Supported Membranes Meet Flat Fluidics: Monitoring Dynamic Cell Adhesion on Pump-Free Microfluidics Chips Functionalized with Supported Membranes Displaying Mannose Domains
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Surface Chemistry, Lithographic Structuring of Fluidic Channels
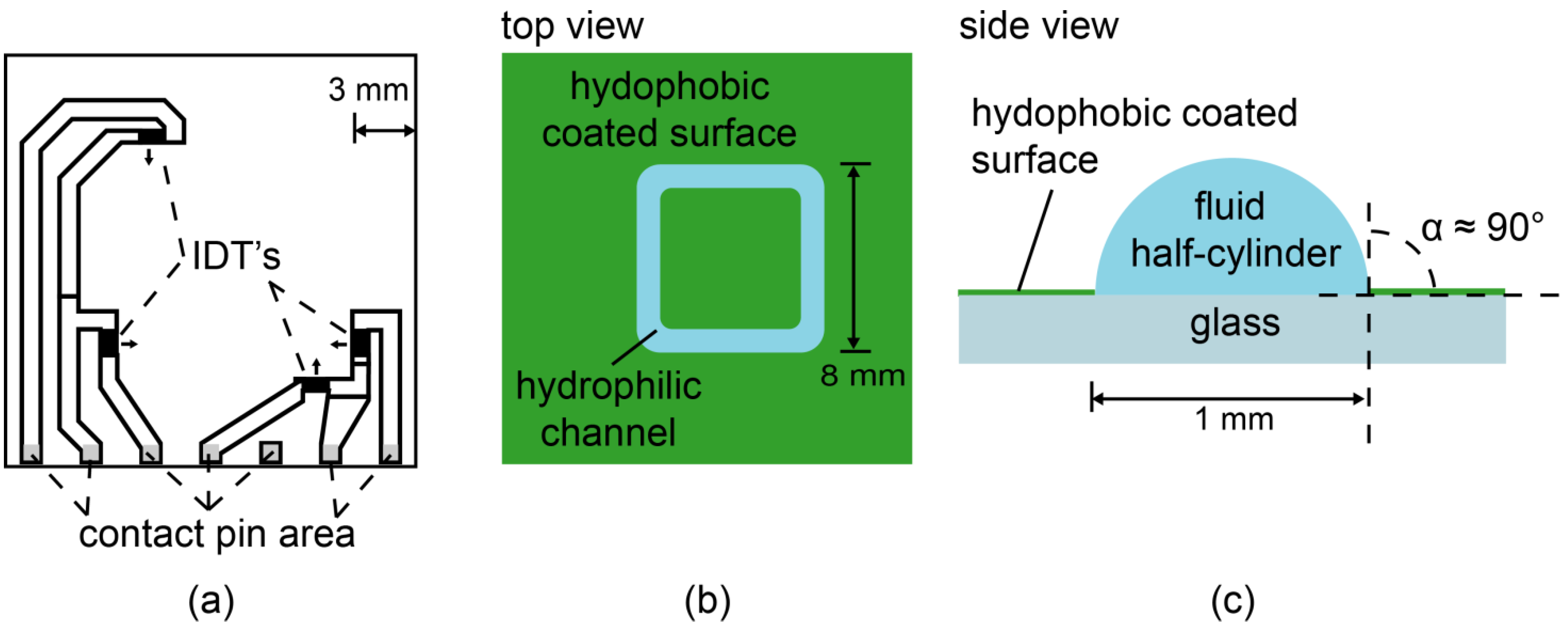
3. Results and Discussion
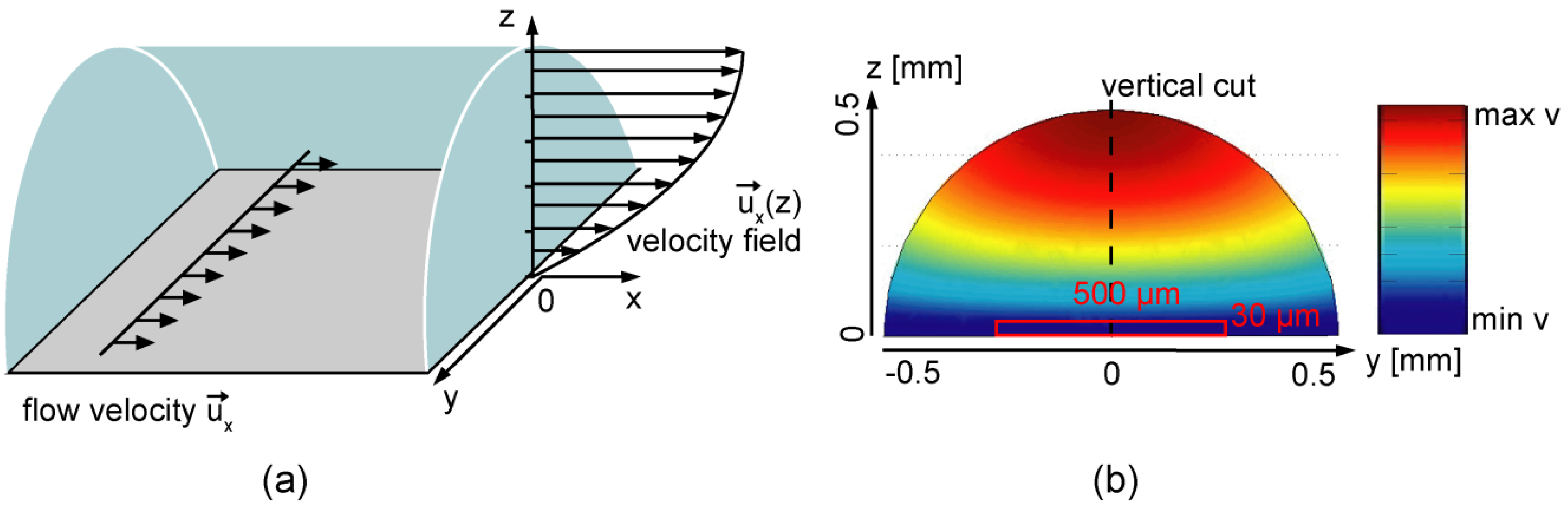
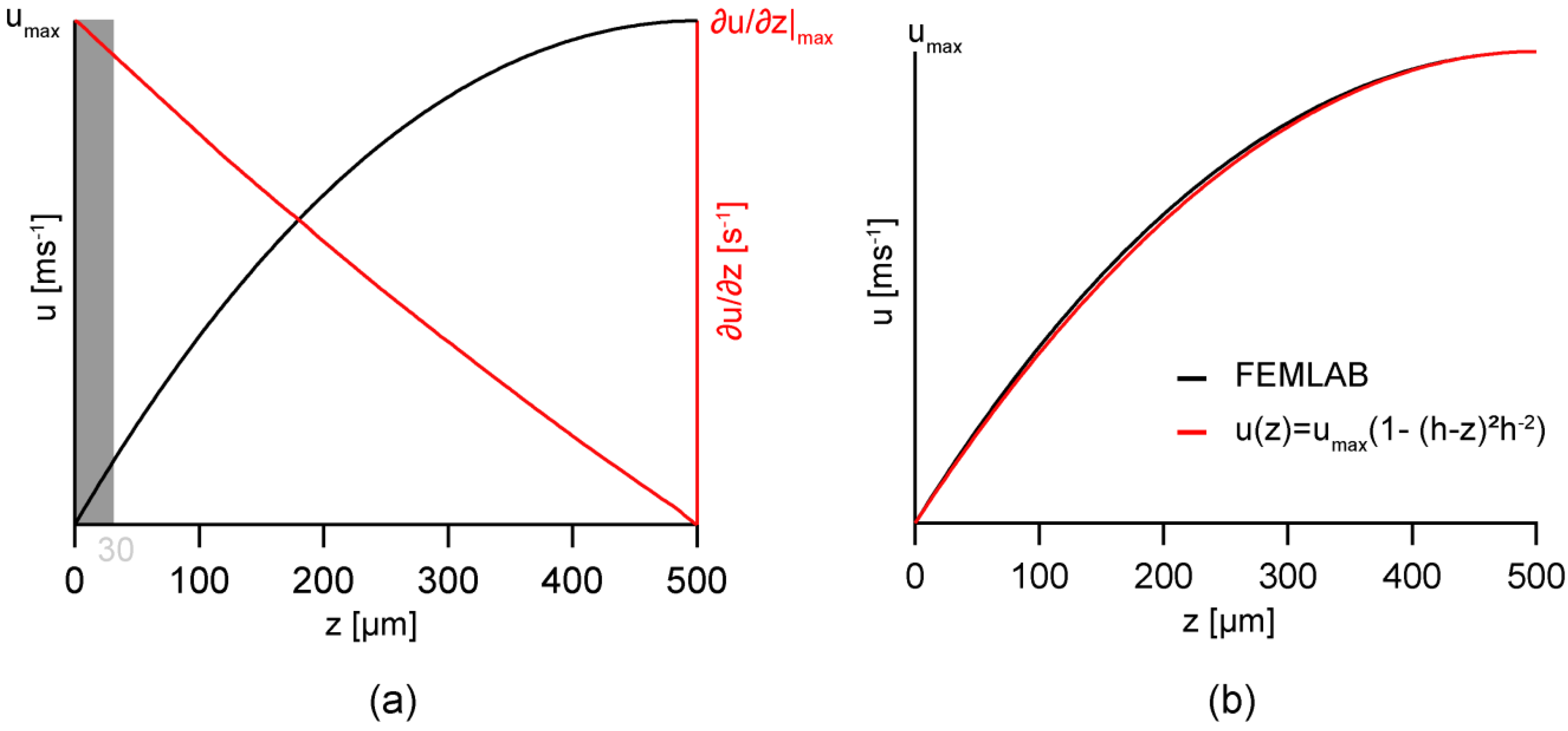
3.1. Modeling of Flow Profiles
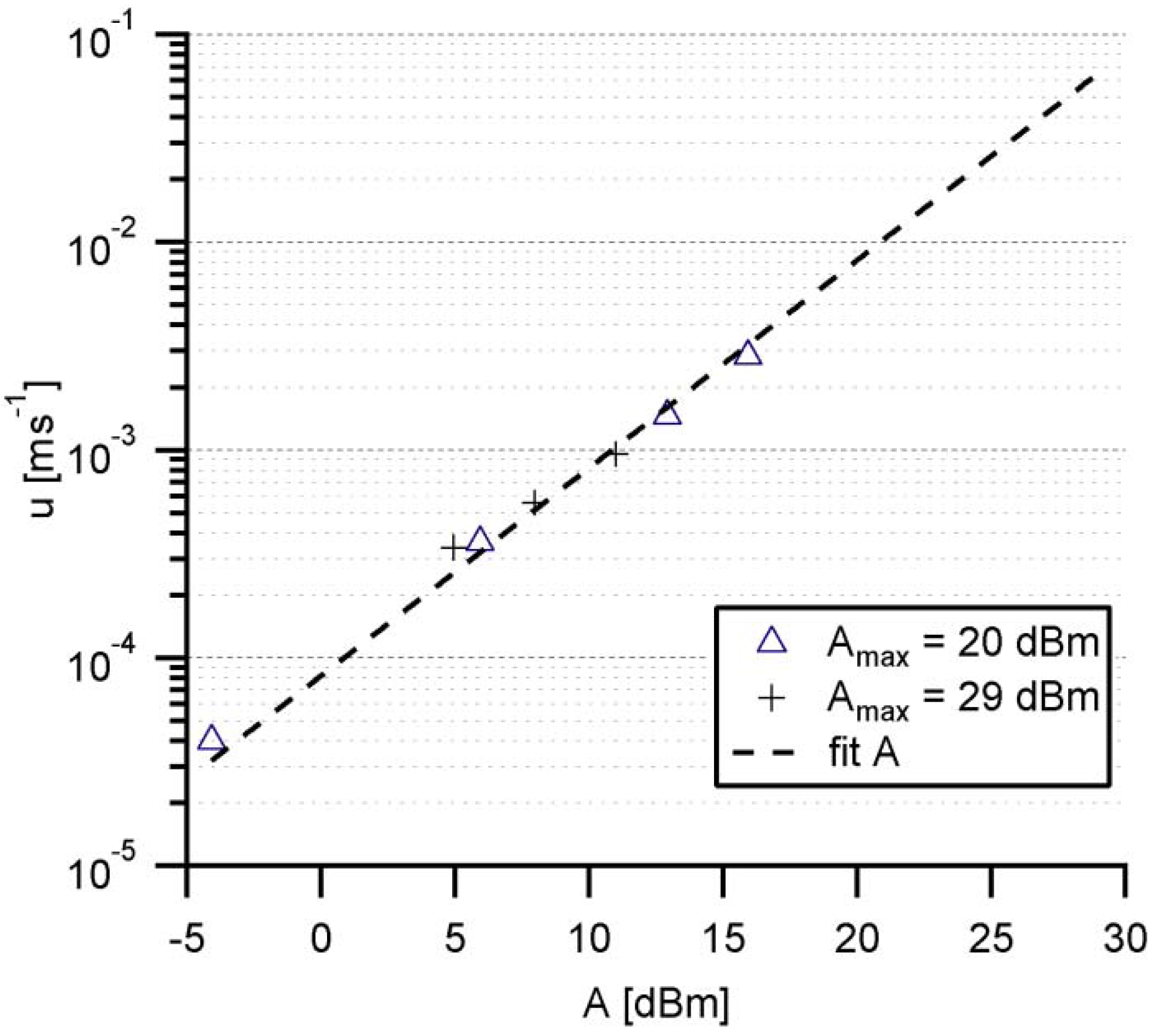
3.2. Calibration of Shear Rates by Acoustic Streaming
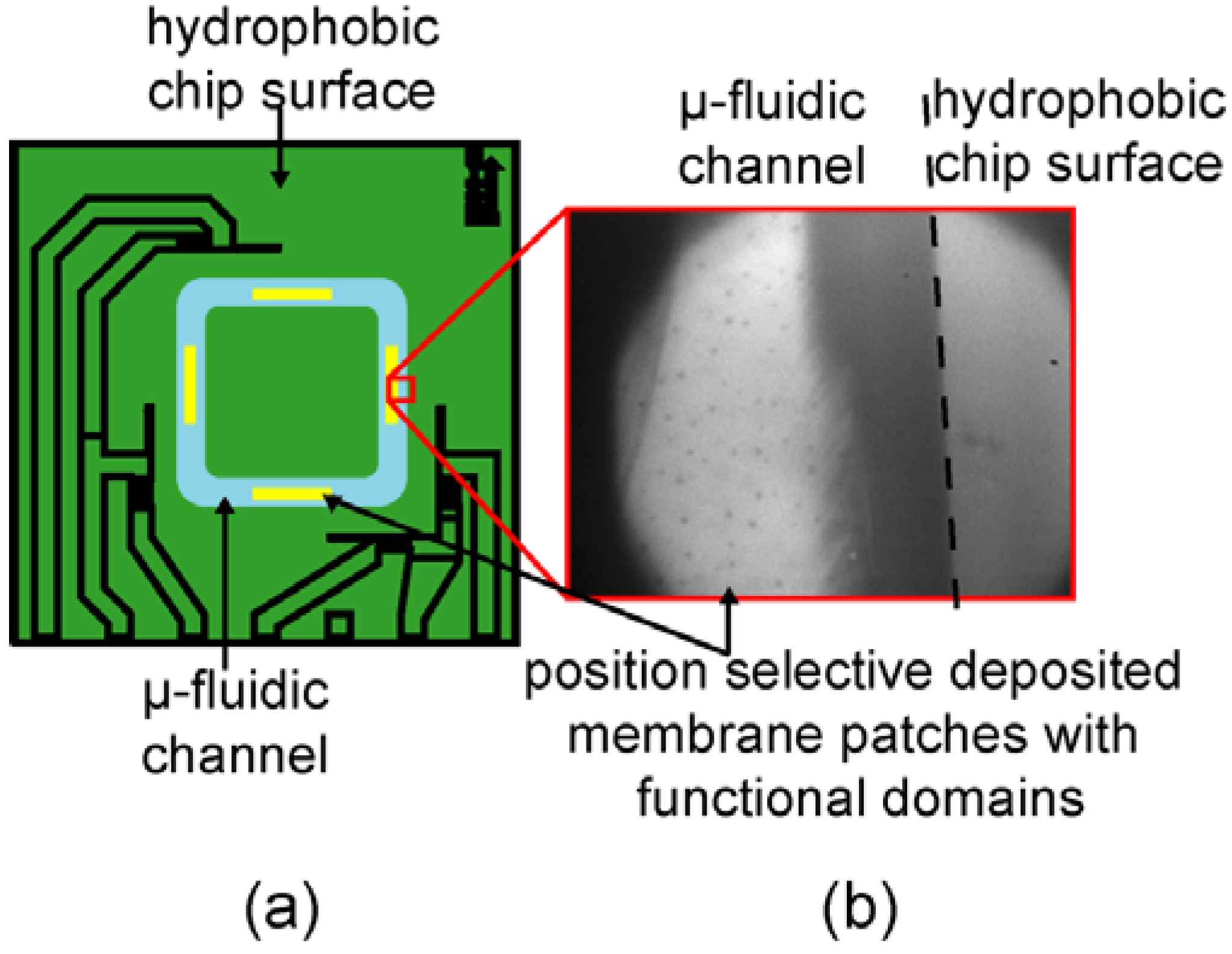
3.3. Position Selective Functionalization of Fluidic Chips with Supported Membranes
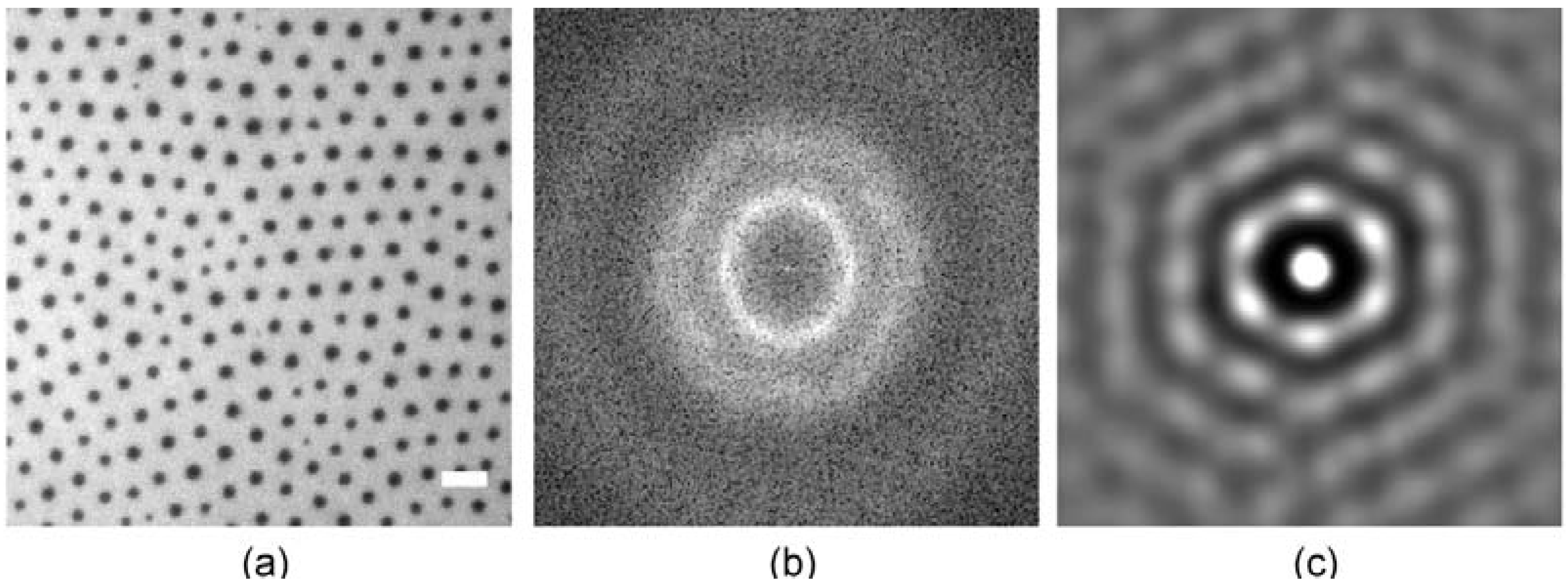
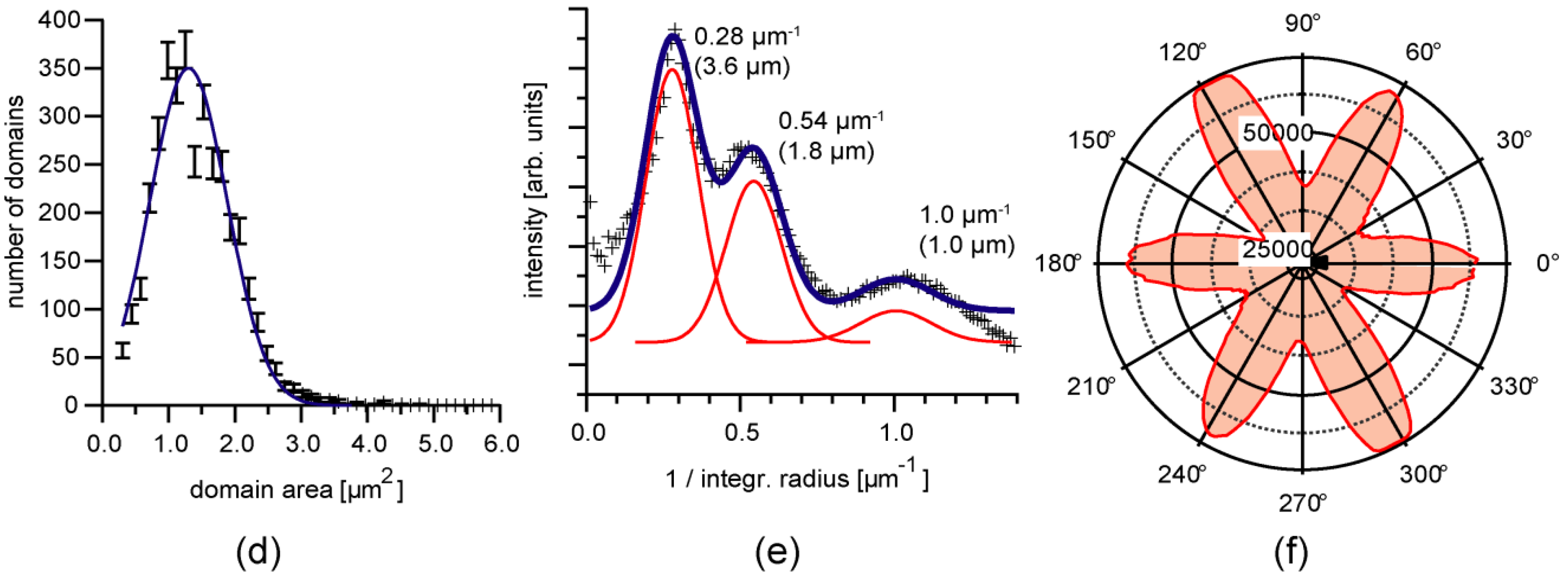
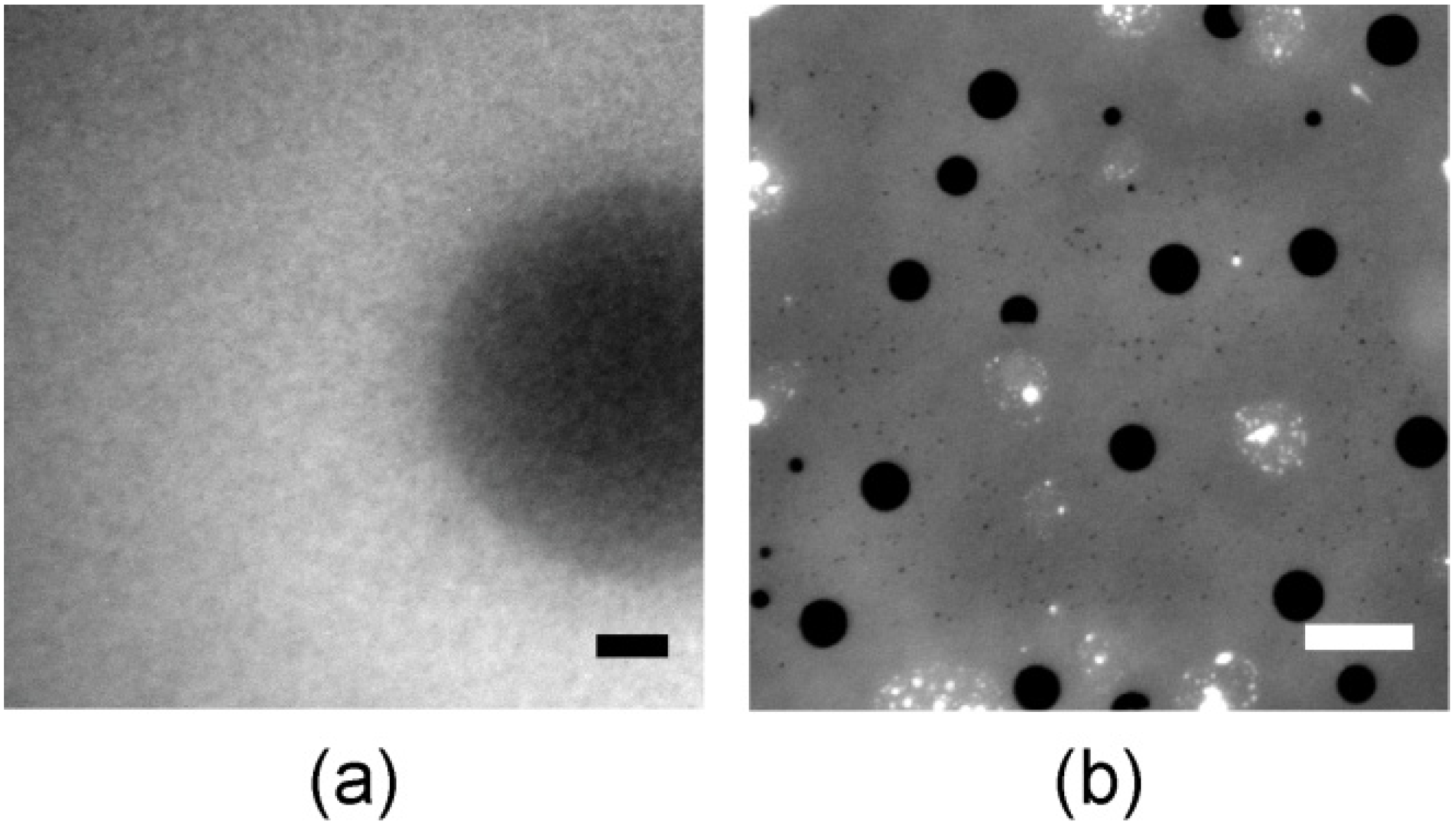

3.4. Cell Adhesion under Various Shear Conditions
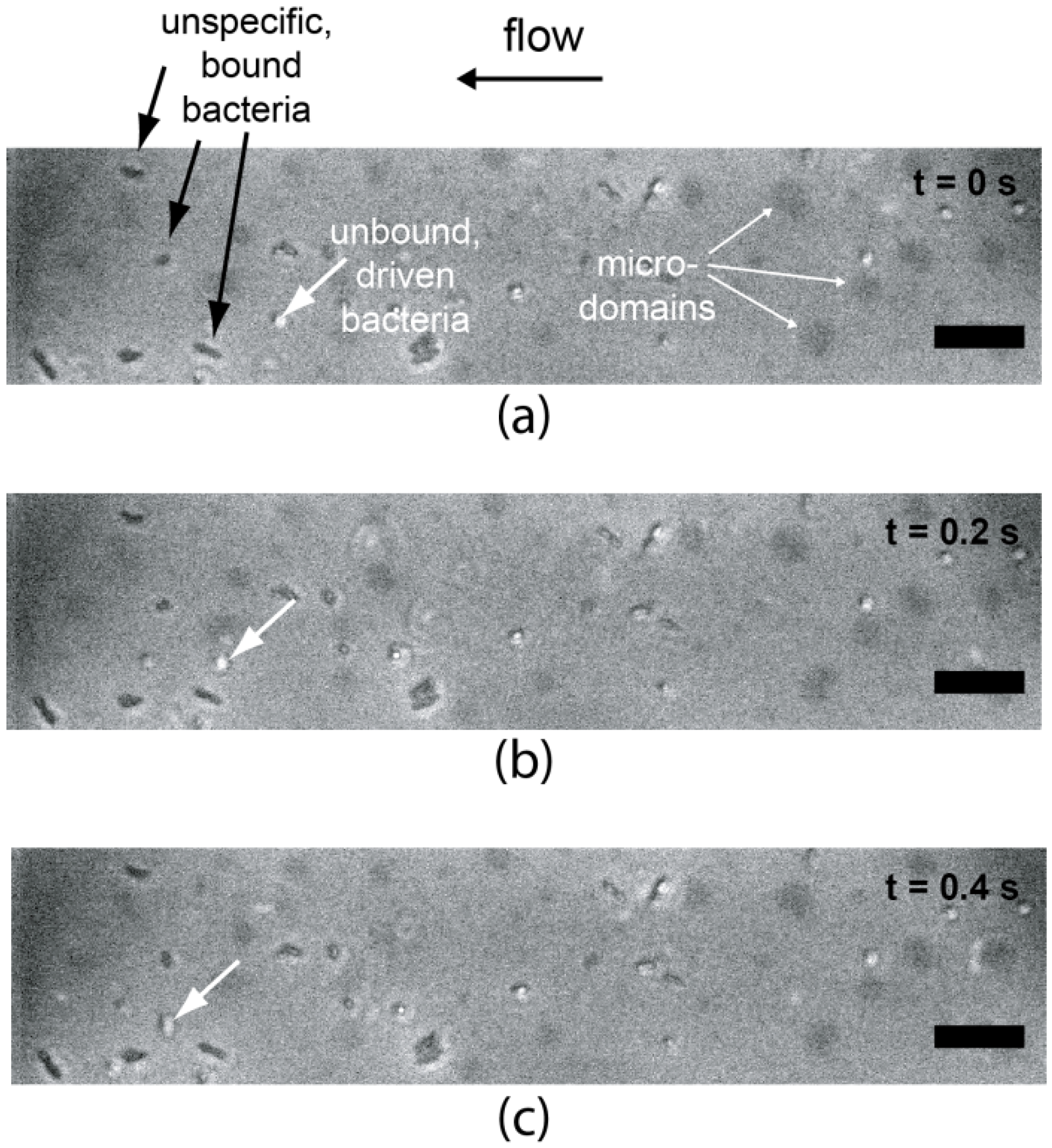
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgement
References
- Brian, A.A.; McConnell, H.M. Allogeneic stimulation of cytotoxic T cells by supported planar membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 6159–6163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamm, L.K.; McConnell, H.M. Supported phospholipid bilayers. Biophys. J. 1985, 47, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sackmann, E. Supported membranes: Scientific and practical applications. Science 1996, 271, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Sackmann, E. Polymer-supported membranes as models of the cell surface. Nature 2005, 437, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grakoui, A.; Bromley, S.K.; Sumen, C.; Davis, M.M.; Shaw, A.S.; Allen, P.M.; Dustin, M.L. The immunological synapse: A molecular machine controlling T cell activation. Science 1999, 285, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goennenwein, S.; Tanaka, M.; Hu, B.; Moroder, L.; Sackmann, E. Functional incorporation of integrins into solid supported membranes on ultrathin films of cellulose: Impact on adhesion. Biophys. J. 2003, 85, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchi-Artzner, V.; Lorz, B.; Hellerer, U.; Kantlehner, M.; Kessler, H.; Sackmann, E. Selective adhesion of endothelial cells to artificial membranes with a synthetic RGD-lipopeptide. Chemistry 2001, 7, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, A.S.; Dellatore, S.M.; Messersmith, P.B.; Miller, W.M. Effects of supported lipid monolayer fluidity on the adhesion of hematopoietic progenitor cell lines to fibronectin-derived peptide ligands for alpha5beta1 and alpha4beta1 integrins. Langmuir 2009, 25, 2994–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroumpoulis, D.; Zhang, H.; Rubalcava, L.; Gliem, J.; Tirrell, M. Cell adhesion and growth to peptide-patterned supported lipid membranes. Langmuir 2007, 23, 3849–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, T.H.; Gaub, H.E.; McConnell, H.M. T-cell-mediated association of peptide antigen and major histocompatibility complex protein detected by energy transfer in an evanescent wave-field. Nature 1986, 320, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ros, A.; Hellmich, W.; Regtmeier, J.; Duong, T.T.; Anselmetti, D. Bioanalysis in structured microfluidic systems. Electrophoresis 2006, 27, 2651–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craighead, H. Future lab-on-a-chip technologies for interrogating individual molecules. Nature 2006, 442, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brody, J.P.; Yager, P.; Goldstein, R.E.; Austin, R.H. Biotechnology at low Reynolds numbers. Biophys. J. 1996, 71, 3430–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wixforth, A.; Strobl, C.; Gauer, C.; Toegl, A.; Scriba, J.; v Guttenberg, Z. Acoustic manipulation of small droplets. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 379, 982–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttenberg, Z.; Muller, H.; Habermuller, H.; Geisbauer, A.; Pipper, J.; Felbel, J.; Kielpinski, M.; Scriba, J.; Wixforth, A. Planar chip device for PCR and hybridization with surface acoustic wave pump. Lab Chip 2005, 5, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennig, M.; Neumann, J.; Wixforth, A.; Radler, J.O.; Schneider, M.F. Dynamic patterns in a supported lipid bilayer driven by standing surface acoustic waves. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 3050–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, M.F.; Guttenberg, Z.; Schneider, S.W.; Sritharan, K.; Myles, V.M.; Pamukci, U.; Wixforth, A. An acoustically driven microliter flow chamber on a chip (muFCC) for cell-cell and cell-surface interaction studies. ChemPhysChem 2008, 9, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friend, J.; Yeo, L.Y. Microscale acoustofluidics: Microfluidics driven via acoustics and ultrasonics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2011, 83, 647–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.J.; Jin, C.Y.; Derzon, D.K.; Huber, T.A.; Last, J.A.; Provencio, P.P.; Gopalan, A.S.; Dugger, M.; Sasaki, D.Y. Synthesis of ether-linked fluorocarbon surfactants and their aggregational properties in organic solvents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 272, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, M.; Ito, Y.; Ogawa, T. Total synthesis of the mollu-series glycosyl ceramides alpha-d-Manp-(1→3)-beta-d-Manp-(1→4)-beta-d-Glcp-(1→1)-Cer and alpha-d-Manp-(1→3)-[beta-d-Xylp-(1→2)]-beta-d-Manp-(1→4)-beta-d-Glcp-(1→1)-Cer. Carbohydr. Res. 1990, 195, 199–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oelke, J.; Pasc, A.; Wixforth, A.; Konovalov, O.; Tanaka, M. Highly uniform, strongly correlated fluorinated lipid nanodomains embedded in biological membrane models. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 213901:1–213901:3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaindl, T.; Oelke, J.; Pasc, A.; Kaufmann, S.; Konovalov, O.V.; Funari, S.S.; Engel, U.; Wixforth, A.; Tanaka, M. Regulation of adhesion behavior of murine macrophage using supported lipid membranes displaying tunable mannose domains. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2010, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S. Surface Acoustic Wave Devices; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1986; p. 208. [Google Scholar]
- Kern, W.; Puotinen, D. Cleaning solutions based on hydrogen peroxide for use in silicon semiconductor technology. RCA Rev. 1970, 31, 187–206. [Google Scholar]
- Hillebrandt, H.; Tanaka, M. Electrochemical characterization of self-assembled alkylsiloxane monolayers on indium-tin oxide (ITO) semiconductor electrodes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 4270–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acheson, D.J. Elementary Fluid Dynamics; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1990; p. 408. [Google Scholar]
- Frommelt, T.; Gogel, D.; Kostur, M.; Talkner, P.; Hanggi, P.; Wixforth, A. Flow patterns and transport in Rayleigh surface acoustic wave streaming: Combined finite element method and raytracing numerics versus experiments. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2008, 55, 2298–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antil, H.; Glowinski, R.; Hoppe, R.H.W.; Linsenmann, C.; Pan, T.W.; Wixforth, A. Modeling, simulation, and optimization of surface acoustic wave driven microfluidic biochips. J. Comput. Math. 2010, 28, 149–169. [Google Scholar]
- Guttenberg, Z.; Rathgeber, A.; Keller, S.; Radler, J.O.; Wixforth, A.; Kostur, M.; Schindler, M.; Talkner, P. Flow profiling of a surface-acoustic-wave nanopump. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 70, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunitake, T. Synthetic bilayer-membranes—Molecular design, self-organization, and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1992, 31, 709–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, J.G.; Krafft, M.P. Fluorinated phosphocholine-based amphiphiles as components of fluorocarbon emulsions and fluorinated vesicles. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1995, 75, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, R.; Sackmann, E.; Evans, E. Molecular friction and epitactic coupling between monolayers in supported bilayers. J. Phys. Paris 1989, 50, 1535–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Oelke, J.; Kaindl, T.; Pasc, A.; Guttenberg, Z.; Wixforth, A.; Tanaka, M. Supported Membranes Meet Flat Fluidics: Monitoring Dynamic Cell Adhesion on Pump-Free Microfluidics Chips Functionalized with Supported Membranes Displaying Mannose Domains. Materials 2013, 6, 669-681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6020669
Oelke J, Kaindl T, Pasc A, Guttenberg Z, Wixforth A, Tanaka M. Supported Membranes Meet Flat Fluidics: Monitoring Dynamic Cell Adhesion on Pump-Free Microfluidics Chips Functionalized with Supported Membranes Displaying Mannose Domains. Materials. 2013; 6(2):669-681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6020669
Chicago/Turabian StyleOelke, Jochen, Thomas Kaindl, Andreea Pasc, Zeno Guttenberg, Achim Wixforth, and Motomu Tanaka. 2013. "Supported Membranes Meet Flat Fluidics: Monitoring Dynamic Cell Adhesion on Pump-Free Microfluidics Chips Functionalized with Supported Membranes Displaying Mannose Domains" Materials 6, no. 2: 669-681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6020669
APA StyleOelke, J., Kaindl, T., Pasc, A., Guttenberg, Z., Wixforth, A., & Tanaka, M. (2013). Supported Membranes Meet Flat Fluidics: Monitoring Dynamic Cell Adhesion on Pump-Free Microfluidics Chips Functionalized with Supported Membranes Displaying Mannose Domains. Materials, 6(2), 669-681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6020669



