Three-Dimensional Landscape Visualizations: New Technique towards Wildfire and Forest Bark Beetle Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Challenges of Wildfire and Bark Beetle Management
2.1. Diverse Land Ownership
2.2. Dynamic Forest Landscapes
2.3. The Uncertainty Effect of Wildfire and Bark Beetle Strategy
2.4. Social Interaction and the Increasing Wildland-Urban Interface
3. Three-Dimensional Landscape Visualizations
3.1. Characteristics of 3-D Landscape Visualization
3.1.1 Multi-spatial
3.1.2. Multi-temporal
3.1.3. Multi-expression
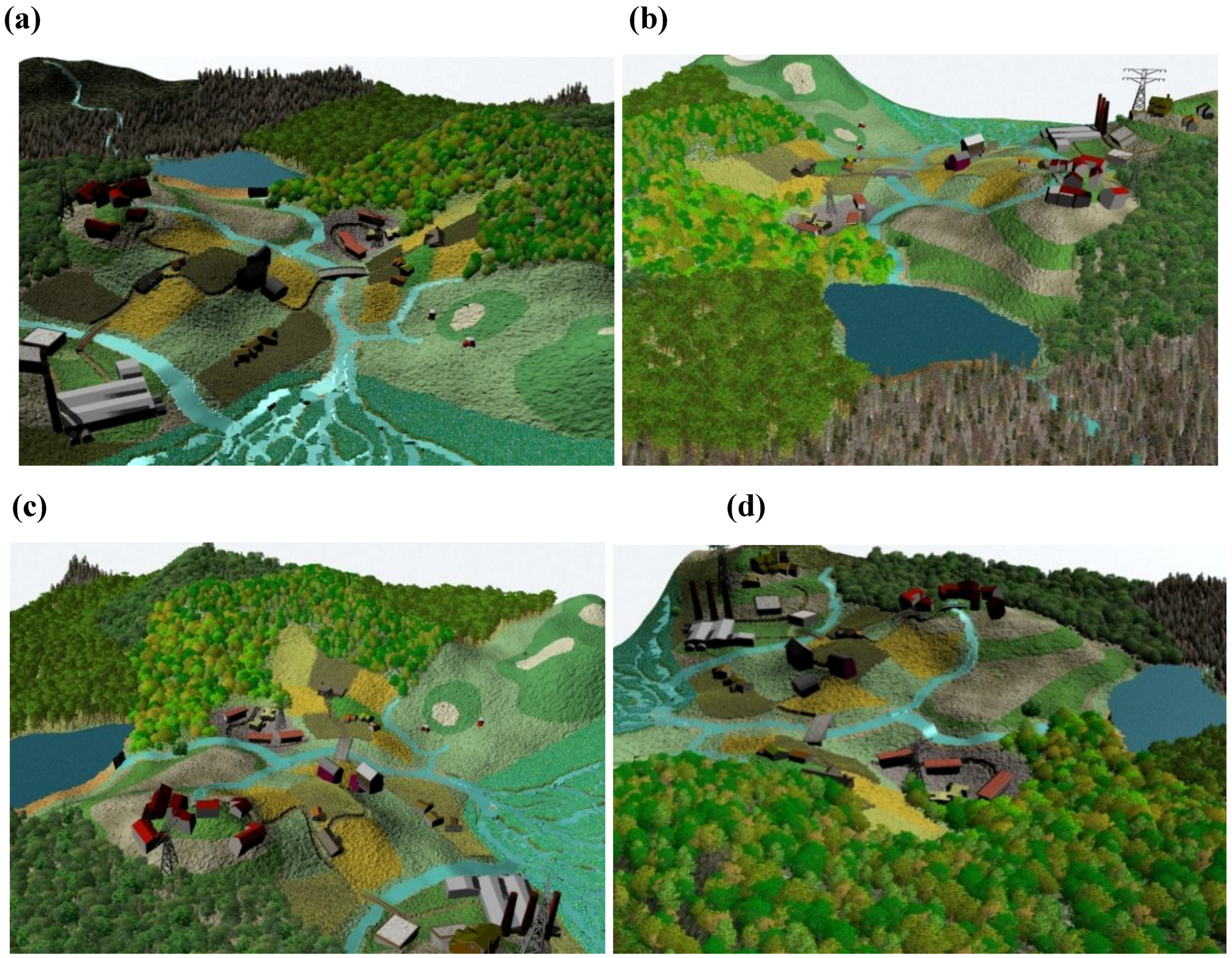
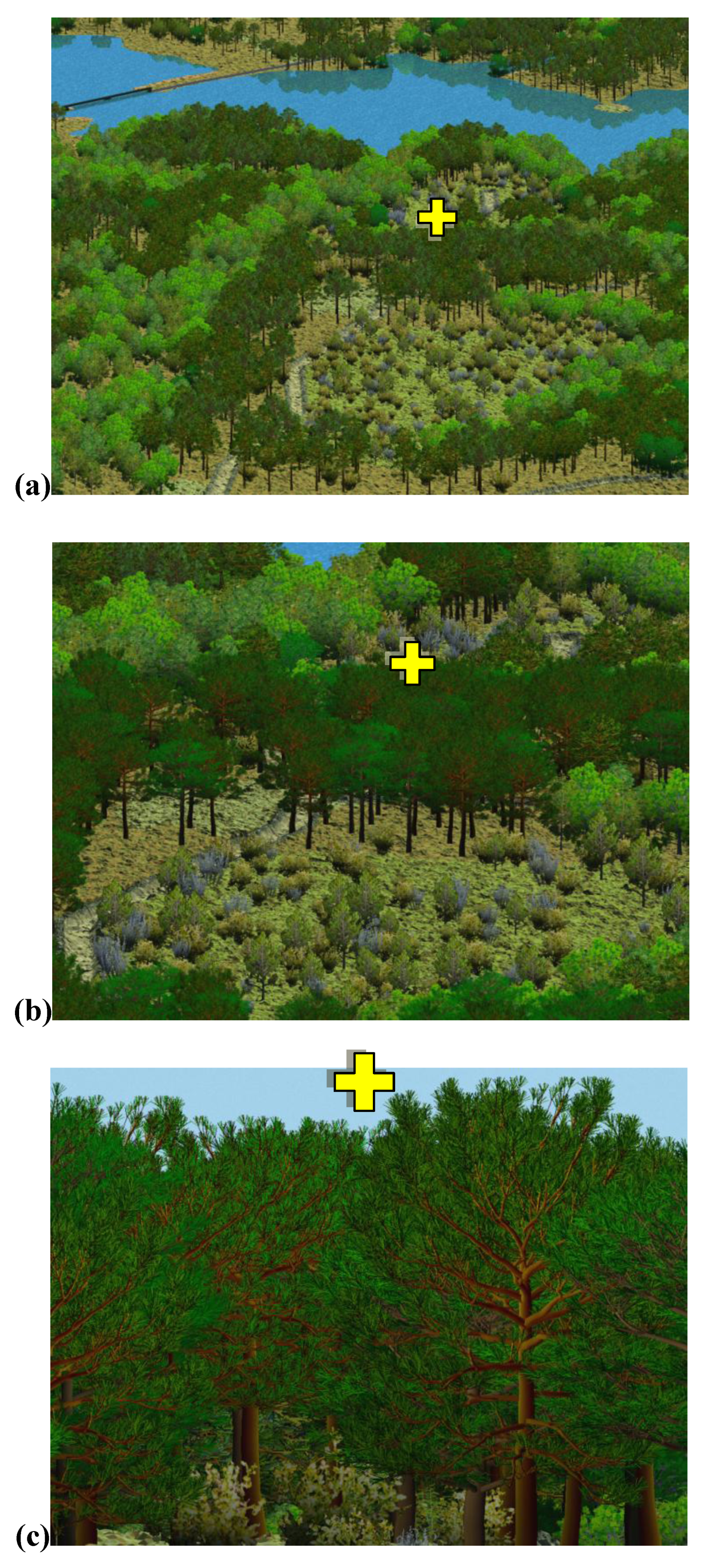

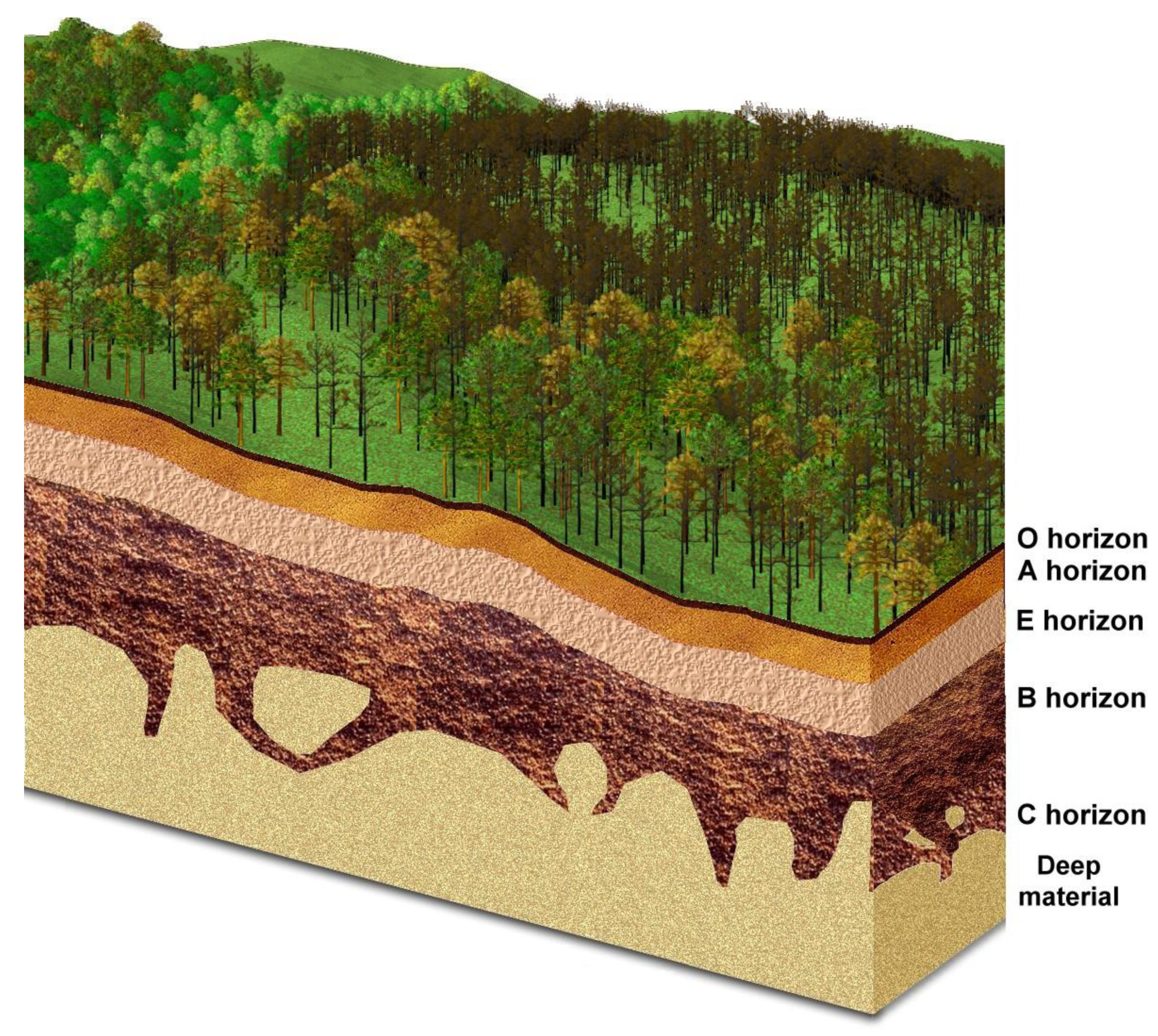
3.2. 3-D Landscape Visualization
4. Incorporating Remote Sensing Images and GIS
5. Incorporating Simulation Models
5.1. Forest Vegetation Simulator (FVS)
5.2. Fire Area Simulator (FARSITE)
5.3. CLEMBEETLE
5.4. Landscape Disturbance and Succession Simulation Model (LANDIS)
6. Discussions
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Agee, J.K. Fire ecology of Pacific Northwest forests; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; pp. 53–74. [Google Scholar]
- McCullough, D.G.; Werner, R.A.; Neumann, D. Fire and insects in northern and boreal forest ecosystems of North America. Ann. Rev. Entom. 1998, 43, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmonds, R.L. Forest Health and Protection; McGraw Hill Co. Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2000; pp. 254–337. [Google Scholar]
- Martell, D.L. Forest fire management. In Fires: Behavior and Ecological Effects; Johnson, E.A., Miyanishi, K., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001; pp. 527–583. [Google Scholar]
- Orland, B. Visualization techniques for incorporation in forest planning geographic information systems. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1994, 30, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, T.C.; Carroll, M.; Moseley, C.; Raish, C. Introduction to people, fire, and forests. In People, Fire, and Forests; Daniel, T.C., Carroll, M., Moseley, C., Raish, C., Eds.; Oregon State University Press: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Waldron, J.D.; Lafon, C.W.; Coulson, R.N.; Cairns, D.M.; Tchakerian, M.D.; Birt, A.; Klepzig, K.D. Simulating the impacts of southern pine beetle and fire on the dynamics of xerophytic pine landscapes in the southern Appalachians. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2007, 10, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, C.D.; Ferguson, D.E.; Harvey, A.E.; Malany, H.S.; Mandzak, J.M.; Mutch, R.W. Managing ecosystems for forest health: An approach and the effects on uses and values. In Assessing Forest Ecosystem Health in the Inland West; Sampson, R.N., Adams, D.L., Eds.; Forest Policy Center: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; pp. 113–133. [Google Scholar]
- Stephens, S.L.; Ruth, L.W. Federal forest-fire policy in the United States. Ecol. Appl. 2005, 15, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, S. Review of the operational IPM program for the southern pine beetle. Integr. Pest Manage. Rev. 2001, 6, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fettig, C.J.; Dlepzig, K.D.; Billings, R.F.; Munson, A.S.; Nebeder, T.E.; Negron, J.F.; Nowak, J.T. The effectiveness of vegetation management practices for prevention and control of bark beetle infestations in coniferous forests of the western and southern United States. For. Ecol. Manage. 2007, 238, 24–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fire and Resource Assessment Program (FRAP). The changing California: forest and range 2003 assessment: assessment summary; US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Department of Forestry and Fire Protection: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2003; pp. 42–197.
- Coster, J.E. Developing integrated management strategies. In The Southern Pine Beetle; Thatcher, R.C., Searcy, J.L., Coster, J.E., Hertel, G.D., Eds.; US Department of Agriculture, Expanded Southern Pine Beetle Research and Application Program, Forest Service, Science and Education Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1980; pp. 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Shindler, B. Public acceptance of wildland fire conditions and fuel reduction practices: challenges for federal forest managers. In People, Fire, and Forests; Daniel, T.C., Carroll, M., Moseley, C., Raish, C., Eds.; Oregon State University Press: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2007; pp. 37–54. [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard, S.R.J.; Salter, J. The role of visualization in forest planning. In Encyclopedia of Forest Sciences; Burley, J., Evans, J., Youngquist, J.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2004; pp. 486–498. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, E.; Bishop, I.D. Communication, perception and visualization. In Visualization in Landscape and Environmental Planning: Technology and Application; Bishop, I., Lange, E., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2005; pp. 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Song, B.; Wang, X.; Williams, T.M.; Mladenoff, D.J.; Chen, J.; Gustafson, E.J.; Hom, J.L.; Crow, T.R. Visualizing a landscape, its changes, and driving processes. In Ecology of Hierarchical Landscapes: from Theory to Application; Chen, J., Saunders, S.C., Brosofske, K.D., Crow, T.R., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 167–191. [Google Scholar]
- Meitner, M.J.; Sheppard, S.R.G.; Cavens, D.; Gandy, R.; Picard, P.; Harshaw, H.; Harrison, D. The multiple roles of environmental data visualization in evaluating alternative forest management strategies. Comput. Electr. Agric. 2005, 49, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, B.; Chen, J.; Zheng, D.; Crow, T.R. Visualizing forest landscapes using public data sources. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 75, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karjalainen, E.; Tynäinen, L. Visualization in forest landscape preference research: A Finnish perspective. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2002, 59, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, R.; Petschek, P. Visualization of Digital Terrain and Landscape Data: A Manual; Springer: London, UK, 2007; pp. 123–254. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Song, B.; Chen, J.; Crow, T.R.; LaCroix, J.J. Challenges in visualizing forests and landscapes. J. For. 2006, 104, 316–319. [Google Scholar]
- Hedden, R.L. Simulation of southern pine beetle-associated timber loss using CLEMBEETLE. In Proceedings of Integrated Pest Management Research Symposium, Asheville, NC, USA, 1985; pp. 288–291.
- Hirtz, P.; Hoffmann, H.; Nüesch, D. Interactive 3D landscape visualization: improved realism through use of remote sensing data and geoinformation. In Proceedings of Computer Graphics International, Canmore, AB, Canada, 1999; pp. 101–108.
- Ervin, S.M. Digital landscape modeling and visualization: A research agenda. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2001, 54, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, M.D.; Moskal, L.M.; Jakubauskas, M.E. 3D visualization for the analysis of forest cover change. Geocarto Int. 2005, 19, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). Standards for digital elevation models. National Mapping Program, Technical Instructions; US Geological Survey: Raston, VA, USA. Available online: http://rockyweb.cr.usgs.gov/nmpstds/demstds.html (accessed on 1 April, 2010 ).
- Doellner, J.; Hinrichs, K. A generic rendering system. IEEE Trans. Visual. Comput. Graphics 2002, 8, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, A.M.; Ghosh, S.K. Remote Sensing and Geographical Information System; Alpha Science: Oxford, UK, 2006; pp. 73–144. [Google Scholar]
- Lillesand, T.M.; Kiefer, R.W. Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 190–308. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, M.G. Landscape changes in nine rural counties in Georgia. Photogram. Eng. Remote Sensing 1990, 56, 379–386. [Google Scholar]
- Rogan, J.; Miller, J. Integrating GIS and remotely sensed data for mapping forest disturbance and change. In Understanding Forest Disturbance and Spatial Pattern: Remote Sensing and GIS Approaches; Wulder, M.A., Franklin, S.E., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 133–171. [Google Scholar]
- Attiwill, P.M. The disturbance of forest ecosystems: The ecological basis for conservative management. For. Ecol. Manage. 1994, 63, 247–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadirian, P.; Bishop, I.D. Integration of augmented reality and GIS: A new approach to realistic landscape visualization. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2008, 86, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crookston, N.L.; Stage, A.R. Percent canopy cover and stand structure statistics from the forest vegetation simulator; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station: Ogden, UT, USA, 1999; pp. 1–16.
- Finney, M.A. FARSITE: fire area simulator—model development and evaluation; US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Intermountain Fire Science Laboratory: Missoula, MT, USA, 1998; pp. 1–52.
- Williams, B.J.; Song, B.; Hom, J.; Duveneck, M. Wildfire visualization using GIS and forest inventory data. In Proceedings of 6th Southern Forestry and Natural Resources GIS Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 37–47.
- Chou, C.-Y.; Song, B.; Hedden, R.L.; Williams, T.M. The simulation of southern pine beetle spot growth in loblolly pine stands. In Proceedings of 6th Southern Forestry and Natural Resources GIS Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 178–195.
- He, H.S.; Mladenoff, D.J. Spatially explicit and stochastic simulation of forest-landscape fire disturbance and succession. Ecology 1999, 80, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.S.; Mladenoff, D.J.; Gustafson, E.J. Study of landscape change under forest harvesting and climate warming-induced fire disturbance. For. Ecol. Manage. 2002, 155, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, D.M.; Lafon, C.W.; Waldron, J.D.; Tchakerian, M.; Coulson, R.N.; Klepzig, K.D.; Birt, A. G.; Xi, W. Simulating the reciprocal interaction of forest landscape structure and southern pine beetle herbivore using LANDIS. Landsc. Ecol. 2008, 23, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, S.R.J.; Meitner, M. Using multi-criteria analysis and visualization for sustainable forest management planning with stakeholder groups. For. Ecol. Manage. 2005, 207, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlian, B.C.; Meitner, M.J. Automating the visual resource management and harvest design process. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 90, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paar, P.; Rohricht, W.; Schuler, J. Towards a planning support system for environmental management and agri-environmental measures—The Colorfields study. J. Environ. Manage. 2008, 89, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seely, B.; Nelson, J.; Wells, R.; Peter, B.; Meitner, M.; Anderson, A.; Harshaw, H.; Sheppard, S.; Bunnell, F.L.; Kimmins, H.; Harrison, D. The application of a hierarchical, decision-support system to evaluate multi-objective forest management strategies: a case study in northeastern British Columbia, Canada. For. Ecol. Manage. 2004, 199, 283–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoltman, A.M. Computer visualization of pre-settlement and current forests in Wisconsin. For. Ecol. Manage. 2007, 246, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meitner, M.; Gandy, R.; Nelson, J. Application of texture mapping to generate and communicate the visual impacts of partial retention systems in boreal forests. For. Ecol. Manage. 2006, 228, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salter, J.D.; Campbell, C.; Journeay, M.; Sheppard, S.R.J. The digital workshop: Exploring the use of interactive and immersive tools in participatory planning. J. Environ. Manage. 2009, 90, 2090–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, S.R.J. Guidance for crystal ball gazers: developing a code of ethics for landscape visualization. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2001, 54, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.L.; Sheppard, S.R.J. Culture and communication: Can landscape visualization improve forest management consultation with indigenous communities? Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 77, 291–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wergles, N.; Muhar, A. The role of computer visualization in the communication of urban design – A comparison of viewer responses to visualizations versus on-site visits. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 91, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orland, B.; Budthimedhee, K.; Uusitalo, J. Considering virtual worlds as representations of landscape realities and as tools for landscape planning. Landsc.Urban Plan. 2001, 54, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chou, C.-Y.; Song, B.; Hedden, R.L.; Williams, T.M.; Culin, J.D.; Post, C.J. Three-Dimensional Landscape Visualizations: New Technique towards Wildfire and Forest Bark Beetle Management. Forests 2010, 1, 82-98. https://doi.org/10.3390/f1020082
Chou C-Y, Song B, Hedden RL, Williams TM, Culin JD, Post CJ. Three-Dimensional Landscape Visualizations: New Technique towards Wildfire and Forest Bark Beetle Management. Forests. 2010; 1(2):82-98. https://doi.org/10.3390/f1020082
Chicago/Turabian StyleChou, Chiao-Ying, Bo Song, Roy L. Hedden, Thomas M. Williams, Joseph D. Culin, and Christopher J. Post. 2010. "Three-Dimensional Landscape Visualizations: New Technique towards Wildfire and Forest Bark Beetle Management" Forests 1, no. 2: 82-98. https://doi.org/10.3390/f1020082
APA StyleChou, C.-Y., Song, B., Hedden, R. L., Williams, T. M., Culin, J. D., & Post, C. J. (2010). Three-Dimensional Landscape Visualizations: New Technique towards Wildfire and Forest Bark Beetle Management. Forests, 1(2), 82-98. https://doi.org/10.3390/f1020082



