Development of a New Radiofluorinated Quinoline Analog for PET Imaging of Phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) in Brain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
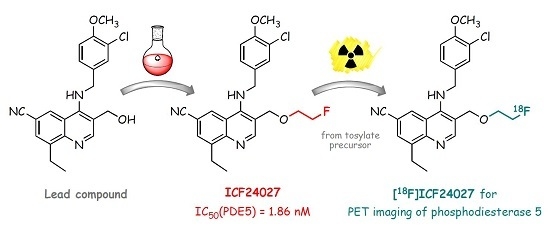
2.1. Organic Chemistry and Inhibitory Activity Towards PDEs
2.2. Radiochemistry
2.3. In Vitro Autoradiographic Studies
2.4. Metabolism Studies of [18F]ICF24027 In Vivo and In Vitro
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Organic Chemistry
4.1.1. General Information
4.1.2. Syntheses
4-[(3-Chloro-4-methoxybenzyl)amino]-8-ethyl-3-[(2-fluoroethoxy)methyl]quinoline-6-carbonitrile (ICF24027)
4-[(3-Chloro-4-methoxybenzyl)amino]-8-ethyl-3-[(2-hydroxyethoxy)methyl]quinoline-6-carbonitrile (ICF24093)
2-((4-[(3-Chloro-4-methoxybenzyl)amino]-6-cyano-8-ethylquinolin-3-yl)methoxy)ethyl 4-methylbenzene-sulfonate (ICF24077)
4.2. Radiochemistry
4.2.1. General
4.2.2. Radiosyntheses
4.2.3. In Vitro Stability and Calculation of LogD Value
4.3. In Vitro Autoradiographic Studies of [18F]ICF24027
4.4. Metabolism Studies of [18F]ICF24027 in Mice
4.5. Metabolism Studies of [18F]ICF24027 with Mouse Liver Microsomes
4.5.1. Chemicals, Reagents and Instruments
4.5.2. Microsomal Incubations with [18F]ICF24027 and ICF24027
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bender, A.T.; Beavo, J.A. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: Molecular regulation to clinical use. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 488–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.; Amanullah, A.M. Therapeutic potentials of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors in cardiovascular disease. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2014, 15, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wallis, R.M.; Corbin, J.D.; Francis, S.H.; Ellis, P. Tissue distribution of phosphodiesterase families and the effects of sildenafil on tissue cyclic nucleotides, platelet function, and the contractile responses of trabeculae carneae and aortic rings in vitro. Am. J. Cardiol. 1999, 83, 3C–12C. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbin, J.D.; Francis, S.H. Pharmacology of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2002, 56, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Zhang, R.; Yang, Z.; Lee, J.; Liu, Y.; Tian, J.; Qin, X.; Ren, Z.; Ding, H.; Chen, Q.; et al. Comparative effectiveness and safety of oral phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors for erectile dysfunction: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Eur. Urol. 2013, 63, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-T.; Xu, Y.; O’Donnell, J. Chapter 7: Inhibition of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases to regulate memory. In Cyclic-Nucleotide Phosphodiesterases in the Central Nervous System: From Biology to Drug Discovery; Hoboken, NJ, USA; John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2014; pp. 171–210. [Google Scholar]
- Kotera, J.; Fujishige, K.; Omori, K. Immunohistochemical localization of cGMP-binding cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase (PDE5) in rat tissues. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2000, 48, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, A.T.; Beavo, J.A. Specific localized expression of cGMP PDEs in Purkinje neurons and macrophages. Neurochem. Int. 2004, 45, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, D.; De Stefano, M.E.; Citro, G.; Modica, A.; Giorgi, M. Expression of cGMP-binding cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase (PDE5) in mouse tissues and cell lines using an antibody against the enzyme amino-terminal domain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1539, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Staveren, W.C.; Steinbusch, H.W.; Markerink-van Ittersum, M.; Behrends, S.; de Vente, J. Species differences in the localization of cGMP-producing and NO-responsive elements in the mouse and rat hippocampus using cGMP immunocytochemistry. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 2155–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakics, V.; Karran, E.H.; Boess, F.G. Quantitative comparison of phosphodiesterase mRNA distribution in human brain and peripheral tissues. Neuropharmacology 2010, 59, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loughney, K.; Hill, T.R.; Florio, V.A.; Uher, L.; Rosman, G.J.; Wolda, S.L.; Jones, B.A.; Howard, M.L.; McAllister-Lucas, L.M.; Sonnenburg, W.K.; et al. Isolation and characterization of cDNAs encoding PDE5A, a human cGMP-binding, cGMP-specific 3′,5′-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Gene 1998, 216, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, C.A.; Nunes, A.K.; Garcia-Osta, A. Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors: Action on the signaling pathways of neuroinflammation, neurodegeneration, and cognition. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 940207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugarte, A.; Gil-Bea, F.; Garcia-Barroso, C.; Cedazo-Minguez, A.; Ramirez, M.J.; Franco, R.; Garcia-Osta, A.; Oyarzabal, J.; Cuadrado-Tejedor, M. Decreased levels of guanosine 3′,5′-monophosphate (cGMP) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) are associated with cognitive decline and amyloid pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2015, 41, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umar, T.; Hoda, N. Selective inhibitors of phosphodiesterases: Therapeutic promise for neurodegenerative disorders. MedChemComm 2015, 6, 2063–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzzo, D.; Staniszewski, A.; Deng, S.X.; Privitera, L.; Leznik, E.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y.; Palmeri, A.; Landry, D.W.; et al. Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibition improves synaptic function, memory, and amyloid-beta load in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 8075–8086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmeri, A.; Privitera, L.; Giunta, S.; Loreto, C.; Puzzo, D. Inhibition of phosphodiesterase-5 rescues age-related impairment of synaptic plasticity and memory. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 240, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, J.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, G.; Liu, A.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, W.; Xu, Y.; Wang, C. Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor sildenafil prevents neuroinflammation, lowers β-amyloid levels and improves cognitive performance in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 250, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puzzo, D.; Loreto, C.; Giunta, S.; Musumeci, G.; Frasca, G.; Podda, M.V.; Arancio, O.; Palmeri, A. Effect of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibition on apoptosis and beta amyloid load in aged mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobsen, S.; Kodahl, G.M.; Olsen, A.K.; Cumming, P. Synthesis, radiolabeling and in vivo evaluation of [11C]RAL-01, a potential phosphodiesterase 5 radioligand. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2006, 33, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chekol, R.; Gheysens, O.; Cleynhens, J.; Pokreisz, P.; Vanhoof, G.; Ahamed, M.; Janssens, S.; Verbruggen, A.; Bormans, G. Evaluation of PET radioligands for in vivo visualization of phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5). Nucl. Med. Biol. 2014, 41, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Vallejo, V.; Ugarte, A.; Garcia-Barroso, C.; Cuadrado-Tejedor, M.; Szczupak, B.; Dopeso-Reyes, I.G.; Lanciego, J.L.; Garcia-Osta, A.; Llop, J.; Oyarzabal, J.; et al. Pharmacokinetic investigation of sildenafil using positron emission tomography and determination of its effect on cerebrospinal fluid cGMP levels. J. Neurochem. 2016, 136, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Maisonial-Besset, A.; Wenzel, B.; Canitrot, D.; Baufond, A.; Chezal, J.-M.; Brust, P.; Moreau, E. Development of new PET neuroimaging probes: Fluorinated quinoline derivatives with high affinity for PDE5. Org. Biomol. Chem. Manuscript in preparation.
- Bi, Y.; Stoy, P.; Adam, L.; He, B.; Krupinski, J.; Normandin, D.; Pongrac, R.; Seliger, L.; Watson, A.; Macor, J.E. Quinolines as extremely potent and selective PDE5 inhibitors as potential agents for treatment of erectile dysfunction. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 1577–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorito, J.; Saeed, F.; Zhang, H.; Staniszewski, A.; Feng, Y.; Francis, Y.I.; Rao, S.; Thakkar, D.M.; Deng, S.X.; Landry, D.W.; et al. Synthesis of quinoline derivatives: Discovery of a potent and selective phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 60, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SB Drug Discovery. Available online: www.sbdrugdiscovery.com (accessed on 14 August 2014).
- Omori, K.; Kotera, J. Overview of PDEs and their regulation. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumming, P. A business of some heat: Molecular imaging of phosphodiesterase 5. J. Neurochem. 2016, 136, 220–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakao, R.; Schou, M.; Halldin, C. Direct plasma metabolite analysis of positron emission tomography radioligands by micellar liquid chromatography with radiometric detection. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 3222–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, S.; Wenzel, B.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Teodoro, R.; Egerland, U.; Kranz, M.; Scheunemann, M.; Höfgen, N.; Steinbach, J.; Brust, P. Synthesis, 18F-radiolabelling and biological characterization of novel fluoroalkylated triazine derivatives for in vivo imaging of phosphodiesterase 2A in brain via positron emission tomography. Molecules 2015, 20, 9591–9615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambla-Alegre, M. Basic principles of MLC. Chromatogr. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Angel, M.J.; Carda-Broch, S.; Torres-Lapasio, J.R.; Garcia-Alvarez-Coque, M.C. Retention mechanisms in micellar liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 1798–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, B.; Krämer, S.D. The biochemistry of drug metabolism—An introduction: Part 2. Redox reactions and their enzymes. Chem. Biodivers. 2007, 4, 257–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchar, M.; Mamat, C. Methods to increase the metabolic stability of 18F-radiotracers. Molecules 2015, 20, 16186–16220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoghbi, S.S.; Shetty, H.U.; Ichise, M.; Fujita, M.; Imaizumi, M.; Liow, J.S.; Shah, J.; Musachio, J.L.; Pike, V.W.; Innis, R.B. PET imaging of the dopamine transporter with [18F]FECNT: A polar radiometabolite confounds brain radioligand measurements. J. Nucl. Med. 2006, 47, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tewson, T.J.; Welch, M.J. Preparation and preliminary biodistribution of no carrier added F-18 fluoroethanol. J. Nucl. Med. 1980, 21, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sephton, S.M.; Dennler, P.; Leutwiler, D.S.; Mu, L.; Wanger-Baumann, C.A.; Schibli, R.; Krämer, S.D.; Ametamey, S.M. Synthesis, radiolabelling and in vitro and in vivo evaluation of a novel fluorinated ABP688 derivative for the PET imaging of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5. Am. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2012, 2, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- French, A.N.; Napolitano, A.; Brocklin, H.F.V.; Brodack, J.W.; Hanson, R.N.; Welch, M.J.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A. The β-heteroatom effect in metabolic defluorination: The interaction of resonance and inductive effects may be a fundamental determinant in the metabolic liability of fluorine-substituted compounds. J. Labelled Comp. Radiopharm. 1991, 30, 431–433. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Pourghiasian, M.; Hundal, N.; Lau, J.; Benard, F.; Dedhar, S.; Lin, K.S. 2-[18F]Fluoroethanol and 3-[18F]fluoropropanol: Facile preparation, biodistribution in mice, and their application as nucleophiles in the synthesis of [18F]fluoroalkyl aryl ester and ether PET tracers. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2013, 40, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evens, N.; Vandeputte, C.; Muccioli, G.G.; Lambert, D.M.; Baekelandt, V.; Verbruggen, A.M.; Debyser, Z.; Van Laere, K.; Bormans, G.M. Synthesis, in vitro and in vivo evaluation of fluorine-18 labelled FE-GW405833 as a PET tracer for type 2 cannabinoid receptor imaging. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 4499–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomae, D.; Servaes, S.; Vazquez, N.; Wyffels, L.; Dedeurwaerdere, S.; Van der Veken, P.; Joossens, J.; Augustyns, K.; Stroobants, S.; Staelens, S. Synthesis and preclinical evaluation of an 18F labeled PDE7 inhibitor for PET neuroimaging. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2015, 42, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funke, U.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Schwan, G.; Maisonial, A.; Scheunemann, M.; Fischer, S.; Hiller, A.; Briel, D.; Brust, P. Radiosynthesis and radiotracer properties of a 7-(2-[18F]fluoroethoxy)-6-methoxypyrrolidinylquinazoline for imaging of phosphodiesterase 10A with PET. Pharmaceuticals 2012, 5, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauleit, D.; Floeth, F.; Herzog, H.; Hamacher, K.; Tellmann, L.; Muller, H.W.; Coenen, H.H.; Langen, K.J. Whole-body distribution and dosimetry of O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2003, 30, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armarego, W.L.F.; Perrin, D.D. Purification of Laboratory Chemicals, 4th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]







© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Wenzel, B.; Dukic-Stefanovic, S.; Teodoro, R.; Ludwig, F.-A.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Schröder, S.; Chezal, J.-M.; Moreau, E.; Brust, P.; et al. Development of a New Radiofluorinated Quinoline Analog for PET Imaging of Phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) in Brain. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9020022
Liu J, Wenzel B, Dukic-Stefanovic S, Teodoro R, Ludwig F-A, Deuther-Conrad W, Schröder S, Chezal J-M, Moreau E, Brust P, et al. Development of a New Radiofluorinated Quinoline Analog for PET Imaging of Phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) in Brain. Pharmaceuticals. 2016; 9(2):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9020022
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jianrong, Barbara Wenzel, Sladjana Dukic-Stefanovic, Rodrigo Teodoro, Friedrich-Alexander Ludwig, Winnie Deuther-Conrad, Susann Schröder, Jean-Michel Chezal, Emmanuel Moreau, Peter Brust, and et al. 2016. "Development of a New Radiofluorinated Quinoline Analog for PET Imaging of Phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) in Brain" Pharmaceuticals 9, no. 2: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9020022
APA StyleLiu, J., Wenzel, B., Dukic-Stefanovic, S., Teodoro, R., Ludwig, F.-A., Deuther-Conrad, W., Schröder, S., Chezal, J.-M., Moreau, E., Brust, P., & Maisonial-Besset, A. (2016). Development of a New Radiofluorinated Quinoline Analog for PET Imaging of Phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) in Brain. Pharmaceuticals, 9(2), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9020022