Effect of Silane Coupling Agent on Tribological Properties of Hemp Fiber-Reinforced Plant-Derived Polyamide 1010 Biomass Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Processing
2.3. Mechanical Properties
2.4. Tribological Properties
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Material Characterization
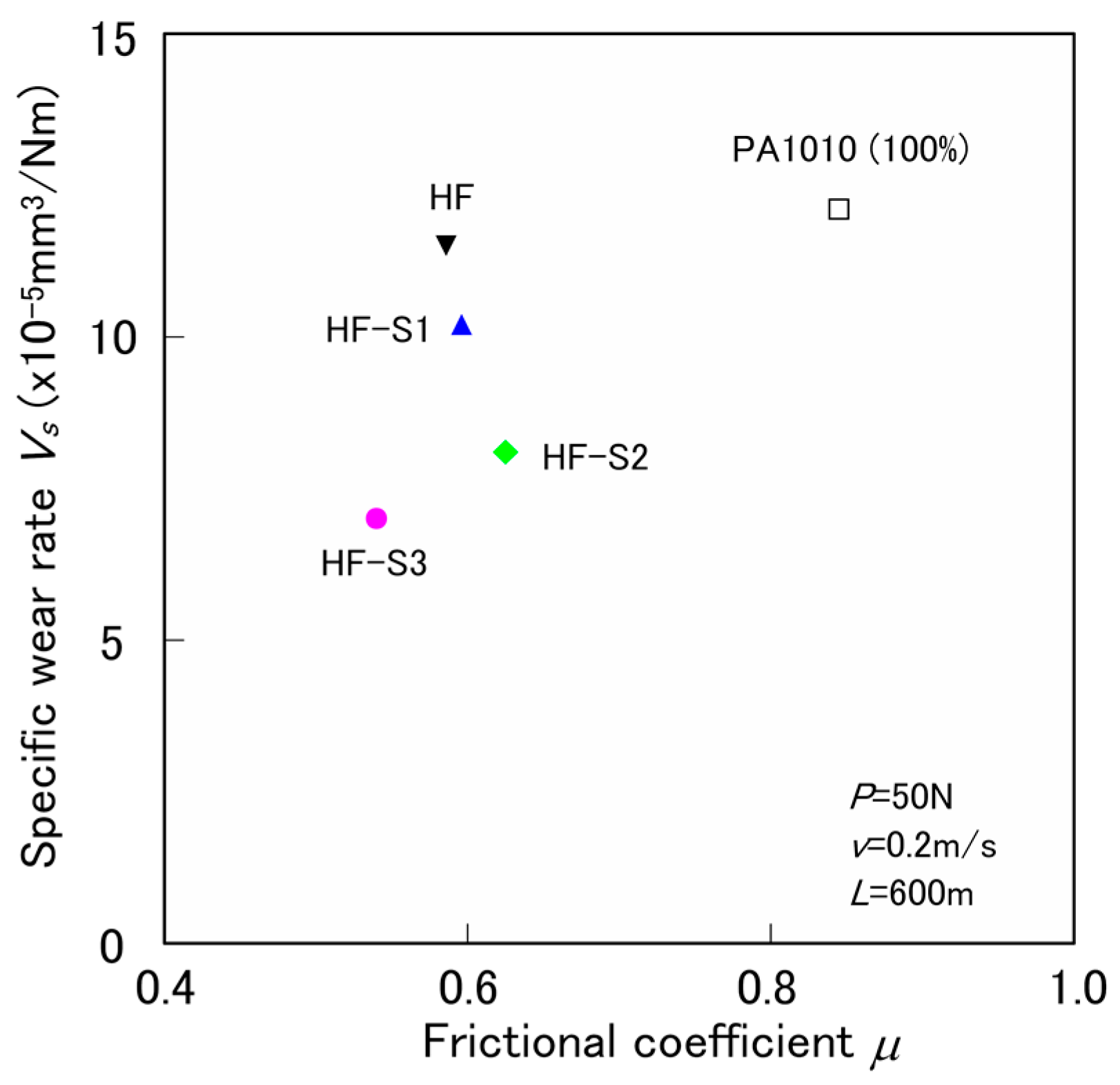
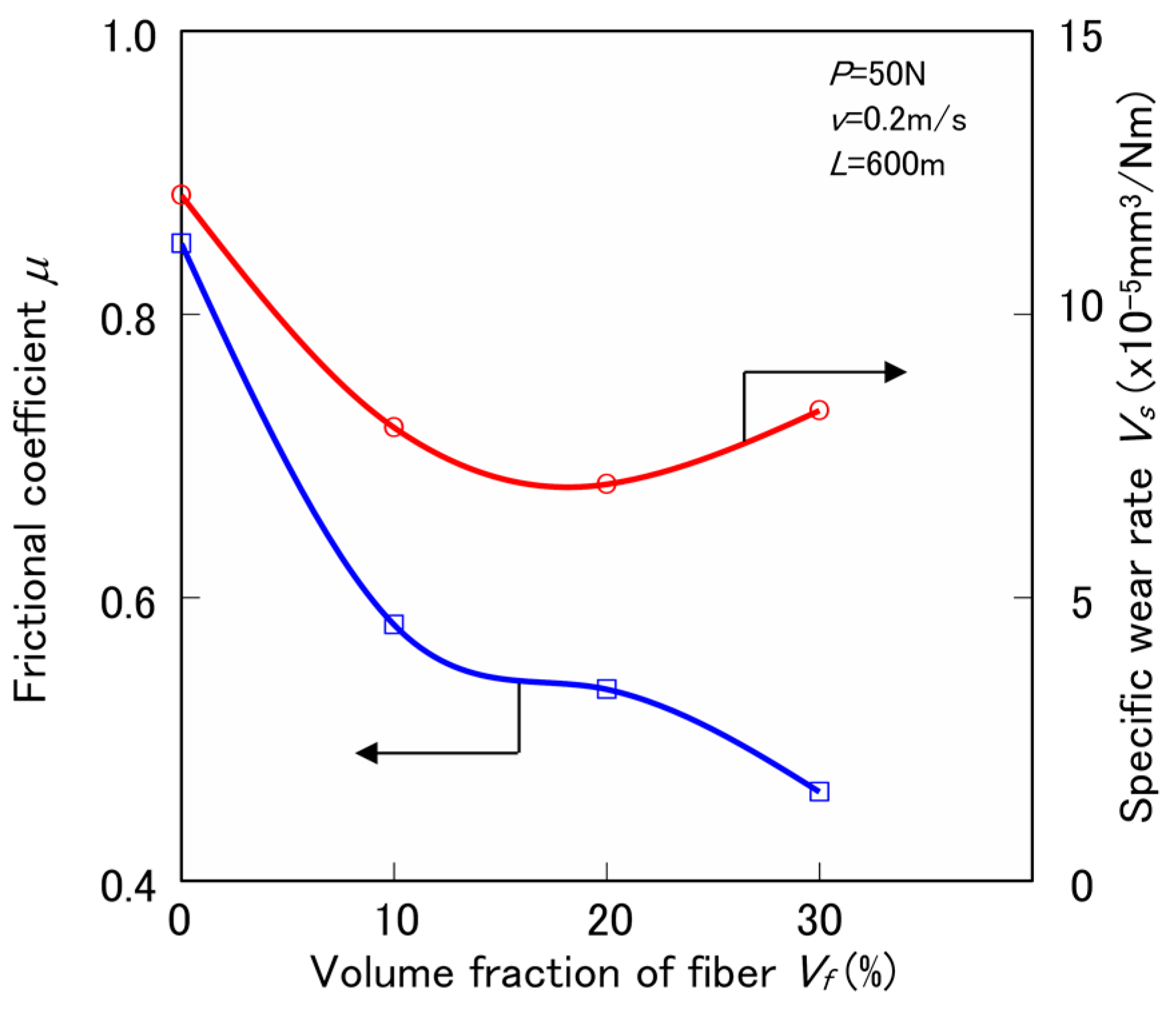
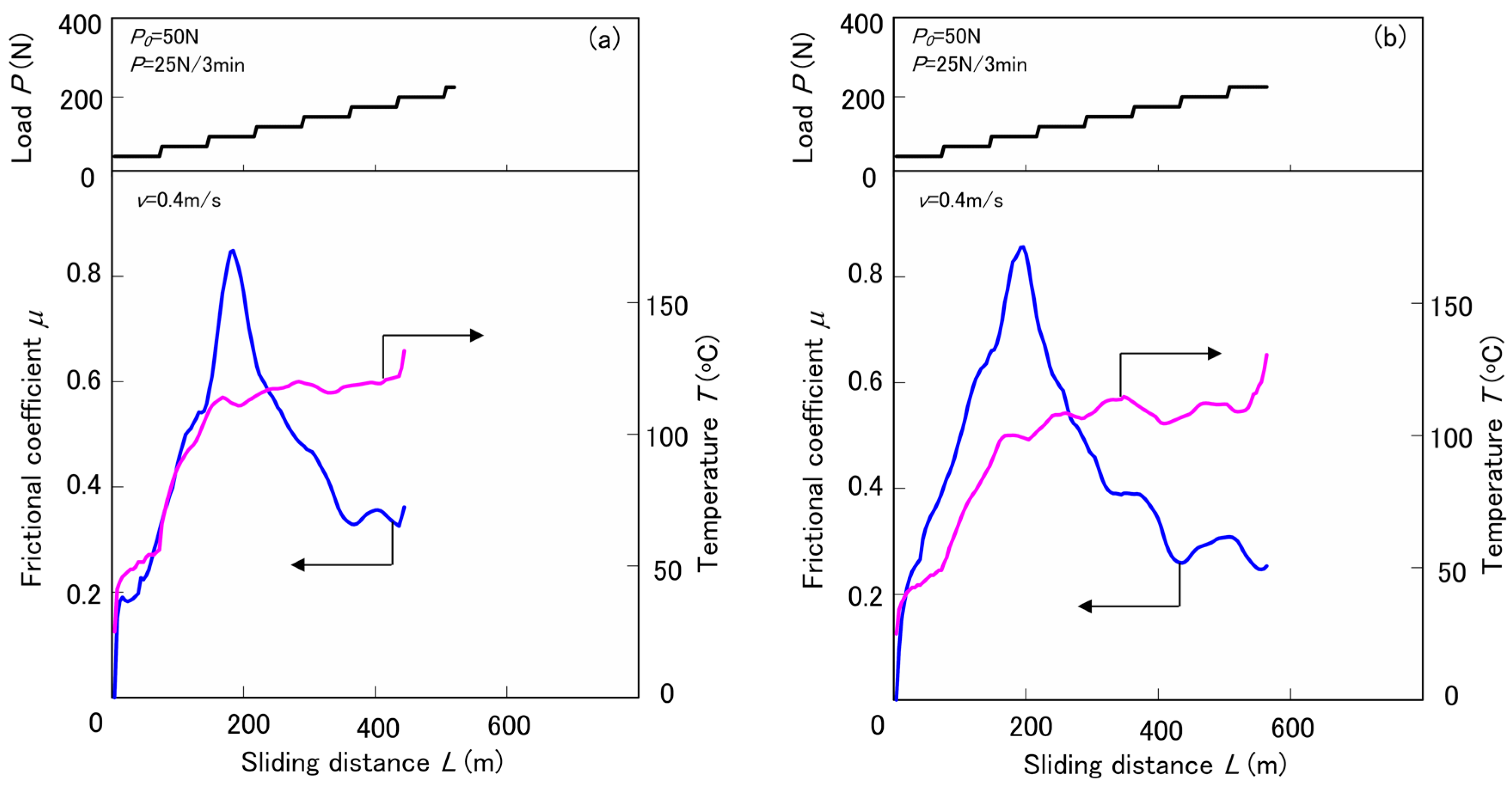
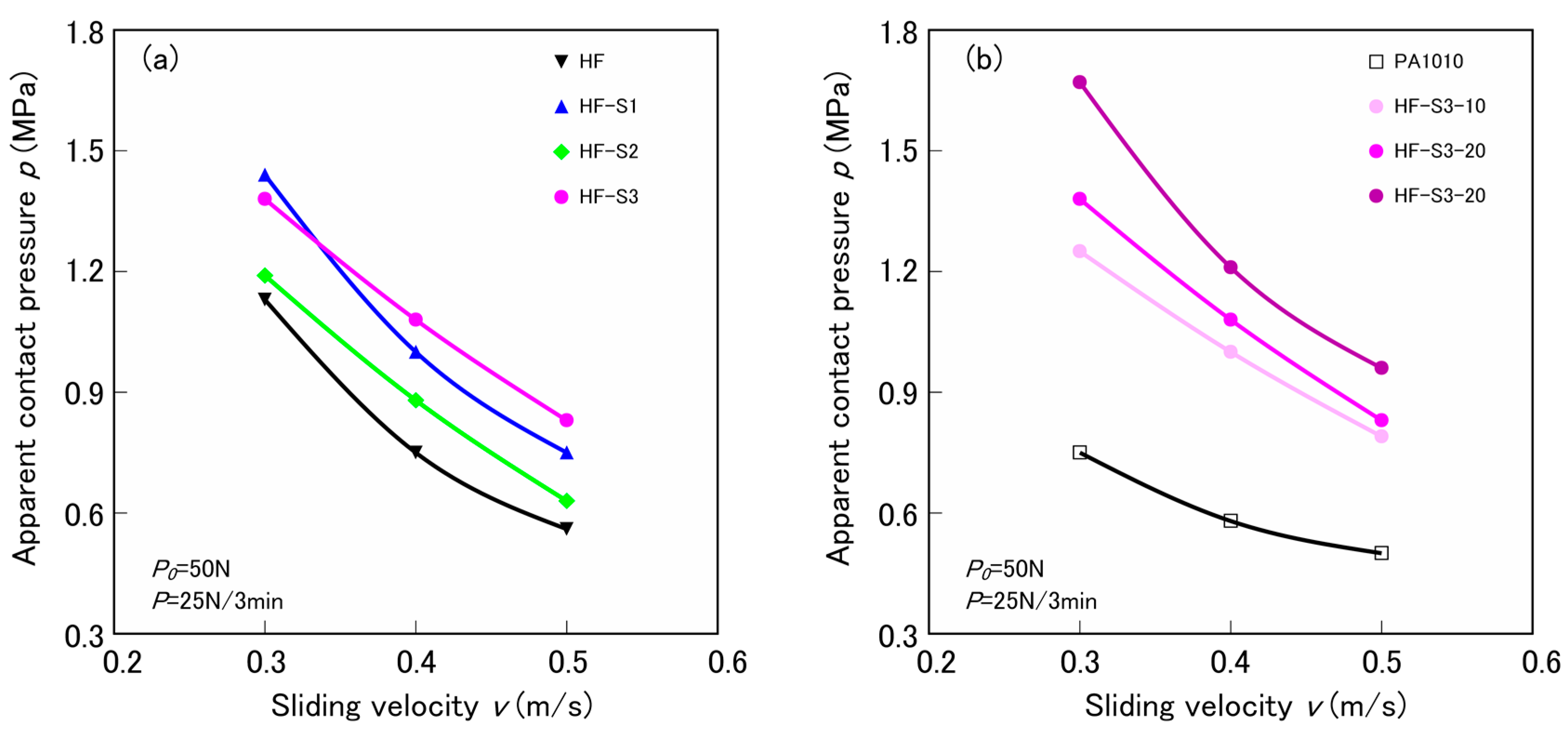
3.2. Tribological Properties by the Constant Normal Load and Constant Sliding Velocity Test
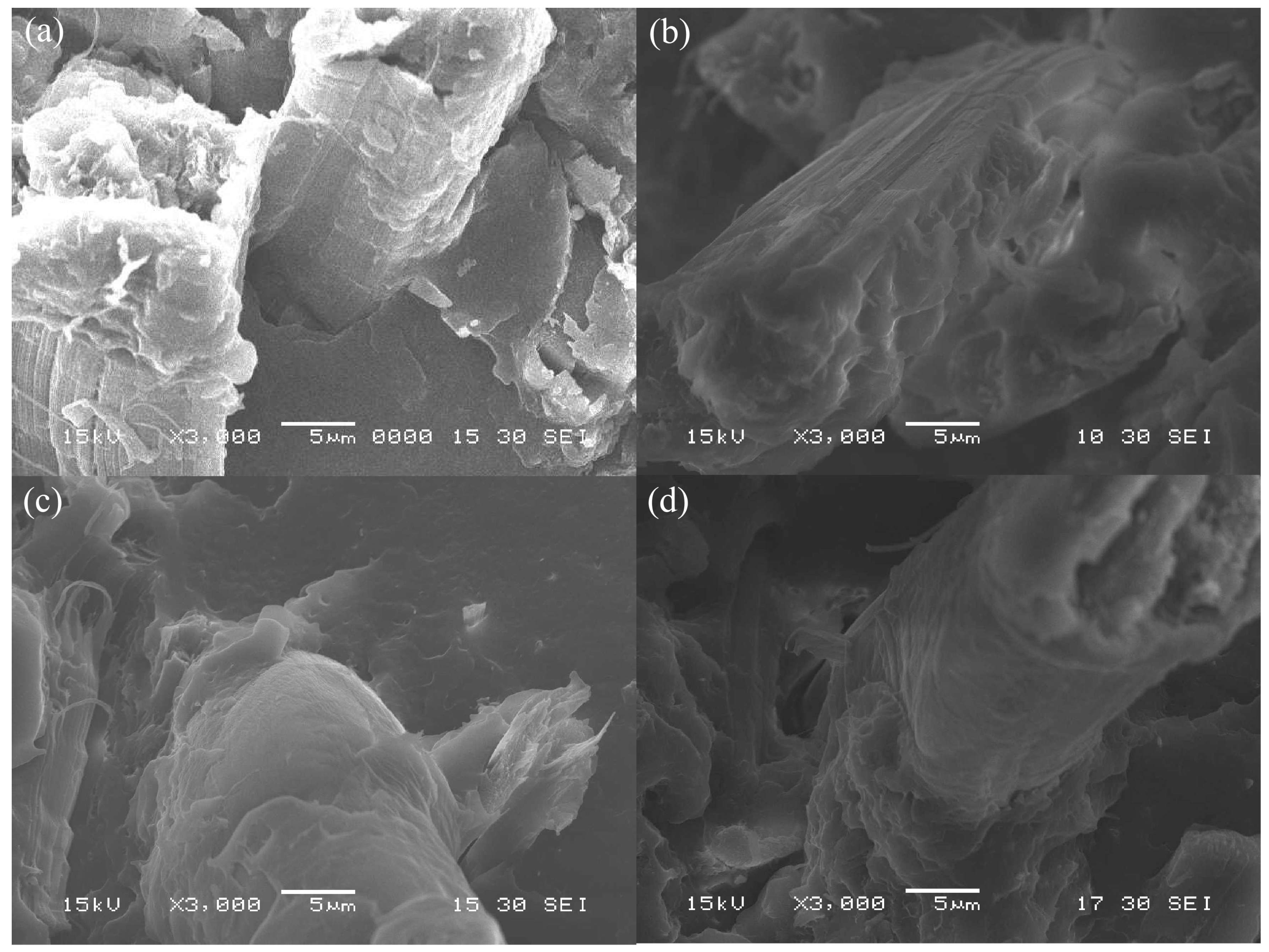
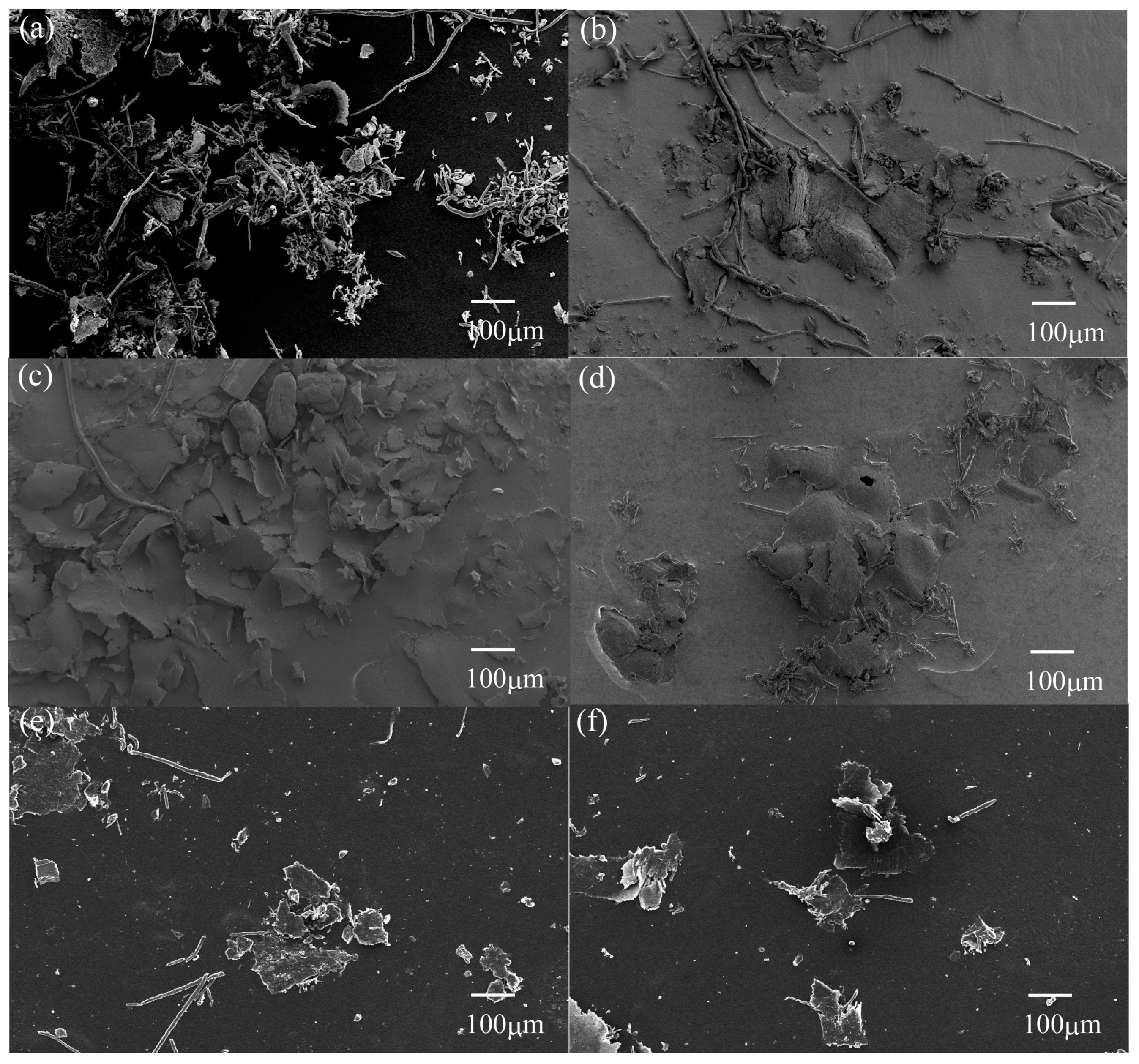
3.3. SEM Observation and Wear Mechanism
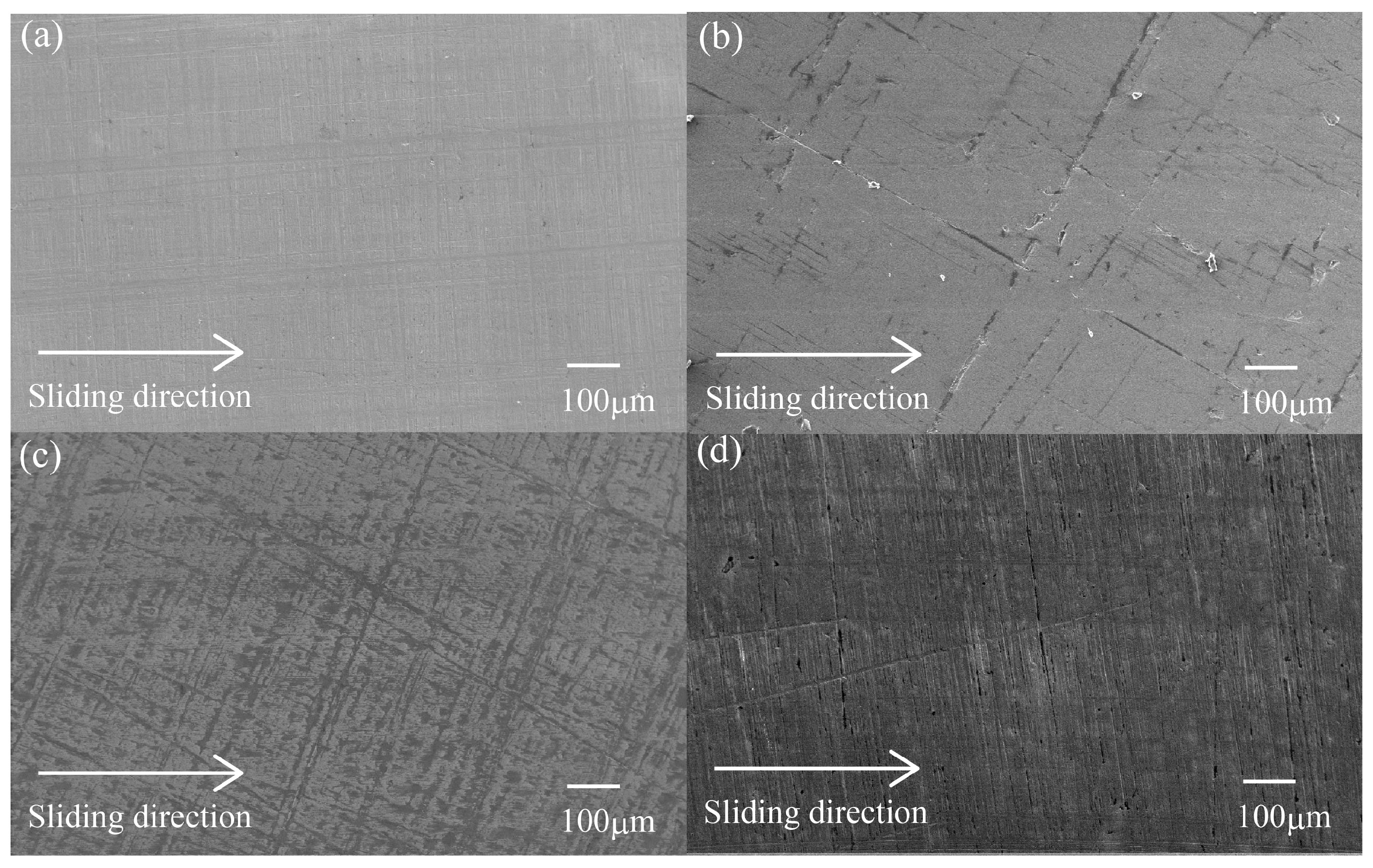
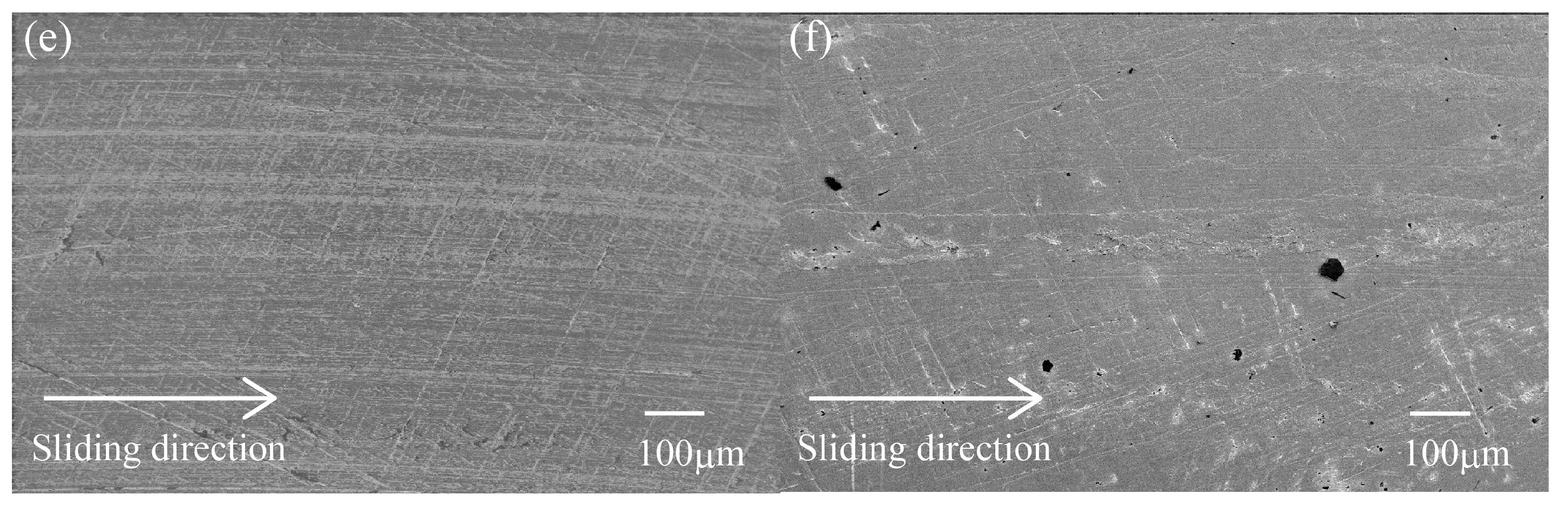
3.3.1. Metallic Counterface
3.3.2. Wear Debris
3.3.3. Worn Surface
3.3.4. Discussion
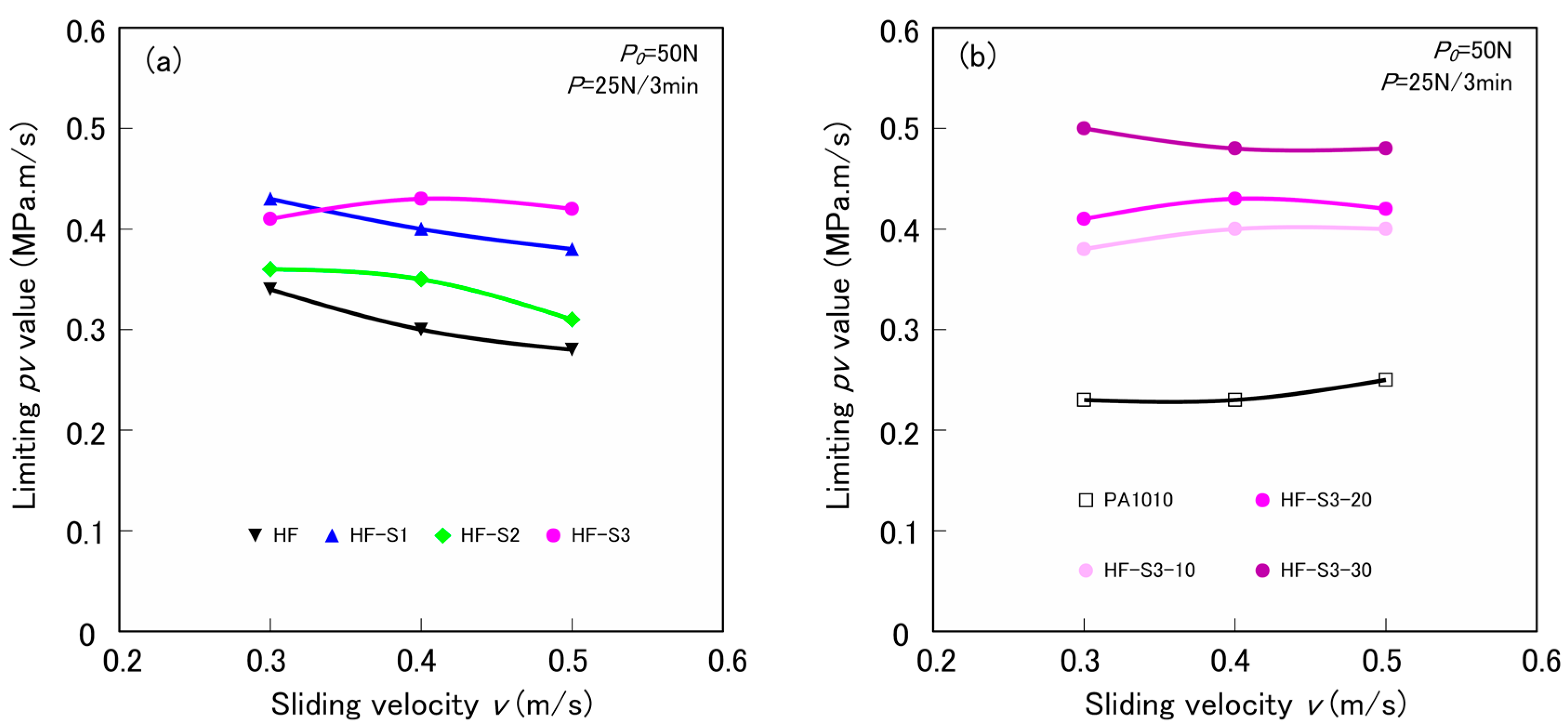
3.4. Limitting pv Value
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wambua, P.; Ivens, J.; Verpoest, L. Natural fibres: Can they replace glass in fibre reinforced plastics? Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.V.; Drzal, L.T.; Mohanty, A.K.; Arora, S. Are natural fiber composites environmentally superior to glass fiber reinforced composites? Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2004, 35, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, S.; Kaith, B.S.; Kaur, I. Pretreatments of natural fibers and their application as reinforcing material in polymer composite—A review. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2009, 49, 1253–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruk, O.; Bledzki, A.K.; Fink, H.-P.; Sain, M. Biocomposites reinforced with natural fibers: 2000–2010. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1552–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koronis, G.; Silva, A.; Fontu, M. Green composites: A review of adequate materials for automotive applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 44, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajiyama, T.; Yasuda, T.; Mimoto, S.; Shimizu, K.; Hayashi, K.; Yamanaka, T.; Murakami, M. Effect of Hexamethylene Diisocyanate as Compatibilizer on the Mechanical Properties of Banana Fiber/Poly (butylene succinate) Composites. Int. Polym. Proc. 2013, 28, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishitani, Y.; Yamanaka, T.; Kajiyama, T.; Kitano, T. Thermal Properties of Hemp Fiber Reinforced Plant-Derived Polyamide Biomass Composites and their Dynamic Viscoelastic Properties in Molten State. In Viscoelastic and Viscoplastic Materials; El-Amin, M., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016; pp. 53–79. ISBN 978-953-51-2603-4. [Google Scholar]
- Oksman, K.; Skrifvars, M.; Selin, J.-F. Natural fibres as reinforcement in polylactic acid (PLA) composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brostow, W.; Deborde, J.-L.; Jaklewicz, M.; Olszynski, P. Tribology with emphasis on polymers: Friction, scratch resistance and wear. J. Mater. Ed. 2003, 25, 119–132. [Google Scholar]
- Myshkin, N.K.; Petrokovets, M.I.; Kovalev, A.V. Tribology of polymers: Friction, wear and mass transfer. Tribol. Int. 2005, 38, 910–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brostow, W.; Kovacevic, V.; Vrsaljko, D.; Whitworth, J. Tribology of polymers and polymer based composites. J. Mater. Ed. 2010, 32, 273–290. [Google Scholar]
- Brostow, W.; Hagg Lobland, H.E. Surface Behavior and Tribology. In Materials: Introduction and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 391–426. ISBN 978-047-05-2379-7. [Google Scholar]
- Chand, N.; Fahim, M. Tribology of Natural Fiber Polymer Composites; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2008; pp. 1–58. ISBN 9781845693930. [Google Scholar]
- Hashmi, S.A.R.; Dwivedi, U.K.; Chand, N. Friction and sliding wear of UHMWPE modified cotton fibre reinforced polyester composites. Tribol. Lett. 2006, 21, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Tayeb, N.S.M. A study on the potential of sugarcane fibers/polyester composite for tribological applications. Wear 2008, 265, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousif, B.F.; El-Tayeb, N.S.M. Adhesive Wear Performance of T-OPRP and UT-OPRP Composites. Tribol. Lett. 2008, 32, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.W.; Yousif, B.F. Potential of kenaf fibres as reinforcement for tribological applications. Wear 2009, 267, 1550–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousif, B.F.; Lau, S.T.W.; McWilliam, S. Polyester composite based on betelnut fibre for tribological applications. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmal, U.; Hashim, J.; Low, K.O. Adhesive wear and frictional performance of bamboo fibres reinforced epoxy composite. Tribol. Int. 2012, 43, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalwan, A.; Yousif, B.F. In State of Art: Mechanical and tribological behaviour of polymeric composites based on natural fibres. Mater. Des. 2013, 48, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmal, U.; Hashim, J.; Ahmad, M.M.H.M. A review on tribological performance of natural fibre polymeric composites. Tribol. Int. 2015, 83, 77–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, B.; Leman, Z.; Jawaid, M.; Ghazali, M.J.; Ishak, M.R.; Abdelgnei, M.A. Dry sliding wear behavior of untreated and treated sugar palm fiber filled phenolic composites using factorial technique. Wear 2017, 380–381, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, T.; Hirao, K.; Kotera, M.; Nakamae, K.; Inagaki, H. Kenaf reinforced biodegradable composite. Composi. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plackett, D.; Andersen, T.L.; Pedersen, W.B.; Nielsen, L. Biodegradable composites based on l-polylactide and jute fibres. Composi. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, M.S.; Drzal, L.T.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Effect of fiber surface treatments on the properties of laminated biocomposites from poly (lactic acid) (PLA) and kenaf fibers. Composi. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yussuf, A.A.; Massoumi, I.; Hassan, A. Comparison of polylactic acid/kenaf and polylactic acid/rise husk composites: The influence of the natural fibers on the mechanical, thermal and biodegradability properties. J. Polym. Environ. 2010, 18, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duigou, A.L.; Davies, P.; Baley, C. Macroscopic analysis of interfacial properties of flax/PLLA biocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 1612–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, P.K.; Singh, I.; Madaan, J. Tribological behavior of natural fiber reinforced PLA composites. Wear 2013, 297, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledzki, A.K.; Gassan, J. Composites reinforced with cellulose based fibres. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1999, 24, 221–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Hill, C.A.S.; Xiao, Z.; Militz, H.; Mai, C. Silane coupling agents used for natural fiber/polymer composites: A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 806–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chonkaew, W.; Minghvanish, W.; Kungliean, U.; Rochanawipart, N.; Brostow, W. Vulcanization characteristics and dynamic mechanical behavior of natural rubber reinforced with silane modified silica. J. Nanosci. Nanotech. 2011, 11, 2018–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, M.J.; Thomas, S. Biofibres and biocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 71, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tabil, L.G.; Panigrahi, S. Chemical treatments of natural fiber for use in natural fiber-reinforced composites: A review. J. Polym. Environ. 2007, 15, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmal, U.; Yousif, B.F.; Rilling, D.; Brevern, P.V. Effect of betelnut fibres treatment and contact conditions on adhesive wear and frictional performance of polyester composites. Wear 2010, 268, 1354–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, N.; Dwivedi, U.K. Effect of coupling agent on abrasive wear behaviour of chopped jute fibre-reinforced polypropylene composites. Wear 2006, 261, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, U.K.; Chand, N. Influence of MA-g-PP on abrasive wear behaviour of chopped sisal fibre reinforced polypropylene composites. J. Mater. Proc. Technol. 2009, 209, 5371–5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, N.; Dwivedi, U.K. Sliding Wear and Friction Characteristics of Sisal Fibre Reinforced Polyester Composites: Effect of Silane Coupling Agent and Applied Load. Polym. Compos. 2008, 29, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva, I.; Jappes, J.T.W.; Suresha, B. Investigation on mechanical and tribological behavior of naturally woven coconut sheath-reinforced polymer composites. Polym. Compos. 2012, 33, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goriparthi, B.K.; Suman, K.N.S.; Rao, N.M. Effect of fiber surface treatments on mechanical and abrasive wear performance of polylactide/jute composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2012, 43, 1800–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasumi, M.; Nishitani, Y.; Kitano, T. Effect of surface treatment on the mechanical properties of hemp fiber reinforced polyamide 1010 composites. In Proceedings of the Polymer Processing Society 28th Annual Meeting (PPS-28), Pattaya, Thailand, 11–15 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nishitani, Y.; Hasumi, M.; Kitano, T. Influence of silane coupling agents on the rheological behavior of hemp fiber filled polyamide 1010 biomass composites in molten state. AIP Conf. Proc. 2015, 1664, 060007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukaida, J.; Nishitani, Y.; Kitano, T. Effect of addition of plants-derived polyamide 11 elastomer on the mechanical and tribological properties of hemp fiber reinforced polyamide 1010 composites. AIP Conf. Proc. 2015, 1664, 060008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishitani, Y.; Mukaida, J.; Yamanaka, T.; Kajiyama, T.; Kitano, T. Thermal properties of hemp fiber filled polyamide 1010 biomass composites and the blend of these composites and polyamide 11 elastomer. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1713, 120007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishitani, Y.; Mukaida, J.; Yamanaka, T.; Kajiyama, T.; Kitano, T. Effect of processing sequence on the dynamic viscoelastic properties of ternary biomass composites (hemp fiber/ PA1010/ PA11E) in the Molten State. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1779, 060004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukaida, J.; Nishitani, Y.; Kajiyama, T.; Yamanaka, T.; Kitano, T. Influence of types of alkali treatment on the mechanical properties of hemp fiber reinforced polyamide 1010 composites. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1779, 060005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukaida, J.; Nishitani, Y.; Kajiyama, T.; Yamanaka, T.; Kitano, T. Effect of type of bio-TPE on the mechanical and tribological properties of plants-derived ternary composites (HF/PA1010/bio-TPE). J. Mater. Test. Res. Assoc. Jpn. 2016, 61, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Nishitani, Y.; Hasumi, M.; Mukaida, J.; Kajiyama, T.; Yamanaka, T.; Kitano, T. Tribological properties of hemp fiber reinforced plant-derived polyamide 1010 biomass composites. Mater. Technol. Jpn. 2017, 35, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Naganuma, M. Plants-derived polyamide “VESTAMID Terra” “VESTAMID HT Plus”. JETI 2011, 59, 88–90. [Google Scholar]
- Nishitani, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Ishii, C.; Sekiguchi, I.; Kitano, T. Effects of addition of functionalized sebs on rheological, mechanical, and tribological properties of polyamide 6 nanocomposites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2010, 50, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishitani, Y.; Ohashi, K.; Sekiguchi, I.; Ishii, C.; Kitano, T. Influence of addition of styrene-ethylene/butylene-styrene copolymer on rheological, mechanical, and tribological properties of polyamide nanocomposites. Polym. Compos. 2010, 31, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, N.; Mukaida, J.; Nishitani, Y.; Kajiyama, T.; Yamanaka, T.; Kitano, T. Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Hemp and Glass Fiber Hybrid Reinforced Plants-Derived Polyamide11 Composites. In Proceedings of the Preprints of Seikei-Kakou Autumnal Meeting 2015, Japanese Society of Polymer Processing, Fukuoka, Japan, 2–3 November 2015; pp. 263–264. [Google Scholar]
- Sgriccia, N.; Hawley, M.C.; Misra, M. Characterization of natural fiber surfaces and natural fiber composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 1632–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, T.; Nishitani, Y.; Kitano, T. Effect of the type of counter materials on the tribological properties of CF/PA66 composites. In Proceedings of the Tribology Conference 2015 Spring Himeji, Japanese Society of Tribologists, Himeji, Japan, 29 May 2015; p. B25. [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara, N.; Mukaida, J.; Nishitani, Y.; Yamanaka, T.; Kajiyama, T.; Kitano, T. Effect of blend ratio of plants-derived TPE on the tribological properties of hemp fiber reinforced polyamide 11 composites. In Proceedings of the International Tribology Conference, Tokyo 2015 (ITC2015), Japanese Society of Tribologists, Tokyo, Japan, 16–20 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, M.; Sekiguchi, I.; Kasahara, M.; Hironaka, S. Polymeric Tribomaterials; Kyoritsu Shuppan Co. Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 1990; pp. 18–20. ISBN 978-4320042643. [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster, J.K. Estimation of the limiting PV relationships for thermoplastic bearing materials. Tribology 1971, 4, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Kashiwagi, K. The Limiting Pressure-Velocity (PV) of Plastics under Unlubricated Sliding. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1982, 22, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Wang, Q.; Wang, T. The effects of crystallinity on the mechanical properties and the limiting PV (pressure x velocity) value of PTFE. Tribol. Int. 2016, 93, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Code | Functional Group | Grade | Chemical name | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Amino | A-1120 | N-(2-aminoethyl)-3-aminopropyltrimethoxy silane | H2NCH2CH2NHCH2CH2CH2Si(OCH3)3 |
| S2 | Epoxy | A-187 | 3-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxy silane |  |
| S3 | Ureido | A-1160 | 3-ureidopropyltrimethoxy silane | 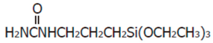 |
| Code | Alkali Treatment | Silane Coupling Agent | Volume Fraction of Fiber Vf (vol %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA1010 | - | - | - |
| HF | - | - | 20 |
| HF-S1 | NaOH | S1 (Aminosilane) | 20 |
| HF-S2 | NaOH | S2 (Epoxysilane) | 20 |
| HF-S3 | NaOH | S3 (Ureidosilane) | 10, 20, 30 |
| Code | Vf (vol %) | Tensile Strength σt (MPa) | Tensile Modulus Et (GPa) | Elongation at Break εt (%) | Izod Impact Strength aiN (kJ/m2) | Durometer Hardness HDD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA1010 | - | 43 ± 1.2 | 1.4 ± 0.17 | 42 ± 5.9 | 5.2 ± 1.11 | 68 ± 1.0 |
| HF | 20 | 52 ± 2.6 | 2.4 ± 0.13 | 8 ± 1.6 | 3.3 ± 0.72 | 75 ± 0.5 |
| HF-S1 | 20 | 53 ± 1.9 | 2.3 ± 0.07 | 8 ± 1.2 | 4.0 ± 0.60 | 77 ± 1.0 |
| HF-S2 | 20 | 51 ± 3.0 | 2.4 ± 0.15 | 8 ± 2.4 | 3.6 ± 0.69 | 75 ± 1.0 |
| HF-S3 | 10 | 53 ± 3.6 | 2.3 ± 0.20 | 11 ± 1.8 | 3.2 ± 0.78 | 76 ± 1.0 |
| HF-S3 | 20 | 56 ± 1.5 | 2.7 ± 0.24 | 4 ± 1.0 | 2.8 ± 0.38 | 78 ± 0.5 |
| HF-S3 | 30 | 64 ± 5.5 | 3.2 ± 0.31 | 4 ± 1.4 | 2.0 ± 0.47 | 77 ± 0.5 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nishitani, Y.; Kajiyama, T.; Yamanaka, T. Effect of Silane Coupling Agent on Tribological Properties of Hemp Fiber-Reinforced Plant-Derived Polyamide 1010 Biomass Composites. Materials 2017, 10, 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10091040
Nishitani Y, Kajiyama T, Yamanaka T. Effect of Silane Coupling Agent on Tribological Properties of Hemp Fiber-Reinforced Plant-Derived Polyamide 1010 Biomass Composites. Materials. 2017; 10(9):1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10091040
Chicago/Turabian StyleNishitani, Yosuke, Tetsuto Kajiyama, and Toshiyuki Yamanaka. 2017. "Effect of Silane Coupling Agent on Tribological Properties of Hemp Fiber-Reinforced Plant-Derived Polyamide 1010 Biomass Composites" Materials 10, no. 9: 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10091040
APA StyleNishitani, Y., Kajiyama, T., & Yamanaka, T. (2017). Effect of Silane Coupling Agent on Tribological Properties of Hemp Fiber-Reinforced Plant-Derived Polyamide 1010 Biomass Composites. Materials, 10(9), 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10091040





