Kaolinite and Silica Dispersions in Low-Salinity Environments: Impact on a Water-in-Crude Oil Emulsion Stability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
 ], the so-called attachment energy, it was argued that a reduction in particle surface charge (or zeta potential) would lead to flocculation and therefore would increase attachment energy. The little observed influence of this is due to the kinetic control of the attachment process. Increased stability with increased particle concentration is due to better surface coverage, according to Yang et al.
], the so-called attachment energy, it was argued that a reduction in particle surface charge (or zeta potential) would lead to flocculation and therefore would increase attachment energy. The little observed influence of this is due to the kinetic control of the attachment process. Increased stability with increased particle concentration is due to better surface coverage, according to Yang et al.2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
- Centrifuge for 5 min to form a tight pellet
- Draw off supernatant and resuspend in 25% solvent/75% water
- Repeat with 50, 70 and 100% solvent solutions
- Heat in an oven at 70 °C for 24 h, after which crush the pellet and dry again
| Species | Fraction (ppm) |
|---|---|
| NaCl | 29,803 |
| CaCl2 | 2104 |
| Na2SO4 | 5903 |
| MgSO4 | 841 |
| TDS | 38,651 |
2.2. Experimental Procedures
2.2.1. Procedure for PH Alteration
2.2.2. Bottle Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Solids Characterization


3.2. Zeta Potential


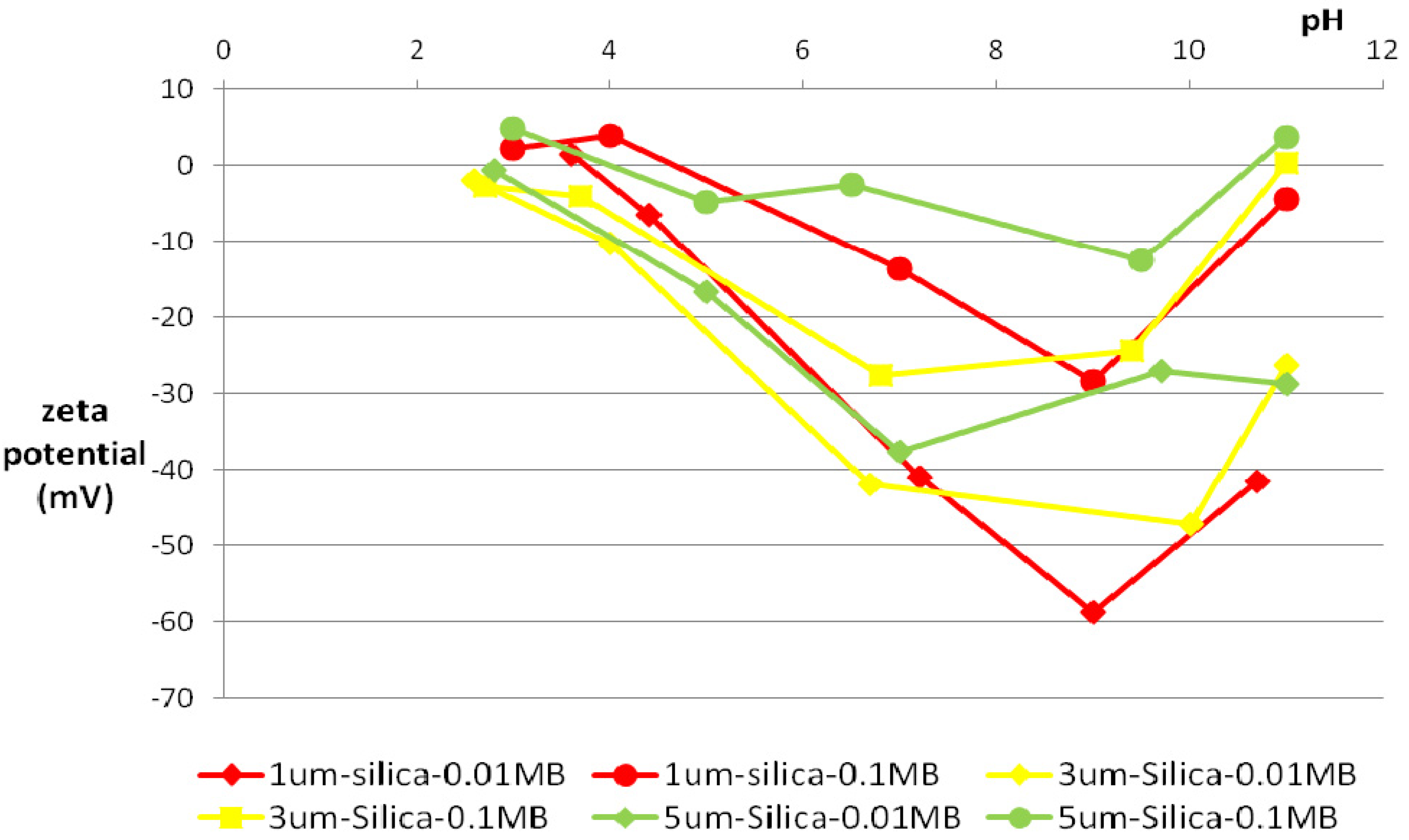
3.3. Particle-Size Distribution

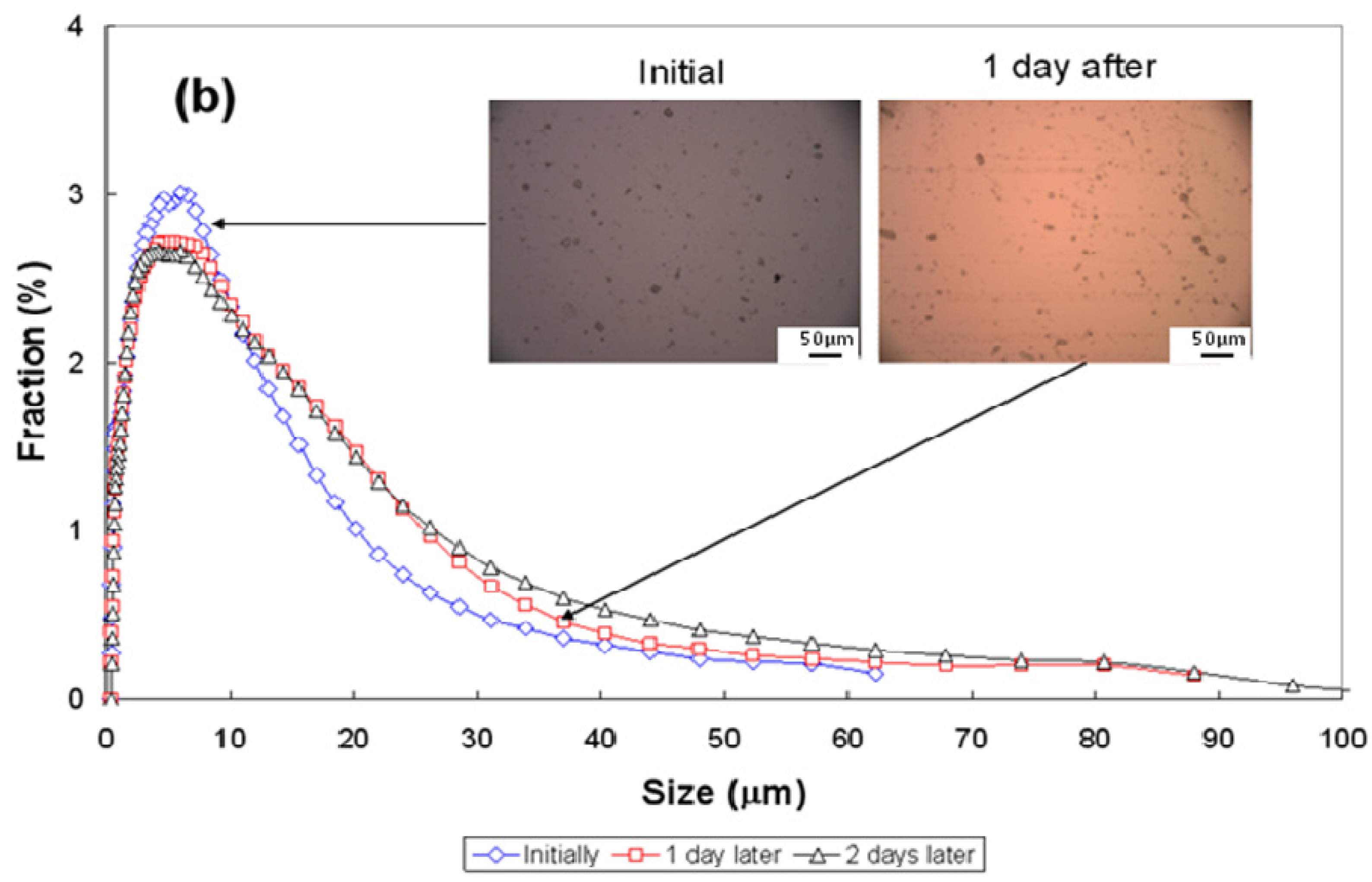




| Conditions | pH~2.5 | pH~7 | pH~11 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial (µm) | 1 day (µm) | 2 days (µm) | Initial (µm) | 1 day (µm) | 2 days (µm) | Initial (µm) | 1 day (µm) | 2 days (µm) | |
| Kaofine 0.01MLB | 1.75 | 2.15 | 2.29 | 1.17 | 1.55 | 1.34 | 1.06 | 1.21 | 1.62 |
| Kaofine 0.1MLB | 1.85 | 2.11 | 2.24 | - | - | - | 1.62 | 4.44 | 3.43 |
| Kaofine 1MLB | 2.55 | 1.70 | 1.84 | 0.81 | 1.25 | 1.29 | 5.15 | 7.93 | 7.72 |
| Kaolinite 0.01MLB | 5.86 | 11.37 | 7.85 | 6.38 | 7.77 | 8.36 | 7.32 | 8.91 | 9.48 |
| Kaolinite 0.1MLB | 5.27 | 10.59 | 8.63 | - | - | - | 7.4 | 8.46 | 10.16 |
| Kaolinite 1MLB | 4.96 | 8.42 | 9.51 | 5.14 | 7.99 | 7.7 | 8.35 | 10.05 | 12.58 |
| 3 µm Silica 0.01MLB | 2.98 | 3.11 | 3.12 | 2.86 | 3.52 | 3.62 | 3.11 | 3.72 | 3.74 |
| 3 µm Silica 0.1MLB | 3.16 | 3.35 | 3.5 | - | - | - | 3.69 | 7.98 | 6.77 |
| 3 µm Silica 1MLB | 3.03 | 3.3 | 3.36 | 2.86 | 3.23 | 3.41 | 4.65 | 13.64 | 17.84 |
3.4. Solid-Stabilized Emulsions
3.4.1. Clay-Stabilized Emulsions



3.4.2. Silica Stabilized Emulsion

4. Closing Remarks

Acknowledgments
References
- Pickering, S.U. Emulsions. J. Chem. Soc. 1907, 91, 2001–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, T.N.; Pugh, R.J.; Franks, G.V.; Jamenson, G.J. The role of particles in stabilizing foams and emulsions. Adv. Colloid Interf. 2008, 137, 57–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arditty, S.; Schmitt, V.; Giermanska-Kahn, J.; Leal-Calderon, F. Materials based on solid-stabilized emulsions. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2004, 275, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binks, B.P. Particles as surfactants—similarities and differences. Curr. Opin. Colloid Int. 2002, 7, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambe, D.E.; Sharma, M.M. Factors controlling the stability of colloid-stabilizd emulsions. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 1993, 157, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztukowski, D.M.; Yarranton, H.W. Oilfield solids and water-in-oil emulsion stability. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2005, 285, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, Z.; Masliyah, J. Bitumen-clay interactions in aqueous media studied by zeta potential distribution measurement. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2002, 252, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Masliyah, J.H. Effect of pH on adsorption and desorption of clay particles at oil-water interface. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 1996, 181, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsamantakis, C.; Masliyah, J.; Yeung, A.; Gentzis, T. The behaviour of micro-bitumen drops in aqueous clay environments. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2005, 288, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, K.; Yeung, A.; Masliyah, J. The viscoplastic properties of crude oil-water interfaces. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 6016–6028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsamantakis, C.; Masliyah, J.; Yeung, A.; Gentzis, T. The Investigation of the interfacial properties of water-in-diluted-bitumen emulsions using micropipette techniques. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2005, 284, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngai, T.; Auweter, H.; Behrens, S.H. Environmental responsiveness of microgel particles and particle-stabilized emulsions. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 8171–8177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruglyakov, P.M.; Nushtayeva, A.V. Investigation of the influence of capillary pressure on stability of a thin layer emulsion stabilized by solid particles. Colloids Surface A 2005, 263, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Niu, Q.; Lan, Q.; Sun, D. Effect of dispersion pH on the formation and stability of pickering emulsions stabilized by layered double hydroxides particles. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2007, 306, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieme, J.; Abend, S.; Lagaly, G. Aggregation in pickering emulsions. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1999, 277, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Alvarado, V. Effects of aqueous-phase salinity on water-in-oil emulsion stability: bottle test determination. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Alvarado, V. Direct current electro-rheological stability determination of water-in-oil emulsions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 13811–13816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Brandvik, A.; Alvarado, V. Probing interfacial water-in-crude oil emulsion stability controls using electrorheology. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 6359–6365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Alvarado, V.; Huzurbazar, S.V. Effect of salinity on water-in-crude oil emulsion stability: evaluation of drop-size distribution proxy. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Hirasaki, G.J.; Miller, C.A.; Ng, S. Effects of clay wettability and process variables on separation of diluted bitumen emulsion. Energy Fuels 2010, 25, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Hirasaki, G.J.; Miller, C.A. Characterization of kaolinite potential for interpretation of wettability alteration in diluted bitumen emulsion separation. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 2350–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friberg, S.E. Emulsion stabilization by solid particles-A two-layer approach: Spherical particles. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2005, 26, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Alvarado, V. Kaolinite and Silica Dispersions in Low-Salinity Environments: Impact on a Water-in-Crude Oil Emulsion Stability. Energies 2011, 4, 1763-1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/en4101763
Wang X, Alvarado V. Kaolinite and Silica Dispersions in Low-Salinity Environments: Impact on a Water-in-Crude Oil Emulsion Stability. Energies. 2011; 4(10):1763-1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/en4101763
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiuyu, and Vladimir Alvarado. 2011. "Kaolinite and Silica Dispersions in Low-Salinity Environments: Impact on a Water-in-Crude Oil Emulsion Stability" Energies 4, no. 10: 1763-1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/en4101763
APA StyleWang, X., & Alvarado, V. (2011). Kaolinite and Silica Dispersions in Low-Salinity Environments: Impact on a Water-in-Crude Oil Emulsion Stability. Energies, 4(10), 1763-1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/en4101763






