3D Printing of Thermo-Responsive Methylcellulose Hydrogels for Cell-Sheet Engineering
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Hydrogel Preparation
2.3. Rheological Analysis
2.4. 3D Printing of MC-Based Hydrogels
2.5. Weight Variation Tests
2.6. In Vitro Biological Tests
2.6.1. Cell Viability Tests
2.6.2. Cell Sheets
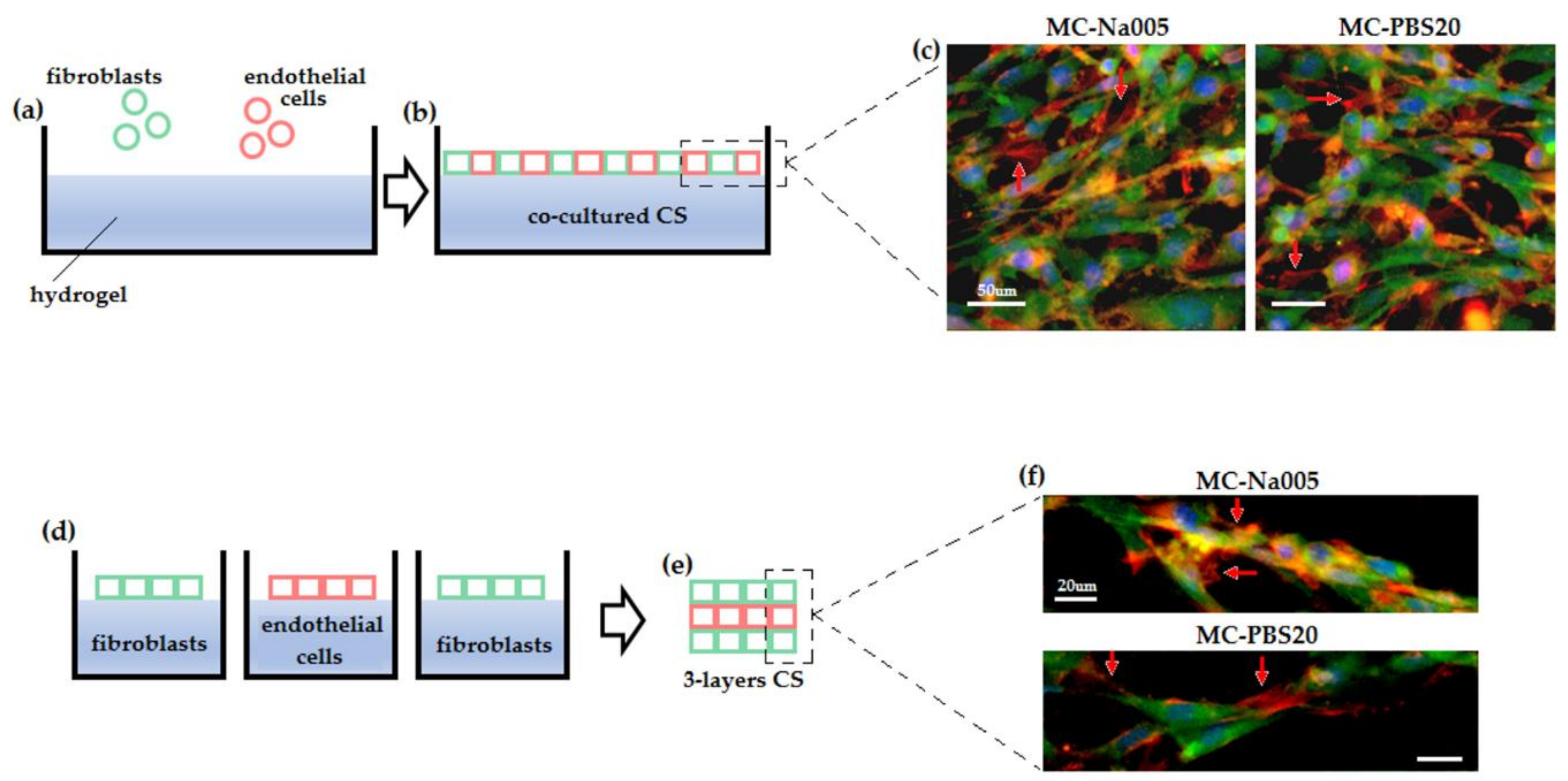
2.6.3. Co-Cultured Cell Sheets
2.6.4. Cell Sheet Superimposition
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Qualitative Analysis of MC-Based Hydrogels
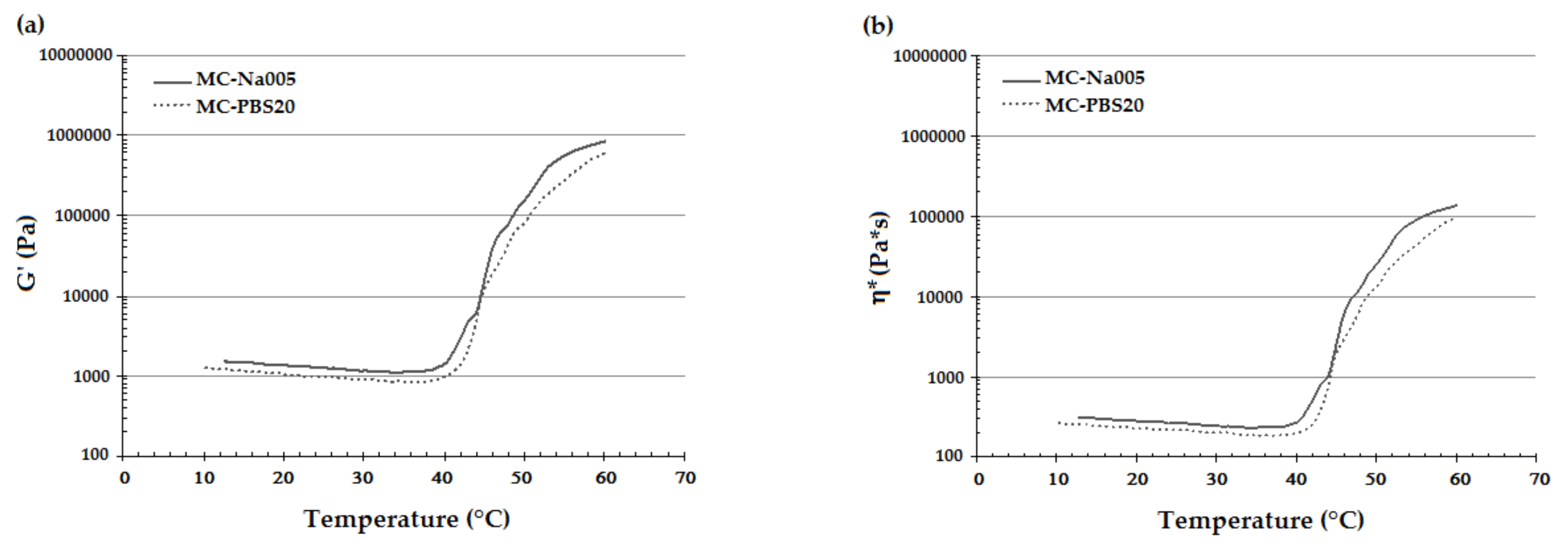
3.2. Rheological Analysis
3.3. 3D Printing of MC-Based Hydrogels
3.4. Weight Variation Tests
3.5. In Vitro Biological Tests
3.5.1. Cell Viability Tests
3.5.2. Characterization of Cell Sheets
3.5.3. Co-Cultured and Three-Layer Cell Sheet Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.; Yamato, M.; Kohno, C.; Nishimoto, A.; Sekine, H.; Fukai, F.; Okano, T. Cell sheet engineering: Recreating tissues without biodegradable scaffolds. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6415–6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, T. Cell sheet-based tissue engineering for fabricating 3-dimensional heart tissues. Circ. J. 2014, 78, 2594–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamato, M.; Okano, T. Cell sheet engineering. Mater. Today 2004, 5, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, P.M. Stimuli-responsive surfaces for bio-applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 2512–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Srivastava, A.; Galaev, I.; Mattiasson, B. Smart polymers: Physical forms and bioengineering applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 1205–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battistella, E.; Varoni, E.; Cochis, A.; Palazzo, B.; Rimondini, L. Degradable polymers may improve dental practice. J. Appl. Biomater. Biomech. 2011, 9, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Tsai, C.C.; Chen, W.; Mi, F.L.; Liang, H.F.; Chen, S.C.; Sung, H.W. Novel living cell sheet harvest system composed of thermoreversible methylcellulose hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thirumala, S.; Gimble, J.M.; Devireddy, R.V. Methylcellulose based thermally reversible hydrogel system for tissue engineering applications. Cells 2013, 2, 460–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sannino, A.; Demitri, C.; Madaghiele, M. Biodegradable Cellulose-based Hydrogels: Design and Applications. Materials 2009, 2, 353–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, N. Kinetics of thermal gelation of methylcellulose and hydroxypropylmethylcellulose in aqueous solutions. Carbohydr. Polym. 1995, 3, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.F.; Hong, M.H.; Ho, R.M.; Chung, C.K.; Lin, Y.H.; Chen, C.H.; Sung, H.W. Novel method using a temperature-sensitive polymer (methylcellulose) to thermally gel aqueous alginate as a pH-sensitive hydrogel. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tate, M.C.; Shear, D.A.; Hoffman, S.W.; Stein, D.G.; LaPlaca, M.C. Biocompatibility of methylcellulose-based constructs designed for intracerebral gelation following experimental traumatic brain injury. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altomare, L.; Cochis, A.; Carletta, A.; Rimondini, L.; Farè, S. Thermo-responsive methylcellulose hydrogels as temporary substrate for cell sheet biofabrication. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2016, 27, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochis, A.; Grad, S.; Stoddart, M.J.; Farè, S.; Altomare, L.; Azzimonti, B.; Alini, M.; Rimondini, L. Bioreactor mechanically guided 3D mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenesis using a biocompatible novel thermo-reversible methylcellulose-based hydrogel. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dababneh, A.B.; Ozbolat, I.T. Bioprinting technology: A current state of the art review. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. Trans. ASME 2014, 136, 061016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.V.; Atala, A. 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandrycky, C.; Wang, Z.; Kim, K.; Kim, D.H. 3D bioprinting for engineering complex tissues. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepper, M.E.; Seshadri, V.; Burg, T.C.; Burg, K.J.; Groff, R.E. Characterizing the effects of cell settling on bioprinter output. Biofabrication 2012, 4, 011001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillemot, F.; Souquet, A.; Catros, S.; Guillotin, B. Laser-assisted cell printing: Principle, physical parameters versus cell fate and perspectives in tissue engineering. Nanomedicine 2010, 5, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozbolat, I.T.; Hospodiuk, M. Current advances and future perspectives in extrusion-based bioprinting. Biomaterials 2016, 76, 321–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfister, A.; Landers, R.; Laib, A.; Hübner, U.; Schmelzeisen, R.; Mülhaupt, R. Biofunctional rapid prototyping for tissue-engineering applications: 3D bioplotting versus 3D printing. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2004, 42, 624–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contessi, N.; Altomare, L.; Filipponi, A.; Farè, S. Thermo-responsive properties of methylcellulose hydrogels for cell sheet engineering. Mater. Lett. 2017, 207, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altomare, L.; Gadegaard, N.; Visai, L.; Tanzi, M.C.; Farè, S. Biodegradable microgrooved polymeric surfaces obtained by photolithography for skeletal muscle cell orientation and myotube development. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1948–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, S.C. Sol-Gel Behavior of Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC) in Ionic Media Including Drug Release. Materials 2011, 4, 1861–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Chang, Y.; Wang, C.C.; Huang, C.H.; Huang, C.C.; Yeh, Y.C.; Hwang, S.M.; Sung, H.W. Construction and characterization of fragmented mesenchymal-stem-cell sheets for intramuscular injection. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 4643–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bain, M.K.; Bhowmick, B.; Maity, D.; Mondal, D.; Mollick, M.M.; Rana, D.; Chattopadhyay, D. Synergistic effect of salt mixture on the gelation temperature and morphology of methylcellulose hydrogel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 51, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.H.J.; Naficy, S.; Yue, Z.; Kapsa, R.; Quigley, A.; Moulton, S.E.; Wallace, G.G. Bio-ink properties and printability for extrusion printing living cells. Biomater. Sci. 2013, 1, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuidema, J.M.; Rivet, C.J.; Gilbert, R.J.; Morrison, F.A. A protocol for rheological characterization of hydrogels for tissue engineering strategies. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2014, 102, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malda, J.; Visser, J.; Melchels, F.P.; Jüngst, T.; Hennink, W.E.; Dhert, W.J.; Groll, J.; Hutmacher, D.W. 25th anniversary article: Engineering hydrogels for biofabrication. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5011–5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Sun, J.; Fan, H.; Zhang, X. An improved complex gel of modified gellan gum and carboxymethyl chitosan for chondrocytes encapsulation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, T.; Fernandez, M.A.; Salvador, A.; Munoz, J.; Fiszman, S.M. Thermogelation properties of methylcellulose (MC) and their effect on a batter formula. Food Hydrocoll. 2005, 19, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütz, K.; Placht, A.M.; Paul, B.; Brüggemeier, S.; Gelinsky, M.; Lode, A. Three-dimensional plotting of a cell-laden alginate/methylcellulose blend: Towards biofabrication of tissue engineering constructs with clinically relevant dimensions. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2017, 11, 1574–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaled, S.A.; Burley, J.C.; Alexander, M.R.; Roberts, C.J. Desktop 3D printing of controlled release pharmaceutical bilayer tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 461, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Zhu, H.; Xu, Z.; Liu, L.; Ma, J.; Zhang, M. A Bioinspired Alginate-Gum Arabic Hydrogel with Micro-/Nanoscale Structures for Controlled Drug Release in Chronic Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 22160–22175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asakawa, N.; Shimizu, T.; Tsuda, Y.; Sekiya, S.; Sasagawa, T.; Yamato, M.; Fukai, F.; Okano, T. Pre-vascularization of in vitro three-dimensional tissues created by cell sheet engineering. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3903–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasagawa, T.; Shimizu, T.; Sekiya, S.; Haraguchi, Y.; Yamato, M.; Sawa, Y.; Okano, T. Design of prevascularized three-dimensional cell-dense tissues using a cell sheet stacking manipulation technology. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 1646–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Sample | MC Concentration (%, w/v) | Salt Type | Salt Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|
| MC-Na005 | 8% | Na2SO4 | 0.05 M |
| MC-PBS20 | 8% | PBS | 20 g/L |
| Sample | LCST [°C] from G’/T Curve | LCST [°C] from η*/T Curve |
|---|---|---|
| MC-Na005 | 41.3 ± 1.1 | 41.7 ± 1.2 |
| MC-PBS20 | 39.4 ± 3.1 | 39.7 ± 3.1 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cochis, A.; Bonetti, L.; Sorrentino, R.; Contessi Negrini, N.; Grassi, F.; Leigheb, M.; Rimondini, L.; Farè, S. 3D Printing of Thermo-Responsive Methylcellulose Hydrogels for Cell-Sheet Engineering. Materials 2018, 11, 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040579
Cochis A, Bonetti L, Sorrentino R, Contessi Negrini N, Grassi F, Leigheb M, Rimondini L, Farè S. 3D Printing of Thermo-Responsive Methylcellulose Hydrogels for Cell-Sheet Engineering. Materials. 2018; 11(4):579. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040579
Chicago/Turabian StyleCochis, Andrea, Lorenzo Bonetti, Rita Sorrentino, Nicola Contessi Negrini, Federico Grassi, Massimiliano Leigheb, Lia Rimondini, and Silvia Farè. 2018. "3D Printing of Thermo-Responsive Methylcellulose Hydrogels for Cell-Sheet Engineering" Materials 11, no. 4: 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040579
APA StyleCochis, A., Bonetti, L., Sorrentino, R., Contessi Negrini, N., Grassi, F., Leigheb, M., Rimondini, L., & Farè, S. (2018). 3D Printing of Thermo-Responsive Methylcellulose Hydrogels for Cell-Sheet Engineering. Materials, 11(4), 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040579









