Finger-Actuated Microfluidic Concentration Gradient Generator Compatible with a Microplate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Concept
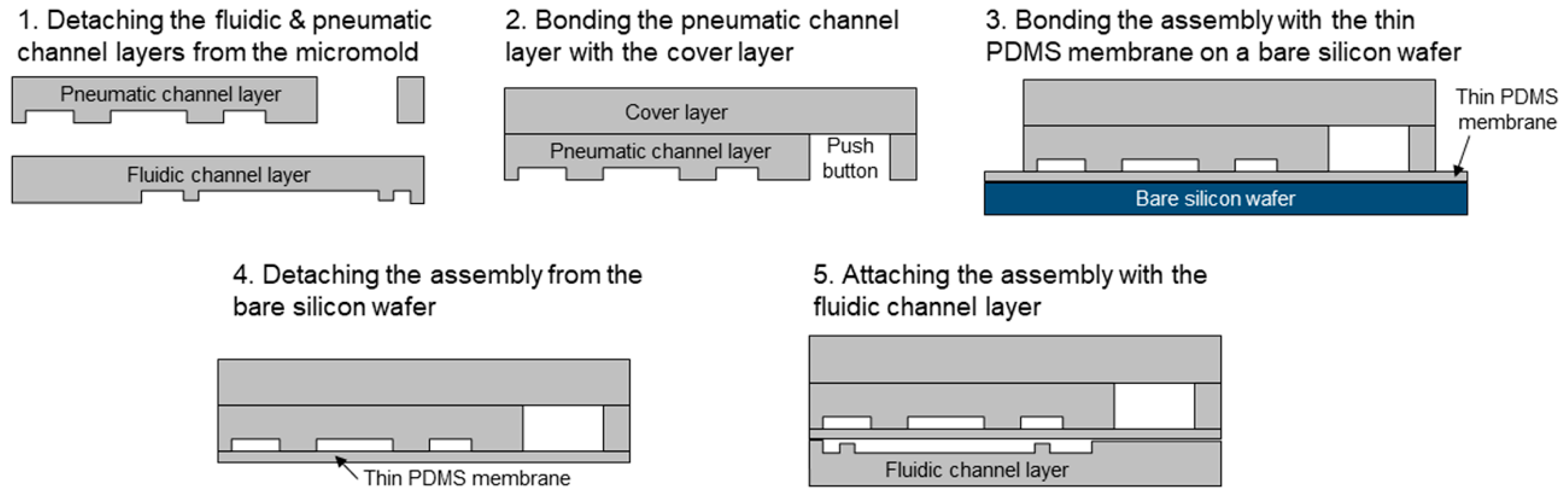
2.2. Device Fabrication
2.3. Analysis of the Concentration and Volume of the Sample Solution
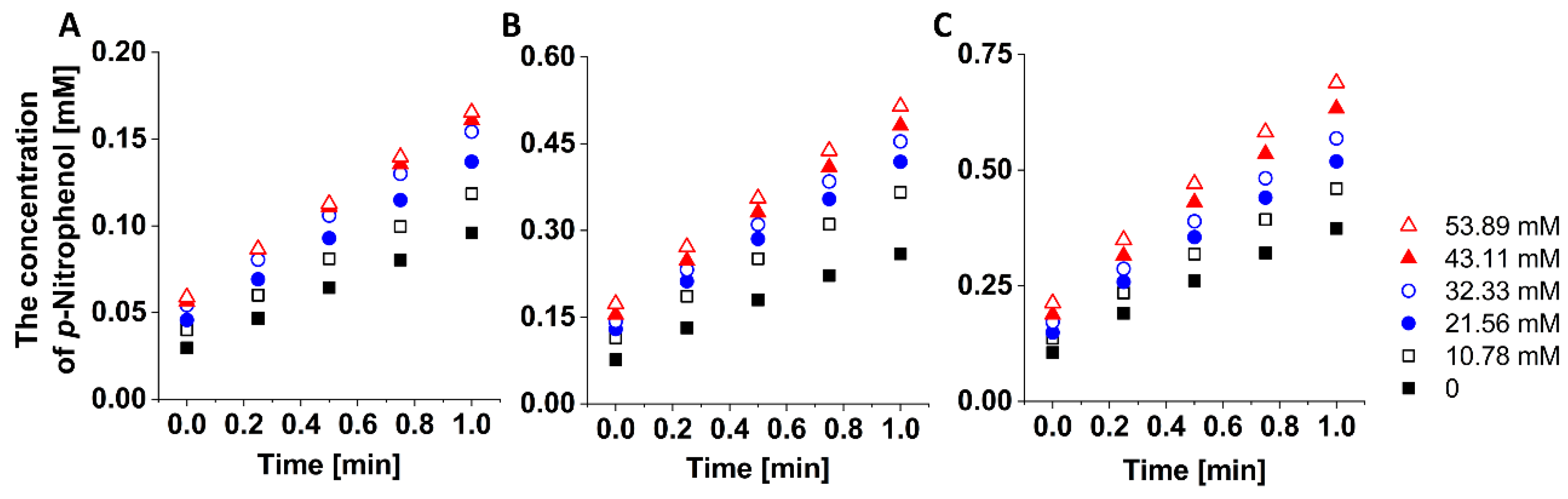
2.4. Enzyme Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Assessment of the Device Operation
3.2. Enzyme Kinetics Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Pang, Y. Concentration gradient generation methods based on microfluidic systems. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 29966–29984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Taylor, D.; Agrawal, N.; Wang, H.; Kim, H.; Han, A.; Rege, K.; Jayaraman, A. A programmable microfluidic cell array for combinatorial drug screening. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 1813–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Li, H.; Wang, N.; Lin, J.-M. Evaluation of the absorption of methotrexate on cells and its cytotoxicity assay by using an integrated microfluidic device coupled to a mass spectrometer. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 9230–9237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Weiss, T.L.; Thapa, H.R.; Devarenne, T.P.; Han, A. A microfluidic photobioreactor array demonstrating high-throughput screening for microalgal oil production. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 1415–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.; Cho, C.H.; Kwon, Y.; Lee, E.S.; Park, J.-K. A microfluidic immunostaining system enables quality assured and standardized immunohistochemical biomarker analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.; Huang, X.; Chu, Q.; Ning, X.; Wang, Y.; Kong, S.-K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Ho, H.-P. A linear concentration gradient generator based on multi-layered centrifugal microfluidics and its application in antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 1452–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, Y. Emerging droplet microfluidics. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7964–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, S.; Yuan, D.; Alici, G.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Warkiani, M.E.; Li, W. Fundamentals and applications of inertial microfluidics: A review. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 10–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olanrewaju, A.; Beaugrand, M.; Yafia, M.; Juncker, D. Capillary microfluidics in microchannels: From microfluidic networks to capillaric circuits. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 2323–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimov, I.K.; Basabe-Desmonts, L.; Garcia-Cordero, J.L.; Ross, B.M.; Park, Y.; Ricco, A.J.; Lee, L.P. Stand-alone self-powered integrated microfluidic blood analysis system (SIMBAS). Lab Chip 2011, 11, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Chen, C.; Lou, B.; Zhang, L.; Wang, E. A self-powered microfluidic origami electrochemiluminescence biosensing platform. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 3866–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shilton, R.J.; Travagliati, M.; Beltram, F.; Cecchini, M. Microfluidic pumping through miniaturized channels driven by ultra-high frequency surface acoustic waves. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 074106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Hahn, Y.K.; You, D.; Oh, S.; Choi, S. A smart multi-pipette for hand-held operation of microfluidic devices. Analyst 2016, 141, 5753–5758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, B.; Xue, P.; Wu, Y.; Bao, J.; Chuah, Y.J.; Kang, Y. A concentration gradient generator on a paper-based microfluidic chip coupled with cell culture microarray for high-throughput drug screening. Biomed. Microdevices 2016, 18, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.H.; Park, J.-K. Development of a microplate reader compatible microfluidic device for enzyme assay. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 107, 980–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, F.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, S.; Cheng, Z. Development of a microplate reader compatible microfluidic chip for ELISA. Biomed. Microdevices 2012, 14, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Chen, T.; Chen, Z.; Fei, P.; Yu, Z.; Pang, Y.; Huang, Y. Squeeze-chip: A finger-controlled microfluidic flow network device and its application to biochemical assays. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 1587–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, K.; Shih, K.C.; Lin, X.; Brubaker, T.A.; Sochol, R.D.; Lin, L. Finger-powered microfluidic systems using multilayer soft lithography and injection molding processes. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 3790–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kim, H.; Lee, W.; Kim, J. Finger-triggered portable PDMS suction cup for equipment-free microfluidic pumping. Micro Nano Syst. Lett. 2018, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.; Park, J.-K. Finger-actuated microfluidic device for the blood cross-matching test. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigma–Aldrich Catalog Number A2356. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/content/dam/sigma-aldrich/docs/Sigma/Datasheet/6/a2356dat.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2019).
- Makboul, H.E.; Ottow, J.C.G. Alkaline phosphatase activity and Michaelis constant in the presence of different clay minerals. Soil Sci. 1979, 128, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

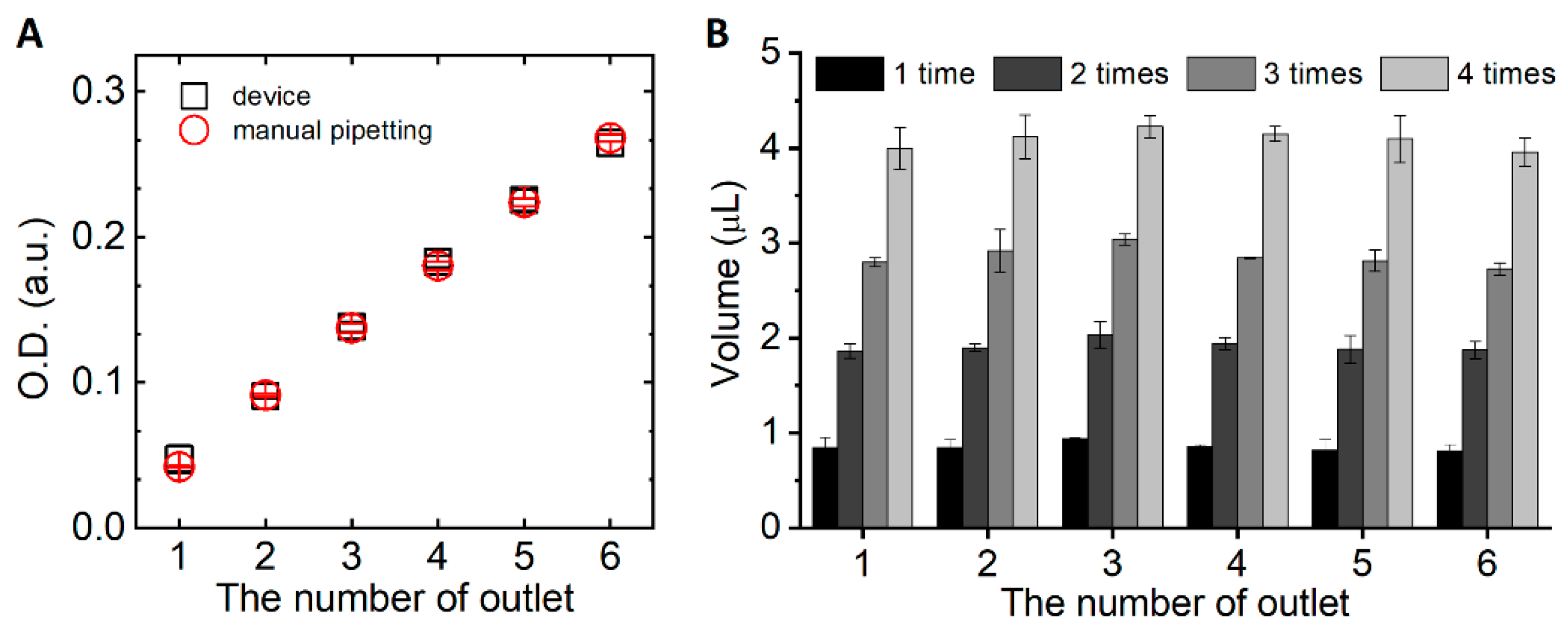

| One-Time Pushing (1 μL) | Two-Time Pushing (2 μL) | Three-Time Pushing (3 μL) | Four-Time Pushing (4 μL) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (μL) | Standard Deviation | CV (%) | Error (%) | Mean (μL) | Standard Deviation | CV (%) | Error (%) | Mean (μL) | Standard Deviation | CV (%) | Error (%) | Mean (μL) | Standard Deviation | CV (%) | Error (%) | |
| Outlet 1 | 0.847 | 0.103 | 12.206 | 15.278 | 1.861 | 0.071 | 3.854 | 6.9195 | 2.797 | 0.048 | 1.742 | 6.762 | 3.995 | 0.215 | 5.403 | 0.111 |
| Outlet 2 | 0.846 | 0.080 | 9.501 | 15.327 | 1.896 | 0.036 | 1.912 | 5.1585 | 2.918 | 0.224 | 7.683 | 2.711 | 4.117 | 0.230 | 5.597 | 2.926 |
| Outlet 3 | 0.939 | 0.007 | 0.796 | 6.002 | 2.032 | 0.140 | 6.915 | 1.637 | 3.038 | 0.058 | 1.938 | 1.289 | 4.226 | 0.119 | 2.816 | 5.654 |
| Outlet 4 | 0.853 | 0.021 | 2.552 | 14.633 | 1.939 | 0.0659 | 3.396 | 3.001 | 2.845 | 0.006 | 0.239 | 5.158 | 4.147 | 0.078 | 1.884 | 3.695 |
| Outlet 5 | 0.818 | 0.110 | 13.539 | 18.105 | 1.879 | 0.146 | 7.792 | 6.002 | 2.813 | 0.114 | 4.057 | 6.233 | 4.096 | 0.248 | 6.071 | 2.418 |
| Outlet 6 | 0.808 | 0.065 | 8.115 | 19.147 | 1.872 | 0.091 | 4.871 | 6.399 | 2.726 | 0.061 | 2.256 | 9.110 | 3.957 | 0.147 | 3.726 | 1.054 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.; Roh, H.; Park, J.-K. Finger-Actuated Microfluidic Concentration Gradient Generator Compatible with a Microplate. Micromachines 2019, 10, 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10030174
Park J, Roh H, Park J-K. Finger-Actuated Microfluidic Concentration Gradient Generator Compatible with a Microplate. Micromachines. 2019; 10(3):174. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10030174
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Juhwan, Hyewon Roh, and Je-Kyun Park. 2019. "Finger-Actuated Microfluidic Concentration Gradient Generator Compatible with a Microplate" Micromachines 10, no. 3: 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10030174
APA StylePark, J., Roh, H., & Park, J.-K. (2019). Finger-Actuated Microfluidic Concentration Gradient Generator Compatible with a Microplate. Micromachines, 10(3), 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10030174







