1. Introduction
Since the early 2000s Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) has been used to estimate forestry parameters [
1,
2,
3,
4]. Terrestrial Laser Scanning (TLS) typically utilizes LiDAR systems mounted on a tripod, from which multiple million points can be collected within minutes. Tree and plot models derived from those TLS clouds commonly became more and more accurate with improved automation in the model computation [
5,
6,
7].
In general, forestry applications are more concerned with timber form and quality and less with the size and arrangement of smaller woody components. However, for estimating above ground biomass (AGB, i.e., the standing mass of carbon), gap fraction, crown shape and other more general ecological properties, higher order branch structure and topology are important. Here we describe the development and application of a new reconstruction tool, SimpleTree, which generates such models.
The identification and accurate modelling of higher order branches is one of the key differences that may arise in the application between an approach aimed specifically at forest management as opposed to a more general approach such as that followed here. The proposed approach results in geometrical models describing the complete above-ground woody tree components in an hierarchical order. Such models can be referred to as Quantitative Structure Models (QSMs) [
8,
9,
10,
11], a convention we will follow here. QSM methods still rely on AGB measurements destructively harvested to be accurately validated [
9,
10,
11].
The SimpleTree method described here produces topologically ordered cylinder parameters (size, orientation) for all branches resolved by the LiDAR data, which can be of the order of thousands of branches per tree. The described method, originally proposed in Hackenberg
et al. [
12], has been shown to demonstrate an average sub-mm fit accuracy for complete tree models. However, results in Hackenberg
et al. [
10] show that with a pure geometrical fitting approach, AGB tends to be overestimated in the thinner branches. Here, we present a statistical solution to this problem.
Estimates of tree AGB are typically hard to validate due to the difficulty of obtaining data from harvested trees. Several recently published tree modelling methods rely on AGB measurements combined with density values to be validated [
9,
10,
11,
13,
14]. Direct measurements of the tree volume can be also done through the usage of a xylometer, but this method is reported time-consuming and error-prone [
15].
Providing research results in the form of an open source software is beneficial in maintaining the relevance of the method in future years. Free software gives users freedom regarding their ability to run the program as needed. Modifications of the program can be performed on open source code. Users can help others by redistributing the software. Contributions to the community can be done by sharing adaptations and new features with others [
16]. Hence the approach here has been to present the tree reconstruction software SimpleTree as an open source tool.
Tree models derived from TLS point clouds can be complex to compute: between different data sets and methods, many parameters can vary. The reflecting surface of woody components in a canopy varies substantially, both within and between species, as well as over an individual. Surface and material properties have a large impact on the reflected intensity values of the beam [
17], especially if the incident angle varies [
18]. Undesirable weather conditions increase the amount of noise in the point clouds [
10]. Different scan modes,
i.e., using multiple scan locations versus scanning from a single location, can have a large impact on the accuracy of the retrieved forestry parameters [
14,
19,
20]. Various methods utilized for co-registration of multiple scans exist, with different strengths and weaknesses [
21,
22]. Additionally, varying the scan resolution will also have an impact on accuracy and may require adapting reconstruction methods. In practice, these acquisition characteristics are a function of instrument performance and a trade-off against time required for data collection.
We consider it necessary to develop methods that are robust to such random effects, while knowing that robustness is likely to be a trade-off with accuracy, time, and user input/effort. Under this assumption free software with open source code seems to be an appropriate tool to develop a robust, and hence more durable approach, as adaptation can also be performed by an experienced end-user.
1.1. Related Work
Nowadays TLS methods have a wide rage in computational forestry. The majority of reconstruction approaches have proposed methods aiming for forest management purposes. Stable and robust parameters—used to predict AGB—are estimated to enable those methods to be applied to a larger scale. Efforts to transform TLS based methods into vehicle based laser scanning (VLS) methods have been reported [
23,
24]. Yao
et al. [
25] predict AGB on plot level utilizing the Diameter at Breast Height (DBH) as an input variable for the following allometric equation:
Stem models derived as proposed in Litkey
et al. [
26] were utilized to detect changes in the forest structure over time in Liang
et al. [
27]. Yang
et al. [
28] retrieve DBH, height, crown width and crown height as well as a digital elevation model and a canopy height model from plot level scans. Kankare
et al. [
14] calculate 83 geometrical and point cloud features for 64 laboratory measured trees and reduce the number of features with lasso regression and stepwise regression. Statistical models using up to eight features as explanatory variables are used to model total AGB, stem AGB, living branch AGB and dead branch AGB. Srinivasan
et al. [
29] predict AGB change utilizing scans of different years in a similar manner, reducing the feature space of TLS derived predictors with stepwise regression to a 3D parameter space. Srinivasan
et al. [
30] analyse the accuracy of DBH, tree height and crown width estimations on plot level scans - utilizing both single and dual scan mode. A more geometrical AGB prediction method is presented in Feliciano
et al. [
31] for mangrove trees. The authors model the stem and the root system as paraboloids/torus sections and derive AGB from the total volume multiplied with a density value and a literature derived biomass expansion factor.
In Othmani
et al. [
32] the authors developed a tree species classification routine based on relief maps of the bark structure. Kretschmer
et al. [
33] detected scars in the stem surface utilized for stem quality prediction. Stem quality was also automatically classified in Kankare
et al. [
34]. Béland
et al. [
35,
36] discuss the capabilities of TLS predictions of leaf area density. Voxel based methods to predict the volume of AGB components are reported as well [
37,
38].
1.1.1. Methods in Computational Forestry producing QSMs of the Branching Structure
QSM methods are capable of measuring the complete woody biomass volume directly. AGB can therefore be predicted in a non destructive way [
10] without relying on harvested ground truth data used to train statistical models [
12]. Also AGB distributions within a single tree can be modelled accurately [
12].
Pfeifer
et al. [
4] present an automatic method capable of modelling the stem and branching structure of a tree. After the input cloud is partitioned into branch segments [
39] for each point the normal vector is generated. From those normals initial guesses for the cylinder axes are derived. The cylinder parameters are adjusted in a least squares sense. Visual output depicts both that the resulting cylinder models are accurate but incomplete.
One reported QSM method is relying on Dijkstra’s algorithm [
41]. In Côté
et al. [
42] TLS points are subdivided into wood and foliage components. Then Dijkstra’s algorithm is applied on the wood points to calculate a skeleton representing the stem and the major branches. To reconstruct the thinner branching structure, high occurrences of foliage are detected in voxel space. Those voxels are called attractors and are connected to the main skeleton in an iterative routine. Radii for cylinder estimations from the final skeleton are estimated from the pipe model theory [
43]. Finally, foliage is added to the models. Validation to ground truth of this method was performed in Côté
et al. [
44] on basal area and total leaf area of 215 trees. The relative difference on plot level between model values and measurements was –0.01% and –0.25% respectively.
Dassot
et al. [
13] investigated point clouds of 42 trees of different species and varying size classes. With Polyworks software (Canadian Measurement-Metrology Inc., Mississauga, ON, Canada) the skeletons of those trees can be determined manually. Wood volume is afterwards calculated by using a geometric fitting procedure utilizing the skeletons. Wrongly fitted cylinders are identified visually and are manually removed from the models. A total relative error of ∼10% for the stems and ∼30% for the branches was estimated in the comparison to the ground truth data.
Eysn
et al. [
45] present another manual QSM approach. In AutoCAD [
46] software 34 scan positions are processed manually for skeletonization of 120 trees with the results being merged subsequently. Cylinders are fitted automatically and outliers are removed manually. Accuracy of this method was assessed for five randomly selected trees using cloud-to-model distance analysis. This showed an average fit accuracy of sub-cm.
Belton
et al. [
47] successfully de-noised point clouds of evergreen trees automatically. Features are here extracted after performing a Principal Component Analysis (PCA) on neighbouring point coordinates. Eigenvalues and their ratios and differences serve as features. Leaf points are isolated from biomass points in feature space through a Gaussian mixture model [
48]. From the points related to woody biomass horizontal slices are generated, into which ellipses are fitted. Neighbouring ellipse center points in different layers are connected to build a skeleton. The extracted skeleton is utilized in a cylinder fitting routine to build a cylindrical tree model. The authors compared the volume of an applied allometric function (34 m
) to the volume results of the cylinder model (74 m
) as validation.
An established tree modelling method from TLS-data is the method developed by Raumonen
et al. [
49]. This method produces a QSM of the tree [
9,
11], as does the SimpleTree method described here. The method [
49] imports a TLS-point cloud and reconstructs the tree as a hierarchical collection of cylinders or other building blocks, as described in Åkerblom
et al. [
50]. From the resulting QSM it is possible to approximate almost any geometrical or topological attribute or distributions describing tree attributes, such as stem and branch volumes and lengths, and branch size distributions for each branching order. In Calders
et al. [
9] this QSM approach was further developed and validated on 65 tree models derived from scans of a native Eucalyptus open forest plot. Comparison to destructively harvested ground truth data revealed a total AGB overestimation of 9.68% and a Concordance Correlation Coefficient (CCC) of 0.98.
Wang
et al. [
40] skeletonize a tree cloud with a minimum distance spanning tree. After the skeleton is generated, the occluded point cloud regions with missing data are recovered. The skeleton is obtained again in a second iteration and smoothed by a Laplacian function. Radii related to skeleton lines are computed in a last step before the tree model can be enriched with leaf models. Tree models were validated with DBH field measurements (
R = 0.92).
Hackenberg
et al. [
12] developed the method which forms the basis of the SimpleTree approach capable of fitting up to 10,000 cylinders into point clouds of
Prunus avium trees. This method was improved and implemented in SimpleTree. The clouds are derived from high resolution scans of multiple scan positions. The scans were barely affected by wind and therefore considered to be of high quality. Spheres centred on the tree skeleton are used to follow the tree’s branching structure from the root to its tips. If the sphere radius is larger than the underlying cylinder radius, the sub point cloud on the sphere surface will represent circular cross sectional areas of the branches. The areas are isolated by clustering and circles can be fitted. Circle center point, sphere center point and circle radius are used as cylinder parameters. The circle is enlarged after the cylinder parameter are stored and when transformed to a 3D sphere, the procedure can be repeated recursively until the complete tree structure is detected. The accuracy of the cylinder fitting is improved with Non-linear Least Squares (NLS) fit. Analysis of point to model distance showed that up to 99% of a tree can be modelled in average sub mm accuracy with this method.
The method was further improved in Hackenberg
et al. [
10]. Before the cylinder fitting routine is applied, input points are segmented into stem and branch points. By adjusting the method’s input parameters according to the sub division a higher fit accuracy can be achieved. Combining the models’ volume estimates with wood density values results in AGB predictions. Additionally various semi automatic de-noising procedures on imperfect point clouds were proposed. On 36 individuals of
Quercus petraea,
Pinus massoniana and
Erythrophleum fordii comparison to ground truth AGB was performed. The total relative error (ERROR_REL) per species was 33.85%, 2.75% and –17.24%. After applying a biomass expansion factor the total errors were reduced to 3.56%, 3.82% and –7.3% respectively.
Very few studies that model trees to a level of detail including thin branch-modelling exist, but have demonstrated the potential of utilizing tree skeletons as a basis for volume predictions. Point clusters belonging to the same cylindrical object can be generated by allocating points to their nearest skeleton segment. It is straightforward to generate cylinders from such clusters [
12,
13,
49]. Therefore we include also works in this section focusing on the automatic extraction of the tree skeleton.
Bucksch
et al. [
51,
52,
53] stored TLS point clouds of trees in an octree structure. Neighbourhood information of octree cells were used to extract a graph. Cycles were removed from the graph, resulting in a representation of the skeleton of the tree. No relevant validation regarding forestry parameters was performed.
Bayer
et al. [
54] revealed the potential of QSMs to predict branch angles, branch length and branch bending. The authors utilized a manual skeletonization approach and also introduced the usage of alpha shapes [
55] for accurate crown volume predictions.
Schilling
et al. [
56] described an automatic reconstruction technique utilizing 2D range images of trees. The 2D raster is subdivided into connected components. If the difference of range values between neighbouring points is smaller than some specified threshold, the points are considered to belong to the same component. With extended boundary tracing, the boundaries of the components are followed. A 2D skeleton is retrieved by applying a Voronoi Diagram, the components are further segmented according to their distance to the skeleton nodes. After the computation of principal curves, those are transformed to 3D to serve as polygonal lines of the final skeleton.
Delagrange
et al. [
57] proposed a method to extract tree skeletons utilizing Dijkstra’s algorithm [
41]. This approach of extracting objects skeletons from point clouds was firstly introduced by Verroust
et al. [
58]. Validation of this method was performed on summed up lengths of cylinder axes. Validation on an
Ulmus americana L. of 2.5 m height revealed that the software could detect 85% of the branch axes. For four three year old saplings of the species
Acer saccharum Marsh. and
Betula alleghaniensis Britt. the error ranged between 2.2% and 9.1%.
1.1.2. Methods in Computer Vision producing QSMs of the Branching Structure
In the computer visualization—various efforts in this field have been done to model trees [
59,
60,
61,
62]—some of the basic principles of the presented methods have been developed. Instead of retrieving accurate forestry parameters, the objective of these works is a realistic appearance of the tree model in a computer rendered scene. A useful overview presenting also some of the history and background of these approaches is given in the thesis of Preuksakarn [
63].
The usage of Dijkstra’s algorithm for tree skeletonization occurred earlier in the field of computer vision than in computational forestry. For example Xu
et al. and Livny
et al. [
64,
65] used it for non validated tree skeletonization approaches. Neighbouring points are linked to each other resulting in a connected graph. On this graph Dijkstra’s algorithm is applied to compute the minimal distance to a preselected root point for each point. Points belonging to the same distance bin are clustered and the centroids of neighbouring clusters are connected to build the tree skeleton.
The method we present here in the SimpleTree tool relies on Hackenberg
et al. [
10,
12]. Here the idea of using sphere-surface cuts with point clouds of trees is utilized. This idea is based on Jayaratna [
66] in the field of computer vision. To our knowledge the author invented the idea of a recursive search along the tree structure utilizing spheres. The base algorithm is quiet similar to the one presented here, which is also described in the appendix. A major difference in Jayaratna [
66] to the SimpleTree approach is the circle fitting routine during the search for cylinders. The author fits planes into the cross-sectional areas of the branches. The intersection of those planes with the spheres serve as the detected circles, rather than fitting circles directly into the sub point cloud. A comparison of the effect of different circle fitting methods is performed in Hackenberg
et al. [
12]. Also none of the proposed post processing routines which improve the fit quality is performed in Jayaratna [
66] as the visual results already satisfied the need of realistic looking models.
Another tree skeleton approach from this classical informatics field is the method of Yan
et al. [
67]. With the flooding algorithm [
68] the point cloud is segmented into clusters. On each cluster a cylinder fitting routine is applied. In case no cylinder can be detected, another subdivision of the cluster into subclusters is performed, followed by a second cylinder fitting routine. The visual inspection revealed a gap-less cylindrical tree model.
Aiteanu
et al. [
69] fit ellipses into surface points utilizing the principal curvatures and principal directions of each points local neighbourhood. If a fitted ellipsis is not perpendicular to the branch axis an adjustment of the parameters is performed. Incorrectly detected ellipses are removed after being detected automatically. Between adjacent ellipses a cylinder surface is generated. The output model can be enriched with textured leaves.
1.1.3. Further Open Source Tree Modelling Software and Point Cloud Processing Libraries
Computree [
70] is an open source platform utilizing TLS clouds. It is capable of generating a digital terrain model (DTM) on a plot level. Stems are detected by fitting circles with a Hough-transformation into slices of the vegetation points above the DTM. Circles in a spatial neighbourhood are combined to form stem models. Besides the DTM the output of Computree consists of a DBH estimator, a stem skeleton, a stem taper function and the height of each detected tree. Some of the algorithms implemented in Computree are described in detail in Othmani
et al. and Ravaglia
et al. [
71,
72]. The software framework allows developer-friendly implementation of methods due to its modular programming approach.
The work of Delagrange
et al. [
57] is available as an open source licensed Python script. A user interface allows access to adjust the earlier mentioned method with parameter modification. In addition, a visualization frame exists.
The increasing amount of publications in the LiDAR field is supported by a wide range of libraries. The Computational Geometry Algorithms Library [
73] offers geometric algorithms for the computation of Voronoi diagrams,
α-shapes, convex hulls and other structures. Both the Point Cloud Library (PCL) [
74] and the Sorted Pulse Data software Library (SPDLib) [
75] give access to methods specialized in the processing of LiDAR point clouds.
1.2. Relevance of the Presented Work in the State of the Art
Various authors [
51,
52,
53,
64,
65,
67] describe methods, where the potential to estimate AGB or wood volume was never validated. Delagrange
et al. [
57] only performed ground truth validation on young and small trees, while the height and size of a tree has a large influence on the modelling potential. The method of Côté
et al. [
42,
44] was optimized for estimating the total leaf area and basal area instead of being trained on AGB predictions. The method of Belton
et al. [
47] was validated on only one individual without reliable ground truth, while the methods of Dassot
et al. and Kankare
et al. [
13,
14] rely on significant manual interaction. This is to be avoided to ensure the methods are as general as possible.
The software SimpleTree (installation instructions on the project homepage [
76], source code on GitHub [
77]) is an open source tool (BSD licence [
78]) implementing the method presented in Hackenberg
et al. [
10,
12]. Besides the method of Raumonen
et al. [
49], the SimpleTree method is the only QSM method validated for AGB estimates on a large number of trees without requiring a large amount of manual interaction. Other publications [
13,
14] contribute as well to the TLS based AGB prediction methods with a comparable sized data set. QSMs though have the beneficial potential to model also AGB distributions within a single tree individual, see
Section 6. Those methods also do not rely on destructive harvested data to be trained [
10].
The implemented method in SimpleTree was optimized regarding run-time efficiency and memory storage. New optimization methods, see
Section 2.2, have been developed to improve the results presented in Hackenberg
et al. [
10]. The software is validated on data sets of 101 trees of six different species.
1.3. Structure of the Manuscript
Section 2 describes the functionalities of the presented software. SimpleTree results are compared to the results of the software tool relying on Raumonen
et al. [
49]. In
Section 3 this comparison method is described. The utilized data sets are presented in
Section 4. In
Section 5 results of AGB estimations of both software tools are given. The results are discussed and interpreted in
Section 6, leading to
Section 8 where the relevance of the tool is debated. An outlook of possible future work is given in
Section 7.
2. Software—SimpleTree
The method implemented in software SimpleTree is the one presented in Hackenberg
et al. [
10,
12], a possible output is depicted in
Figure 1. For all methods utilizing a TLS point cloud with
n points the minimal expected runtime complexity of
has been reached. The worst case complexity for the
α hull computation is
[
55], but the input data is limited to the number of detected cylinders.
Figure 1.
A QSM modelling with SimpleTree of a
P. avium cloud:
(a) the input cloud coloured by the second principal component [
47];
(b) over 4500 cylindrical output features are coloured by the diameter of the represented AGB component;
(c) secondary derived output features,
i.e., single branches, are coloured differently;
(d) the branching order of the underlying tree component is coloured differently;
(e) an abstract representation of the crown [
54].
Figure 1.
A QSM modelling with SimpleTree of a
P. avium cloud:
(a) the input cloud coloured by the second principal component [
47];
(b) over 4500 cylindrical output features are coloured by the diameter of the represented AGB component;
(c) secondary derived output features,
i.e., single branches, are coloured differently;
(d) the branching order of the underlying tree component is coloured differently;
(e) an abstract representation of the crown [
54].
While the results of those publications were produced with a Java implementation, the presented version of software SimpleTree is written in C++. The PCL library [
74] provides efficient functions for the implementation of the method. PCL’s mathematical operations are based on the linear algebra library Eigen [
79].
k-nearest neighbour searches are performed by the Fast Library for Approximate Nearest Neighbours (FLANN) [
80]. PCL also ships with its own visualization library based on VTK (the Visualization Toolkit) [
81].
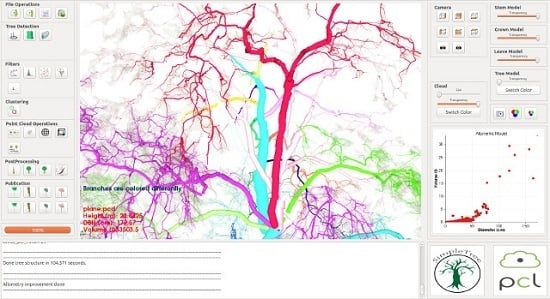
For the user interface of software SimpleTree (
Figure 2) the QT Framework [
82] was utilized.
Figure 2.
Screen-shot of the SimpleTree user interface.
Figure 2.
Screen-shot of the SimpleTree user interface.
The following sections describe methods provided by software SimpleTree. Methodname (a, b) is here-on a wild-card for a method with name Methodname, utilizing input parameters a and b. The dialogues utilized for user input of parameters include useful standard parameters, but to improve the results given by SimpleTree functionalities those standard parameters usually need to be adjusted to the point cloud quality.
2.1. Filter and Clustering Routines
Radius Outlier Removal (
r, k) [
83]
This method iterates over all points in the input cloud. For each point the number of neighbours inside a range r is computed. If a point has less than k neighbours, it is removed from the point cloud.
Statistical Outlier Removal (
sdMult, k) [
83]
This method iterates over all points in the input cloud. For each point the average distance to its k nearest neighbours is computed. Mean m and standard deviation are calculated for those distances. If a point’s average distance is larger than or smaller than , it is marked as an outlier and removed from the cloud.
Voxel Grid Filtering (
cellsize) [
83]
This method is an information loss reduced down-sampling approach. Over the point cloud a three-dimensional voxel grid is generated. The cell size of the voxels equals . If a voxel contains at least one point, for the output cloud a point is generated. The output point is the centroid of all contained points, which minimizes the information loss of the down-sampling procedure compared to using the voxel center point.
Curvature Filtering (min1, max1, min2, max2, min3, max3)
A PCA is performed for each point’s neighbourhood.
,
and
denote the normalized Eigenvalues for each point. For all
minimum
and maximum
value are computed.
and
are percentage numbers. A point is considered an outlier, if its
is smaller than
or larger than
.
and
are processed in the same manner. The thresholds are adjusted with a slider and before the removal-confirmation all noise points are marked via transparency and colourisation in real time according to the slider values (
Figure 3).
Figure 3.
Usage of curvature filtering routine. Outlier points, i.e., non woody material points, are coloured red transparent.
Figure 3.
Usage of curvature filtering routine. Outlier points, i.e., non woody material points, are coloured red transparent.
Intensity Filtering (min, max)
All points whose intensity is smaller than or larger than are marked as outliers and are removed from the cloud. The thresholds are adjusted with a slider and before confirmation the points which will be deleted are visualized with a red, transparent color.
Crop Sphere | Crop Box (radius)
A manual noise removal tool which generates a sphere. The center point can be set on any cloud point by mouse interaction. The sphere can be adjusted too. After confirmation, all points inside the sphere are removed from the cloud. A similar tool utilizing a box instead of the sphere exists in addition.
Euclidean Clustering (
clusterTolerance, minPts, numCluster) [
83]
A simple but fast spatial clustering operation is applied. The output cloud will contain the
largest clusters containing at least
points. If only a smaller number of clusters exists,
is set automatically to this number. Points are separated into two clusters, if the distance between the closest point pair exceeds
. This operation is faster than the Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN) [
84], which was used in Hackenberg
et al. [
10,
12].
2.2. Tree Modeling
Stem Point Detection [
10] ()
The stem point detection does not use input parameters. A PCA is performed on each input points neighbourhood of a
Voxel-Grid (0.02) filtered input cloud. If the eigenvalues
,
and
fulfil user-hidden thresholds, the point is accepted as a preliminary detected stem point. On these points
Euclidean Clustering (0.05, 1, 100) is performed and the output is marked as further detected stem-points. By a simple buffering operation (buffer width = 0.05 m) with the original cloud, the original cloud can be enriched with stem point information. Downscaling and up-scaling was not used in [
10] and is now included to improve runtime performance.
Spherefollowing Method [
10,
12] (
sphereMultiplier, epsClusterStem, epsClusterBranch, epsSphere, minPtsRansacStem, minPtsRansacBranch, minPtsClusterStem, minPtsClusterBranch, minRadiusSphereStem, minRadiusSphereBranch)
The method is used to fit cylinders into a de-noised point cloud and to build the tree model. Stem points should be detected before running this method. Spheres are utilized to follow the branching structure of the tree from the root to its tips.
A sphere with a center point on a skeleton axis cuts the point cloud. All points within a distance of
to the sphere-surface are considered to be used to detect the next sphere and are put into a sub point cloud
.
is subdivided into
and
.
(
is processed in same manner) is clustered then with
Euclidean Clustering (
, 5 ,
) into
i clusters
. The number of returned clusters is set to five, as this is the maximum expected number of cross sectional areas located on a sphere surface. Each cluster represents a cross-sectional area of the stem/branch. A circle is fitted with the Random Sample Consensus (RANSAC) [
85,
86] algorithm into
, if the number of points in
exceeds
, and with the more robust but less accurate median method proposed in Hackenberg
et al. [
12] otherwise. The center point of the circle, the center point of the sphere and the circle radius are chosen as cylinder parameters. The circle is enlarged with
and transformed to a three dimensional sphere. The procedure is repeated recursively until no more cross sectional areas can be found.
The detected cylinders are improved with RANSAC [
85] algorithm, the former Java implementation utilized NLS fit. More details on the method itself and further post-processing steps on the detected cylinders are given in Hackenberg
et al. [
10,
12], as well as in the
Appendix D.
Parameters extractable from the final tree model are discussed in the section output.
Parameter Optimization (iterations, criterion, seeds)
The Spherefollowing Method uses ten input parameters. To enable an automatic search for optimal parameters, initial parameters have to be set by the user. Then a multi-threaded parameter search starts. In each iteration step new parameter sets are created. For one creation each parameter is chosen from a normal distribution centred around the parameter value from the last iteration. For each set a tree model is build. The average euclidean distance from the point cloud to the model is computed. If this distance is smaller than the last found optimal distance, the method stores the distance and the parameter set. If after one iteration the distance improvement is smaller than , the search is stopped. If the number of iterations exceeds , the search stops. The best parameter set is printed out after completion.
Allometric improvement (a, b, fac, minRad)
A new parameter named is generated for each cylinder. The of a cylinder is the cylinder’s volume plus the of all the cylinder’s children. If analysed against the radius of the cylinder, an allometric model of the form can be fitted via NLS fit.
Figure 4(a) depicts this analysis for a
Prunus avium model. The point cloud is of high quality and so are the models [
12]. The coefficient of determination (
) for this model is 0.979, revealing a strong natural pattern un-discussed in computational forestry. It needs to be mentioned, that the usage of the
for non linear model fits is criticized [
87]. Still many commercial software packages,
i.e., Prism, Origin, Matlab, SPSS and SAS, calculate the
for non linear fits.
Figure 4.
An allometric model derived from: (a) a single Prunus avium; (b) twelve Pinus massoniana.
Figure 4.
An allometric model derived from: (a) a single Prunus avium; (b) twelve Pinus massoniana.
The parameters
a and
b need to be computed externally (an R-script is provided on the project home page). The method can detect overestimated cylinders as outliers of this function, see
Figure 4(b) for poorer quality models which need the allometric improvement. Outliers are considered the cylinders with a
GrowthVolume smaller than their predicted
GrowthVolume divided by
. Their radii are adjusted to be in accordance with their fixed
GrowthVolume.
All cylinder radii smaller than minRad are set to minRad in a last step. If this method is combined with the Parameter Optimization, the minimum radius can be automatically computed.
Crown Computation (α)
Modelling the crown as a convex hull utilizing cylinders as input data was already proposed in Hackenberg
et al. [
12,
88],
Figure 5(a).
In addition,
α-shapes [
55] can be generated, as suggested in Bayer
et al. [
54]. For the
α-shape generation of a point cloud an input parameter
α is needed. If
α is zero, the shape is the point cloud itself, for an
α value near
∞ the shape is the convex hull.
Figure 5(b) and
Figure 5(c) depict different
α-shapes with values 0.2 and 0.1.
Figure 5.
Different crown models for a Prunus avium: (a) the convex hull; (b) the α hull with ; (b) the α hull with .
Figure 5.
Different crown models for a Prunus avium: (a) the convex hull; (b) the α hull with ; (b) the α hull with .
With an appropriate
α-value the modelling of the leaf-space occupation is possible [
54].
2.3. Point Cloud Processing
Iterative Closest Point (ICP) (
β) [
74,
89]
ICP is an algorithm for aligning two different point clouds representing the same object proposed in Besl and McKay [
89]. The algorithm is supposed to be executed successfully, if the clouds are initially aligned,
Figure 6(a)–
Figure 6(d).
The initial alignment is performed in two steps. Both clouds are automatically transformed, so that the base of each tree is in the origin of the coordinate system,
Figure 6(a). Afterwards the source cloud is rotated with angle
β around the z-axis. The angle can be manually found out by using a slider for its value with in-real-time visualized rotation update,
Figure 6(b). Then the ICP algorithm can be started,
Figure 6(c),
Figure 6(d). Aligning two clouds of the same tree from different time-stamps with ICP was also proposed in Kaasalainen
et al. [
8].
Merge ()
This function merges two point clouds.
Figure 6.
Alignment of a
P. avium cloud [
12] of winter 2012 to the cloud of of the same tree after pruning in winter 2013:
(a) red cloud (2012) and green cloud (2013) are automatically initial aligned;
(b) red and green cloud are the same as in
(a), the yellow cloud (2012) is a manually rotated version of the red cloud;
(c) the final result - the green cloud is the target cloud and the red one the manually aligned cloud and the yellow cloud the ICP improved version of the red cloud;
(d) the final result from another point of view.
Figure 6.
Alignment of a
P. avium cloud [
12] of winter 2012 to the cloud of of the same tree after pruning in winter 2013:
(a) red cloud (2012) and green cloud (2013) are automatically initial aligned;
(b) red and green cloud are the same as in
(a), the yellow cloud (2012) is a manually rotated version of the red cloud;
(c) the final result - the green cloud is the target cloud and the red one the manually aligned cloud and the yellow cloud the ICP improved version of the red cloud;
(d) the final result from another point of view.
2.4. Output Data
Multiple output files are generated.
Cloud To Model Distance
This file contains one entry per point in the input cloud. The entry is the minimum distance from the point to the model. For performance reasons the maximum distance is 0.1 m, if the real distance is larger than this value, the entry will be 0.1 m.
Single Value Tree Parameters
This file contains the entries for the total tree volume and the stem volume. Solid volume is the volume of all compartments with a diameter larger 7 cm. The tree’s height and its length are included, as well as the DBH and the root diameter at lowest z-coordinate. The stem volume from the root up to the first branch and the stem volume up to the crown base are printed with additionally the crown base height. The crown volume and the crown surface from the convex hull crown model and lastly the crown projection area are additional output parameters. In Hackenberg
et al. [
12] more detailed definitions on various output parameters are given.
Complete Cylinder Model
This file contains one entry per row for each cylinder consisting of: x,y,z-coordinates of start and end point, as well as the radius. Length and volume, also computable from the first named parameters, are included, a unique segment ID of the segment containing the cylinder next, as well as this segment’s parent segment ID. The segment ID with the parent information allows the full reconstruction of the tree structure in external software, as cylinders are stored in the order in which they occur in the segment. Therefore the stored branch ID is also already computable meta-data. The growth volume is saved, as well as the branch order.
3. Software—Comparison Method Raumonen et al. (2013)
The results of SimpleTree applied to destructively sampled estimates will be compared against the results of the approach of Raumonen
et al. [
49]. There are two main procedures in this method [
49]: first the point cloud is segmented into stem and individual branches, and then the segments are approximated with cylinders or other fundamental geometric primitives. For the segmentation, the point cloud is partitioned into small subsets, which correspond to small connected patches in the tree surface. The partition into patches and the segmentation are done twice: first large uniform size patches give a rough approximation of the local branch sizes and the branching structure. The actual patch sizes used in this first segmentation are relatively insensitive and in this paper we used patches whose minimum diameters was set to 12 cm (the size randomly varies between the given minimum and twice the minimum). This first segmentation then determines the variable sizes of the patches in the second partition, which is used for a more detailed segmentation. The user given minimum diameters at the base of the stem and tips of the branches determine the sizes of the patches in the second partition. In this paper we set the minimum diameters at the base to 8 cm and at the tips to 1 cm.
Each segment is approximated with cylinders that are fitted in the least squares sense to small sub-segments. The ratio between length and radius of the sub-segments is roughly equal to a user given input. Also the initial radii of the sub-segments are estimated and based on the estimated radii outlier points are removed. After the fitting of the cylinders into a segment, the radii are checked to correct too large and too small radii: partially linearly decreasing tapers for the stem and parabolic tapers for the branches are used to give the local maximum and minimum radius. The tapers are estimated from the fitted data for the first
of the branch length and at the tip of the branch the radius is set to small maximum value [
9].
Additionally, the SimpleTree Allometric improvement was used in a second statistical improvement instead of the taper improvement. Parameters a and b were directly computed per model within the Matlab code with the standard Matlab NLS fitting routine.
The partitions into patches are random and thus each modelling run results in small differences in segmentation and thus in small differences in the resulting QSM. To estimate the variability of the result we made 500 models from one of the trees with the same input parameters and the distribution of total volumes of these models is shown in
Figure 7.
Figure 7.
Distribution of total volumes of 500 QSM models made with the same input parameters.
Figure 7.
Distribution of total volumes of 500 QSM models made with the same input parameters.
This distribution is taken then as an approximation of the real model result distribution and to estimate the sample size effects we can use it for simulated sampling: For each sample size, from 1 to 30, we took 10000 random samples and computed the sample means.
Figure 8 shows the variations of the sample means for each sample size and with sample size five or higher the maximum difference to the actual mean is about 1.5% and the standard deviation is about 0.3% of the mean. Thus five models are enough to reach small variability in the sampling. In this paper five models were computed and the results shown are the averages with standard deviations computed from the five models.
Figure 8.
The variation of the sample means as a function of sample size. The standard deviation and the difference of minimum and maximum sample means are given as percentages to the mean of the distribution.
Figure 8.
The variation of the sample means as a function of sample size. The standard deviation and the difference of minimum and maximum sample means are given as percentages to the mean of the distribution.
All the models were based on fixed patch diameters described above and only the relative cylinder length and the relative radius for outlier point removal were selected with the following simple optimization procedure: we made the models for all the parameter combinations and then selected the optimum based on the median point-to-model distances. The values for the relative cylinder lengths were 2, 3, 4 and 5. The values for the relative radius for the outlier removal were 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0 and 3.5 (i.e., all the points whose distance from the estimated cylinder axis is over 3.5 times the estimated radius are removed).
5. Results
The effect of the parameter optimization was analysed. All manual de-noised clouds of
Q. petraea were modelled five times with
Parameter Optimization (
iteration, 0.0001, 81). In six different runs
iteration was set to 0, 1, 2, 4, 6 and 8. The
Spherefollowing Method (1.8, 0.035, 0.015, 0.025, 500, 1111200, 12, 3, 0.07, 0.03) was additionally improved with the
Allometric improvement (240.559, 2.72, 2.5, 0.0025) in the optimization routine. The average standard deviation of the AGB volume prediction per tree in
of five model runs with a fixed number of iteration was calculated first (
Figure 9(a)).
The total relative error (Error) of the mean value of the five predictions was computed (
Figure 9(b)), as well as the average coefficient of determination (
) of the five linear models with the form
with
x being the TLS derived biomass and
y being the ground truth biomass, see
Figure 9(c). In
Figure 9(d) the influence of
on the CCC between ground truth and TLS predicted biomass is depicted.
Visualization in addition revealed, that with increasing
iterations parameter, more crown branches can be detected (
Figure 10). No negative side effects were observed,
i.e., no non existing branches were added to the models.
By detecting the majority of the last remaining undetected branches during the modelling, the total relative error of the biomass prediction rises. Without the Parameter Optimization (...) the overestimation for twelve Q. petraea trees is , the error stabilizes at a maximum of with at least four iterations of the Parameter Optimization (...).
With only one iteration in the Parameter Optimization (...), the ERROR_REL is , leaving an estimated of total biomass undetected. The accuracy of the AGB volume prediction is with one iteration yet unstable, as the average value for the standard deviation of one tree modelling is , while it can be reduced to with at least one more iteration.
The adjusted coefficient of correlation () is with any number larger one of iterations improved to a value of instead of .
Figure 9.
Impact on the number of iterations during parameter search on: (a) the average standard deviation of the volume prediction on tree level; (b) the average total relative error of the biomass prediction on complete data set level; (c) the of the model predicting ground truth biomass from TLS derived biomass; (d) the CCC between ground truth and TLS predicted biomass.
Figure 9.
Impact on the number of iterations during parameter search on: (a) the average standard deviation of the volume prediction on tree level; (b) the average total relative error of the biomass prediction on complete data set level; (c) the of the model predicting ground truth biomass from TLS derived biomass; (d) the CCC between ground truth and TLS predicted biomass.
Figure 10.
Visualization of the modelling of a Q. petraea (a) the input cloud; (b) the model with unoptimized parameters; (c) the model with optimized parameters (six iterations).
Figure 10.
Visualization of the modelling of a Q. petraea (a) the input cloud; (b) the model with unoptimized parameters; (c) the model with optimized parameters (six iterations).
With Parameter Optimization (≥4, 0.0001, 81) the majority of AGB is successfully detected. There seems to be a systematic error of overestimation in the modelling of the . The prediction accuracy on tree level is quantified by a value of . The systematical error results in a reduction of the CCC to though, as the overestimation of five percent is hidden by the fact that not all branches are detected with only one iteration, where the CCC reaches its maximum of .
The computation for the analysis, consisting of more than 100,000 tree modelling runs computed within less than three days on seven Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-2600K CPU @ 3.40GHz cores (Intel, Santa Clara, CA, USA).
In addition, the effect of the
Allometric Improvement (240.559, 2.72, 2.5, 0.0025) was analyzed (see
Figure 11). The twelve
Q. petraea were modelled one time with the statistical improvement and one time without. Each modelling run of the complete data set took ∼10 min. The parameters
a and
b were computed from the non improved data set,
was estimated by visual inspection of the same plot (
Figure 11(a)). The
was set in a manner, that the tip of the branches had a minimum diameter of half a centimetre (
Figure 11(c)),
Figure 11(d)).
The outlier cylinders, whose
is larger than the threshold depicted by the upper border in
Figure 11(a), were not modified. Still such outliers don’t occur in
Figure 11(b) and we conclude, that only erroneous cylinders with overestimated radii exist and have to be handled. The outliers outside the upper border are derived from the inclusion of multiple child relation cylinders with overestimated radii in the computation of their respective
. Additionally it is stated, that the curvature of the allometric function is enlarged by the appliance of this statistical improvement.
A linear model of the form of Equation (
2) is calculated for both data sets. The
for the unimproved data is 0.59, applying the
Allometric Improvement (...) leads to a value of 0.85. The overestimation of ∼25.89% is reduced to ∼2.42% with the improvement. The CCC rises from 0.45 to 0.92 (
Figure 11(e),
Figure 11(f)).
In the same manner results are computed for the
P. massoniana. The scans were modelled with the
Spherefollowing Method (3, 0.035, 0.025, 0.02, 200, 1111200, 3, 5, 0.07, 0.05). In one run with
Allometric Improvement (137.498, 2.62, 2.5, 0.0025) inside the
Parameter Optimization (6, 0.0001, 81) search (
Figure 12(b),
Figure 12(d),
Figure 12(f)) and one time without those improvements (
Figure 12(a),
Figure 12(c),
Figure 12(e)). In the comparison to the ground truth data the
was improved from 0.81 to 0.95, the ERROR_REL reduced from 34.63% to 3.59% and the CCC improved from 0.65 to 0.97. The calculation with the
Parameter Optimization (...) took ∼3.5 h, the other ∼10 min.
The E. fordii scans were modeled with the Spherefollowing Method (1.5, 0.03, 0.02, 0.02, 10, 10, 3, 3, 0.07, 0.025). In one computation the Allometric Improvement (95.551, 2.5, 2, 0.015–0.025) inside the Parameter Optimization (6, 0.0001, 81) search was performed, a second run excluded those improvements.
Twig points have been near completely removed due to coverage by leaves, as show in Hackenberg
et al. [
10]. Therefore the minimum radius in
Allometric Improvement (...) was set to a value derived from the automatic parameter search to prevent the smaller branches treated as twigs (
Figure 13(a)). Additionally, an NLS model of the form
was fitted on the improved data (
Figure 13(b)).
c was utilized as an additive component on biomass estimators to account to the removal of twigs. In the comparison to the ground truth data the
was improved from 0.80 to 0.92, the ERROR_REL reduced from –14.92% to –4.59% and the CCC improved from 0.80 to 0.92 (
Figure 13(a),
Figure 13(b),
Figure 13(e),
Figure 13(f)). The calculation with the
Parameter Optimization (...) took ∼2 h, the other ∼10 min.
Figure 11.
Effect of the allometric improvement on Q. petraea: (a) the fitted model based on the unimproved data; (b) the fitted model based on the improved data; (c) the model visualization without the improvement; (d) the model visualization with the improvement; (e) AGB estimation without the improvement; (f) AGB estimation with the improvement.
Figure 11.
Effect of the allometric improvement on Q. petraea: (a) the fitted model based on the unimproved data; (b) the fitted model based on the improved data; (c) the model visualization without the improvement; (d) the model visualization with the improvement; (e) AGB estimation without the improvement; (f) AGB estimation with the improvement.
Figure 12.
Effect of the allometric improvement and the automatic parameter search on P. massoniana: (a) the fitted model based on the unimproved data; (b) the fitted model based on the improved data; (c) the model visualization without the improvement; (d) the model visualization with the improvement; (e) AGB estimation without the improvement; (f) AGB estimation with the improvement.
Figure 12.
Effect of the allometric improvement and the automatic parameter search on P. massoniana: (a) the fitted model based on the unimproved data; (b) the fitted model based on the improved data; (c) the model visualization without the improvement; (d) the model visualization with the improvement; (e) AGB estimation without the improvement; (f) AGB estimation with the improvement.
Figure 13.
Effect of the allometric improvement and the automatic parameter search on E. fordii: (a) the fitted model based on the unimproved data; (b) the fitted model based on the improved data; (c) the model visualization without the improvement; (d) the model visualization with the improvement; (e) AGB estimation without the improvement; (f) AGB estimation with the improvement.
Figure 13.
Effect of the allometric improvement and the automatic parameter search on E. fordii: (a) the fitted model based on the unimproved data; (b) the fitted model based on the improved data; (c) the model visualization without the improvement; (d) the model visualization with the improvement; (e) AGB estimation without the improvement; (f) AGB estimation with the improvement.
All three data sets (
E. fordii,
Q. petraea and
P. massoniana) have additionally been modeled with the comparison QSM approach of Raumonen
et al. [
49] in three different manners. One time the cylinder radii have not been adjusted statistically, one time the taper correction has been used and one time the allometric improvement was utilized (
Figure 14).
Figure 14.
Effect on different statistical radii adjustments in the Raumonen
et al. approach [
49] for:
(a) Q. petraea;
(b) P. massoniana;
(c) E. fordii.
Figure 14.
Effect on different statistical radii adjustments in the Raumonen
et al. approach [
49] for:
(a) Q. petraea;
(b) P. massoniana;
(c) E. fordii.
For Q. petraea and P. massoniana the approach without radius correction revealed a large overestimation for both species (41% and 35%). The (0.37 and 0.84) and CCC (0.25 and 0.66) both had the lowest values with this modelling approach. The taper correction reduced the overestimation (ERROR_REL of 22% and –12%) as well as it improved the (0.53 and 0.96) and the CCC (0.49 and 0.91). Best results were produced by applying the allometric improvement, reducing the ERROR_REL further (20% and –1%), improving the (0.68 and 0.97) as well as the CCC (0.57 and 0.99). For E. fordii the ERROR_REL was lowest in the no improvement result (-9% instead of –21% for the taper correction or –17% for the allometric approach). The was approximately stable over all three runs (0.91, 0.93 and 0.92), the CCC due to its Error influence best for the no correction approach (0.91 instead of 0.78 or 0.80).
For all four data sets SimpleTree results are compared directly against the Raumonen
et al. [
49] results. For both methods the manual de-noised data sets of
P. massoniana,
Q. petraea and
E. fordii have been utilized. The Raumonen
et al. [
49] results have been improved in all three cases with the allometric approach, although for
E. fordii better CCC could have been achieved without corrections. The
Eucalyptus spp. data set was handled differently. The Raumonen method results have been taken from Calders
et al. [
9]. For the SimpleTree results manual de-noised data has been used with a
Parameter Optimization (
6, 0.0001, 81) utilizing the same parameter set for all 65 trees in the
Spherefollowing Method (
3.0, 0.1, 0.1, 0.045, 200, 1200, 3, 3, 0.1, 0.1). Parameters
a and
b were considered poor in the allometric improvement, as the NLS model did not show high quality as other allometric models did (
Figure 15).
Figure 15.
Allometric function for all utilized Eucalypt species.
Figure 15.
Allometric function for all utilized Eucalypt species.
For
P. massoniana the Raumonen
et al. [
49] results revealed an CCC of 0.99, SimpleTree results a CCC of 0.97.
Q. petraea results revealed with the Raumonen
et al. [
49] approach 20% overestimation, resulting in a CCC of 0.57. SimpleTree results could achieve a CCC of 0.92 at the modelling of this species.
E. fordii scans with removed twigs resulted in an underestimation for both species. The CCC is 0.80 for the Raumonen
et al. [
49] results and 0.92 for SimpleTree. For
Eucalyptus spp. the CCC of Raumonen
et al. [
49] modelling is 0.98 and 0.94 for the SimpleTree results (
Figure 16). In addition, a final comparative result was produced including all 101 trees of the six species (
Table 1).
Table 1.
Results for all six analysed species.
Table 1.
Results for all six analysed species.
| Method | Error | R 2 adj. | CCC |
|---|
| Raumonen et al. (2013) [49] | 8.80 | 0.97 | 0.98 |
| SimpleTree | 7.24 | 0.91 | 0.95 |
Figure 16.
Comparison of two different QSM methods between ground truth AGB and TLS derived AGB of the species: (a) P. massoniana; (b) Q. petraea; (c) E. fordii; (d) Eucalyptus spp.
Figure 16.
Comparison of two different QSM methods between ground truth AGB and TLS derived AGB of the species: (a) P. massoniana; (b) Q. petraea; (c) E. fordii; (d) Eucalyptus spp.
6. Discussion
Software SimpleTree implements a method capable of producing cylinder models that match field-measured estimates of volume and/or biomass to within ∼8% for all analysed tree species. While in Hackenberg
et al. [
10,
12] only high resolution point clouds have been used as input data for this method, the utilization of
Eucalyptus spp. data revealed the possibility to adapt this method to work on plot level scans.
Modelling twelve
Q. petraea clouds (500,000 to 1,500,000 points per cloud) could be achieved within 10 min, which is a significant improvement from earlier works [
12]. The average computation time per model for those clouds excluding stem point detection and visualization routines, but including cloud to model distance computation is ∼17 seconds on one core or ∼2.4 seconds with the multi-threaded approach on seven cores (numbers derived from
Parameter Optimization analysis with more than 100,000 modelling runs of
Q. petraea).
Hackenberg
et al. [
10] results showed, that the modelling of twigs can be problematic and might lead to an overestimation of AGB results for the complete tree. The
Allometric improvement was introduced as a statistical improvement method to account for this problem. The average error for the
Q. petraea models was reduced to 2% with this improvement, Hackenberg
et al. [
10] results showed here an ERROR_REL of 34%. Fitting an allometric function of the form of Equation (3) can also estimate the AGB of removed twigs, this can be observed for the
E. fordii models.
Calders
et al. [
9] did propose the taper correction applied to the QSM models to achieve a similar effect. By including the
Allometric improvement in the Raumonen
et al. [
49] code, a comparison between the taper and the allometric correction could be performed. For all three data sets,
i.e.,
Q. petraea, P. massoniana and
E. fordii clouds, the comparison revealed that the allometric approach seems to be superior to the taper corrections. For
E. fordii the additive component to estimate the removed twigs was not utilized in the Raumonen
et al. [
49] modelling, a further improvement of the results could be expected by implementing this function.
The automatic estimation for the minimum radius parameter in the Allometric improvement can still be problematic. For Q. petraea and P. massoniana clouds the minimum diameter was set to 0.5 cm in software SimpleTree, as here the cylinder models reached to the tip of twigs. The results proved this approach reasonable. In E. fordii clouds twig-points were removed during the de-noising procedures. A hard-coded threshold of 0.5 cm is therefore not desired. As the quality of the de-noised clouds representing the main branching structure of those trees is still considered high, the automatic search for this parameter was successful. In the Eucalyptus spp. clouds also twigs have been removed, but the cloud quality is poorer here. The point density is lower, noise points could not have been removed as efficiently and the double effect of small twigs due to imperfect co-registration of multiple scans was observed more often. Those reasons forced the optimization routine to find a minimum radius of 4 or 4.5 cm for the majority of trees. SimpleTree reconstructed results should in fact underestimate the ground truth volume for Eucapytus spp. due to the removal of twigs. We assume that the main reason in unexpected overestimation is an overestimated minimum radius.
Also problematic for Eucalyptus spp. is the fact, that for three species with different growth patterns only one allometric function was applied.
Utilizing the average euclidean cloud to model distance as an error term in parameter optimization seems to be beneficial for both for the SimpleTree software as well as for the Raumonen
et al. [
49] approach. In Calders
et al. [
9] parameters of QSM modelling have been optimized by visual inspection for completeness of the models. This user dependent decision was replaced by a fully automatic parameter search. As an automatic approach is considered superior to a supervised one in general, this is considered an improvement. The remaining problem in the minimum radius search for the allometric correction was already mentioned before.
Direct comparison between the Raumonen
et al. [
49] modelling and the SimpleTree software by utilizing the combined data set of all 101 trees reveals, that the CCC of the Raumonen
et al. [
49] approach is slightly higher (0.98 instead of 0.95). By a more detailed look utilizing each data set by itself it becomes clear, that both methods have their strengths. For
P. massoniana both approaches resulted in a high CCC (Raumonen
et al. [
49] = 0.99 and SimpleTree = 0.98), the Raumonen
et al. [
49] results are slightly better. We consider the TLS reconstructed results for both approaches as highly accurate and the minor prediction errors for this species are already in the range of ground truth errors which have to be expected [
94].
For
E. fordii SimpleTree results have been more accurate (CCC of 0.92 instead of 0.80). The reason here might be partially in the usage of Equation (3) instead of Equation (1) in the SimpleTree software. Also the Raumonen
et al. [
49] approach without statistical radii correction resulted here in a higher CCC of 0.91 but was not used for comparison as it was desired to apply the same exact approach for all data sets.
For
Q. petraea clouds SimpleTree results revealed a CCC of 0.92, while the Raumonen
et al. [
49] results showed a CCC of 0.57.
The
Eucalyptus spp. scans revealed a slight superior CCC results for the Raumonen
et al. [
49] approach with a value of 0.98 instead of 0.94 for the SimpleTree results.
It should here be mentioned, that
E. fordii,
P. massoniana and
Q. petraea scans were already used in Hackenberg
et al. [
10] utilizing the
Sphere Following method, while the
Eucalyptus spp. data set was used for QSM [
49] modelling in Calders
et al. [
9].
The following comparisons to other methods are made for general guidance only; they use different data from those used here, and the reconstruction methods rely on different assumptions. As a result the direct comparison with the method of Raumonen
et al. [
49] should be considered the only truly direct result.
Belton
et al. [
47] utilized a single reconstructed tree model to validate the volume estimates of their method. The comparison of the reconstructed volume and mass to the results of an allometric function leads to an ERROR_REL of ∼117%. However, allometric functions potentially contain large and unquantified errors. Calders
et al. [
9] show this in relation to destructive measurements and compared to lidar-derived QSMs. The target tree used by Belton
et al. [
47] is larger than any tree used here. The pure magnitude of the error indicates that SimpleTree models tend to be more accurate. However, until the same point clouds are analysed by the different methods, direct accuracy comparisons cannot be established. We note that the proposed de-noising procedure in the work of Belton
et al. [
47] may be preferable to that used in SimpleTree, as it does not require manual interaction.
Dassot
et al. [
13] reported an ERROR_REL of ∼10% for the stem predictions and ∼30% for the branch prediction of 42 processed trees. The unreported ERROR_REL of total AGB volume therefore has to be between this values, but is considered to be near ∼10%, as branches only contribute minor to total AGB. The ERROR_REL of SimpleTree results for the combined data set for total AGB is described with a value of 7.24%. Therefore SimpleTree results seem to be more accurate than the one of Dassot
et al. [
13]. The SimpleTree method also does not rely on manual interaction after preliminary threshold adjustment.
Kankare
et al. [
14] achieved an Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) of 12.93% and 11.90% on AGB estimations of a data set containing two coniferous tree species—no Akaike information criterion given here [
95,
96]. The correlation coefficients of 0.95 and 0.98 correspond to
values of 0.96 and 0.90, with smaller expected
values. The RMSE cannot be transformed to the here utilized ERROR_REL. On coniferous trees SimpleTree results reveal the highest correlation to the destructive biomass estimators, indicated by an
value of 0.95 and an error of less than 4%. As the SimpleTree reconstruction method works best on coniferous trees, the software might be better suitable for AGB predictions, but the accuracy benefit is considered minor. Regarding the combined data set results it appears that both methods are quite accurate,
i.e., mostly agree ≤ 10% error. Besides not relying on manual measurements for feature extraction the SimpleTree software also has the additional benefits of being open source and implementing a QSM method. These two points are discussed briefly in the following section.
6.1. The Benefit of Open Source
The Computree [
70] platform is written in C++ and supports PCL usage. Due to the strict modularization, efficient integration of other methods is possible. In fact, while not being considered stable yet, the Spherefollowing routine of SimpleTree was isolated from the user interface and could be integrated in the Computree platform. One of the strength of available Computree modules is the automatic segmentation of plot level scans into isolated tree clouds. Those isolated clouds can be further processed with the SimpleTree algorithm, as can be seen in
Figure 17.
Figure 17.
A visual output of the SimpleTree algorithm within the Computree platform.
Figure 17.
A visual output of the SimpleTree algorithm within the Computree platform.
On the left picture the segmentation of a single scan mode point cloud with heavy occlusion is depicted. The segmentation was performed with Computree core functionalities into ground cloud and individual tree clouds. From the ground cloud a DTM was generated with another core functionality of Computree, while from the tree clouds SimpleTree cylinder models were created. Such a symbioses reduces the amount a single scientist has to perform by itself.
6.2. The Benefit of QSMs
Besides accurate AGB estimations QSMs can give answers to several forestry relevant questions. This section is meant to give some applied examples performed on a single test model of a Prunus avium. These results should be seen as preliminary results not meant to be used in other works before deeper analysis is performed on a larger amount of trees.
Stem curves can be extracted efficiently from the results models, as can be seen in
Figure 18. This stem curve is not validated on ground truth data, but shows a strong natural pattern.
Figure 18.
Stem curve of a Prunus avium.
Figure 18.
Stem curve of a Prunus avium.
Additionally the branches of the same target tree have been binned according to the height of their base. The utilized bin width here is half a meter, within a bin the volume of all contained branches was summed up. In
Figure 19 only three major whorls are visible, the height of the first whirl can be defined as the crown base.
Figure 19.
Branch volume distribution in height bins of the stem of a Prunus avium.
Figure 19.
Branch volume distribution in height bins of the stem of a Prunus avium.
The method of Côté
et al. [
42] relies on the pipe model theory [
43]. This theory states, that the cross sectional area before a branch junction equals the sum of the cross sectional areas after the branch junction. We converted the median radii of segments into cross sectional areas. In
Figure 20 the cross sectional area of parent segments is plotted against the sum of areas of the child segments. The fitted linear model has only a slope of 0.944. This can be seen as an indicator, that the pipe model theory has to be adjusted with nowadays superior methods.
Figure 20.
Improvement possibilities of the pipe model theory [
43] with a
Prunus avium model.
Figure 20.
Improvement possibilities of the pipe model theory [
43] with a
Prunus avium model.
A time series analysis utilizing SimpleTree is in preparation by Sheppard
et al. [
97]. Clouds of several
Prunus avium were transformed into the same coordinate system with the ICP functionality. Several thousand segment pairs of the resulting QSMs from different years have been matched according to their spatial distance. In
Figure 21 the median diameter of those matched segments is depicted. The color red refers to a bad match, while the color green is considered a good match. The good matches show a clear increasing trend, quantification and discussion are performed in Sheppard
et al. [
97].
Figure 21.
Time series analysis of several Prunus avium.
Figure 21.
Time series analysis of several Prunus avium.