Two Saporin-Containing Immunotoxins Specific for CD20 and CD22 Show Different Behavior in Killing Lymphoma Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Immunotoxin Purification and Characterization
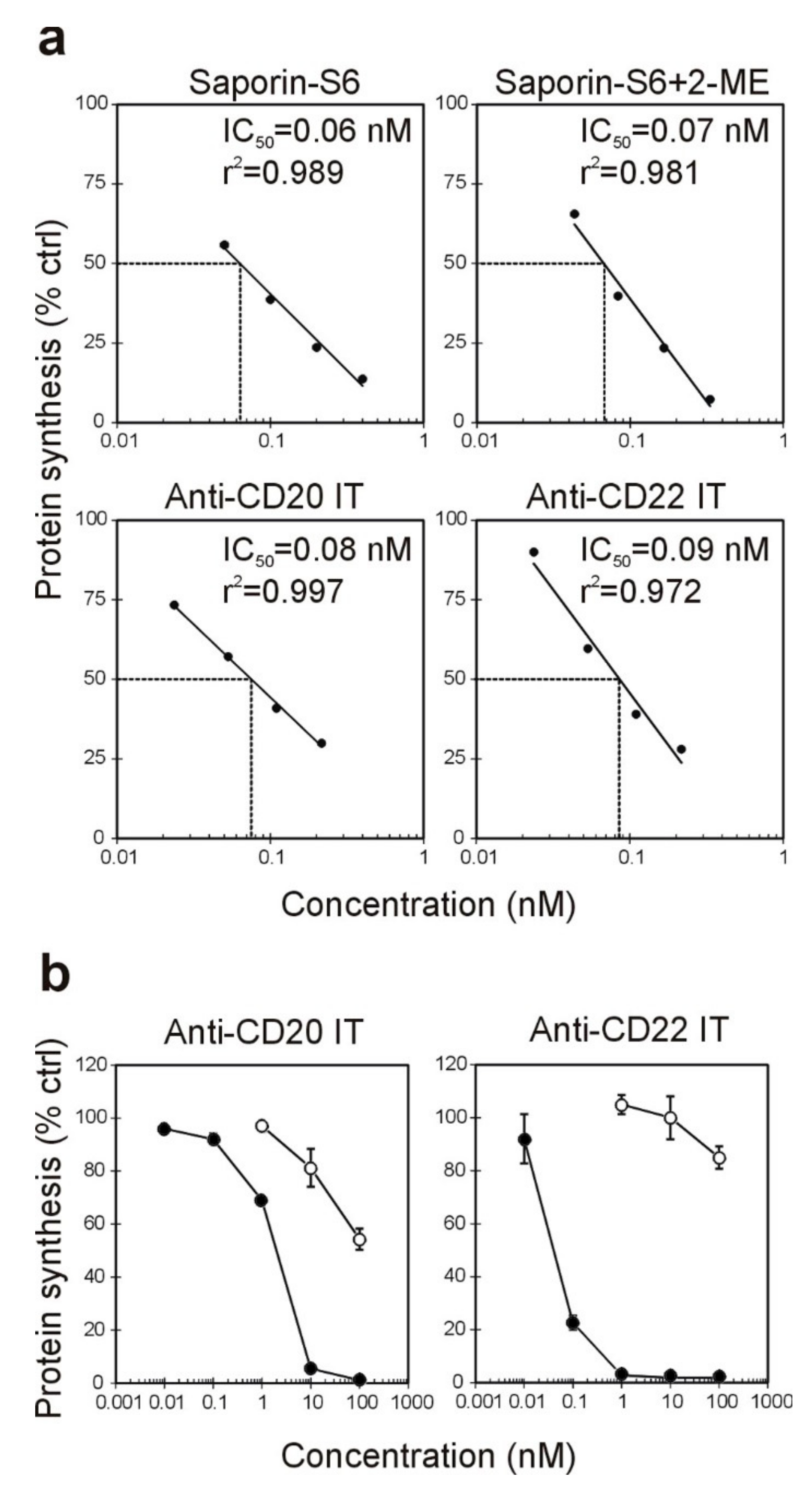
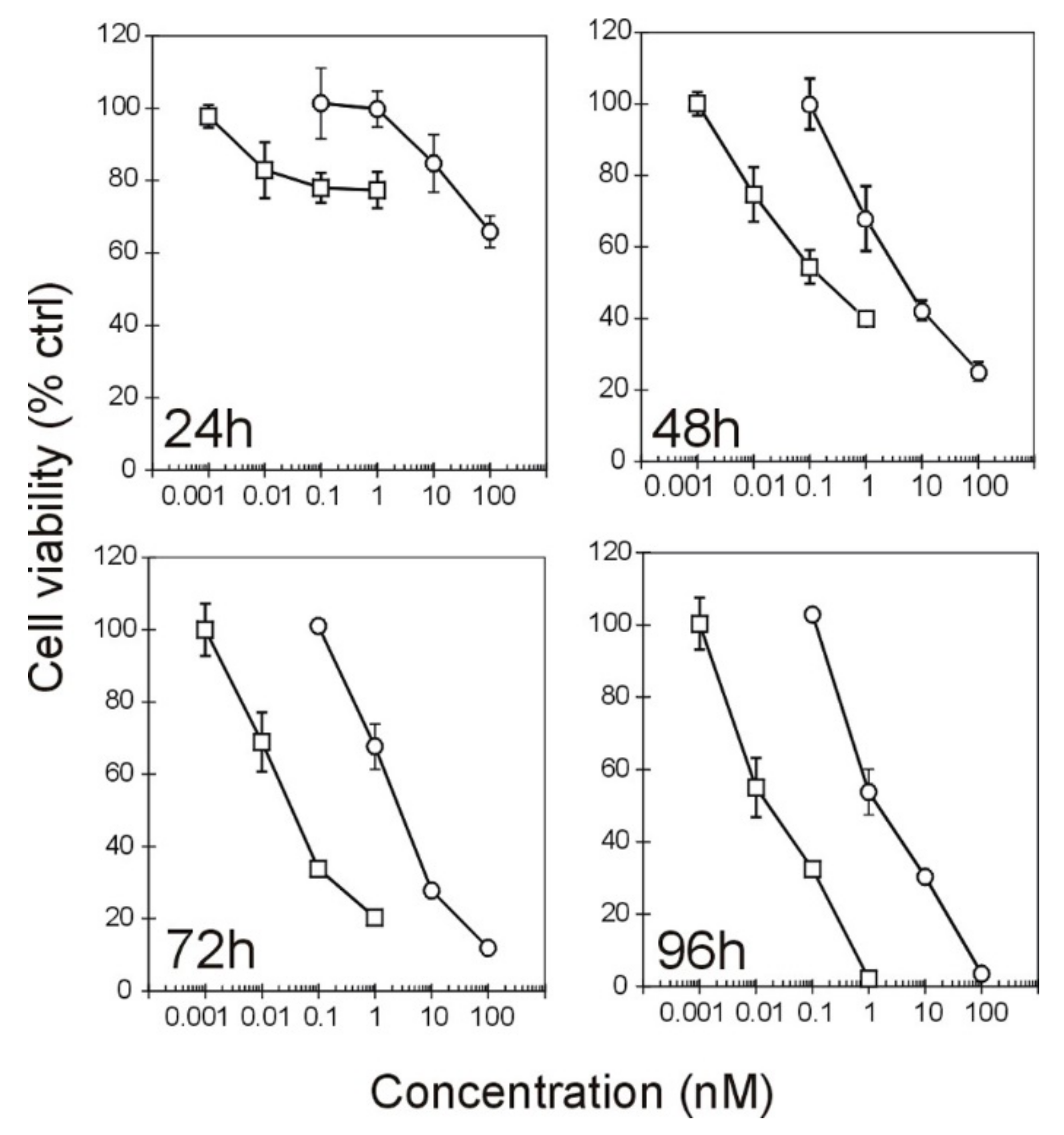
2.2. Effect of the Immunotoxins on Raji Protein Synthesis and Cell Viability
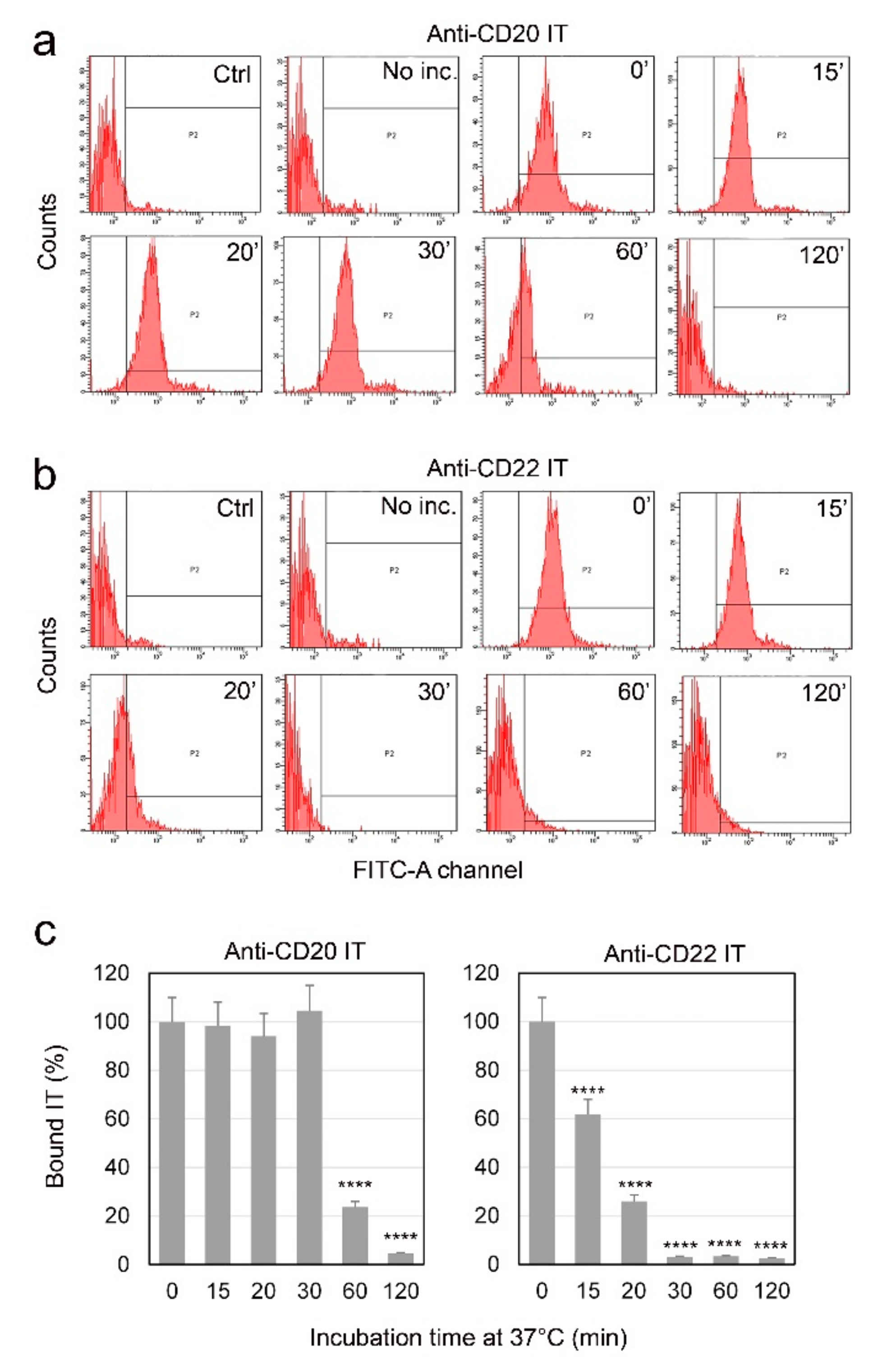
2.3. Evaluation of Internalization Time of the Immunotoxins
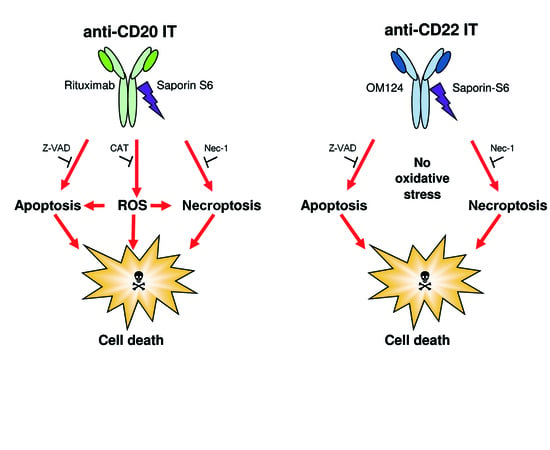
2.4. Evaluation of Cell Death Pathways Induced by Immunotoxins in Raji Cells
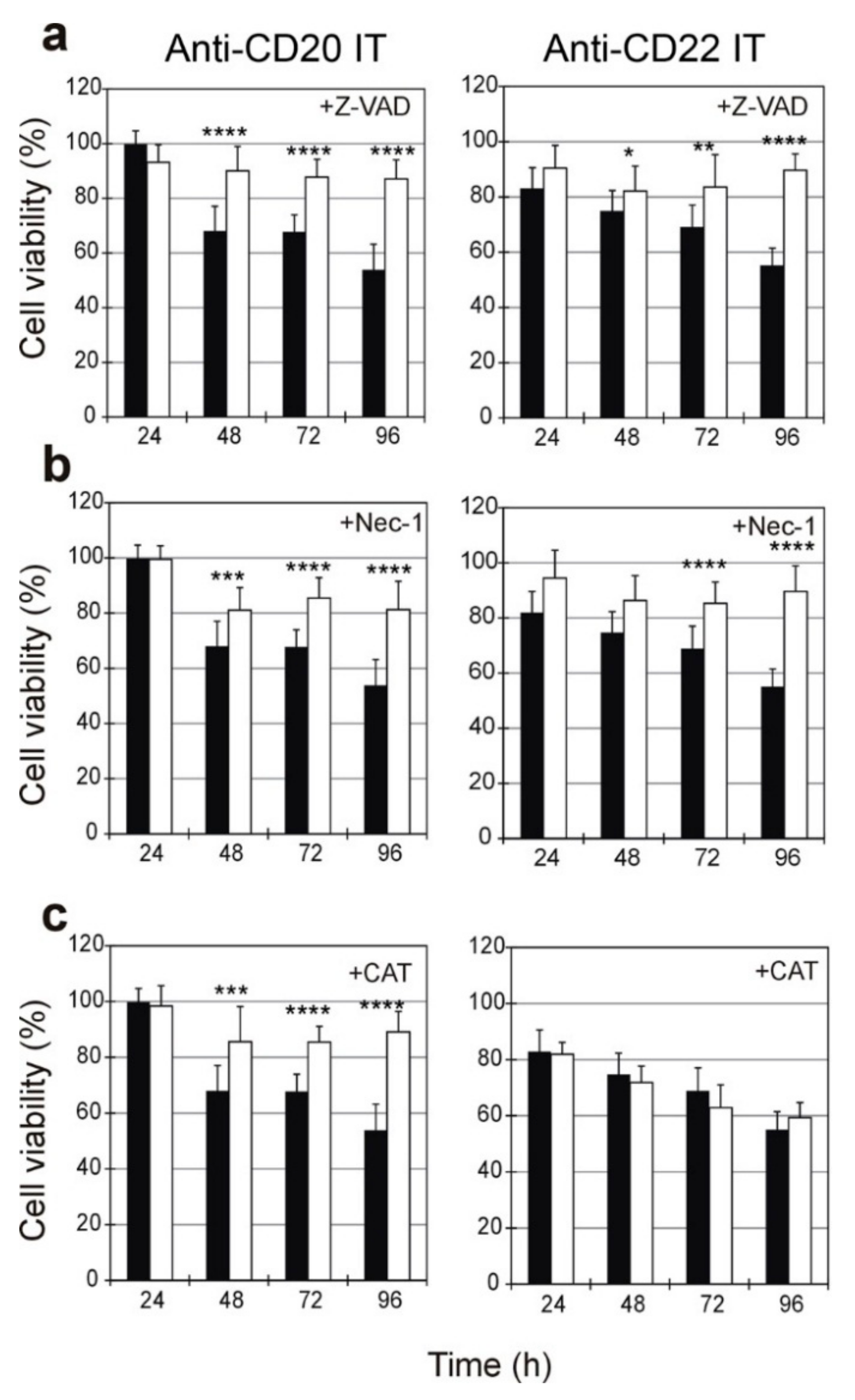
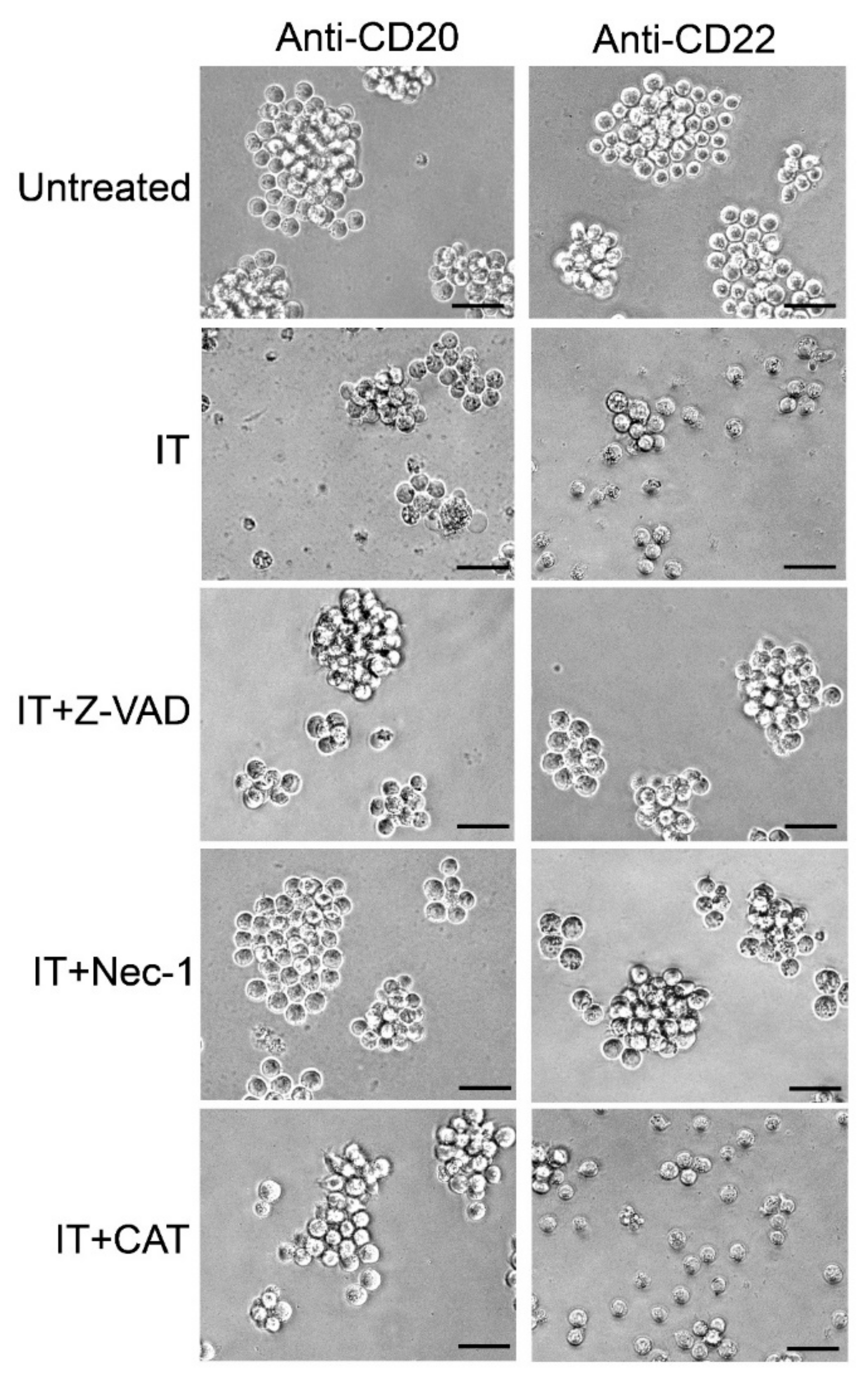
2.5. Evaluation of the Protective Effect of Apoptosis and Necroptosis Inhibitors Z-VAD and Necrostatin-1 and the H2O2 Scavenger Catalase on Raji Cells
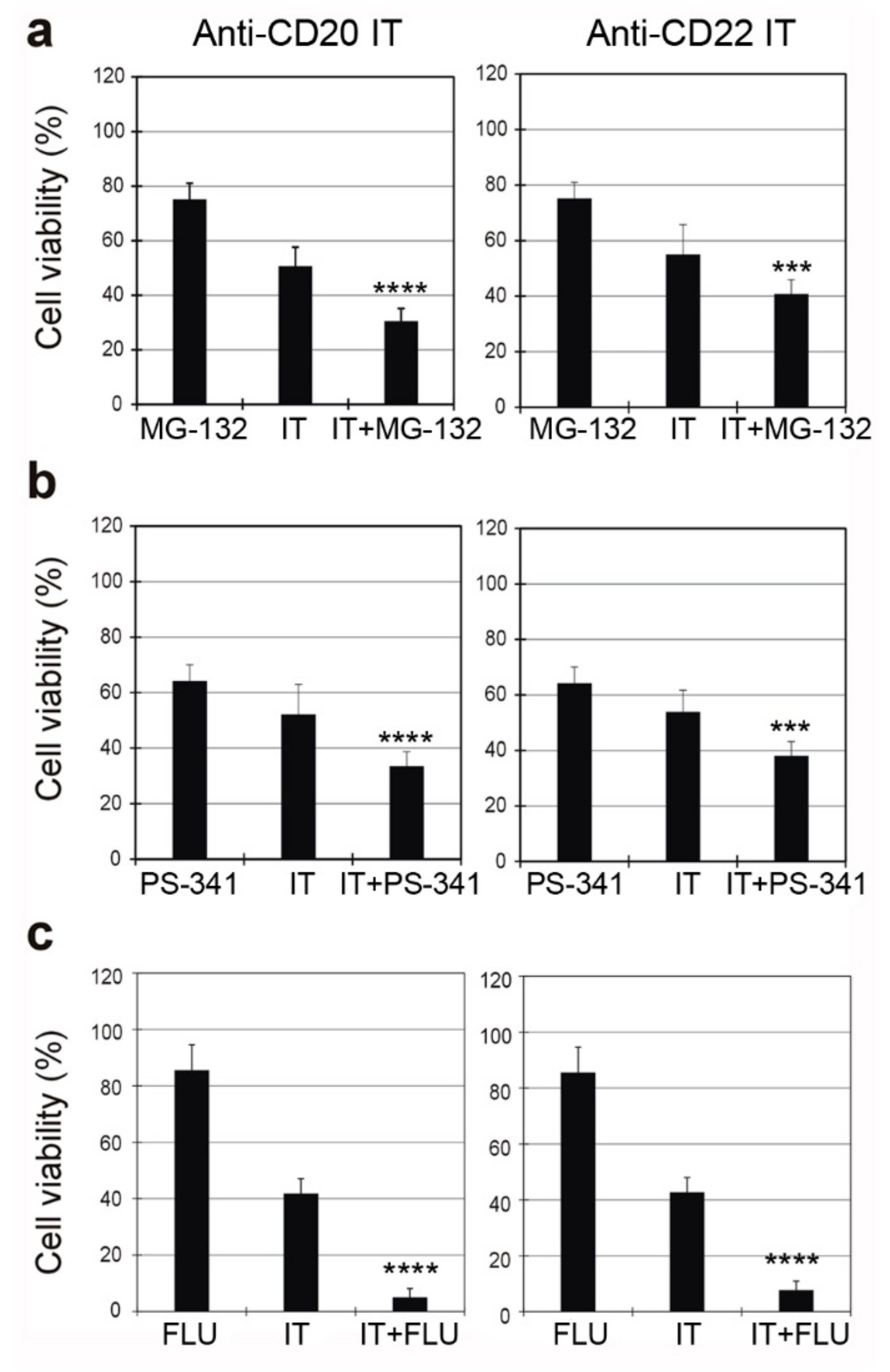
2.6. Combined Cytotoxic Effect of ITs with the Proteasome Inhibitors MG-132 and PS-341 and with the Chemotherapeutic Drug Fludarabine
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Immunotoxins
4.2. Cells
4.3. Reagents and Kits
4.4. Cell Protein Synthesis Inhibition Assays
4.5. Cell Viability Assay
4.6. Cell Binding Assay
4.7. Evaluation of Apoptosis
4.8. Statistical Analyses
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Polito, L.; Mancuso, R.; Mercatelli, D.; Bortolotti, M.; Bolognesi, A. mAbs targeting CD20 and other lymphocyte CD markers in lymphoma treatment. In Monoclonal Antibodies in Oncology; Uckun, F.M., Ed.; Future Medicine: London, UK, 2013; pp. 6–19. [Google Scholar]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Maiello, S.; Battelli, M.G.; Bolognesi, A. Rituximab and other new anti-CD20 mAbs for Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma treatment. Eur. Med. J. 2014, 2, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Govindan, S.V.; Goldenberg, D.M. New antibody conjugates in cancer therapy. Sci. World J. 2010, 10, 2070–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teicher, B.A.; Chari, R.V. Antibody conjugate therapeutics: challenges and potential. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 6389–6397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolognesi, A.; Polito, L. Immunotoxins and other conjugates: Pre-clinical studies. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2004, 4, 563–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilabert-Oriol, R.; Weng, A.; von Mallinckrodt, B.; Melzig, M.F.; Fuchs, H.; Thakur, M. Immunotoxins constructed with ribosome-inactivating proteins and their enhancers: a lethal cocktail with tumor specific efficacy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 6584–6643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreras, J.M.; Citores, L.; Iglesias, R.; Jiménez, P.; Girbés, T. Use of ribosome-inactivating proteins from Sambucus for the construction of immunotoxins and conjugates for cancer therapy. Toxins (Basel) 2011, 3, 420–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankel, A.E.; Kreitman, R.J.; Sausville, E.A. Targeted toxins. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Pedrazzi, M.; Bolognesi, A. Immunotoxins and other conjugates containing saporin-S6 for cancer therapy. Toxins (Basel) 2011, 3, 697–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolognesi, A.; Bortolotti, M.; Maiello, S.; Battelli, M.G.; Polito, L. Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins from Plants: A Historical Overview. Molecules 2016, 21, E1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polito, L.; Djemil, A.; Bortolotti, M. Plant Toxin-Based Immunotoxins for Cancer Therapy: A Short Overview. Biomedicines 2016, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Maro, A.; Citores, L.; Russo, R.; Iglesias, R.; Ferreras, J.M. Sequence comparison and phylogenetic analysis by the Maximum Likelihood method of ribosome-inactivating proteins from angiosperms. Plant Mol. Biol. 2014, 85, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Maiello, S.; Battelli, M.G.; Bolognesi, A. Plants Producing Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins in Traditional Medicine. Molecules 2016, 21, E1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stirpe, F.; Battelli, M.G. Ribosome-inactivating proteins: progress and problems. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 1850–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolognesi, A.; Tazzari, P.L.; Olivieri, F.; Polito, L.; Lemoli, R.; Terenzi, A.; Pasqualucci, L.; Falini, B.; Stirpe, F. Evaluation of immunotoxins containing single-chain ribosome-inactivating proteins and an anti-CD22 monoclonal antibody (OM124): in vitro and in vivo studies. Br. J. Haematol. 1998, 101, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polito, L.; Bolognesi, A.; Tazzari, P.L.; Farini, V.; Lubelli, C.; Zinzani, P.L.; Ricci, F.; Stirpe, F. The conjugate Rituximab/saporin-S6 completely inhibits clonogenic growth of CD20-expressing cells and produces a synergistic toxic effect with Fludarabine. Leukemia 2004, 18, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolognesi, A.; Polito, L.; Farini, V.; Bortolotti, M.; Tazzari, P.L.; Ratta, M.; Ravaioli, A.; Horenstein, A.L.; Stirpe, F.; Battelli, M.G.; et al. CD38 as a target of IB4 mAb carrying saporin-S6: design of an immunotoxin for ex vivo depletion of hematological CD38+ neoplasia. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2005, 19, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flavell, D.J.; Warnes, S.L.; Bryson, C.J.; Field, S.A.; Noss, A.L.; Packham, G.; Flavell, S.U. The anti-CD20 antibody rituximab augments the immunospecific therapeutic effectiveness of an anti-CD19 immunotoxin directed against human B-cell lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2006, 134, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Mercatelli, D.; Battelli, M.G.; Bolognesi, A. Saporin-S6: A useful tool in cancer therapy. Toxins (Basel) 2013, 5, 1698–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vooijs, W.C.; Otten, H.G.; van Vliet, M.; van Dijk, A.J.; de Weger, R.A.; de Boer, M.; Bohlen, H.; Bolognesi, A.; Polito, L.; de Gast, G.C. B7-1 (CD80) as target for immunotoxin therapy for Hodgkin’s disease. Br. J. Cancer 1997, 76, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falini, B.A.; Bolognesi, A.; Flenghi, L.; Tazzari, P.L.; Broe, M.K.; Stein, H.; Dürkop, H.; Aversa, F.; Corneli, P.; Pizzolo, G.; et al. Response of refractory Hodgkin’s disease to monoclonal anti-CD30 immunotoxin. Lancet 1992, 339, 1195–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, L.; Valbonesi, P.; Bonora, E.; Gorini, P.; Bolognesi, A.; Stirpe, F. Polynucleotide:adenosine glycosidase activity of ribosome-inactivating proteins: effect on DNA, RNA and poly(A). Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, L.; Bolognesi, A.; Valbonesi, P.; Polito, L.; Olivieri, F.; Stirpe, F. Polynucleotide: adenosine glycosidase activity of immunotoxins containing ribosome-inactivating proteins. J. Drug Target. 2000, 8, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battelli, M.G.; Barbieri, L.; Bolognesi, A.; Buonamici, L.; Valbonesi, P.; Polito, L.; van Damme, E.J.; Peumans, W.J.; Stirpe, F. Ribosome-inactivating lectins with polynucleotide:adenosine glycosidase activity. FEBS Lett. 1997, 408, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Farini, V.; Battelli, M.G.; Barbieri, L.; Bolognesi, A. Saporin induces multiple death pathways in lymphoma cells with different intensity and timing as compared to ricin. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vago, R.; Marsden, C.J.; Lord, J.M.; Ippoliti, R.; Flavell, D.J.; Flavell, S.U.; Ceriotti, A.; Fabbrini, M.S. Saporin and ricin A chain follow different intracellular routes to enter the cytosol of intoxicated cells. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 4983–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolognesi, A.; Polito, L.; Scicchitano, V.; Orrico, C.; Pasquinelli, G.; Musiani, S.; Santi, S.; Riccio, M.; Bortolotti, M.; Battelli, M.G. Endocytosis and intracellular localisation of the type 1 ribosome-inactivating protein saporin-S6. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2012, 26, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Horrix, C.; Raviv, Z.; Flescher, E.; Voss, C.; Berger, M.R. Plant ribosome-inactivating proteins type II induce the unfolded protein response in human cancer cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 1269–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilabert-Oriol, R.; Thakur, M.; Haussmann, K.; Niesler, N.; Bhargava, C.; Görick, C.; Fuchs, H.; Weng, A. Saponins from Saponaria officinalis L. Augment the Efficacy of a Rituximab-Immunotoxin. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 1525–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan-Chang, L.; O’Donnell, R.T.; Tuscano, J.M. Targeting CD22 in B-cell malignancies: Current status and clinical outlook. BioDrugs 2013, 27, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, T.; Mavratzas, A.; Kiesgen, S.; Haase, S.; Bötticher, B.; Exner, E.; Mier, W.; Grosse-Hovest, L.; Jäger, D.; Arndt, M.A.; et al. A Humanized Anti-CD22-Onconase Antibody-Drug Conjugate Mediates Highly Potent Destruction of Targeted Tumor Cells. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 561814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.B.; Zhang, Y.N.; Ding, D.; Pan, L.Q.; Miao, D.; Xu, S.; Zhang, C.; Luo, P.H.; et al. Preclinical studies of targeted therapies for CD20-positive B lymphoid malignancies by Ofatumumab conjugated with auristatin. Investig. New Drugs 2014, 32, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polson, A.G.; Calemine-Fenaux, J.; Chan, P.; Chang, W.; Christensen, E.; Clark, S.; de Sauvage, F.J.; Eaton, D.; Elkins, K.; Elliott, J.M.; et al. Antibody-drug conjugates for the treatment of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: target and linker-drug selection. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2358–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Countouriotis, A.; Moore, T.B.; Sakamoto, K.M. Cell surface antigen and molecular targeting in the treatment of hematologic malignancies. Stem Cells 2002, 20, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolotti, M.; Bolognesi, A.; Battelli, M.G.; Polito, L. High in vitro anti-tumor efficacy of dimeric Rituximab/Saporin-S6 immunotoxin. Toxins (Basel) 2016, 8, E192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieber, T.; Schoeler, D.; Ringel, F.; Pascu, M.; Schriever, F. Selective internalization of monoclonal antibodies by B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells. Br. J. Haematol. 2003, 121, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolognesi, A.; Tazzari, P.L.; Olivieri, F.; Polito, L.; Falini, B.; Stirpe, F. Induction of apoptosis by ribosome-inactivating proteins and related immuntoxins. Int. J. Cancer 1996, 68, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, A.; Polito, L.; Tazzari, P.L.; Lemoli, R.M.; Lubelli, C.; Fogli, M.; de Boer, M.; Stirpe, F. In vitro anti-tumor activity of anti-CD80 and anti-CD86 immunotoxins containing type 1 ribosome-inactivating proteins. Br. J. Haematol. 2000, 110, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Farini, V.; Pedrazzi, M.; Tazzari, P.L.; Bolognesi, A. ATG-saporin-S6 immunotoxin: A new potent and selective drug to eliminate activated lymphocytes and lymphoma cells. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 147, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Pedrazzi, M.; Mercatelli, D.; Battelli, M.G.; Bolognesi, A. Apoptosis and necroptosis induced by stenodactylin in neuroblastoma cells can be completely prevented through caspase inhibition plus catalase or necrostatin-1. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenabeele, P.; Galluzzi, L.; Vanden Berghe, T.; Kroemer, G. Molecular mechanisms of necroptosis: An ordered cellular explosion. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 11, 700–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels-Wells, T.R.; Helguera, G.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Leoh, L.S.; Erb, M.A.; Diamante, G.; Casero, D.; Pellegrini, M.; Martínez-Maza, O.; Penichet, M.L. Insights into the mechanism of cell death induced by saporin delivered into cancer cells by an antibody fusion protein targeting the transferrin receptor 1. Toxicol. In Vitro 2013, 27, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fengling, M.; Fenju, L.; Wanxin, W.; Lijia, Z.; Jiandong, T.; Zu, W.; Xin, Y.; Qingxiang, G. Rituximab sensitizes a Burkitt lymphoma cell line to cell killing byX-irradiation. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2009, 48, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honeychurch, J.; Alduaij, W.; Azizyan, M.; Cheadle, E.J.; Pelicano, H.; Ivanov, A.; Huang, P.; Cragg, M.S.; Illidge, T.M. Antibody-induced nonapoptotic cell death in human lymphoma and leukemia cells is mediated through a novel reactive oxygen species-dependent pathway. Blood 2012, 119, 3523–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooqi, A.A.; Li, K.T.; Fayyaz, S.; Chang, Y.T.; Ismail, M.; Liaw, C.C.; Yuan, S.S.; Tang, J.Y.; Chang, H.W. Anticancer drugs for the modulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxidative stress. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 5743–5752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czuczman, M.S.; Olejniczak, S.; Gowda, A.; Kotowski, A.; Binder, A.; Kaur, H.; Knight, J.; Starostik, P.; Deans, J.; Hernandez-Ilizaliturri, F.J. Acquirement of rituximab resistance in lymphoma cell lines is associated with both global CD20 gene and protein down-regulation regulated at the pretranscriptional and posttranscriptional levels. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 1561–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, P.C.; Hernandez-Ilizaliturri, F.J.; Bangia, N.; Olejniczak, S.H.; Czuczman, M.S. Regulation of CD20 in rituximab-resistant cell lines and B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battelli, M.G.; Scicchitano, V.; Polito, L.; Farini, V.; Barbieri, L.; Bolognesi, A. Binding and intracellular routing of the plant-toxic lectins, lanceolin and stenodactylin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1800, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.M.; Churchill, E.; McKnight, H.; Mahaffey, C.M.; Ma, Y.; O'Donnell, R.T.; Tuscano, J.M. The HB22.7 Anti-CD22 monoclonal antibody enhances bortezomib- mediated lymphomacidal activity in a sequence dependent manner. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2011, 4, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, L.; Brigotti, M.; Perocco, P.; Carnicelli, D.; Ciani, M.; Mercatali, L.; Stirpe, F. Ribosome-inactivating proteins depurinate poly(ADP-ribosyl)ated poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and have transforming activity for 3T3 fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 2003, 538, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrush, G.R.; Lark, L.R.; Clinchy, B.C.; Vitetta, E.S. Immunotoxins: an update. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1996, 14, 49–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhumathi, J.; Verma, R.S. Therapeutic targets and recent advances in protein immunotoxins. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzo, E.; Di Maro, A. A new age for biomedical applications of Ribosome Inactivating Proteins (RIPs): From bioconjugate to nanoconstructs. J. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 23, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FitzGerald, D.J.; Wayne, A.S.; Kreitman, R.J.; Pastan, I. Treatment of hematologic malignancies with immunotoxins and antibody-drug conjugates. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6300–6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosio, F.; Stella, B.; Cerioni, S.; Gastaldi, D.; Arpicco, S. Advances in anticancer antibody-drug conjugates and immunotoxins. Recent Pat. Anticancer Drug Discov. 2014, 9, 35–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, L.; Bolognesi, A.; Stirpe, F. Purification and conjugation of type 1 ribosome-inactivating proteins. In Immunotoxins: Methods and Protocols; Hall, W.A., Ed.; Humana Press: New York City, NY, USA, 2001; Volume 166, pp. 71–85. [Google Scholar]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Mercatelli, D.; Mancuso, R.; Baruzzi, G.; Faedi, W.; Bolognesi, A. Protein synthesis inhibition activity by strawberry tissue protein extracts during plant life cycle and under biotic and abiotic stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 15532–15545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
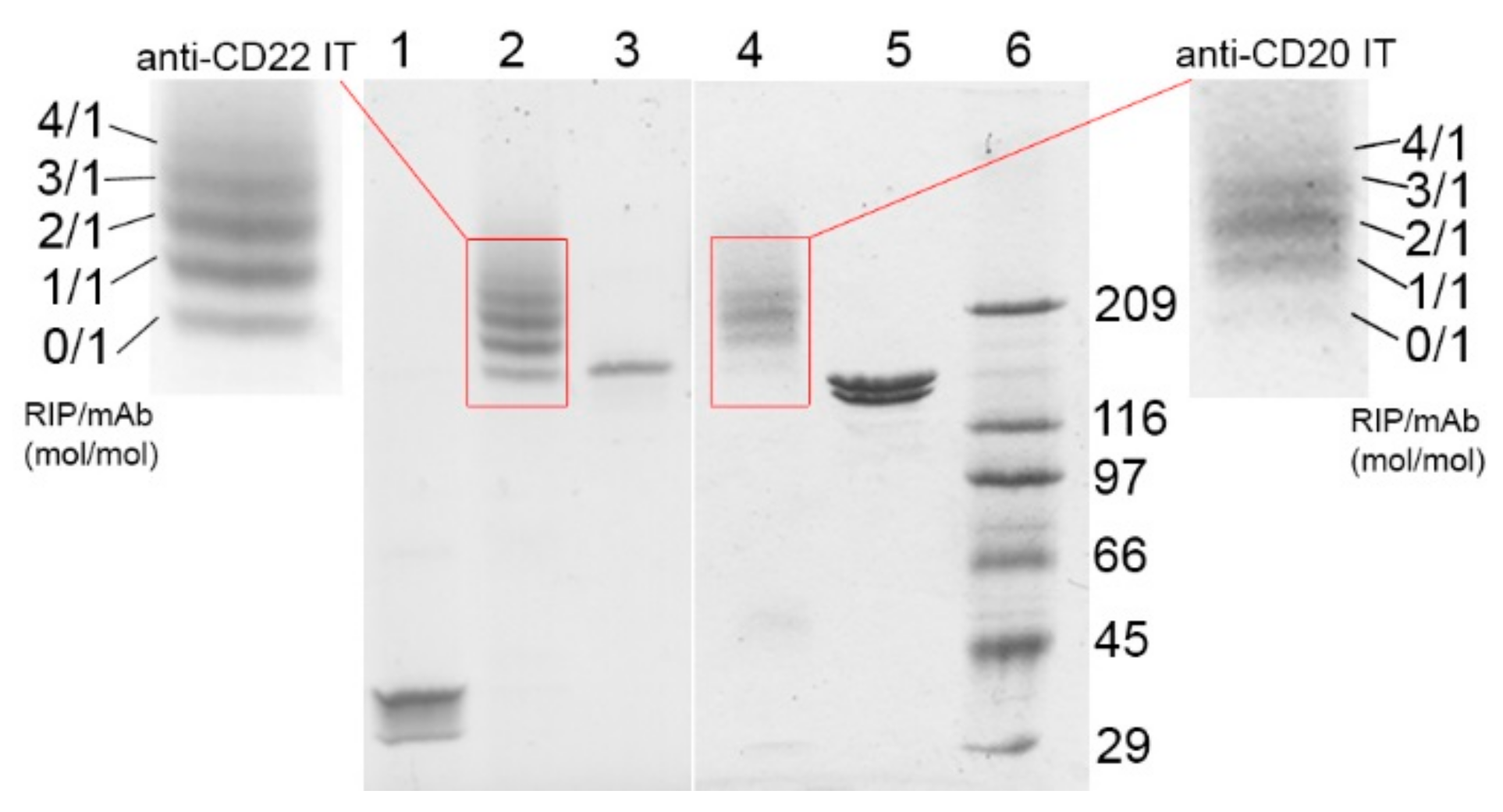

| Immunotoxin | Linker #/Ab | Linker #/RIP | RIP/Ab |
|---|---|---|---|
| anti-CD20 IT | (mol/mol) | (mol/mol) | (mol/mol) |
| 3.32 | 0.92 | 1.85 | |
| anti-CD22 IT | 2.31 | 1.09 | 1.41 |
| Immunotoxin | Cell-Free | Raji Cells § | Jurkat Cells # | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 * (nM) | IC50 * (nM) | EC50 * (nM) | EC50 * (nM) | |
| anti-CD20 IT | 0.08 | 1.99 | 4.06 | >100 |
| anti-CD22 IT | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.05 | >100 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Polito, L.; Mercatelli, D.; Bortolotti, M.; Maiello, S.; Djemil, A.; Battelli, M.G.; Bolognesi, A. Two Saporin-Containing Immunotoxins Specific for CD20 and CD22 Show Different Behavior in Killing Lymphoma Cells. Toxins 2017, 9, 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9060182
Polito L, Mercatelli D, Bortolotti M, Maiello S, Djemil A, Battelli MG, Bolognesi A. Two Saporin-Containing Immunotoxins Specific for CD20 and CD22 Show Different Behavior in Killing Lymphoma Cells. Toxins. 2017; 9(6):182. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9060182
Chicago/Turabian StylePolito, Letizia, Daniele Mercatelli, Massimo Bortolotti, Stefania Maiello, Alice Djemil, Maria Giulia Battelli, and Andrea Bolognesi. 2017. "Two Saporin-Containing Immunotoxins Specific for CD20 and CD22 Show Different Behavior in Killing Lymphoma Cells" Toxins 9, no. 6: 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9060182
APA StylePolito, L., Mercatelli, D., Bortolotti, M., Maiello, S., Djemil, A., Battelli, M. G., & Bolognesi, A. (2017). Two Saporin-Containing Immunotoxins Specific for CD20 and CD22 Show Different Behavior in Killing Lymphoma Cells. Toxins, 9(6), 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9060182