Design of Friction Stir Welding Tool for Avoiding Root Flaws
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. FVM of Friction Stir Welding
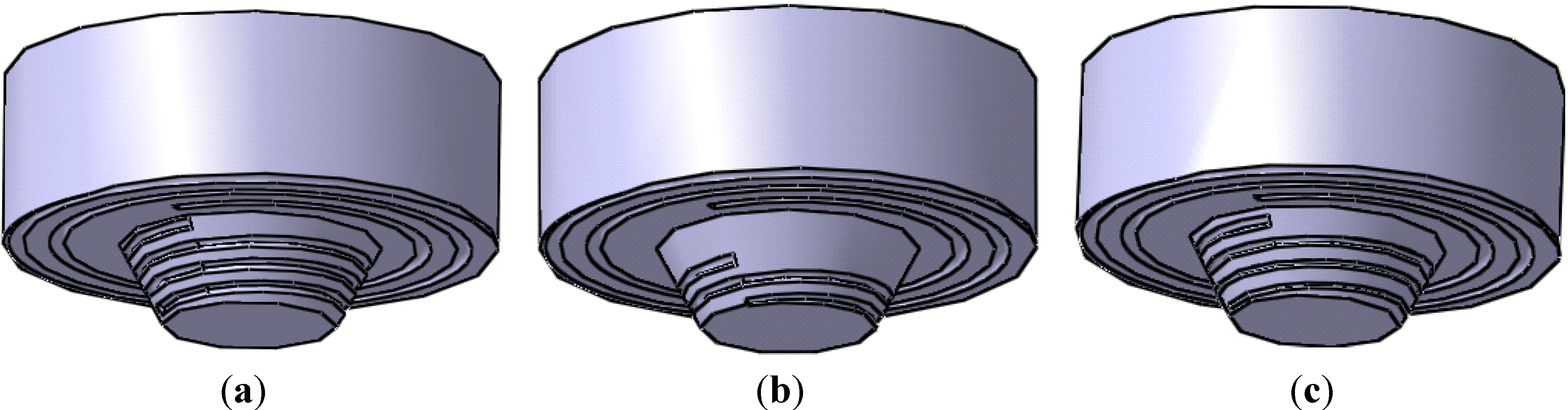
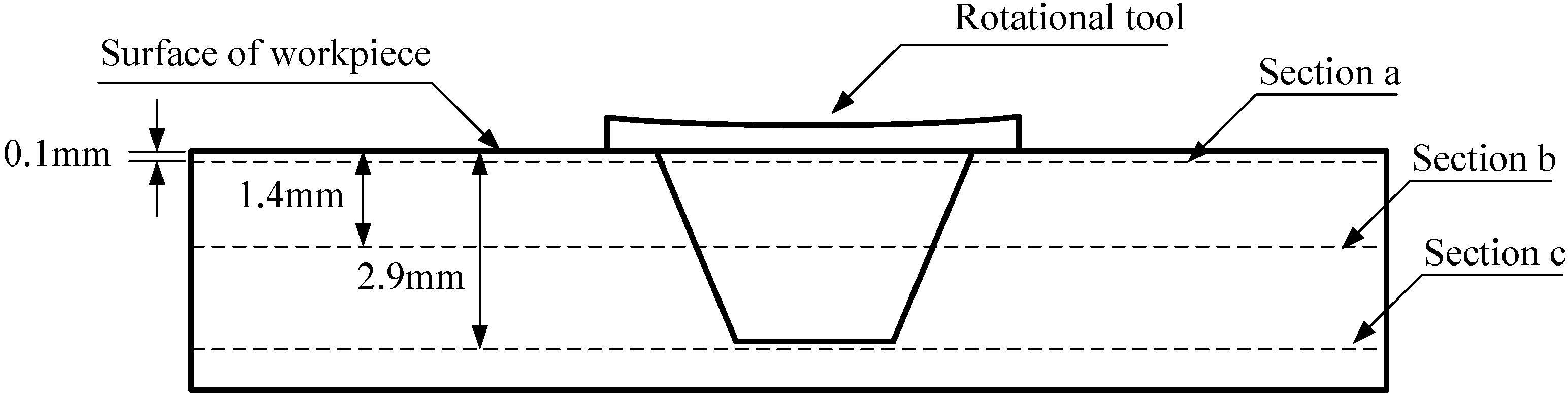
2.1. The Designed Rotational Tool
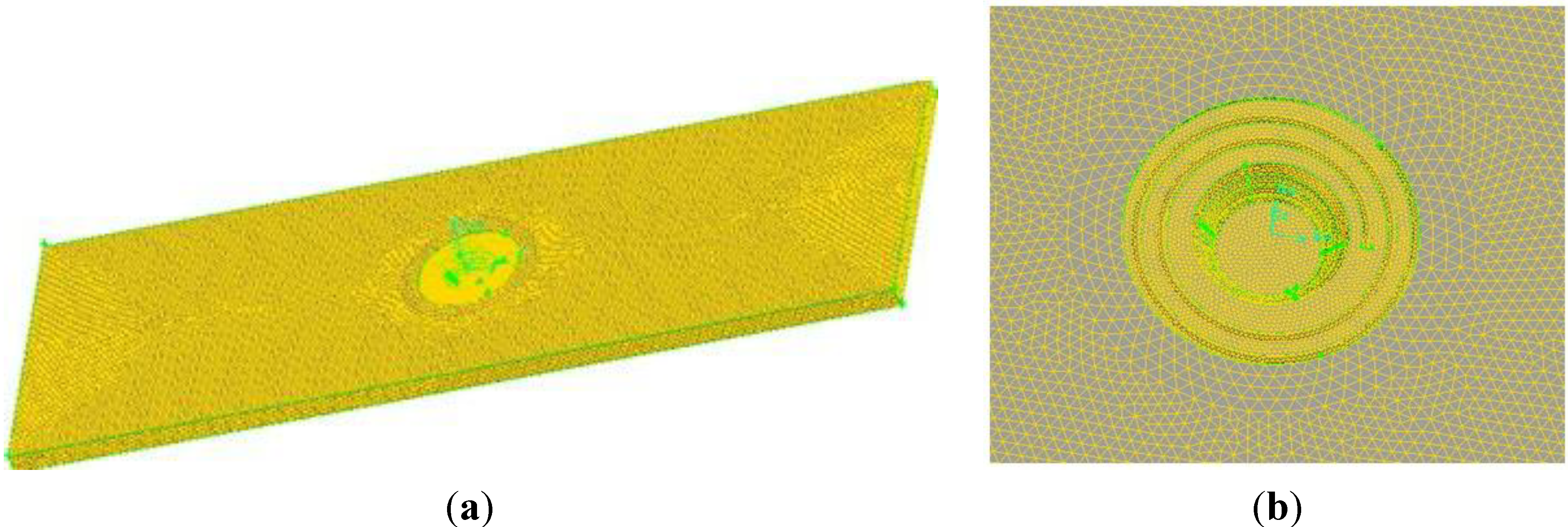
2.2. Mesh Generation
2.3. Material Parameters
2.4. Boundary Condition
3. Results and Discussion
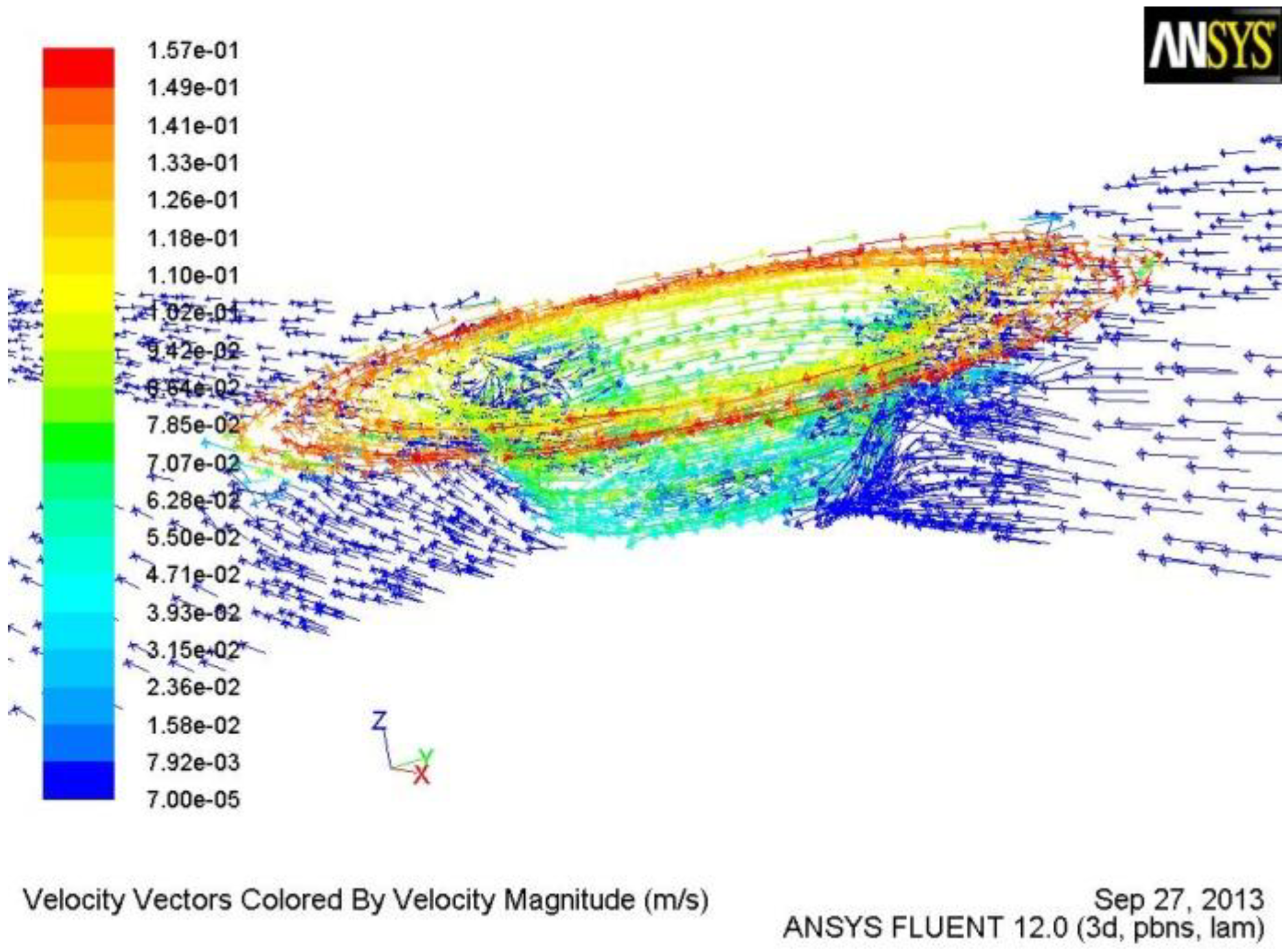
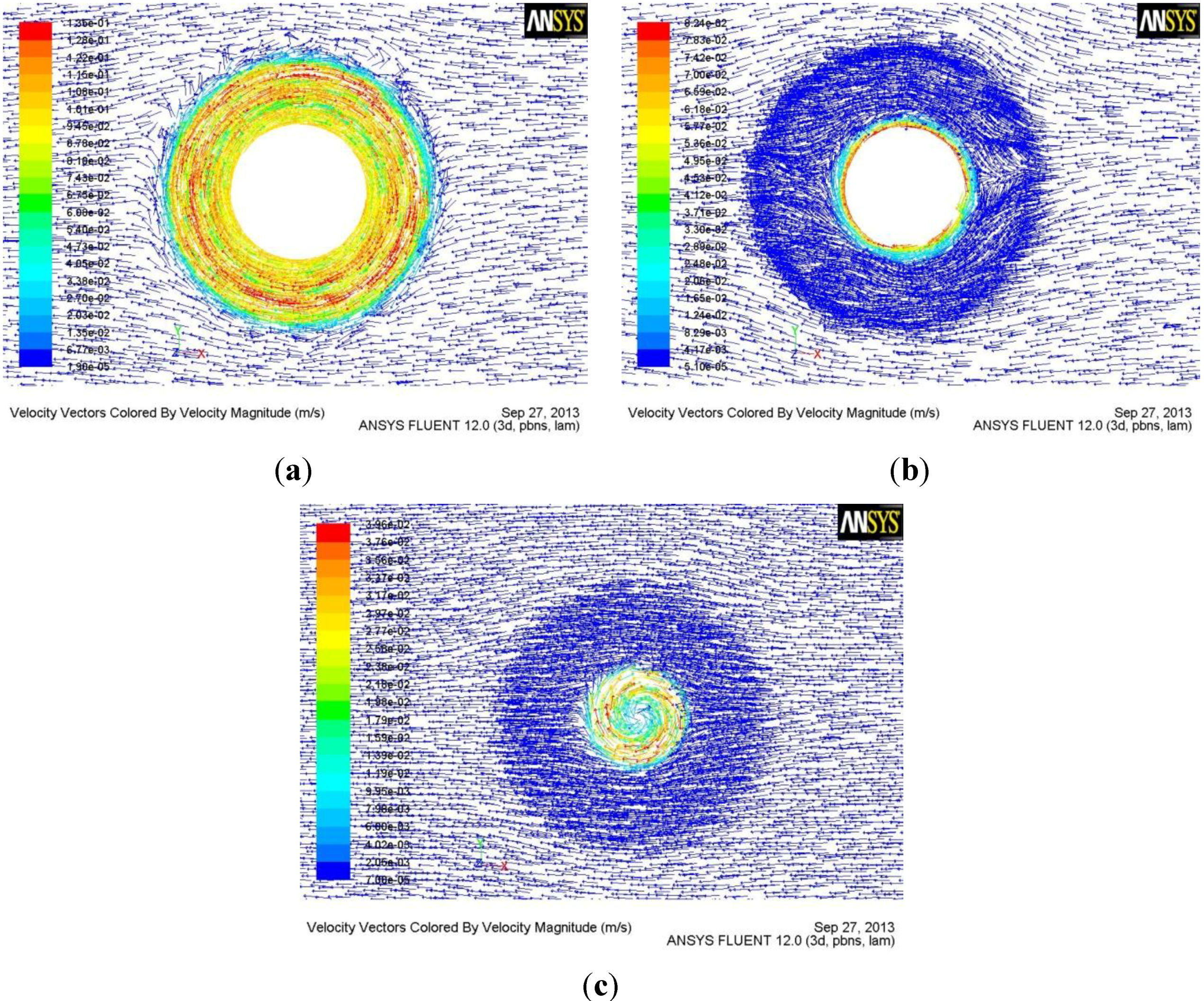
3.1. Material Flow Behavior of the Tool with Tapered-Flute Pin during FSW

3.2. Effect of Flute Geometry on Material Flow
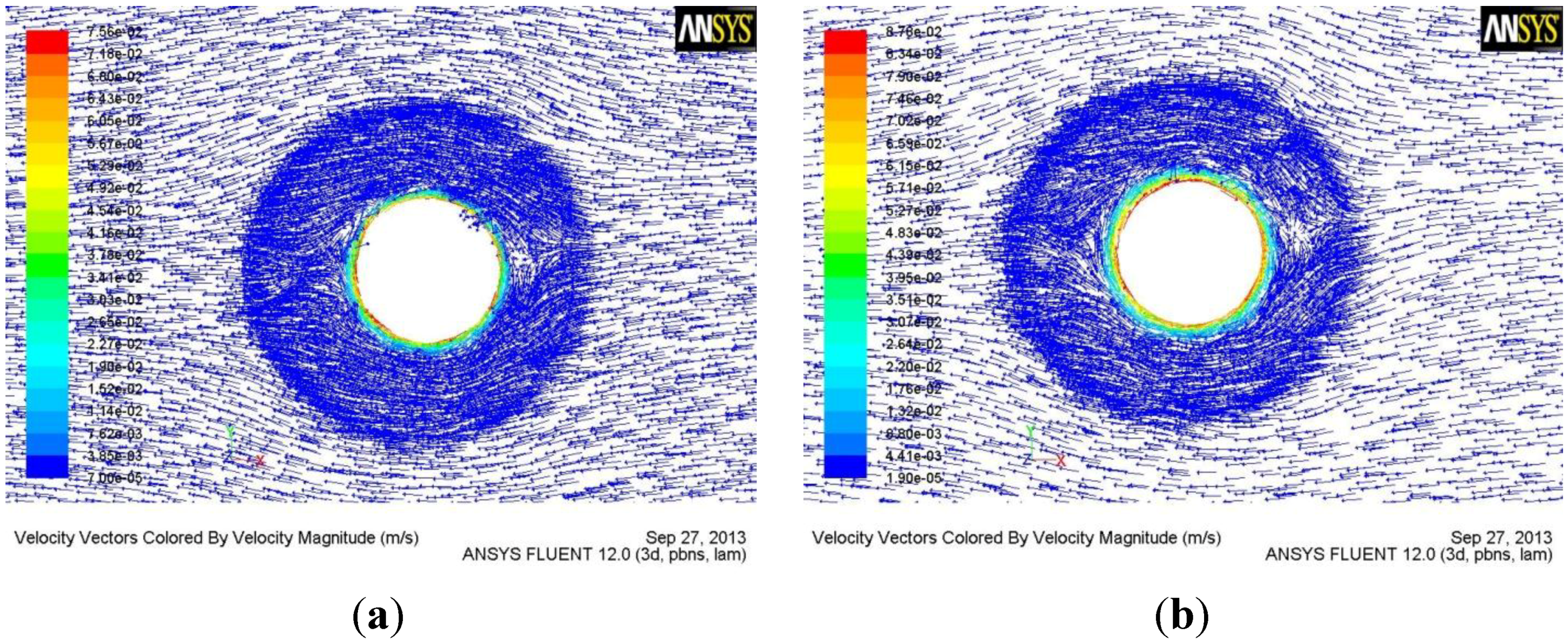
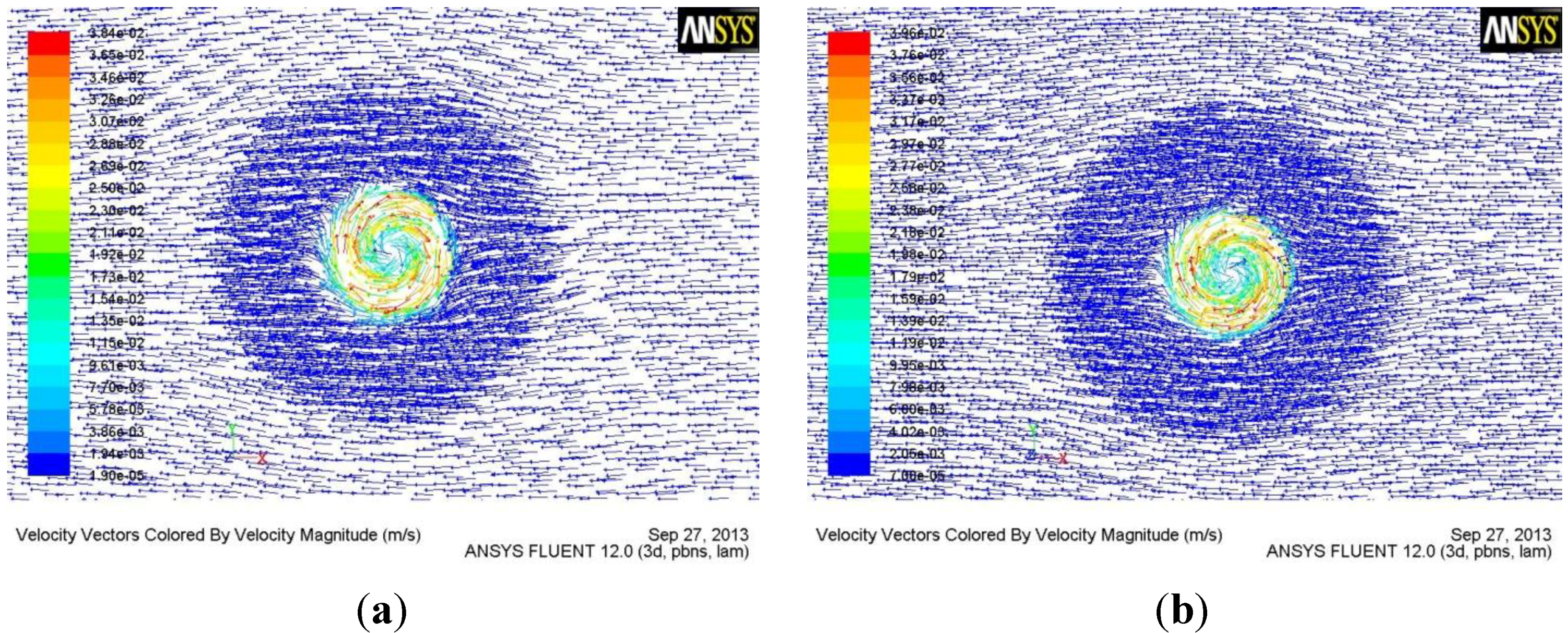
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fonda, R.W.; Knipling, K.E.; Bingert, J.F. Microstructural evolution ahead of the tool in aluminum friction stir welds. Scr. Mater. 2007, 58, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.S.; Ma, Z.Y. Friction stir welding and processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2005, 50, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandan, R.; Debroy, T.; Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Recent advances in friction-stir welding-process, weldment structure and properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2008, 53, 980–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrin, N.; Chen, D.L.; Cao, X.; Jahazi, M. Microstructure and tensile properties of friction stir welded AZ31B magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 472, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, T.U.; Reynolds, A.P. Visualization of the material flow in AA2195 friction-stir welds using a marker insert technique. Metall. Mater. Trans. 2001, 32A, 2879–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.S.; Zhang, W.B.; Shi, L.; Chen, M.A. Visualization and simulation of plastic material flow in friction stir welding of 2024 aluminium alloy plates. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2011, 22, 1446–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Pourahmad, P.; Abbasi, M. Materials flow and phase transformation in friction stir welding of Al 6013/Mg. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2012, 23, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.D.; Shi, Q.Y.; Zhang, L.G.; Zou, A.L.; Gao, S.S.; Zan, L.V. Numerical simulation of material flow behavior of friction stir welding influenced by rotational tool geometry. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2012, 63, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grujicic, M.; Arakere, G.; Pandurangan, B.; Ochterbeck, J.M.; Yen, C.-F.; Cheeseman, B.A.; Reynolds, A.P.; Sutton, M.A. Computational analysis of material flow during friction stir welding of AA5059 aluminum alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2012, 21, 1824–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grujicic, M.; Pandurangan, B.; Yen, C.-F.; Cheeseman, B.A. Modifications in the AA5083 Johnson-Cook material model for use in friction stir welding computational analyses. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2012, 21, 2207–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Jahazi, M. Effect of tool rotational speed and probe length on lap joint quality of a friction stir welded magnesium alloy. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffa, G.; Hua, J.; Shivpuri, R.; Fratini, L. Design of the friction stir welding tool using the continuum based FEM model. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2006, 419, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.B.; Yan, K.; Lin, T.; Chen, S.B.; Zhao, Y. The investigation of typical welding defects for 5456 aluminum alloy friction stir welds. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 433, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lin, S.B.; Wu, L.; Feng, J.C.; Ma, S.L. Defects formation procedure and mathematic model for defects fress friction stir welding of magnesium alloy. Mater. Des. 2006, 27, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.D.; Zou, A.L.; Yue, Y.M.; Luan, G.H.; Jin, Y.Y.; Fu, L. Numerical simulation of effect of rotational tool with screw on material flow behavior of friction stir welding of Ti6Al4V alloy. Acta. Metall. Sin. 2012, 25, 365–373. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, S.; Xing, J.; Yue, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, S. Design of Friction Stir Welding Tool for Avoiding Root Flaws. Materials 2013, 6, 5870-5877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6125870
Ji S, Xing J, Yue Y, Ma Y, Zhang L, Gao S. Design of Friction Stir Welding Tool for Avoiding Root Flaws. Materials. 2013; 6(12):5870-5877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6125870
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Shude, Jingwei Xing, Yumei Yue, Yinan Ma, Liguo Zhang, and Shuangsheng Gao. 2013. "Design of Friction Stir Welding Tool for Avoiding Root Flaws" Materials 6, no. 12: 5870-5877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6125870



