Comparison of Milk Fat Globule Membrane (MFGM) Proteins of Chianina and Holstein Cattle Breed Milk Samples Through Proteomics Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
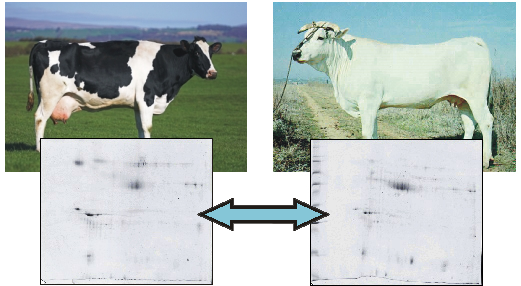
2. Results and Discussion

| SSP | Mw. kDa | PI | No. peptides | Mascot Score | NCBI accession number | Protein ID | Fold of Variation (C/F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 60.734 | 4.69 | 10 | 669 | gi|115495209 | zymogen granule membrane glycoprotein 2 (GP2) [Bos taurus] | −0.27854 |
| 16 | 45.704 | 8.59 | 13 | 987 | gi|2136760 | adipocyte differentiation-related protein (ADRP) [Bos taurus] | 0.39175 |
| 28 | 83.695 | 7.07 | 8 | 635 | gi|3914346 | Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (PIGR) | −0.35186 |
| 56 | 45.704 | 7.07 | 16 | 987 | gi|2136760 | glycoprotein antigen MGP57/53. mammary gland - bovine | 0.28378 |
3. Experimental Procedure
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Smolenski, S.H.; Fiona , Y.S.; Kwan, J.B.; Farr, V.; Davis, S.R.; Stelwagen, K.; Wheeler, T.T. Characterisation of host defence proteins in milk using a proteomic approach grant. J. Prot. Res. 2007, 6, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelwagen, K.; Davis, S.R.; Farr, V.C.; Eichler, S.J.; Politis, I. Effect of once daily milking and concurrent somatotropin on mammary tight junction permeability and yield of cows. J. Dairy Sci. 1994, 77, 2994–3001. [Google Scholar]
- Lacy-Hulbert, S.J.; Woolford, M.W.; Nicholas, G.D.; Prosser, C.G.; Stelwagen, K. Effect of milking frequency and pasture intake on milk yield and composition of late lactation cows. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen, H.; Marnila, P.; Gill, H.S. Milk immunoglobulins and complement factors. Br. J. Nutr. 2000, 84, S75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, S.S. Plasmin system and microbial proteases in milk: characteristics, roles, and relationship. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 6628–6634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prosser, C.G. Insulin-like growth factors in milk and mammary gland. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 1996, 1, 297–306. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, P.P.; Uribe-Luna, S.; Conneely, O.M. Lactoferrin and host defense. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2002, 80, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, P.E. Changes in the composition and yield of the mammary secretion of cows during the initiation of lactation. J. Endocrinol. 1973, 59, 231–247. [Google Scholar]
- Hurley, W.L. Mammary gland function during involution. J. Dairy Sci. 1989, 72, 1637–1646. [Google Scholar]
- Reinhardt, T.A.; Lippolis, J.D. Developmental changes in the milk fat globule membrane proteome during the transition from colostrum to milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 2307–2318. [Google Scholar]
- Goldman, A.S. Expression of functional immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory factors in human milk. Clin. Perinatol. 1999, 26, 361–377. [Google Scholar]
- Clare, D.A.; Swaisgood, H.E. Bioactive milk peptides: a prospectus. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.C. Proteomics reveal a link between the endoplasmic reticulum and lipid secretory mechanisms in mammary epithelial cells. Electrophoresis 2000, 21, 3470–3482. [Google Scholar]
- Charlwood, J.; Hanrahan, S.; Tyldesley, R.; Langridge, J.; Dwek, M.; Camilleri, P. Use of proteomic methodology for the characterizacharacterization of human milk fat globular membrane proteins. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 301, 314–324. [Google Scholar]
- Quaranta, S.; Giuffrida, M.G.; Cavaletto, M.; Giunta, C.; Godovac- Zimmermann, J.; Canas, B.; Fabris, C.; Bertino, E.; Mombro, M.; Conti, A. Human proteome enhancement: High-recovery method and improved two-dimensional map of colostral fat globule membrane proteins. Electrophoresis 2001, 22, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar]
- Pucci-Minafra, I.; Fontana, S.; Cancemi, V.; Alaimo, V.; Minafra, S. Proteomic patterns of cultured breast cancer cells and epithelial mammary cells. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 963, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fortunato, D.; Giuffrida, M.G.; Cavaletto, M.; Garoffo, L.P.; Dellavalle, G.; Napolitano, L.; Giunta, C.; Fabris, C.; Bertino, E.; Coscia, A.; Conti, A. Structural proteome of human colostral fat globule membrane proteins. Proteomics 2003, 3, 897–905. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, J.M.; Mottaz, L.R.; Yu, D.J.; Anderson, R.J.; Moore, W.N.; Chen, K.J.; Auberry, E.F.; Strittmatter, M.E.; Monroe, B.D.; Thrall, D.G.; Camp, I.I.; Smith, R.D. Multidimensional proteome analysis of human mammary epithelial cells. J. Proteome Res. 2004, 3, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, C.R.; Morris, V.; Griffiths, V.; Page, V.; Pitt, A.; Stein, T.; Gusterson, B.A. Proteomic analysis of the mouse mammary gland is a powerful tool to identify novel proteins that are differentially expressed during mammary development. Proteomics 2006, 6, 694–5704. [Google Scholar]
- Reinhardt, T.A.; Lippolis, J.D. Bovine milk fat globule membrane proteome. J. Dairy Res. 2006, 73, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mather, I.H.; Keenan, T.W. Origin and secretion of milk lipids. J. Mammary Gland Biol.Neoplasia 1998, 3, 259–273. [Google Scholar]
- Mather, I.H.; Keenan, T.W. The cell biology of milk secretion: Historical notes. Introduction J. Mammary Gland Biol.Neoplasia 1998, 3, 227–232. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, J.A.; Scallan, C.D.; Ceriani, R.L.; Hamosh, M. Structural and functional aspects of three major glycoproteins of the human milk fat globule membrane. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2001, 501, 179–187. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, C.; Briad-Bion, V.; Menard, O.; Russeau, F.; Pradel, P.; Besle, J.M. Phospholipid, sphingolipid, and fatty acid compositions of the milk fat globule membrane are modified by diet. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 5226–5236. [Google Scholar]
- Fong, B.Y.; Norris, C.S. Quantification of milk fat globule membrane proteins using selected reaction monitoring mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 6021–6028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, J.A.; Hamosh, M.; Scallan, C.D.; Ceriani, R.L.; Henderson, T.R.; Mehta, N.R.; Armand, M.; Hamosh, P. Milk fat globule glycoproteins in human milk and in gastric aspirates of mother’s milk-fed preterm infants. Pediatr. Res. 1998, 44, 499–450. [Google Scholar]
- Noh, S.K.; Koo, S.L. Milk sphingomyelin is more effective than egg sphingomyelin in inhibiting intestinal absorption of cholesterol and fat in rats. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 2611–2616. [Google Scholar]
- McPherson, A.V.; Kitchen, B.J. Reviews of the progress dairy science: the bovine milk fat globule membrane—its formation, composition, structure and behaviour in milk and dairy products. J. Dairy Res. 1983, 50, 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, I.H. Proteins of the milk-fat-globule membrane as markers of mammary epithelial cells and apical plasma membrane. In The Mammary Gland: Development, Regulation and Function; Neville, M.C., Daniel, C.W., Eds.; Plenum Publ. Corp.: New York, NY, USA, 1987; pp. 217–267. [Google Scholar]
- Sordillo, L.M.; Shafer-Weaver, K.; De Rosa, D. Immunobiology of the mammary gland. J. Dairy Sci. 1997, 80, 1851–1865. [Google Scholar]
- Goldman, A.S. The immune system of human milk: antimicrobial, antiinflammatory and immunomodulating properties. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. 1993, 12, 664–671. [Google Scholar]
- Reiter, B. Review of the progress of dairy science: antimicrobial systems in milk. J. Dairy Res. 1978, 45, 131–147. [Google Scholar]
- Newburg, D.S. Human milk glycoconjugates that inhibit pathogens. Curr. Med. Chem. 1999, 6, 117–127. [Google Scholar]
- Hamosh, M.; Peterson, J.A.; Henderson, T.R.; Scallan, C.D.; Kivan, R.; Creiani, R.L.; Armand, M.; Mehta, N.R.; Hamosh, P. Protective function of human milk: The milk fat globule. Semin. Perinatol. 1999, 23, 242–249. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, J.A.; Patton, S.; Hamosh, M. Glycoproteins of thehuman milk fat globule in the protection of the breast-fed infant against infections. Biol. Neonate 1998, 74, 143–162. [Google Scholar]
- Ofek, I.; Sharon, N. Adhesins as lectins: Specificity and role in infection. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 1990, 151, 91–113. [Google Scholar]
- Keenan, T.W.; Patton, S. The structure of milk: implications for sampling and storage. In Handbook of Milk Composition; Jensen, R.G., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1995; pp. 5–49. [Google Scholar]
- Wooding, F.B. The mechanism of secretion of the milk fat globule. J. Cell Sci. 1971, 9, 805–821. [Google Scholar]
- Newburg, D.S. Human milk glycoconjugates that inhibit pathogens. Curr. Med. Chem. 1999, 6, 117–127. [Google Scholar]
- Cleary, T.G. Human milk protective mechanisms. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2004, 554, 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Stefferl, A.; Schubari, A.; Storch, M.; Amini, A.; Mather, I.; Lassm, H.; Linington, C. Butyrophilin, a milk protein, modulates the encephalitogenic T cell response to myelin oligoddendrocyte glycoprotein in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 2859–2865. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guggenmos, J.A.; Schubari, S.; Ogg, S.; Anderson, M.; Olsson, T.; Mather, I.H.; Linington, C. Antibody cross-reactivity between myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein and the milk butyrophilin in multiple sclerosis. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 661–668. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, O.; Kamata, S.; Hayashi, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Sakou, T.; Motoyoshi, S. Inhibitory effect of cream and milk fat globule membrane on hypercholesterolemia in the rat. Anim. Sci. Technol. (Japan) 1992, 63, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar]
- Picariello, G.; Ferranti, P.; Mamone, G.; Roepstorff, P.; Addeo, P. Identification of N-linked glycoproteins in human milk by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. Proteomics 2008, 8, 3833–3847. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, O.; Hotta, K.; Goso, Y.; Ishihara, K.; Sugun, T.; Morita, M.; Wadstrom, T.; Schauer, K. Milk fat globule membrane substances inhibit mouse intestinal beta-glucuronidase. J. Food Sci. 1993, 58, 753–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanno, C. Secretory membranes of the lactating mammary gland. Protoplasma 1990, 159, 184–208. [Google Scholar]
- Keenan, T.W.; Powell, E.M.; Sasaki, M.; Eigle, W.N.; Franke, W. Membranes of mammary gland. XIV. Isolation and partial characterization of a high molecular weight glycoprotein fraction from bovine milk fat globule membrane. Cytobiologie 1977, 15, 96–115. [Google Scholar]
- Astaire, J.C.; Ward, R.; German, J.B.; Jimenez-Flores, R. Concentration of polar MFGM lipids from buttermilk by microfiltration and supercritical fluid extraction. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 2297–2307. [Google Scholar]
- Oshida, K.; Shimizu, T.; Takase, M.; Tamura, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Yamashiro, Y. Effect of dietary sphingomyelin on central nervous system myelination in developing rats. Pediatr. Res. 2003, 53, 580–592. [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel, M.A.; Maier, S.F.; Einstein, G.O. “Brainspecific” nutrients: A memory cure? Nutrition 2003, 19, 955–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horrocks, L.A.; Farooqui, A.A. Docosahexaenoic acid in the diets: Its importance in main and restoration of neural membrane function. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2004, 70, 351–372. [Google Scholar]
- Spitsberg, V.L. Bovine milk fat globule membrane as a potential nutraceutical. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 88, 2289–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, N. Regulation and functional relevance of milk fat globules and their components in the mammary gland. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 2019–2027. [Google Scholar]
- Hanayama, R.; Nagata, S. Impaired involution of mammary glands in the absence of milk fat globule. EGF factor 8. PNAS 2005, 102, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, T.G.; Cundiff, L.V.; Ferrell, C.L. Molecular cloning of glycoprotein antigens MGP57/53 recognized by monoclonal antibodies raised against bovine milk fat globule membrane. J. Anim. Sci. 1991, 69, 2762–2769. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spitsberg, V.L.; Gorewit, R.C. Isolation, purification and characterization of fatty-acid-binding protein from milk fat globule membrane: Effect of bovine growth hormone treatment. Pak. J. Nutr. 2002, 1, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Spitsberg, V.L.; Matitashvili, E.; Gorewit, R.C. Association of fatty acid binding protein and glycoprotein CD36 in the bovine mammary gland. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 230, 872–878. [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani, H.; Aoki, N.; Nakagawa, Y.; Jin-No, S.; Aoyama, K.; Oshima, K.; Ohira, S.; Sato, C.; Nadano, D.; Matsuda, T. Weaning-induced expression of a milk-fat globule protein, MFG-E8, in mouse mammary glands as demonstrated by the analyses of its mRNA, protein and phosphatidylserine-binding activity. Biochem. J. 2006, 395, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, M.H.; Graversen, H.; Fedosov, S.N.; Petersen, T.E.; Rasmussen, J.T. Functional analyses of two cellular binding domains of bovine lactadherin. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 6200–6206. [Google Scholar]
- Hanayama, R.; Nagata, S. Impaired involution of mammary glands in the absence of milk fat globule EGF factor 8. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 16886–16891. [Google Scholar]
- Hanayama, R.; Tanaka, M.; Miwa, K.; Shinohara, A.; Iwamatsu, A.; Nagata, S. Identification of a factor that links apoptotic cells to phagocytes. Nature 2002, 417, 182–187. [Google Scholar]
- Hanayama, R.; Tanaka, M.; Miyasaka, K.; Aozasa, K.; Koike, M.,; Uchiyama, Y.; Nagata, S. Autoimmune disease and impaired uptake of apoptotic cells in MFGE8- deficient mice. Science 2004, 304, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atabai, K.; Fernandez, R.; Huang, X.; Ueki, I.; Kline, A.; Li, Y.; Sadatmansoori, S.; Smith-Steinhart, C.; Zhu, W.; Pytela, R.; Werb, Z.; Sheppard, D. Mfge8 is critical for mammary gland remodeling during involution. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 5528–5537. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.P.; Serrero, G. Adipose differentiation-related protein (ADRP) stimulateslipid accumulation and lipid droplet formation in murine fibroblasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1992, 89, 7856–7860. [Google Scholar]
- Eisinger, D.P.; Serrero, G. Structure of the gene encoding mouse adipose differentiation-related protein (ADRP). Genomics 1993, 16, 638–644. [Google Scholar]
- Heid, H.W.; Schno-Lzer, M.; Keenan, T.W. Adipocyte differentiation-related protein is secreted into milk as a constituent of milk lipid globule membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 270, 19439–19445. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchette-Mackie, E.J.; Dwyer, N.K.; Barber, T.; Coxey, R.A.; Takeda, T.; Rondinone, C.M.; Theodorakis, J.T.; Greenberg, A.S.; Londos, C. Perilipin is located on the surface layer of intracellular lipid droplets in adipocytes. J. Lipid Res. 1995, 36, 1211–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Zaczek, M.; Keenan, T.W. Morphological evidence for an endoplasmic reticulum origin of milk lipid globules obtained using lipid-selective staining procedures. Protoplasma 1990, 159, 179–182. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, S.; Wahl, D.; Mangold, B.L.K.; Robison, R.; Raymackers, J.; Meheus, L.; Anderson, N.L.; Cordier, A. Induction of the adipose differentiation-related protein in liver of etomoxir-treated rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 218, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hood, L.; Kronemberg, M.; Hunkapiller, T. T cell antigen receptors and the immunoglobulin supergene family. Cell 1985, 40, 225–229. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, T.B.; Lam, T.L.; Au, T.K.; Ye, X.Y.; Wan, C.C. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase, protease and integrase by bovine milk proteins. Life Sci. 2001, 69, 2217–2223. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, T.B.; Yea, X.Y. A polymeric immunoglobulin receptor-like milk protein with inhibitory activity on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 2242–2249. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Lowe, A.W. The pancreatic zymogen granule membrane protein, GP2, binds Escherichia coli type 1. BMC Gastroenterol. 2009, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, S.D.; Sakamoto, K.; Venu, R.P. GP2, the homologue to the renal cast protein uromodulin, is a major component of intraductal plugs in chronic pancreatitis. J. Clin. Invest. 1993, 92, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPherson, A.V.; Kitchen, B.J. Reviews of the progress dairy science: the bovine milk fat globule membrane—its formation, composition, structure and behaviour in milk and dairy products. J. Dairy Res. 1983, 50, 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, I.H. Proteins of the milk-fat-globule membrane as markers of mammary epithelial cells and apical plasma membrane. In The Mammary Gland: Development,Regulation and Function; Neville, M.C., Daniel, C.W., Eds.; Plenum Publ. Corp.: New York, NY, USA, 1987; pp. 217–267. [Google Scholar]
- Keenan, T.W.; Mather, I.H.; Dylewski, D.P. Physical equilibria: lipid phase. In Fundamentals of Dairy Chemistry, 3rd; Wong, N.P., Ed.; Van Nostrand Reinhold Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1987; pp. 511–582. [Google Scholar]
- Mather, I.H. A review and proposed nomenclature for major proteins of the milk-fat globule membrane. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 203–247. [Google Scholar]
- Keenan, T.W.; Patton, S. The structure of milk: Implications for sampling and storage. The milk lipid globule membrane. In A Handbook of Milk Composition; Jensen, R.G., Ed.; Academic Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 5–50. [Google Scholar]
- Quaranta, S.; Giuffrida, M.G.; Cavaletto, M.; Giunta, C.; Godovac, J.; Zimmermann, B.; Cañas, C.; Fabris, C.; Bertino, E.; Mombrò, M.; Conti, A. Human proteome enhancement: High-recovery method and improved two-dimensional map of colostral fat globule membrane proteins. Electrophoresis 2001, 22, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar]
- Wessel, D.; Flugge, U.I. A method for the quantitative recovery of protein in dilute solution in the presence of detergents and lipids. Anal. Biochem. 1984, 138, 141–143. [Google Scholar]
- Shevchenko, A.; Wilm, M.; Vorm, O.; Mann, M. Mass spectrometric sequencing of proteins from silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 850–858. [Google Scholar]
- Timperio, A.M.; D'Alessandro, A.; Pariset, L.; D'Amici, G.M.; Valentini, A.; Zolla, L. Comparative proteomics and transcriptomics analyses of livers from two different Bos taurus breeds: “Chianina and Holstein Friesian”. J. Proteomics 2009, 73, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Murgiano, L.; Timperio, A.M.; Zolla, L.; Bongiorni, S.; Valentini, A.; Pariset, L. Comparison of Milk Fat Globule Membrane (MFGM) Proteins of Chianina and Holstein Cattle Breed Milk Samples Through Proteomics Methods. Nutrients 2009, 1, 302-315. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu1020302
Murgiano L, Timperio AM, Zolla L, Bongiorni S, Valentini A, Pariset L. Comparison of Milk Fat Globule Membrane (MFGM) Proteins of Chianina and Holstein Cattle Breed Milk Samples Through Proteomics Methods. Nutrients. 2009; 1(2):302-315. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu1020302
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurgiano, Leonardo, Anna Maria Timperio, Lello Zolla, Silvia Bongiorni, Alessio Valentini, and Lorraine Pariset. 2009. "Comparison of Milk Fat Globule Membrane (MFGM) Proteins of Chianina and Holstein Cattle Breed Milk Samples Through Proteomics Methods" Nutrients 1, no. 2: 302-315. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu1020302
APA StyleMurgiano, L., Timperio, A. M., Zolla, L., Bongiorni, S., Valentini, A., & Pariset, L. (2009). Comparison of Milk Fat Globule Membrane (MFGM) Proteins of Chianina and Holstein Cattle Breed Milk Samples Through Proteomics Methods. Nutrients, 1(2), 302-315. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu1020302