Quantifying Impacts of Land-Use/Cover Change on Urban Vegetation Gross Primary Production: A Case Study of Wuhan, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Processing
2.2.1. Satellite Data and Products
2.2.2. Meteorological Data
3. Methods
3.1. Generation of the NDVI Time Series Using STARFM
3.2. Creation of Land-Cover Maps
3.3. Estimation of GPP
3.4. Analysis of Impacts of LUCC on GPP
4. Results
4.1. The Synthetic NDVI
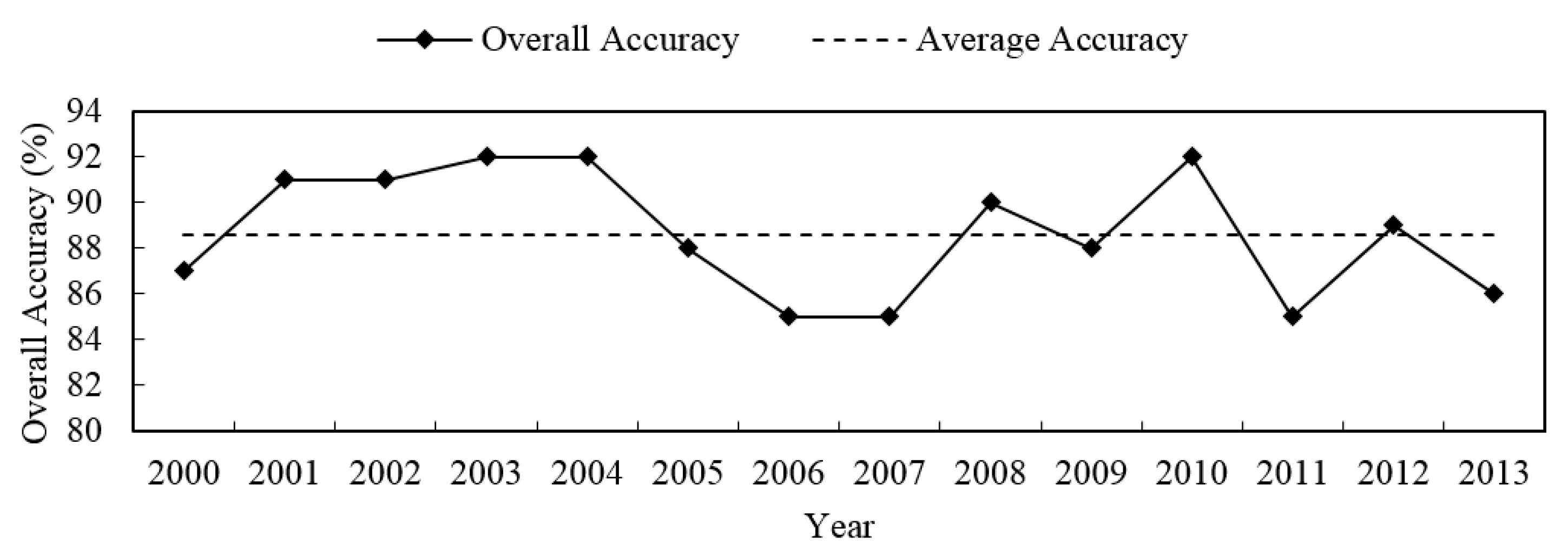
4.2. Validation of GPP Estimates
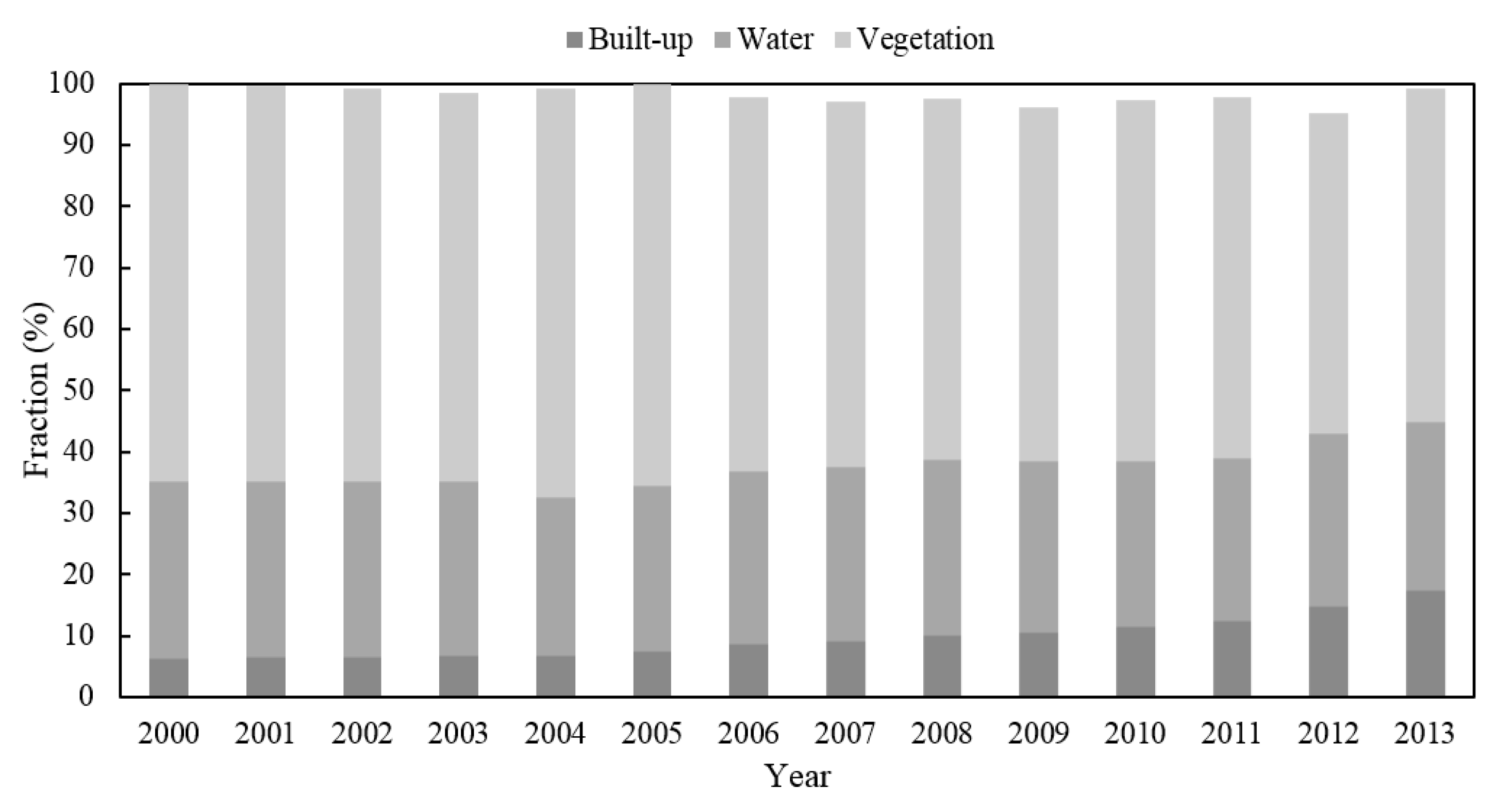
4.3. LUCC in the Study Area
4.4. Impacts of LUCC on GPP
5. Discussion
5.1. GPP Estimated at 30 m Spatial Resolution
5.2. Impacts of LUCC on GPP
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grimm, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.; Bai, X.; Briggs, J.M. Global change and the ecology of cities. Science 2008, 319, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Wang, R.; Paulussen, J.; Liu, X. Comprehensive concept planning of urban greening based on ecological principles: A case study in Beijing, China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2005, 72, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; DeFries, R.; Asner, G.P. Global consequences of land use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milesi, C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Nemani, R.R.; Running, S.W. Assessing the impact of urban land development on net primary productivity in the southeastern United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, M.L.; Bounoua, L.; DeFries, R.; Lawrence, W.T.; Stutzer, D.; Tucker, C.J.; Ricketts, T. The consequences of urban land transformation on net primary productivity in the United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 89, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, F.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; He, Z. Assessing the differences in net primary productivity between pre- and post-urban land development in China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 171–172, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyantuyev, A.; Wu, J. Urbanization alters spatiotemporal patterns of ecosystem primary production: A case study of the Phoenix metropolitan region, USA. J. Arid Environ. 2009, 73, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liu, M.; An, S.; Chen, J.M.; Yan, P. Assessing the impact of urbanization on regional net primary productivity in Jiangyin County, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 85, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Shao, H.; Shi, P.; Zhu, W.; Pan, Y. How does the conversion of land cover to urban use affect net primary productivity? A case study in Shenzhen city, China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 149, 2054–2060. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, X.; Xia, L. Assessment impacts of weather and land use/land-cover (LULC) change on urban vegetation net primary productivity (NPP): A case study in Guangzhou, China. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4125–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, C.S.; Randerson, J.T.; Field, C.B.; Matson, P.A.; Vitousek, P.M.; Mooney, H.A.; Klooster, S.A. Terrestrial ecosystem production: A process model based on global satellite and surface data. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1993, 7, 811–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Running, S.W.; Thornton, P.E.; Nemani, R.; Glassy, J.M. Global Terrestrial Gross and Net Primary Productivity from the Earth Observing System. In Methods in Ecosystem Science; Sala, O.E., Jackson, R.B., Mooney, H.A., Howarth, R.W., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 44–57. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Heinsch, F.A.; Nemani, R.R.; Running, S.W. Improvements of the MODIS terrestrial gross and net primary production global data set. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nightingale, J.M.; Coops, N.C.; Waring, R.H.; Hargrove, W.W. Comparison of MODIS gross primary production estimates for forests across the U.S.A. with those generated by a simple process model, 3-PGS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, D.; Rahman, A.; Cordova, V.; Elmasri, B.; Baldocchi, D.; Bolstad, P.; Flanagan, L.; Goldstein, A.; Hollinger, D.; Misson, L. A new model of gross primary productivity for North American ecosystems based solely on the enhanced vegetation index and land surface temperature from MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1633–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Peng, Y.; Masek, J.G.; Rundquist, D.C.; Verma, S.B.; Suyker, A.; Baker, J.M.; Hatfield, J.L.; Meyers, T. Remote estimation of crop gross primary production with Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S.; Storey, J.C.; Choate, M.J.; Hayes, R.W. Four years of Landsat-7 onorbit geometric calibration and performance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 2786–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, R.E.; Nishihama, M.; Fleig, A.J.; Kuyper, J.A.; Roy, D.P.; Storey, J.C.; Patt, F.S. Achieving sub-pixel geolocation accuracy in support of MODIS land science. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Masek, J.; Schwaller, M.; Hall, H. On the blending of the Landsat and MODIS surface reflectance: Predicting daily Landsat surface reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, D.P.; Ju, J.; Lewis, P.; Schaaf, C.; Gao, F.; Hansen, M.; Lindquist, E. Multi-temporal MODIS–Landsat data fusion for relative radiometric normalization, gap filling, and prediction of Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3112–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilker, T.; Wulder, M.A.; Coops, N.C.; Seitz, N.; White, J.C.; Gao, F. Generation of dense time series synthetic Landsat data through data blending with MODIS using a spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1988–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaert, C.M.; García-Haro, F.J. A comparison of STARFM and an unmixing-based algorithm for Landsat and MODIS data fusion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, T.; Song, C.; Bolstad, P.V.; Band, L.E. Downscaling real-time vegetation dynamics by fusing multi-temporal MODIS and Landsat NDVI in topographically complex terrain. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2499–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.J.; de Beurs, K.M.; Wynne, R.H.; Gao, F. Evaluation of Landsat and MODIS data fusion products for analysis of dryland forest phenology. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Lucas, R.; Bunting, P.; Verbesselt, J.; Armston, J. Multi-resolution time series imagery for forest disturbance and regrowth monitoring in Queensland, Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, D. Generation and evaluation of gross primary productivity using Landsat data through blending with MODIS data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churkina, G. Modeling the carbon cycle of urban systems. Ecol. Model. 2008, 216, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; He, Q.; Ming, L.; Tang, S. Urban growth and its determinants across the Wuhan urban agglomeration, central China. Habitat Int. 2014, 44, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanniah, K.D.; Beringer, J.; Hutley, L.B.; Tapper, N.J.; Zhu, X. Evaluation of Collection 4 and 5 of the MODIS gross primary productivity product and algorithm improvement at a tropical savanna site in northern Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1808–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D.P.; Ritts, W.D.; Cohen, W.B.; Gower, S.T.; Running, S.W.; Zhao, M.; Costa, M.H.; Kirschbaum, A.A.; Ham, J.M.; Saleska, S.R.; et al. Evaluation of MODIS NPP and GPP products across multiple biomes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D.P.; Ritts, W.D.; Zhao, M.; Kurc, S.A.; Dunn, A.L.; Wofsy, S.C.; Small, E.E.; Running, S.W. Assessing interannual variation in MODIS-based estimates of gross primary production. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1899–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinsch, F.A.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W.; Kimball, J.S.; Nemani, R.R.; Davis, K.J.; Bolstad, P.V.; Cook, B.D.; Desai, A.R.; Ricciuto, D.M.; et al. Evaluation of remote sensing based terrestrial productivity from MODIS using regional tower eddy flux network observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1908–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaramuzza, P.; Micijevic, E.; Chander, G. SLC gap-filled products phase one methodology. Available online: https://landsat.usgs.gov/sites/default/files/documents/SLC_Gap_Fill_Methodology.pdf (accessed on 6 March 2018).
- Murray, F.W. On the computation of saturation vapor pressure. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1991, 6, 203–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Wang, Y.; Fensholt, R.; Wang, K.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Y. Mapping and Evaluation of NDVI Trends from Synthetic Time Series Obtained by Blending Landsat and MODIS Data around a Coalfield on the Loess Plateau. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4255–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menenti, M.; Azzali, S.; Verhoef, W.; van Swol, R. Mapping agroecological zones and time lag in vegetation growth by means of fourier analysis of time series of NDVI images. Adv. Space Res. 1993, 13, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteith, J.L. Solar radiation and productivity in tropical ecosystems. J. Appl. Ecol. 1972, 9, 747–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Drought-Induced Reduction in Global Terrestrial Net Primary Production from 2000 through 2009. Science 2010, 329, 940–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myneni, R.B.; Williams, D.L. On the relationship between FAPAR and NDVI. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 49, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liang, S.; Yu, G.; Yuan, W.; Cheng, X.; Xia, J.; Zhao, T.; Feng, J.; Ma, Z.; Ma, M.; et al. Estimation of gross primary production over the terrestrial ecosystems in China. Ecol. Model. 2013, 261–262, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Yang, R.; Dong, Y.-X.; Liu, Y.-X.; Qiu, L.-R. The influence of rapid urbanization and land use changes on terrestrial carbon sources/sinks in Guangzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 70, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutzen, P.J. New directions: The growing urban heat and pollution “island” effect—Impact on chemistry and climate. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3539–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, J.W.; Jones, C.G.; Dawson, T.E. Urbanization effects on tree growth in the vicinity of New York City. Nature 2003, 424, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhong, J.; Sun, Z.; Yang, W. Spatial Pattern of Carbon Sequestration and Urban Sustainability: Analysis of Land-Use and Carbon Emission in Guang’an, China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, L.J.; Pearson, L.; Pearson, C.J. Sustainable urban agriculture: Stocktake and opportunities. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2010, 8, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Grass | EBF | DBF | Crop | Built-Up | Bare | Water | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grass | 0 | −5.9 | −5.5 | −42.2 | 2.5 | 3.5 | 8.5 |
| EBF | 7.6 | 0 | 0 | 121.8 | 0.1 | 1.0 | 12.2 |
| DBF | 6.7 | 0 | 0 | 71.5 | 2.4 | 6.8 | 52.7 |
| Crop | 46.0 | −93.3 | −65.4 | 0 | 0 | 374.2 | 356.5 |
| Built-up | −8.3 | −0.7 | −17.1 | −272.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Bare | −5.9 | −1.6 | −13.2 | −464.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Water | −7.6 | −9.1 | −63.9 | −361.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Du, W.; Su, H.; Wang, S.; Guan, Q. Quantifying Impacts of Land-Use/Cover Change on Urban Vegetation Gross Primary Production: A Case Study of Wuhan, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10030714
Liu S, Du W, Su H, Wang S, Guan Q. Quantifying Impacts of Land-Use/Cover Change on Urban Vegetation Gross Primary Production: A Case Study of Wuhan, China. Sustainability. 2018; 10(3):714. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10030714
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shishi, Wei Du, Hang Su, Shanqin Wang, and Qingfeng Guan. 2018. "Quantifying Impacts of Land-Use/Cover Change on Urban Vegetation Gross Primary Production: A Case Study of Wuhan, China" Sustainability 10, no. 3: 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10030714
APA StyleLiu, S., Du, W., Su, H., Wang, S., & Guan, Q. (2018). Quantifying Impacts of Land-Use/Cover Change on Urban Vegetation Gross Primary Production: A Case Study of Wuhan, China. Sustainability, 10(3), 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10030714






