A Conus regularis Conotoxin with a Novel Eight-Cysteine Framework Inhibits CaV2.2 Channels and Displays an Anti-Nociceptive Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Collection and Venom Extraction
2.2. Chemicals, Solvents and Materials
2.3. Peptide Purification
2.4. Amino Acid Sequencing
2.5. Data Analysis
2.6. Culture of SCG Neurons
2.7. Electrophysiological Recording
2.8. Current Measurements and Analysis
2.9. Experimental Animals
2.10. Hot-Plate Test
2.11. Formalin Test
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Sequence of the Native Peptide
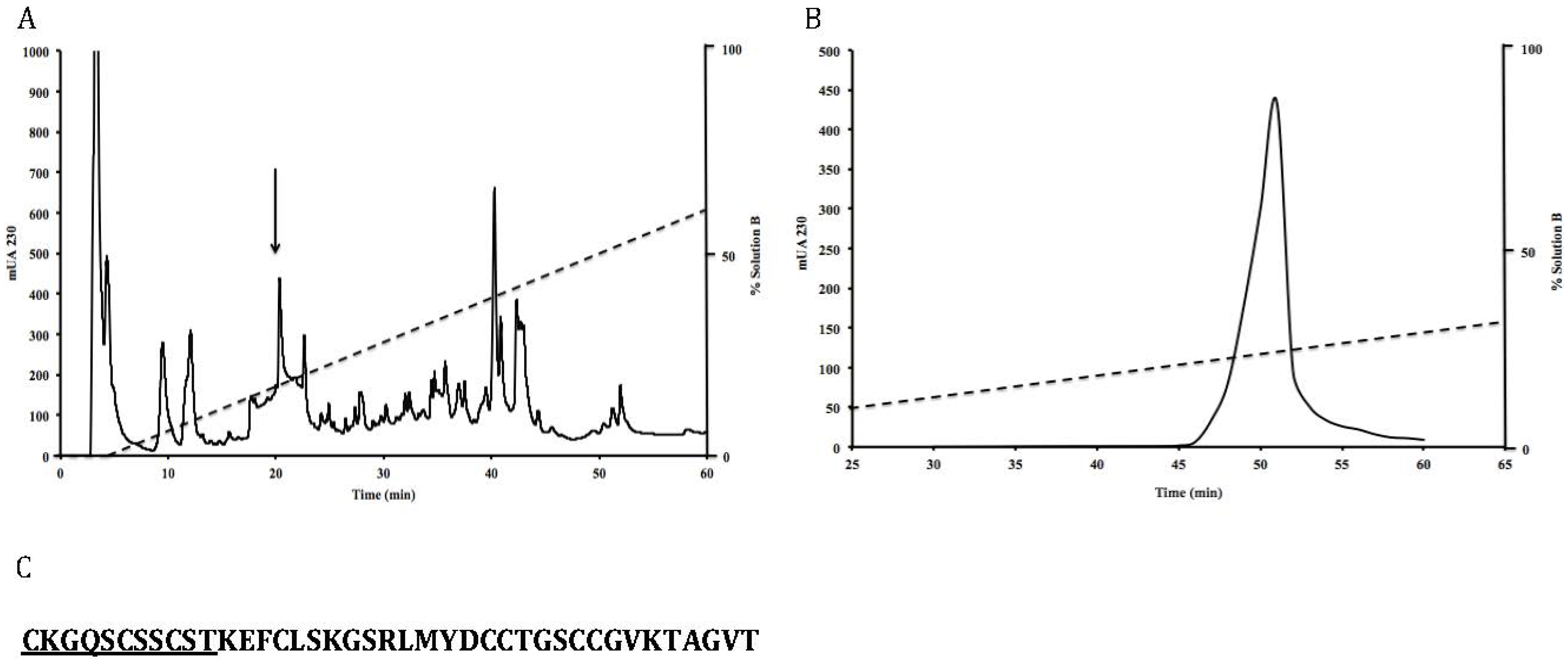
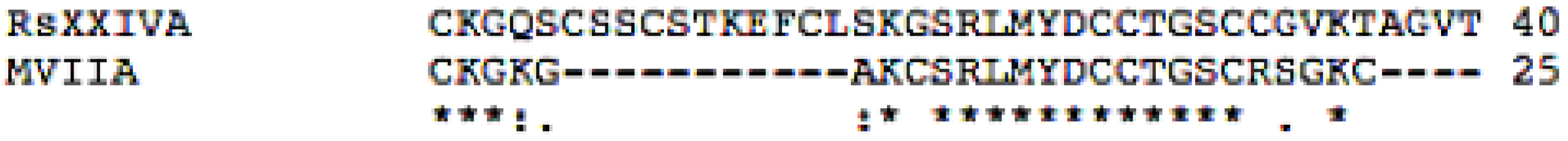
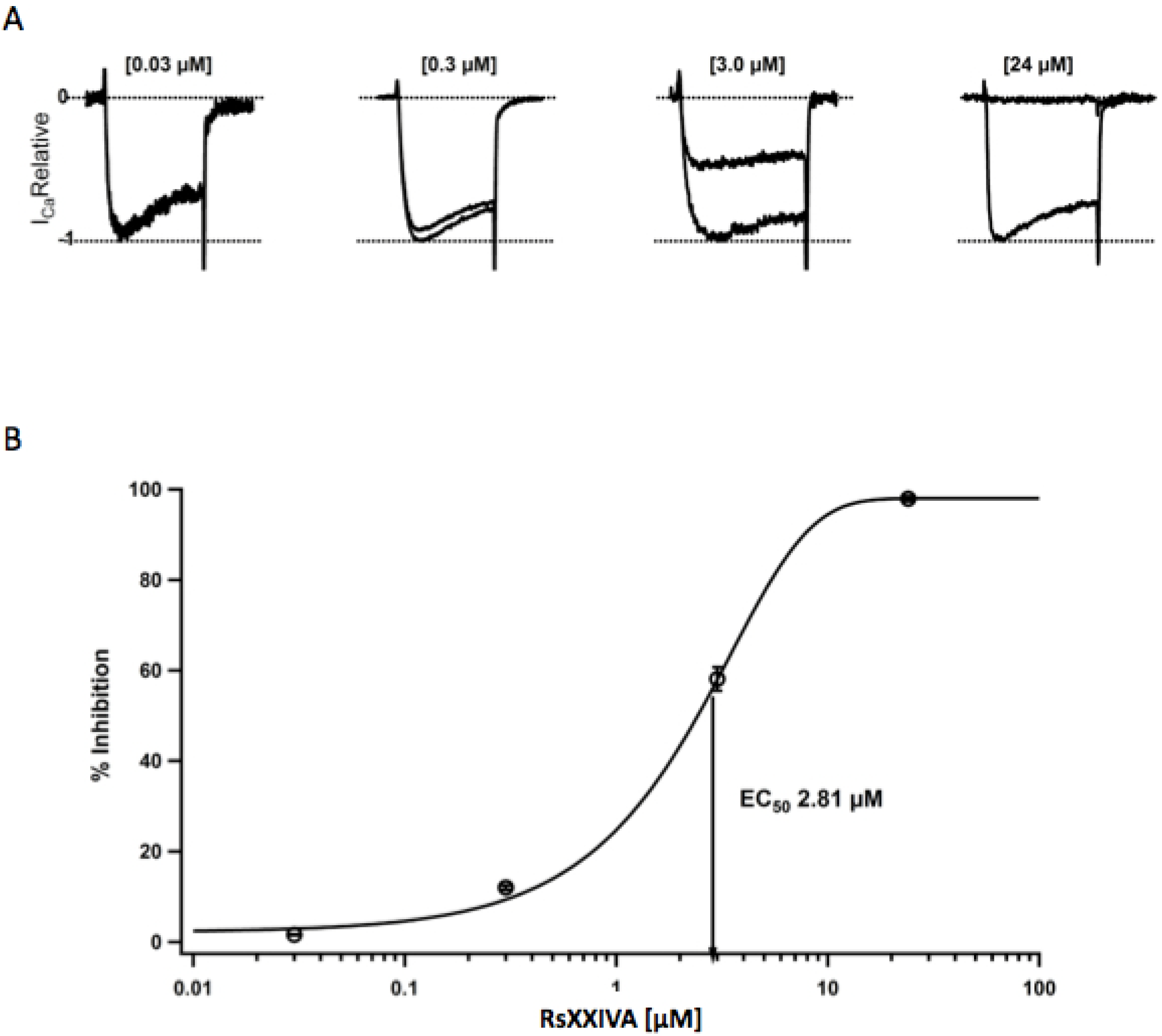
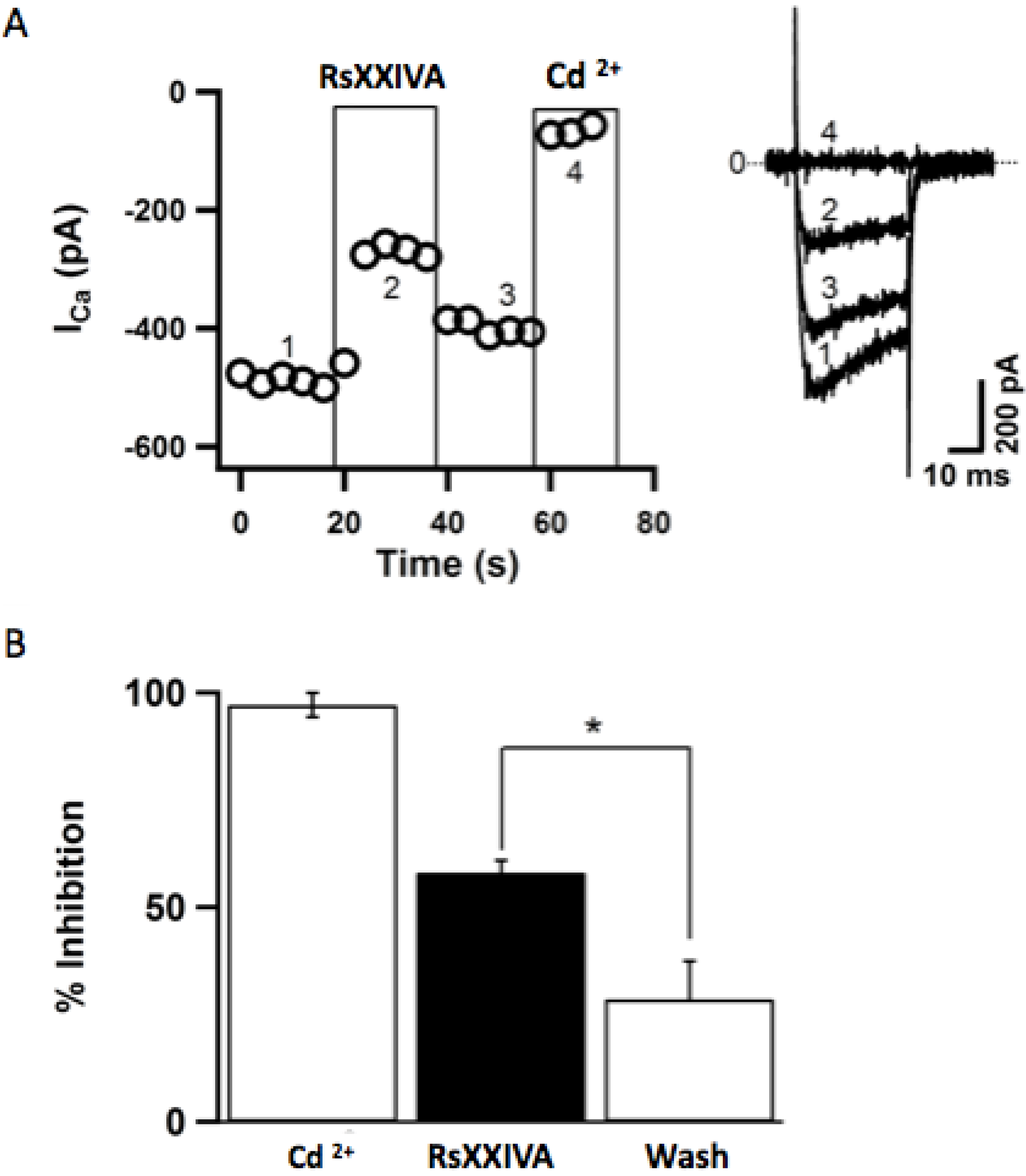
3.2. Effects of Toxin RsXXIVA on CaV2.2 Calcium Channel Current
3.3. Analgesic Activity of RsXXIVA


4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
References
- Han, T.S.; Teichert, R.W.; Olivera, B.M.; Bulaj, G. Conus Venoms—A rich source of peptide-based therapeutics. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 2462–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twede, V.D.; Miljanich, G.; Olivera, B.M.; Bulaj, G. Neuroprotective and cardioprotective conopeptides: An emerging class of drug leads. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Devel. 2009, 12, 231–239. [Google Scholar]
- Craik, D.J.; Adams, D.J. Chemical modification of conotoxins to improve stability and activity. ACS Chem. Biol. 2007, 2, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, B.M. Conus peptides: Biodiversity-based discovery and exogenomics. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 31173–31177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Khoo, K.K.; Xu, S.; Zhou, M.; Boonyalai, N.; Perugini, M.A.; Shao, X.; Chi, C.; Galea, C.A.; Wang, C.; et al. A helical conotoxin from Conus imperialis has a novel cysteine framework and defines a new superfamily. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 14973–14983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, L.J.; Gray, W.R.; Yoshikami, D.; Olivera, B.M. Conus venoms: A rich source of neuroactive peptides. J. Toxicol. 1985, 4, 107–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, W.R.; Olivera, B.M.; Cruz, L.J. Peptide toxins from venomous Conus snails. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 1988, 57, 665–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, J.M.; Olivera, B.M.; Cruz, L.J. Conus peptides as probes for ion channels. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 294, 605–624. [Google Scholar]
- Bingham, J.P.; Mitsunaga, E.; Bergeron, Z.L. Drugs from slugs-Past, present and future perspectives of ω-conotoxin research. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 183, 83:1–83:18. [Google Scholar]
- Kass, Q.; Westermann, J.C.; Halai, R.; Wang, C.K.; Craik, D.J. ConoServer, a database for conopeptide sequences and structures. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 445–446. [Google Scholar]
- Bernáldez, J.; López, O.; Licea, A.; Salceda, E.; Arellano, R.O.; Vega, R.; Soto, E. Electrophysiological characterization of a novel small peptide from the venom of Conus californicus that targets voltage-gated neuronal Ca2+ channels. Toxicon 2011, 57, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, D.E.; Li, B.; García-Ferreiro, R.E.; Hernández-Ochoa, E.O.; Yan, K.; Gautam, N.; Catterall, W.A.; Mackie, K.; Hille, B. G-Protein β-subunit specificity in the fast membrane-delimited inhibition of Ca2+ channels. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 9163–9170. [Google Scholar]
- Hamill, O.P.; Marty, A.; Neher, E.; Sakmann, B.; Sigworth, F.J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cell and cell-free membrane patches. Pflug. Arch. 1981, 391, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmberg, A.B.; Bannon, A.W. Current Protocols in Neuroscience; Wiley: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1999; pp. 8.9.1–8.9.15, doi:10.1002/0471142301. [Google Scholar]
- Dubuisson, D.; Dennis, S.G. The formalin test: A quantitative study of analgesic effects of morphine, miperidine, and brain stem stimulation in rat and cats. Pain 1977, 4, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, B.M.; Cruz, L.J. Conotoxins, in retrospect. Toxicon 2001, 39, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, K.J.; Schroeder, T.; Lewis, R. Structure–Activity relationships of ω-conotoxins at N-type voltage-sensitive calcium channels. J. Mol. Recognit. 2000, 13, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, T.; Kim, J.I.; Kobayashi, K.; Kodera, Y.; Maeda, T.; Sato, K. Three-dimensional structure in solution of the calcium channel blocker ω-conotoxin MVIIA. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 10256–10265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowersox, S.S.; Luther, R. Pharmacotherapeutic potential of ω-conotoxin MVIIA (SNX-111), an N-type neuronal calcium channel bloquer found in the venom of Conus magus. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1651–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintz, I.M.; Bean, B.P. Block of calcium channels in rat neurons by synthetic ω-Aga-IVA. Neuropharmacology 1993, 32, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, L.M.; Morrill, J.A.; Bean, B.P. ω-Conotoxin block of N-type calcium channels in frog and rat sympathetic neurons. J. Neurosci. 1994, 14, 5011–5027. [Google Scholar]
- García-Ferreiro, R.E.; Hernández-Ochoa, E.O.; García, D.E. Modulation of N-type Ca2+channel current kinetics by PMA in rat sympathetic neurons. Pflug. Arch. 2001, 442, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.-P.; Doering, C.J.; Winkfein, R.J.; Beedle, A.M.; Spafford, J.D.; Zamponi, G.W. Determinants of inhibition of transientrly expressed voltage-gated calcium channels by ω-conotoxins GVIA and MVIIA. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 20171–20178. [Google Scholar]
- Randolph, B.C.; Peters, M. Analgesic effectiveness of ketorolac compared to meperidine in the rat formalin test. Anesth. Prog. 1997, 44, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.; Liu, L.; Shao, X.; Chi, C.; Wang, C. Identification of a novel class of conotoxins defined as V-conotoxins with a unique cysteine pattern and signal peptide sequence. Peptides 2008, 29, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczek, O.; Wei, D.; Babon, J.J.; Yang, X.; Fiedler, B.; Chen, P.; Yoshikami, D.; Olivera, B.M.; Bulaj, G.; Norton, R.S. Structure and sodium channel activity of an excitatory I1-superfamily conotoxin. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 9929–9940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.A.; Begley, G.S.; Czerwiec, E.; Stenberg, L.M.; Jacobs, M.; Kalume, D.E.; Roepstorff, P.; Stenflo, J.; Furie, B.C.; Furie, B. Precursors of novel Gla-containing conotoxins contain a carboxy-terminal recognition site that directs gamma-carboxylation. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 9150–9159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, M.B.; Lopez-Vera, E.; Ortiz, E.; Becerril, B.; Possani, L.D.; Olivera, B.M.; Heimer de la Cotera, E.P. A novel conotoxin from Conus delessertii with posttranslationally modified lysine residues. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 11130–11136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.D.; Liu, L.; Shao, X.X.; Peng, C.; Chi, C.W.; Guo, Z.Y. Isolation and cloning of a conotoxin with a novel cysteine pattern from Conus caracteristicus. Peptides 2008, 29, 1521–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliger, C.A.; Richmond, T.A.; Lebaric, Z.N.; Pierce, N.T.; Sweedler, J.V.; Gilly, W.F. Diversity of conotoxin types from Conus californicus reflects a diversity of prey types and a novel evolutionary history. Toxicon 2011, 57, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauferstein, S.; Huys, I.; Kuch, U.; Melaun, C.; Tytgat, J.; Mebs, D. Novel conopeptides of the I-superfamily occur in several clades of cone snails. Toxicon 2004, 44, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, C.; Gockel, H.H.; Gruhn, K.; Krumova, E.K.; Edel, M.A. Increased risk of suicide under intrathecal ziconotide treatment?—A warning. Pain 2011, 152, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scroggs, R.S.; Fox, A.P. Calcium curent variation between acutely isolated adult rat dorsal root ganglion neurons of different size. J. Physiol. 1992, 445, 639–658. [Google Scholar]
- Sanger, G.J.; Ellis, E.S.; Harries, M.H.; Tilford, N.S.; Wardle, K.A.; Benham, C.D. Rank-Order inhibition by ω-conotoxins in human and animal autonomic nerve preparations. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 388, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, M.J.; Flinn, J.P.; Pallaghy, P.K.; Murphy, R.; Whorlow, S.L.; Wright, C.E.; Norton, R.S.; Angus, J.A. Structure-function relationships of ω-conotoxin GVIA. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 12014–12023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernáldez, J.; Román-González, S.A.; Martínez, O.; Jiménez, S.; Vivas, O.; Arenas, I.; Corzo, G.; Arreguín, R.; García, D.E.; Possani, L.D.; et al. A Conus regularis Conotoxin with a Novel Eight-Cysteine Framework Inhibits CaV2.2 Channels and Displays an Anti-Nociceptive Activity. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1188-1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11041188
Bernáldez J, Román-González SA, Martínez O, Jiménez S, Vivas O, Arenas I, Corzo G, Arreguín R, García DE, Possani LD, et al. A Conus regularis Conotoxin with a Novel Eight-Cysteine Framework Inhibits CaV2.2 Channels and Displays an Anti-Nociceptive Activity. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(4):1188-1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11041188
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernáldez, Johanna, Sergio A. Román-González, Oscar Martínez, Samanta Jiménez, Oscar Vivas, Isabel Arenas, Gerardo Corzo, Roberto Arreguín, David E. García, Lourival D. Possani, and et al. 2013. "A Conus regularis Conotoxin with a Novel Eight-Cysteine Framework Inhibits CaV2.2 Channels and Displays an Anti-Nociceptive Activity" Marine Drugs 11, no. 4: 1188-1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11041188
APA StyleBernáldez, J., Román-González, S. A., Martínez, O., Jiménez, S., Vivas, O., Arenas, I., Corzo, G., Arreguín, R., García, D. E., Possani, L. D., & Licea, A. (2013). A Conus regularis Conotoxin with a Novel Eight-Cysteine Framework Inhibits CaV2.2 Channels and Displays an Anti-Nociceptive Activity. Marine Drugs, 11(4), 1188-1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11041188







