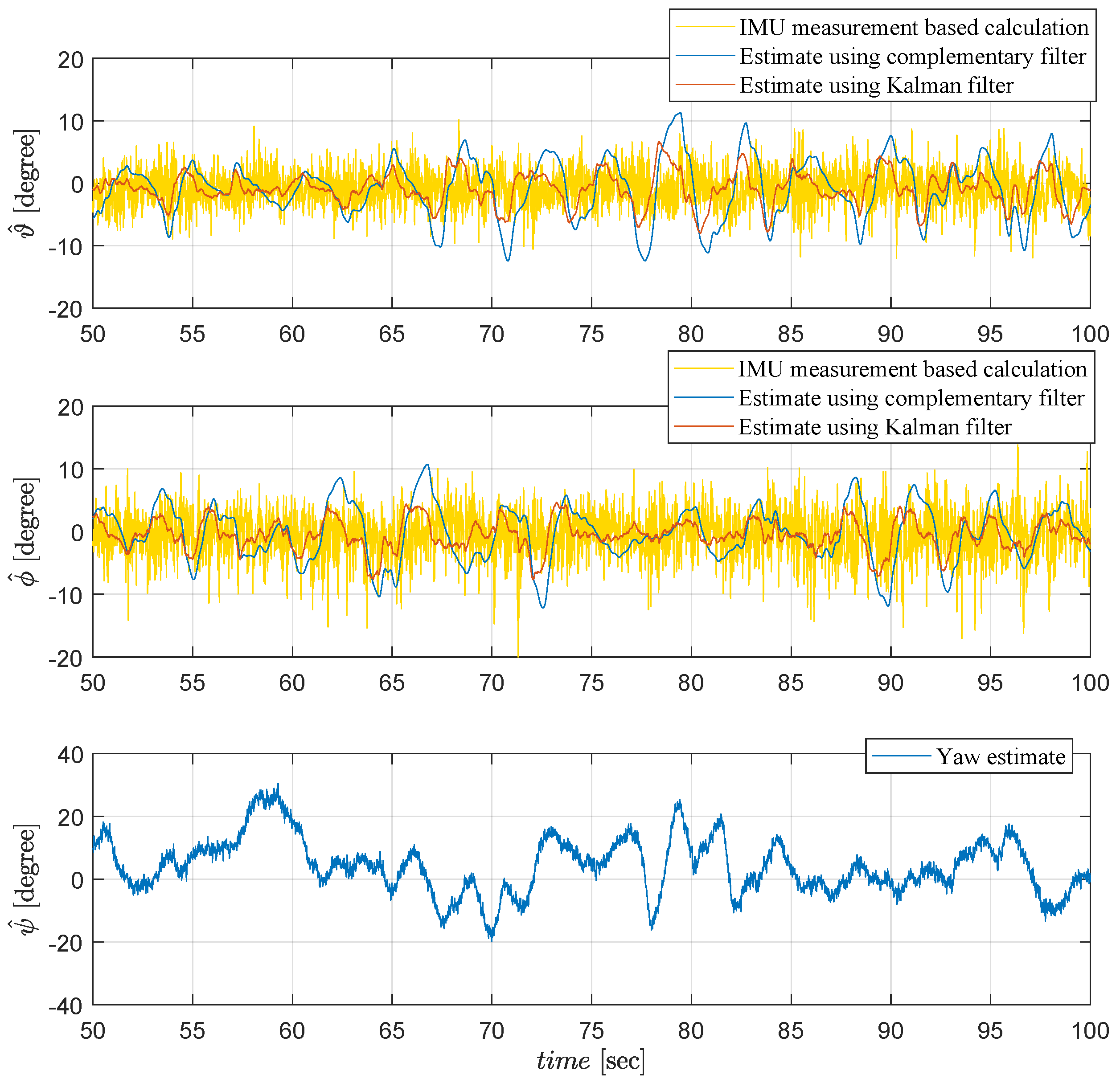
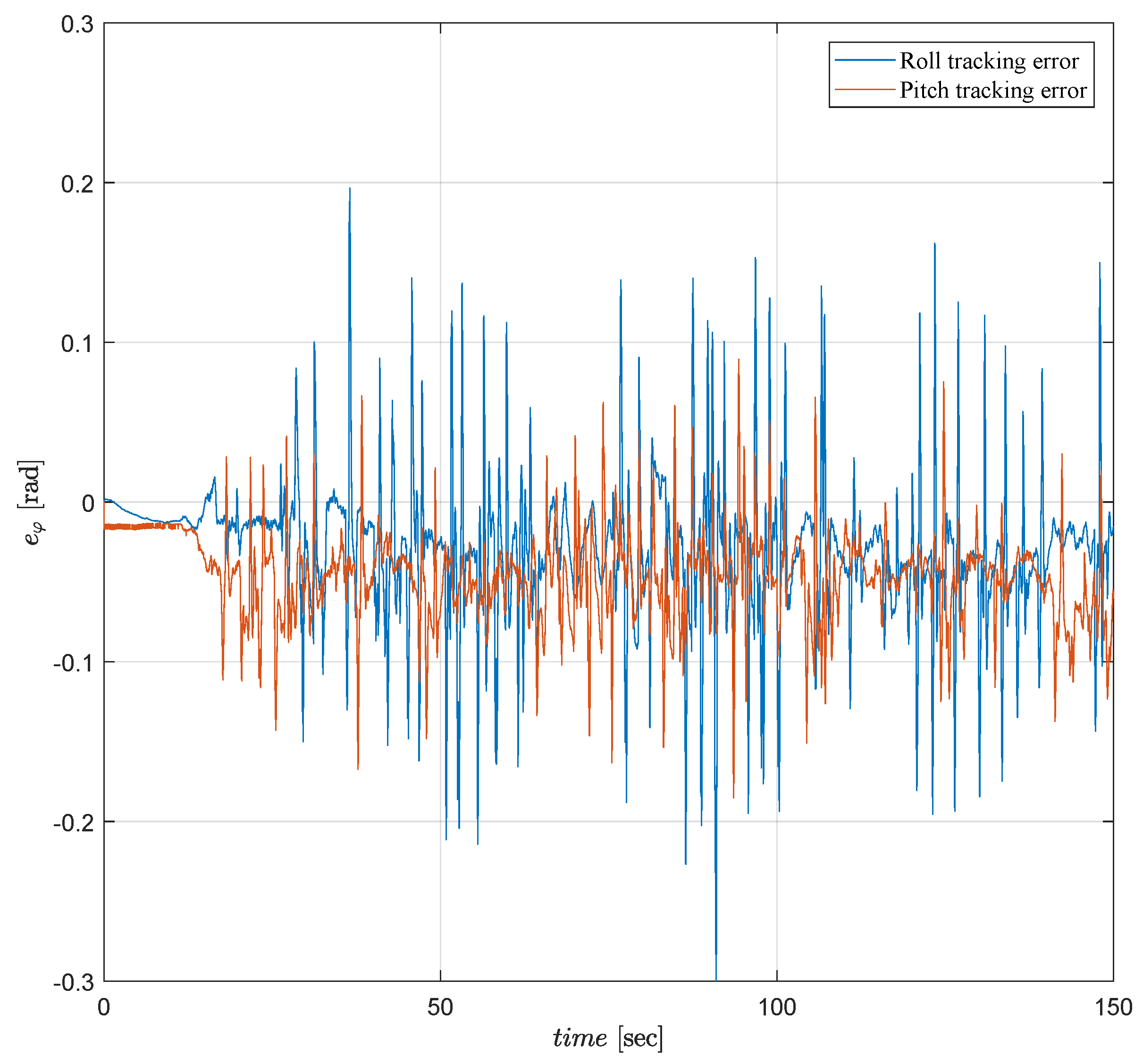
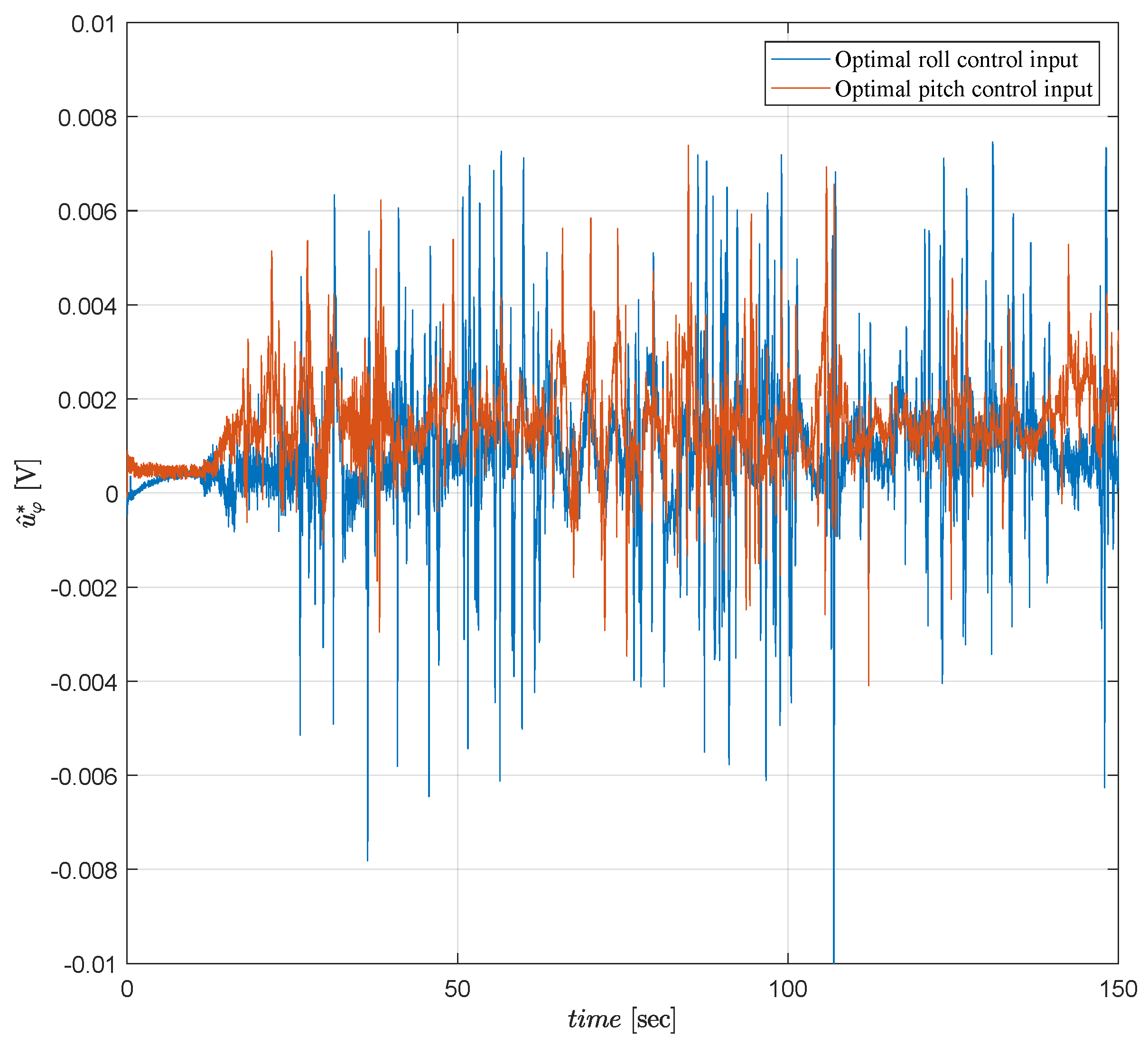
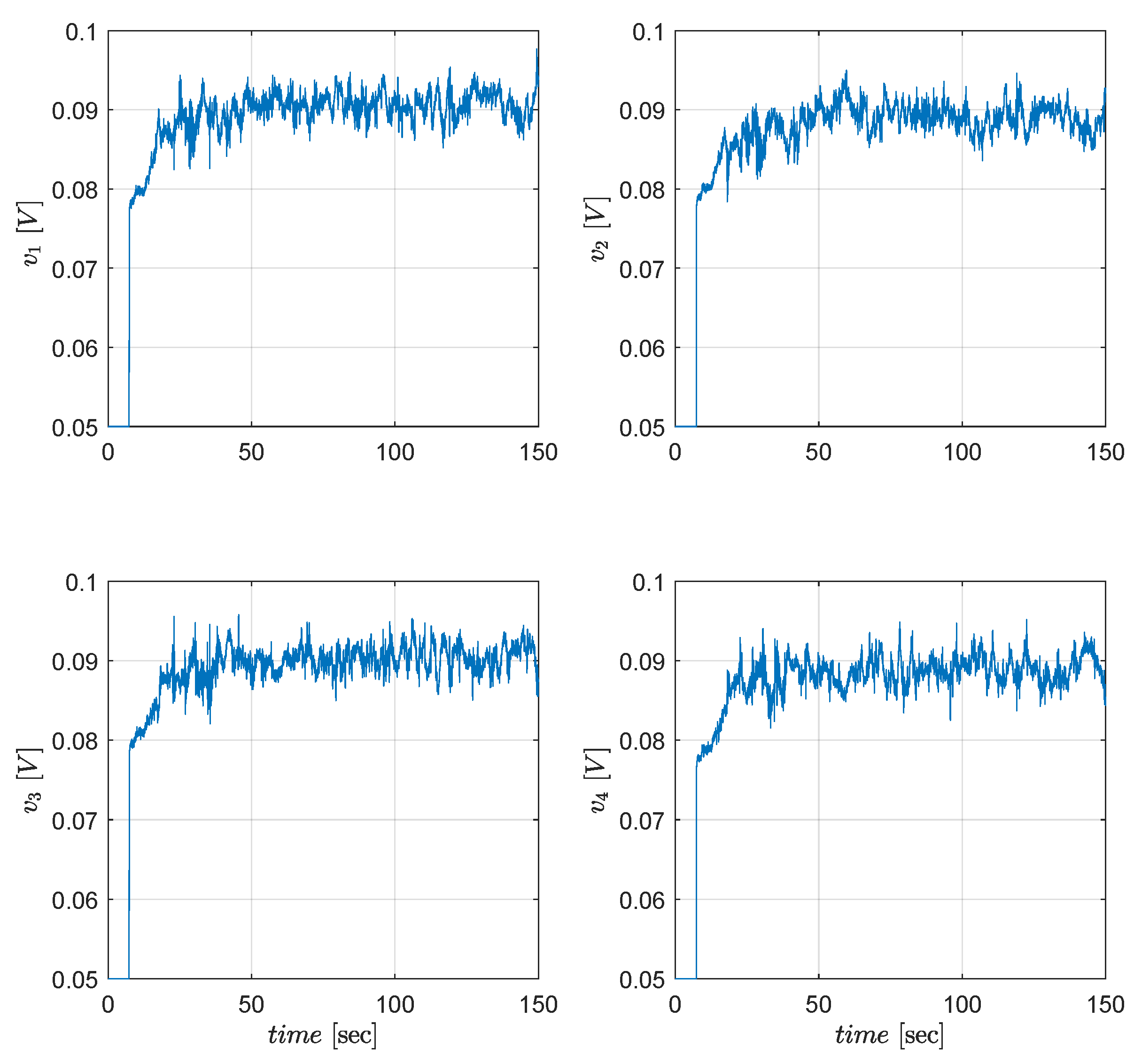
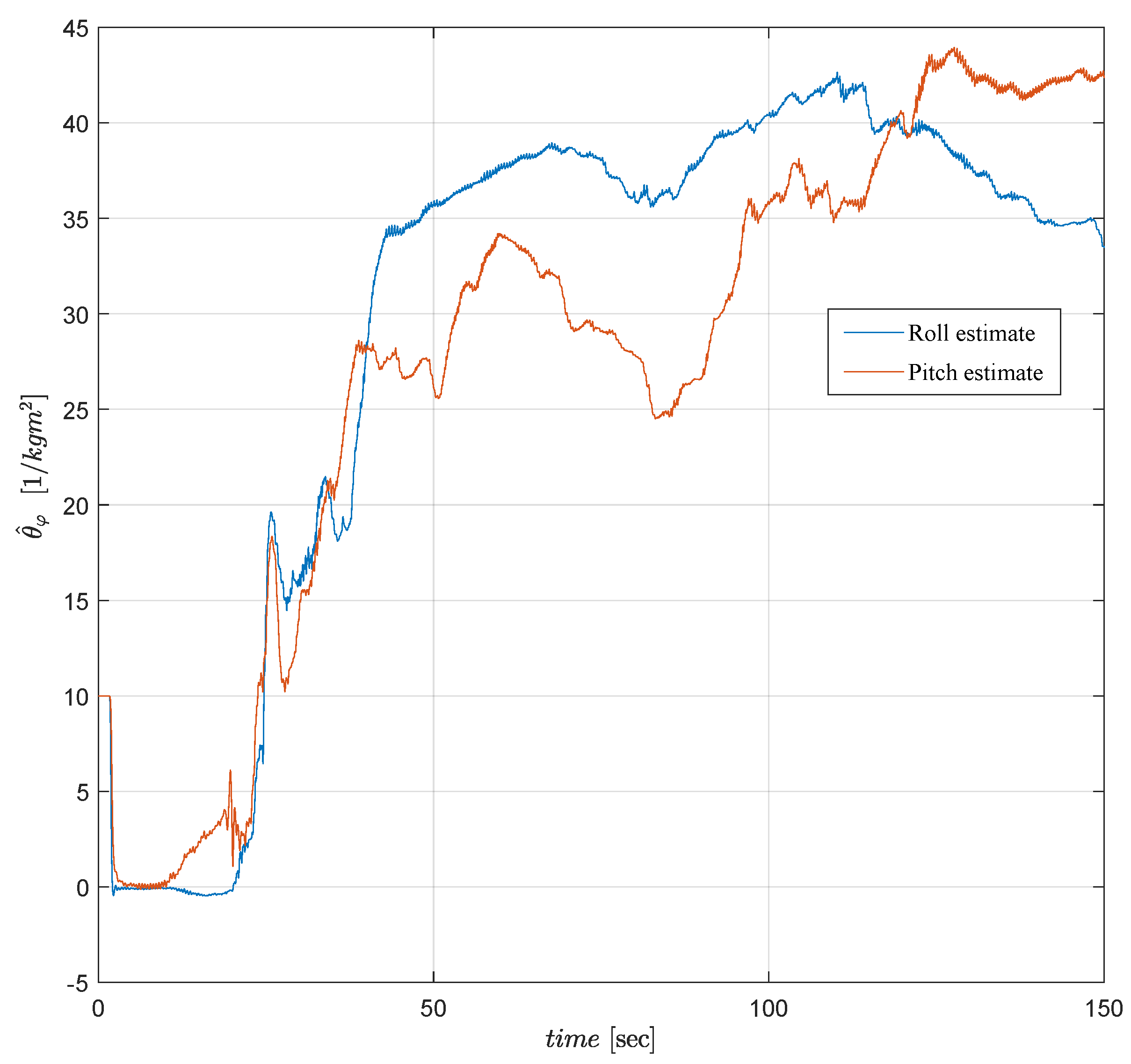
6.3. Experimental Results
6.4. Comparative Simulations and Observations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bouabdallah, S.; Noth, A.; Siegwart, R. PID vs. LQ control techniques applied to an indoor micro quadrotor. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems(IROS), Sendai, Japan, 28 September–2 October 2004; pp. 2451–2456. [Google Scholar]
- Spedicato, S.; Notarstefano, G. Minimum-time trajectory generation for quadrotors in constrained environments. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2018, 26, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Cheng, L.; Yao, Y. A Robust inner and outer loop control method for trajectory tracking of a quadrotor. Sensors 2017, 17, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koksal, N.; Hao, A.; Fidan, B. Two-level nonlinear tracking control of a quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2016, 49, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayebi, A.; McGilvray, S. Attitude stabilization of a VTOL quadrotor aircraft. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2006, 14, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Hoffmann, G.M.; Waslander, S.L.; Tomlin, C.J. Aerodynamics and control of autonomous quadrotor helicopters in aggressive maneuvering. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Kobe, Japan, 12–17 May 2009; pp. 3277–3282. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T. Robust adaptive attitude tracking on SO(3) with an application to a quadrotor UAV. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2013, 21, 1924–1930. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Bai, Y.; Lu, G.; Zhong, Y. Robust attitude control of uncertain quadrotors. IET Control Theory Appl. 2013, 7, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xi, J.; Zhong, Y. Robust attitude stabilization for nonlinear quadrotor systems with uncertainties and delays. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 5585–5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaguirre-Espinosa, C.; Munoz-Vazquez, A.J.; Sanchez-Orta, A.; Parra-Vega, V.; Castillo, P. Attitude control of quadrotors based on fractional sliding modes: Theory and experiments. IET Control Theory Appl. 2016, 10, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexis, K.; Nikolakopoulos, G.; Tzes, A. Switching model predictive attitude control for a quadrotor helicopter subject to atmospheric disturbances. Control Eng. Pract. 2011, 19, 1195–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satici, A.C.; Poonawala, H.; Spong, M.W. Robust optimal control of quadrotor UAVs. IEEE Access 2013, 1, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, E.; Alba-Flores, R. On the Infinite-horizon LQ tracker. Syst. Control Lett. 2000, 40, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alba-Flores, R.; Barbieri, E. Real-time infinite horizon linear-quadratic tracking controller for vibration quenching in flexible beams. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Taipei, Taiwan, 8–11 October 2006; pp. 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Modares, H.; Lewis, F.L. Linear quadratic tracking control of partially-unknown continuous-time systems using reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2014, 59, 3051–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suicmez, E.C.; Kutay, A.T. Optimal path tracking control of a quadrotor UAV. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Orlando, FL, USA, 27–30 May 2014; pp. 115–125. [Google Scholar]
- Benziane, L.; El Hadri, A.; Seba, A.; Benallegue, A.; Chitour, Y. Attitude estimation and control Using linearlike complementary filters: Theory and experiment. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2016, 24, 2133–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, I.; Corke, P. System identification, estimation and control for a cost effective open-source quadcopter. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Saint Paul, MN, USA, 14–18 May 2012; pp. 2202–2209. [Google Scholar]
- Magnussen, Ø.; Ottestad, M.; Hovland, G. Experimental validation of a quaternion-based attitude estimation with direct input to a quadcopter control system. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Atlanta, GA, USA, 28–31 May 2013; pp. 480–485. [Google Scholar]
- Mahony, R.; Hamel, T.; Pflimlin, J.M. Complementary filter design on the special orthogonal group SO(3). In Proceedings of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control Conference (CDC) and European Control Conference (ECC), Seville, Spain, 15 December 2005; pp. 1477–1484. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Stingu, E.; Lewis, F. Design and implementation of a structured flight controller for a 6DoF quadrotor using quaternions. In Proceedings of the 17th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation, Thessaloniki, Greece, 24–26 June 2009; pp. 1233–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Baerveldt, A.J.; Klang, R. A low-cost and low-weight attitude estimation system for an autonomous helicopter. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Engineering Systems (INES), Budapest, Hungary, 17 September 1997; pp. 391–395. [Google Scholar]
- Henriques, B.S.M. Estimation and Control of a Quadrotor Attitude. Master’s Thesis, Instituto Superior Técnico, Lisbon University, Lisboa, Portugal, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, H.; Park, J.; Lee, D.; Kim, H.J. Build your own quadrotor: Open-source projects on unmanned aerial vehicles. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2012, 19, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, F.; Goddemeier, N.; Bertram, T. Attitude estimation and control of a quadrocopter. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 October 2010; pp. 1072–1077. [Google Scholar]
- Ferdinando, H.; Khoswanto, H.; Purwanto, D. Embedded Kalman filter for Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) on the ATMega8535. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Innovations in Intelligent Systems and Applications (INISTA), Trabzon, Turkey, 2–4 July 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Yang, Y. Quadrotor aircraft attitude estimation and control based on Kalman filter. In Proceedings of the Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Hefei, China, 25–27 July 2012; pp. 5634–5639. [Google Scholar]
- Redhyka, G.G.; Setiawan, D.; Soetraprawata, D. Embedded sensor fusion and moving-average filter for Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) on the micro controller-based stabilized platform. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Automation, Cognitive Science, Optics, Micro Electro-Mechanical System, and Information Technology (ICACOMIT), Bandung, Indonesia, 29–30 October 2015; pp. 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Foxlin, E. Inertial head tracker sensor fusion by a complementary separate bias Kalman filter. In Proceedings of the IEEE Virtual Reality Annual Inter-national Symposium, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 30 March–3 April 1996; pp. 185–194. [Google Scholar]
- Evren, S.; Yavuz, F.; Unel, M. High Precision stabilization of pan-tilt systems using reliable angular acceleration feedback from a master–slave Kalman filter. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2017, 88, 97–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marins, J.L.; Yun, X.; Bachmann, E.R.; McGhee, R.B.; Zyda, M.J. An extended Kalman filter for quaternion-based orientation estimation using MARG sensors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Maui, HI, USA, 29 October–3 November 2001; Volume 4, pp. 2003–2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, A.; Golnaraghi, M. A quaternion-based orientation estimation algorithm using an inertial measurement unit. In Proceedings of the Position Location and Navigation Symposium, Monterey, CA, USA, 26–29 April 2004; pp. 268–272. [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini, A.M. Quaternion-based extended Kalman filter for determining orientation by inertial and magnetic sensing. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 53, 1346–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatini, A.M. Kalman-filter-based orientation determination using inertial/magnetic sensors: Observability analysis and performance evaluation. Sensors 2011, 11, 9182–9206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesecq, S.; Gentil, S.; Daraoui, N. Quadrotor attitude estimation with data losses. In Proceedings of the European Control Conference (ECC), Budapest, Hungary, 23–26 August 2009; pp. 3851–3856. [Google Scholar]
- Rehbinder, H.; Hu, X. Nonlinear state estimation for rigid-body motion with low-pass sensors. Syst. Control Lett. 2000, 40, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crassidis, J.L.; Markley, F.L. Unscented filtering for spacecraft attitude estimation. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2003, 26, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Pierre, M.; Gingras, D. Comparison between the unscented Kalman filter and the extended Kalman filter for the position estimation module of an integrated navigation information system. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Parma, Italy, 14–17 June 2004; pp. 831–835. [Google Scholar]
- De Marina, H.G.; Pereda, F.J.; Giron-Sierra, J.M.; Espinosa, F. UAV attitude estimation using unscented Kalman filter and TRIAD. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 4465–4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, J. Effective adaptive Kalman filter for MEMS-IMU/magnetometers integrated attitude and heading reference systems. J. Navig. 2013, 66, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Analog Devices. Tri-Axis Inertial Sensor with Magnetometer, ADIS16405; Analog Devices: Norwood, MA, USA, 2009; Available online: http://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/ADIS16400_16405.pdf (accessed on 26 July 2018).
- Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Hatch, R.R.; Zhang, Y. Adaptive Filter for a Miniature MEMS based Attitude and Heading Reference System. In Proceedings of the Position Location and Navigation Symposium, Monterey, CA, USA, 26–29 April 2004; pp. 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, B.; Li, Q.; Liu, T. How Magnetic Disturbance Influences the Attitude and Heading in Magnetic and Inertial Sensor-Based Orientation Estimation. Sensors 2018, 18, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koksal, N.; Fidan, B.; Buyukkabasakal, K. Real-time Implementation of Decentralized Adaptive Formation Control on Multi-quadrotor Systems. In Proceedings of the European Control Conference (ECC), Linz, Austria, 15–17 July 2015; pp. 3162–3167. [Google Scholar]
- Ioannou, P.A.; Fidan, B. Adaptive Control Tutorial; Advances in Design and Control; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Naidu, D.S. Optimal Control Systems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, B.D.; Moore, J.B. Optimal Control: Linear Quadratic Methods; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Quanser Inc. Qball-X4:User Manual; Quanser Inc.: Markham, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Test 1 Video. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OVZ_zg4SS0Y (accessed on 21 December 2018).
- Test 2 Video. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wsKiPJJjj68 (accessed on 21 December 2018).







| Gyroscope | Accelerometer | Magnetometer | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Range | ±305 (deg/s) | ±18 (g) | ± 3.5 (gauss) |
| Sensitivity | 0.05 (deg/s/LSB) | 3.33 (mg/LSB) | 0.5 (mgauss/LSB) |
| m (kg) | l (m) | K (N) | (Nm) | b (rad/s) | (kg m) | (kg m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.4 | 0.2 | 120 | 4 | 15 | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| ALQT | Roll [rad] | Pitch [rad] |
|---|---|---|
| with Kalman filter | 0.0012 | 0.0012 |
| with comp. filter | 0.0027 | 0.0029 |
| ALQT | Roll [voltage/s] | Pitch [voltage/s] |
|---|---|---|
| with Kalman filter | 0.00071 | 0.00066 |
| with comp. filter | 0.00086 | 0.00140 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koksal, N.; Jalalmaab, M.; Fidan, B. Adaptive Linear Quadratic Attitude Tracking Control of a Quadrotor UAV Based on IMU Sensor Data Fusion. Sensors 2019, 19, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19010046
Koksal N, Jalalmaab M, Fidan B. Adaptive Linear Quadratic Attitude Tracking Control of a Quadrotor UAV Based on IMU Sensor Data Fusion. Sensors. 2019; 19(1):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19010046
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoksal, N., M. Jalalmaab, and B. Fidan. 2019. "Adaptive Linear Quadratic Attitude Tracking Control of a Quadrotor UAV Based on IMU Sensor Data Fusion" Sensors 19, no. 1: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19010046
APA StyleKoksal, N., Jalalmaab, M., & Fidan, B. (2019). Adaptive Linear Quadratic Attitude Tracking Control of a Quadrotor UAV Based on IMU Sensor Data Fusion. Sensors, 19(1), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19010046






