Mitigating the Stress of Drought on Soil Respiration by Selective Thinning: Contrasting Effects of Drought on Soil Respiration of Two Oak Species in a Mediterranean Forest
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Stand History and Tree Species Composition
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Field Measurements
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
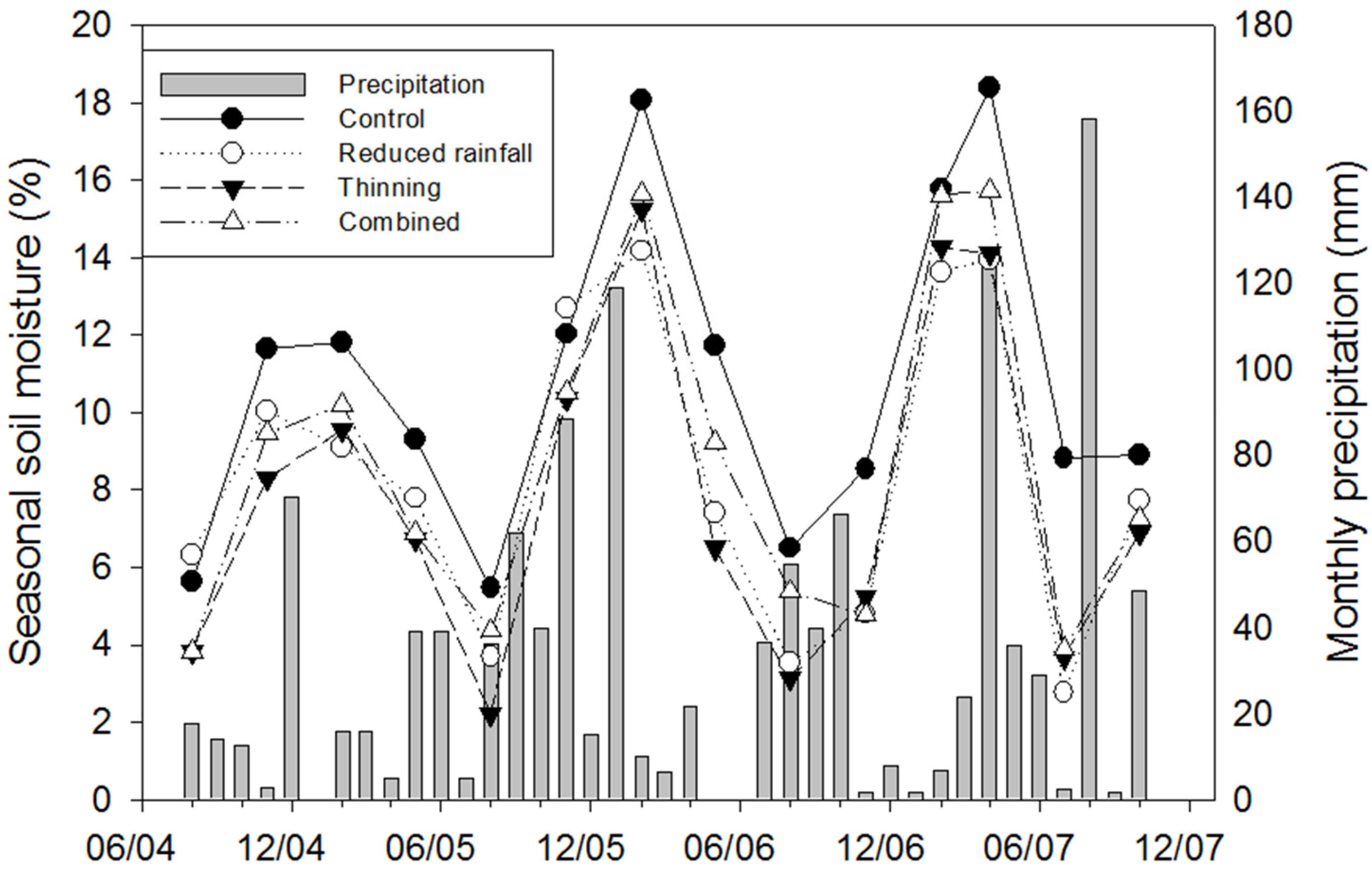
3.1. Temporal Variation in Ts and Soil Moisture
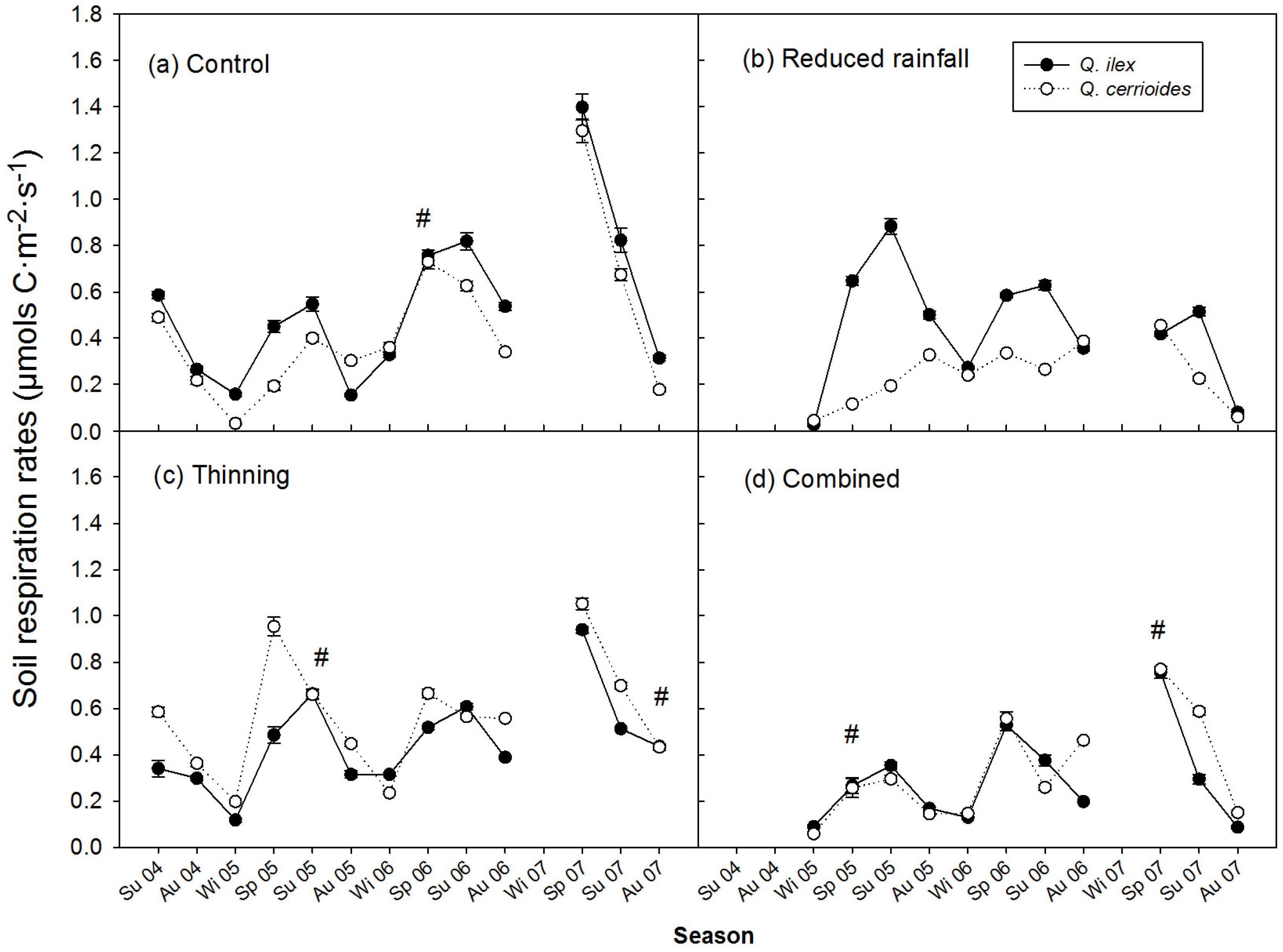
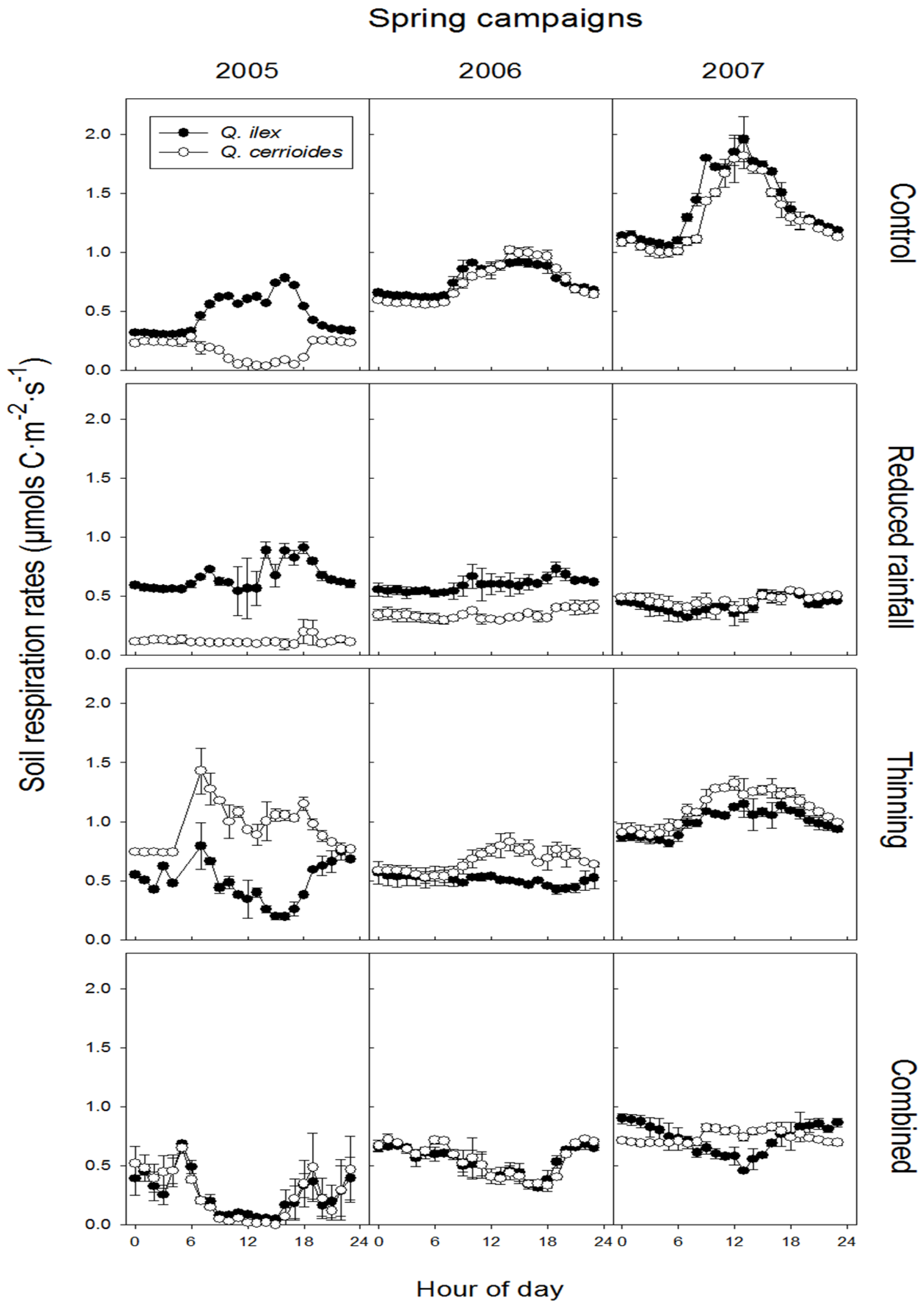
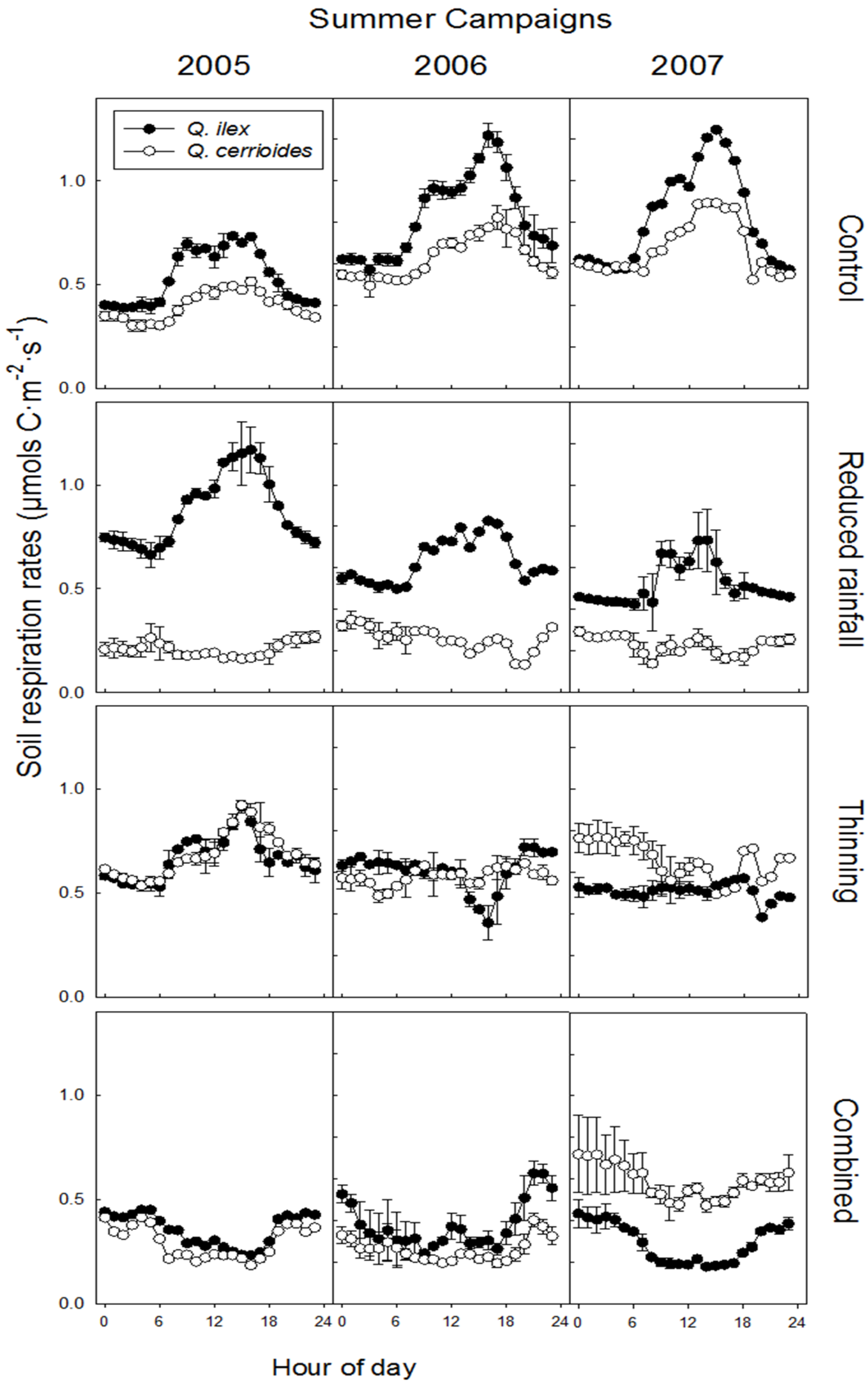
3.2. Treatment Effect on SR
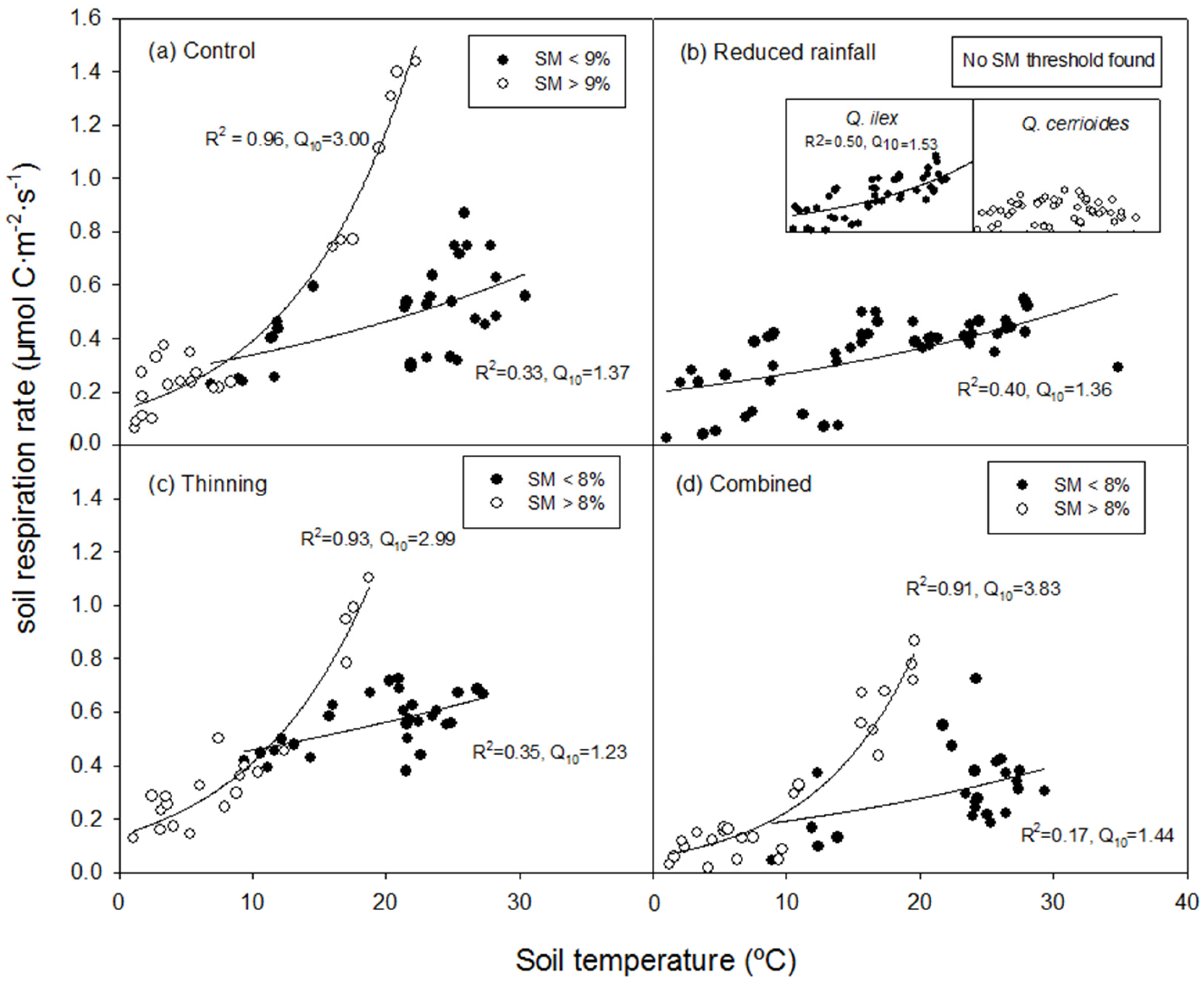
3.3. Relationship Between SR and Ts
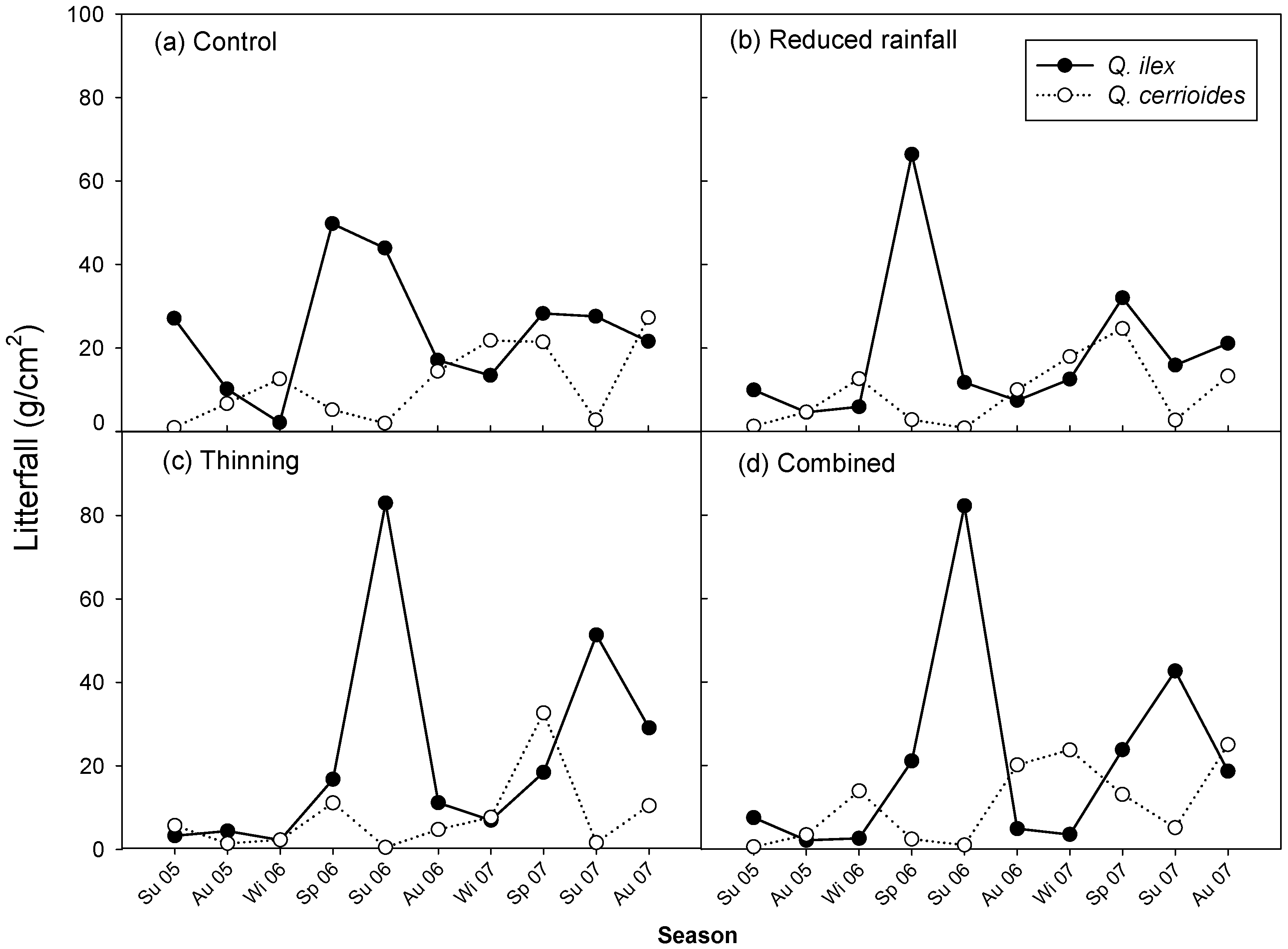
3.4. Temporal Variation in Litterfall
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
- Q10 of SR was clearly modulated by soil moisture, with a threshold value around 8%–9%. Reduced rainfall decreased both SR and Q10, unlike selective thinning;
- Selective thinning had less effect on SR under Q. ilex, but increased the SR rate under Q. cerrioides in the first two years;
- Reduced rainfall significantly depressed SR rate under Q. cerrioides by 50%, especially during the growing season, and the drought effect accumulated over years. Reduced rainfall increased SR rate under Q. ilex during the growing season by 50%;
- Selective thinning mitigated the negative effect of drought on SR rate under Q. cerrioides, although the mitigation was only significant during spring and during the last year of the experiment.
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan, Y.; Birdsey, R.A.; Fang, J.; Houghton, R.; Kauppi, P.E.; Kurz, W.A.; Phillips, O.L.; Shvidenko, A.; Lewis, S.L.; Canadell, J.G.; et al. A large and persistent carbon sink in the world’s forests. Science 2011, 333, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlesinger, W.H.; Andrews, J.A. Soil respiration and the global carbon cycle. Biogeochemistry 2000, 48, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melillo, J.M.; Steudler, P.A.; Aber, J.D.; Newkirk, K.; Lux, H.; Bowles, F.P.; Catricala, C.; Magill, A.; Ahrens, T.; Morrisseau, S.; et al. Soil warming and carbon-cycle feedbacks to the climate system. Science 2002, 298, 2173–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giorgi, F. Climate change hot-spots. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L08707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowell, D.P.; Jones, R.G. Causes and uncertainty of future summer drying over Europe. Clim. Dyn. 2006, 27, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Quéré, C.; Peters, G.P.; Andres, R.J.; Andrew, R.M.; Boden, T.; Ciais, P.; Friedlingstein, P.; Houghton, R.A.; Marland, G.; Moriarty, R.; et al. Global carbon budget 2013. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2013, 6, 689–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raich, J.W.; Schlesinger, W.H. The global carbon dioxide flux in soil respiration and its relationship to vegetation and climate. Tellus B 1992, 44, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raich, J.W.; Potter, C.S. Global patterns of carbon dioxide emissions from soils. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 1995, 9, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gärdenäs, A.I. Soil respiration fluxes measured along a hydrological gradient in a Norway spruce stand in south Sweden (Skogaby). Plant Soil 2000, 221, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Moncrieff, J.B. The dependence of soil CO2 efflux on temperature. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, B.W.; Kolb, T.E.; Hart, S.C.; Kaye, J.P.; Dore, S.; Montes-Helu, M. Thinning reduces soil carbon dioxide but not methane flux from southwestern USA ponderosa pine forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 255, 4047–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Han, H.; Kang, F.; Liu, K.; Song, Y.; Zhou, B.; Li, Y. Short-term effects of thinning on soil respiration in a pine (Pinus tabulaeformis) plantation. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2013, 50, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, P.F.; Arens, S.J.T.; Chimner, R.A.; Welker, J.M. Temperature and Microtopography Interact to Control Carbon Cycling in a High Arctic Fen. Ecosystems 2008, 11, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, W.; Zu, Y. Influence of long-term thinning on the biomass carbon and soil respiration in a larch (Larix gmelinii) forest in Northeastern China. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginn, S.E.; Seiler, J.R.; Cazell, B.H.; Kreh, R.E. Physiological and growth responses of eight-year-old loblolly pine stands to thinning. For. Sci. 1991, 37, 1030–1040. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, J.A.; Seiler, J.R.; Nowak, J.; Ginn, S.E.; Kreh, R.E. Growth and physiological responses of young loblolly pine stands to thinning. For. Sci. 1997, 43, 529–534. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Chambers, J.L.; Guddanti, S.; Barmett, J.P. Thinning, fertilization, and crown position interact to control physiological responses of loblolly pine. Tree Physiol. 1999, 19, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Qi, Y.; Xu, M.; Misson, L.; Goldstein, A.H. Forest thinning and soil respiration in a ponderosa pine plantation in the Sierra Nevada. Tree Physiol. 2005, 25, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selig, M.F.; Seiler, J.R.; Tyree, M.C. Soil carbon and CO2 efflux as influenced by the thinning of loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) plantations on the Piedmont of Virginia. For. Sci. 2008, 54, 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Baldocchi, D.D. Spatial–temporal variation in soil respiration in an oak–grass savanna ecosystem in California and its partitioning into autotrophic and heterotrophic components. Biogeochemistry 2005, 73, 183–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.-L.; Yan, W.-D.; Fang, X.; Kang, W.-X.; Deng, X.-W.; Wang, G.-J. Influence of Thinning on Soil CO2 Efflux in Chinemse Fir Plantations. Pedosphere 2009, 19, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.W.; Curtis, P.S. Effects of forest management on soil C and N storage: Meta analysis. For. Ecol. Manag. 2001, 140, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, H.A. Carbon-gaining capacity and allocation patterns of mediterranean-climate plants. In Mediterranean-Type Ecosystems; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1983; pp. 103–119. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, E.; Belk, E.; Boone, R.D. Soil water content and temperature as independent or confounded factors controlling soil respiration in a temperate mixed hardwood forest. Glob. Chang. Biol. 1998, 4, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, J.P.; Hart, S.C. Restoration and canopy-type effects on soil respiration in a ponderosa pine-bunchgrass ecosystem. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 1062–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borken, W.; Savage, K.; Davidson, E.A.; Trumbore, S.E. Effects of experimental drought on soil respiration and radiocarbon efflux from a temperate forest soil. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2006, 12, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, K.E.; Davidson, E.A. Interannual variation of soil respiration in two New England forests. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2001, 15, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borken, W.; Davidson, E.A.; Savage, K.; Gaudinski, J.; Trumbore, S.E. Drying and Wetting Effects on Carbon Dioxide Release from Organic Horizons. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, F.; Jia, Y. Effects of shoot removal and soil water content on root respiration of spring wheat and soybean. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2006, 56, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio, D.; Penuelas, J.; Ogaya, R.; Llusià, J. Seasonal soil and leaf CO2 exchange rates in a Mediterranean holm oak forest and their responses to drought conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 2447–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuschner, C.; Hertel, D.; Coners, H.; Büttner, V. Root competition between beech and oak: A hypothesis. Oecologia 2001, 126, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puhe, J. Growth and development of the root system of Norway spruce Picea abies in forest stands—A review. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 175, 253–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, T.F.; Qin, D.; Plattner, G.-K.; Tignor, M.; Allen, S.K.; Boschung, J.; Nauels, A.; Xia, Y.; Bex, V.; Midgley, P.M. Climate change 2013: The physical science basis. In The Working Group I contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rey, A.N.A.; Pegoraro, E.; Tedeschi, V.; Parri, I.D.E.; Jarvis, G.; Valentini, R. Annual variation in soil respiration and its components in a coppice oak forest in Central Italy. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2002, 8, 851–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichstein, M.; Rey, A.; Freibauer, A.; Tenhunen, J.; Valentini, R.; Banza, J.; Casals, P.; Cheng, Y.F.; Grünzweig, M.J.; Irvine, J.; Joffre, R.; et al. Modeling temporal and large-scale spatial variability of soil respiration from soil water availability, temperature and vegetation productivity indices. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2003, 17, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, R. EUROFLUX: An integrated network for studying the long-term responses of biospheric exchanges of carbon, water, and energy of European forests. In Fluxes of Carbon, Water and Energy of European Forests; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ninyerola, M.; Pons, X.; Roure, J.M. A methodological approach of climatological modelling of air temperature and precipitation through GIS techniques. Int. J. Climatol. 2000, 20, 1823–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotillas, M.; Sabaté, S.; Gracia, C.; Espelta, J.M. Growth response of mixed mediterranean oak coppices to rainfall reduction: Could selective thinning have any influence on it? For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 258, 1677–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retana, J.; Espelta, J.M.; Gracia, M.; Riba, M. Ecology of Mediterranean Evergreen Oak Forests; Rodà, F., Retana, J., Gracia, C.A., Bellot, J., Eds.; Ecological Studies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; Volume 137. [Google Scholar]
- Espelta, J.M.; Rodrigo, A.; Habrouk, A.; Meghelli, N.; Ordónez, J.L.; Retana, J. Land use changes, natural regeneration patterns, and restoration practices after a large wildfire in NE Spa. In Challenges for Fire Ecology, Landscape, Restoration; Trabaud, L., Prodon, R., Eds.; Fire and Biological Processes; Backhuys Publications: Leiden, The Netherland, 2002; pp. 315–324. [Google Scholar]
- Espelta, J.M.; Retana, J.; Habrouk, A. Resprouting patterns after fire and response to stool cleaning of two coexisting Mediterranean oaks with contrasting leaf habits on two different sites. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 179, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van’t Hoff, J.H. Lectures on Theoretical and Physical Chemistry; Edward Arnold: London, UK, 1898. [Google Scholar]
- Zeileis, A.; Hothorn, T.; Hornik, K. Model-Based Recursive Partitioning. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2008, 17, 492–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masyagina, O.V.; Prokushkin, S.G.; Koike, T. The influence of thinning on the ecological conditions and soil respiration in a larch forest on Hokkaido Island. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2010, 43, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köster, K.; Püttsepp, Ü.; Pumpanen, J. Comparison of soil CO2 flux between uncleared and cleared windthrow areas in Estonia and Latvia. For. Ecol. Manag. 2011, 262, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bréda, N.; Granier, A.; Aussenac, G. Effects of thinning on soil and tree water relations, transpiration and growth in an oak forest (Quercus petraea (Matt.) Liebl.). Tree Physiol. 1995, 15, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivar, J.; Bogino, S.; Rathgeber, C.; Bonnesoeur, V.; Bravo, F. Thinning has a positive effect on growth dynamics and growth-climate relationships in Aleppo pine (Pinus halepensis) trees of different crown classes. Ann. For. Sci. 2014, 71, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skopp, J.; Jawson, M.D.; Doran, J.W. Steady-State Aerobic Microbial Activity as a Function of Soil Water Content. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1990, 54, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimel, J.; Balser, T.C.; Wallenstein, M. Microbial stress, response physiology and its implications for ecosystem function. Ecology 2007, 88, 1386–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruehr, N.K.; Offermann, C.A.; Gessler, A.; Winkler, J.B.; Ferrio, J.P.; Buchmann, N.; Barnard, R.L. Drought effects on allocation of recent carbon: From beech leaves to soil CO2 efflux. New Phytol. 2009, 184, 950–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasibeder, R.; Fuchslueger, L.; Richter, A.; Bahn, M. Summer drought alters carbon allocation to roots and root respiration in mountain grassland. New Phytol. 2015, 205, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, A.J.; Pregitzer, K.S.; Zogg, G.P.; Zak, D.R. Drought reduces root respiration in sugar maple forests. Ecol. Appl. 1998, 8, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Lin, G. Water regulated effects of photosynthetic substrate supply on soil respiration in a semiarid steppe. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2011, 17, 1990–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brando, P.M.; Nepstad, D.C.; Davidson, E.A.; Trumbore, S.E.; Ray, D.; Camargo, P. Drought effects on litterfall, wood production and belowground carbon cycling in an Amazon forest: Results of a throughfall reduction experiment. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 1839–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Zhang, J. Effects of water stress on photosynthesis, chlorophyll fluorescence and photoinhibition in wheat plants. Funct. Plant Biol. 1998, 25, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, P.C. Respuestas Ecofisiológicas Y Estructurales a la Recurrencia, Duración E Intensidad de la Sequía en Plantaciones Y Bosques Mixtos de Quercus ilex, Quercus pubescens Y Quercus cerrioides. Doctoral Dissertation, Institut de Recerca i Tecnologia Agroalimentaries IRTA, Universitat Autonoma de Barcelona UAB, Catalonia, Spain, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hinko-Najera, N.; Fest, B.; Livesley, S.J.; Arndt, S.K. Reduced throughfall decreases autotrophic respiration, but not heterotrophic respiration in a dry temperate broadleaved evergreen forest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 200, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londo, A.J.; Messina, M.G.; Schoenholtz, S.H. Forest Harvesting Effects on Soil Temperature, Moisture, and Respiration in a Bottomland Hardwood Forest. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Chen, J.; North, M.; Erickson, H.E.; Bresee, M.; Le Moine, J. Short-term effects of experimental burning and thinning on soil respiration in an old-growth, mixed-conifer forest. Environ. Manag. 2004, 33, S148–S159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, J.A.; Sigurdsson, B.D. Effects of early thinning and fertilization on soil temperature and soil respiration in a poplar plantation. Icel. Agric. Sci. 2010, 23, 97–109. [Google Scholar]
- Olajuyigbe, S.; Tobin, B.; Saunders, M.; Nieuwenhuis, M. Forest thinning and soil respiration in a Sitka spruce forest in Ireland. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 157, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Bao, W.; Zhu, B.; Cheng, W. Responses of soil respiration and its temperature sensitivity to thinning in a pine plantation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 171–172, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Birdsey, R.A.; Johnson, K.D.; Dupuy, J.M.; Hernandez-Stefanoni, J.L.; Richardson, K. Modeling Carbon Stocks in a Secondary Tropical Dry Forest in the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustad, L.E.; Huntington, T.G.; Boone, R.D. Controls on soil respiration: Implications for climate change. Biogeochemistry 2000, 48, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohlenius, B. Short-Term Influence of Clear-Cutting on Abundance of Soil-Microfauna (Nematoda, Rotatoria and Tardigrada) in a Swedish Pine Forest Soil. J. Appl. Ecol. 1982, 19, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, I.A.; Lankreijer, H.; Matteucci, G.; Kowalski, A.S.; Buchmann, N.; Epron, D.; Pilegaard, K.; Kutsch, W.; Longdoz, B.; Grünwald, T.; et al. Productivity overshadows temperature in determining soil and ecosystem respiration across European forests. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2001, 7, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Cheng, W. Photosynthesis controls of rhizosphere respiration and organic matter decomposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 1915–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Högberg, P.; Nordgren, A.; Buchmann, N.; Taylor, A.F.S.; Ekblad, A.; Högberg, M.N.; Nyberg, G.; Ottosson-Löfvenius, M.; Read, D.J. Large-scale forest girdling shows that current photosynthesis drives soil respiration. Nature 2001, 411, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, B.C.; Sabate, S.; Gracia, C.A. Thinning effects on carbon allocation to fine roots in a Quercus ilex forest. Tree Physiol. 2003, 23, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aussenac, G.; Granier, A. Effects of thinning on water stress and growth in Douglas-fir. Can. J. For. Res. 1988, 18, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassal, R.S.; Black, T.A.; Novak, M.D.; Gaumont-Guay, D.; Nesic, Z. Effect of soil water stress on soil respiration and its temperature sensitivity in an 18-year-old temperate Douglas-fir stand. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2008, 14, 1305–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suseela, V.; Conant, R.T.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Dukes, J.S. Effects of soil moisture on the temperature sensitivity of heterotrophic respiration vary seasonally in an old-field climate change experiment. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suseela, V.; Dukes, J.S. The responses of soil and rhizosphere respiration to simulated climatic changes vary by season. Ecology 2013, 94, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zha, T.S.; Jia, X.; Wu, B.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Qin, S.G. Soil moisture modifies the response of soil respiration to temperature in a desert shrub ecosystem. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, R.; der Peijl, M.J. A simple model to explain the dominance of low-productive perennials in nutrient-poor habitats. Oikos 1993, 66, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendse, F. Competition between plant populations at low and high nutrient supplies. Oikos 1994, 71, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.S.; Eamus, D. Seasonal patterns of xylem sap pH, xylem abscisic acid concentration, leaf water potential and stomatal conductance of six evergreen and deciduous Australian savanna tree species. Aust. J. Bot. 2002, 50, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eamus, D.; Myers, B.; Duff, G.; Williams, D. Seasonal changes in photosynthesis of eight savanna tree species. Tree Physiol. 1999, 19, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Treatment | Q. ilex | Q. cerrioides | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ts (°C) | Natural rainfall | 14.88 a | 14.98 a | 14.93 a |
| Reduced rainfall | 16.77 a | 15.99 a | 16.38 a | |
| No Thinning | 16.31 a | 15.67 a | 15.99 a | |
| Thinning | 15.30 a | 15.28 a | 15.29 a | |
| SR (µmol C m−2·s−1) | Natural rainfall | 0.45 a | 0.47 a | 0.46 a |
| Reduced rainfall | 0.38 a | 0.30 b | 0.34 b | |
| No Thinning | 0.47 a | 0.33 a | 0.40 a | |
| Thinning | 0.36 b | 0.44 b | 0.40 a |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, C.-T.; Sperlich, D.; Sabaté, S.; Sánchez-Costa, E.; Cotillas, M.; Espelta, J.M.; Gracia, C. Mitigating the Stress of Drought on Soil Respiration by Selective Thinning: Contrasting Effects of Drought on Soil Respiration of Two Oak Species in a Mediterranean Forest. Forests 2016, 7, 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/f7110263
Chang C-T, Sperlich D, Sabaté S, Sánchez-Costa E, Cotillas M, Espelta JM, Gracia C. Mitigating the Stress of Drought on Soil Respiration by Selective Thinning: Contrasting Effects of Drought on Soil Respiration of Two Oak Species in a Mediterranean Forest. Forests. 2016; 7(11):263. https://doi.org/10.3390/f7110263
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Chao-Ting, Dominik Sperlich, Santiago Sabaté, Elisenda Sánchez-Costa, Miriam Cotillas, Josep Maria Espelta, and Carlos Gracia. 2016. "Mitigating the Stress of Drought on Soil Respiration by Selective Thinning: Contrasting Effects of Drought on Soil Respiration of Two Oak Species in a Mediterranean Forest" Forests 7, no. 11: 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/f7110263
APA StyleChang, C.-T., Sperlich, D., Sabaté, S., Sánchez-Costa, E., Cotillas, M., Espelta, J. M., & Gracia, C. (2016). Mitigating the Stress of Drought on Soil Respiration by Selective Thinning: Contrasting Effects of Drought on Soil Respiration of Two Oak Species in a Mediterranean Forest. Forests, 7(11), 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/f7110263







