Insulinotropic and Muscle Protein Synthetic Effects of Branched-Chain Amino Acids: Potential Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes and Sarcopenia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Branched Chain Amino Acids
3. Insulinotropic Properties of Amino Acids
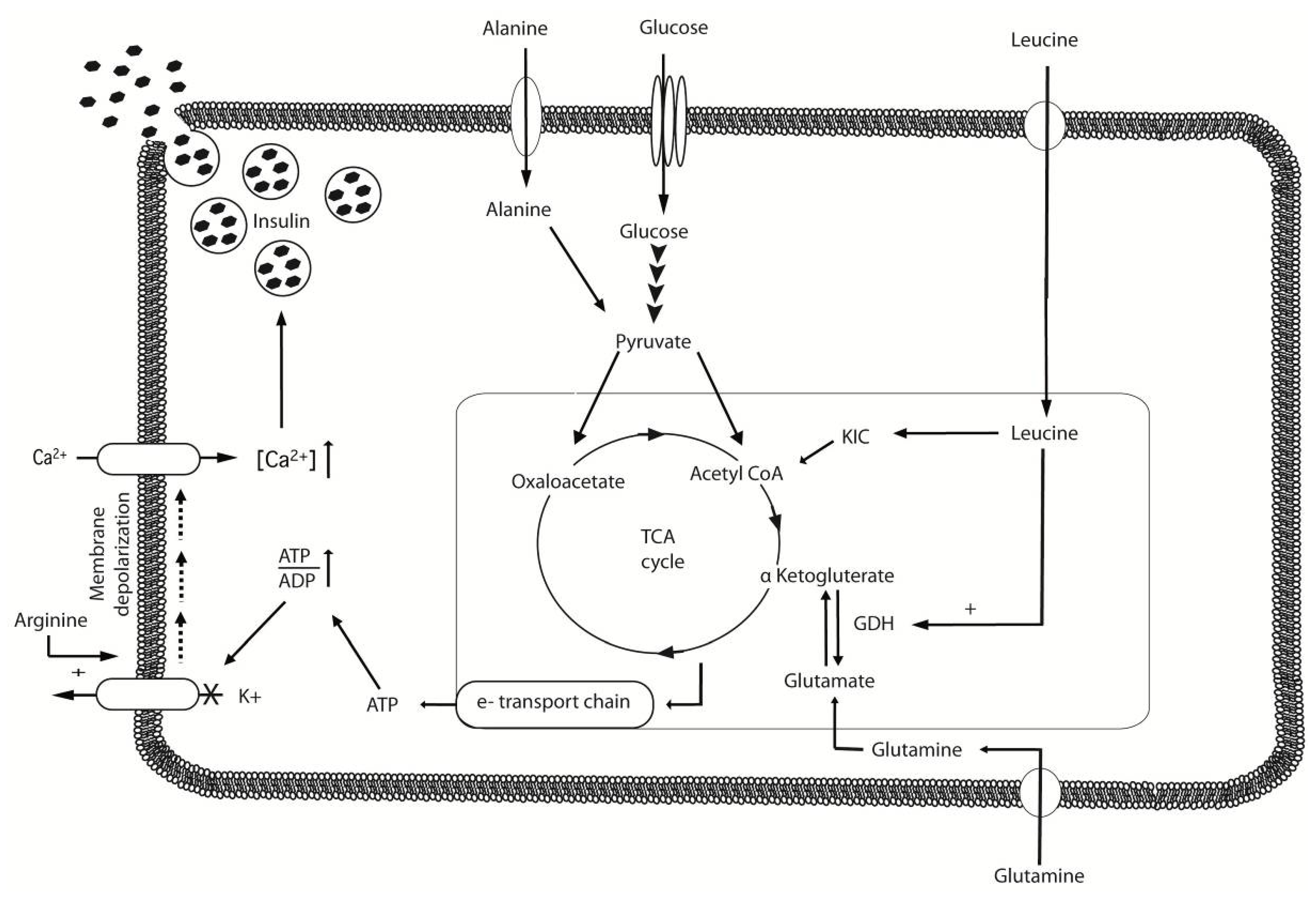
4. BCAA and Muscle Metabolic Health
5. Conclusions
Conflict of Interest
References
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Baeyens, J.P.; Bauer, J.M.; Boirie, Y.; Cederholm, T.; Landi, F.; Martin, F.C.; Michel, J.P.; Rolland, Y.; Schneider, S.M.; et al. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing 2010, 39, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candow, D.G.; Forbes, S.C.; Little, J.P.; Cornish, S.M.; Pinkoski, C.; Chilibeck, P.D. Effect of nutritional interventions and resistance exercise on aging muscle mass and strength. Biogerontology 2012, 13, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, S.C.; Little, J.P.; Candow, D.G. Exercise and nutritional interventions for improving aging muscle health. Endocrine 2012, 42, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haran, P.H.; Rivas, D.A.; Fielding, R.A. Role and potential mechanisms of anabolic resistance in sarcopenia. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2012, 3, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Leenders, M.; van Loon, L.J. Leucine as a pharmaconutrient to prevent and treat sarcopenia and type 2 diabetes. Nutr. Rev. 2011, 69, 675–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breen, L.; Phillips, S.M. Skeletal muscle protein metabolism in the elderly: Interventions to counteract the “anabolic resistance” of ageing. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimball, S.R.; Jefferson, L.S. Regulation of global and specific mRNA translation by oral administration of branched-chain amino acids. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 313, 423–427. [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbertson, D.; Smith, K.; Babraj, J.; Leese, G.; Waddell, T.; Atherton, P.; Wackerhage, H.; Taylor, P.M.; Rennie, M.J. Anabolic signaling deficits underlie amino acid resistance of wasting, aging muscle. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 422–424. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, S.; Marliss, E.B.; Morais, J.; Chevalier, S.; Gougeon, R. Insulin resistance of protein metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 2008, 57, 56–63. [Google Scholar]
- Welle, S.; Thornton, C.; Statt, M.; McHenry, B. Postprandial myofibrillar and whole body protein synthesis in young and old human subjects. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 267, E599–E604. [Google Scholar]
- Floyd, J.C.; Fajans, S.S.; Pek, S.; Thiffault, C.A.; Knopf, R.F.; Conn, J.W. Synergistic effect of essential amino acids and glucose upon insulin secretion in man. Diabetes 1970, 19, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Manders, R.J.; Koopman, R.; Sluijsmans, W.E.; van den Berg, R.; Verbeek, K.; Saris, W.H.; Wagenmakers, A.J.; van Loon, L.J. Co-ingestion of a protein hydrolysate with or without additional leucine effectively reduces post-prandial blood glucose excursions in Type 2 diabetic men. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 1294–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Riazi, R.; Wykes, L.J.; Ball, R.O.; Pencharz, P.B. The total branched-chain amino acid requirement in young healthy adult men determined by indicator amino acid oxidation by use of L-[1-13C]phenylalanine. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar]
- Layman, D.K.; Baum, J.I. Dietary protein impact on glycemic control during weight loss. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 968S–973S. [Google Scholar]
- Millward, D.J. Sufficient protein for our elders? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 1187–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Kimball, S.R.; Jefferson, L.S. Signaling pathways and molecular mechanisms through which branched-chain amino acids mediate translational control of protein synthesis. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 227S–231S. [Google Scholar]
- Alvestrand, A.; Hagenfeldt, L.; Merli, M.; Oureshi, A.; Eriksson, L.S. Influence of leucine infusion on intracellular amino acids in humans. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 1990, 20, 293–298. [Google Scholar]
- Louard, R.J.; Barrett, E.J.; Gelfand, R.A. Effect of infused branched-chain amino acids on muscle and whole-body amino acid metabolism in man. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 1990, 79, 457–466. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, K.S.; Schwartz, R.G.; Welle, S. Leucine as a regulator of whole body and skeletal muscle protein metabolism in humans. Am. J. Physiol. 1992, 263, E928–E934. [Google Scholar]
- Greiwe, J.S.; Kwon, G.; McDaniel, M.L.; Semenkovich, C.F. Leucine and insulin activate p70 S6 kinase through different pathways in human skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 281, E466–E471. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Long, W.; Fryburg, D.A.; Barrett, E.J. The regulation of body and skeletal muscle protein metabolism by hormones and amino acids. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 212S–217S. [Google Scholar]
- Kimball, S.R. The role of nutrition in stimulating muscle protein accretion at the molecular level. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 1298–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Kimball, S.R.; Jefferson, L.S. Molecular mechanisms through which amino acids mediate signaling through the mammalian target of rapamycin. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2004, 7, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennie, M.J.; Wackerhage, H.; Spangenburg, E.E.; Booth, F.W. Control of the size of the human muscle mass. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2004, 66, 799–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, S.; Dreyer, H.C.; Drummond, M.J.; Glynn, E.L.; Cadenas, J.G.; Yoshizawa, F.; Volpi, E.; Rasmussen, B.B. Nutrient signalling in the regulation of human muscle protein synthesis. J. Physiol. 2007, 582, 813–823. [Google Scholar]
- Deldicque, L.; Theisen, D.; Francaux, M. Regulation of mTOR by amino acids and resistance exercise in skeletal muscle. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 94, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Kato, H.; Hirabayashi, Y.; Murakami, H.; Suzuki, H. Modulations of muscle protein metabolism by branched-chain amino acids in normal and muscle-atrophying rats. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 234S–236S. [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson, H.K.; Nilsson, P.A.; Nilsson, J.; Chibalin, A.V.; Zierath, J.R.; Blomstrand, E. Branched-chain amino acids increase p70S6k phosphorylation in human skeletal muscle after resistance exercise. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 287, E1–E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baar, K.; Esser, K. Phosphorylation of p70(S6k) correlates with increased skeletal muscle mass following resistance exercise. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 276, C120–C127. [Google Scholar]
- Busquets, S.; Alvarez, B.; Llovera, M.; Agell, N.; Lopez-Soriano, F.J.; Argiles, J.M. Branched-chain amino acids inhibit proteolysis in rat skeletal muscle: Mechanisms involved. J. Cell. Physiol. 2000, 184, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicastro, H.; Artioli, G.G.; Costa Ados, S.; Solis, M.Y.; da Luz, C.R.; Blachier, F.; Lancha, A.H., Jr. An overview of the therapeutic effects of leucine supplementation on skeletal muscle under atrophic conditions. Amino Acids 2011, 40, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri, M. Signaling in muscle atrophy and hypertrophy. Physiology 2008, 23, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, D.J. Skeletal muscle hypertrophy and atrophy signaling pathways. Inter. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2005, 37, 1974–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, S.; Volpi, E. Amino acids and muscle loss with aging. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 277S–280S. [Google Scholar]
- Burd, N.A.; Wall, B.T.; van Loon, L.J. The curious case of anabolic resistance: Old wives’ tales or new fables? J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 112, 1233–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennie, M.J. Anabolic resistance: The effects of aging, sexual dimorphism, and immobilization on human muscle protein turnover. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2009, 34, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanos, C.S.; Kobayashi, H.; Sheffield-Moore, M.; Aarsland, A.; Wolfe, R.R. A high proportion of leucine is required for optimal stimulation of the rate of muscle protein synthesis by essential amino acids in the elderly. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 291, E381–E387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, H.C.; Drummond, M.J.; Pennings, B.; Fujita, S.; Glynn, E.L.; Chinkes, D.L.; Dhanani, S.; Volpi, E.; Rasmussen, B.B. Leucine-enriched essential amino acid and carbohydrate ingestion following resistance exercise enhances mTOR signaling and protein synthesis in human muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 294, E392–E400. [Google Scholar]
- Wall, B.T.; Hamer, H.M.; de Lange, A.; Kiskini, A.; Groen, B.B.; Senden, J.M.; Gijsen, A.P.; Verdijk, L.B.; van Loon, L.J. Leucine co-ingestion improves post-prandial muscle protein accretion in elderly men. Clin. Nutr. 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Koopman, R.; Verdijk, L.; Manders, R.J.; Gijsen, A.P.; Gorselink, M.; Pijpers, E.; Wagenmakers, A.J.; van Loon, L.J. Co-ingestion of protein and leucine stimulates muscle protein synthesis rates to the same extent in young and elderly lean men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 623–632. [Google Scholar]
- Casperson, S.L.; Sheffield-Moore, M.; Hewlings, S.J.; Paddon-Jones, D. Leucine supplementation chronically improves muscle protein synthesis in older adults consuming the RDA for protein. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhaff, P.L.; Karagounis, L.G.; Peirce, N.; Simpson, E.J.; Hazell, M.; Layfield, R.; Wackerhage, H.; Smith, K.; Atherton, P.; Selby, A.; Rennie, M.J. Disassociation between the effects of amino acids and insulin on signaling, ubiquitin ligases, and protein turnover in human muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 295, E595–E604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallotta, J.A.; Kennedy, P.J. Response of plasma insulin and growth hormone to carbohydrate and protein feeding. Metabolism 1968, 17, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowitz, D.; Merimee, T.J.; Maffezzoli, R.; Burgess, J.A. Patterns of hormonal release after glucose, protein, and glucose plus protein. Lancet 1966, 2, 454–456. [Google Scholar]
- Nuttall, F.Q.; Gannon, M.C.; Wald, J.L.; Ahmed, M. Plasma glucose and insulin profiles in normal subjects ingesting diets of varying carbohydrate, fat, and protein content. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1985, 4, 437–450. [Google Scholar]
- Nuttall, F.Q.; Mooradian, A.D.; Gannon, M.C.; Billington, C.; Krezowski, P. Effect of protein ingestion on the glucose and insulin response to a standardized oral glucose load. Diabetes Care 1984, 7, 465–470. [Google Scholar]
- Gannon, M.C.; Nuttall, F.Q.; Lane, J.T.; Burmeister, L.A. Metabolic response to cottage cheese or egg white protein, with or without glucose, in type II diabetic subjects. Metabolism 1992, 41, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannon, M.C.; Nuttall, F.Q.; Grant, C.T.; Ercan-Fang, S.; Ercan-Fang, N. Stimulation of insulin secretion by fructose ingested with protein in people with untreated type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 1998, 21, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Fajans, S.S.; Knopf, R.F.; Floyd, J.C., Jr.; Power, L.; Conn, J.W. The experimental induction in man of sensitivity to leucine hypoglycemia. J. Clin. Invest. 1963, 42, 216–229. [Google Scholar]
- Floyd, J.C., Jr.; Fajans, S.S.; Conn, J.W.; Knopf, R.F.; Rull, J. Stimulation of insulin secretion by amino acids. J. Clin. Invest. 1966, 45, 1487–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, J.C., Jr.; Fajans, S.S.; Conn, J.W.; Thiffault, C.; Knopf, R.F.; Guntsche, E. Secretion of insulin induced by amino acids and glucose in diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1968, 28, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, J.C., Jr.; Fajans, S.S.; Knopf, R.F.; Conn, J.W. Evidence that insulin release is the mechanism for experimentally induced leucine hypoglycemia in man. J. Clin. Invest. 1963, 42, 1714–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, J.C., Jr.; Fajans, S.S.; Pek, S.; Thiffault, C.A.; Knopf, R.F.; Conn, J.W. Synergistic effect of certain amino acid pairs upon insulin secretion in man. Diabetes 1970, 19, 102–108. [Google Scholar]
- Blachier, F.; Leclercq-Meyer, V.; Marchand, J.; Woussen Colle, M.C.; Mathias, P.C.; Sener, A.; Malaisse, W.J. Stimulus-secretion coupling of arginine-induced insulin release. Functional response of islets to L-arginine and L-ornithine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1989, 1013, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sener, A.; Hutton, J.C.; Malaisse, W.J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of amino acid-induced insulin release. Synergistic effects of L-glutamine and 2-keto acids upon insulin secretion. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1981, 677, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaisse, W.J.; Plasman, P.O.; Blachier, F.; Herchuelz, A.; Sener, A. Stimulus-secretion coupling of arginine-induced insulin release: Significance of changes in extracellular and intracellular pH. Cell Biochem. Funct. 1991, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- McClenaghan, N.H.; Barnett, C.R.; O’Harte, F.P.; Flatt, P.R. Mechanisms of amino acid-induced insulin secretion from the glucose-responsive BRIN-BD11 pancreatic B-cell line. J. Endocrinol. 1996, 151, 349–357. [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers, D.G.; Schuit, F.C.; in’t Veld, P.A.; Maes, E.; Hooghe-Peters, E.L.; van de Winkel, M.; Gepts, W. Interplay of nutrients and hormones in the regulation of insulin release. Endocrinology 1985, 117, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwanstecher, C.; Meyer, M.; Schwanstecher, M.; Panten, U. Interaction of N-benzoyl-D-phenylalanine and related compounds with the sulphonylurea receptor of beta-cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 123, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Kwon, G.; Cruz, W.S.; Marshall, C.A.; McDaniel, M.L. Metabolic regulation by leucine of translation initiation through the mTOR-signaling pathway by pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes 2001, 50, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajoix, A.D.; Reggio, H.; Chardes, T.; Peraldi-Roux, S.; Tribillac, F.; Roye, M.; Dietz, S.; Broca, C.; Manteghetti, M.; Ribes, G.; Wollheim, C.B.; Gross, R. A neuronal isoform of nitric oxide synthase expressed in pancreatic beta-cells controls insulin secretion. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1311–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsholme, P.; Brennan, L.; Rubi, B.; Maechler, P. New insights into amino acid metabolism, beta-cell function and diabetes. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 2005, 108, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sener, A.; Malaisse, W.J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of amino acid-induced insulin release. Insulinotropic action of L-alanine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1573, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, M.J.; Yule, D.I.; Gallacher, D.V.; Petersen, O.H. Effects of alanine on insulin-secreting cells: Patch-clamp and single cell intracellular Ca2+ measurements. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1990, 1055, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, L.; Shine, A.; Hewage, C.; Malthouse, J.P.; Brindle, K.M.; McClenaghan, N.; Flatt, P.R.; Newsholme, P. A nuclear magnetic resonance-based demonstration of substantial oxidative L-alanine metabolism and L-alanine-enhanced glucose metabolism in a clonal pancreatic beta-cell line: Metabolism of L-alanine is important to the regulation of insulin secretion. Diabetes 2002, 51, 1714–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahien, L.A.; MacDonald, M.J.; Kmiotek, E.H.; Mertz, R.J.; Fahien, C.M. Regulation of insulin release by factors that also modify glutamate dehydrogenase. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 13610–13614. [Google Scholar]
- Sener, A.; Malaisse, W.J. L-leucine and a nonmetabolized analogue activate pancreatic islet glutamate dehydrogenase. Nature 1980, 288, 187–189. [Google Scholar]
- Panten, U.; Kriegstein, E.; Poser, W.; Schonborn, J.; Hasselblatt, A. Effects of L-leucine and alpha-ketoisocaproic acid upon insulin secretion and metabolism of isolated pancreatic islets. FEBS Lett. 1972, 20, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, R.; Wagenmakers, A.J.; Manders, R.J.; Zorenc, A.H.; Senden, J.M.; Gorselink, M.; Keizer, H.A.; van Loon, L.J. Combined ingestion of protein and free leucine with carbohydrate increases postexercise muscle protein synthesis in vivo in male subjects. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 288, E645–E653. [Google Scholar]
- Porte, D., Jr.; Kahn, S.E. beta-cell dysfunction and failure in type 2 diabetes: Potential mechanisms. Diabetes 2001, 50, S160–S163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polonsky, K.S.; Sturis, J.; Bell, G.I. Seminars in Medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston. Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus—a genetically programmed failure of the beta cell to compensate for insulin resistance. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loon, L.J.C.; Kruishoop, M.; Menheere, P.P.C.A.; Wagenmakers, A.J.M.; Saris, W.H.M.; Keizer, H.A. Amino acid ingestion strongly enhances insulin secretion in patients with long-term type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 625–630. [Google Scholar]
- Manders, R.J.; Wagenmakers, A.J.; Koopman, R.; Zorenc, A.H.; Menheere, P.P.; Schaper, N.C.; Saris, W.H.; van Loon, L.J. Co-ingestion of a protein hydrolysate and amino acid mixture with carbohydrate improves plasma glucose disposal in patients with type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 76–83. [Google Scholar]
- Manders, R.J.; Praet, S.F.; Meex, R.C.; Koopman, R.; de Roos, A.L.; Wagenmakers, A.J.; Saris, W.H.; van Loon, L.J. Protein hydrolysate/leucine co-ingestion reduces the prevalence of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 2721–2722. [Google Scholar]
- Manders, R.J.; Praet, S.F.; Vikstrom, M.H.; Saris, W.H.; van Loon, L.J. Protein hydrolysate co-ingestion does not modulate 24 h glycemic control in long-standing type 2 diabetes patients. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 63, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frid, A.H.; Nilsson, M.; Holst, J.J.; Bjorck, I.M. Effect of whey on blood glucose and insulin responses to composite breakfast and lunch meals in type 2 diabetic subjects. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, M.; Stenberg, M.; Frid, A.H.; Holst, J.J.; Bjorck, I.M. Glycemia and insulinemia in healthy subjects after lactose-equivalent meals of milk and other food proteins: The role of plasma amino acids and incretins. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 1246–1253. [Google Scholar]
- Gannon, M.C.; Nuttall, F.Q. Effect of a high-protein, low-carbohydrate diet on blood glucose control in people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2004, 53, 2375–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannon, M.C.; Nuttall, F.Q.; Saeed, A.; Jordan, K.; Hoover, H. An increase in dietary protein improves the blood glucose response in persons with type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 78, 734–741. [Google Scholar]
- Nuttall, F.Q.; Schweim, K.; Hoover, H.; Gannon, M.C. Effect of the LoBAG30 diet on blood glucose control in people with type 2 diabetes. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 99, 511–519. [Google Scholar]
- Astrup, A. The satiating power of protein—a key to obesity prevention? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Weigle, D.S.; Breen, P.A.; Matthys, C.C.; Callahan, H.S.; Meeuws, K.E.; Burden, V.R.; Purnell, J.Q. A high-protein diet induces sustained reductions in appetite, ad libitum caloric intake, and body weight despite compensatory changes in diurnal plasma leptin and ghrelin concentrations. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Lejeune, M.P.; Kovacs, E.M.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S. Additional protein intake limits weight regain after weight loss in humans. Br. J. Nutr. 2005, 93, 281–289. [Google Scholar]
- Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S.; Lejeune, M.P. Protein intake and body-weight regulation. Appetite 2005, 45, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Due, A.; Toubro, S.; Skov, A.R.; Astrup, A. Effect of normal-fat diets, either medium or high in protein, on body weight in overweight subjects: A randomised 1-year trial. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2004, 28, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsholme, P.; Brennan, L.; Bender, K. Amino Acid Metabolism, {beta}-Cell Function, and Diabetes. Diabetes 2006, 55, S39–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiebaud, D.; Jacot, E.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Maeder, E.; Jequier, E.; Felber, J.P. The effect of graded doses of insulin on total glucose uptake, glucose oxidation, and glucose storage in man. Diabetes 1982, 31, 957–963. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, K.F.; Befroy, D.; Dufour, S.; Dziura, J.; Ariyan, C.; Rothman, D.L.; DiPietro, L.; Cline, G.W.; Shulman, G.I. Mitochondrial dysfunction in the elderly: Possible role in insulin resistance. Science 2003, 300, 1140–1142. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, K.F.; Dufour, S.; Befroy, D.; Garcia, R.; Shulman, G.I. Impaired Mitochondrial Activity in the Insulin-Resistant Offspring of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogensen, M.; Sahlin, K.; Fernstrom, M.; Glintborg, D.; Vind, B.F.; Beck-Nielsen, H.; Hojlund, K. Mitochondrial Respiration Is Decreased in Skeletal Muscle of Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1592–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Antona, G.; Ragni, M.; Cardile, A.; Tedesco, L.; Dossena, M.; Bruttini, F.; Caliaro, F.; Corsetti, G.; Bottinelli, R.; Carruba, M.O.; Valerio, A.; Nisoli, E. Branched-Chain Amino Acid Supplementation Promotes Survival and Supports Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Middle-Aged Mice. Cell Metab. 2010, 12, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, K.; LeBlanc, R.E.; Loh, D.; Schwartz, G.J.; Yu, Y.H. Increasing dietary leucine intake reduces diet-induced obesity and improves glucose and cholesterol metabolism in mice via multimechanisms. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1647–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solerte, S.B.; Fioravanti, M.; Locatelli, E.; Bonacasa, R.; Zamboni, M.; Basso, C.; Mazzoleni, A.; Mansi, V.; Geroutis, N.; Gazzaruso, C. Improvement of Blood Glucose Control and Insulin Sensitivity during a Long-Term (60 Weeks) Randomized Study with Amino Acid Dietary Supplements in Elderly Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 101, S82–S88. [Google Scholar]
- Valerio, A.; D’Antona, G.; Nisoli, E. Branched-chain amino acids, mitochondrial biogenesis, and healthspan: An evolutionary perspective. Aging 2011, 3, 464–478. [Google Scholar]
- Newgard, C.B.; An, J.; Bain, J.R.; Muehlbauer, M.J.; Stevens, R.D.; Lien, L.F.; Haqq, A.M.; Shah, S.H.; Arlotto, M.; Slentz, C.A.; et al. A Branched-Chain Amino Acid-Related Metabolic Signature that Differentiates Obese and Lean Humans and Contributes to Insulin Resistance. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.J.; Larson, M.G.; Vasan, R.S.; Cheng, S.; Rhee, E.P.; McCabe, E.; Lewis, G.D.; Fox, C.S.; Jacques, P.F.; Fernandez, C.; et al. Metabolite profiles and the risk of developing diabetes. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 448–453. [Google Scholar]
- Patti, M.E.; Brambilla, E.; Luzi, L.; Landaker, E.J.; Kahn, C.R. Bidirectional modulation of insulin action by amino acids. J. Clin. Invest. 1998, 101, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay, F.; Jacques, H.; Marette, A. Modulation of insulin action by dietary proteins and amino acids: Role of the mammalian target of rapamycin nutrient sensing pathway. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2005, 8, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, F.; Marette, A. Amino acid and insulin signaling via the mTOR/p70 S6 kinase pathway. A negative feedback mechanism leading to insulin resistance in skeletal muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 38052–38060. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Manders, R.J.; Little, J.P.; Forbes, S.C.; Candow, D.G. Insulinotropic and Muscle Protein Synthetic Effects of Branched-Chain Amino Acids: Potential Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes and Sarcopenia. Nutrients 2012, 4, 1664-1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu4111664
Manders RJ, Little JP, Forbes SC, Candow DG. Insulinotropic and Muscle Protein Synthetic Effects of Branched-Chain Amino Acids: Potential Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes and Sarcopenia. Nutrients. 2012; 4(11):1664-1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu4111664
Chicago/Turabian StyleManders, Ralph J., Jonathan P. Little, Scott C. Forbes, and Darren G. Candow. 2012. "Insulinotropic and Muscle Protein Synthetic Effects of Branched-Chain Amino Acids: Potential Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes and Sarcopenia" Nutrients 4, no. 11: 1664-1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu4111664



