Amaranthus caudatus Stimulates Insulin Secretion in Goto-Kakizaki Rats, a Model of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Plant Material
2.3. Plant Extract Preparation
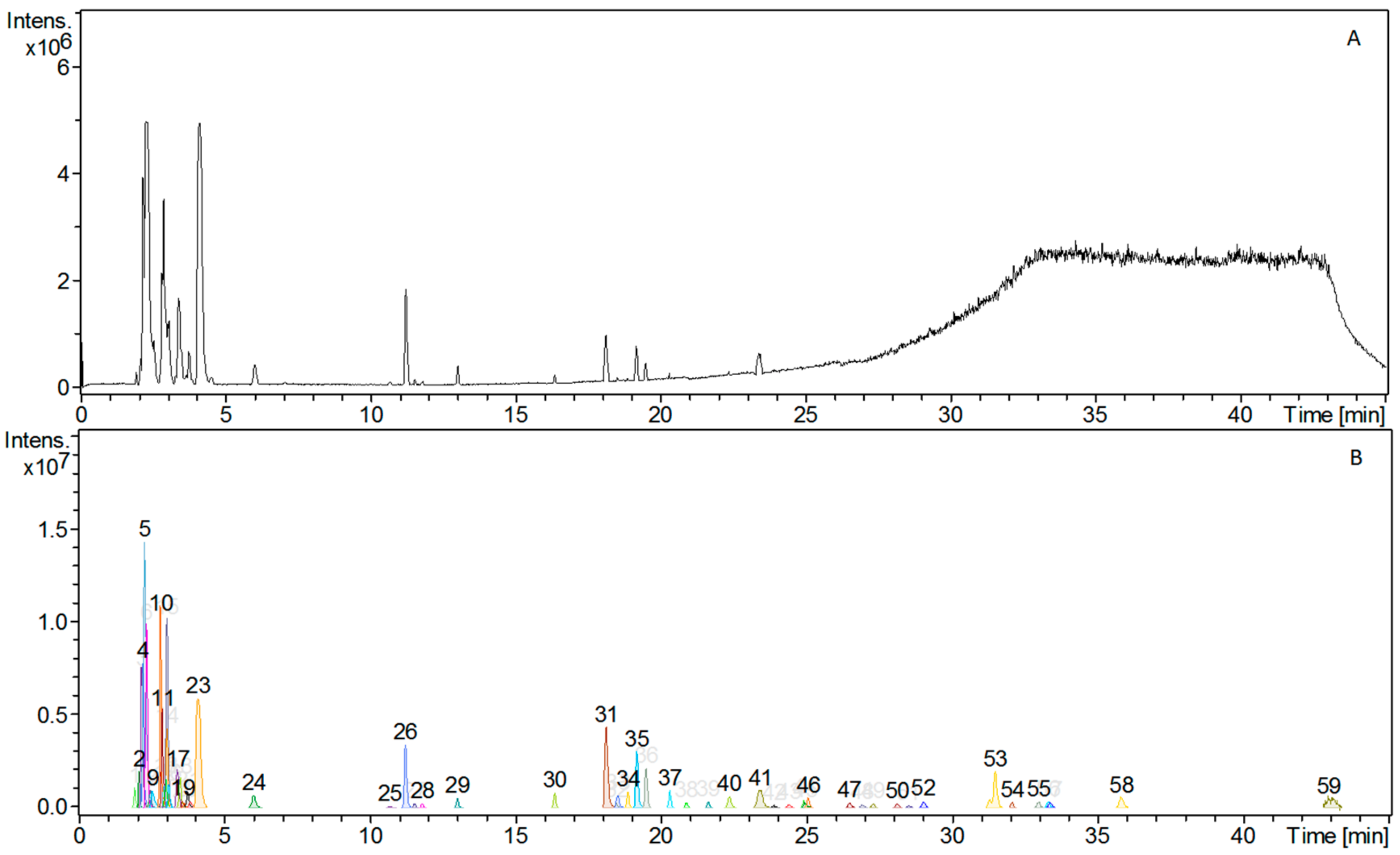
2.4. LC-MS (Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry) Analysis
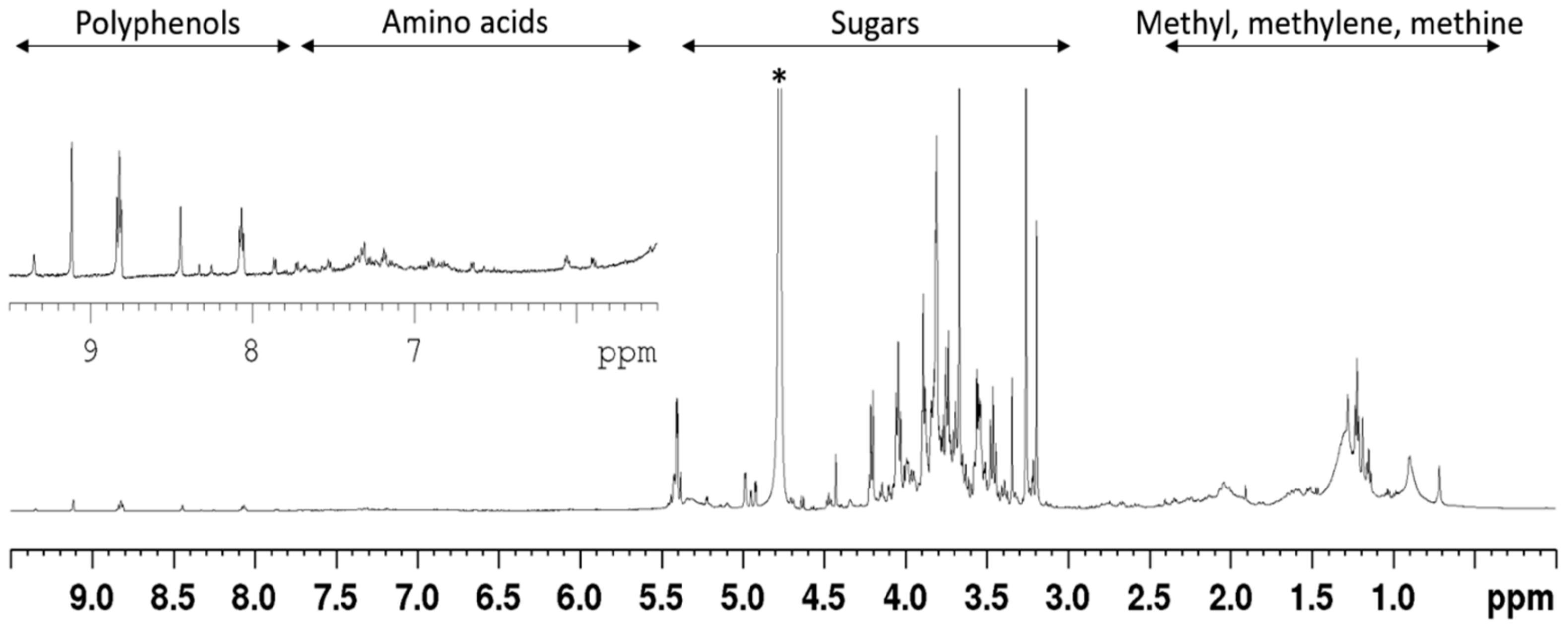
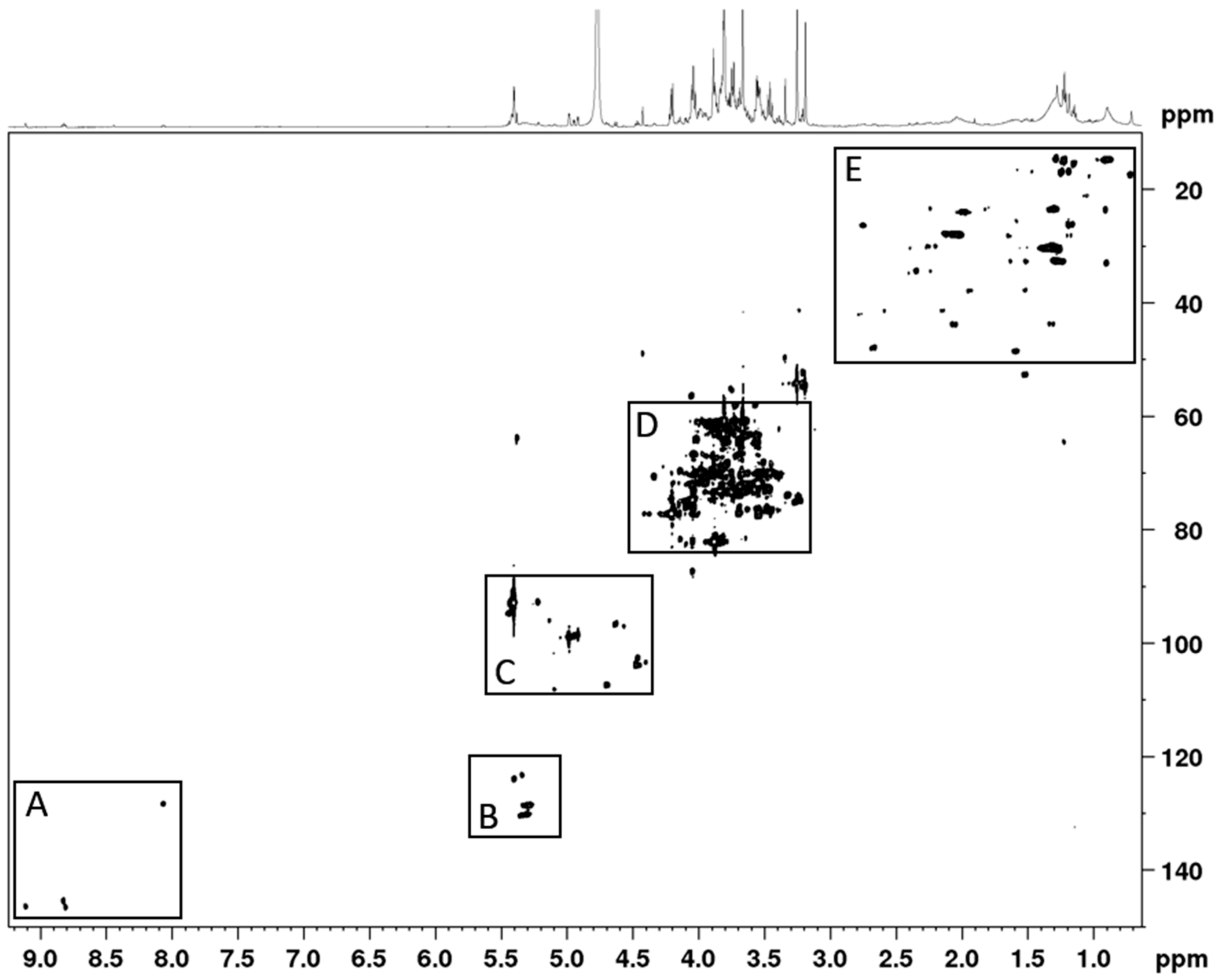
2.5. NMR Analysis
2.6. Sub-Acute Oral Toxicity
2.7. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
2.8. Long-Term Treatment Evaluation
2.9. Pancreatic Islets Isolation
2.10. Islet Insulin Secretion
2.11. Islet Perifusion
2.12. Mechanisms of Insulin Secretion Induced by AC
2.13. Cytotoxicity
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phytochemical Constituents of AC Extract
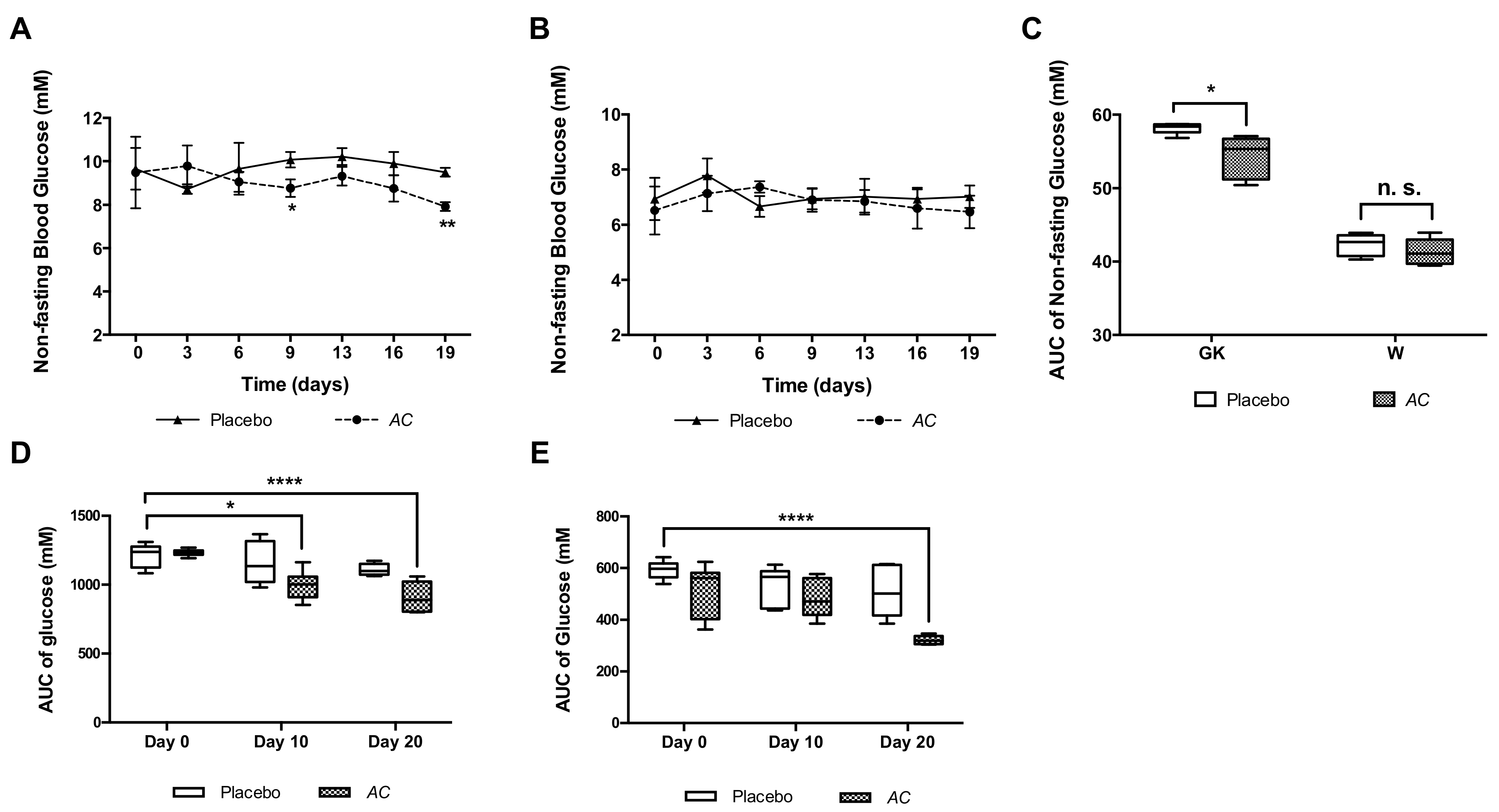
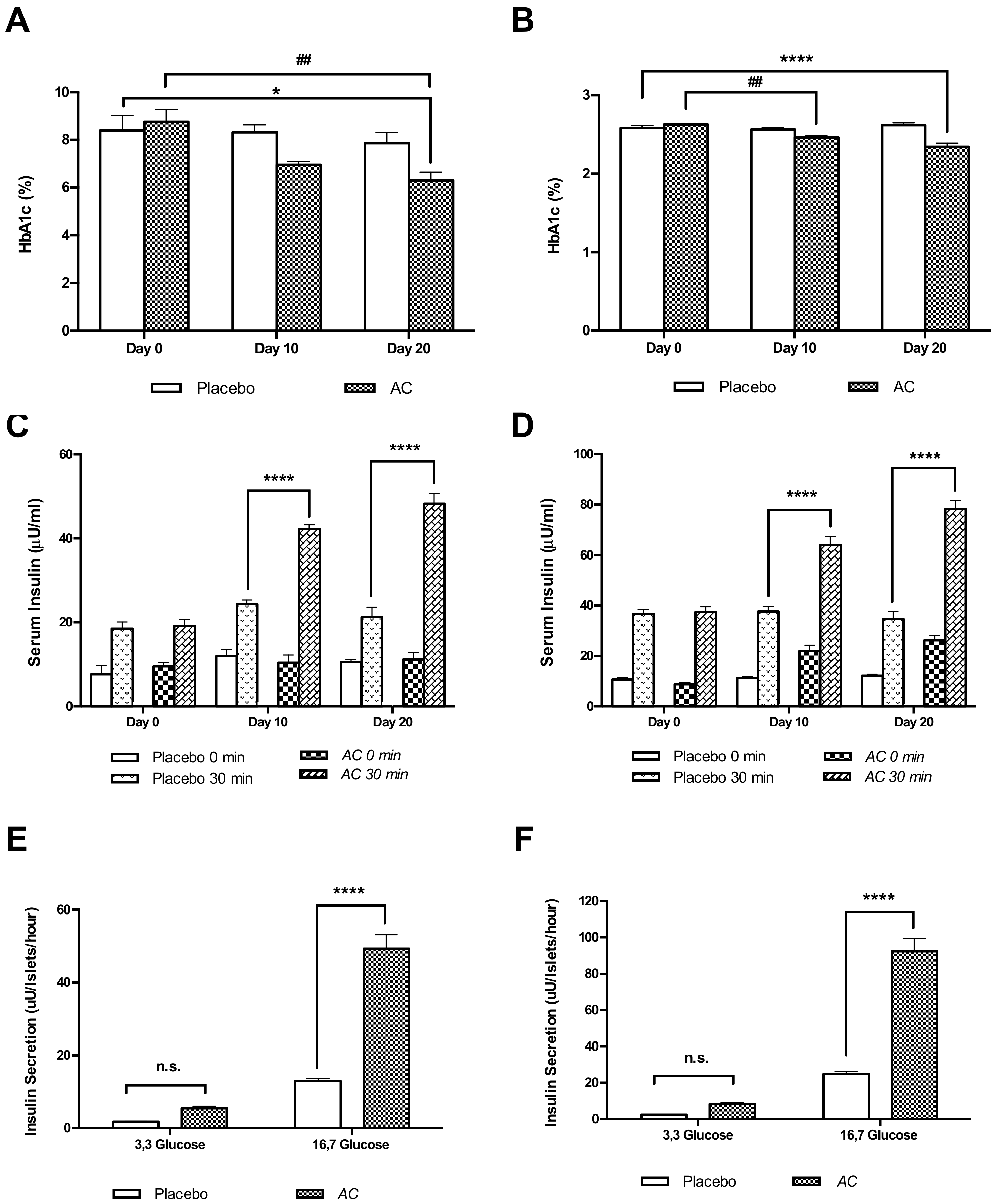
3.2. AC Improves Glucose Tolerance in GK and W Rats by Increasing Serum Insulin Levels
3.3. Long-Term Oral Treatment with AC Improves Glucose Tolerance and Insulin Secretion
3.4. AC Stimulates In Vitro Insulin Secretion in a Concentration-Dependent Manner
3.5. The AC Effect on Kinetics of Insulin Secretion
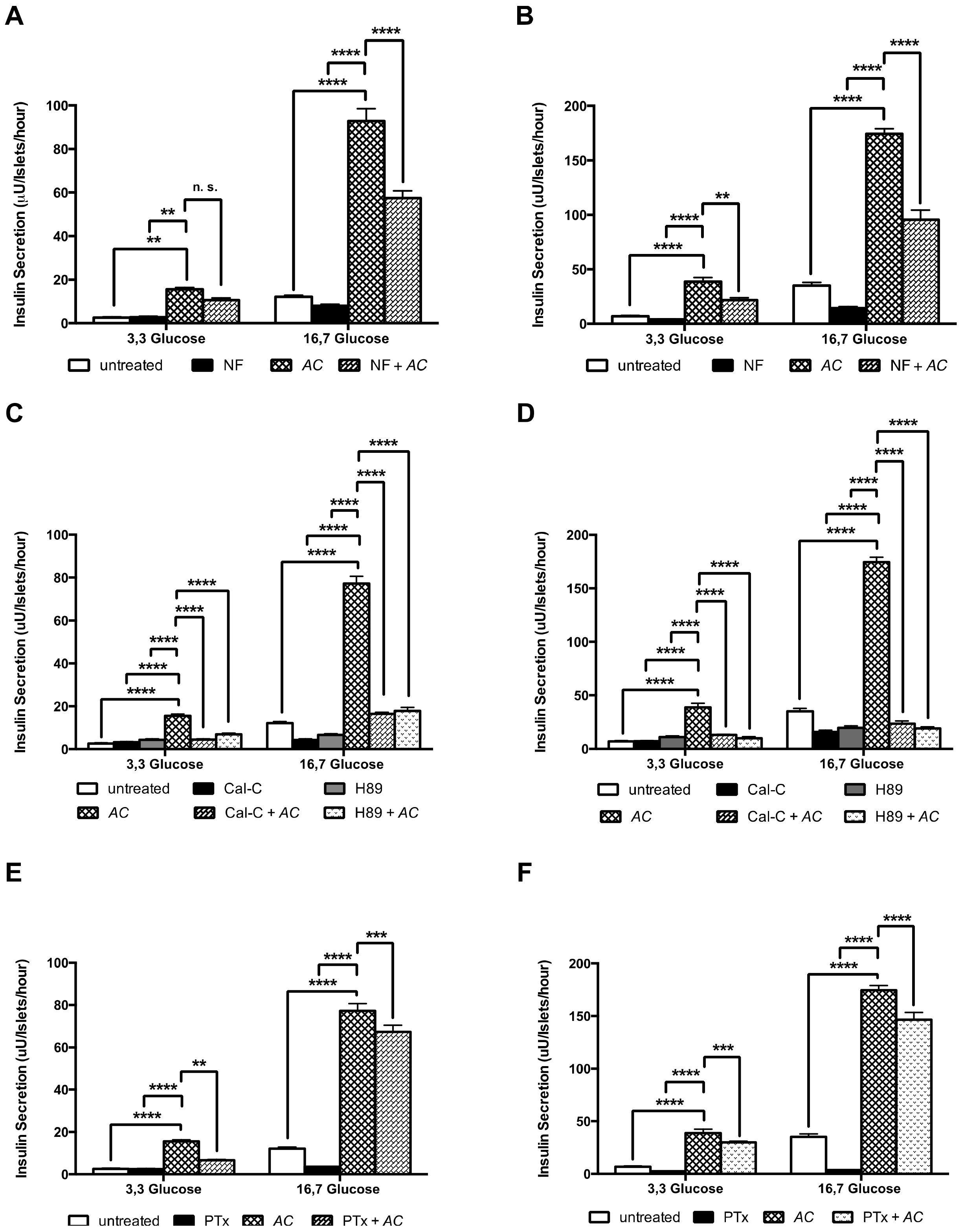
3.6. AC Stimulates Insulin Secretion through the Activation of PKC and PKA Systems and Partially by L-Type Calcium Channels and G Protein-Coupled Exocytosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ostenson, C.G. The pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus: An overview. Acta Physiol. Scand. 2001, 171, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, S.E.; Cooper, M.E.; Del Prato, S. Pathophysiology and treatment of type 2 diabetes: Perspectives on the past, present, and future. Lancet 2014, 383, 1068–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Report on Diabetes; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ogurtsova, K.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Huang, Y.; Linnenkamp, U.; Guariguata, L.; Cho, N.H.; Cavan, D.; Shaw, J.E.; Makaroff, L.E. IDF diabetes atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2007, 128, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownlee, M. The pathobiology of diabetic complications: A unifying mechanism. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlstrom, E.; Sandholm, N. Progress in defining the genetic basis of diabetic complications. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2017, 17, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thrasher, J. Pharmacologic management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: Available therapies. Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 120, S4–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios, J.L.; Francini, F.; Schinella, G.R. Natural products for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Planta Med. 2015, 81, 975–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.S.; Sohn, E.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Jung, D.H.; Jang, D.S.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, J.S. Effects of kiom-79 on hyperglycemia and diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 111, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magrone, T.; Perez de Heredia, F.; Jirillo, E.; Morabito, G.; Marcos, A.; Serafini, M. Functional foods and nutraceuticals as therapeutic tools for the treatment of diet-related diseases. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2013, 91, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.-W.; Sang, Y.-B.; Sun, W.-L.; Yu, H.-S.; Ma, B.-P.; Xiu, Z.-L.; Dong, Y.-S. Combination of flavonoids from Oroxylum Indicum seed extracts and acarbose improves the inhibition of postprandial blood glucose: In vivo and in vitro study. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 91, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, A.; Ulrih, N.P. An overview of herbal products and secondary metabolites used for management of type two diabetes. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, P.-G.; Jesús, S.-G. A critical review of bioactive food components, and of their functional mechanisms, biological effects and health outcomes. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Mandave, P.; Khadke, S.; Karandikar, M.; Pandit, V.; Ranjekar, P.; Kuvalekar, A.; Mantri, N. Antidiabetic, lipid normalizing, and nephroprotective actions of the strawberry: A potent supplementary fruit. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicero, A.F.; Tartagni, E.; Ertek, S. Nutraceuticals for metabolic syndrome management: From laboratory to benchside. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2013, 12, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, L.; Bhaumik, E.; Raychaudhuri, U.; Chakraborty, R. Role of nutraceuticals in human health. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santini, A.; Tenore, G.C.; Novellino, E. Nutraceuticals: A paradigm of proactive medicine. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 96, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijngaard, H.H.; Arendt, E.K. Buckwheat. Cereal Chem. J. 2006, 83, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Jubete, L.; Arendt, E.K.; Gallagher, E. Nutritive value and chemical composition of pseudocereals as gluten-free ingredients. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 60 (Suppl. 4), 240–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos Diaz, J.M.; Kirjoranta, S.; Tenitz, S.; Penttilä, P.A.; Serimaa, R.; Lampi, A.-M.; Jouppila, K. Use of amaranth, quinoa and kañiwa in extruded corn-based snacks. J. Cereal Sci. 2013, 58, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, R.; Medici, A.; Guerrini, A.; Scalia, S.; Poli, F.; Muzzoli, M.; Sacchetti, G. Wild Amaranthus Caudatus seed oil, a nutraceutical resource from ecuadorian flora. J. Agri. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 5455–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venskutonis, P.R.; Kraujalis, P. Nutritional components of Amaranth seeds and vegetables: A review on composition, properties, and uses. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2013, 12, 381–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conforti, F.; Statti, G.; Loizzo, M.R.; Sacchetti, G.; Poli, F.; Menichini, F. In vitro antioxidant effect and inhibition of α-amylase of two varieties of Amaranthus Caudatus seeds. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 1098–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Lakshman, K.; Jayaveera, K.N.; Sheshadri Shekar, D.; Narayan Swamy, V.B.; Khan, S.; Velumurga, C. In vitro α-amylase inhibition and antioxidant activities of methanolic extract of Amaranthus Caudatus Linn. Oman Med. J. 2011, 26, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girija, K.; Lakshman, K.; Udaya, C.; Sabhya, S.G.; Divya, T. Anti-diabetic and anti-cholesterolemic activity of methanol extracts of three species of Amaranthus. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2011, 1, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostenson, C.G.; Khan, A.; Abdel-Halim, S.M.; Guenifi, A.; Suzuki, K.; Goto, Y.; Efendic, S. Abnormal insulin secretion and glucose metabolism in pancreatic islets from the spontaneously diabetic GK rat. Diabetologia 1993, 36, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. Test No. 407: Repeated Dose 28-Day Oral Toxicity Study in Rodents; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lokman, F.E.; Gu, H.F.; Wan Mohamud, W.N.; Yusoff, M.M.; Chia, K.L.; Ostenson, C.G. Antidiabetic effect of oral borapetol B compound, isolated from the plant tinospora crispa, by stimulating insulin release. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 727602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbert, V.; Lau, K.S.; Gottlieb, C.W.; Bleicher, S.J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1965, 25, 1375–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoa, N.K.; Phan, D.V.; Thuan, N.D.; Ostenson, C.G. Insulin secretion is stimulated by ethanol extract of Anemarrhena asphodeloides in isolated islet of healthy Wistar and diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. Experimental Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2004, 112, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoa, N.K.; Norberg, A.; Sillard, R.; Van Phan, D.; Thuan, N.D.; Dzung, D.T.; Jornvall, H.; Ostenson, C.G. The possible mechanisms by which phanoside stimulates insulin secretion from rat islets. J. Endocrinol. 2007, 192, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lokman, E.F.; Gu, H.F.; Wan Mohamud, W.N.; Östenson, C.-G. Evaluation of antidiabetic effects of the traditional medicinal plant Gynostemma pentaphyllum and the possible mechanisms of insulin release. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 120572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelletier, J.; Domingues, N.; Castro, M.M.; Ostenson, C.G. In vitro effects of bis(1,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxy-4-pyridinonato)oxidovanadium(iv), or vo(dmpp)2, on insulin secretion in pancreatic islets of type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2016, 154, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.L.T.; Lin, Y.; Bartolome, A.P.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chiu, S.-C.; Yang, W.-C. Herbal therapies for type 2 diabetes mellitus: Chemistry, biology, and potential application of selected plants and compounds. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 378657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero-Quintero, K.C.; Moreno-Rojas, R.; Molina, E.A.; Colina-Barriga, M.S.; Sanchez-Urdaneta, A.B. Effect of consumption of bread with amaranth (Amaranthus Dubius Mart. ex Thell.) on glycemic response and biochemical parameters in Sprague dawley rats. Nutr. Hosp. 2014, 31, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rahmatullah, M.; Hosain, M.; Rahman, S.; Rahman, S.; Akter, M.; Rahman, F.; Rehana, F.; Munmun, M.; Kalpana, M.A. Antihyperglycaemic and antinociceptive activity evaluation of methanolic extract of whole plant of Amaranthus Tricolour L. (Amaranthaceae). Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 10, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ashok Kumar, B.S.; Lakshman, K.; Jayaveea, K.N.; Sheshadri Shekar, D.; Saleemulla, K.; Thippeswamy, B.S.; Veerapur, V.P. Antidiabetic, antihyperlipidemic and antioxidant activities of methanolic extract of Amaranthus Viridis Linn in alloxan induced diabetic rats. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 64, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy, G.; Lakshman, K.; Pruthvi, N.; Chandrika, P.U. Antihyperglycemic and hypolipidemic activity of methanolic extract of Amaranthus Viridis leaves in experimental diabetes. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2011, 43, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sangameswaran, B.; Jayakar, B. Anti-diabetic, anti-hyperlipidemic and spermatogenic effects of Amaranthus Spinosus Linn. on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Nat. Med. 2008, 62, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahren, B. Islet G protein-coupled receptors as potential targets for treatment of type 2 diabetes. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, C.J.; Berggren, P.O. New horizons in cellular regulation by inositol polyphosphates: Insights from the pancreatic β-cell. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 65, 641–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Q.-F.; Dong, Y.; Yang, H.; Lou, X.; Ding, J.; Xu, T. Protein kinase activation increases insulin secretion by sensitizing the secretory machinery to Ca2+. J. Gen. Physiol. 2004, 124, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zambrana, S.; Lundqvist, L.C.E.; Veliz, V.; Catrina, S.-B.; Gonzales, E.; Östenson, C.-G. Amaranthus caudatus Stimulates Insulin Secretion in Goto-Kakizaki Rats, a Model of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2. Nutrients 2018, 10, 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10010094
Zambrana S, Lundqvist LCE, Veliz V, Catrina S-B, Gonzales E, Östenson C-G. Amaranthus caudatus Stimulates Insulin Secretion in Goto-Kakizaki Rats, a Model of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2. Nutrients. 2018; 10(1):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10010094
Chicago/Turabian StyleZambrana, Silvia, Lena C. E. Lundqvist, Virginia Veliz, Sergiu-Bogdan Catrina, Eduardo Gonzales, and Claes-Göran Östenson. 2018. "Amaranthus caudatus Stimulates Insulin Secretion in Goto-Kakizaki Rats, a Model of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2" Nutrients 10, no. 1: 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10010094
APA StyleZambrana, S., Lundqvist, L. C. E., Veliz, V., Catrina, S.-B., Gonzales, E., & Östenson, C.-G. (2018). Amaranthus caudatus Stimulates Insulin Secretion in Goto-Kakizaki Rats, a Model of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2. Nutrients, 10(1), 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10010094



