Comparative Proteomic Analysis Reveals Proteins Putatively Involved in Toxin Biosynthesis in the Marine Dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
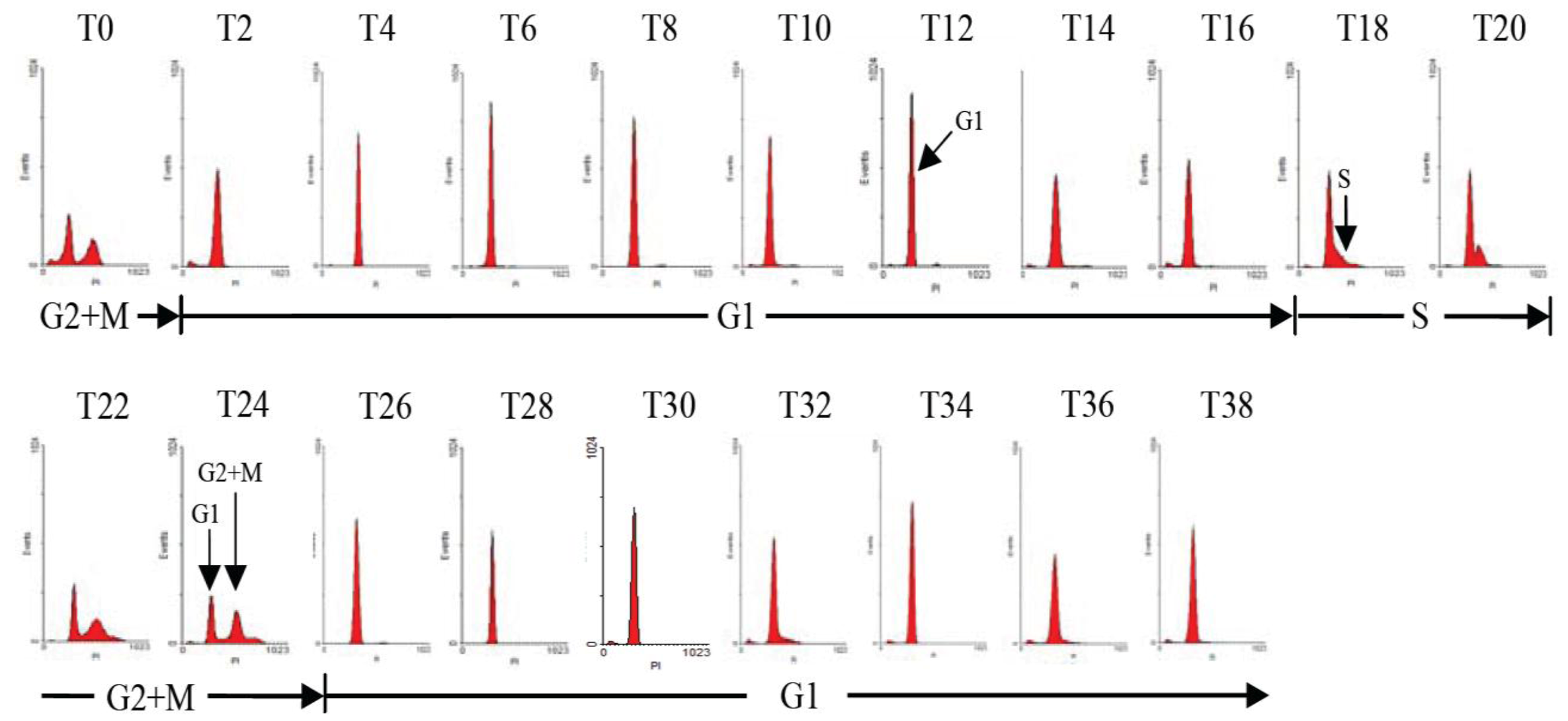
2.1. Diel Phasing of the Cell Cycle of A. catenella
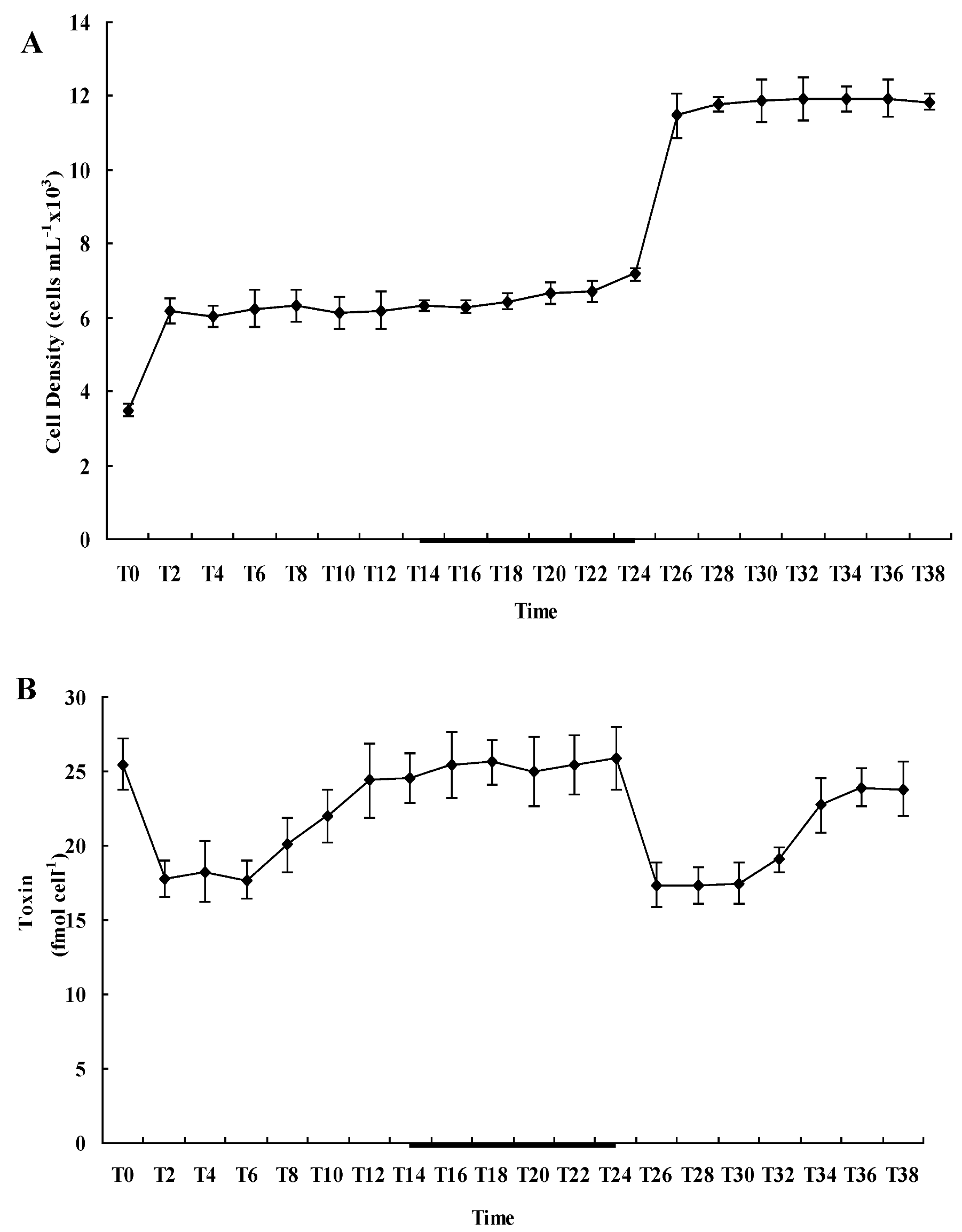
2.2. Diel Variations of Cell Density and Toxin Content of A. catenella
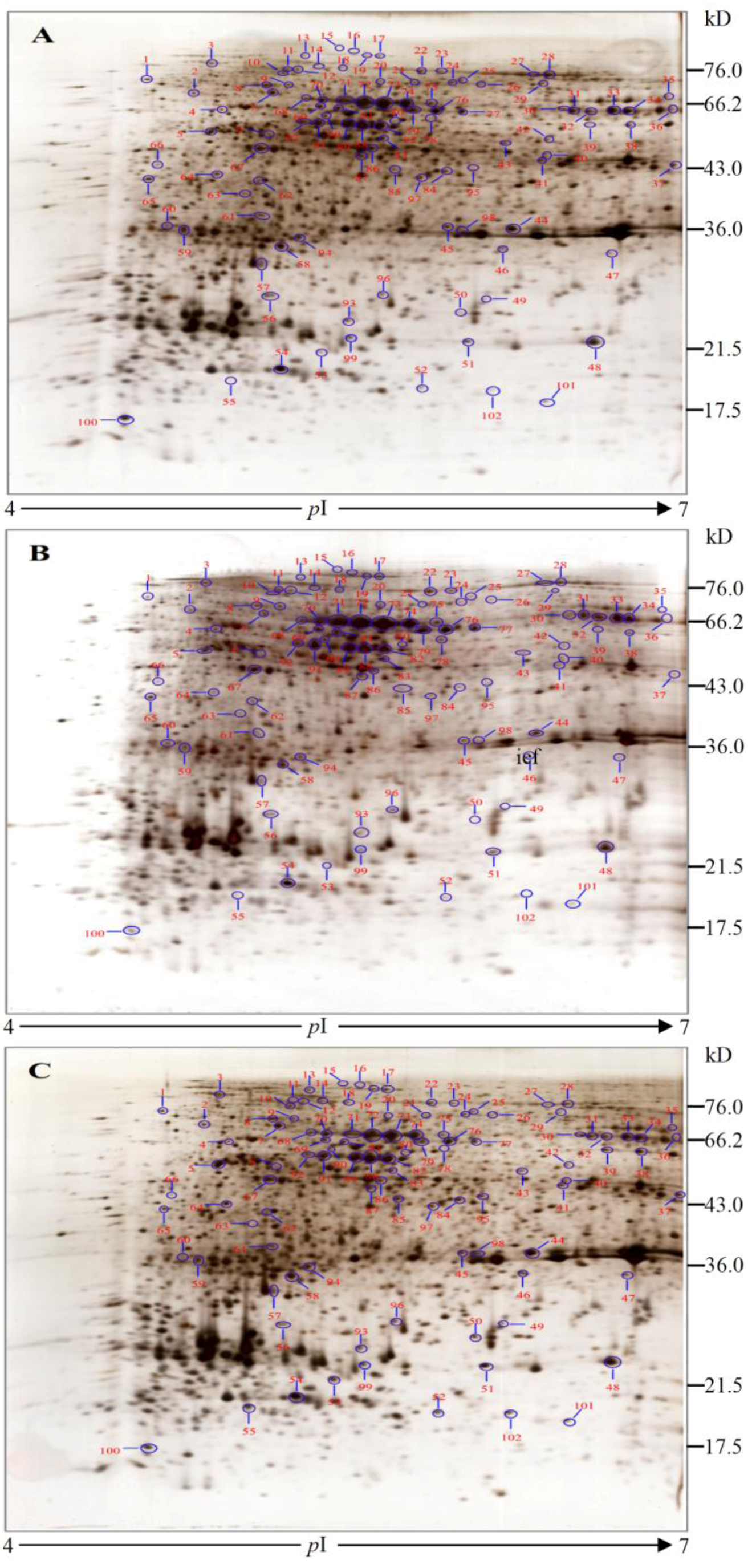
2.3. Protein Identification and Variation at Different Toxin Biosynthesis Stages
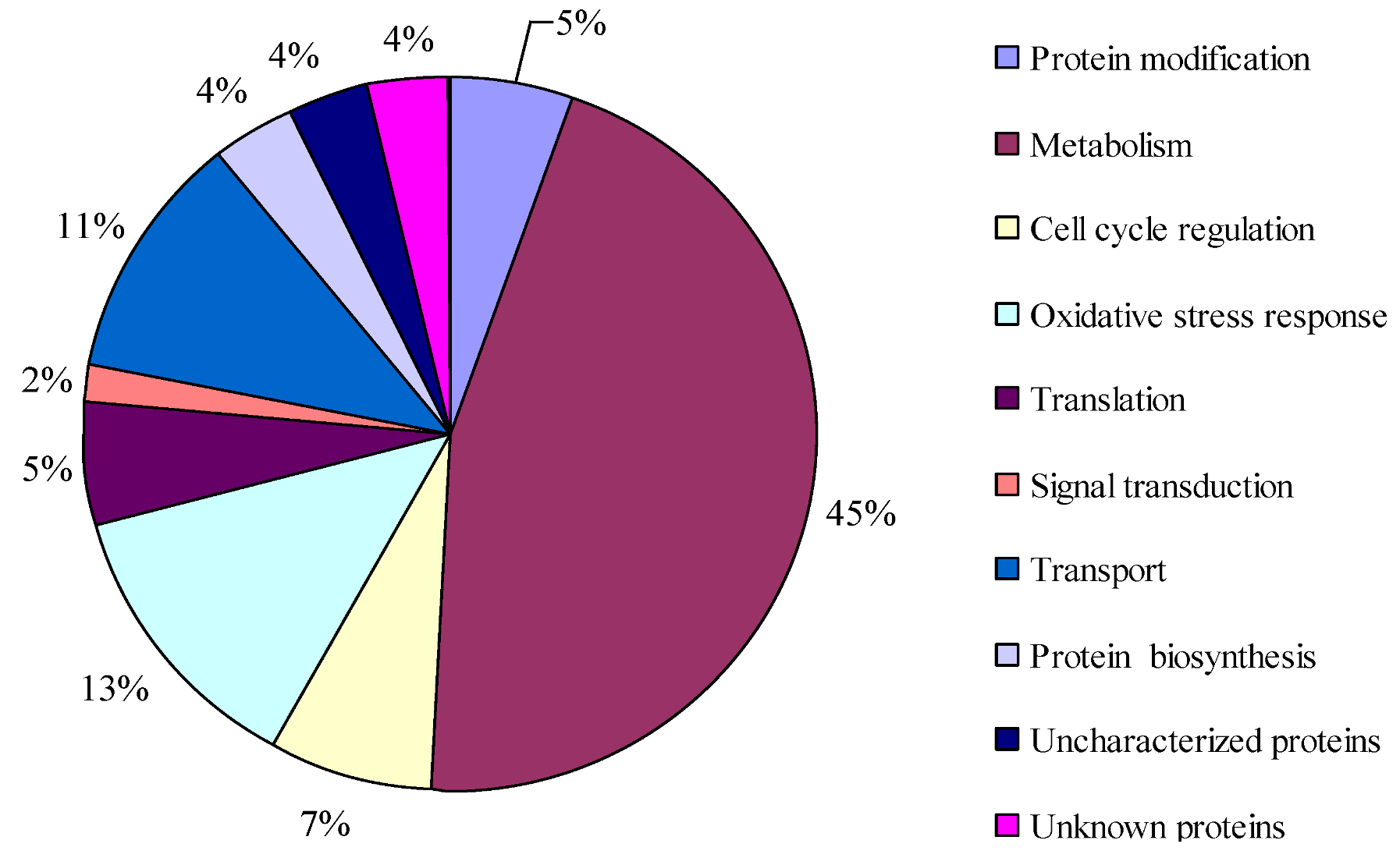
2.4. Proteins Putatively Involved in Toxin Biosynthesis
| Spot id | Accession number | Protein score | Protein score CI% | Peptide count | MW/pI | Protein description | Function | T28 vs. T24 | T34 vs. T24 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foldchange | P-Value | Fold change | P-Value | ||||||||
| Metabolism | |||||||||||
| 31 | 46909371 | 145 | 100 | 4 | 34.39/5.81 | Methionine adenosyltransferase (MAT), (Nucula proxima) | catalyses the synthesis of S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) from methionine and ATP | 1.26 | 0.450 | 0.40 | 0.043 |
| 32 | 158524698 | 149 | 100 | 3 | 35.30/5.59 | Methionine adenosyltransferase (MAT), (Terebratulina retusa) | 1.89 | 0.173 | 0.47 | 0.033 | |
| 33 | 71370920 | 202 | 100 | 3 | 35.08/6.82 | Methionine adenosyltransferase (MAT), partial (Haliotis rufescens) | 1.15 | 0.767 | 0.40 | 0.034 | |
| 34 | 225685869 | 121 | 100 | 3 | 45.52/5.54 | Methionine S-adenosyltransferase (MAT), (Thalassionema nitzschioides) | 0.92 | 0.942 | 0.46 | 0.042 | |
| 36 | 225685865 | 92 | 99.248 | 2 | 51.08/5.73 | methionine S-adenosyltransferase (MAT), (Detonula confervacea) | 2.50 | 0.007 | 0.18 | 0.091 | |
| 77 | 211939908 | 120 | 99.999 | 9 | 27.97/5.74 | S-adenosylhomocysteinase (SAH), (Amphidinium carteriae) | an intermediate in the synthesis of cysteine and formed by the demethylation of SAM | 2.89 | 0.001 | 0.86 | 0.905 |
| 76 | 211939908 | 150 | 100 | 8 | 27.97/5.74 | Adenosylhomocysteinase (AdoHcy), (Amphidinium carteriae) | an enzyme that converts SAH to homocysteine and adenosine | 2.20 | 0.003 | 0.49 | 0.117 |
| 79 | 211939908 | 116 | 99.997 | 7 | 27.97/5.74 | 3.32 | 0.003 | 0.88 | 0.985 | ||
| 7 | 58613455 | 389 | 100 | 2 | 28.67/4.78 | chloroplast ferredoxin-NAD + reductase (FNRs), (Heterocapsa triquetra) | ferredoxin-NADP reductase type 1 family; Oxidation reduction | 0.13 | 0.007 | 1.19 | 0.641 |
| 40 | 170723385 | 296 | 100 | 15 | 38.10/5.92 | ornithine carbamoyltransferase (OTC), (Pseudomonas putida W619) | Cellular amino acid metabolic process; involved in arginine (Arg) biosynthesis | 0.45 | 0.088 | 1.61 | 0.003 |
| 55 | 26987276 | 87 | 97.728 | 2 | 19.18/4.77 | inorganic pyrophosphatase (PPi), (Pseudomonas putida KT2440) | Phosphate metabolic process; catalyzes the conversion of pyrophosphate to phosphate ions | 1.00 | 1.000 | 11.55 | 0.003 |
| 78 | 148546281 | 660 | 100 | 18 | 46.73/5.66 | arginine deiminase (ADI), (Pseudomonas putida F1) | participates in arginine and proline metabolism | 3.30 | <0.001 | 0.20 | 0.008 |
| 94 | 115901552 | 122 | 97.645 | 1 | 35.22/4.70 | similar to sulfotransferase (SULT), (Strongylocentrotus purpuratus) | sulfotransferase activity | 0.44 | 0.043 | 1.24 | 0.459 |
| Oxidative stress response | |||||||||||
| 95 | 26990544 | 110 | 99.989 | 6 | 35.89/5.61 | alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH), (Pseudomonas putida KT2440) | Oxidation reduction; zinc ion binding | 0.45 | 0.871 | 7.63 | 0.001 |

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Organism and Culture Conditions
3.2. Synchronization of A. catenella
3.3. Cell Count
3.4. Cell Cycle Defined
3.5. Toxin Analysis
3.6. Protein Extraction and Quantification
3.7. 2-DE Analysis
3.8. MALDI-TOF-TOF MS Analysis
3.9. Protein Interaction Network Analysis
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Supplementary Files
References
- Anderson, D.M.; Alpermann, T.J.; Cembella, A.D.; Masseret, E.; Montresor, M. The globally distributed genus Alexandrium: Multifaceted roles in marine ecosystems and impacts on human health. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 10–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Z. Neurotoxins from marine dinoflagellates: A brief review. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 349–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallegraeff, G.M. A review of harmful algal blooms and their apparent global increase. Phycologia 1993, 32, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.F. Medicine of diguanidino-prine-hydride compounds for giving up drug-taking. CN Patent 1192903, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bocazr, B.A.; Beitler, M.K.; Liston, J.; Sullivan, J.J.; Cattolico, R.A. Paralytic shellfish toxins in Protogonyaulax tamarensis and Protogonyaulax catenella in axenic culture. J. Plant Physiol. 1988, 88, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Kulis, D.M.; Sullivan, J.J.; Hall, S. Toxin composition variations in one isolate of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium fundyense. Toxicon 1990, 28, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Kulis, D.M.; Sullivan, J.J.; Lee, C. Dynamics and physiology of saxitoxin production bythe dinoflagellates Alexandrium spp. Mar. Biol. 1990, 104, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taroncher-Oldenburg, G.; Kulis, D.M.; Anderson, D.M. Toxin variability during the cell cycle of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium fundyense. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1177–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Taroncher-Oldenburg, G.; Kulis, D.M.; Anderson, D.M. Coupling of saxitoxin biosynthesis to the G1 phase of the cell cycle in the dinoflagellate Alexandrin fundyense: Temperature and nutrient effects. Nat. Toxins 1999, 7, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taroncher-Oldenburg, G.; Anderson, D.M. Identification and characterization of three differentially expressed genes, encoding S-Adenosylhomocysteine Hydrolase, Methionine Aminopeptidase, and a Histone-Like protein, in the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium fundyense. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 2105–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamasaki, K.; Horie, M.; Tokimitsu, A.; Toda, T.; Taguchi, S. Variability in toxicity of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense isolated from Hiroshima Bay, western Japan, as a reflection of changing environmental conditions. J. Plankton Res. 2001, 23, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.F.; Lu, Y.H. Influence of environmental and nutritional factor son growth, toxicity, and toxin profile of dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum. Toxicon 2001, 38, 1491–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etheridge, S.M.; Roesler, C.S. Effects of temperature, growth, irradiance, and salinity on photosynthesis, growth rates, total toxicity, and toxin composition for Alexandrium fundyense isolates form the Gulf of Maine and the Bay of Fundy. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2005, 52, 2491–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.G.; Hong, H.S.; Wang, D.Z. A sulfotransferase specific to N-21 of gonyautoxin 2/3 from the crude enzyme extraction of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense CI01. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2007, 25, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stüken, A.; Orr, R.J.S.; Kellmann, R.; Murray, S.A.; Neilan, B.A.; Jakobsen, K.J. Discovery of nuclear-encoded genes for the neurotoxin saxitoxin in dinoflagellates. PLoS One 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlow, L.D.; Koutoulis, A.; Hallegraeff, G.M. S-Adenosylmethionine synthetase genes from eleven marine dinoflagellates. Phycologia 2007, 46, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, I.; John, U.; Beszteri, S.; Glöeckner, G.; Krock, B.; Goesmann, A.; Cembella, A.D. Comparative gene expression in toxic versus non-toxic strains of the marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum. BMC Genomics 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, I.; Beszteri, S.; Tillmann, U.; Cembella, A.; John, U. Growth-And nutrient-dependent gene expression in the toxigenic marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum. Harmful Algae 2011, 12, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mihali, T.K.; Kellmann, R.; Neilan, B.A. Characterisation of the paralytic shellfish toxin biosynthesis gene clusters in Anabaena circinalis AWQC131C and Aphanizomenon sp. NH-5. BMC Biochem. 2009, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, A.; Loram, J.; Hackett, J.; Anderson, D.M.; Plumley, F.G.; Bhattacharya, D. Origin of saxitoxin biosynthetic genes in cyanobacteria. PLoS One 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, A.; Evans, A.N.; Kulis, D.M.; Hackett, J.D.; Erdner, D.L.; Anderson, D.M.; Bhattacharya, D. Transcriptome profiling of a toxic dinoflagellate reveals a gene-rich protist and a potential impact on gene expression due to bacterial presence. PLoS One 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.L.; Lo, S.C.; Hodgkiss, I.J. Proteomic study of a model causative agent of harmful red tide, Prorocentrum triestinum I: Optimization of sample preparation methodologies for analyzing with two-dimensional electrophoresis. Proteomics 2002, 2, 1169–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.L.; Hodgkiss, I.J.; Lu, S.H.; Lo, S.C. Use of two-dimensional electrophoresis proteome reference maps of dinoflagellates for species recognization of causative agents of harmful algal blooms. Proteomics 2004, 4, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Z.; Lin, L.; Gu, H.F.; Chan, L.L.; Hong, H.S. Comparative studies on morphology, ITS sequence and protein profile of Alexandrium tamarense and A. catenella isolated from the China Sea. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Z.; Lin, L.; Wang, M.H.; Li, C.; Hong, H.S. Proteomic analysis of a toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella under different growth phases and conditions. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.L.; Sit, W.H.; Lam, P.K.; Hsieh, D.P.; Hodgkiss, I.J.; Wan, J.M.; Ho, A.Y.; Choi, N.M.; Wang, D.Z.; Dudgeon, D. Identification and characterization of a “biomarker of toxicity” from the proteome of the paralytic shellfish toxin-producing dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense (Dinophyceae). Proteomics 2006, 6, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; He, Z.P.; Hong, H.S. Quantitative proteomic analysis of differentially expressed proteins in the toxicity-lost mutant of Alexandrium catenella (Dinophyceae) in the exponential phase. J. Proteomics 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Lin, L.; Wang, D.Z. Effects of nutrient limitation on cell cycle, toxin content and composition of Alexandrium tamarense CI01. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2012, 31, 352–357. [Google Scholar]
- Sako, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Uchida, A.; Arakawa, O.; Noguchi, T.; Ishida, Y. Purification and characterization of a sulfotransferase specific to N-21 of saxitoxin and gonyautoxin 2+3 from the toxic dinoflagellate Gymnodinium catenatum (Dinophyceae). J. Phycol. 2003, 7, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Pomati, F.; Burns, B.P.; Neilan, B.A. Identification of an Na(+)-dependent transporter associated with saxitoxin-producing strains of the cyanobacterium Anabaena circinalis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 4711–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidie, K.B.; Ryan, J.C.; Barbier, M.; Van Dolah, F.M. Gene expression in Florida red tide dinoflagellate Karenia brevis: Analysis of an expressed sequence tag library and development of DNA microarray. Mar. Biotechnol. 2005, 7, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toulza, E.; Shin, M.S.; Blanc, G.; Audic, S.; Laabir, M.; Collos, Y.; Claverie, J.M.; Grzebyk, D. Gene expression in proliferating cells of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella (Dinophyceae). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 4521–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, P.; Fuentes, D.; Valdés, J.; Shmaryahu, A.; Zúñiga, A.; Holmes, D.; Valenzuela, P.D. Preparation and analysis of an Expressed Sequence Tag library from the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella. Mar. Biotechnol. 2008, 10, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Z.; Li, C.; Xie, Z.X.; Dong, H.P.; Lin, L.; Hong, H.S. Homology-Driven proteomics of dinoflagellates with unsequenced genome by MALDI-TOF/TOF and automated de novo sequencing. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosenko, T.; Bhattacharya, D. Horizontal gene transfer in chromalveolates. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Z.; Dong, H.P.; Li, C.; Xie, Z.X.; Lin, L.; Hong, H.S. Identification and characterization of cell wall proteins of a toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella using 2-D DIGE and MALDI TOF-TOF mass spectrometry. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Castiñeira, J.R.; López-Marqués, R.L.; Losadab, M.; Serrano, A. A thermostable K(+)-stimulated vacuolar-type pyrophosphatase from the hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga maritima. FEBS Lett. 2001, 496, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, Y. Chemical and Enzymatic Transformation of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Marine Organisms. In Harmful Algal Blooms; Lassus, P., Arzul, G., Erard, E., Gentien, P., Marcaillou, C., Eds.; Lavoisier: Paris, France, 1995; pp. 475–480. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, T.; Sako, Y.; Uchida, A.; Ishida, Y.; Arakawa, O.; Noguchi, T.; Ishida, Y. Purification and properties of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins sulfotransferase from toxic dinoflagellate Gymnodinium catenatum. In Harmful and Toxic Algal Blooms; Yasumoto, T., Oshima, Y., Fukuyo, Y., Eds.; IOC (UNESCO): Paris, France, 1996; pp. 499–502. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, T.; Sako, Y.; Kakutani, T.; Fujii, A.; Uchida, A. Comparative Study of Two Sulfotransferase for Sulfation to N-21 of Gymnodinium catenatum and Alexandrium catenella Toxins. In Harmful Algae; Reguera, B., Blanco, J., Fernandez, M.L., Wyatt, T., Eds.; TOC (UNESCO): Vigo Xunta de Galicia, Spain, 1998; pp. 366–369. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, M.D.; Selvin, R.C.; Claus, W.; Guillard, R.L. Media for the culture of oceanic ultraphytoplankton. J. Phycol. 1987, 23, 633–638. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, R.J.; Chisholm, S.W. Effects of light and nitrogen limitation on the cell cycle of the dinoflagellate Amphidinium carteri. J. Plankton Res. 1986, 8, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, Y.; Sugino, K.; Yasumoto, T. Latest Advances in HPLC Analysis of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins. In Seventh International IUPAC Symposium on Mycotoxins and Phycotoxins; Natori, S., Hashimoto, K., Veno, Y., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 319–326. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, M.; Szklarczyk, D.; Franceschini, A.; Campillos, M.; Van Mering, C.; Jensen, L.J.; Beyer, A.; Bork, P. STITCH 2: An interaction network database for small molecules and proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, D552–D556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, D.-Z.; Gao, Y.; Lin, L.; Hong, H.-S. Comparative Proteomic Analysis Reveals Proteins Putatively Involved in Toxin Biosynthesis in the Marine Dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 213-232. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11010213
Wang D-Z, Gao Y, Lin L, Hong H-S. Comparative Proteomic Analysis Reveals Proteins Putatively Involved in Toxin Biosynthesis in the Marine Dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(1):213-232. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11010213
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Da-Zhi, Yue Gao, Lin Lin, and Hua-Sheng Hong. 2013. "Comparative Proteomic Analysis Reveals Proteins Putatively Involved in Toxin Biosynthesis in the Marine Dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella" Marine Drugs 11, no. 1: 213-232. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11010213
APA StyleWang, D.-Z., Gao, Y., Lin, L., & Hong, H.-S. (2013). Comparative Proteomic Analysis Reveals Proteins Putatively Involved in Toxin Biosynthesis in the Marine Dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella. Marine Drugs, 11(1), 213-232. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11010213