Microstructural and Performance Analysis of TP304H/T22 Dissimilar Steel Welded Joints
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
3. Microstructure of Welded Joints
4. Mechanical Properties of Welded Joints
4.1. Hardness
4.2. Tensile Properties at Different Temperatures
5. Numerical Simulation of High-Temperature Tension of Welded Joints
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- No damage features, such as creep cavities and intergranular cracks, were found in the microstructure of the welded joints. On the side of the TP304H close to the fusion line, austenite grains grew from the base metal matrix to the weld recrystallization zone. The microstructure of the heat-affected zone (HAZ) on the T22 side was refined, which provided the HAZ with better crack initiation resistance.
- (2)
- The microhardness test results show that tube sample weld zone and base metal had a significant hardness difference. The microstructure analysis revealed that the strong resistance of the grains to dislocation movement during deformation and the significant increase in dislocation proliferation resulted in the highest hardness values at the weld and that crack initiation and propagation were more likely to occur.
- (3)
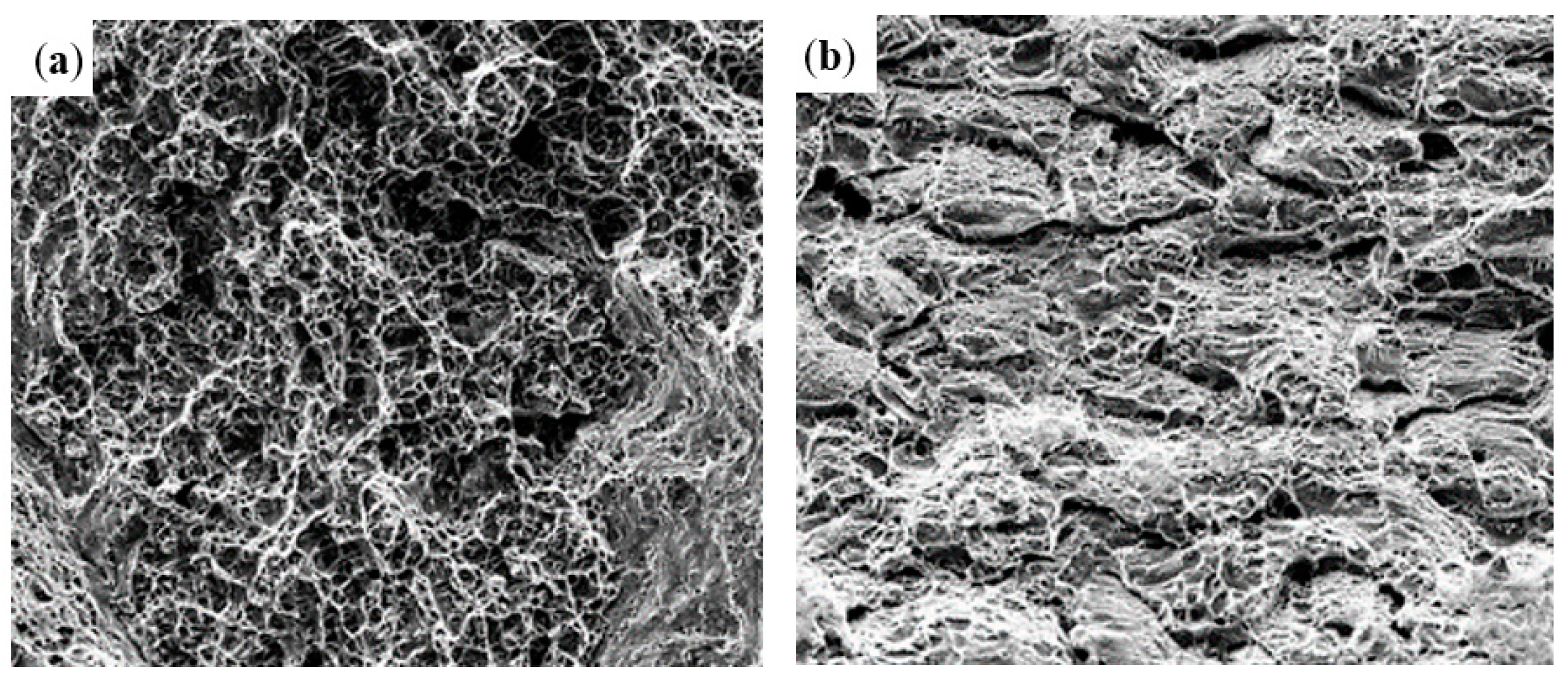
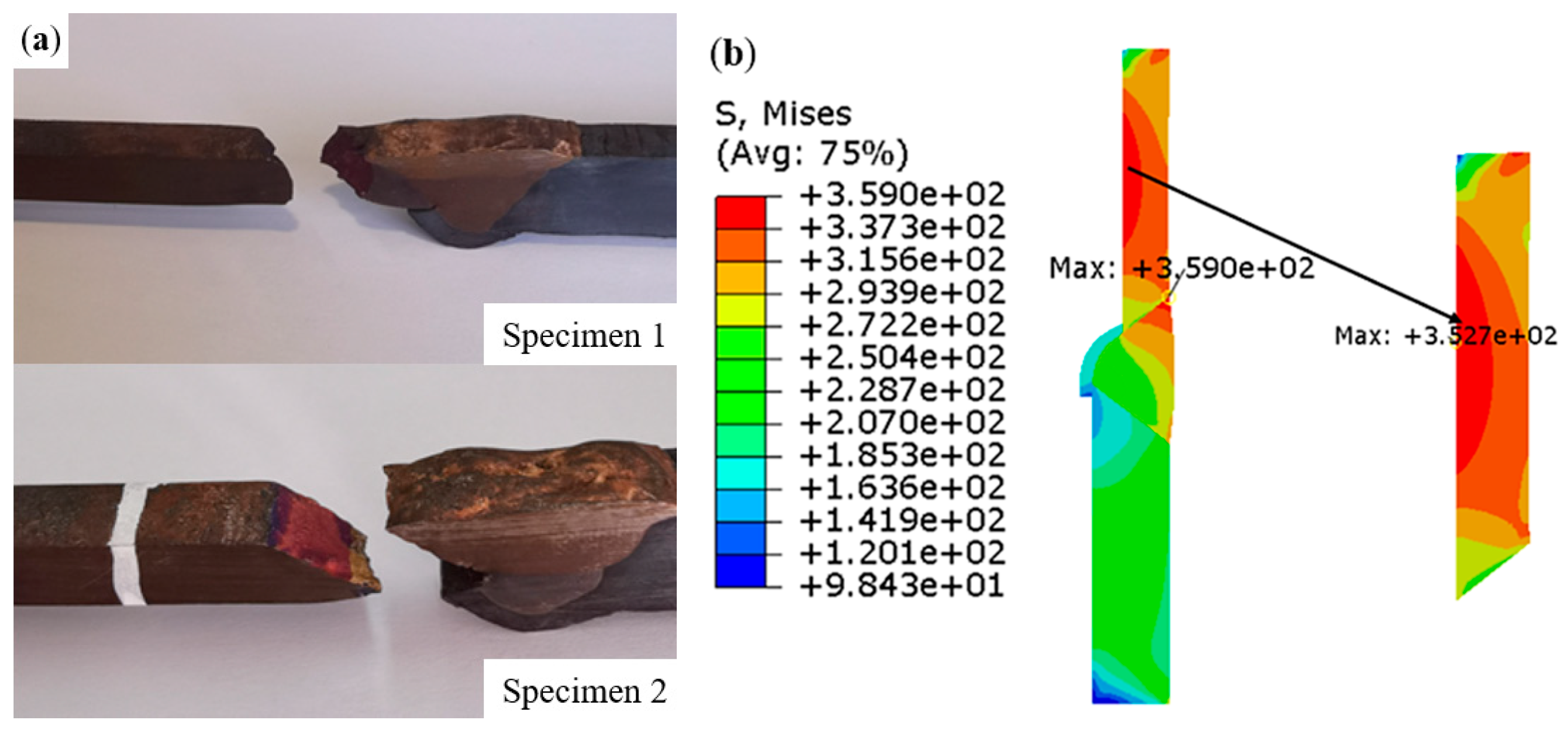
- The high-temperature tensile test of the welded joint showed that fracture occurs in the base metal, or the TP304H side fusion zone. In addition, the numerical simulation results also show that in the actual high-temperature tensile process, in those two parts of the high stress area, damage defects were prone to initiation. The high-temperature tensile fracture morphology indicates that the fracture form was a mixed fracture. The joint fractured at the weld under room-temperature tensile tests, and the fracture showed the characteristics of a ductile fracture.
- (4)
- The tensile test results showed that the welded joints fractured at different locations after a long period of service than those unserved. Combined with the numerical simulation results, the weak position of the welded joints of the in-service dissimilar steel was clarified. This is a reference for the safe and stable operation of in-service dissimilar steel welded joints.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ratković, N.; Lazić, V.; Arsić, D.; Nikolić, R.R.; Prokić, C.R.; Popović, O. Microstructure in the Joining Zone during the Friction Welding of the Two Dissimilar Steels. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2018, 70, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.D.; Zhang, Z.B.; Xu, G.; Ma, Y.C.; Niu, K.; Tang, W.S. Failure Reason Analysis of TP304H/T22 Type Dissimilar Steel Weld after Serving for Long Time. Hot Work. Technol. 2019, 48, 175–178+182. [Google Scholar]
- Karthick, K.; Malarvizhi, S.; Balasubramanian, V. Microstructural Characterization of Dissimilar Weld Joint between Ferritic Steel and Stainless Steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 37, 1257–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Sahu, M.; Singh, P.K.; Kumar, S.; Ghosh, M.; Sagar, S.P. Assessment of Mechanical Properties for Dissimilar Metal Welds: A Nondestructive Approach. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2019, 28, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikiran, K.; Das, G.; Kumar, S.; Singh, P.K.; Sivaprasad, K.; Ghosh, M. Evaluation of Microstructure at Interfaces of Welded Joint between Low Alloy Steel and Stainless Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2019, 50, 2784–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Mi, G.; Wang, C. Microstructure and Performance of Hybrid Laser-Arc Welded High-Strength Low Alloy Steel and Austenitic Stainless Steel Dissimilar Joint. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 122, 105878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.L.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, G.H.; Wang, J.Q.; Liu, J.J.; Yu, X.H.; Hua, J.; Zhang, J.H.; Tang, W.M. High Temperature Tensile Test and Creep Rupture Strength Prediction of T92/Super304H Dissimilar Steel Weld Joints. Mater. High Temp. 2014, 31, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Ni, L.; Lei, Z.; Chen, Y.; Hu, X. Microstructure and Tensile Properties of Laser Welded Dissimilar Ti-22Al-27Nb and TA15 Joints. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 87, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, P.; Cao, Z.; Hai, M.; Qiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, J. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of K-TIG Welded Dissimilar Joints between TC4 and TA17 Titanium Alloys. Mater. Charact. 2023, 196, 112644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Du, J.; Li, L.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Z. Creep Behavior and Damage Evolution of T92/Super304H Dissimilar Weld Joints. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2019, 26, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, R.; Sidhu, B.S. Microstructural and Mechanical Studies of T91/T22 Welded Joints. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2018, 71, 1985–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettahar, K.; Bouabdallah, M.; Badji, R.; Gaceb, M.; Kahloun, C.; Bacroix, B. Microstructure and Mechanical Behavior in Dissimilar 13Cr/2205 Stainless Steel Welded Pipes. Mater. Des. 2015, 85, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, T.G.; Cao, X.Y.; Lu, Y.H.; Shoji, T. In-Situ SEM Study of Crack Initiation and Propagation Behavior in a Dissimilar Metal Welded Joint. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 729, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, Q.Q.; Lin, S.B.; Zhou, J.; Fan, C.L.; Yang, C.L. Mechanism of Crack Initiation of Dissimilar Joints be-tween 2219 Aluminum Alloy and 5A06 Aluminum Alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2019, 48, 775–781. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Cai, Z.; Huo, X.; Fan, M.; He, Y.; Yao, X.; Pan, J.; Li, K. Near-Threshold Fatigue Crack Growth Behavior of the Weld Metal and Heat-Affected Zone in an Ex-Service CrMoV Steel Joint. Int. J. Fatigue 2022, 164, 107175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajani Derazkola, H.; Khodabakhshi, F. Intermetallic Compounds (IMCs) Formation during Dissimilar Friction-Stir Welding of AA5005 Aluminum Alloy to St-52 Steel: Numerical Modeling and Experimental Study. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 100, 2401–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhai, X.; Bian, G.; Zhang, T.; Dong, P. Improvement in Tensile Strength of Mg/Al Alloy Dissimilar Friction Stir Welding Joints by Reducing Intermetallic Compounds. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 861, 157942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Deng, D. Numerical Simulation of Residual Stress of Butt-Welded Joint Involved in Complex Column-Beam Welded Structure. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 83, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adomako, N.K.; Shin, G.; Park, N.; Park, K.; Kim, J.H. Laser Dissimilar Welding of CoCrFeMnNi-High Entropy Alloy and Duplex Stainless Steel. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 85, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xue, H.; Yang, F.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; He, J.; Bashir, R. Mechanical Properties Evaluation and Crack Propagation Behavior in Dissimilar Metal Welded Joints of 304 L Austenitic Stainless Steel and SA508 Low-Alloy Steel. Sci. Technol. Nucl. Install. 2022, 2022, e3038397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.T.; Jiang, S.Y.; Chen, Y.P.; Xiong, Z.Y.; Hu, D.A.; Cheng, D.H. Numerical simulation of laser welding of magnesium and steel dissimilar metal based on ABAOUS. Trans. Mater. Heat Treat. 2021, 42, 134–141. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.; Fang, Z.; Yang, J.; Zheng, J.; Wang, S. Numerical Simulation of S355JR-316L Dissimilar Metal Welding. Weld. World 2022, 66, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielewski, H.; Skrzypczyk, A.; Tofil, S.; Witkowski, G.; Rutkowski, S. Numerical Simulation of Laser Welding Dissimilar Low Carbon and Austenitic Steel Joint. Open Eng. 2020, 10, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perulli, P.; Dassisti, M.; Casalino, G. Thermo-Mechanical Simulation of Hybrid Welding of DP/AISI 316 and TWIP/AISI 316 Dissimilar Weld. Materials 2020, 13, 2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazooki, A.M.A.; Hermans, M.J.M.; Richardson, I.M. Finite Element Simulation and Experimental Investigation of Thermal Tensioning during Welding of DP600 Steel. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2017, 22, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidová, E.; Sunil Kumar, M.R.; Schmid, M.; Bozkurt, F. Role of Nb in the Failure of Dual-Phase Steel in Heterogeneous Welds. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 116, 104708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R. Behaviours of Oxides Scale of Welded T22 Steels in Thermal Cyclic Conditions. Mater. Lett. 2022, 308, 131215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okonkwo, B.O.; Ming, H.; Wang, J.; Meng, F.; Xu, X.; Han, E.-H. Microstructural Characterization of Low Alloy Steel A508–309/308L Stainless Steel Dissimilar Weld Metals. Int. J. Press. Vessels Pip. 2021, 190, 104297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Material | Cr | Mo | Mn | Si | C | S | P | Fe | Ni | Nb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T22 | 2.08 | 0.92 | 0.44 | 0.22 | 0.088 | 0.016 | 0.0098 | Balance | - | - |
| Material | Cr | Ni | Mn | Si | C | P | S | Fe | Mo | Nb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP304H | 18.82 | 9.82 | 1.52 | 0.55 | 0.045 | 0.026 | 0.012 | Balance | - | - |
| Locations | C | O | Al | Si | Ti | Cr | Mn | Fe | Ni | Nb | Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 02 | 9.55 | 34.97 | 26.94 | - | 18.38 | 2.22 | 1.58 | - | 6.35 | - | - |
| 03 | 7.33 | - | - | 2.34 | 2.69 | 15.41 | 3.31 | 10.43 | 26.25 | 32.23 | - |
| 04 | 5.52 | - | - | 0.98 | - | 16.51 | 4.45 | 18.51 | 50.66 | 3.37 | - |
| 05 | 9.03 | - | - | 0.51 | - | 14.23 | 3.72 | 17.26 | 53.86 | 1.40 | - |
| 06 | 2.75 | - | - | 0.49 | - | 16.30 | 2.29 | 18.32 | 58.53 | - | 1.32 |
| Specimen | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Standard Tensile Strength (GB/T 5310-2017) (MPa) | Fracture Positions |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (HT) | 389 | ≥381 (TP304H at high temperature) | TP304H side base metal |
| 2 (HT) | 334 | TP304H side fusion line | |
| 3 (RT) | 476 | ≥515 (TP304H at room temperature) | Welding seam |
| 4 (RT) | 330 | ≥415 (T22 at room temperature) | Welding seam |
| Material | Density (t/mm3) | Expansion (°C−1) | Poisson Ratio | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Yield Stress (MPa) | Plastic Strain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T22 | 7.8 × 10−9 | 1.46 × 10−5 | 0.3 | 169,000 | 105 | 0 |
| 210 | 0.02 | |||||
| TP304H | 7.8 × 10−9 | 1.86 × 10−5 | 0.31 | 156,000 | 159 | 0 |
| 320 | 0.02 | |||||
| N06600 | 7.8 × 10−9 | 1.5 × 10−5 | 0.31 | 182,000 | 240 | 0 |
| 560 | 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Wang, T.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lin, H.; Liu, H.; Zhao, X.; Cheng, X. Microstructural and Performance Analysis of TP304H/T22 Dissimilar Steel Welded Joints. Materials 2023, 16, 4474. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16124474
Sun J, Wang T, Liu F, Zhang Z, Chen Y, Lin H, Liu H, Zhao X, Cheng X. Microstructural and Performance Analysis of TP304H/T22 Dissimilar Steel Welded Joints. Materials. 2023; 16(12):4474. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16124474
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jian, Tong Wang, Fuguang Liu, Zhoubo Zhang, Yunhui Chen, He Lin, Hui Liu, Xiaohui Zhao, and Xiaole Cheng. 2023. "Microstructural and Performance Analysis of TP304H/T22 Dissimilar Steel Welded Joints" Materials 16, no. 12: 4474. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16124474






