Effects of Resveratrol Supplementation on Methotrexate Chemotherapy‐Induced Bone Loss
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Trials and Specimen Collection
2.2. Ex Vivo Osteoclast Formation Potential of Bone Marrow Cells of Treated Rats
2.3. Histomorphometric Analyses of Growth Plate and Metaphysis Bone
2.4. Quantitative Real Time Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Effects of RES Supplementation at the Higher Dose
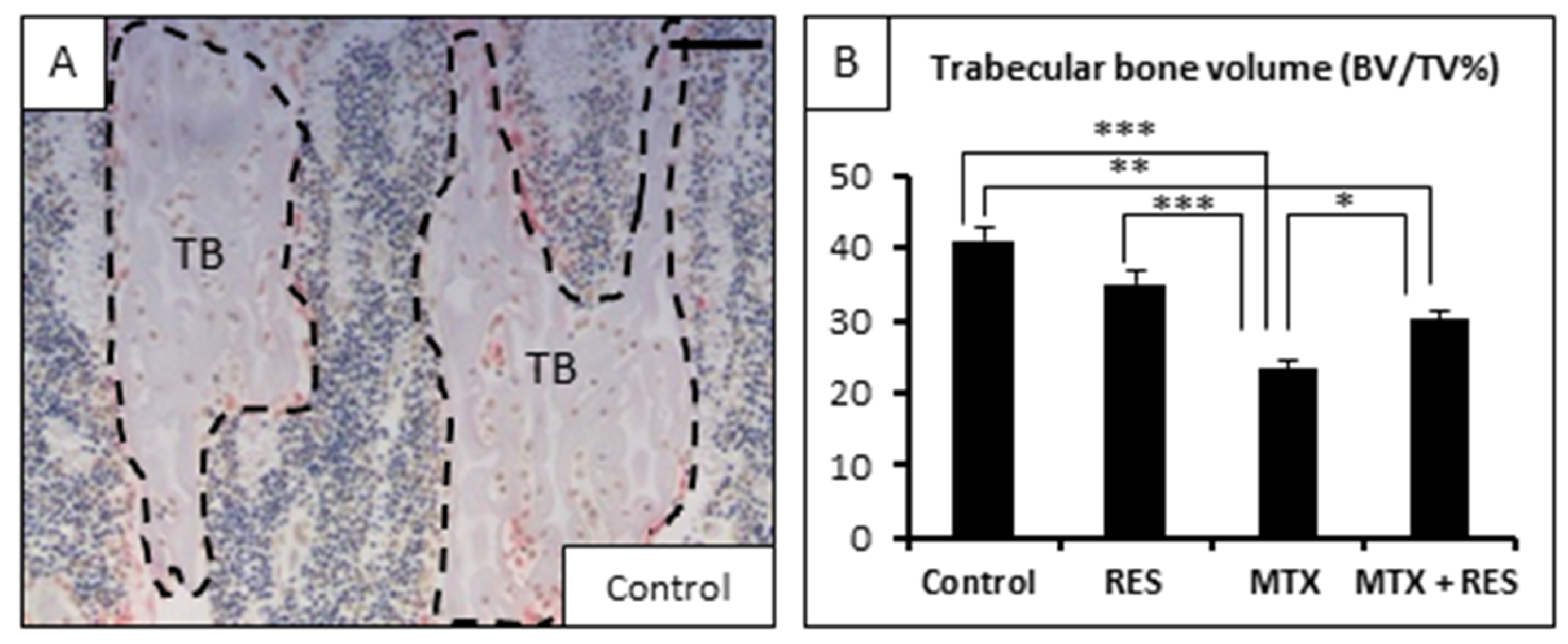
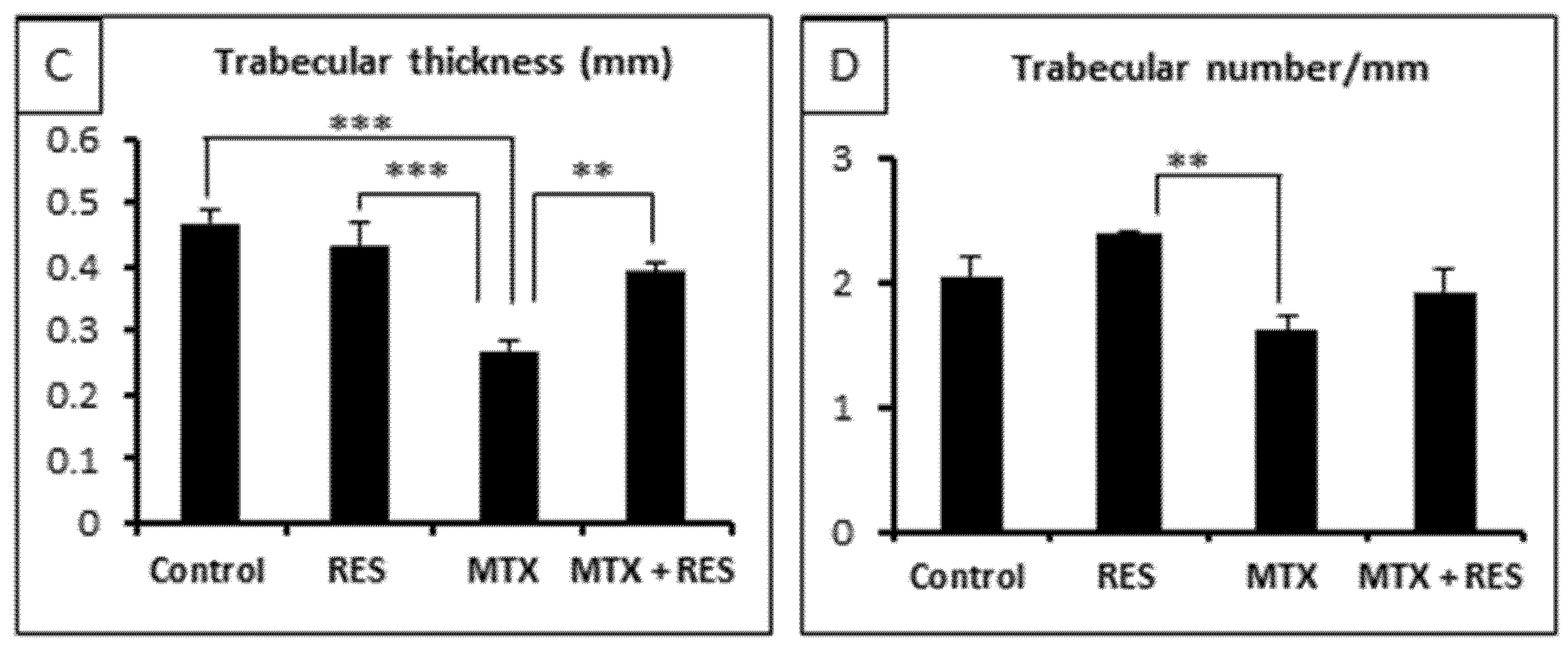
3.2. Effects of RES Supplementation (1 mg/kg) on Structures of Growth Plate and Metaphysis
3.3. Treatment Effects on Osteoblast Number and Osteogenesis-Related Genes
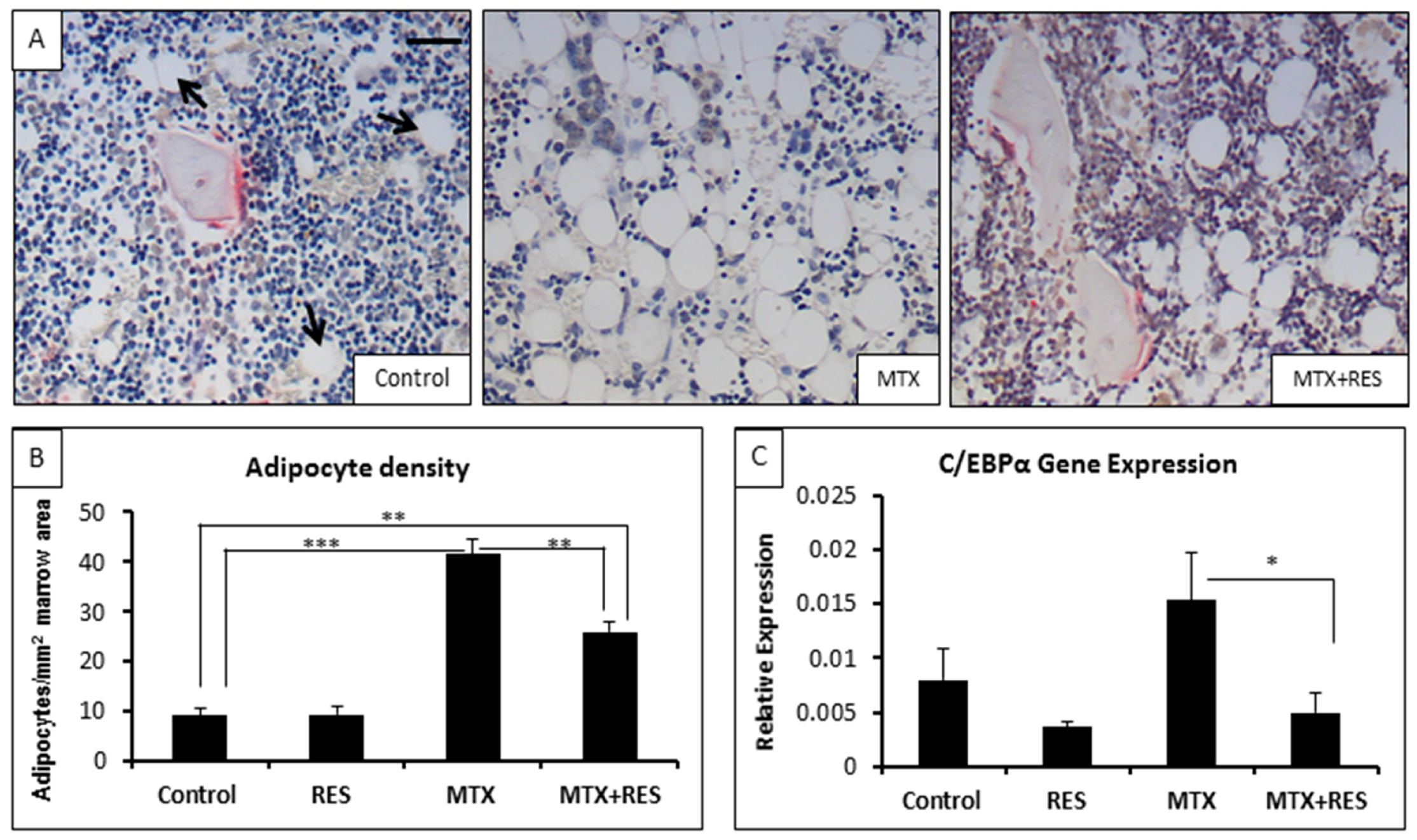
3.4. Changes in Adipocyte Density in the Bone Marrow
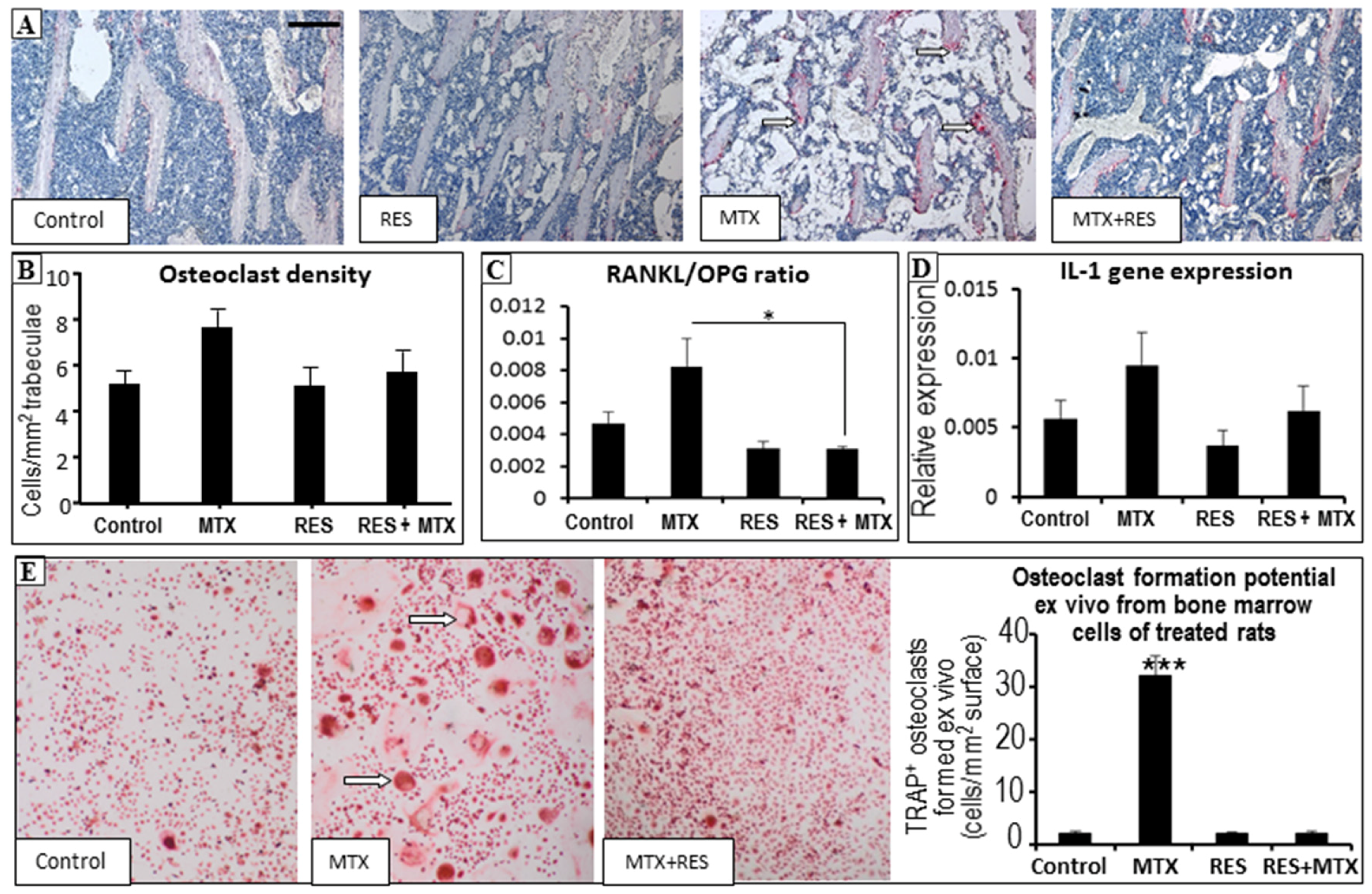
3.5. Effects on Osteoclast Density and Osteoclast Formation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corrie, P.G. Cytotoxic chemotherapy: Clinical aspects. Medicine 2008, 36, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, J.; de Jonge, M.J.A. Achievements and future of chemotherapy. Eur. J. Cancer 2000, 36, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, T.; Symonds, R.P. Principles of chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Obstet. Gynaecol. Reprod. Med. 2009, 19, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, C.J.; Cool, J.C.; Scherer, M.A.; Macsai, C.E.; Fan, C.; Covino, M.; Foster, B.K. Cellular mechanisms for methotrexate chemotherapy-induced bone growth defects. Bone 2007, 41, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.; Cool, J.C.; Scherer, M.A.; Foster, B.K.; Shandala, T.; Tapp, H.; Xian, C.J. Damaging effects of chronic low-dose methotrexate usage on primary bone formation in young rats and potential protective effects of folinic acid supplementary treatment. Bone 2009, 44, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xian, C.J.; Cool, J.C.; Scherer, M.A.; Fan, C.; Foster, B.K. Folinic acid attenuates methotrexate chemotherapy-induced damages on bone growth mechanisms and pools of bone marrow stromal cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2008, 214, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiou, K.R.; Scherer, M.A.; Fan, C.M.; Cool, J.C.; King, T.J.; Foster, B.K.; Xian, C.J. Methotrexate chemotherapy reduces osteogenesis but increases adipogenesis potential in the bone marrow. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiou, K.R.; Foster, B.K.; Xian, C.J. Damage and recovery of the bone marrow microenvironment induced by cancer chemotherapy—Potential regulatory role of chemokine CXCL12/receptor CXCR4 signalling. Curr. Mol. Med. 2010, 10, 440–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shandala, T.; Shen Ng, Y.; Hopwood, B.; Yip, Y.C.; Foster, B.K.; Xian, C.J. The role of osteocyte apoptosis in cancer chemotherapy-induced bone loss. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 2889–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiou, K.R.; Nadhanan, R.R.; Fan, C.M.; Xian, C.J. Methotrexate-induced bone marrow adiposity is mitigated by folinic acid supplementation through the regulation of WNT/β-catenin signalling. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 230, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, D.L.; Vander Griend, R.A.; Wronski, T.J.; Miller, G.J.; Keith, E.E.; Graves, J.E. The short- and long-term effects of methotrexate on the rat skeleton. Bone 1995, 16, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, T.J.; Georgiou, K.R.; Cool, J.C.; Scherer, M.A.; Ang, E.S.M.; Foster, B.K.; Xu, J.; Xian, C.J. Methotrexate chemotherapy promotes osteoclast formation in the long bone of rats via increased pro-inflammatory cytokines and enhanced NF-κB activation. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gass, M.; Dawson-Hughes, B. Preventing osteoporosis-related fractures: An overview. Am. J. Med. 2006, 119, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiou, K.R.; Hui, S.K.; Xian, C.J. Regulatory pathways associated with bone loss and bone marrow adiposity caused by aging, chemotherapy, glucocorticoid therapy and radiotherapy. Am. J. Stem Cells 2012, 1, 205–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Li, Y.; Quarles, L.D.; Song, T.; Pan, W.; Zhou, H.; Xiao, Z. Resveratrol enhances proliferation and osteoblastic differentiation in human mesenchymal stem cells via RR-dependent ERK1/2 activation. Phytomedicine 2007, 14, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baur, J.A.; Sinclair, D.A. Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: The in vivo evidence. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picard, F.; Kurtev, M.; Chung, N.; Topark-Ngarm, A.; Senawong, T.; De Oliveira, R.M.; Leid, M.; McBurney, M.W.; Guarente, L. Sirt1 promotes fat mobilization in white adipocytes by repressing PPAR-γ. Nature 2004, 429, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomb, D.J.; Laurent, G.; Haigis, M.C. Sirtuins regulate key aspects of lipid metabolism. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom. 2010, 1804, 1652–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayalam, S.; Yang, J.-Y.; Ambati, S.; Della-Fera, M.A.; Baile, C.A. Resveratrol induces apoptosis and inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Phytother. Res. 2008, 22, 1367–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, C.; Rayalam, S.; Della-Fera, M.A.; Baile, C.A. Phytochemicals and adipogenesis. Biofactors 2010, 36, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Shang, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Gao, G.; Guo, C.; Chen, B.; Liu, Q.; Gong, Y.; Shao, C. Resveratrol augments the canonical WNT signaling pathway in promoting osteoblastic differentiation of multipotent mesenchymal cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2009, 315, 2953–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Andersson, G.; Lindgren, U.; Li, Y. Resveratrol prevents rankl-induced osteoclast differentiation of murine osteoclast progenitor raw 264.7 cells through inhibition of ros production. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 401, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucciolla, V.; Borriello, A.; Oliva, A.; Galletti, P.; Zappia, V.; Della Ragione, F. Resveratrol: From basic science to the clinic. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 2495–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, O.-H.; Jang, H.-J.; Chae, H.-S.; Oh, Y.-C.; Choi, J.-G.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, Y.C.; Sohn, D.H.; Park, H.; et al. Anti-inflammatory mechanisms of resveratrol in activated HMC-1 cells: Pivotal roles of NFκB and mapk. Pharmacol. Res. 2009, 59, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baile, C.A.; Yang, J.-Y.; Rayalam, S.; Hartzell, D.L.; Lai, C.-Y.; Andersen, C.; Della-Fera, M.A. Effect of resveratrol on fat mobilization. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1215, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habauzit, V.; Horcajada, M.-N. Phenolic phytochemicals and bone. Phytochem. Rev. 2008, 7, 313–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habold, C.; Momken, I.; Ouadi, A.; Bekaert, V.; Brasse, D. Effect of prior treatment with resveratrol on density and structure of rat long bones under tail-suspension. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2011, 29, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.M.; Shandala, T.; Nguyen, L.; Muhlhausler, B.S.; Chen, K.; Howe, P.R.; Xian, C.J. Effects of resveratrol supplementation on bone growth in young rats and microarchitecture and remodeling in ageing rats. Nutrients 2014, 6, 5871–5887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juan, M.E.; Vinardell, M.P.; Planas, J.M. The daily oral administration of high doses of trans-resveratrol to rats for 28 days is not harmful. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.P.; Li, W.X.; Yu, B.; Huang, J.; Sun, J.; Huo, J.S.; Liu, C.X. Effects of trans-resveratrol from polygonum cuspidatum on bone loss using the ovariectomized rat model. J. Med. Food 2005, 8, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.M.; Foster, B.K.; Hui, S.K.; Xian, C.J. Prevention of bone growth defects, increased bone resorption and marrow adiposity with folinic acid in rats receiving long-term methotrexate. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Georgiou, K.R.; McKinnon, R.A.; Keefe, D.M.; Howe, P.R.; Xian, C.J. Combination chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide, epirubicin and 5-fluorouracil causes trabecular bone loss, bone marrow cell depletion and marrow adiposity in female rats. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2016, 34, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, G.J.; van der Wilt, C.L.; van Moorsel, C.J.A.; Kroep, J.R.; Bergman, A.M.; Ackland, S.P. Basis for effective combination cancer chemotherapy with antimetabolites. Pharmacol. Therap. 2000, 87, 227–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, P.-C.; Hou, S.-M.; Chen, R.-J.; Peng, H.-W.; Hsieh, C.-F.; Kuo, M.-L.; Yen, M.-L. Resveratrol promotes osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells by up-regulating RUNX2 gene expression via SIRT1/FOXO3A axis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2011, 26, 2552–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Foster, B.K.; Wallace, W.H.; Xian, C.J. Pathobiology and prevention of cancer chemotherapy-induced bone growth arrest, bone loss, and osteonecrosis. Curr. Mol. Med. 2011, 11, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiou, K.R.; King, T.J.; Scherer, M.A.; Zhou, H.; Foster, B.K.; Xian, C.J. Attenuated Wnt/β-catenin signalling mediates methotrexate chemotherapy-induced bone loss and marrow adiposity in rats. Bone 2012, 50, 1223–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckesjö, C.-M.; Li, Y.; Lindgren, U.; Haldosén, L.-A. Activation of sirt1 decreases adipocyte formation during osteoblast differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2006, 21, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer-Posovszky, P.; Kukulus, V.; Tews, D.; Unterkircher, T.; Debatin, K.-M.; Fulda, S.; Wabitsch, M. Resveratrol regulates human adipocyte number and function in a SIRT1-dependent manner. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.A.; Lien, H.M.; Kao, M.C.; Lo, U.G.; Lin, L.C.; Lin, C.J.; Chang, S.J.; Chen, C.C.; Hsieh, J.T.; Lin, H.; et al. Sensitization of radioresistant prostate cancer cells by resveratrol isolated from arachis hypogaea stems. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Dudley, J.I.; Das, D.K. Dose-dependency of resveratrol in providing health benefits. Dose Response 2010, 8, 478–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmet, I.; Tae, H.J.; Lakatta, E.G.; Talan, M. Long-term low dose dietary resveratrol supplement reduces cardiovascular structural and functional deterioration in chronic heart failure in rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 95, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, R.H.; Nealon, R.S.; Scholey, A.; Howe, P.R. Low dose resveratrol improves cerebrovascular function in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 26, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Te Winkel, M.L.; Pieters, R.; Hop, W.C.; Roos, J.C.; Bokkerink, J.P.; Leeuw, J.A.; Bruin, M.C.; Kollen, W.J.; Veerman, A.J.; de Groot-Kruseman, H.A.; et al. Bone mineral density at diagnosis determines fracture rate in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated according to the DCOG-ALL9 protocol. Bone 2014, 59, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liem, N.L.; Papa, R.A.; Milross, C.G.; Schmid, M.A.; Tajbakhsh, M.; Choi, S.; Ramirez, C.D.; Rice, A.M.; Haber, M.; Norris, M.D.; et al. Characterization of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia xenograft models for the preclinical evaluation of new therapies. Blood 2004, 103, 3905–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Li, T.; Wang, L.; Su, Y.; Xian, C.J. Dioscorea bulbifera polysaccharide and cyclophosphamide combination enhances anti-cervical cancer effect and attenuates immunosuppression and oxidative stress in mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 5, 19185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, A.; Bennett, L.L. Resveratrol enhances the efficacy of sorafenib mediated apoptosis in human breast cancer MCF7 cells through ROS, cell cycle inhibition, caspase 3 and PARP cleavage. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 1906–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Umebayashi, M.; Doi, K.; Morisaki, T.; Shirasawa, S.; Tsunoda, T. Resveratrol overcomes cellular resistance to vemurafenib through dephosphorylation of akt in BRAF-mutated melanoma cells. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 3585–3589. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Varoni, E.M.; Lo Faro, A.F.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Iriti, M. Anticancer molecular mechanisms of resveratrol. Front. Nutr. 2016, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Wu, M.; Ren, C.; Zhen, Y.; Ma, X.; Diao, Y.; Ma, X.; Deng, S.; et al. Differential sensitivities of bladder cancer cell lines to resveratol are unrelated to its metabolic profile. Oncotarget 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Cyclophilin A | GAGCTGTTTGCAGACAAAGTTC | CCTGGCACATGAATCCTGG |
| Runx2 | TCACAAATCCTCCCCAAGTGG | GAATGCGCCCTTAAATCACTGA |
| OSX | GCTTTTCTGTGGCAAGAGGTTC | CTGATGTTTCTCAAGTGGTCG |
| Osteocalcin | AAGCCTTCATGTCCAAGCAGG | AGGCGGTGTTGAAGCCATACT |
| C/EBPα | TCGCCATGCCGGGAGAACTCTAAC | CTGGAGGTGGCTGCTCATCGGGG |
| RANKL | CCGTGCAAAGGGAATTACAAC | GAGCCACGAACCTTCCATCA |
| OPG | GGAGACACACCTCGCAAGA | CGACACTGCTTTCACAGAGG |
| TNF-α | ATGGCCCAGACCCTCACACTCAGA | CTCCGCTTGGTGGTTTGCTACGAC |
| IL-1 | GTTTCCCTCCCTGCTCTGACA | GACAATGCTGCCTCGTGACC |
| IL-6 | CAGCGATGATGCACTGTCAGA | CCAGGTAGAAACGGAACTCCA |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, A.M.C.; Shandala, T.; Soo, P.P.; Su, Y.; King, T.J.; Chen, K.; Howe, P.R.; Xian, C.J. Effects of Resveratrol Supplementation on Methotrexate Chemotherapy‐Induced Bone Loss. Nutrients 2017, 9, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9030255
Lee AMC, Shandala T, Soo PP, Su Y, King TJ, Chen K, Howe PR, Xian CJ. Effects of Resveratrol Supplementation on Methotrexate Chemotherapy‐Induced Bone Loss. Nutrients. 2017; 9(3):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9030255
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Alice M. C., Tetyana Shandala, Pei Pei Soo, Yu‐Wen Su, Tristan J. King, Ke‐Ming Chen, Peter R. Howe, and Cory J. Xian. 2017. "Effects of Resveratrol Supplementation on Methotrexate Chemotherapy‐Induced Bone Loss" Nutrients 9, no. 3: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9030255
APA StyleLee, A. M. C., Shandala, T., Soo, P. P., Su, Y., King, T. J., Chen, K., Howe, P. R., & Xian, C. J. (2017). Effects of Resveratrol Supplementation on Methotrexate Chemotherapy‐Induced Bone Loss. Nutrients, 9(3), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9030255







