Interaction between Single Nucleotide Polymorphism and Urinary Sodium, Potassium, and Sodium-Potassium Ratio on the Risk of Hypertension in Korean Adults
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
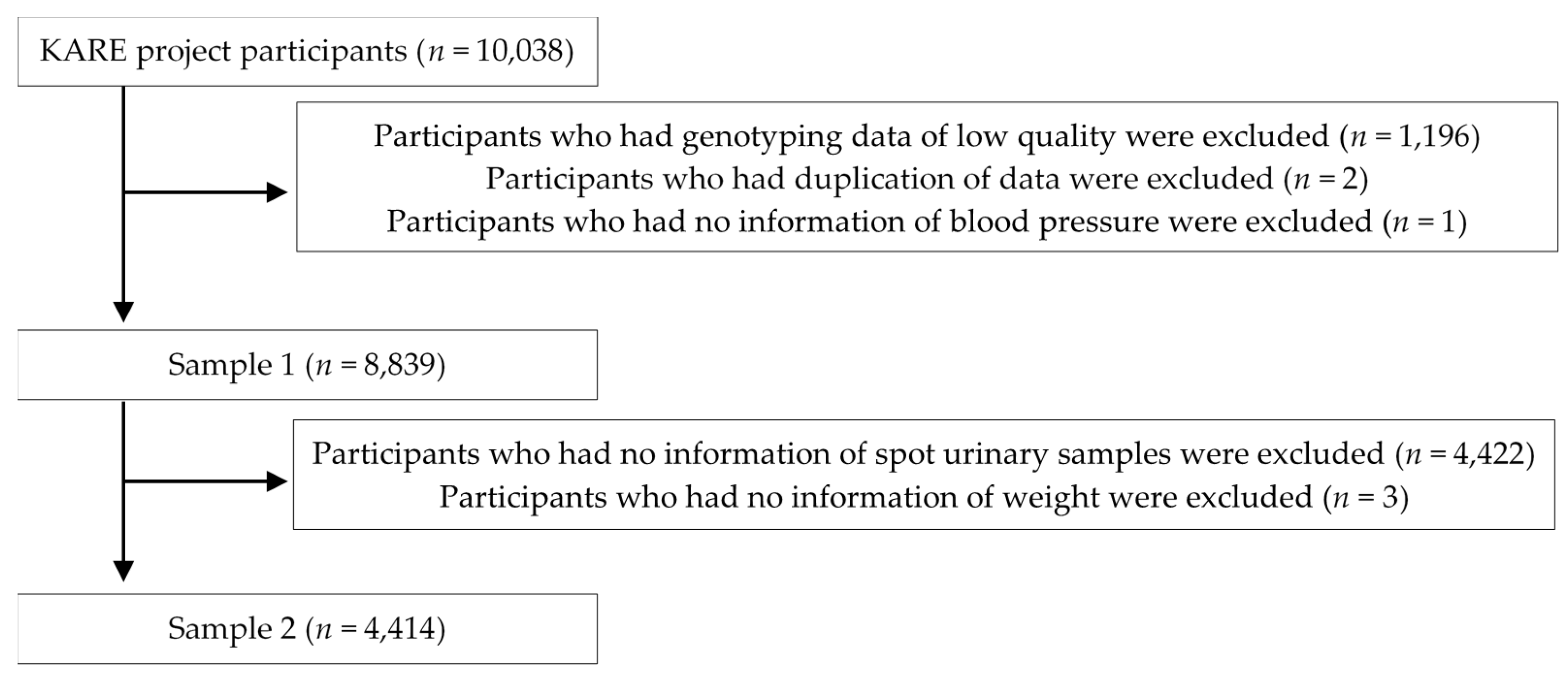
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Anthropometric Measurement and Collection of Urinary Samples
2.3. Genotyping and Imputation of SNPs
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism |
| GWAS | Genome wide association study |
| BRLMM | Bayesian Robust Linear Modeling Mahalanobis |
| GLM | General linear model |
| ORs | Odds ratios |
| CIs | Confidence intervals |
| LD | Linkage disequilibrium |
| 24HUNa | 24 h urinary Na |
| 24HUK | 24 h urinary K |
| 24HUNa-K ratio | 24 h urinary Na-K ratio |
References
- Mackay, J.; Mensah, G.A. The Atlas of Heart Disease and Stroke; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Alwan, A. Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Diseases 2010; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Health and Welfare of Korea; Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Korea Health Statistics 2014: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (knhanes vi-2); Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Cheongju, Korea, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, K.W.; Jin, H.S.; Cho, Y.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, J.E.; Cho, N.H.; Shin, C.; Lee, S.H.; Park, H.K.; Oh, B. Replication of the wellcome trust genome-wide association study on essential hypertension in a korean population. Hypertens. Res. 2009, 32, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, K.W.; Jin, H.S.; Lim, J.E.; Kim, S.; Go, M.J.; Oh, B. Recapitulation of two genomewide association studies on blood pressure and essential hypertension in the korean population. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 55, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.K.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, G.Y.; Baik, I.; Lim, H.E.; Park, C.G.; Lee, J.B.; Kim, Y.H.; Lim, S.Y.; Kim, H.; et al. Obesity phenotype and incident hypertension: A prospective community-based cohort study. J. Hypertens. 2013, 31, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, K.W.; Jin, H.S.; Lim, J.E.; Cho, Y.S.; Go, M.J.; Jung, J.; Lee, J.E.; Choi, J.; Shin, C.; Hwang, S.Y.; et al. Non-synonymous single-nucleotide polymorphisms associated with blood pressure and hypertension. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2010, 24, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.S.; Hong, K.W.; Lim, J.E.; Hwang, S.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Shin, C.; Park, H.K.; Oh, B. Genetic variations in the sodium balance-regulating genes ENaC, NEDD4L, NDFIP2 and USP2 influence blood pressure and hypertension. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2010, 33, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, S.H.; Yun, C.H.; Kim, J.H.; Thomas, R.J.; Shin, C. Genetic association of short sleep duration with hypertension incidence—a 6-year follow-up in the korean genome and epidemiology study. Circ. J. 2012, 76, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, K.W.; Go, M.J.; Jin, H.S.; Lim, J.E.; Lee, J.Y.; Han, B.G.; Hwang, S.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Park, H.K.; Cho, Y.S.; et al. Genetic variations in ATP2B1, CSK, ARSG and CSMD1 LOCI are related to blood pressure and/or hypertension in two korean cohorts. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2010, 24, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.S.; Sober, S.; Hong, K.W.; Org, E.; Kim, B.Y.; Laan, M.; Oh, B.; Jeong, S.Y. Age-dependent association of the polymorphisms in the mitochondria-shaping gene, OPA1, with blood pressure and hypertension in korean population. Am. J. Hypertens. 2011, 24, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, M.Y.; Yang, S.J.; Oh, S.W.; Park, Y.; Kim, C.I.; Park, H.K.; Park, S.W.; Park, C.Y. Novel genetic variations associated with salt sensitivity in the korean population. Hypertens. Res. 2011, 34, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binia, A.; Jaeger, J.; Hu, Y.; Singh, A.; Zimmermann, D. Daily potassium intake and sodium-to-potassium ratio in the reduction of blood pressure: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Hypertens. 2015, 33, 1509–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.; Raj, T.S.; Trudeau, L.; Bacon, S.L.; Padwal, R.; Webster, J.; Campbell, N. The science of salt: A systematic review of clinical salt studies 2013 to 2014. J. Clin. Hypertens. (Greenwich) 2015, 17, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendriksen, M.A.; van Raaij, J.M.; Geleijnse, J.M.; Breda, J.; Boshuizen, H.C. Health gain by salt reduction in europe: A modelling study. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0118873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacks, F.M.; Svetkey, L.P.; Vollmer, W.M.; Appel, L.J.; Bray, G.A.; Harsha, D.; Obarzanek, E.; Conlin, P.R.; Miller, E.R., 3rd; Simons-Morton, D.G.; et al. Effects on blood pressure of reduced dietary sodium and the dietary approaches to stop hypertension (dash) diet. Dash-sodium collaborative research group. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, F.J.; Li, J.; MacGregor, G.A. Effect of longer term modest salt reduction on blood pressure: Cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. BMJ 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aburto, N.J.; Ziolkovska, A.; Hooper, L.; Elliott, P.; Cappuccio, F.P.; Meerpohl, J.J. Effect of lower sodium intake on health: Systematic review and meta-analyses. BMJ 2013, 346, f1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, V.; Chang, E.T. Sodium-to-potassium ratio and blood pressure, hypertension, and related factors. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 712–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gay, H.C.; Rao, S.G.; Vaccarino, V.; Ali, M.K. Effects of different dietary interventions on blood pressure: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Hypertension 2016, 67, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelton, P.K.; He, J.; Cutler, J.A.; Brancati, F.L.; Appel, L.J.; Follmann, D.; Klag, M.J. Effects of oral potassium on blood pressure. Meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. JAMA 1997, 277, 1624–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Who Guideline: Sodium Intake for Adults and Children; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- McLean, R.M. Measuring population sodium intake: A review of methods. Nutrients 2014, 6, 4651–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Okamura, T.; Miura, K.; Kadowaki, T.; Ueshima, H.; Nakagawa, H.; Hashimoto, T. A simple method to estimate populational 24-h urinary sodium and potassium excretion using a casual urine specimen. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2002, 16, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, T.; Itoh, K.; Uezono, K.; Sasaki, H. A simple method for estimating 24 h urinary sodium and potassium excretion from second morning voiding urine specimen in adults. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1993, 20, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mente, A.; O’Donnell, M.J.; Rangarajan, S.; McQueen, M.J.; Poirier, P.; Wielgosz, A.; Morrison, H.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Di, C.; et al. Association of urinary sodium and potassium excretion with blood pressure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, M.; Mente, A.; Rangarajan, S.; McQueen, M.J.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Yan, H.; Lee, S.F.; Mony, P.; Devanath, A.; et al. Urinary sodium and potassium excretion, mortality, and cardiovascular events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, M.J.; Yusuf, S.; Mente, A.; Gao, P.; Mann, J.F.; Teo, K.; McQueen, M.; Sleight, P.; Sharma, A.M.; Dans, A.; et al. Urinary sodium and potassium excretion and risk of cardiovascular events. JAMA 2011, 306, 2229–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaw, K.-T.; Bingham, S.; Welch, A.; Luben, R.; O’Brien, E.; Wareham, N.; Day, N. Blood pressure and urinary sodium in men and women: The norfolk cohort of the european prospective investigation into cancer (epic-norfolk). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 1397–1403. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Franco, V.; Oparil, S. Salt sensitivity, a determinant of blood pressure, cardiovascular disease and survival. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2006, 25, 247S–255S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.S.; Go, M.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Heo, J.Y.; Oh, J.H.; Ban, H.J.; Yoon, D.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, D.J.; Park, M.; et al. A large-scale genome-wide association study of asian populations uncovers genetic factors influencing eight quantitative traits. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabbee, N.; Speed, T.P. A genotype calling algorithm for affymetrix SNP arrays. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchini, J.; Howie, B.; Myers, S.; McVean, G.; Donnelly, P. A new multipoint method for genome-wide association studies by imputation of genotypes. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature 2007, 447, 661–678. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, C.S.; Eberle, M.A.; Rieder, M.J.; Yi, Q.; Kruglyak, L.; Nickerson, D.A. Selecting a maximally informative set of single-nucleotide polymorphisms for association analyses using linkage disequilibrium. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 74, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plink. Available online: http://pngu.mgh.harvard.edu/~purcell/plink (accessed on 4 July 2016).
- Haddy, F.J.; Pamnani, M.B. Role of dietary salt in hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1995, 14, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, U.N. Nutritional factors in the pathobiology of human essential hypertension. Nutrition 2001, 17, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, P.P.; Black, H.R. The role of diet in the genesis and treatment of hypertension. Med. Clin. North. Am. 1993, 77, 831–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, A.C.; Bis, J.C.; Hwang, S.J.; Ehret, G.B.; Lumley, T.; Rice, K.; Muzny, D.; Gibbs, R.A.; Boerwinkle, E.; Psaty, B.M.; et al. Sequence analysis of six blood pressure candidate regions in 4,178 individuals: The cohorts for heart and aging research in genomic epidemiology (charge) targeted sequencing study. PLoS One 2014, 9, e109155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Gao, P.; Jin, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, D. Common variants in the ATP2B1 gene are associated with hypertension and arterial stiffness in chinese population. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 1867–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Li, H.; Qi, Q.; Lu, L.; Gan, W.; Loos, R.J.; Lin, X. Common variants in or near fgf5, cyp17a1 and mthfr genes are associated with blood pressure and hypertension in chinese hans. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, J.F.; Matthews, G.J.; Townsend, R.R.; Raj, D.S.; Kanetsky, P.A.; Budoff, M.; Fischer, M.J.; Rosas, S.E.; Kanthety, R.; Rahman, M.; et al. Candidate gene association study of coronary artery calcification in chronic kidney disease: Findings from the cric study (chronic renal insufficiency cohort). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.; Gaunt, T.R.; Newhouse, S.J.; Padmanabhan, S.; Tomaszewski, M.; Kumari, M.; Morris, R.W.; Tzoulaki, I.; O’Brien, E.T.; Poulter, N.R.; et al. Blood pressure loci identified with a gene-centric array. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 89, 688–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Waas, M.; Neggers, S.J.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Blijdorp, K.; van der Geest, I.M.; Pieters, R.; van den Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M. Treatment factors rather than genetic variation determine metabolic syndrome in childhood cancer survivors. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.P.; Wang, H.; Li, C.Z.; Zhao, H.; You, L.; Shi, D.H.; Sun, X.H.; Lv, H.; Wang, F.; Wen, Z.Q.; et al. The common single-nucleotide polymorphism RS2681472 is associated with early-onset preeclampsia in northern han chinese women. Reprod. Sci. 2014, 21, 1423–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, B.; Tang, W.; Wang, Q. Polymorphism near the ATP2B1 gene is associated with hypertension risk in east asians: A meta-analysis involving 15 909 cases and 18 529 controls. Blood Press. 2012, 21, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, S.G.; Hwang, J.Y.; Uhmn, S.; Go, M.J.; Oh, B.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, J.W. Male-specific genetic effect on hypertension and metabolic disorders. Hum. Genet. 2014, 133, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, V.; McDonough, C.W.; Gong, Y.; El Rouby, N.M.; Sa, A.C.; Taylor, K.D.; Chen, Y.D.; Gums, J.G.; Chapman, A.B.; Turner, S.T.; et al. Large-scale gene-centric analysis identifies polymorphisms for resistant hypertension. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e001398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, T.N.; Takeuchi, F.; Tabara, Y.; Edwards, T.L.; Kim, Y.J.; Chen, P.; Li, H.; Wu, Y.; Yang, C.F.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Genome-wide association study meta-analysis reveals transethnic replication of mean arterial and pulse pressure loci. Hypertension 2013, 62, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Wang, L.; Lin, X.; Huang, J.; Charles Gu, C.; He, M.; Shen, H.; He, J.; Zhu, J.; Li, H.; et al. Genome-wide association study in chinese identifies novel loci for blood pressure and hypertension. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Shi, J.; Huang, W.; Sun, J.; Wu, Y.; Duan, Q.; Luo, J.; Lange, L.A.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Zheng, S.L.; et al. Variant near FGF5 has stronger effects on blood pressure in chinese with a higher body mass index. Am. J. Hypertens. 2015, 28, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyaki, K.; Htun, N.C.; Song, Y.; Ikeda, S.; Muramatsu, M.; Shimbo, T. The combined impact of 12 common variants on hypertension in japanese men, considering gwas results. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2012, 26, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, B.; Shen, Y.; Reilly, K.H.; Wang, X.; Mi, J. Recapitulation of four hypertension susceptibility genes (CSK, CYP17A1, MTHFR, and FGF5) in east asians. Metabolism 2013, 62, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamrefors, V.; Sjogren, M.; Almgren, P.; Wahlstrand, B.; Kjeldsen, S.; Hedner, T.; Melander, O. Pharmacogenetic implications for eight common blood pressure-associated single-nucleotide polymorphisms. J. Hypertens. 2012, 30, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, B.; Zhao, X.; Chandak, G.R.; Shen, Y.; Cheng, H.; Hou, D.; Wang, X.; Mi, J. Influence of obesity on association between genetic variants identified by genome-wide association studies and hypertension risk in chinese children. Am. J. Hypertens. 2013, 26, 990–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, D.; Ehret, G.B.; Rice, K.; Verwoert, G.C.; Launer, L.J.; Dehghan, A.; Glazer, N.L.; Morrison, A.C.; Johnson, A.D.; Aspelund, T.; et al. Genome-wide association study of blood pressure and hypertension. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotta, K.; Kitamoto, A.; Kitamoto, T.; Mizusawa, S.; Teranishi, H.; Matsuo, T.; Nakata, Y.; Hyogo, H.; Ochi, H.; Nakamura, T.; et al. Genetic variations in the CYP17A1 and NT5C2 genes are associated with a reduction in visceral and subcutaneous fat areas in japanese women. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 57, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Lai, X.; Chen, B.; Xu, Y.; Huang, B.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, S.; Yao, J.; Jiang, Q.; Huang, H.; et al. Genetic variations in CYP17A1, CACNB2 and PLEKHA7 are associated with blood pressure and/or hypertension in she ethnic minority of china. Atherosclerosis 2011, 219, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.E.; Levy, D.; Rose, L.; Johnson, A.D.; Ridker, P.M.; Chasman, D.I. Discovery and replication of novel blood pressure genetic loci in the women’s genome health study. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, K.; Gu, M.; Gao, P.; Zhu, D. Confirmation of top polymorphisms in hypertension genome wide association study among han chinese. Clin. Chim. Acta 2010, 411, 1491–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, F.; Isono, M.; Katsuya, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Yokota, M.; Sugiyama, T.; Nabika, T.; Fujioka, A.; Ohnaka, K.; Asano, H.; et al. Blood pressure and hypertension are associated with 7 loci in the japanese population. Circulation 2010, 121, 2302–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, E.R.; Young, J.H.; Li, Y.; Dreisbach, A.W.; Keating, B.J.; Musani, S.K.; Liu, K.; Morrison, A.C.; Ganesh, S.; Kutlar, A.; et al. Association of genetic variation with systolic and diastolic blood pressure among african americans: The candidate gene association resource study. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 2273–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, B.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chandak, G.R.; Cheng, H.; Hou, D.; Li, Y.; Ott, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Association of common variants in/near six genes (ATP2B1, CSK, MTHFR, CYP17A1, STK39 and FGF5) with blood pressure/hypertension risk in chinese children. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2014, 28, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteith, G.R.; Kable, E.P.; Kuo, T.H.; Roufogalis, B.D. Elevated plasma membrane and sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ pump mrna levels in cultured aortic smooth muscle cells from spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 230, 344–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Ishida, Y.; Okunade, G.; Shull, G.E.; Paul, R.J. Role of plasma membrane Ca2+-atpase in contraction-relaxation processes of the bladder: Evidence from pmca gene-ablated mice. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2006, 290, C1239–C1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pande, J.; Mallhi, K.K.; Sawh, A.; Szewczyk, M.M.; Simpson, F.; Grover, A.K. Aortic smooth muscle and endothelial plasma membrane Ca2+ pump isoforms are inhibited differently by the extracellular inhibitor caloxin 1b1. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2006, 290, C1341–C1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levinson, N.M.; Visperas, P.R.; Kuriyan, J. The tyrosine kinase CSK dimerizes through its SH3 domain. PLoS One 2009, 4, e7683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloutier, J.F.; Veillette, A. Association of inhibitory tyrosine protein kinase p50csk with protein tyrosine phosphatase pep in T cells and other hemopoietic cells. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 4909–4918. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Autero, M.; Saharinen, J.; Pessa-Morikawa, T.; Soula-Rothhut, M.; Oetken, C.; Gassmann, M.; Bergman, M.; Alitalo, K.; Burn, P.; Gahmberg, C.G.; et al. Tyrosine phosphorylation of CD45 phosphotyrosine phosphatase by P50CSK kinase creates a binding site for P56LCK tyrosine kinase and activates the phosphatase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994, 14, 1308–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruppelt, A.; Mosenden, R.; Gronholm, M.; Aandahl, E.M.; Tobin, D.; Carlson, C.R.; Abrahamsen, H.; Herberg, F.W.; Carpen, O.; Tasken, K. Inhibition of t cell activation by cyclic adenosine 5′-monophosphate requires lipid raft targeting of protein kinase a type I by the a-kinase anchoring protein ezrin. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 5159–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, Y.; Renaux, B.; Bjorge, J.; Saifeddine, M.; Fujita, D.J.; Hollenberg, M.D. Csrc is a major cytosolic tyrosine kinase in vascular tissue. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1999, 77, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touyz, R.M.; Wu, X.H.; He, G.; Park, J.B.; Chen, X.; Vacher, J.; Rajapurohitam, V.; Schiffrin, E.L. Role of c-src in the regulation of vascular contraction and Ca2+ signaling by angiotensin II in human vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Hypertens. 2001, 19, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touyz, R.M.; He, G.; Wu, X.H.; Park, J.B.; Mabrouk, M.E.; Schiffrin, E.L. Src is an important mediator of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2-dependent growth signaling by angiotensin ii in smooth muscle cells from resistance arteries of hypertensive patients. Hypertension 2001, 38, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mureebe, L.; Nelson, P.R.; Yamamura, S.; Lawitts, J.; Kent, K.C. Activation of PP60C-SRC is necessary for human vascular smooth muscle cell migration. Surgery 1997, 122, 138–144, discussion 144–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.E. Control of sodium excretion by angiotensin ii: Intrarenal mechanisms and blood pressure regulation. Am. J. Physiol. 1986, 250, R960–972. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, S.K.; Chasman, D.I.; Larson, M.G.; Guo, X.; Verwoert, G.; Bis, J.C.; Gu, X.; Smith, A.V.; Yang, M.L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Effects of long-term averaging of quantitative blood pressure traits on the detection of genetic associations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 95, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albinsson, S.; Sward, K. Targeting smooth muscle micrornas for therapeutic benefit in vascular disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 75, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkes, C.; Webster, J. National approaches to monitoring population salt intake: A trade-off between accuracy and practicality? PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| SNP | CHR | Position | Locus | Gene Symbol | Location | MA | MAF | RAF | OR 1 | STAT | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs10924160 | 1 | 243519469 | 1q44 | KIF26B | intron | C | 0.345 | 0.345 | 1.180 | 4.146 | 3.39 × 10−5 |
| rs7554672 | 1 | 219339781 | 1q41 | LOC101929750 | intron | A | 0.411 | 0.589 | 0.826 | −4.799 | 1.60 × 10−6 |
| rs7419838 | 2 | 38894349 | 2p22.1 | DHX57 | intron | A | 0.117 | 0.883 | 0.766 | −4.160 | 3.19 × 10−5 |
| rs1997377 | 2 | 38805170 | 2P22.1 | GALM | intron | T | 0.111 | 0.889 | 0.750 | −4.316 | 1.59 × 10−5 |
| rs1562855 | 2 | 38861972 | 2p22.1 | GEMIN6 | intron | C | 0.142 | 0.858 | 0.781 | −4.314 | 1.60 × 10−5 |
| rs11917719 | 3 | 24186676 | 3p24.2 | THRB | intron | T | 0.157 | 0.843 | 0.796 | −4.082 | 4.47 × 10−5 |
| rs513130 | 5 | 72456095 | 5q13.2 | TMEM171 | intron | T | 0.405 | 0.595 | 0.838 | −4.334 | 1.46 × 10−5 |
| rs6457792 | 6 | 34872421 | 6p21.31 | UHRF1BP1 | intron | G | 0.097 | 0.097 | 1.305 | 4.293 | 1.76 × 10−5 |
| rs10260451 | 7 | 142918347 | 7q35 | EPHA1-AS1 | intron | A | 0.177 | 0.823 | 0.799 | −4.070 | 4.70 × 10−5 |
| rs1643270 | 7 | 130826034 | 7q32.3 | MKLN1 | intron | C | 0.479 | 0.479 | 1.197 | 4.569 | 4.90 × 10−6 |
| rs3800688 | 7 | 130843015 | 7q32.3 | PODXL | intron | G | 0.419 | 0.419 | 1.197 | 4.600 | 4.23 × 10−6 |
| rs16927774 | 8 | 62771785 | 8q12.3 | ASPH | Intron | C | 0.213 | 0.787 | 0.820 | −4.091 | 4.30 × 10−5 |
| rs911782 | 10 | 123996033 | 10q26.13 | TACC2 | intron | T | 0.141 | 0.141 | 1.242 | 4.067 | 4.75 × 10−5 |
| rs10466739 | 11 | 78290369 | 11q14.1 | TENM4 | intron | C | 0.198 | 0.198 | 1.221 | 4.286 | 1.82 × 10−5 |
| rs11105368 | 12 | 88598572 | 12q21.33 | ATP2B1 | Intron | C | 0.376 | 0.624 | 0.810 | −5.247 | 1.55 × 10−7 |
| rs1378942 | 15 | 72864420 | 15q24.1 | CSK | Intron | A | 0.172 | 0.828 | 0.793 | −4.380 | 1.19 × 10−5 |
| rs3784789 | 15 | 72869605 | 15q24.1 | CSK, MIR4513 | Intron, upstream | G | 0.169 | 0.831 | 0.799 | −4.167 | 3.08 × 10−5 |
| rs11866964 | 16 | 48217182 | 16q12.1 | ZNF423 | intron | A | 0.231 | 0.769 | 0.826 | −4.102 | 4.10 × 10−5 |
| rs1858821 | 22 | 30006454 | 22q12.2 | LIMK2 | downstream | T | 0.145 | 0.855 | 0.788 | −4.221 | 2.44 × 10−5 |
| rs4141404 | 22 | 30005185 | 22q12.2 | LIMK2 | 3′ UTR | A | 0.145 | 0.855 | 0.788 | −4.221 | 2.44 × 10−5 |
| rs2040533 | 22 | 30009110 | 22q12.2 | PIK3IP1 | missense, 3′ UTR | G | 0.146 | 0.854 | 0.788 | −4.211 | 2.54 × 10−5 |
| rs2413035 | 22 | 29930460 | 22q12.2 | RNF185 | intron | T | 0.149 | 0.851 | 0.791 | −4.075 | 4.61 × 10−5 |
| Urinary Factors | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 (n = 1471) | T2 (n = 1472) | T3 (n = 1471) | p-Difference | p-Trend | |
| 24HUNa (mEq/day) | 127.8 ± 16.8 4 | 163.4 ± 8.3 | 205.8 ± 29.7 | ||
| Age (years) 1 | 51.9 ± 0.2 a,5 | 52.4 ± 0.2 a | 53.5 ± 0.2 b | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) 2 | 23.8 ± 0.1 a | 24.5 ± 0.1 b | 25.3 ± 0.1 c | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Energy Intake (kcal/day) 2 | 1984.0 ± 21.7 a | 2036.3 ± 21.6 a, b | 2105.1 ± 21.8 b | 0.0004 | <0.0001 |
| Sex, women (%) 3 | 57.0 6 | 58.2 | 59.0 | 0.580 | 0.299 |
| Cigarette Smoking, current (%) 2 | 28.3 | 23.4 | 21.9 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Alcohol Drinking, current (%) 2 | 41.4 | 44.4 | 42.4 | 0.178 | 0.588 |
| Regular Exercise, yes (%) 2 | 51.6 | 54.6 | 57.9 | 0.003 | 0.001 |
| Chronic Disease, yes (%) 2 | 34.7 | 45.0 | 54.2 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Family History, yes (%) 2 | 18.3 | 17.9 | 18.7 | 0.887 | 0.753 |
| Area, Ansan (%) 2 | 52.4 | 53.7 | 48.9 | 0.026 | 0.040 |
| Income, ≥2,000,000 KRW (%) 2 | 31.6 | 31.2 | 25.5 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| 24HUK (mEq/day) | 33.8 ± 3.4 | 42.6 ± 2.5 | 55.6 ± 9.1 | ||
| Age (years) | 50.7 ± 0.2 a | 52.4 ± 0.2 b | 54.6 ± 0.2 c | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.8 ± 0.1 a | 24.6 ± 0.1 b | 25.2 ±0.1 c | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Energy Intake (kcal/day) | 1940.6 ± 21.5 a | 2031.5 ± 21.7 b | 2158.7 ± 22.0 c | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Sex, women (%) | 53.1 | 59.7 | 61.6 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Cigarette Smoking, current (%) | 26.3 | 22.7 | 25.1 | 0.049 | 0.396 |
| Alcohol Drinking, current (%) | 43.7 | 41.8 | 42.2 | 0.594 | 0.496 |
| Regular Exercise, yes (%) | 48.4 | 52.3 | 64.1 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Chronic Disease, yes (%) | 35.6 | 45.6 | 53.0 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Family History, yes (%) | 17.9 | 17.8 | 19.8 | 0.404 | 0.226 |
| Area, Ansan (%) | 70.1 | 57.5 | 25.4 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Income, ≥2,000,000 KRW (%) | 35.9 | 30.8 | 20.0 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| 24HUNa-K Ratio | 3.0 ± 0.4 | 3.8 ± 0.2 | 4.8 ± 0.5 | ||
| Age (years) | 53.6 ± 0.2 c | 52.5 ± 0.2 b | 51.7 ± 0.2 a | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.5 ± 0.1 | 24.6 ± 0.1 | 24.5 ± 0.1 | 0.781 | 0.815 |
| Energy Intake (kcal/day) | 2104.7 ± 21.9 b | 2030.4 ± 21.8 a | 1992.4 ± 21.5 a | 0.001 | 0.0003 |
| Sex, women (%) | 58.7 | 60.5 | 55.1 | 0.009 | 0.045 |
| Cigarette Smoking, current (%) | 27.1 | 23.2 | 23.7 | 0.007 | 0.008 |
| Alcohol Drinking, current (%) | 42.0 | 41.5 | 44.5 | 0.144 | 0.120 |
| Regular Exercise, yes (%) | 59.8 | 54.1 | 49.6 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Chronic Disease, yes (%) | 44.1 | 45.4 | 44.4 | 0.832 | 0.911 |
| Family History, yes (%) | 19.1 | 18.3 | 17.4 | 0.499 | 0.239 |
| Area, Ansan (%) | 31.1 | 54.5 | 70.0 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Income, ≥2,000,000 KRW (%) | 23.9 | 31.0 | 33.1 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Urinary Factors | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | p-Difference | p-Trend | |
| Tanaka Formula | |||||
| 24HUNa (mEq/day) | 127.8 ± 16.8 1 | 163.4 ± 8.3 | 205.8 ± 29.7 | ||
| SBP (mmHg) | |||||
| Model 1 3 | 116.0 ± 0.4 a, 2 | 117.6 ± 0.4 b | 121.7 ± 0.4 c | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Model 2 4 | 121.9 ± 1.0 a | 122.7 ± 1.0 a | 125.8 ± 1.0 b | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| DBP (mmHg) | |||||
| Model 1 | 73.7 ± 0.3 a | 75.2 ± 0.3 b | 77.0 ± 0.3 c | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Model 2 | 76.6 ± 0.6 a | 77.6 ± 0.6 a | 78.6 ± 0.7 b | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| 24HUK (mEq/day) | 33.8 ± 3.4 | 42.6 ± 2.5 | 55.6 ± 9.1 | ||
| SBP (mmHg) | |||||
| Model 1 | 117.0 ± 0.4 a | 117.5 ± 0.4 a | 120.9 ± 0.4 b | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Model 2 | 123.8 ± 1.0 | 122.7 ± 1.0 | 123.5 ± 1.0 | 0.182 | 0.718 |
| DBP (mmHg) | |||||
| Model 1 | 74.4 ± 0.3 a | 74.8 ± 0.3 a | 76.7 ± 0.3 b | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Model 2 | 77.7 ± 0.7 | 77.1 ± 0.7 | 77.7 ± 0.7 | 0.188 | 0.991 |
| 24HUNa-K ratio | 3.0 ± 0.4 | 3.8 ± 0.2 | 4.8 ± 0.5 | ||
| SBP (mmHg) | |||||
| Model 1 | 118.1 ± 0.4 | 118.2 ± 0.4 | 119.1 ± 0.4 | 0.188 | 0.093 |
| Model 2 | 121.5 ± 1.0 a | 123.1 ± 1.0 b | 125.5 ± 1.0 c | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| DBP (mmHg) | |||||
| Model 1 | 75.3 ± 0.3 | 75.1 ± 0.3 | 75.5 ± 0.3 | 0.491 | 0.487 |
| Model 2 | 76.8 ± 0.7 a | 77.3 ± 0.6a | 78.5 ± 0.6 b | 0.0002 | <0.0001 |
| Kawasaki Formula | |||||
| 24HUNa (mEq/day) | 158.0 ± 25.2 | 213.8 ± 13.5 | 286.4 ± 53.7 | ||
| SBP (mmHg) | |||||
| Model 1 | 116.0 ± 0.4 a | 118.0 ± 0.4 b | 121.3 ± 0.4 c | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Model 2 | 121.8 ± 1.0 a | 123.0 ± 1.0a | 125.4 ± 1.0 b | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| DBP (mmHg) | |||||
| Model 1 | 73.8 ± 0.3 a | 75.2 ± 0.3 b | 76.8 ± 0.3 c | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Model 2 | 76.7 ± 0.6 a | 77.5 ± 0.6 a | 78.5 ± 0.6 b | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Kawasaki Formula | |||||
| 24HUK (mEq/day) | 41.8 ± 4.6 | 54.0 ± 3.4 | 73.3 ± 14.4 | ||
| SBP (mmHg) | |||||
| Model 1 | 116.9 ± 0.4 a | 117.8 ± 0.4 a | 120.7 ± 0.4 b | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Model 2 | 123.6 ± 1.0 | 123.0 ± 1.0 | 123.4 ± 1.0 | 0.592 | 0.753 |
| DBP (mmHg) | |||||
| Model 1 | 74.2 ± 0.3 a | 75.2 ± 0.3 b | 76.4 ± 0.3 c | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Model 2 | 77.5 ± 0.7 | 77.5 ± 0.7 | 77.5 ± 0.7 | 0.998 | 0.950 |
| 24HUNa-K ratio | 2.9 ± 0.5 | 3.9 ± 0.3 | 5.2 ± 0.7 | ||
| SBP (mmHg) | |||||
| Model 1 | 117.7 ± 0.4 | 118.4 ± 0.4 | 119.2 ± 0.4 | 0.056 | 0.017 |
| Model 2 | 121.3 ± 1.0 a | 123.4 ± 1.0 b | 125.4 ± 1.0 c | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| DBP (mmHg) | |||||
| Model 1 | 75.1 ± 0.3 | 75.3 ± 0.3 | 75.6 ± 0.3 | 0.451 | 0.210 |
| Model 2 | 76.6 ± 0.6 a | 77.6 ± 0.6 a,b | 78.4 ± 0.7 b | 0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Urinary Factors | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | p-Trend | |
| Tanaka Formula | ||||
| 24HUNa (mEq/day) | 127.8 ± 16.8 1 | 163.4 ± 8.3 | 205.8 ± 29.7 | |
| Model 1 3 | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.08 (0.89–1.30) 2 | 1.59 (1.33–1.91) | <0.0001 |
| Model 2 4 | 1.00 (ref.) | 0.93 (0.76–1.13) | 1.21 (1.00–1.48) | 0.037 |
| 24HUK (mEq/day) | 33.8 ± 3.4 | 42.6 ± 2.5 | 55.6 ± 9.1 | |
| Model 1 | 1.00 (ref.) | 0.96 (0.79–1.15) | 1.19 (0.99–1.43) | 0.037 |
| Model 2 | 1.00 (ref.) | 0.79 (0.65–0.97) | 0.89 (0.72–1.10) | 0.400 |
| 24HUNa-K ratio | 3.0 ± 0.4 | 3.8 ± 0.2 | 4.8 ± 0.5 | |
| Model 1 | 1.00 (ref.) | 0.94 (0.79–1.13) | 1.14 (0.95–1.36) | 0.161 |
| Model 2 | 1.00 (ref.) | 0.96 (0.79–1.18) | 1.22 (0.99–1.49) | 0.056 |
| Kawasaki Formula | ||||
| 24HUNa (mEq/day) | 158.0 ± 25.2 | 213.8 ± 13.5 | 286.4 ± 53.7 | |
| Model 1 | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.22 (1.01–1.47) | 1.57 (1.31–1.89) | <0.0001 |
| Model 2 | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.07 (0.88–1.31) | 1.27 (1.04–1.55) | 0.014 |
| 24HUK (mEq/day) | 41.8 ± 4.6 | 54.0 ± 3.4 | 73.3 ± 14.4 | |
| Model 1 | 1.00 (ref.) | 0.99 (0.82–1.20) | 1.14 (0.95–1.37) | 0.125 |
| Model 2 | 1.00 (ref.) | 0.85 (0.70–1.05) | 0.88 (0.71–1.09) | 0.302 |
| 24HUNa-K ratio | 2.9 ± 0.5 | 3.9 ± 0.3 | 5.2 ± 0.7 | |
| Model 1 | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.06 (0.89–1.27) | 1.20 (1.00–1.44) | 0.046 |
| Model 2 | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.11 (0.91–1.35) | 1.27 (1.04–1.56) | 0.022 |
| Urinary Factors | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | p-Interaction | |
| 24HUNa-K Ratio | ||||
| CSK (rs1378942) | 0.013 | |||
| AA | 1.00 (ref.) | 0.08 (0.01–0.67) 1 | 0.69 (0.20–2.42) | |
| AC | 0.61 (0.24–1.56) | 0.77 (0.30–1.96) | 0.67 (0.26–1.72) | |
| CC (wild type) | 0.87 (0.35–2.16) | 0.80 (0.32–2.00) | 1.11 (0.44–2.76) | |
| 24HUNa-K Ratio | ||||
| CSK-MIR4513 (rs3784789) | 0.027 | |||
| GG | 1.00 (ref.) | 0.08 (0.01–0.72) | 0.77 (0.22–2.71) | |
| CG | 0.61 (0.24–1.54) | 0.74 (0.29–1.88) | 0.68 (0.27–1.75) | |
| CC (wild type) | 0.86 (0.35–2.14) | 0.80 (0.32–1.99) | 1.08 (0.43–2.70) | |
| Urinary Factors | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | p-Interaction | |
| 24HUNa (mEq/day) | ||||
| LOC101929750 (rs7554672) | 0.028 | |||
| AA | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.33 (0.77–2.29) 1 | 0.79 (0.44–1.43) | |
| AG | 1.33 (0.82–2.14) | 1.25 (0.77–2.01) | 1.92 (1.20–3.06) | |
| GG (wild type) | 1.75 (1.07–2.84) | 2.04 (1.26–3.31) | 2.16 (1.33–3.50) | |
| 24HUK (mEq/day) | ||||
| LOC101929750 (rs7554672) | 0.034 | |||
| GG (wild type) | 1.00 (ref.) | 0.92 (0.67–1.27) | 0.72 (0.52–1.01) | |
| AG | 0.65 (0.48–0.89) | 0.58 (0.42–0.79) | 0.74 (0.55–1.01) | |
| AA | 0.67 (0.44–1.03) | 0.36 (0.22–0.58) | 0.40 (0.26–0.62) | |
| MKLN1 (rs1643270) | 0.034 | |||
| CC | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.55 (1.01–2.38) | 1.22 (0.80–1.87) | |
| CT | 1.16 (0.79–1.70) | 0.83 (0.56–1.22) | 0.85 (0.58–1.26) | |
| TT (wild type) | 0.97 (0.63–1.48) | 0.74 (0.48–1.14) | 0.89 (0.58–1.38) | |
| 24HUNa-K Ratio | ||||
| CSK (rs1378942) | 0.012 | |||
| AA | 1.00 (ref.) | 0.09 (0.01–0.83) | 0.80 (0.23–2.75) | |
| AC | 0.67 (0.27–1.69) | 0.94 (0.38–2.35) | 0.73 (0.29–1.84) | |
| CC (wild type) | 0.93 (0.38–2.26) | 0.99 (0.41–2.42) | 1.25 (0.51–3.05) | |
| CSK-MIR4513 (rs3784789) | 0.026 | |||
| GG | 1.00 (ref.) | 0.10 (0.01–0.89) | 0.89 (0.26–3.09) | |
| CG | 0.66 (0.26–1.66) | 0.91 (0.36–2.28) | 0.74 (0.26–1.88) | |
| CC (wild type) | 0.92 (0.38–2.25) | 0.99 (0.40–2.42) | 1.22 (0.50–2.99) | |
| TENM4 (rs10466739) | 0.034 | |||
| TT (wild type) | 1.00 (ref.) | 0.99 (0.77–1.26) | 1.09 (0.85–1.40) | |
| CT | 0.86 (0.63–1.16) | 1.06 (0.78–1.45) | 1.43 (1.07–1.93) | |
| CC | 0.31 (0.11–0.93) | 1.49 (0.78–2.85) | 0.90 (0.43–1.87) | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, Y.M.; Kwock, C.K.; Kim, K.; Kim, J.; Yang, Y.J. Interaction between Single Nucleotide Polymorphism and Urinary Sodium, Potassium, and Sodium-Potassium Ratio on the Risk of Hypertension in Korean Adults. Nutrients 2017, 9, 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9030235
Park YM, Kwock CK, Kim K, Kim J, Yang YJ. Interaction between Single Nucleotide Polymorphism and Urinary Sodium, Potassium, and Sodium-Potassium Ratio on the Risk of Hypertension in Korean Adults. Nutrients. 2017; 9(3):235. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9030235
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Yeong Mi, Chang Keun Kwock, Kyunga Kim, Jihye Kim, and Yoon Jung Yang. 2017. "Interaction between Single Nucleotide Polymorphism and Urinary Sodium, Potassium, and Sodium-Potassium Ratio on the Risk of Hypertension in Korean Adults" Nutrients 9, no. 3: 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9030235
APA StylePark, Y. M., Kwock, C. K., Kim, K., Kim, J., & Yang, Y. J. (2017). Interaction between Single Nucleotide Polymorphism and Urinary Sodium, Potassium, and Sodium-Potassium Ratio on the Risk of Hypertension in Korean Adults. Nutrients, 9(3), 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9030235





