Aryl Polyphosphonates: Useful Halogen-Free Flame Retardants for Polymers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
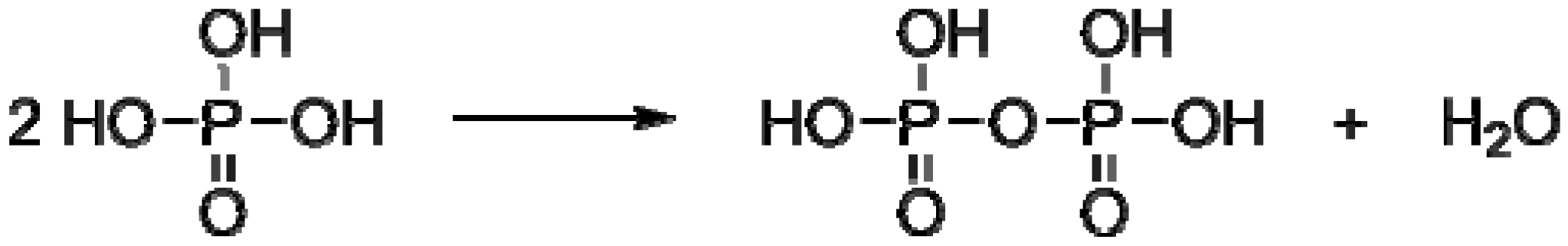

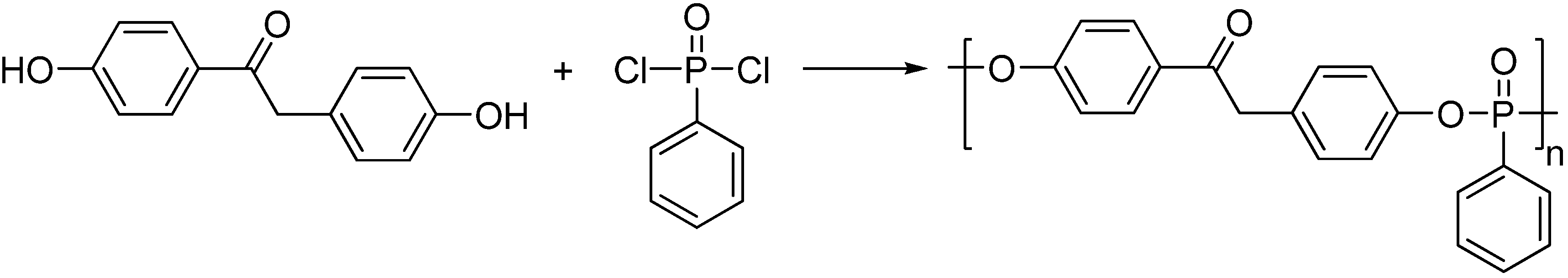
2. Main-Chain Phosphorus-Containing Aryl Polyphosphonates
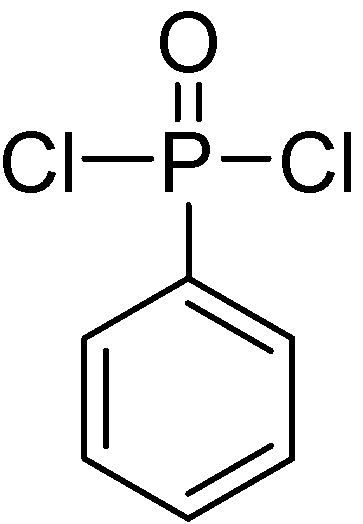
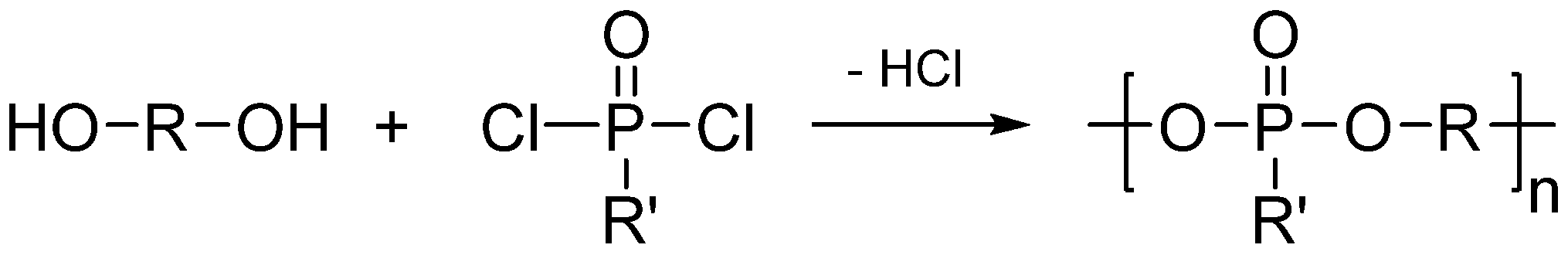
| No. | R | R' | MC-ArPPN content (wt %) | Properties of the PET blends | Properties of the PBT blends | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P content (wt %) | LOI (vol%) | P content (wt %) | LOI (vol%) | ||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 17.0 | 0 | 16.5 | ||
| 1 |  | 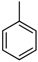 | 5 | 0.54 | 18.6 | 0.60 | 18.7 |
| 10 | 1.30 | 21.0 | 1.27 | 19.4 | |||
| 2 |  |  | 5 | 0.48 | 18.9 | 0.64 | 18.1 |
| 10 | 1.53 | 22.0 | 1.17 | 19.4 | |||
| 3 | 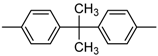 | 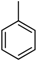 | 10 | 1.09 | 18.8 | 0.83 | 18.3 |
| Matrix | PPP content (wt %) | Intrinsic viscosity of PPP (dL/g) | Phosphorus content (wt %) | LOI (vol %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET | 5 | 0.46 | 0.52 | 18.6 |
| 10 | 0.46 | 1.16 | 19.9 | |
| 5 | 0.17 | 0.54 | 18.6 | |
| 10 | 0.17 | 1.33 | 20.0 | |
| PBT | 5 | 0.46 | 0.58 | 18.7 |
| 10 | 0.46 | 1.19 | 20.4 | |
| 5 | 0.17 | 0.66 | 18.7 | |
| 10 | 0.17 | 1.30 | 20.7 |

| Sample | Heat release capacity (J/(g.K)) | Char yield at 800 °C (wt %) |
|---|---|---|
| BHDB-PPN | 81 ± 11 | 52.0 |
| polyethylene | 1676 | 0 |
| polystyrene | 927 | 0 |
| polycarbonate (BPA) | 359 | 21.7 |
| poly(ethylene terephthalate) | 332 | 5.1 |
| poly(vinyl chloride) | 138 | 15.3 |
| poly(2,6-dimethylene 1,4-phenyleneoxide) | 409 | 25.5 |
| poly(phenyl sulfone) | 153 | 38.4 |
| Vectra C LCP a | 164 | 40.6 |
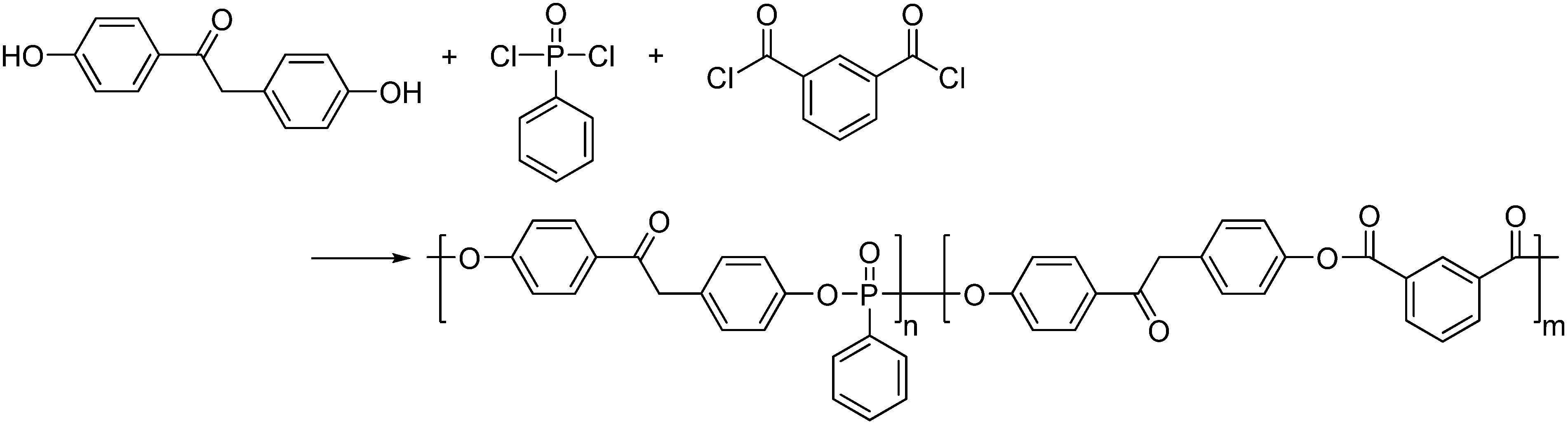
| iPC : PPC (molar ratio) | Heat release capacity (J/(g.K)) | Thermal stability parameters a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 wt % loss temperature (°C) | Char yield at 800 °C (wt %) | ||
| 100:0 | 65 ± 5 | 340 | 45 |
| 77:23 | 48 ± 4 | 346 | 50 |
| 57:43 | 41 ± 3 | 383 | 56 |
| 46:54 | 36 ± 2 | 367 | 54 |
| 39:61 | 40 ± 3 | 390 | 57 |
| 23:77 | 59 ± 5 | 394 | 55 |
| 0:100 | 81 ± 11 | 397 | 52 |
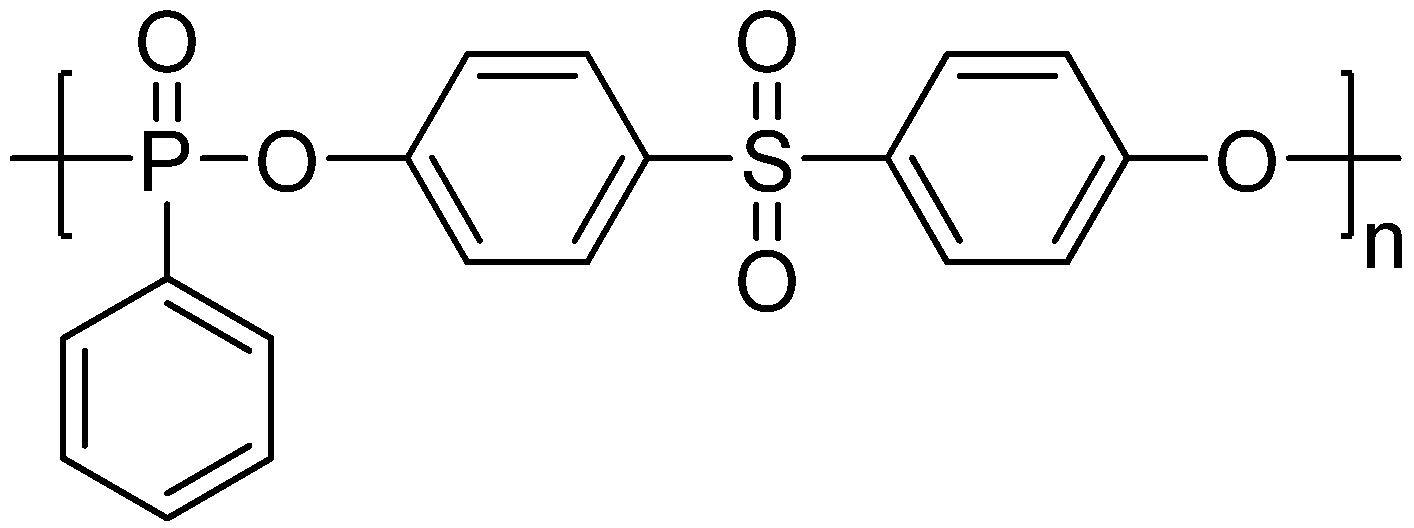

| PC (wt %) | Flame retardants (wt %) | Flame retardancy | Charyield at 700 °C (wt %) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSPPP | SSK | LOI | UL-94 rating | ||
| 100 | 0 | 0 | 26.3 | V-2 | |
| 95 | 5 | 0 | 31.9 | V-2 | |
| 95 | 4.5 | 0.5 | 36.8 | V-0 | 18.2 |
| 95 | 4 | 1 | 35.2 | V-0 | 20.3 |
| 95 | 2 | 3 | 32.9 | V-0 | 16.5 |
| 95 | 0 | 5 | 33.0 | V-0 | |
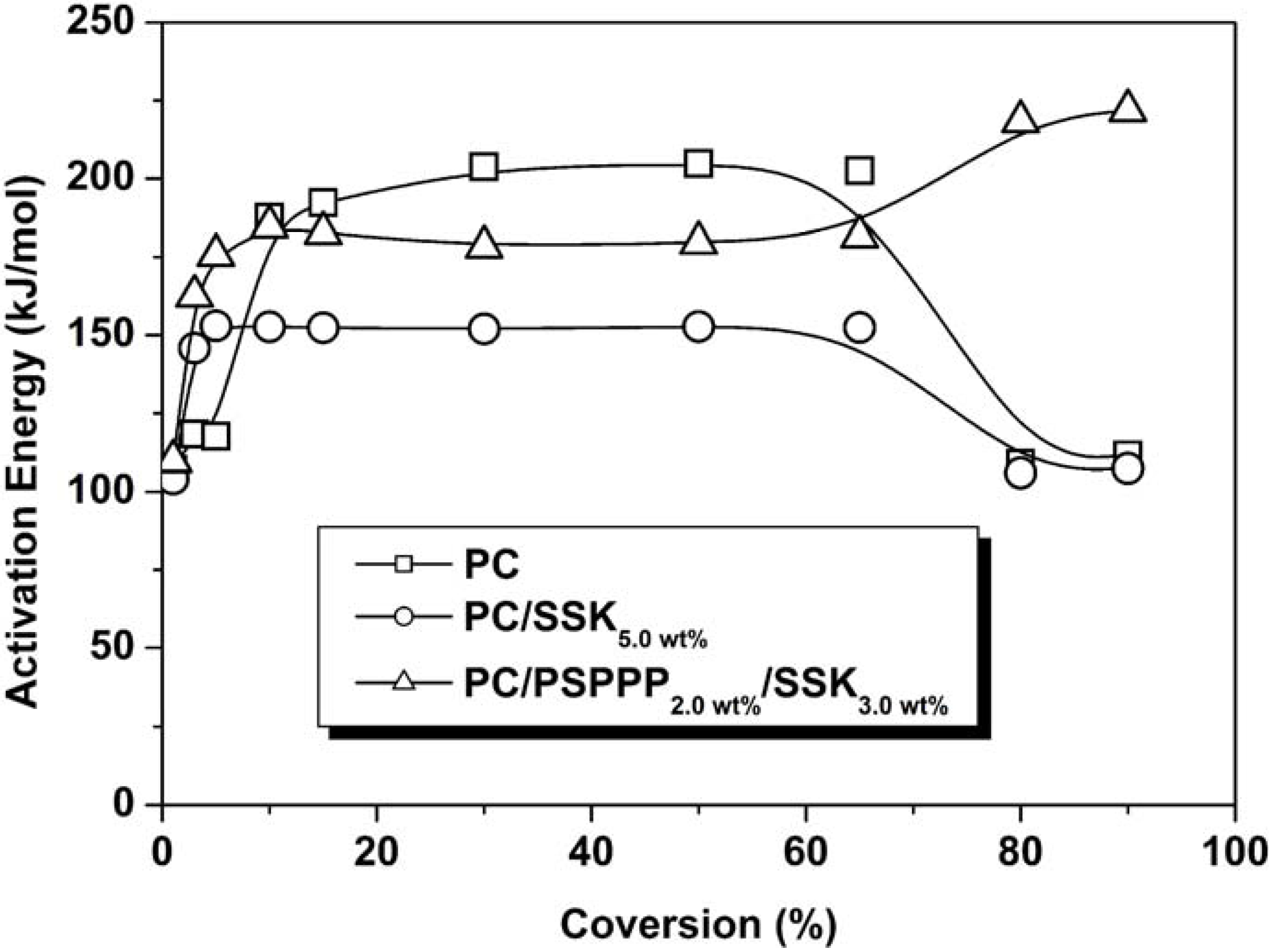
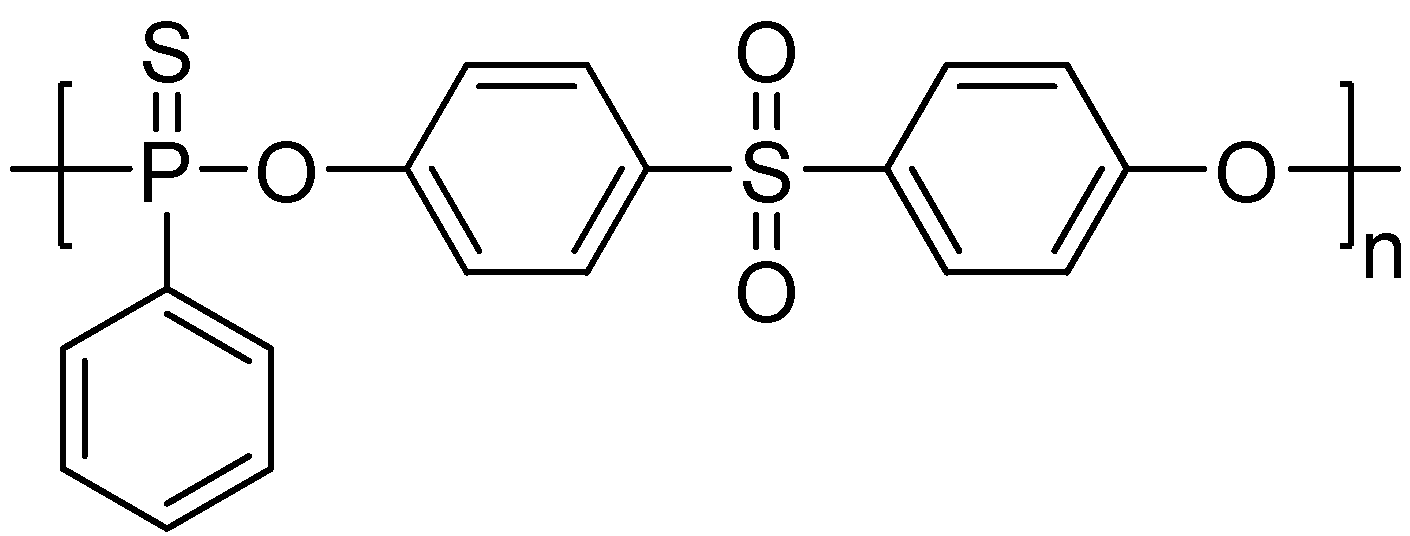
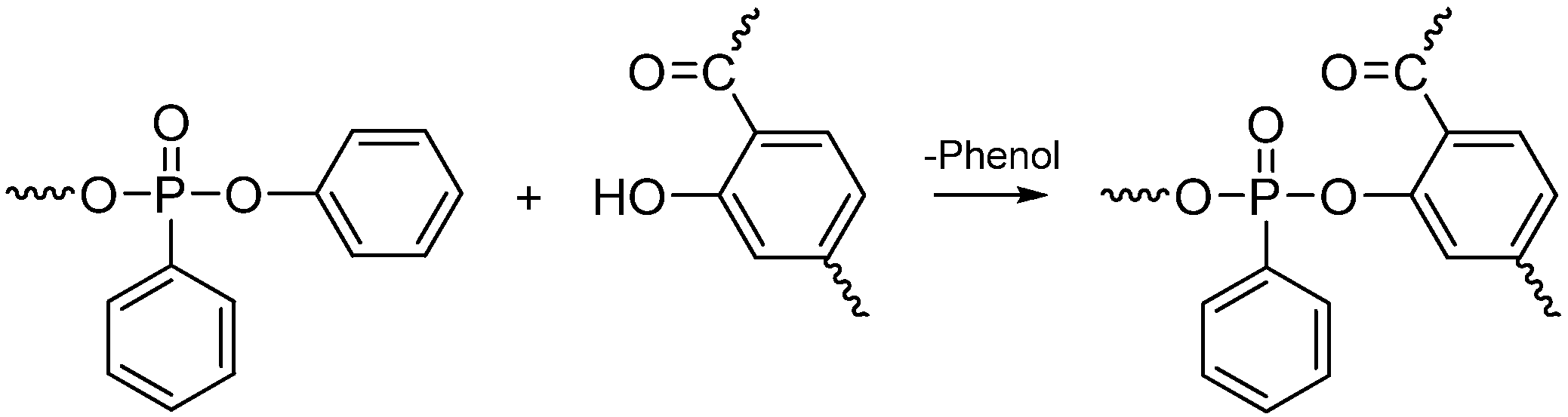
3. Main-Chain/Side-Chain Combined Phosphorus-Containing Aryl Polyphosphonates

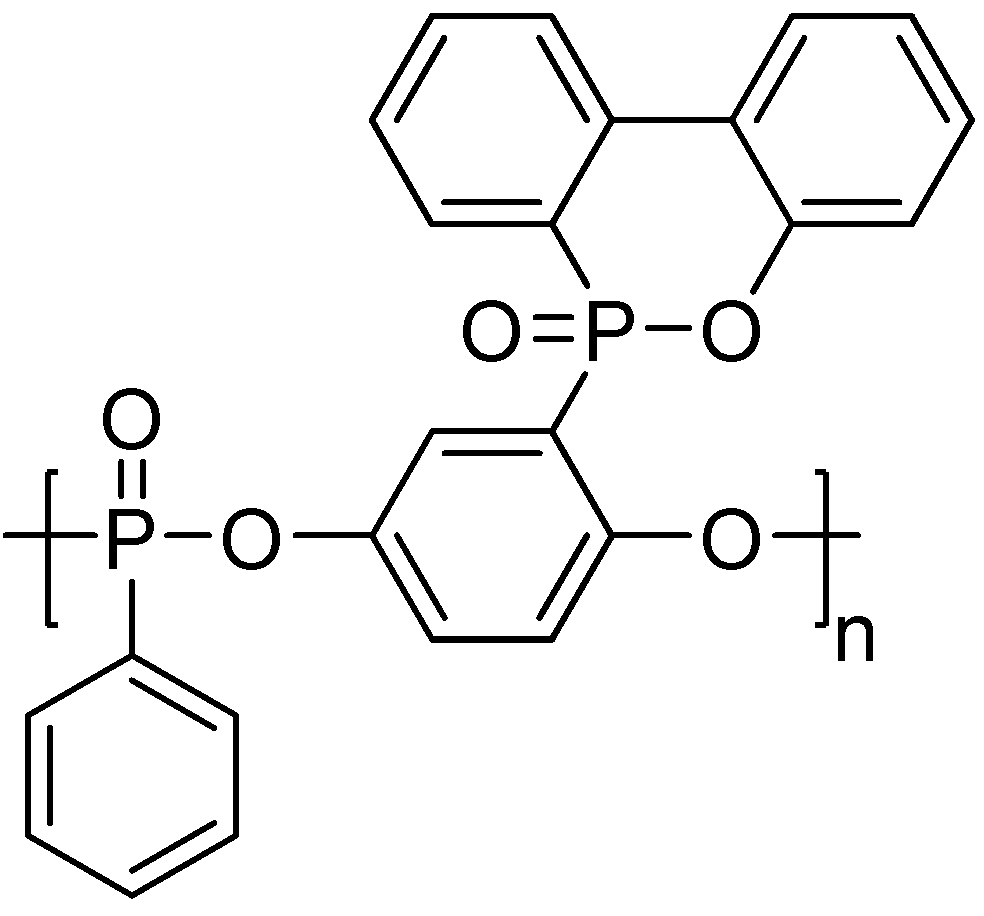
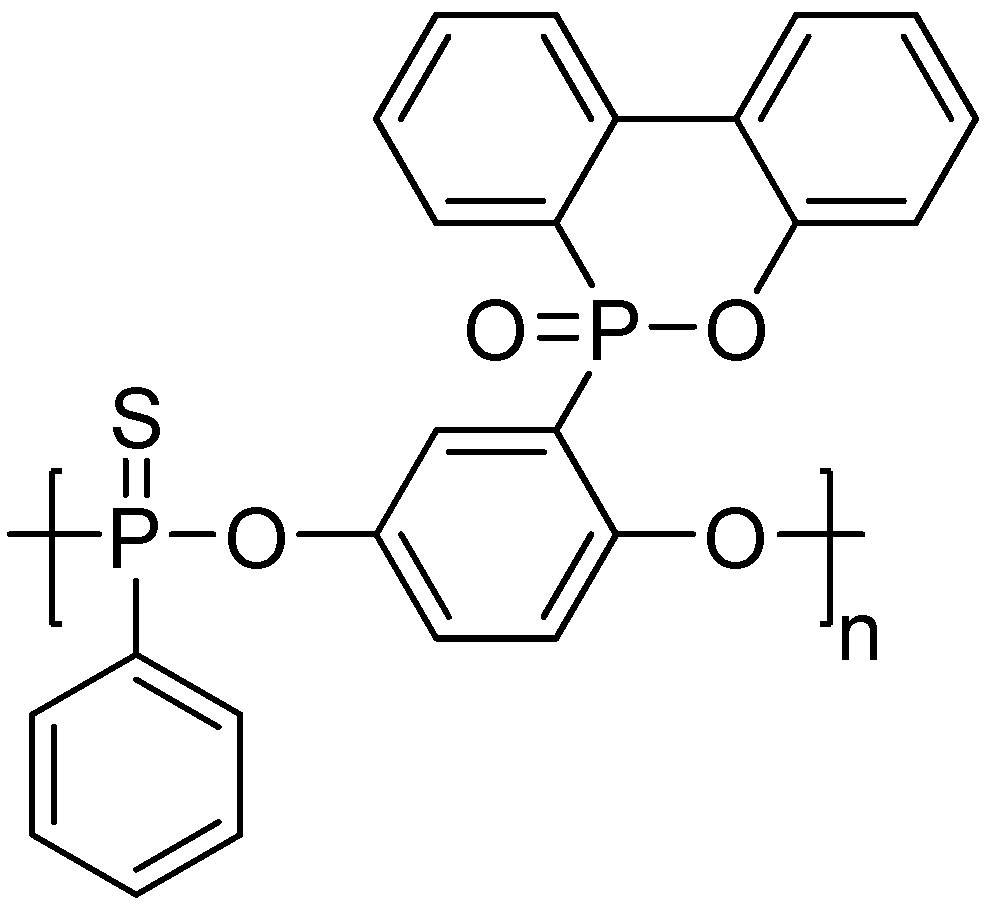
| Sample | First ignition | Second ignition | UL-94 rating | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Burning time (s) a | Observed dripping b | Burning time (s) | Observed dripping | ||
| PET/2% PDPTP | 0 | drip | 2 | drip | V-2 |
| PET/5% PDPTP | 0 | heavy | 0 | heavy | V-0 |
| PET/10% PDPTP | 0 | drip | 0 | drip | V-0 |
| PET/2% PDPPP | 0 | drip | 2 | drip | V-2 |
| PET/5% PDPPP | 0 | drip | 0 | drip | V-0 |
| PET/8% PDPPP | 0 | drip | 0 | drip | V-0 |
| PET/5% PDPPP/5% PSTPP | 0 | drip | 0 | drip | V-0 |
| PET/2% PSTPP | >180 | scarcely | none c | none | NR |
| PET/5% PSTPP | >180 | scarcely | none | none | NR |
| PET/10% PSTPP | >180 | no | none | none | NR |
| PET/20% PSTPP | 1 | no | 2 | no | V-0 |
- a Average time to self-extinguishing after ignition;
- b Indicated that samples did (yes) or did not (no) drip onto the cotton patch underneath the bar during the UL-94 test.
- c There is no enough sample left after the first ignition, hence the second ignition cannot be carried out in that case.
4. Conclusions and Prospect
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Lu, S.-Y.; Hamerton, I. Recent developments in the chemistry of halogen-free flame retardant polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2002, 27, 1661–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J. A review of phosphorus-containing flame retardants. J. Fire Sci. 1992, 10, 470–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaronson, A.M.; Bright, D.A. Oligomeric phosphate esters as flame retardants. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 1996, 110, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, E.D.; Levchik, S.V.; Ravey, M.; Zhu, W.M. A survey of recent progress in phosphorus-based flame retardants and some mode of action studies. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 1999, 146, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, G.; Harris, C.; Manku, J. Design of new organophosphorus flame retardants. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 1999, 146, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouritz, A.P.; Gibson, A.G. Fire Properties of Polymer Composite Materials; Springer: Dordrecht, the Netherlands, 2006; pp. 266–269. [Google Scholar]
- Laoutid, L.; Bonnaud, L.; Alexandre, M.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.-M.; Dubois, P. New prospects in flame retardant polymer materials: from fundamentals to nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2009, 63, 100–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, S.; Banerjee, S.; Palit, S.K. Phosphorus-containing polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1993, 18, 227–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stackman, R.W. Phosphorus-based additives for flame retardant polyester. 2. Polymeric phosphorus esters. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1982, 21, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toy, A.D.F. Aryl phosphorus containing resins and the method of preparing the same. US Patent 2,435,252, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Ranganathan, T.; Zilberman, J.; Farris, R.J.; Coughlin, E.B.; Emrick, T. Synthesis and characterization of halogen-free antiflammable polyphosphonates containing 4,4’-bishydroxydeoxybenzoin. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 5974–5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, R.N.; Lyon, R.E. Molar group contributions to polymer flammability. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 87, 548–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellzey, K.A.; Ranganathan, T.; Zilberman, J.; Coughlin, E.B.; Farris, R.J.; Emrick, T. Deoxybenzoin-based polyarylate as halogen-free fire-resistant polymers. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 3553–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, T.; Ku, B.-C.; Zilberman, J.; Beaulieu, M.; Farris, R.J.; Coughlin, E.B.; Emrick, T. Poly(arylate-phosphonate) copolymers with deoxybenzoin in the backbone: synthesis, characterization, and thermal properites. J. Polym. Sci, Polym. Chem. 2007, 45, 4573–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, T.; Beaulieu, M.; Zilberman, J.; Smith, K.D.; Westmoreland, P.R.; Farris, R.J.; Coughlin, E.B.; Emrick, T. Thermal degradation of deoxybenzoin polymers studies by pyrolysis-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourbigot, S.; Duquesne, S. Fire retardant polymers: recent developments and opportunities. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 2283–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Z.; Zheng, C.-Y.; Yang, K.-K. Synthesis and characterization of polysulfonyl diphenylene phenyl phosphonate. Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1999, 15, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Masai, Y.; Kato, Y.; Fukui, N. Fireproof, thermoplastic polyester-polyaryl phosphonate composition. US Patent 3,719,727, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.-S. Phosphorus-containing polymers. II. Preparation and properties of copoly(carbonate-phosphonate)s. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1983, 28, 2439–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Z. Flame-Retardation Design of PET Fibers. Sichuan Science & Technology Press: Chengdu, Sichuang, China, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-Z.; Zheng, C.-Y.; Wu, D.-C. Properties of polyethylene terephthalate/polysulfonyldiphenylene phenylphosphanate flame-retardant systems. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 1997, 18, 472–476. [Google Scholar]
- Granzow, A. Flame retardation by phosphorus-compounds. Acc. Chem. Res. 1978, 11, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Z.; Zheng, C.-Y.; Wu, D.-C. Flame-retardant action of polysulfonyldiphenylene phenylphosphonate on PET. Acta Polym. Sin. 1996, 4, 439–445. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-Z. Solubility parameters of poly(sulfonyldiphenylene phenylphosphonate) and its miscibility with PET. J. Polym. Sci., Polym. Phys. 2003, 41, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Z.; Xia, Y.Z. Investigation on the toxicity of polysulfonyldiphenylene phenylphosphonate. Explor. Nature 1996, 3, 82. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-Z.; Li, W.-F.; Xia, Y.-Z.; Sun, H. Study on the flame retardancy of PET masterbatch. Polyester Ind. 1992, 1, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-Z. Effect of flame retardant SF-FR on rheological properties of fiber-forming polymers. Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1992, 4, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-Z.; Zheng, C.-Y.; Wu, D.-C. Studies on the crystallizability and crystallization kinetics of flame-retardant PET by DSC. Acta Polym. Sin. 1993, 4, 479. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-Z.; Xia, Y.Z.; Luo, S.-J. Spinning of flame retardant PET and the structure and properties of the fibers. Chinese Syn. Fiber Ind. 1993, 3, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-Z. Dyeability of flame retardant PET fibers. Chinese Text. J. 1992, 13, 569. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-Z.; Zheng, C.-Y.; Wu, D.-C. Kinetics of the thermooxidative degradation of flame-retardant PET. Chinese Syn. Fibers 1993, 5, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-Z. Flame retardation of PBT. Flame Retard. Mater. Tech. 1991, 2, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Balabanovich, A.I.; Engelmann, J. Fire retardant and charring effect of poly(sulfonyldiphenylene phenylphosphonate) in poly(butylene terephthalate). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2003, 79, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jachowicz, J.; Kryszewsky, M.; Kowalski, P. Thermal degradation of poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide). I. The mechanism of degradation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1978, 22, 2891–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Z.; Yi, B.; Wu, B.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y. Thermal behaviors of flame-retardant polycarbonates containing diphenyl sulfonate and poly(sulfonyl phenylene phosphonate). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 89, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, V. Flame retardant polycarbonate composition. US Patent 3,940,366, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Ishli, K.; Shimomai, K. Flame-retardant polycarbonate resin composition and a molded product using the same. US Patent 6,432,550, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn, K.J.; Gallucci, R.R.; Georgiev, E.M. Flame retardant polycarbonate resin/ABS graft copolymer blends. US Patent 6,605,659, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Levchik, S.V.; Weil, E.D. Overview of recent developments in the flame retardancy of polycarbonate. Polym. Int. 2005, 54, 981–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, D.-M.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Yang, B.; Zhao, G.-M. A novel non-dripping oligomeric flame retardant for polyethylene terephthalate. Eur. Polym. J. 2004, 40, 1909–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Z.; Ban, D.-M.; Wu, B. Non-halogen polymer-type additive with fire resisting melting-dropping properties, and its preparing process and usage. Chinese Patent CN1376760, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-Z.; Ban, D.-M.; Chang, Y.-L.; Zhao, G.-M.; Yang, B. Polymer type phosphatic fire retardant, preparation method and usage. Chinese Patent CN1563152, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, T. Cyclic organophosphorus compounds and process for making them. US Patent 3,702,878, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, T.; Oishi, H.; Hirayama, T. Formation of cyclic organic phosphorus compound. JP Patent 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Shigeru, O.; Shigeo, S. Phosphorus-containing epoxy compounds and preparation thereof. JP Patent 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Endo, S.; Kashihara, T.; Osaka, A.; Shizuki, T.; Ikegami, T. Phosphorus-containing compounds. US Patent 4,127,590, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Endo, S.; Kashihara, T.; Osaka, A.; Shizuki, T.; Ikegami, T. Phosphorus-containing polyesters. US Patent 4,157,436, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Rieckert, H.; Dietrich, J.; Keller, H. Adduct preparation used as flame retardant e.g., in polyester fibre(s). DE 19711523, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, Y.-I.; Kang, C.-S.; Choi, T.-G.; Song, J.-M. Flame retardant polybutyleneterephthalate resin. WO 02/42374, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer, A.; Seibold, S.; Lohstroh, W.; Walter, O.; Döring, M. Synthesis and properties of flame-retardant epoxy resins based on DOPO and one of its analog DPPO. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 105, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-L.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Ban, D.-M.; Yang, B.; Zhao, G.-M. A novel phosphorus-containing polymer as a highly effective flame retardant. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2004, 289, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Ban, D.-M.; Liu, X.-H.; Zhou, Q. Burning behavior and pyrolysis products of flame-retardant PET containing sulfur-containing aryl polyphosphate. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2006, 76, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, D.-M. Syntheses and applications of sulfur-containing aryl polyphosphonates as flame retardants for poly(ethylene terephthalate). Ph.D. Thesis, Sichuan University, Sichuan, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Schut, J.H. Polyphosphonate: new flame-retardant cousin of polycarbonate. Available online: http://www.ptonline.com/articles/200907cu1.html (accessed on July, 2009).
- Freitag, D.; Go, P.; Stahl, G. Compositions comprising polyphosphonates and additives that exhibit and advantageous combination of properties, and methods related thereto. US2007,203,269, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Freitag, D. Poly(block-phosphonato-ester) and poly(block-phosphonato-carbonate) and methods of making same. WO2007022008, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Freitag, D. Methods for the production of block copolycarbonate/phosphonates and compositions therefrom. WO2007065094, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Freitag, D.; Go, P. Insoluble and branched polyphosphonates and methods related thereto. WO2009018336, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- New company, FRX Polymers, launched to provide first commercially available polyphosphonate flame retardants. Available online: http://www.frxpolymers.com/frx_launch.htm (accessed on September, 2007).
- Products list of Weili Flame-Retardant Chemicals Co. Ltd., Chengdu, China. Available online: http://www.weilichem.com (accessed on January, 2006).
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Wang, Y.-Z. Aryl Polyphosphonates: Useful Halogen-Free Flame Retardants for Polymers. Materials 2010, 3, 4746-4760. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3104746
Chen L, Wang Y-Z. Aryl Polyphosphonates: Useful Halogen-Free Flame Retardants for Polymers. Materials. 2010; 3(10):4746-4760. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3104746
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Li, and Yu-Zhong Wang. 2010. "Aryl Polyphosphonates: Useful Halogen-Free Flame Retardants for Polymers" Materials 3, no. 10: 4746-4760. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3104746
APA StyleChen, L., & Wang, Y.-Z. (2010). Aryl Polyphosphonates: Useful Halogen-Free Flame Retardants for Polymers. Materials, 3(10), 4746-4760. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3104746




