Leveraging Ferroelectret Nanogenerators for Acoustic Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
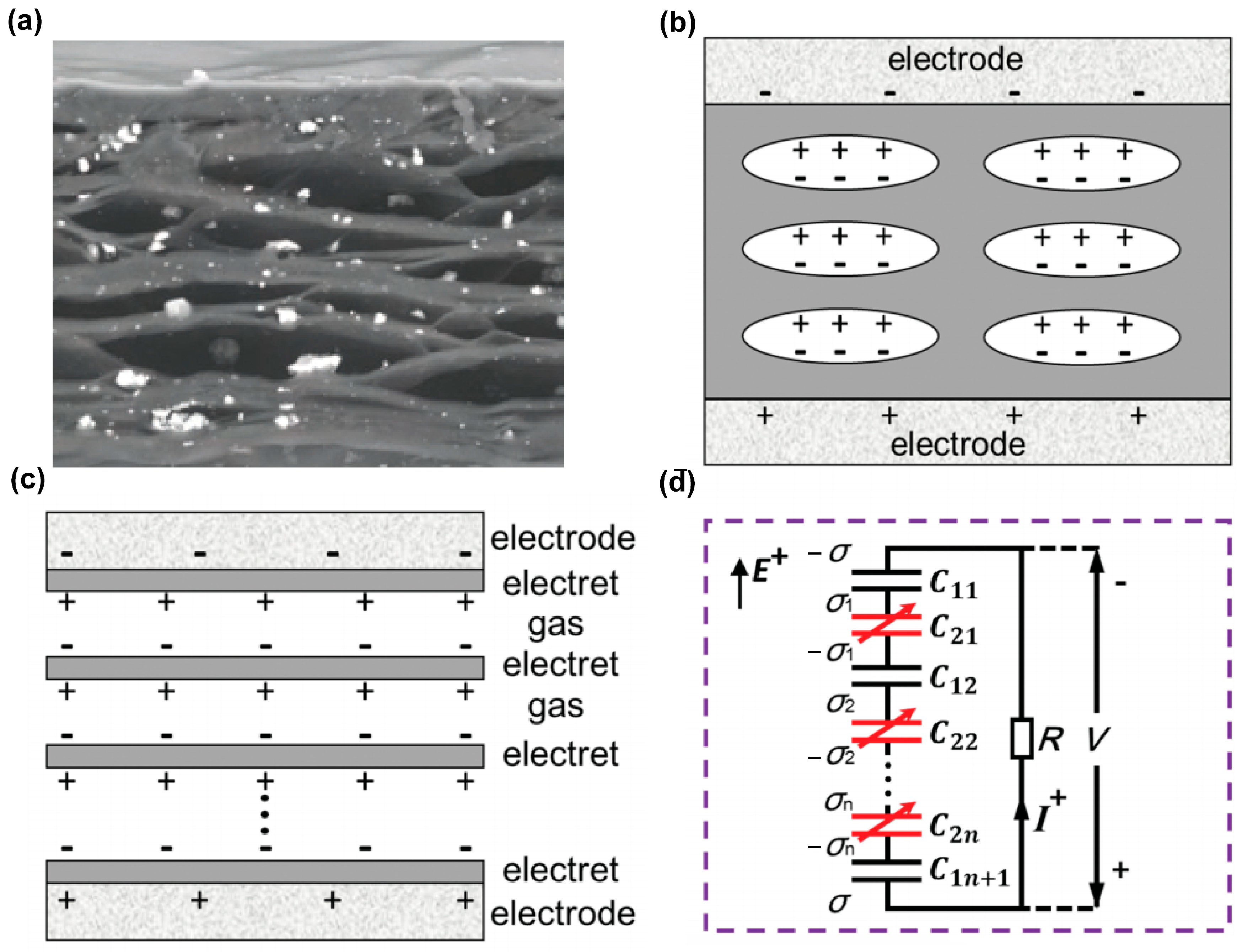
2. Fundamentals of FENG
2.1. Working Principle of FENG
2.2. Preparation Method of FENG
3. Acoustic Applications of FENG
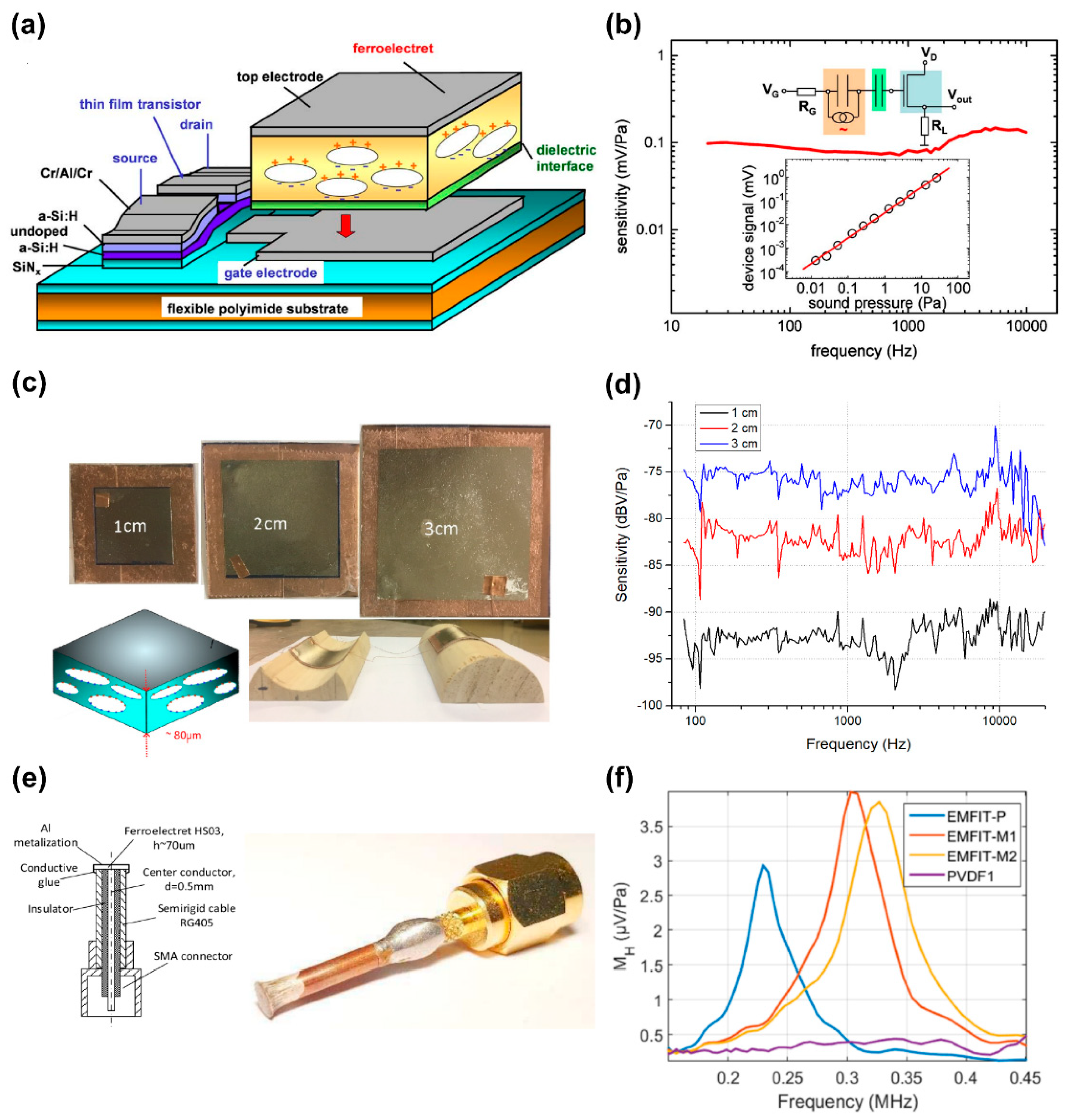
3.1. Acoustic Sensing
3.1.1. Microphones
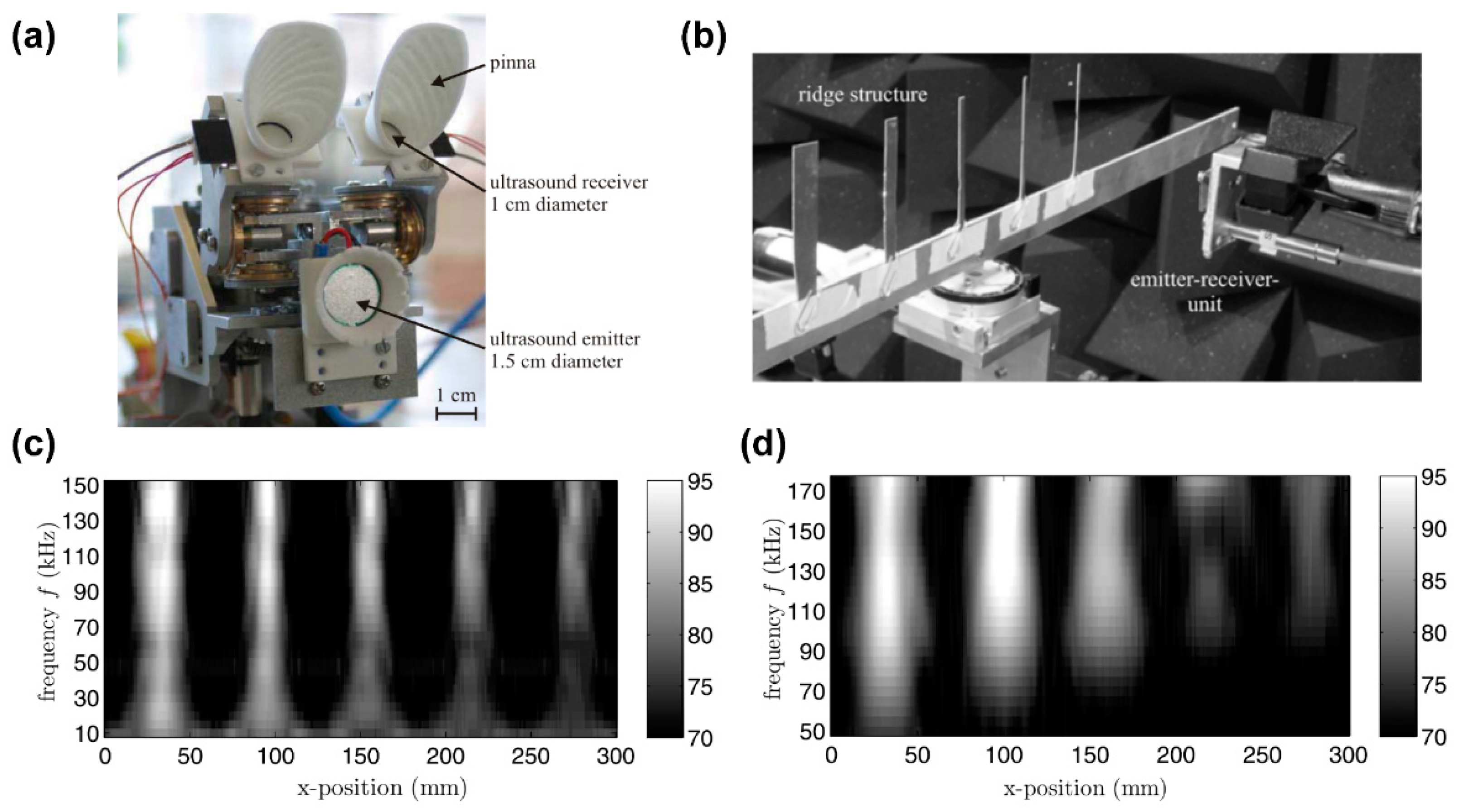
3.1.2. Ultrasonic Localization
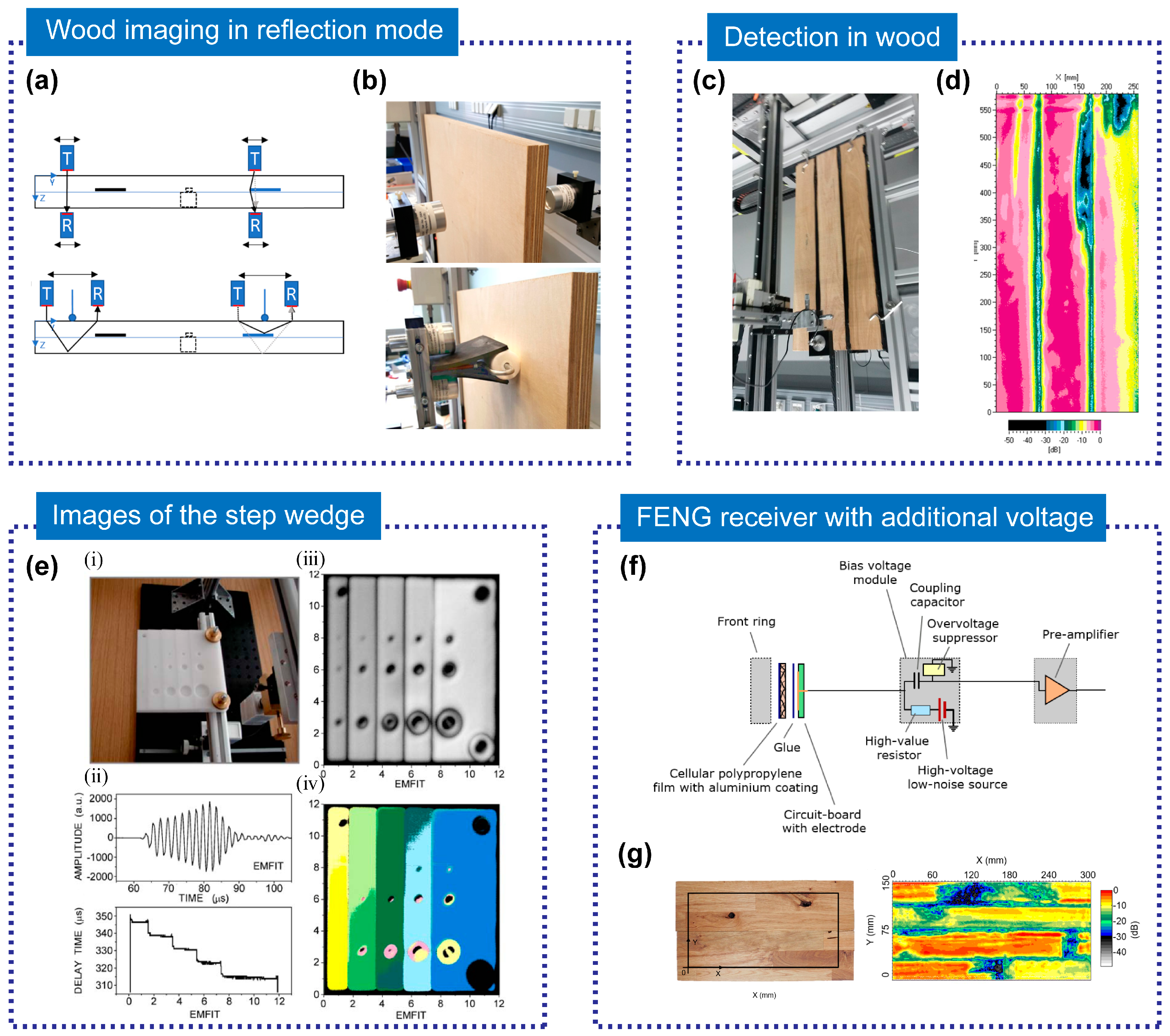
3.1.3. Ultrasonic Medical Imaging
3.1.4. Nondestructive Testing
3.2. Acoustic Actuation
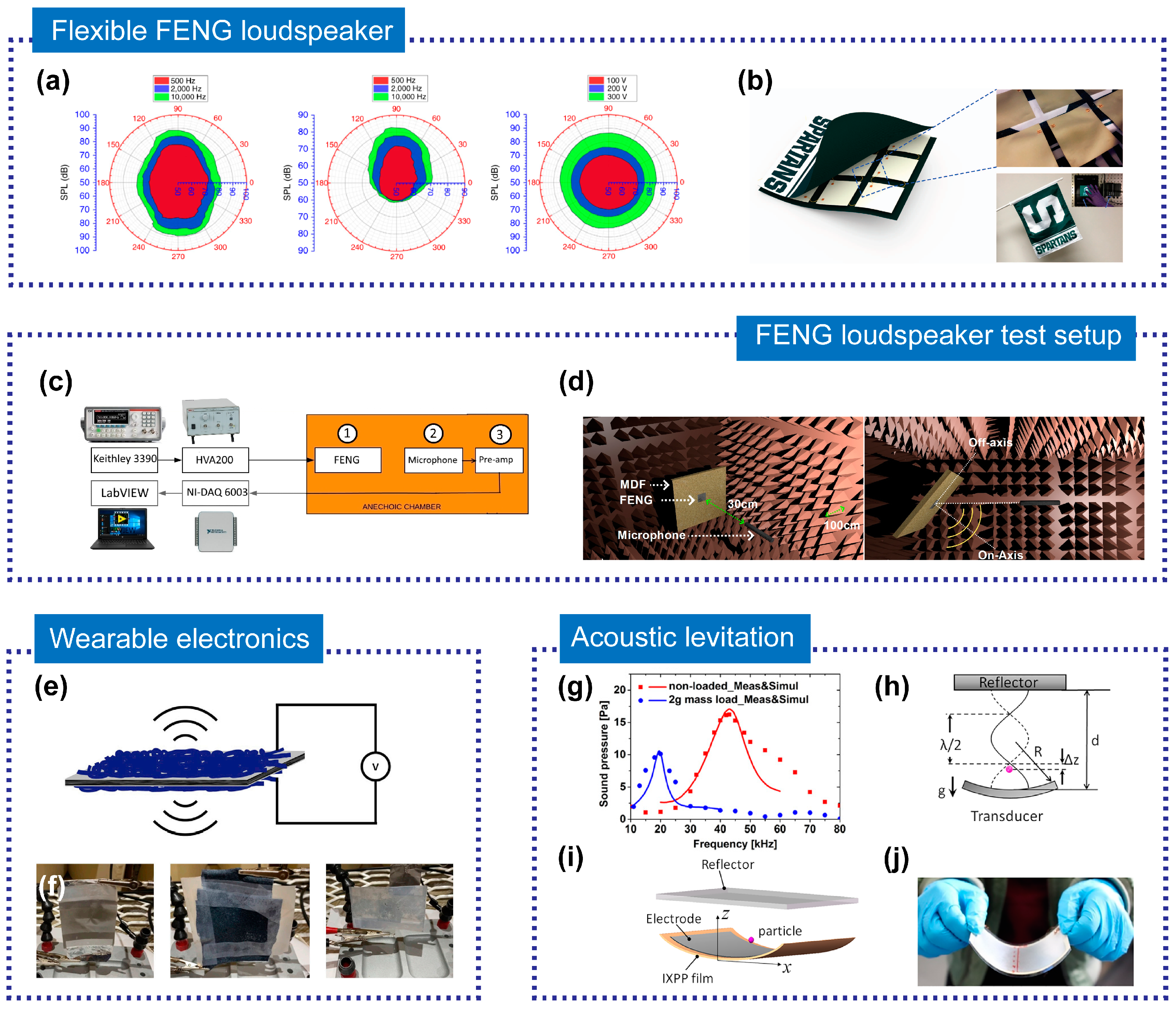
3.2.1. Loudspeakers
3.2.2. Acoustic Levitators
3.2.3. Vortex Generators
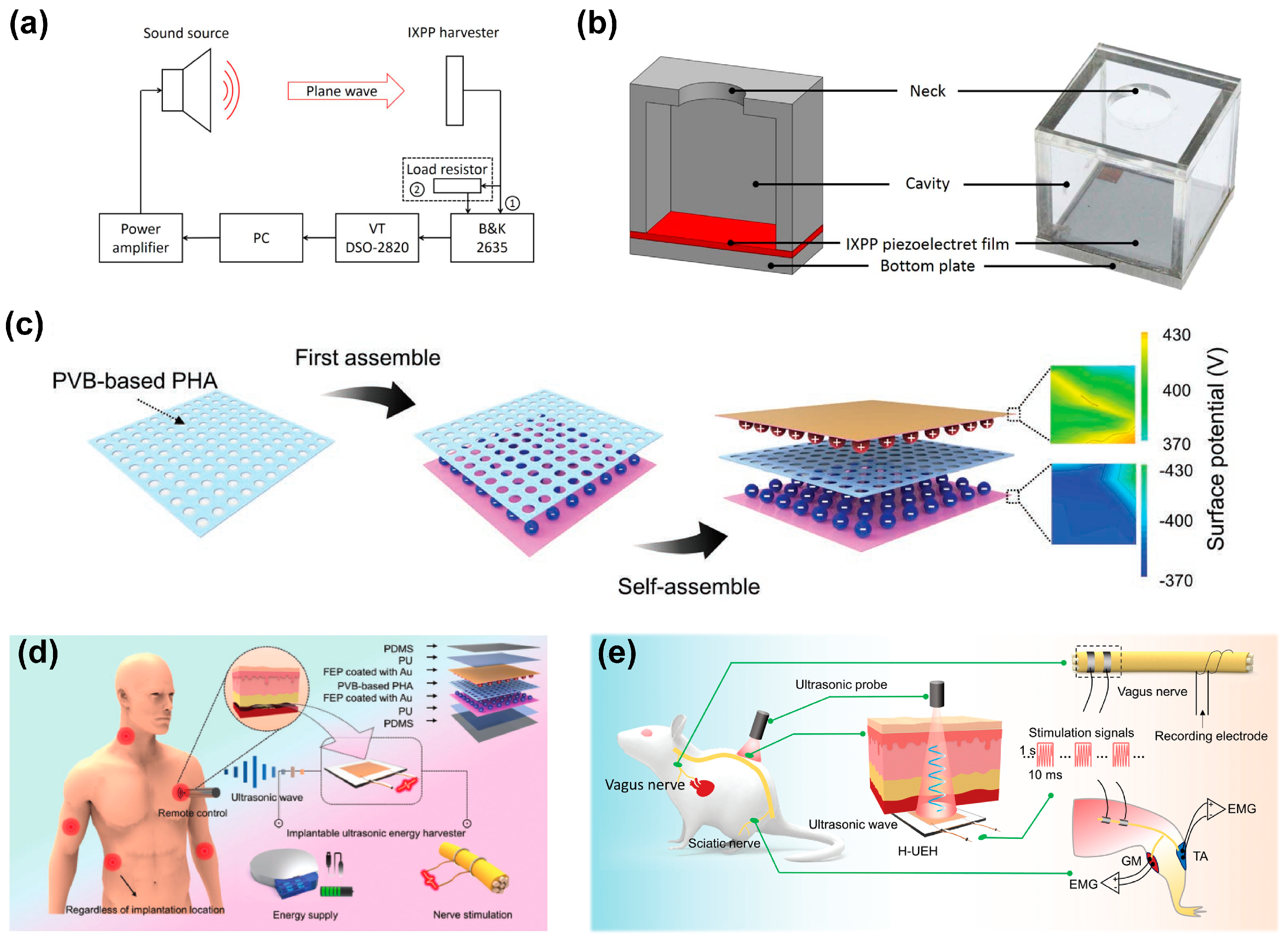
3.3. Acoustic Energy Harvesting
4. Summary and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moussatov, A.; Gusev, V.; Castagnède, B. Self-Induced Hysteresis for Nonlinear Acoustic Waves in Cracked Material. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 124301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inserra, C.; Biwa, S.; Chen, Y. Influence of Thermal Damage on Linear and Nonlinear Acoustic Properties of Granite. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2013, 62, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pasquale, G.; Rufer, L.; Basrour, S.; Somà, A. Modeling and Validation of Acoustic Performances of Micro-Acoustic Sources for Hearing Applications. Sens. Actuators A 2016, 247, 614–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matt, H.M.; di Scalea, F.L. Macro-Fiber Composite Piezoelectric Rosettes for Acoustic Source Location in Complex Structures. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalecki, D. Mechanical Bioeffects of Ultrasound. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 6, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.B.; Ripepe, M. Volcano Infrasound: A Review. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2011, 206, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.; Cao, Y.; Sepúlveda, N.; Li, W. Quick Self-Assembly of Bio-Inspired Multi-Dimensional Well-Ordered Structures Induced by Ultrasonic Wave Energy. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.A. Medical Ultrasound Imaging. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2007, 93, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, T.; Ealo, J.L.; Papakonstantinou, K.; Pazos, J.F. Design of Acoustic Lenses for Ultrasonic Human-Computer Interaction. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium, Orlando, FL, USA, 18–21 October 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Z.; Peng, Y.; Pala, S.; Liang, Y.; Lin, L. 3D Ultrasonic Object Detections with >1 Meter Range. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 34th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Gainesville, FL, USA, 25–29 January 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 386–389. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Z.; Pala, S.; Peng, Y.; Lin, L. Bimorph Pinned Piezoelectric Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducers for Space Imaging Applications. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2021, 30, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Pala, S.; Liang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Lin, L. A Single Chip Directional Loudspeaker Based on PMUTS. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 34th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Gainesville, FL, USA, 25–29 January 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 895–898. [Google Scholar]
- Wear, K.A.; Liu, Y. Considerations for Choosing Sensitive Element Size for Needle and Fiber-Optic Hydrophones—Part II: Experimental Validation of Spatial Averaging Model. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2019, 66, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palitó, T.T.C.; Assagra, Y.A.O.; Altafim, R.A.P.; Carmo, J.P.; Altafim, R.A.C. Hydrophone Based on 3D Printed Polypropylene (PP) Piezoelectret. Electron. Lett. 2019, 55, 203–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Bai, P.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Ultrathin, Rollable, Paper-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Acoustic Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Sound Recording. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4236–4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Chen, P.; Xu, Z.; Mo, X.; Jin, H.; Yang, W.; Wang, S.; Duan, J.; Hu, B.; Luo, Z.; et al. Hybrid-Piezoelectret Based Highly Efficient Ultrasonic Energy Harvester for Implantable Electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2200589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Torres, D.; Wang, T.; Wang, C.; Sepúlveda, N. Flexible and Biocompatible Polypropylene Ferroelectret Nanogenerator (FENG): On the Path toward Wearable Devices Powered by Human Motion. Nano Energy 2016, 30, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, M.; Shi, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Ying, H.; Zhang, Q. Polymer Electrets and Their Applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, M.M.A.C.; Soares, I.N.; Assagra, Y.A.O.; Sousa, F.S.I.; Nordi, T.M.; Dourado, D.M.; Gounella, R.H.; Carmo, J.P.; Altafim, R.A.C.; Altafim, R.A.P. Piezoelectrets: A Brief Introduction. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 22317–22328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, W.; Sepulveda, N. Performance of Self-Powered, Water-Resistant Bending Sensor Using Transverse Piezoelectric Effect of Polypropylene Ferroelectret Polymer. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 10327–10335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ealo, J.L.; Seco, F.; Jimenez, A.R. Broadband EMFi-Based Transducers for Ultrasonic Air Applications. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2008, 55, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Torres, D.; Díaz, R.; Wang, Z.; Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Lin Wang, Z.; Sepúlveda, N. Nanogenerator-Based Dual-Functional and Self-Powered Thin Patch Loudspeaker or Microphone for Flexible Electronics. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutor, A.; Rupitsch, S.; Lerch, R. A8.2—Research on Ferroelectret Based Ultrasound Transducers. In Proceedings of the Proceedings SENSOR 2011, Nürnberg, Germany, 7–9 June 2011; AMA: Wunstorf, Germany, 2011; pp. 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- Holzmann, H.; Park, Y.J.; Stoll, G.; Atzrodt, H.; Herold, S. Design and Optimization of Lightweight Bending Strain Energy Harvesters Using Irradiation Cross-Linked Polypropylene Ferroelectret. Smart Mater. Struct. 2023, 32, 125013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Dali, O.; Von Seggern, H.; Sessler, G.M.; Pondrom, P.; Zhukov, S.; Zhang, X.; Kupnik, M. Ferroelectret Energy Harvesting with 3D-printed Air-spaced Cantilever Design. Nano Sel. 2022, 3, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A. Skin-like Ferroelectret Films for Advanced Robotics, Human-Machine Interfaces. Scilight 2023, 2023, 241102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Song, C.; Zhang, F.; Dai, Y.; He, P.; Zhang, X. Soft, Multifunctional, Robust Film Sensor Using a Ferroelectret with Significant Longitudinal and Transverse Piezoelectric Activity for Biomechanical Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 51291–51300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Bian, Y.; Liu, J.; Xiang, Y.; Ding, T.; Zhu, W.; Xuan, F.-Z. Ferroelectrets: Recent Developments. IET Nanodielectr. 2022, 5, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cao, Y.; Wang, C.; Sepúlveda, N. Ferroelectret Nanogenerators for the Development of Bioengineering Systems. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2023, 4, 101388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graz, I.; Kaltenbrunner, M.; Keplinger, C.; Schwödiauer, R.; Bauer, S.; Lacour, S.P.; Wagner, S. Flexible Ferroelectret Field-Effect Transistor for Large-Area Sensor Skins and Microphones. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 073501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupitsch, S.; Lerch, R.; Strobel, J.; Streicher, A. Ultrasound Transducers Based on Ferroelectret Materials. IEEE Trans. Dielect. Electr. Insul. 2011, 18, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirce, J.; Svilainis, L.; Camacho, J.; Gomez Alvarez-Arenas, T. Ferroelectret Ultrasonic Transducers for Pulse-Echo Water Immersion. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vössing, K.J.; Gaal, M.; Niederleithinger, E. Air-Coupled Ferroelectret Ultrasonic Transducers for Nondestructive Testing of Wood-Based Materials. Wood Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1527–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dsouza, H.; Van Schyndel, A.; Pastrana, J.; Cao, Y.; Hunter, E.; Rakerd, B.; Sepúlveda, N. Ferroelectret Nanogenerators for Loudspeaker Applications: A Comprehensive Study. J. Sound Vib. 2020, 468, 115091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploner, M.; Wang, N.; Wu, C.; Daniels, R.; Huo, J.; Sotzing, G.A.; Cao, Y. Ultrathin, All-Organic, Fabric-Based Ferroelectret Loudspeaker for Wearable Electronics. iScience 2022, 25, 105607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chadda, R.; Sessler, G.M.; Kupnik, M. Ferroelectret-Based Flexible Transducers: A Strategy for Acoustic Levitation and Manipulation of Particles. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 147, EL421–EL427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Sessler, G.M.; Kupnik, M. Acoustic Energy Harvesting with Irradiated Cross-Linked Polypropylene Piezoelectret Films. Phys. Scr. 2019, 94, 095002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Q.; Huang, X.; Jia, X.; Cheng, B.; Wang, L.; Qin, Y. Fiber-Based Electret Nanogenerator with a Semisupported Structure for Wearable Electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 46840–46847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, S. Piezo-, Pyro- and Ferroelectrets: Soft Transducer Materials for Electromechanical Energy Conversion. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2006, 13, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, W.; Figueroa, J.; Wang, T.; Torres, D.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.L.; Sepúlveda, N. Impact-Activated Programming of Electro-Mechanical Resonators through Ferroelectret Nanogenerator (FENG) and Vanadium Dioxide. Nano Energy 2018, 43, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, W. A Monolithic Self-Sensing Precision Stage: Design, Modeling, Calibration, and Hysteresis Compensation. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 20, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, X. Compensation of Hysteresis in Piezoelectric Actuators without Dynamics Modeling. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2013, 199, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, X.; Li, Z. Inverse Compensation for Hysteresis in Piezoelectric Actuator Using an Asymmetric Rate-Dependent Model. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2013, 84, 115003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzir, S. The discovery of the piezoelectric effect. In The Beginnings of Piezoelectricity: A Study in Mundane Physics; Katzir, S., Ed.; Boston Studies in Philosophy of Science; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 15–64. ISBN 978-1-4020-4670-4. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Cao, Y.; Sepúlveda, N. Thin Film Piezoelectric Nanogenerator Based on (100)-Oriented Nanocrystalline AlN Grown by Pulsed Laser Deposition at Room Temperature. Micromachines 2023, 14, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Van Turnhout, J.; Daniels, R.; Wu, C.; Huo, J.; Gerhard, R.; Sotzing, G.; Cao, Y. Ion-Boosting the Charge Density and Piezoelectric Response of Ferroelectrets to Significantly High Levels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 42705–42712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wu, N.; Zhong, J.; Zhong, Q.; Zhao, S.; Wang, B.; Cheng, X.; Li, S.; Liu, K.; Hu, B.; et al. Theoretical Study of Cellular Piezoelectret Generators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 1964–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessler, G.M.; Hillenbrand, J. Electromechanical Response of Cellular Electret Films. In Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on Electrets (ISE 10). Proceedings (Cat. No.99 CH36256), Athens, Greece, 22–24 September 1999; pp. 261–264. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, X.; Zhou, H.; Li, W.; Xu, Z.; Duan, J.; Huang, L.; Hu, B.; Zhou, J. Piezoelectrets for Wearable Energy Harvesters and Sensors. Nano Energy 2019, 65, 104033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, J.Q.; Gómez Álvarez-Arenas, T. Modification of Mechanical and Electromechanical Resonances of Cellular Ferroelectret Films Depending on the External Load. Polymers 2021, 13, 3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Figueroa, J.; Pastrana, J.J.; Li, W.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.L.; Sepúlveda, N. Flexible Ferroelectret Polymer for Self-Powering Devices and Energy Storage Systems. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 17400–17409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Figueroa, J.; Li, W.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.L.; Sepúlveda, N. Understanding the Dynamic Response in Ferroelectret Nanogenerators to Enable Self-Powered Tactile Systems and Human-Controlled Micro-Robots. Nano Energy 2019, 63, 103852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dsouza, H.; Pastrana, J.; Figueroa, J.; Gonzalez-Afanador, I.; Davila-Montero, B.M.; Sepúlveda, N. Flexible, Self-Powered Sensors for Estimating Human Head Kinematics Relevant to Concussions. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegener, M.; Wirges, W.; Gerhard-Multhaupt, R. Piezoelectric Polyethylene Terephthalate (PETP) Foams—Specifically Designed and Prepared Ferroelectret Films. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2005, 7, 1128–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; Chen, J.; Wan, Z.; Wang, S.; Xia, Z. Piezoelectric Properties of Irradiation-Crosslinked Polypropylene Ferroelectrets. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 182901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Daniels, R.; Connelly, L.; Sotzing, M.; Wu, C.; Gerhard, R.; Sotzing, G.A.; Cao, Y. All-Organic Flexible Ferroelectret Nanogenerator with Fabric-Based Electrodes for Self-Powered Body Area Networks. Small 2021, 17, 2103161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Daniels, R.; Connelly, L.; Ronzello, J.; Sotzing, G.A.; Cao, Y. All-Organic Flexible Ferroelectret Nanogenerator for Wearable Electronics. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena (CEIDP), East Rutherford, NJ, USA, 18–30 October 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 259–262. [Google Scholar]
- Zhukov, S.; Fedosov, S.; von Seggern, H. Piezoelectrets from Sandwiched Porous Polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) Films: Influence of Porosity and Geometry on Charging Properties. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2011, 44, 105501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Seggern, H.; Zhukov, S.; Fedosov, S. Importance of Geometry and Breakdown Field on the Piezoelectric d(33) Coefficient of Corona Charged Ferroelectret Sandwiches. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. IEEE Trans. 2011, 18, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seggern, H.; Zhukov, S.; Fedosov, S. Poling Dynamics and Thermal Stability of FEP/ePTFE/FEP Sandwiches. IEEE Trans. Dielect. Electr. Insul. 2010, 17, 1056–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegener, M.; Bauer, S. Microstorms in Cellular Polymers: A Route to Soft Piezoelectric Transducer Materials with Engineered Macroscopic Dipoles. Chemphyschem 2005, 6, 1014–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, S.; Gerhard-Multhaupt, R.; Sessler, G.M. Ferroelectrets: Soft Electroactive Foams for Transducers. Phys. Today 2004, 57, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Shi, H.; Tan, X.; Sepúlveda, N. Nanogenerator-Based Bidirectional Pressure Sensor Array and Its Demonstration in Underwater Invasive Species Detection. Nano Res. 2022, 16, 11822–11831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ealo, J.L.; Camacho, J.J.; Fritsch, C. Airborne Ultrasonic Phased Arrays Using Ferroelectrets: A New Fabrication Approach. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2009, 56, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cui, Y.; Zhong, J. Recent Advances in Nanogenerators-Based Flexible Electronics for Electromechanical Biomonitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 186, 113290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bowen, C.R.; Ghosh, S.K.; Mandal, D.; Khanbareh, H.; Arafa, M.; Wan, C. Ferroelectret Materials and Devices for Energy Harvesting Applications. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 118–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tat, T.; Chen, J. Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Self-Powered Drug Delivery. Trends Chem. 2021, 3, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Pondrom, P.; Sessler, G.M.; Ma, X. Ferroelectret Nanogenerator with Large Transverse Piezoelectric Activity. Nano Energy 2018, 50, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Beeby, S. Textiles Based Ferroelectret Generator with Enhanced Energy Harvesting Performance. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Flexible and Printable Sensors and Systems (FLEPS), Manchester, UK, 16–19 August 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Assagra, Y.A.O.; Altafim, R.A.P.; Do Carmo, J.P.; Altafim, R.A.C.; Rychkov, D.; Wirges, W.; Gerhard, R. A New Route to Piezo-Polymer Transducers: 3D Printing of Polypropylene Ferroelectrets. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2020, 27, 1668–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Saini, D.; Mandal, D. 3D Printed Ferroelectret with Giant Piezoelectric Coefficient. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2022, 120, 182901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Zhang, X. Air-Coupled Ultrasonic Transducers Based on Laminated Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene and Porous Polytetrafluoroethylene Ferroelectrets. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2018, 25, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Jana, S.; Ghosh, S.K.; Mahanty, B.; Mallick, Z.; Sarkar, S.; Sinha, C.; Mandal, D. Three-Dimensional MOF-Assisted Self-Polarized Ferroelectret: An Effective Autopowered Remote Healthcare Monitoring Approach. Langmuir 2020, 36, 11477–11489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Bowen, C.R.; Deville, S. Ice-Templated Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) Ferroelectrets. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wan, X.; Mo, X.; Lin, S.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Jin, H.; Duan, J.; et al. Electrostatic Assembly of Laminated Transparent Piezoelectrets for Epidermal and Implantable Electronics. Nano Energy 2021, 89, 106450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukov, S.; Ma, X.; Seggern, H.V.; Sessler, G.M.; Dali, O.B.; Kupnik, M.; Zhang, X. Biodegradable Cellular Polylactic Acid Ferroelectrets with Strong Longitudinal and Transverse Piezoelectricity. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 117, 112901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, O.; Mighri, F.; Rodrigue, D. Time and Thermal Stability Improvement of Polyethylene Ferroelectrets. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessler, G.M. Acoustic Sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1991, 26, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovtun, V.; Döring, J.; Wegener, M.; Bartusch, J.; Beck, U.; Erhard, A.; Borisov, V. Air-Coupled Ultrasonic Applications of Ferroelectrets. Ferroelectrics 2008, 370, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillenbrand, J.; Sessler, G.M. Piezoelectret Microphones with High Sensitivity. In Proceedings of the 2005 12th International Symposium on Electrets, Salvador, Brazil, 11–14 September 2005; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 125–128. [Google Scholar]
- Palitó, T.T.C.; Assagra, Y.A.O.; Altafim, R.A.P.; Carmo, J.P.; Altafim, R.A.C. Low-Cost Electro-Acoustic System Based on Ferroelectret Transducer for Characterizing Liquids. Measurement 2019, 131, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streicher, A.; Kaltenbacher, M.; Lerch, R.; Peremans, H. Broadband EMFi Ultrasonic Transducer for Bat Research. In Proceedings of the IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, 2005, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 18–21 September 2005; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 3, pp. 1629–1632. [Google Scholar]
- Vössing, K.J.; Gaal, M.; Niederleithinger, E. Imaging Wood Defects Using Air Coupled Ferroelectret Ultrasonic Transducers in Reflection Mode. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 241, 118032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sessler, G.M.; Wang, Y. Fluoroethylenepropylene Ferroelectret Films with Cross-Tunnel Structure for Piezoelectric Transducers and Micro Energy Harvesters. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 074109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dsouza, H.; Wheeler, J.; Sepulveda, N. Ferro-Electret Nanogenerators as Flexible Microphones. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE SENSORS, Montreal, QC, Canada, 27–30 October 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar, J.Q.; Alvarez-Arenas, T.G.; Svilainis, L. Ferroelectret Hydrophone. 2021 IEEE Int. Ultrason. Symp. (IUS) 2021, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svilainis, L.; Chaziachmetovas, A.; Eidukynas, V.; Alvarez-Arenas, T.G.; Dixon, S. Miniature Ferroelectret Microphone Design and Performance Evaluation Using Laser Excitation. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2022, 69, 3392–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl, T.; Ealo, J.L.; Bang, H.J.; Holm, S.; Khuri-Yakub, P. Applications of Airborne Ultrasound in Human–Computer Interaction. Ultrasonics 2014, 54, 1912–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X. Test, Modeling, and Analysis of Air-Coupled Ultrasonic Transducer Based on Piezoelectret Film. AIP Adv. 2020, 10, 065014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Tong, L.; Xiang, Y.; Qiu, X.; Deng, M.; Xuan, F. Design, Fabrication and Characterization of Emfi-Based Ferroelectret Air-Coupled Ultrasonic Transducer. Sens. Actuators A 2019, 296, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streicher, A.; Muller, R.; Peremans, H.; Lerch, R. Broadband Ultrasonic Transducer for a Artificial Bat Head. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Ultrasonics, Honululu, HI, USA, 5–8 October 2003; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Volume 2, pp. 1364–1367. [Google Scholar]
- Allevato, G.; Hinrichs, J.; Rutsch, M.; Adler, J.P.; Jager, A.; Pesavento, M.; Kupnik, M. Real-Time 3-D Imaging Using an Air-Coupled Ultrasonic Phased-Array. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2021, 68, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez Álvarez-Arenas, T.E.; Díez, L. Ferroelectret Transducers for Water Immersion and Medical Imaging. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Tours, France, 18–21 September 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Schlaberg, H.I.; Duffy, J.S. Piezoelectric Polymer Composite Arrays for Ultrasonic Medical Imaging Applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1994, 44, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaal, M.; Bartusch, J.; Dohse, E.; Schadow, F.; Köppe, E. Focusing of Ferroelectret Air-Coupled Ultrasound Transducers. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1706, 080001. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar, J.Q.; Gómez Álvarez-Arenas, T. Optimization of Ferroelectret Transducers for Pulse-Echo Water Immersion Operation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Glasgow, UK, 6–9 October 2019; pp. 2604–2607. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez Alvarez-Arenas, T.E. Air-Coupled Piezoelectric Transducers with Active Polypropylene Foam Matching Layers. Sensors 2013, 13, 5996–6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez Alvarez-Arenas, T.E. Air-Coupled Piezoelectric Transducers with Active Matching Layers. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium, Orlando, FL, USA, 18–21 October 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 860–863. [Google Scholar]
- Wolter, B.; Gabi, Y.; Conrad, C. Nondestructive Testing with 3MA—An Overview of Principles and Applications. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, S.K.; Vishwakarma, M.; Soni, P.A. Advances and Researches on Non Destructive Testing: A Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 3690–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez Álvarez-Arenas, T.E.; Calás, H.; Cuello, J.E.; Fernández, A.R.; Muñoz, M. Noncontact Ultrasonic Spectroscopy Applied to the Study of Polypropylene Ferroelectrets. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 074110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadouche, A.; Safizadeh, M.S.; Bird, J.; Dmochowski, W.; Forsyth, D.S. A Comparative Study of Air-Coupled Ultrasound Sensor and Accelerometer in Detecting Bearing Defects. In Proceedings of the World Tribology Congress III, Washington, DC, USA, 12–16 September 2005; pp. 893–894. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez Álvarez-Arenas, T.E. Simultaneous Determination of the Ultrasound Velocity and the Thickness of Solid Plates from the Analysis of Thickness Resonances Using Air-Coupled Ultrasound. Ultrasonics 2010, 50, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiitta, M.; Tiitta, V.; Gaal, M.; Heikkinen, J.; Lappalainen, R.; Tomppo, L. Air-Coupled Ultrasound Detection of Natural Defects in Wood Using Ferroelectret and Piezoelectric Sensors. Wood Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 1051–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovtun, V.; Döring, J.; Bartusch, J.; Beck, U.; Erhard, A.; Yakymenko, Y. Ferroelectret Non-Contact Ultrasonic Transducers. Appl. Phys. A 2007, 88, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaal, M.; Caldeira, R.; Bartusch, J.; Schadow, F.; Vossing, K.; Kupnik, M. Air-Coupled Ultrasonic Ferroelectret Receiver with Additional Bias Voltage. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2019, 66, 1600–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sborikas, M.; Ealo, J.L.; Wegener, M. Piezoelectric Cellular PP Films with Enhanced Performance for Low Frequency Ultrasound. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 225, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazos-Ospina, J.F.; Ealo, J.L.; Camacho, J. New Dual-Focalization Ferroelectret-Based Array for Air-Coupled Ultrasonic Inspection of Textiles. NDT & E Int. 2015, 74, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaal, M.; Bartusch, J.; Dohse, E.; Kreutzbruck, M.; Amos, J. Air-Coupled Ultrasonic Testing of Metal Adhesively Bonded Joints Using Cellular Polypropylene Transducers. AIP Conf. Proc. 2014, 1581, 471–478. [Google Scholar]
- Ealo, J.L.; Prieto, J.C.; Seco, F. Airborne Ultrasonic Vortex Generation Using Flexible Ferroelectrets. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelect. Freq. Contr. 2011, 58, 1651–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heydt, R.; Pelrine, R.; Joseph, J.; Eckerle, J.; Kornbluh, R. Acoustical Performance of an Electrostrictive Polymer Film Loudspeaker. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2000, 107, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antila, M.; Muurinen, T.; Linjama, J.; Nykanen, H. Measurement Methods of Flat Panel Electromechanical Film Loudspeaker: International Symposium on Active Control of Sound and Vibration, ACTIVE 97. In Proceedings of the ACTIVE 97, the 1997 International Symposium on Active Control of Sound and Vibration, Budapest, Hungary, 21–23 August 1997; pp. 607–618. [Google Scholar]
- Pillai, M.A.; Deenadayalan, E. A Review of Acoustic Energy Harvesting. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2014, 15, 949–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Cao, Z.; Luo, J.; Chou, X. Recent Developments of Acoustic Energy Harvesting: A Review. Micromachines 2019, 10, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, S.B.; Sheplak, M.; Cattafesta, L.N.; Nishida, T. A MEMS Acoustic Energy Harvester. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2006, 16, S174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Zhao, J.; Ma, X.; Zhang, M.; Yuan, W.; Yang, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Pan, Y. Multi-Frequency Sound Energy Harvesting Using Helmholtz Resonators with Irradiated Cross-Linked Polypropylene Ferroelectret Films. AIP Adv. 2021, 11, 115002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Von Seggern, H.; Sessler, G.M.; Kupnik, M. Mechanical Energy Harvesting with Ferroelectrets. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2020, 36, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Askari, H.; Chen, J. Nanogenerators for Smart Cities in the Era of 5G and Internet of Things. Joule 2021, 5, 1391–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Application | Materials | Manufacturing Methods | Charging Methods | Piezoelectric Coefficients | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy harvesting | PVB/FEP | FEP-PVB-FEP layer stack | Corona discharging | 4680 pC/N | 2022 [16] |
| Energy harvesting | PET/silk | PET-silk-PET layer stack and hot-pressing | Corona discharging | 1600 pC/N | 2020 [69] |
| Energy harvesting | FEP | Hot-pressing | Contact charging | 3.0 Vm/N | 2018 [68] |
| Sensing | PP | 3D-printing | Contact charging | 200 pC/N | 2020 [70] |
| Sensing | P(VDF-TrFE) | 3D-printing | Contact charging | 1600 pC/N | 2022 [71] |
| Sensing | FEP/PTFE | Patterning and fusion bonding method | Contact charging | 400 pC/N | 2018 [72] |
| Sensing/energy harvesting | PVDF/Cd/INH | Solvent casting | Self-polarization | 143 pC/N | 2020 [73] |
| Sensing/energy harvesting | PVDF | Freeze casting | Corona charging | 264 pC/N | 2019 [74] |
| Sensing/energy harvesting | FEP/ePTFE | FEP-ePTFE-FEP-ePTFE-FEP stack | Corona charging with an extra boost of external positive and negative ions | 1600 pC/N | 2022 [46] |
| Materials | FEP | PP | PP | FEP/PTFE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Applications | Microphone | Ultrasonic localization | Ultrasonic medical imaging | Nondestructive testing |
| Year | 2014 [84] | 2011 [31] | 2020 [32] | 2018 [72] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Z.; Cai, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, W. Leveraging Ferroelectret Nanogenerators for Acoustic Applications. Micromachines 2023, 14, 2145. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14122145
Song Z, Cai X, Wang Y, Yang W, Li W. Leveraging Ferroelectret Nanogenerators for Acoustic Applications. Micromachines. 2023; 14(12):2145. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14122145
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Ziling, Xianfa Cai, Yiqin Wang, Wenyu Yang, and Wei Li. 2023. "Leveraging Ferroelectret Nanogenerators for Acoustic Applications" Micromachines 14, no. 12: 2145. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14122145
APA StyleSong, Z., Cai, X., Wang, Y., Yang, W., & Li, W. (2023). Leveraging Ferroelectret Nanogenerators for Acoustic Applications. Micromachines, 14(12), 2145. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14122145






