Assessment of Soil Quality of Croplands in the Corn Belt of Northeast China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site Descriptions
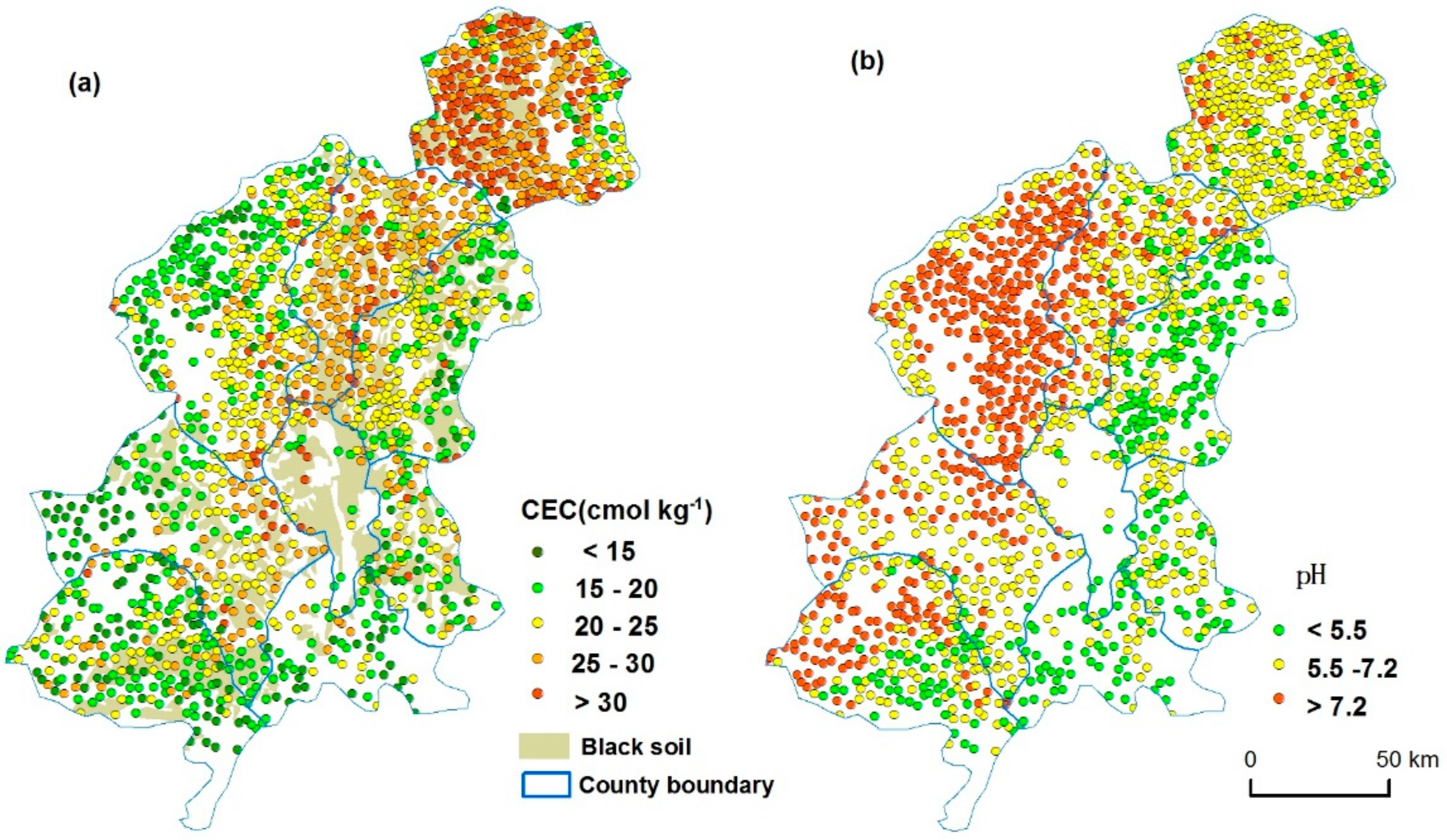
2.2. Soil Sampling and Analysis
2.3. Environmental Data
2.4. Soil Quality Assessment Method
2.4.1. Indicators Selection and Scoring
2.4.2. Selection of Indicators in the Minimum Data Set
2.4.3. Weight Assignment and Soil Quality Index
2.4.4. Criteria of Soil Quality Grades
2.4.5. Indices Validation
3. Results
3.1. Soil Quality Assessment Based on the TDS Indicator Method
3.2. Soil Quality Assessment Based on the MDS Indicator Method
3.3. Indices Validation
3.4. Effects of Environmental Attributes
4. Discussion
4.1. Indicator Method and Indices
4.2. Soil Quality
4.3. Association with Environmental Factors and Agricultural Management Practices
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Indictor | Protocol | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk density, BD | Core method | [20] |
| Soil organic matter, SOM | Potassium dichromate oxidation | [20] |
| pH | Saturated soil paste | [20] |
| Cation exchange capacity, CEC | Ammonium acetate extraction | [20] |
| Total nitrogen, TN | Kjeldahl | [20] |
| Total phosphorus, TP | Digestion, spectrophotometer detection | [21] |
| Total potassium, TK | NaOH fusion | [20] |
| Alkali-dissolvable nitrogen, AN | Alkaline hydrolysis diffusion | [20] |
| Extractable phosphorus, AP | Sodium bicarbonate Olsen method | [21] |
| Extractable potassium, AK | Flame photometric method | [20] |
| Extractable Cu, ACu | Flame photometer detection | [20] |
| Extractable Fe, AFe | Flame photometer detection | [20] |
| Extractable Zn, AZn | Flame photometer detection | [20] |
| Indicator Method | Items | Soil Quality Grade | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade I Very High | Grade II High | Grade III Moderate | Grade IV Low | GradeV Very Low | ||
| TDS | class | >0.60 | 0.48–0.60 | 0.45–0.48 | 0.40–0.45 | <0.40 |
| MDS | class | >0.60 | 0.54–0.60 | 0.44–0.54 | 0.38–0.44 | <0.38 |
| MDS Grades | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Total | ||
| TDS grades | 1 | 23 | 18 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 44 |
| 2 | 6 | 41 | 57 | 4 | 0 | 108 | |
| 3 | 0 | 9 | 123 | 44 | 6 | 182 | |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 52 | 64 | 9 | 125 | |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 26 | 21 | 48 | |
| Total | 29 | 68 | 236 | 138 | 36 | 507 | |
| Test Method | Direct Comparison | Pearson |
|---|---|---|
| value | 53.65 | 0.75 * |
References
- Liu, Z.J.; Zhou, W.; Shen, J.B.; Li, S.T.; Liang, G.Q.; Wang, X.B.; Sun, J.W.; Ai, C. Soil quality assessment of acid sulfate paddy soils with different productivities in Guangdong Province, China. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.S.; Karlen, D.L.; Cambardella, C.A. The soil management assessment framework: A quantitative soil quality evaluation method. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 1945–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, J.W.; Parkin, T.B. Defining and assessing soil quality. In Defining Soil Quality for a Sustainable Environment; Doran, J.W., Ed.; Special Publication No. 35; SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1994; pp. 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Karlen, D.L.; Mausbach, M.J.; Doran, J.W.; Cline, R.G.; Harris, R.F.; Schuman, G.E. Soil quality: A concept, definition, and framework for evaluation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1997, 61, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zornoza, R.; Acosta, J.A.; Bastida, E.; Dominguez, S.G.; Toledo, D.M.; Faz, A. Identification of sensitive indicators to assess the interrelationship between soil quality, management practices and human health. Soil 2015, 1, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingebiel, A.A.; Montgomery, P.H. Land capability classification. In USDA Handbook; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1961; Volume 210. [Google Scholar]
- Maurício, R.C.; Cássio, A.T.; Douglas, K. Soil Quality Evaluation Using the Soil Management Assessment Framework (SMAF) in Brazilian Oxisols with Contrasting Texture. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Solo. 2017, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhou, S.L.; Zhao, Q.G. Evaluation of spatial and temporal changes of soil quality based on geostatistical analysis in the hill region of subtropical China. Geoderma 2003, 115, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legaz, B.V.; De, S.; Maia, D.; Teixeira, R.F.M.; Anton, A.; Putman, B.; Sala, S. Soil quality, properties, and functions in life cycle assessment: An evaluation of models. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, W.E.; Pierce, F.J. The dynamics of soil quality as a measure of sustainable management. In Defining Soil Quality for a Sustainable Environment; Doran, J.W., Ed.; Special Publication No. 35; SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1994; pp. 37–51. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, S.S.; Karlen, D.L.; Mitchell, J.P. A comparison of soil quality indexing methods for vegetable production systems in Northern California. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 40, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.L.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, O.; Han, D.R.; Li, F.D. A comparison of soil quality evaluation methods for Fluvisol alongthe lower Yellow River. Catena 2017, 152, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.S.; Carroll, C.R. Designing a soil quality assessment tool for sustainable agroecosystem management. Ecol. Appl. 2001, 11, 1573–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.Q.; Guo, E.L.; Yan, D.H.; Sun, Z.Y. The impacts of long-term and year-to year temperature change on corn yield in China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 119, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.W.; Wang, Z.M.; Zhang, B.; Song, K.S. Spatial distribution of soil organic carbonand analysis of related factors in croplands of the black soil region, Northeast China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 113, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.F.; Li, C.F.; Zhang, H.H. Soil spatial analysis and agricultural land use optimization by use optimization by using GIS. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2003, 13, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.B.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Sui, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.L.; Herbert, S.J.; Ding, G. Soil degradation: A problem threatening the sustainable development of agriculture in Northeast China. Plant. Soil. Environ. 2010, 56, 87–97. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.B.; Jeremy, L.D.; Huang, B.; Zhao, Y.C.; Sun, W.X.; Gu, Z.Q. Evaluating soil quality indices in an agricultural region of Jiangsu Province, China. Geoderma 2009, 149, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Definiens, A.G. Definiens Professional 8.6 User Guide; Definiens AG: Munchen, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Y.; Li, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.N.; Yang, L.M. Spatial Patterns and the regional Differences of rural settlements in Jilin Province, China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, W.D.; Wang, Z.M.; liu, M.Y.; Lu, C.Y.; Jia, M.M.; Mao, D.H.; Ren, C.Y. Spatio-temporal Dynamics analysis of cropland in Northeasst China during 1990–2013 based on remote sensing. Trans. CSAE 2016, 32, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.L.; Jiang, L.L.; Liu, X.B. Soil nutrient variance by slope position in a Mollisol farmland area of Northeast China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.M.; Zhang, B.; Song, K.S. Soil orgainic carbon under different landscape attributes in croplands of Northeast China. Plant. Soil. Environ. 2008, 54, 420–427. [Google Scholar]
- Govaerts, B.; Sayreb, K.D.; Deckersa, J. A minimum data set for soil quality assessment of wheat and corn cropping in the highlands of Mexico. Soil. Tillage Res. 2006, 87, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazel, R.; Rossana, M.; Hossein, A.B.; Zahra, F.; Sima, R.B. Assessment of soil quality indices in agricultural lands of Qazvin province, Iran. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 40, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, M.K.; Lala, R.; Ebinger, M. Determining soil quality indicators by factor analysis. Soil. Tillage Res. 2006, 87, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Sui, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.D.; Meng, K.; Herbert, S.J. Spatial variability of nutrient properties in black soil of northeast China. Pedosphere 2007, 17, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaling, E.M.A.; Braun, A.R. Soil fertility research in Sub-Saharan Africa: New dimension new challenges. Commun. Soil Sci. Plan. 1996, 3–4, 365–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, S.A.; Gilkes, R.J.; Andrews, S.S. A minimum data set for assessing soil quality in rangelands. Geoderma 2006, 136, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logsdon, S.D.; Karlen, D.L. Bulk density as a soil quality indicator during conversion to no-tillage. Soil. Tillage Res. 2004, 78, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, F.D.; Manzano, M.; Marquet, P.A.; Gaxiola, A. Microbial communities in soil chrono sequences with distinct parent material: The effect of soil pH and litter quality. J. Ecol. 2017, 105, 1709–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, K.O.; Maysoon, M.M.; Johnathan, D.H.; Phillip, W.S. Changes in soil surface chemistry after fifty years of tillage and nitrogen fertilization. Geoderma 2017, 308, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.B.; Wang, D.Y.; Li, H.; Liu, S.H. Urbanization-induced site condition changes of peri-urban cultivated land in the black soil region of northeast China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 80, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, A.E.; Laird, D.A.; Mallarino, A.P. Nitrogen fertilization and cropping system impacts on soil quality in Midwestern Mollisols. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 70, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, A.P.; Owensby, C.E.; kulyingyong, S. Change in soil chemical properties due to 40 years of fertilization. Soil Sci. 1990, 182, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, J.E.; Bindi, M. Consequences of climate change for European agricultural productivity, land use and policy. Eur. J. Agron. 2002, 16, 239–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.F.; Xion, G.Y.; Zhang, J.M. The effect of straw reapplication on yields of grain crops and soil fertility in Jianghan Plain. Huibei Agric. Sci. 2008, 47, 169–173. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]





| Indicators | FT | SSF | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLD (cm) | U(x) | 10 | 20 | |
| OHD (cm) | U(x) | 0 | 100 | |
| CEC (cmol kg−1) | U(x) | 4.9 | 44 | |
| SOM (g kg−1) | U(x) | 10 | 50 | |
| TN (g kg−1) | U(x) | 0.75 | 2.86 | |
| TP (g kg−1) | U(x) | 0.4 | 1 | |
| TK (g kg−1) | U(x) | 10 | 30 | |
| AN (mg kg−1) | U(x) | 15.1 | 1140 | |
| AP (mg kg−1) | U(x) | 5 | 100 | |
| AK (mg kg−1) | U(x) | 40 | 100 | |
| Acu (mg kg−1) | U(x) | 2 | 5 | |
| Afe (mg kg−1) | U(x) | 2 | 40 | |
| Azn (mg kg−1) | U(x) | 0.5 | 3 | |
| OHT (cm) | L(x) | 10 | 25 | |
| BD (g cm−3) | L(x) | 1.25 | 2 | |
| pH | R(x) | 4.6 | 8.4 |
| PCs | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eigenvalue | 2.459 | 2.045 | 1.663 | 1.627 | 1.181 | ||
| Percent | 15.371 | 12.781 | 10.392 | 10.167 | 7.38 | ||
| Cumulative percent | 15.371 | 28.152 | 38.544 | 48.711 | 56.091 | ||
| Eigenvectors | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | Grouping | Norm value |
| CLD | 0.052 | 0.495 | 0.077 | 0.284 | −0.215 | 2 | 0.839 |
| BD | 0.053 | −0.428 | 0.142 | 0.195 | −0.038 | 2 | 0.692 |
| OHD | −0.528 | 0.264 | 0.575 | −0.186 | −0.309 | 3 | 1.244 |
| OHT | 0.614 | −0.294 | −0.445 | 0.222 | 0.306 | 1 | 1.275 |
| CEC | 0.612 | 0.369 | −0.180 | −0.297 | −0.067 | 1 | 1.184 |
| pH | 0.177 | 0.594 | −0.334 | 0.242 | −0.016 | 2 | 1.039 |
| SOM | 0.658 | −0.122 | 0.424 | −0.016 | −0.111 | 1 | 1.187 |
| TN | 0.663 | 0.310 | 0.299 | −0.266 | −0.155 | 1 | 1.253 |
| TP | 0.064 | −0.390 | 0.284 | 0.475 | 0.122 | 4 | 0.916 |
| TK | −0.266 | 0.491 | 0.028 | −0.060 | 0.598 | 5 | 1.047 |
| AN | 0.352 | −0.017 | 0.443 | 0.121 | −0.154 | 3 | 0.827 |
| AP | −0.195 | 0.093 | 0.420 | 0.232 | 0.388 | 3 | 0.819 |
| AK | 0.404 | −0.348 | 0.232 | −0.439 | 0.257 | 4 | 1.063 |
| ACu | 0.264 | 0.558 | 0.096 | 0.093 | 0.170 | 2 | 0.934 |
| AFe | 0.144 | 0.046 | −0.111 | 0.743 | −0.350 | 4 | 1.057 |
| AZn | 0.172 | 0.152 | 0.406 | 0.395 | 0.372 | 3 | 0.901 |
| Indicator | TDS | MDS | Indicator | TDS | MDS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COM | Weight | COM | Weight | COM | Weight | COM | Weight | ||
| CLD | 0.3804 | 0.0424 | TP | 0.4771 | 0.0532 | ||||
| BD | 0.2460 | 0.0274 | TK | 0.6738 | 0.0751 | 0.5971 | 0.1337 | ||
| OHD | 0.8050 | 0.0897 | AN | 0.3588 | 0.0400 | ||||
| OHT | 0.8090 | 0.0901 | 0.3034 | 0.0679 | AP | 0.4277 | 0.0477 | ||
| EC | 0.6360 | 0.0709 | 0.6662 | 0.1491 | AK | 0.5966 | 0.0665 | ||
| pH | 0.5547 | 0.0618 | 0.7643 | 0.1711 | ACu | 0.4282 | 0.0477 | ||
| SOM | 0.6403 | 0.0713 | 0.6673 | 0.1494 | AFe | 0.7088 | 0.0790 | 0.6949 | 0.1556 |
| TN | 0.7202 | 0.0802 | 0.7742 | 0.1733 | AZn | 0.5121 | 0.0571 | ||
| Indicators | Mean | Standard Deviation | CV (%) | Minimum | Maximum | Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLD (cm) | 19.32 | 2.57 | 13.30 | 14.00 | 25.00 | 11.00 |
| BD (g cm−3) | 1.32 | 0.23 | 17.42 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 1.00 |
| OHD (cm) | 2.90 | 8.13 | 280.34 | 0.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| OHT (cm) | 4.74 | 12.17 | 256.75 | 1.00 | 65.00 | 64.00 |
| CEC (cmol kg−1) | 22.82 | 6.72 | 29.45 | 4.90 | 44.31 | 39.41 |
| pH | 6.51 | 1.05 | 16.13 | 4.65 | 8.45 | 3.80 |
| SOM (g kg−1) | 24.44 | 6.42 | 26.27 | 1.44 | 51.00 | 49.56 |
| TN (g kg−1) | 1.30 | 0.42 | 32.31 | 0.10 | 2.86 | 2.76 |
| TP (g kg−1) | 0.59 | 0.25 | 42.37 | 0.10 | 1.46 | 1.36 |
| TK (g kg−1) | 20.89 | 5.12 | 24.51 | 5.95 | 47.26 | 41.31 |
| AN (mg kg−1) | 121.91 | 42.38 | 34.76 | 15.10 | 1140.00 | 1124.90 |
| AP (mg kg−1) | 25.55 | 25.64 | 100.35 | 0.30 | 180.45 | 180.15 |
| AK (mg kg−1) | 136.69 | 52.15 | 38.15 | 39.22 | 326.93 | 287.71 |
| ACu (mg kg−1) | 3.03 | 2.68 | 88.45 | 0.05 | 19.33 | 19.28 |
| AFe (mg kg−1) | 31.86 | 27.79 | 87.23 | 1.38 | 208.00 | 206.62 |
| AZn (mg kg−1) | 1.66 | 1.19 | 71.69 | 0.00 | 10.13 | 10.13 |
| Indicator Method | Items | Soil Quality Grade | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade I | Grade II | Grade III | Grade IV | Grade V | ||
| TDS | Area (ha) | 170,806 | 402,741 | 1,127,540 | 688,314 | 230,870 |
| Area% | 6.52 | 15.37 | 43.03 | 26.27 | 8.81 | |
| MDS | Area (ha) | 292,226 | 752,031 | 1,045,347 | 679,934 | 337,766 |
| Area% | 9.40 | 24.20 | 33.64 | 21.88 | 10.87 | |
| Yushu | Nongan | Dehui | Jiutai | Gongzhuling | Lishu | Yitong | Changchun | Shuangyang | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IQITDS | 0.472 | 0.423 | 0.468 | 0.463 | 0.426 | 0.425 | 0.464 | 0.484 | 0.489 |
| IQIMDS | 0.534 | 0.438 | 0.497 | 0.455 | 0.438 | 0.444 | 0.501 | 0.522 | 0.531 |
| Factors | Classes | Unit | IQI | SDIQI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parent material | alluvial deposits | 0.493 a | 0.090 | |
| deluvium | 0.461 b | 0.055 | ||
| lacustrine deposit | 0.524 a,b | 0.114 | ||
| aeolian sediment | 0.373 c | 0.073 | ||
| loess | 0.490 a | 0.088 | ||
| Soil type | black soil | 0.527 b | 0.0711 | |
| dark brown forest soil | 0.499 a | 0.072 | ||
| Chernozems | 0.464 c | 0.090 | ||
| aeolian soil | 0.431 d | 0.097 | ||
| paddy soil | 0.562 b | 0.069 | ||
| meadow soil | 0.454 a,c,d | 0.088 | ||
| Fertilizer amount | <300 | kg/ha | 0.485 a | 0.073 |
| ≥300 | 0.480 a | 0.066 | ||
| Annual precipitation | <550 | mm | 0.465 | 0.068 |
| ≥550 | 0.505 | 0.065 | ||
| ≥10 °C accumulated temperature | <2900 | °C | 0.521 | 0.055 |
| ≥2900 | 0.441 | 0.059 | ||
| DEM | <200 | m | 0.457 a | 0.048 |
| ≥200 | 0.446 b | 0.050 | ||
| slope | <3 | degree | 0.491 a | 0.070 |
| >3 | 0.472 b | 0.068 | ||
| Straw incorporation | 0 | 0.565 a | 0.074 | |
| <3500 | kg/ha | 0.519 b | 0.082 | |
| 3500–6500 | 0.439 c | 0.078 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Li, H.; Yang, L.; Ren, Y. Assessment of Soil Quality of Croplands in the Corn Belt of Northeast China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10010248
Li X, Li H, Yang L, Ren Y. Assessment of Soil Quality of Croplands in the Corn Belt of Northeast China. Sustainability. 2018; 10(1):248. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10010248
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaoyan, Huiying Li, Limin Yang, and Yongxing Ren. 2018. "Assessment of Soil Quality of Croplands in the Corn Belt of Northeast China" Sustainability 10, no. 1: 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10010248
APA StyleLi, X., Li, H., Yang, L., & Ren, Y. (2018). Assessment of Soil Quality of Croplands in the Corn Belt of Northeast China. Sustainability, 10(1), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10010248




