Fast-Response Liquid Crystal Microlens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Polymer-Dispersed/Stabilized Nematic Liquid Crystal Microlens
2.1. Principles

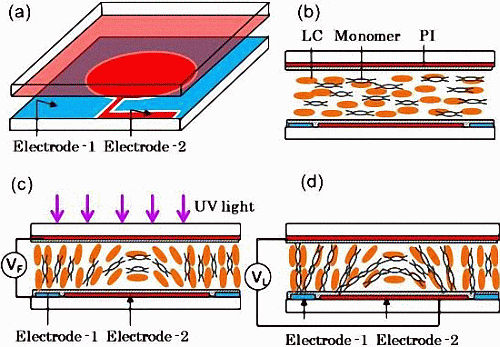
 , where neff(θ) is the effective refractive index expressed by Equation (1). If the LC molecules, located at different positions, could be controlled to have various reorientation angles, then the light will experience various refractive indices accordingly, as shown in Figure 1d. Here, the light incident on the center and border experience neff(θ) and ne, respectively, the optical path difference (OPD) between the center and border can be expressed as:
, where neff(θ) is the effective refractive index expressed by Equation (1). If the LC molecules, located at different positions, could be controlled to have various reorientation angles, then the light will experience various refractive indices accordingly, as shown in Figure 1d. Here, the light incident on the center and border experience neff(θ) and ne, respectively, the optical path difference (OPD) between the center and border can be expressed as:




2.2. Microlens Using Nanosized Polymer-Dispersed Liquid Crystal Droplets

2.3. Polymer-Stabilized Liquid Crystal (PSLC) Microlens
2.3.1. PSLC Microlens Using a Patterned Photomask

2.3.2. PNLC Microlens Using Patterned Electrode

2.3.3. Reconfigurable Fabrication of PNLC Lens/Microlens

2.3.4. Polymeric Lenticular Microlens Array for 2D/3D Switchable Displays




3. Polymer-Stabilized Blue Phase LC Microlens
3.1. Operation Principles


3.2. PS-BPLC Microlens with Planar Electrode

3.3. BPLC Microlens with Curved Electrode




3.4. PS-PBLC Microlens with Multi-Electrode


3.5. Fresnel PS-PBLC Microlens


4. Conclusions and Outlook
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schadt, M.; Helfrich, W. Voltage-dependent optical activity of a twisted nematic liquid crystal. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1971, 18, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Xu, S.; Wu, S.T. Voltage-expandable liquid crystal surface. Lab Chip. 2011, 11, 3426–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricot, C.; Hareng, M.; Spitz, E. Optical Projection Device and an Optical Reader Incorporating This Device. U.S. Patent 4,037,929, 29 January 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Bryant, D.; Heugten Van, T.; Bos, P.J. Near-diffraction-limited and low-haze electro-optical tunable liquid crystal lens with floating electrodes. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 8371–8381. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.C.; Collings, N.; Chen, M.S.; Lin, Y.H. A holographic projection system with an electrically tuning and continuously adjustable optical zoom. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 27222–27229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Chen, M.S.; Lin, H.C. An electrically tunable optical zoom system using two composite liquid crystal lenses with a large zoom ratio. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 4714–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Chen, H.S. Electrically tunable-focusing and polarizer-free liquid crystal lenses for ophthalmic applications. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 9428–9436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.C.; Lin, Y.H. A fast response and large electrically tunable-focusing imaging system based on switching of two modes of a liquid crystal lens. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 063505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nose, T.; Masuda, S.; Sato, S.; Li, J.; Chien, L.C.; Bos, P.J. Effects of low polymer content in a liquid-crystal microlens. Opt. Lett. 1997, 22, 351–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumov, A.F.; Loktev, M.Y.; Guralnik, I.R.; Vdovin, G. Liquid-crystal adaptive lenses with modal control. Opt. Lett. 1998, 23, 992–994. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kumar, S. Electrically controllable microlens array fabricated by anisotropic phase separation from liquid-crystal and polymer composite materials. Opt. Lett. 2003, 28, 1147–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.D. Fabrication of a focal length variable microlens array based on a nematic liquid crystal. Opt. Mater. 2003, 21, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Wu, S.T. Tunable electronic lens using a gradient polymer network liquid crystal. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presnyakov, V.V.; Galstian, T.V. Electrically tunable polymer stabilized liquid-crystal lens. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 103101–103106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, M.; Ye, M.; Sato, S. Optical particle manipulation using an LC device with eight-divided circularly hole-patterned electrodes. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 10059–10065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Chen, H.S.; Lin, H.C.; Tsou, Y.S.; Hsu, H.K.; Li, W.Y. Polarizer-free and fast response microlens arrays using polymer-stabilized blue phase liquid crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 113505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.Y.; Chao, P.C.P.; Hsueh, C.W. A new low-voltage-driven GRIN liquid crystal lens with multiple ring electrodes in unequal widths. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 18506–18518. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, M.C.; Fan, F.; Lee, C.Y.; Murauski, A.; Chigrinov, V.; Kwok, H.S. Tunable lens by spatially varying liquid crystal pretilt angles. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 083109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Sergan, V.; Van Heugten, T.; Duston, D.; Bhowmik, A.; Bos, P.J. Surface localized polymer aligned liquid crystal lens. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 7133–7138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, S.; Takahashi, S.; Nose, T.; Sato, S.; Ito, H. Liquid-crystal microlens with a beam-steering function. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 4772–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xu, S.; Ren, H.; Wu, S.T. Reconfigurable fabrication of scattering-free polymer network liquid crystal prism/grating/lens. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 161106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, J.H.; Park, S.C.; Kim, S.U.; Choi, Y.; Lee, S.D. Physical mechanism for flat-to-lenticular lens conversion in homogeneous liquid crystal cell with periodically undulated electrode. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 864–869. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.W.; Huang, Y.P.; Chen, P.C. Dual direction overdriving method for accelerating 2D/3D switching time of liquid crystal lens on auto-stereoscopic display. J. Disp. Technol. 2012, 8, 559–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, C.W.; Pateras, E.S. Liquid crystal lens review. Ophthal. Physiol. Opt. 1990, 10, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.C.; Chen, M.S.; Lin, Y.H. A review of electrically tunable focusing liquid crystal lenses. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 2011, 12, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Lin, Y.H.; Fan, Y.H.; Wu, S.T. Polarization-independent phase modulation using a polymer-dispersed liquid crystal. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 141110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Ren, H.; Wu, Y.H.; Zhao, Y.; Fang, J.; Ge, Z.; Wu, S.T. Polarization-independent liquid crystal phase modulator using a thin polymer-separated double-layered structure. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 8746–8752. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Song, Y.; Zhu, J.L.; Ni, S.B.; Wang, Y.J.; Sun, X.Y.; Lu, J.G.; Yang, B.R.; Shieh, H.P.D. Blue phase LC/polymer fresnel lens fabricated by holographics. J. Disp. Technol. 2014, 10, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Hsieh, C.W. Polarization-independent and high-diffraction-efficiency Fresnel lenses based on blue phase liquid crystals. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 502–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, S.T. Polarization-independent adaptive lens with two different blue-phase liquid-crystal layers. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 3216–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Wu, S.T. Polarization independent blue-phase liquid crystal cylindrical lens with a resistive film. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 2568–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Li, Y.; Lin, H.Y.; Wu, S.T. Design of polarization-insensitive multi-electrode GRIN lens with a blue-phase liquid crystal. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 17402–17407. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wu, S.T. Polarization independent adaptive microlens with a blue-phase liquid crystal. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 8045–8050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.H.; Huang, L.S.; Lin, C.H.; Kuo, C.T. Polarization-independent and fast tunable microlens array based on blue phase liquid crystals. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ye, M.; Sato, S. Liquid crystal lens with stacked structure of liquid-crystal layers. Opt. Commun. 2005, 250, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wen, C.H.; Wu, S.T. Polarization-independent and submillisecond response phase modulators using a 90° twisted dual-frequency liquid crystal. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 021103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Lin, Y.H.; Wu, S.T. Polarization-independent and fast-response phase modulators using double-layered liquid crystal gels. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 061123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuh, A.Y.G.; Ko, S.W.; Huang, S.H.; Chen, Y.Y.; Lin, T.H. Polarization-independent liquid crystal lens based on axially symmetric photoalignment. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 2294–2300. [Google Scholar]
- Kao, Y.Y.; Chao, P.C.P. A new fual-grequency liquid crystal lens with ring-and-pie electrodes and a driving scheme to prevent disclination lines and improve recovery time. Sensors 2011, 11, 5402–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pishnyak, O.; Sato, S.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Electrically tunable lens based on a dual-frequency nematic liquid crystal. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 4576–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schadt, M. Dielectric heating and relaxations in nematic liquid crystals. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1981, 66, 319–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kumar, S. Fabrication of electrically controllable microlens array using liquid crystals. J. Lightwave Technol. 2005, 23, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kumar, S. Fast switchable and bistable microlens array using ferroelectric liquid crystals. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 43, 7050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.M.; Gwag, J.; Choi, Y.; Lee, K.H.; Yu, C.J.; Kim, J.H. Fast switching characteristics of a microlens array using the electroclinic effect of SmA* liquid crystals. Appl. Opt. 2009, 48, 3737–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, L.; Ge, Z.; Wu, S.T.; Lee, S.H. Low voltage blue-phase liquid crystal displays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 231101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Gauza, S.; Jiao, M.; Xianyu, H.; Wu, S.T. Electro-optics of polymer-stabilized blue phase liquid crystal displays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 101104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseba, Y.; Kikuchi, H.; Nagamura, T.; Kajiyama, T. Large electro-optic Kerr effect in nanostructured chiral liquid-crystal composites over a wide temperature range. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 2311–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, H.; Yokota, M.; Hisakado, Y.; Yang, H.; Kajiyama, T. Polymer-stabilized liquid crystal blue phases. Nat. Mater. 2002, 1, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Rao, L.; Jiao, M.; Li, Y.; Cheng, H.C.; Wu, S.T. Polymer-stabilized optically isotropic liquid crystals for next-generation display and photonics applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 7870–7877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wu, S.T. Polymer-stabilized blue phase liquid crystals: a tutorial. Opt. Mater. Express 2011, 1, 1527–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xianyu, H.; Sun, J.; Kula, P.; Dabrowski, R.; Tripathi, S.; Twieg, R.J.; Wu, S.T. Low absorption liquid crystals for mid-wave infrared applications. Opt. Expr. 2011, 19, 10843–10848. [Google Scholar]
- Khoo, I.C.; Wu, S.T. Optics and Nonlinear Optics of Liquid Crystals; World Scientific: Singapore, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Wu, S.T. Introduction to Adaptive Lenses; Wiley: Hoboken, New Jersey, NY, US, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Fan, Y.H.; Lin, Y.H.; Wu, S.T. Tunable-focus microlens arrays using nanosized polymer-dispersed liquid crystal droplets. Opt. Commun. 2005, 247, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presnyakov, V.; Asatryan, K.; Galstian, T.; Tork, A. Polymer-stabilized liquid crystal for tunable microlens applications. Opt. Express 2002, 10, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Fan, Y.H.; Gauza, S.; Wu, S.T. Tunable microlens arrays using polymer network liquid crystal. Opt. Commun. 2004, 230, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauza, S.; Wang, H.; Wen, C.H.; Wu, S.T.; Seed, A.J.; Dabrowski, R. High birefringence isothiocyanato tolane liquid crystals. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 42, 3463–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauza, S.; Wen, C.H.; Wu, S.T.; Janarthanan, N.; Hsu, C.S. Super high birefringence isothiocyanato biphenyl-bistolane liquid crystals. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 43, 7634–7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doane, J.W.; Vaz, N.A.; Wu, B.G.; Žumer, S. Field controlled light scattering from nematic microdroplets. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1986, 48, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, C.V.; Hudson, S.D.; Chien, L.C. Morphology of polymer-stabilized liquid crystals. Chem. Mater. 1995, 7, 2300–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Fan, Y.H.; Wu, S.T. Polymer network liquid crystals for tunable microlens arrays. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2004, 37, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhou, Z.; Ren, H.; Seung, H.; Wang, Q. A microlens array based on polymer network liquid crystal. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 053105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Xu, S.; Wu, S.T. Polymer-stabilized liquid crystal microlens array with large dynamic range and fast response time. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 3144–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Xu, S.; Wu, S.T. Gradient polymer network liquid crystal with a large refractive index change. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 26464–26472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, Y.; Wu, S.T. Submillisecond-response and scattering-free infrared liquid crystal phase modulators. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 20124–20129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodgate, G.J.; Harrold, J.; Jacobs, A.M.S.; Moseley, R.R.; Ezra, D. Flat-panel autostereoscopic displays: characterization and enhancement. In Proceedings of the SPIE 3957, Stereoscopic Displays and Virtual Reality Systems VII, San Jose, CA, USA, 22 January 2000; p. 153.
- Choi, H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.; Cho, S.W.; Lee, B. Wide-viewing-angle 3D/2D convertible display system using two display devices and a lens array. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 8424–8432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, T.; de Zwart, S.T.; Willemsen, O.H.; Hiddink, M.G.H.; Ijzerman, W.L. 2D/3D switchable displays. In Proceedings of SPIE 6196, Photonics in Multimedia, 61960H, Strasbourg, France, 3 April 2006.
- Krijn, M.P.C.M.; de Zwart, S.T.; de Boer, D.K.G.; Willemsen, O.H.; Sluijter, M. 2D/3D displays based on switchable lenticulars. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 2008, 16, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, A.; Saishu, T.; Kashiwagi, M.; Taira, K.; Hirayama, Y. Autostereoscopic partial 2-D/3-D switchable display using liquid-crystal gradient index lens. SID Symp. Dig. 2010, 41, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Huang, Y.C.; Huang, Y.P.; Huang, J.F. Fast switching fresnel liquid crystal lens for autostereoscopic 2D/3D display. SID Symp. Dig. 2010, 41, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.K.; Lai, Y.F.; Chen, Y.C. An effective hybrid depth-generation algorithm for 2D-to-3D conversion in 3D displays. J. Disp. Technol. 2013, 9, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flack, J.; Harrold, J.; Woodgate, G.J. A prototype 3D mobile phone equipped with a next-generation autostereoscopic display. In Proceedings of SPIE 6490, Stereoscopic Displays and Virtual Reality Systems XIV, San Jose, CA, USA, 28 January 2007.
- Ren, H.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wu, S.T. Switchable focus using a polymeric lenticular microlens array and a polarization rotator. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 7916–7925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wu, S.T. Optically anisotropic microlens array film directly formed on a single substrate. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 29304–29312. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, T.B. Electromechanics of Particles; Cambridge Universtiy Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.M.; Gauza, S.; Xianyu, H.; Wu, S.T. Submillisecond gray-level response time of a polymer-stabilized blue-phase liquid crystal. J. Disp. Technol. 2010, 6, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Cheng, H.C.; Gauza, S.; Li, Y.; Jiao, M.; Rao, L.; Wu, S.T. Extended Kerr effect of polymer-stabilized blue-phase liquid crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 071105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuta, H.; Iwata, K.; Shimomura, H. First-order aberration of a double-focus lens made of a uniaxial crystal. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1992, 9, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesso, J.P.; Duncan, A.J.; Sibbett, W.; Padgett, M.J. Aberrations introduced by a lens made from a birefringent material. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 592–598. [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi, H.; Higuchi, H.; Haseba, Y.; Iwata, T. Fast electro-Optical switching in polymer-stabilized liquid crystalline blue ohases for display application. SID Symp. Dig. 2007, 38, 1737–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.F.; Tsai, C.Y.; Lu, J.K.; Sugiura, N. Mechanism of hysteresis in polymer-network stabilized blue phase liquid crystal. Polymer 2013, 54, 1876–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Ren, H.; Wu, S.-T. Fast-Response Liquid Crystal Microlens. Micromachines 2014, 5, 300-324. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi5020300
Xu S, Li Y, Liu Y, Sun J, Ren H, Wu S-T. Fast-Response Liquid Crystal Microlens. Micromachines. 2014; 5(2):300-324. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi5020300
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Su, Yan Li, Yifan Liu, Jie Sun, Hongwen Ren, and Shin-Tson Wu. 2014. "Fast-Response Liquid Crystal Microlens" Micromachines 5, no. 2: 300-324. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi5020300
APA StyleXu, S., Li, Y., Liu, Y., Sun, J., Ren, H., & Wu, S.-T. (2014). Fast-Response Liquid Crystal Microlens. Micromachines, 5(2), 300-324. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi5020300