Spatiotemporal Patterns of Ozone and Cardiovascular and Respiratory Disease Mortalities Due to Ozone in Shenzhen
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
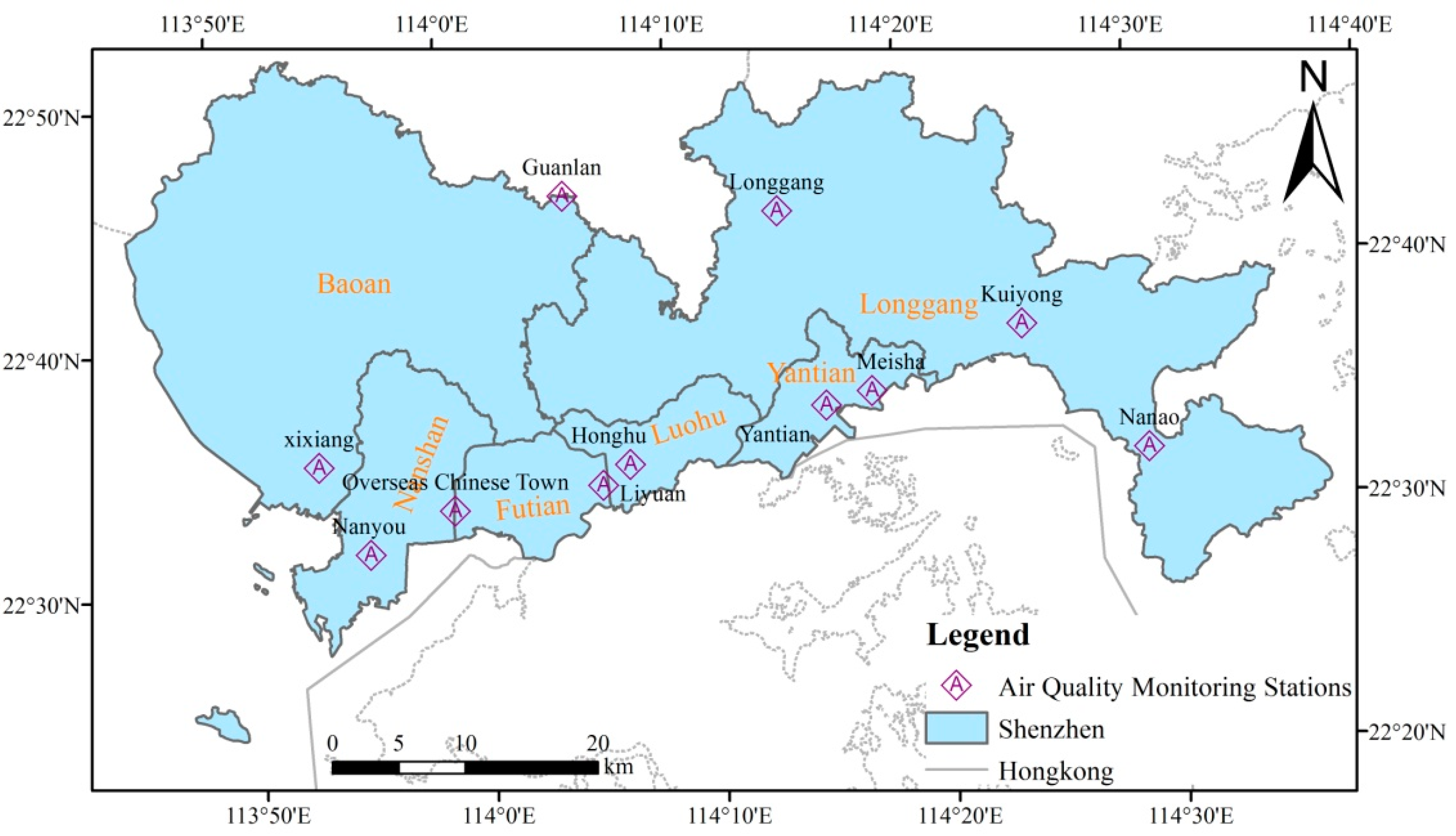
2.1. Study Area and Population
2.2. Data Sources
2.2.1. Mortality Data
2.2.2. Air Pollutants and Meteorological Data
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Statistical Results
3.2. Correlation Coefficients
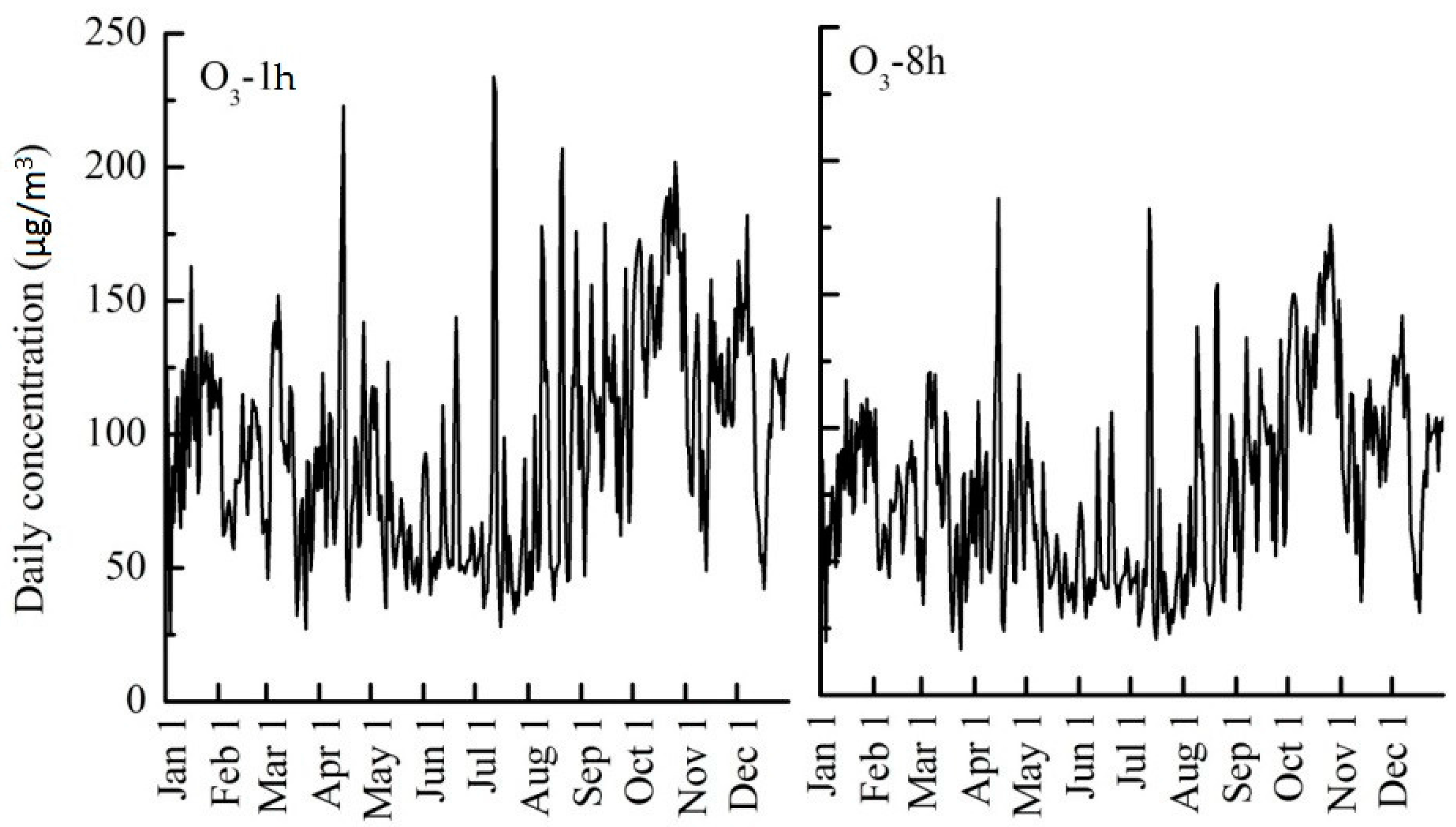
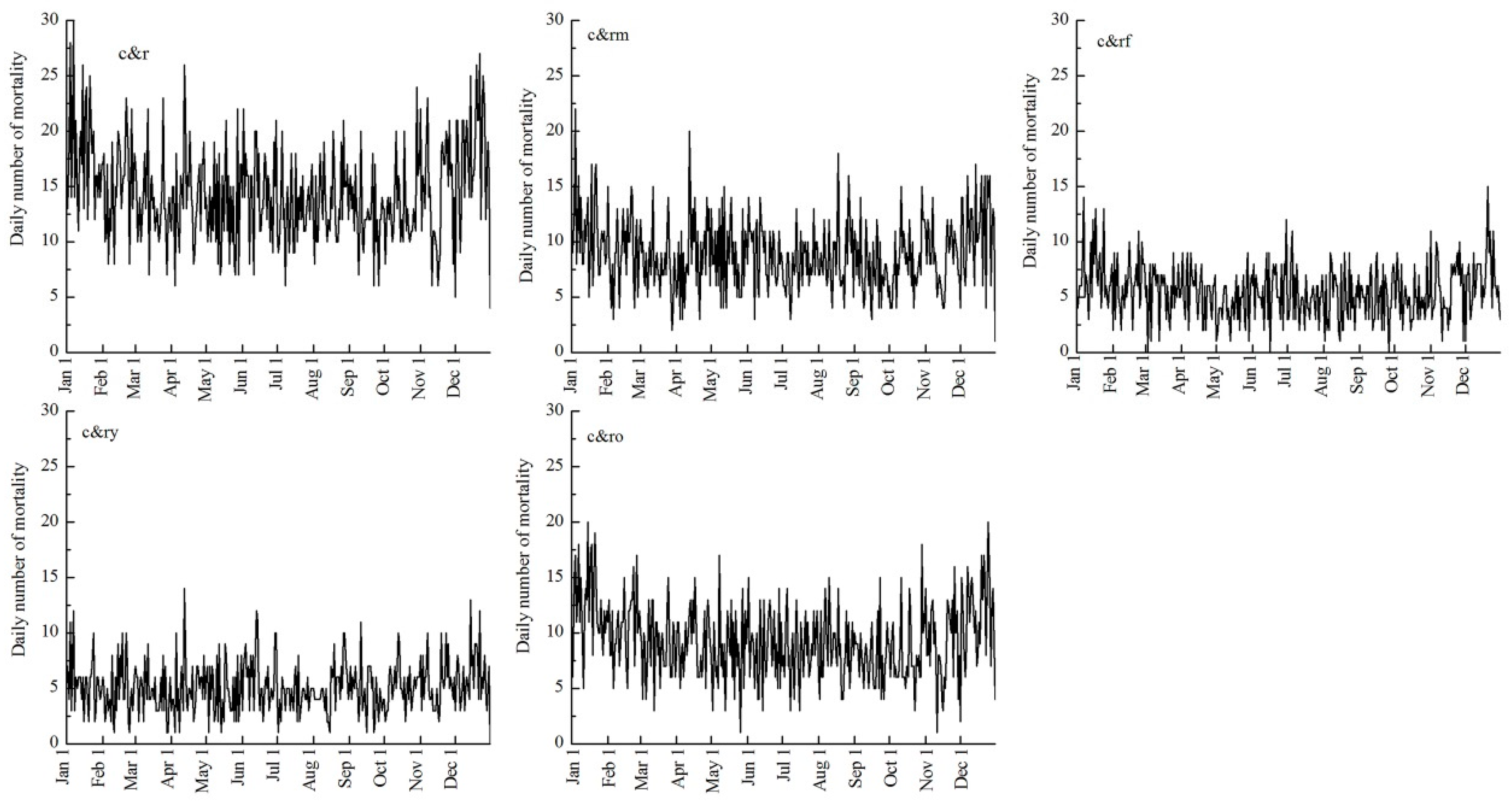
3.3. Temporal Changes
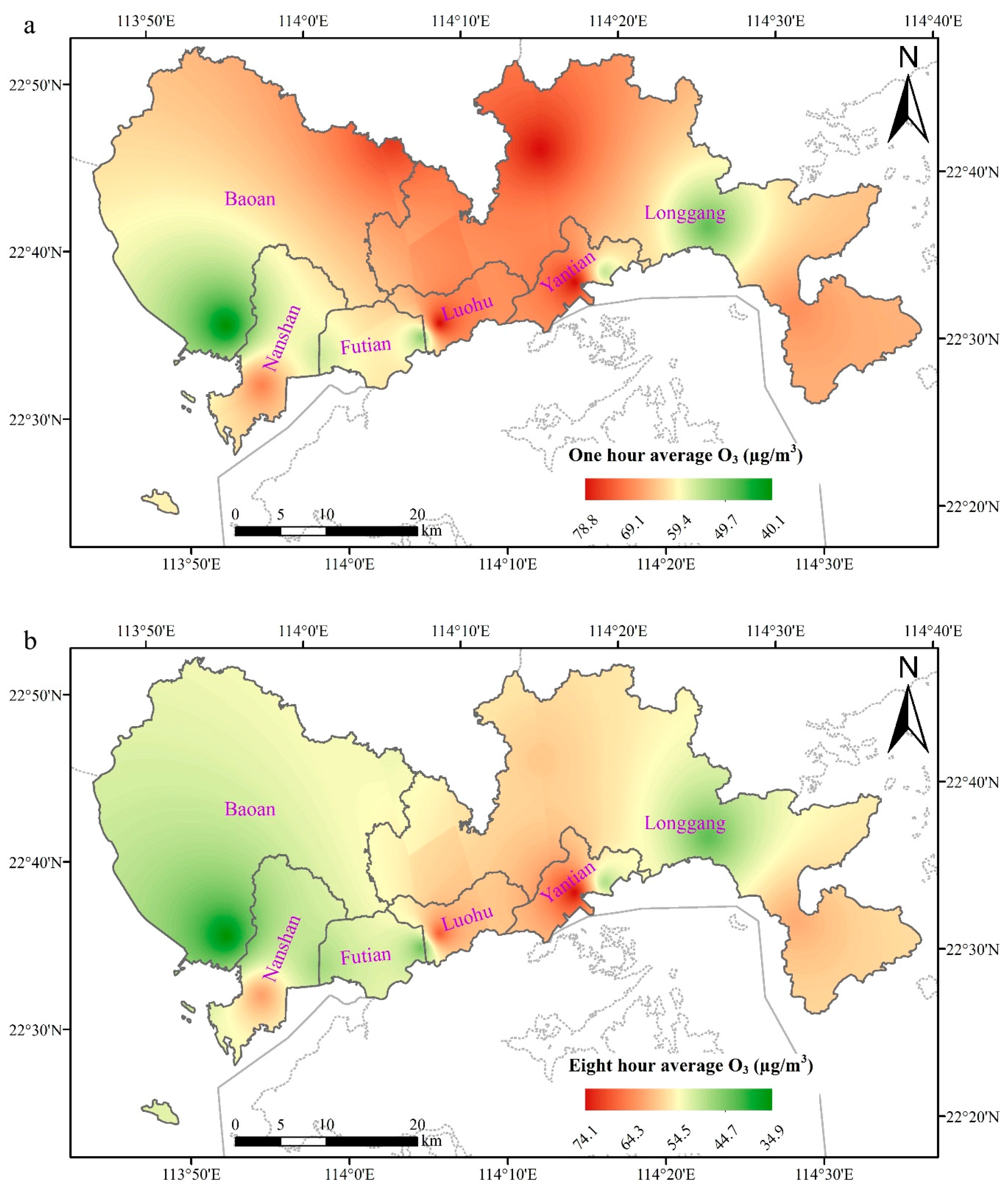
3.4. Spatial Differences
3.5. Temporal Differences between Different Urban Function Areas
3.6. Health Effects
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hao, Y.; Balluz, L.; Strosnider, H.; Wen, X.J.; Li, C.; Qualters, J.R. Ozone, fine particulate matter, and chronic lower respiratory disease mortality in the United States. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, R.D.; Samoli, E.; Pham, L.; Dominici, F.; Touloumi, G.; Ramsay, T.; Burnett, R.T.; Krewski, D.; Le Tertre, A.; Cohen, A.; et al. Acute effects of ambient ozone on mortality in Europe and North America: Results from the APHENA study. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2013, 6, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pride, K.R.; Peel, J.L.; Robinson, B.F.; Busacker, A.; Grandpre, J.; Bisgard, K.M.; Yip, F.Y.; Murphy, T.D. Association of short-term exposure to ground-level ozone and respiratory outpatient clinic visits in a rural location—Sublette County, Wyoming, 2008–2011. Environ. Res. 2015, 137, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahi, A.M.; Omraninava, A.; Goli, M.; Soheilarezoomand, H.R.; Mirzaei, N. The effects of air pollution on cardiovascular and respiratory causes of emergency admission. Emergency 2014, 2, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Petito, B.C.; Goodman, J.E.; Sax, S.N.; Loftus, C.T. Providing perspective for interpreting cardiovascular mortality risks associated with ozone exposures. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 72, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arjomandi, M.; Wong, H.; Donde, A.; Frelinger, J.; Dalton, S.; Ching, W.; Power, K.; Balmes, J.R. Exposure to medium and high ambient levels of ozone causes adverse systemic inflammatory and cardiac autonomic effects. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2015, 308, H1499–H1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brook, R.D.; Franklin, B.; Cascio, W.; Hong, Y.; Howard, G.; Lipsett, M.; Luepker, R.; Mittleman, M.; Samet, J.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; et al. Air pollution and cardiovascular disease: A statement for healthcare professionals from the Expert Panel on Population and Prevention Science of the American Heart Association. Circulation 2004, 109, 2655–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.P.; Freeman, B.A. Promotion of cardiovascular disease by exposure to the air pollutant ozone. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2009, 297, L205–L208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devlin, R.B.; Duncan, K.E.; Jardim, M.; Schmitt, M.T.; Rappold, A.G.; Diaz-Sanchez, D. Controlled exposure of healthy young volunteers to ozone causes cardiovascular effects. Circulation 2012, 126, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazucha, M.J.; Bates, D.V.; Bromberg, P.A. Mechanism of action of ozone on the human lung. J. Appl. Physiol. 1989, 67, 1535–1541. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). 2013 Final Report Integrated Science Assessment of Ozone and Related Photochemical Oxidants; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2013.
- Adams, W. Effects of ozone exposure at ambient air pollution episode levels on exercise performance. Sports Med. 1987, 4, 395–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahle, J.J.; Neas, L.M.; Devlin, R.B.; Case, M.W.; Schmitt, M.T.; Madden, M.C.; Diaz-Sanchez, D. Interaction effects of temperature and ozone on lung function and markers of systemic inflammation, coagulation, and fibrinolysis: A crossover study of healthy young volunteers. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryparis, A.; Forsberg, B.; Katsouyanni, K.; Analitis, A.; Touloumi, G.; Schwartz, J.; Samoli, E.; Medina, S.; Anderson, H.R.; Niciu, E.M.; et al. Acute effects of ozone on mortality from the “air pollution and health: A European approach” project. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 170, 1080–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ebenstein, A.; Greenstone, M.; Li, H. Evidence on the impact of sustained exposure to air pollution on life expectancy from China’s Huai River policy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12936–12941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Honda, Y.; Hashizume, M.; Guo, Y.L.; Wu, C.F.; Kan, H.; Jung, K.; Lim, Y.H.; Yi, S.; Kim, H. Short-term exposure to fine and coarse particles and mortality: A multicity time-series study in East Asia. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 207, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wei, B.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, F.; Rosenberg, M.; Yang, L.; Huang, J.; Krafft, T.; Wang, W. A study of air pollutants influencing life expectancy and longevity from spatial perspective in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 487, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Q.; Zhao, W.; Gong, Z.; Zhao, W.; Tang, T. Fine Particulate Matter Pollution and Hospital Admissions for Respiratory Diseases in Beijing, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 11880–11892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Chen, A.; Chen, R.; Qi, Y.; Ye, J.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Liang, Z.; Liang, Q.; Guo, D.; et al. Acute effect of ambient air pollution on heart failure in Guangzhou, China. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 177, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Li, L.; Krafft, T.; Lv, J.; Wang, W.; Pei, D. Study on the association between ambient air pollution and daily cardiovascular and respiratory mortality in an urban district of Beijing. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 2109–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, W.; Lv, J.; Krafft, T.; Xu, J. Time-series studies on air pollution and daily outpatient visits for allergic rhinitis in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 2486–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anger, A.; Dessens, O.; Xi, F.; Barker, T.; Wu, R. China’s air pollution reduction efforts may result in an increase in surface ozone levels in highly polluted areas. Ambio 2016, 45, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskaran, K.; Gasparrini, A.; Hajat, S.; Smeeth, L.; Armstrong, B. Time series regression studies in environmental epidemiology. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 42, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, S. Gerneralized Additive Models: An Introduction with R; Chapman &Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, E.; Zanobetti, A.; Coull, B.; Schwartz, J.; Gold, D.R.; Koutrakis, P. Ozone trends and their relationship to characteristic weather patterns. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Zhou, L.; Yu, Y.; Wang, L.; Lu, J.; Wang, W.; Krafft, T. Spatiotemporal patterns of particulate matter (PM) and associations between PM and mortality in Shenzhen, China. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacour, S.A.; de Monte, M.; Diot, P.; Brocca, J.; Veron, N.; Colin, P.; Leblond, V. Relationship between ozone and temperature during the 2003 heat wave in France: Consequences for health data analysis. BMC Public Health 2006, 6, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhat, S.C.; Almeida, M.B.; Silva-Filho, L.V.; Farhat, J.; Rodrigues, J.C.; Braga, A.L. Ozone is associated with an increased risk of respiratory exacerbations in patients with cystic fibrosis. Chest 2013, 144, 1186–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudway, I.S.; Kelly, F.J. Ozone and the lung: A sensitive issue. Mol. Aspects Med. 2000, 21, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paffett, M.L.; Zychowski, K.E.; Sheppard, L.; Robertson, S.; Weaver, J.M.; Lucas, S.N.; Campen, M.J. Ozone Inhalation Impairs Coronary Artery Dilation via Intracellular Oxidative Stress: Evidence for Serum-Borne Factors as Drivers of Systemic Toxicity. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 146, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Almeida, S.P.; Casimiro, E.; Calheiros, J. Short-term association between exposure to ozone and mortality in Oporto, Portugal. Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudarzi, G.; Geravandi, S.; Foruozandeh, H.; Babaei, A.A.; Alavi, N.; Niri, M.V.; Khodayar, M.J.; Salmanzadeh, S.; Mohammadi, M.J. Cardiovascular and respiratory mortality attributed to ground-level ozone in Ahvaz, Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Song, X.; Shima, M.; Tamura, K.; Deng, F.; Guo, X. Acute effect of ambient ozone on heart rate variability in healthy elderly subjects. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2011, 21, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Sun, Y.; Ha, S.; Talbott, E.O.; Lissaker, C.T. Association between ozone exposure and onset of stroke in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, USA, 1994–2000. Neuroepidemiology 2013, 41, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, M.L.; Zanobetti, A.; Dominici, F. Who is more affected by ozone pollution? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 180, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabello, N.; Mishra, V.; Sinha, U.; DiAngelo, S.L.; Chroneos, Z.C.; Ekpa, N.A.; Cooper, T.K.; Caruso, C.R.; Silveyra, P. Sex differences in the expression of lung inflammatory mediators in response to ozone. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2015, 309, L1150–L1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanderson, M.G. Effect of Climate Change on Isoprene Emissions and Surface Ozone Levels. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welty, L.J. Are the Acute Effects of Particulate Matter on Mortality in the National Morbidity, Mortality, and Air Pollution Study the Result of Inadequate Control for Weather and Season? A Sensitivity Analysis using Flexible Distributed Lag Models. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 162, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Items | Ave | SD | Min | 25% | Mid | 75% | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c&r | 14.4 | 4.4 | 4.0 | 12.0 | 14.0 | 17.0 | 30.0 |
| c&r-m | 8.9 | 3.3 | 1.0 | 7.0 | 9.0 | 11.0 | 22.0 |
| c&r-f | 5.5 | 2.5 | 0.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 7.0 | 15.0 |
| c&r-y | 5.1 | 2.3 | 0.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 6.0 | 14.0 |
| c&r-o | 9.3 | 3.5 | 1.0 | 7.0 | 9.0 | 12.0 | 20.0 |
| T (°C) | 23.1 | 5.2 | 9.8 | 19.4 | 24.2 | 27.7 | 31.2 |
| H (%) | 74.8 | 15.5 | 24.0 | 67.0 | 78.0 | 87.0 | 100.0 |
| P (hPa) | 1005.2 | 6.2 | 986.8 | 1000.5 | 1005.1 | 1010.8 | 1019.2 |
| W (m/s) | 2.1 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 1.6 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 5.5 |
| NO2 (μg/m3) | 39.6 | 15.7 | 14.0 | 28.0 | 36.0 | 47.0 | 111.0 |
| CO (μg/m3) | 1207.2 | 221.3 | 700.0 | 1030.0 | 1200.0 | 1344.3 | 1966.6 |
| O3-1h (μg/m3) | 95.9 | 41.3 | 26.0 | 60.0 | 90.0 | 121.3 | 234.0 |
| O3-8h (μg/m3) | 76.8 | 34.9 | 17.0 | 47.0 | 74.0 | 100.0 | 186.0 |
| PM2.5 (μg/m3) | 39.6 | 24.8 | 9.0 | 20.0 | 35.0 | 52.0 | 135.0 |
| Headline | T (°C) | H (%) | P (hPa) | W (m/s) | NO2 | CO | O3-1h | O3-8h | PM2.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T (°C) | 1 | ||||||||
| H (%) | 0.377 ** | 1 | |||||||
| P (hPa) | −0.818 ** | −0.534 ** | 1 | ||||||
| W (m/s) | 0.009 | −0.003 | −0.103 | 1 | |||||
| NO2 | −0.381 ** | −0.270 ** | 0.346 ** | −0.471 ** | 1 | ||||
| CO | −0.493 ** | −0.295 ** | 0.473 ** | −0.077 | 0.345 ** | 1 | |||
| O3-1h | −0.115 * | −0.574 ** | 0.298 ** | −0.163 ** | 0.367 ** | 0.314 ** | 1 | ||
| O3-8h | −0.139 ** | −0.601 ** | 0.328 ** | −0.106 ** | 0.291 ** | 0.311 ** | 0.980 ** | 1 | |
| PM2.5 | −0.503 ** | −0.589 ** | 0.544 ** | −0.159 ** | 0.565 ** | 0.617 ** | 0.604 ** | 0.615 ** | 1 |
| Items | c&r | c&r-m | c&r-f | c&r-y | c&r-o | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER (95% CI) | ER (95% CI) | ER (95% CI) | ER (95% CI) | ER (95% CI) | ||
| O3-1h | L0 | −0.34 (−0.46–0.22) | 0.30 (0.14–0.45) | −1.31 (−1.51–−1.11) | −1.70 (−1.91–−1.40) | 0.35 (0.20–0.51) |
| L1 | 0.64 (0.54–−0.75) | 0.62 (0.49–0.76) | 0.68 (0.5–0.85) | 0.72 (0.55–0.90) | 0.55 (0.41–0.69) | |
| L2 | 0.58 (0.48–0.69) | 0.30 (0.18–0.42) | 1.07 (0.92–1.23) | 0.46 (0.30–0.63) | 0.66 (0.53–0.77) | |
| L3 | 0.17 (0.07–0.26) | 0.15 (0.02–0.27) | 0.21 (0.06–0.36) | 0.04 (−0.12–0.20) | 0.28 (0.16–0.40) | |
| L01 | 0.36 (0.21–0.50) | 0.76 (0.58–0.94) | −0.24 (−0.47–−0.01) | −0.44 (−0.68–−0.21) | 0.72 (0.53–0.90) | |
| L02 | 0.71 (0.56–0.88) | 0.80 (0.61–0.99) | 0.62 (0.38–0.86) | 0.07 (−0.18–0.31) | 1.01 (0.83–1.20) | |
| L03 | 0.69 (0.53–0.84) | 0.78 (0.58–0.97) | 0.59 (0.34–0.85) | 0.03 (−0.23–0.28) | 1.00 (0.81–1.19) | |
| O3-8h | L0 | −0.15 (−0.30–0.00) | 0.45 (0.26–0.64) | −1.06 (−1.31–−0.85) | −2.02 (−0.23–0.29) | 0.79 (0.81–1.20) |
| L1 | 0.59 (0.45–0.72) | 0.49 (0.32–0.65) | 0.77 (0.55–0.98) | 0.88 (0.66–1.10) | 0.37 (0.20–0.53) | |
| L2 | 0.83 (0.70–0.95) | 0.57 (0.41–0.72) | 1.28 (1.00–1.48) | 0.47 (0.27–0.70) | 1.04 (0.89–1.19) | |
| L3 | 0.45 (0.33–0.56) | 0.43 (0.28–0.58) | 0.47 (0.28–0.66) | 0.04 (−0.15–0.23) | 0.67 (0.53–0.82) | |
| L01 | 0.41 (0.24–0.59) | 0.73 (0.51–0.95) | −0.04 (−0.32–0.24) | −0.55 (−0.84–−0.26) | 0.84 (0.53–0.82) | |
| L02 | 0.95 (0.77–1.30) | 1.00 (0.77–1.23) | 0.91 (0.61–1.21) | −0.01 (−0.31–0.30) | 1.40 (1.17–1.63) | |
| L03 | 1.08 (0.88–1.27) | 1.14 (0.90–1.38) | 1.01 (0.70–1.32) | 0.03 (−0.29–0.34) | 1.59 (1.35–1.83) | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Krafft, T. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Ozone and Cardiovascular and Respiratory Disease Mortalities Due to Ozone in Shenzhen. Sustainability 2017, 9, 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9040559
Wang L, Bai Y, Zhang F, Wang W, Liu X, Krafft T. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Ozone and Cardiovascular and Respiratory Disease Mortalities Due to Ozone in Shenzhen. Sustainability. 2017; 9(4):559. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9040559
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Li, Yu Bai, Fengying Zhang, Wuyi Wang, Xiaojian Liu, and Thomas Krafft. 2017. "Spatiotemporal Patterns of Ozone and Cardiovascular and Respiratory Disease Mortalities Due to Ozone in Shenzhen" Sustainability 9, no. 4: 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9040559
APA StyleWang, L., Bai, Y., Zhang, F., Wang, W., Liu, X., & Krafft, T. (2017). Spatiotemporal Patterns of Ozone and Cardiovascular and Respiratory Disease Mortalities Due to Ozone in Shenzhen. Sustainability, 9(4), 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9040559





