Impact of Frequency of Multi-Vitamin/Multi-Mineral Supplement Intake on Nutritional Adequacy and Nutrient Deficiencies in U.S. Adults
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Micronutrient Intake from Food
2.3. Definition of MVMS and Micronutrient Intake from MVMS
2.4. Biomarkers of Nutrient Deficiencies
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. MVMS Usage
3.2. Impact of MVMS Use and Frequency of Use
3.3. Impact of Frequency of MVMS Usage
3.4. Impact of Frequency of MVMS Usage on Biomarkers of Nutrient Deficiencies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; U.S. Department of Agriculture. Scientific Report of the 2015 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee. 2015. Available online: http://health.gov/dietaryguidelines/2015-scientific-report/ (accessed on 17 January 2017).
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; U.S. Department of Agriculture. 2015–2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 8th ed.; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. Available online: http://health.gov/dietaryguidelines/2015/guidelines/ (accessed on 17 January 2017).
- Briefel, R.R.; Johnson, C.L. Secular trends in dietary intake in the United States. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2004, 24, 401–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, R.L.; Gahche, J.J.; Lentino, C.V.; Dwyer, J.T.; Engel, J.S.; Thomas, P.R.; Betz, J.M.; Sempos, C.T.; Picciano, M.F. Dietary supplement use in the United States, 2003–2006. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, T.C.; McBurney, M.; Fulgoni, V.L. Multivitamin/mineral supplement contribution to micronutrient intakes in the United States, 2007–2010. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2014, 33, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantor, E.D.; Rehm, C.D.; Du, M.; White, E.; Giovannucci, E.L. Trends in Dietary Supplement Use among US Adults from 1999–2012. JAMA 2016, 316, 1464–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subar, A.F.; Block, G. Use of vitamin and mineral supplements: Demographics and amounts of nutrients consumed. The 1987 Health Interview Survey. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1990, 132, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. The Use of Dietary Supplements. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/databriefs/dietary.pdf (accessed on 8 September 2016).
- Bailey, R.L.; Gahche, J.J.; Miller, P.E.; Thomas, P.R.; Dwyer, J.T. Why US adults use dietary supplements. JAMA Intern. Med. 2013, 173, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, A.; MacKay, D.; Wong, A. Consumer attitudes about the role of multivitamins and other dietary supplements: Report of a survey. Nutr. J. 2015, 14, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yetley, E.A. Multivitamin and multimineral dietary supplements: Definitions, characterization, bioavailability, and drug interactions. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 269S–276S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fulgoni, V.L., III; Keast, D.R.; Bailey, R.L.; Dwyer, J. Foods, fortificants and supplements: Where do Americans get their nutrients? J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 1847–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J.G.; Hwang, H.R.; Jeong, D.W.; Cho, Y.H.; Choi, E.J.; Yi, Y.H.; Tak, Y.J.; et al. Vitamin-Mineral Supplement Use Patterns in Elderly Koreans: Data from the 2007–2008 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2016, 37, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Second National Report on Biochemical Indicators of Diet and Nutrition in the U.S. Population 2012; National Center for Environmental Health: Atlanta, GA, USA, April 2012. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/nutritionreport/pdf/nutrition_book_complete508_final.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2016).
- CDC, National Center for Health Statistics. About the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/aboutnhanes.htm (accessed on 13 May 2016).
- Ahuja, J.K.A.; Montville, J.B.; Omolewa-Tomobi, G.; Martin, C.L.; Heendeniya, K.Y.; Steinfeldt, L.C.; Anand, J.; Adler, M.E.; LaComb, R.P.; Moshfegh, A. USDA Food and Nutrient Database for Dietary Studies, 5.0; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, Food Surveys Research Group: Beltsville, MD, USA, 2012.
- U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. USDA Food and Nutrient Database for Dietary Studies 2011–2012. 2014. Available online: https://www.ars.usda.gov/northeast-area/beltsville-md/beltsville-human-nutrition-research-center/food-surveys-research-group/ (accessed on 13 May 2016).
- U.S. Department of Agriculture National Agriculture Library: National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference. Available online: http://ndb.nal.usda.gov/ (accessed on 13 May 2016).
- Otten, J.J.; Hellwig, J.P.; Meyers, L.D. (Eds.) Dietary Reference Intakes, the Essential Guide to Nutrient Requirements; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- CDC, National Center for Health Statistics. Questionnaires, Datasets and Related Documentation, NHANES [Internet]. Hyattsville (MD). Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/nhanes_questionnaires.htm (accessed on 13 May 2016).
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey-Laboratory Files. CDC National Health Center for Health Statistics: Atlanta, GA, USA. Available online: http://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/search/datapage.aspx?Component=Laboratory (accessed on 13 May 2016).
- Cook, J.D.; Flowers, C.H.; Skikne, B.S. The quantitative assessment of body iron. Blood 2003, 101, 3359–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tooze, J.A.; Kipnis, V.; Buckman, D.W.; Carroll, R.J.; Freedman, L.S.; Guenther, P.M.; Krebs-Smith, S.M.; Subar, A.F.; Dodd, K.W. A mixed-effects model approach for estimating the distribution of usual intake of nutrients: The NCI method. Stat. Med. 2010, 29, 2857–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ames, B.N. Low micronutrient intake may accelerate the degenerative diseases of aging through allocation of scarce micronutrients by triage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 17589–17594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairfield, K.M.; Fletcher, R.H. Vitamins for chronic disease prevention in adults: Scientific review. JAMA 2002, 287, 3116–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshfegh, A.J.; Rhodes, D.G.; Bare, D.J.; Murayi, T.; Clemens, J.C.; Rumpler, W.V.; Paul, D.R.; Sebastian, R.S.; Kuczynski, K.J.; Ingwersen, L.A.; et al. The USDA AMPM reduces bias in collection of energy intake. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
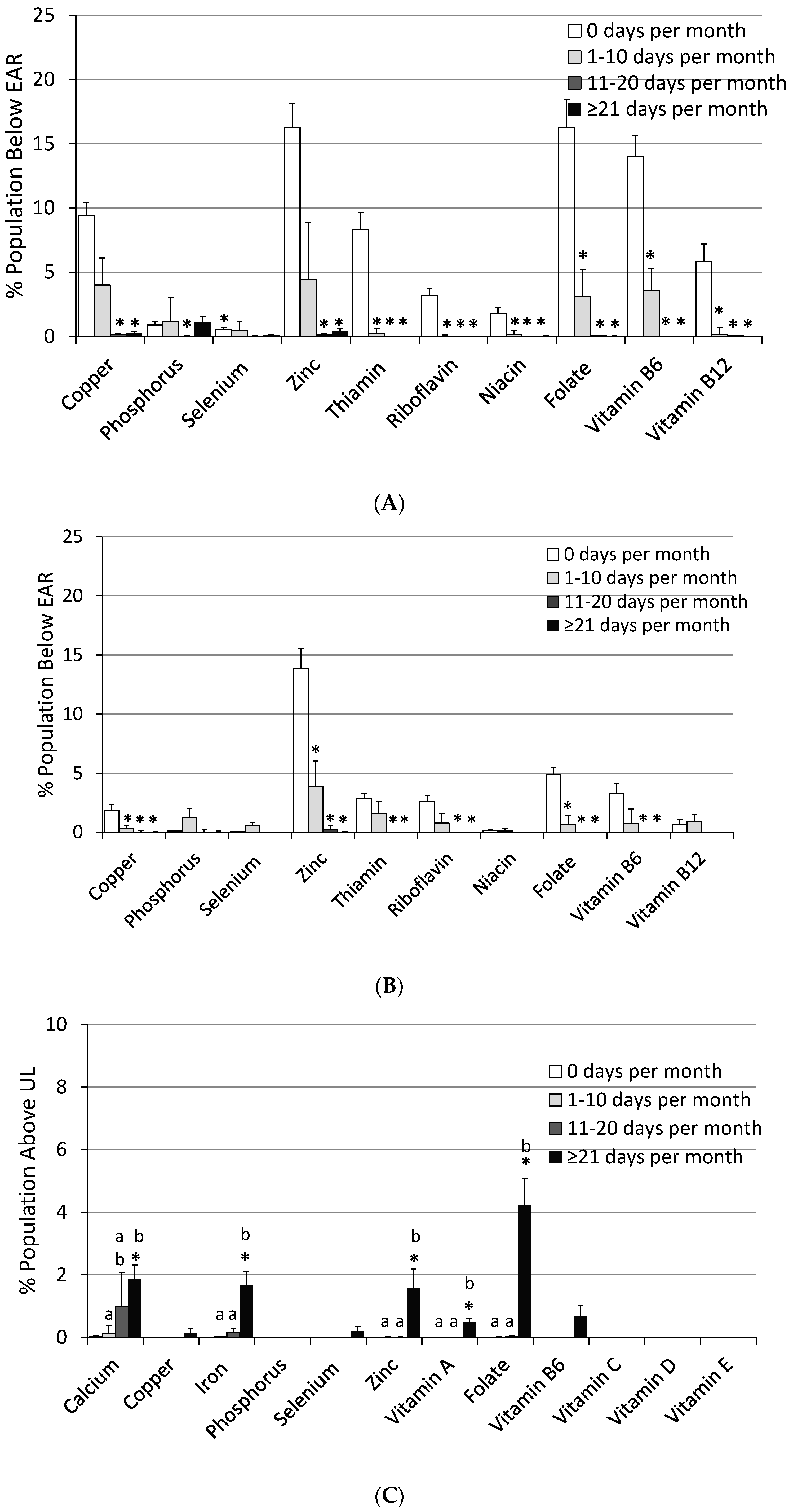
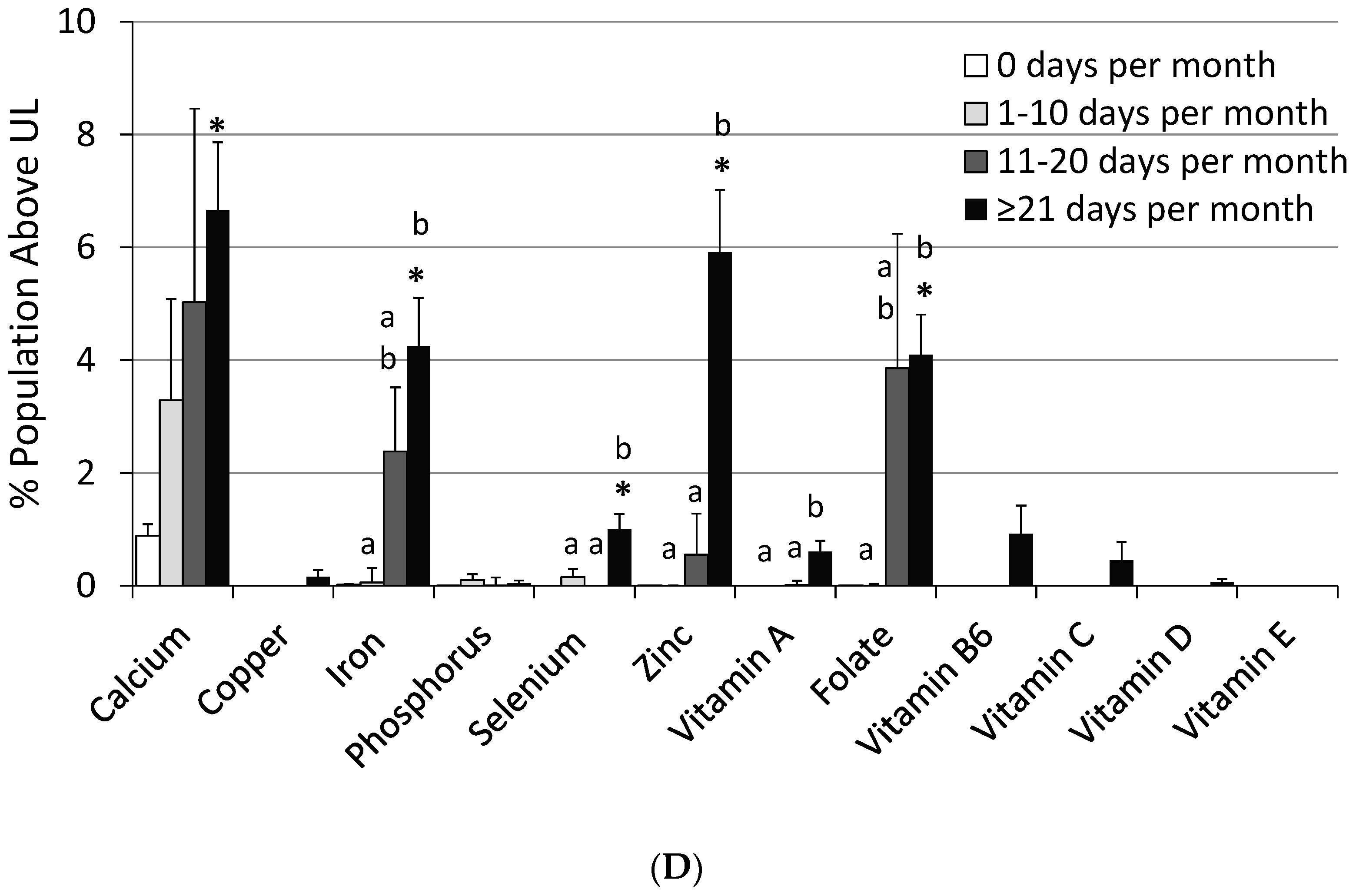
| Nutrient | Usual Intake | % Population Below EAR | % Population Above UL | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food Only | Food + Supplement. | Food Only | Food + Supplement | Food Only | Food + Supplement | |
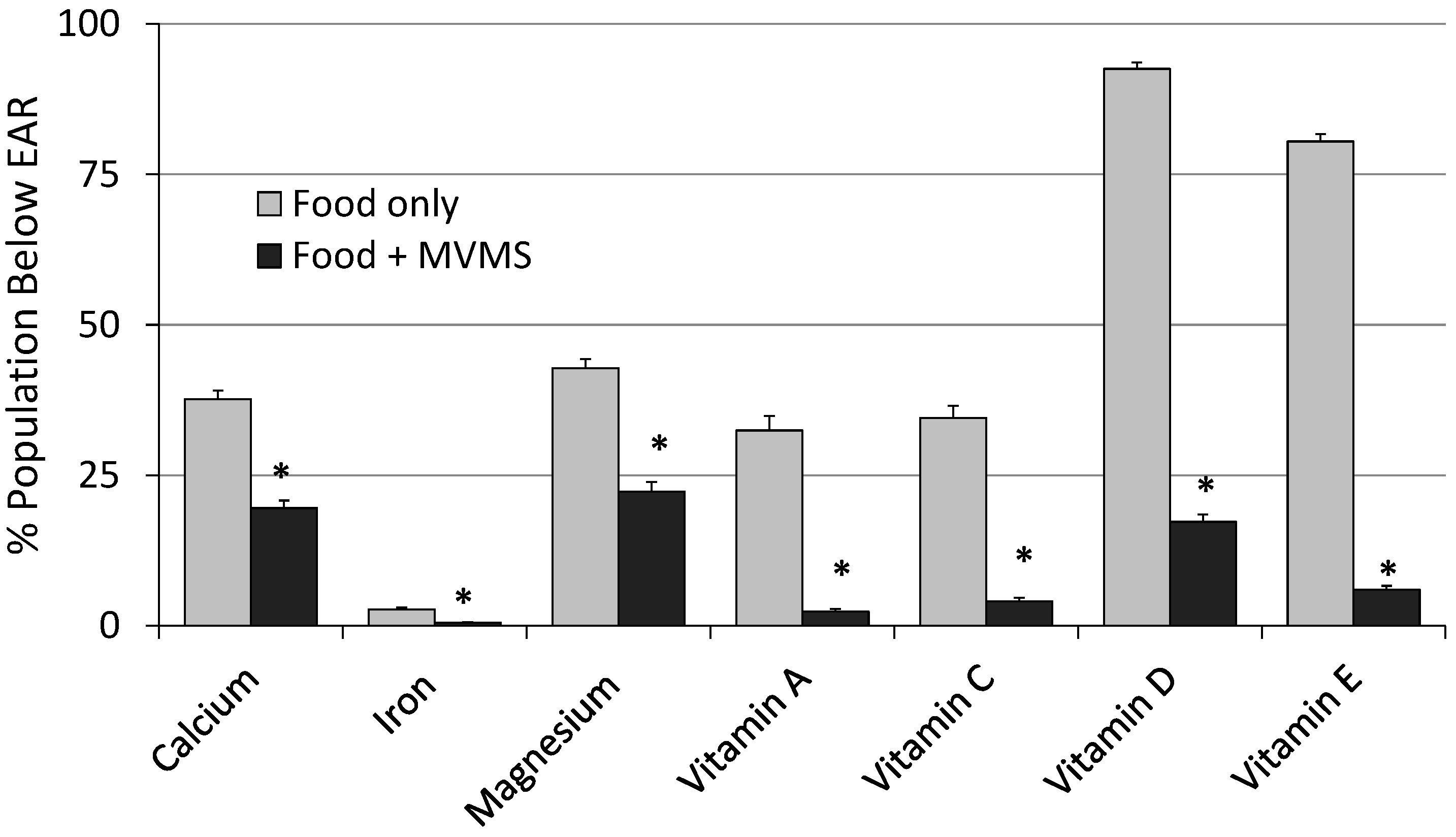
| Calcium (mg) | 1061 ± 15 | 1277 ± 1 * | 37.7 ± 1.4 | 19.6 ± 1.3 * | 1.42 ± 0.29 | 3.66 ± 0.49 * |
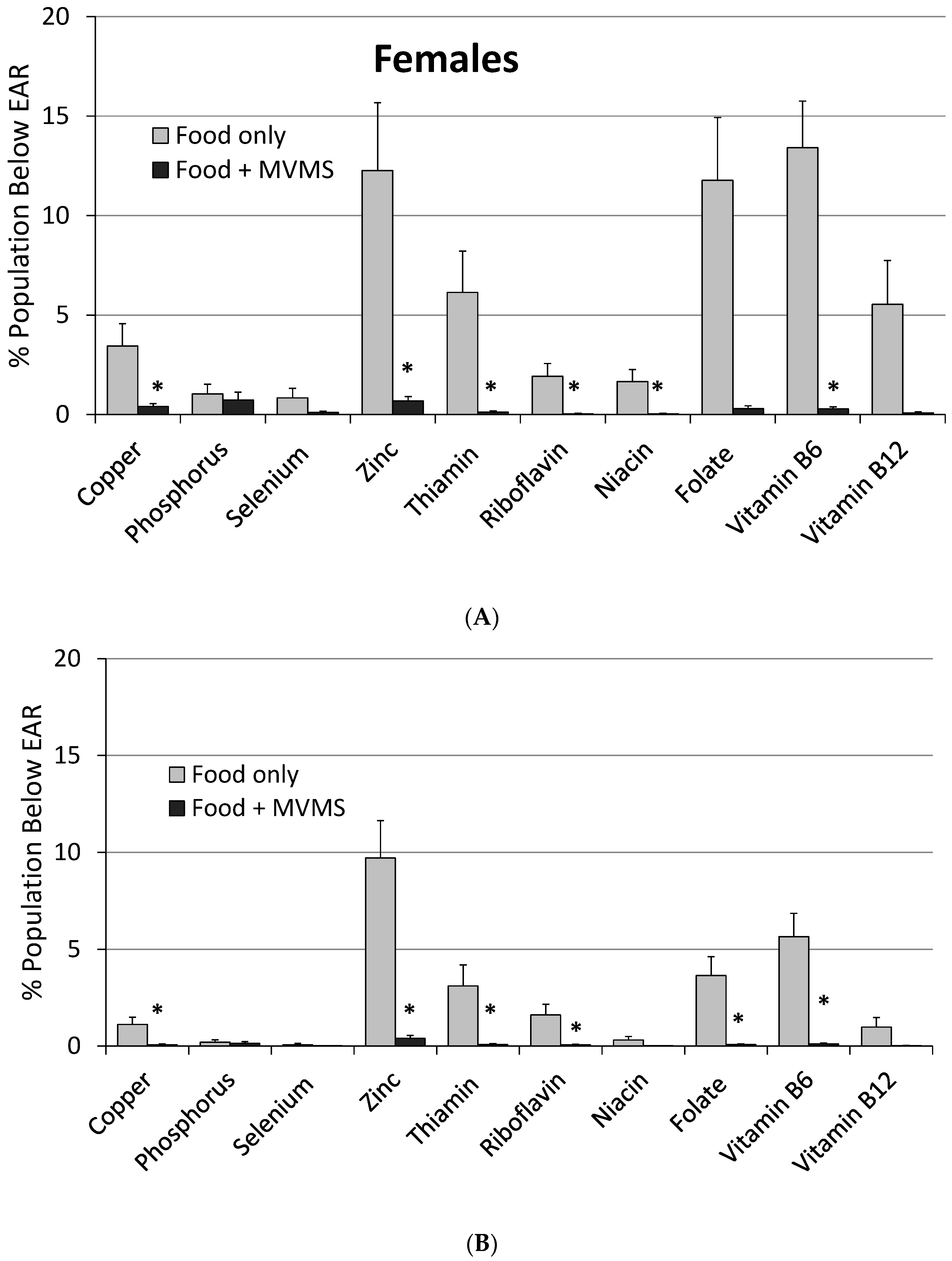
| Copper (mg) | 1.41 ± 0.02 | 2.40 ± 0.03 * | 2.3 ± 0.6 | 0.22 ± 0.08 * | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.07 |
| Iron (mg) | 16.2 ± 0.2 | 23.8 ± 0.3 * | 2.71 ± 0.33 | 0.50 ± 0.12 * | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 2.25 ± 0.29 * |
| Magnesium (mg) | 330 ± 4 | 389 ± 5 * | 42.8 ± 1.5 | 22.3 ± 1.6 * | ND | ND |
| Phosphorus (mg) | 1451 ± 14 | 1475 ± 18 | 0.58 ± 0.27 | 0.58 ± 0.27 | 0.01 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.02 |
| Selenium (µg) | 113 ± 1 | 177 ± 9 * | 0.51 ± 0.23 | 0.06 ± 0.04 | 0.00 ± 000 | 0.35 ± 0.10 * |
| Zinc (mg) | 12.1 ± 0.1 | 23.5 ± 0.3 * | 11.0 ± 2.0 | 0.54 ± 0.1 * | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 2.47 ± 0.41 * |
| Vitamin A (RAE, µg) a | 738 ± 20 | 1602 ± 26 * | 32.5 ± 2.4 | 2.34 ± 0.43 * | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.37 ± 0.09 * |
| Thiamin (mg) | 1.71 ± 0.02 | 8.5 ± 1.3 * | 4.74 ± 1.15 | 0.09 ± 0.03 * | -- | -- |
| Riboflavin (mg) | 2.29 ± 0.03 | 7.5 ± 0.5 * | 1.75 ± 0.54 | 0.04 ± 0.02 * | -- | -- |
| Niacin (mg) | 26.1 ± 0.3 | 45.4 ± 0.7 * | 0.98 ± 0.36 | 0.03 ± 0.01 * | ND | ND |
| Folate DFE (µg) b | 588 ± 9 | 1197 ± 14 * | 7.96 ± 1.67 | 0.21 ± 0.07 * | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 3.25± 0.36 * |
| Vitamin B6 (mg) | 2.20 ± 0.03 | 8.72 ± 0.55 * | 9.89 ± 1.44 | 0.19 ± 0.05 * | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.57 ± 0.17 * |
| Vitamin B12 (µg) | 5.55 ± 0.13 | 31.8 ± 2.4 * | 3.33 ± 1.26 | 0.05 ± 0.02 * | -- | -- |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 92.9 ± 2.6 | 188 ± 6 * | 34.6 ± 2.0 | 4.09 ± 0.53 * | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.15 ± 0.11 |
| Vitamin D (µg) | 5.17 ± 0.16 | 17.1 ± 0.3 * | 92.5 ± 1.1 | 17.3 ± 1.2 * | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.02 |
| Vitamin E (mg) c | 9.27 ± 0.16 | 37.3 ± 1.3 * | 80.4 ± 1.2 | 5.96 ± 0.65 * | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| Nutrients | Usual Intake | % Population Below EAR | % Population Above UL | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 Days Per Month | 1 to 10 Days Per Month | 11 to 20 Days Per Month | 21 Days or More Per Month | 0 Days Per Month | 1 to 10 Days Per Month | 11 to 20 Days Per Month | 21 Days or More Per Month | 0 Days Per Month | 1 to 10 Days Per Month | 11 to 20 Days Per Month | 21 Days or More Per Month | |
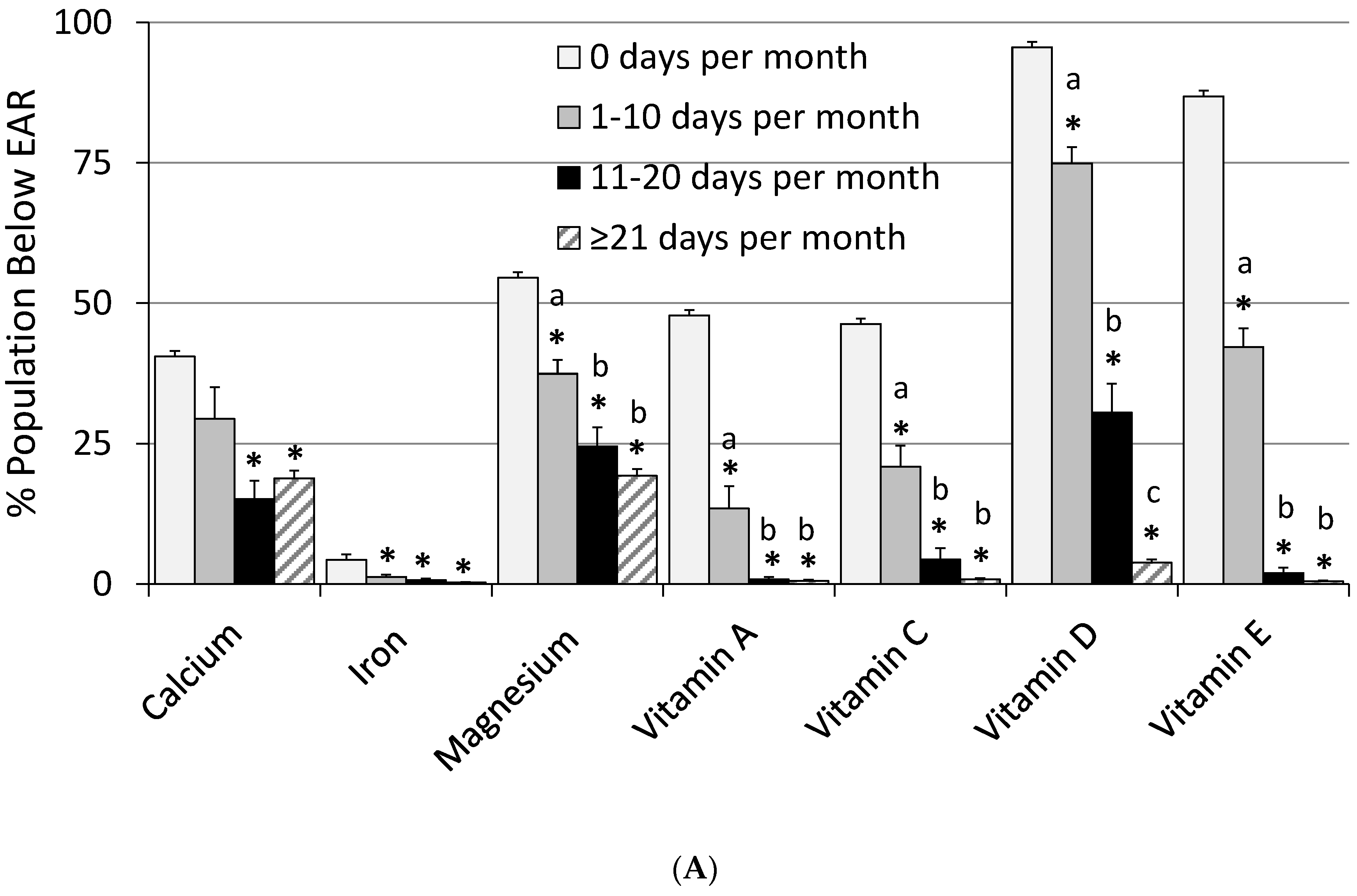
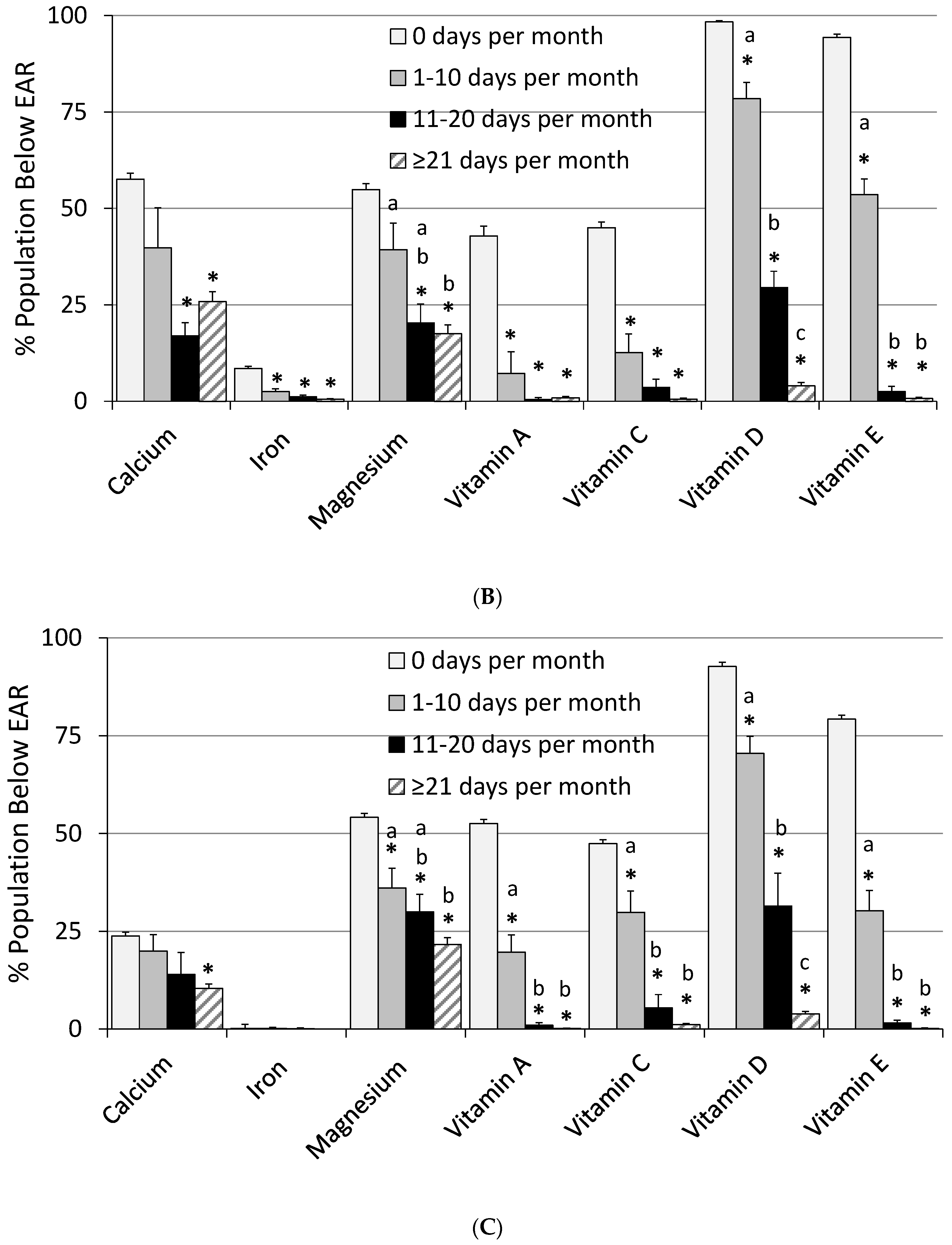
| Calcium (mg) | 986 ± 9 | 1143 ± 57 *,a | 1284 ± 47 *,a,b | 1299 ± 21 *,b | 40.5 ± 0.8 | 29.4 ± 5.6 | 15.2 ± 3.2 * | 18.8 ± 1.4 * | 0.47 ± 0.09 | 1.93 ± 0.85 | 2.89 ± 1.61 | 4.13 ± 0.62 * |
| Copper (mg) | 1.30 ± 0.01 | 1.63 ± 0.03 *,a | 2.11 ± 0.06 *,b | 2.59 ± 0.04 *,c | 5.66 ± 0.49 | 2.17 ± 1.1 * | 0.11 ± 0.09 * | 0.15 ± 0.06 * | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.15 ± 0.10 |
| Iron (mg) | 15.3 ± 0.2 | 18.6 ± 0.5 *,a | 22.9 ± 0.9 *,b | 24.9 ± 0.5 *,b | 4.3 ± 0.3 | 1.31 ± 0.40 * | 0.67 ± 0.30 * | 0.26 ± 0.11 * | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.13 a | 1.27 ± 0.56 a,b | 2.90 ± 0.46 *,b |
| Magnesium (mg) | 304 ± 3 | 345 ± 6 *,a | 369 ± 15 *,a,b | 401 ± 6 *,b | 54.6 ± 1.2 | 37.4 ± 2.5 *,a | 24.5 ± 3.4 *,b | 19.3 ± 1.2 *,b | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Phosphorus (mg) | 1409 ± 9 | 1468 ± 38 | 1506 ± 54 | 1467 ± 26 | 0.49 ± 0.13 | 1.15 ± 0.91 | 0.06 ± 0.08 * | 0.58 ± 0.23 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.04 ± 0.05 | 0.00 ± 0.06 | 0.01 ± 0.03 |
| Selenium (µg) | 115 ± 1 | 126 ± 4 *,a | 152 ± 6 *,b | 191 ± 12 *,c | 0.28 ± 0.11 | 0.44 ± 0.42 * | 0.00 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.03 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.08 ± 0.07 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.51 ± 0.14 *,b |
| Zinc (mg) | 11.7 ± 0.1 | 14.4 ± 0.4 *,a | 19.8 ± 0.5 *,b | 25.8 ± 0.3 *,c | 15.1 ± 1.4 | 3.87 ± 2.40 * | 0.17 ± 0.10 * | 0.22 ± 0.08 * | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.01 a | 0.27 ± 0.32 a | 3.59 ± 0.53 *,b |
| Vitamin A (µg) a | 620 ± 14 | 894 ± 38 *,a | 1261 ± 48 *,b | 1797 ± 38 *,c | 47.8 ± 2.2 | 13.4 ± 4.0 *,a | 0.81 ± 0.46 *,b | 0.57 ± 0.20 *,b | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.04 a | 0.53 ± 0.11 *,b |
| Thiamin (mg) | 1.64 ± 0.01 | 3.28 ± 0.22 *,a | 4.92 ± 0.47 *,b | 10.2 ± 1.5 *,c | 5.51 ± 0.62 | 0.89 ± 0.68 * | 0.00 ± 0.00 * | 0.00 ± 0.00 * | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Riboflavin (mg) | 2.13 ± 0.03 | 3.68 ± 0.22 *,a | 5.40 ± 0.45 *,b | 8.59 ± 0.46 *,c | 2.90 ± 0.37 | 0.53 ± 0.37 * | 0.00 ± 0.00 * | 0.00 ± 0.00 * | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Niacin (mg) | 26.2 ± 0.2 | 30.1 ± 1.1 *,a | 39.3 ± 0.9 *,b | 49.5 ± 0.9 *,c | 0.95 ± 0.23 | 0.08 ± 0.22 * | 0.00 ± 0.01 * | 0.00 ± 0.00 * | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Folate DFE (µg) b | 551 ± 7 | 728 ± 37 *,a | 1028 ± 33 *,b | 1318 ± 16 *,c | 10.5 ± 1.2 | 2.19 ± 1.12 * | 0.00 ± 0.01 * | 0.01 ± 0.005 * | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.02 a | 1.58 ± 1.10 a,b | 4.05 ± 0.58 *,b |
| Vitamin B6 (mg) | 2.13 ± 0.03 | 3.71 ± 0.23 *,a | 5.87 ± 0.50 *,b | 10.2 ± 0.5 *,c | 8.56 ± 0.79 | 2.01 ± 0.86 * | 0.00 ± 0.00 * | 0.00 ± 0.00 * | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.79 ± 024 *,b |
| Vitamin B12 (µg) | 5.3 ± 0.1 | 8.9 ± 0.5 *,a | 16.4 ± 1.0 *,b | 39.0 ± 2.3 *,c | 3.31 ± 0.61 | 0.38 ± 0.46 * | 0.04 ± 0.04 * | 0.00 ± 0.00 * | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 83.9 ± 2.6 | 110 ± 7 *,a | 158 ± 9 *,b | 208 ± 8 *,c | 46.3 ± 1.4 | 20.9 ± 3.8 *,a | 4.37 ± 2.02 *,b | 0.83 ± 0.23 *,b | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.21 ± 0.15 |
| Vitamin D (µg) | 4.8 ± 0.1 | 8.0 ± 0.04 *,a | 13.2 ± 0.6 *,b | 19.5 ± 0.3 *,c | 95.6 ± 0.6 | 74.9 ± 2.9 *,a | 30.5 ± 5.1 *,b | 3.86 ± 0.50 *,c | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.03 |
| Vitamin E (mg) c | 8.3 ± 0.1 | 13.8 ± 0.4 *,a | 25.9 ± 1.3 *,b | 43.8 ± 1.1 *,c | 86.9 ± 1.0 | 42.2 ± 3.3 *,a | 2.01 ± 0.90 *,b | 0.50 ± 0.16 *,b | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| Variables | N | Odds Ratio (99% CI) of Deficiency by Frequency of MVMS Use | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 Days | 1 to 30 Days | 1 to 10 Days | 11 to 20 Days | 21 Days or More | ||
| Deficient Vitamin B6 (<20 nmol/L) a | 14,596 | 1.00 | 0.36 (0.27, 0.48) * | 0.47 (0.27, 0.82) * | 0.33 (0.19, 0.56) * | 0.34 (0.22, 0.52) * |
| Deficient Vitamin B12 (<200 pg/mL) b | 13,345 | 1.00 | 0.42 (0.22, 0.80) * | 0.43 (0.12, 1.57) | 0.42 (0.04, 4.60) | 0.42 (0.22, 0.78) * |
| Deficient Vitamin C (<11.4 µmol/L) c | 6423 | 1.00 | 0.31 (0.12, 0.82) * | 0.34 (0.09, 1.37) | 0.44 (0.08, 2.30) | 0.27 (0.09, 0.84) * |
| Deficient Vitamin D (<30 mmol/L) d | 17,655 | 1.00 | 0.34 (0.23, 0.48) * | 0.88 (0.40, 1.95) a | 0.22 (0.08, 0.59) *,b | 0.24 (0.15, 0.40) *,b |
| Deficient Body Iron (<0 mg/kg) a | 3916 | 1.00 | 0.63 (0.33, 1.22) | 0.58 (0.16, 2.14) | 1.10 (0.40, 3.07) | 0.50 (0.18, 1.39) |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blumberg, J.B.; Frei, B.B.; Fulgoni, V.L., III; Weaver, C.M.; Zeisel, S.H. Impact of Frequency of Multi-Vitamin/Multi-Mineral Supplement Intake on Nutritional Adequacy and Nutrient Deficiencies in U.S. Adults. Nutrients 2017, 9, 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9080849
Blumberg JB, Frei BB, Fulgoni VL III, Weaver CM, Zeisel SH. Impact of Frequency of Multi-Vitamin/Multi-Mineral Supplement Intake on Nutritional Adequacy and Nutrient Deficiencies in U.S. Adults. Nutrients. 2017; 9(8):849. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9080849
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlumberg, Jeffrey B., Balz B. Frei, Victor L. Fulgoni, III, Connie M. Weaver, and Steven H. Zeisel. 2017. "Impact of Frequency of Multi-Vitamin/Multi-Mineral Supplement Intake on Nutritional Adequacy and Nutrient Deficiencies in U.S. Adults" Nutrients 9, no. 8: 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9080849
APA StyleBlumberg, J. B., Frei, B. B., Fulgoni, V. L., III, Weaver, C. M., & Zeisel, S. H. (2017). Impact of Frequency of Multi-Vitamin/Multi-Mineral Supplement Intake on Nutritional Adequacy and Nutrient Deficiencies in U.S. Adults. Nutrients, 9(8), 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9080849








