Novel Tetragonal Boron Pnictides BX (X = N, P, As, Sb, Bi) with Square B2X2 Motifs from Crystal Chemistry and First Principles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Computational Framework
3. Crystal Chemistry
3.1. Developing Binary Equiatomic Compounds
3.2. Projection of the Charge Density
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Mechanical Properties from Elastic Constants
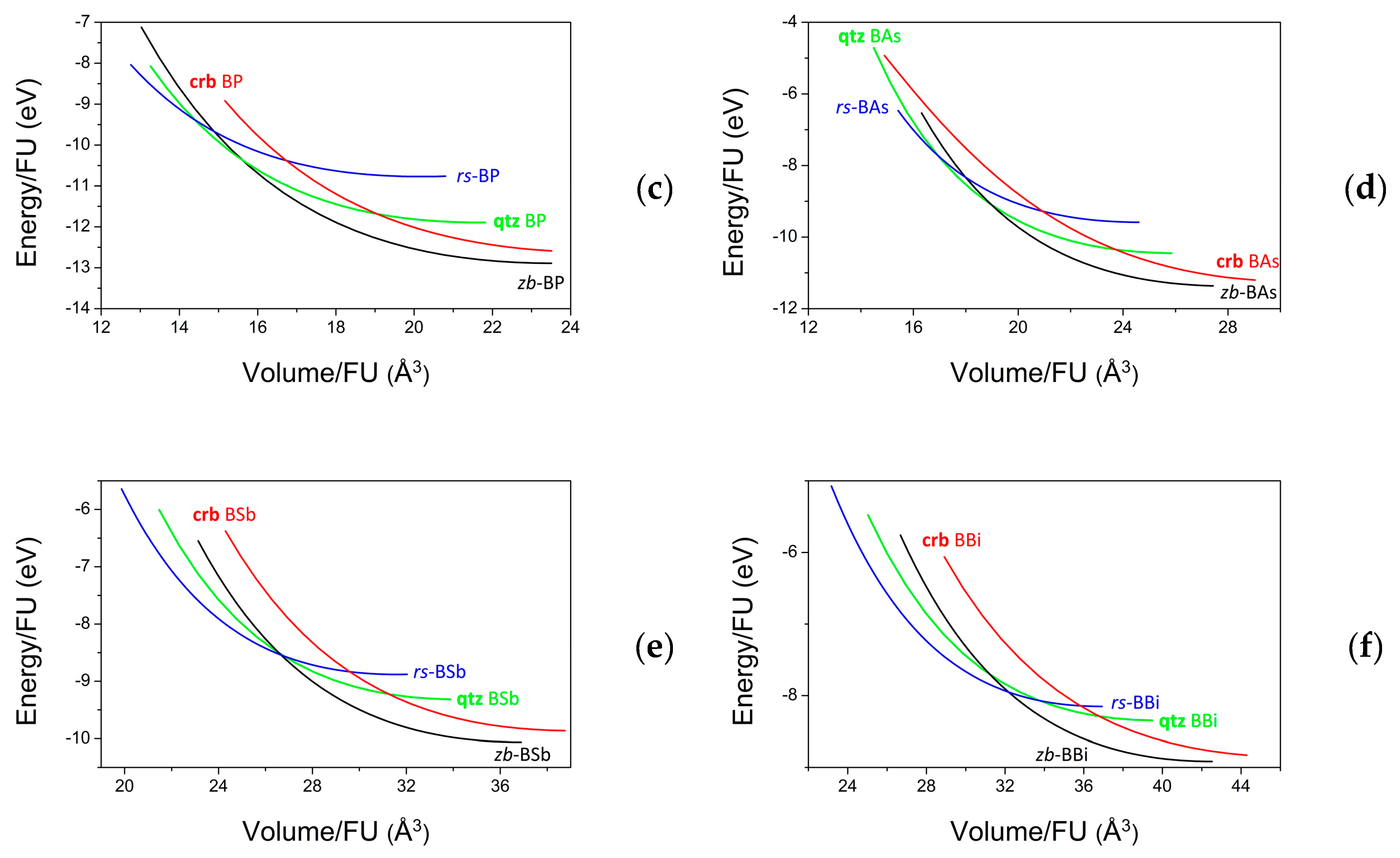
4.2. Equations of State
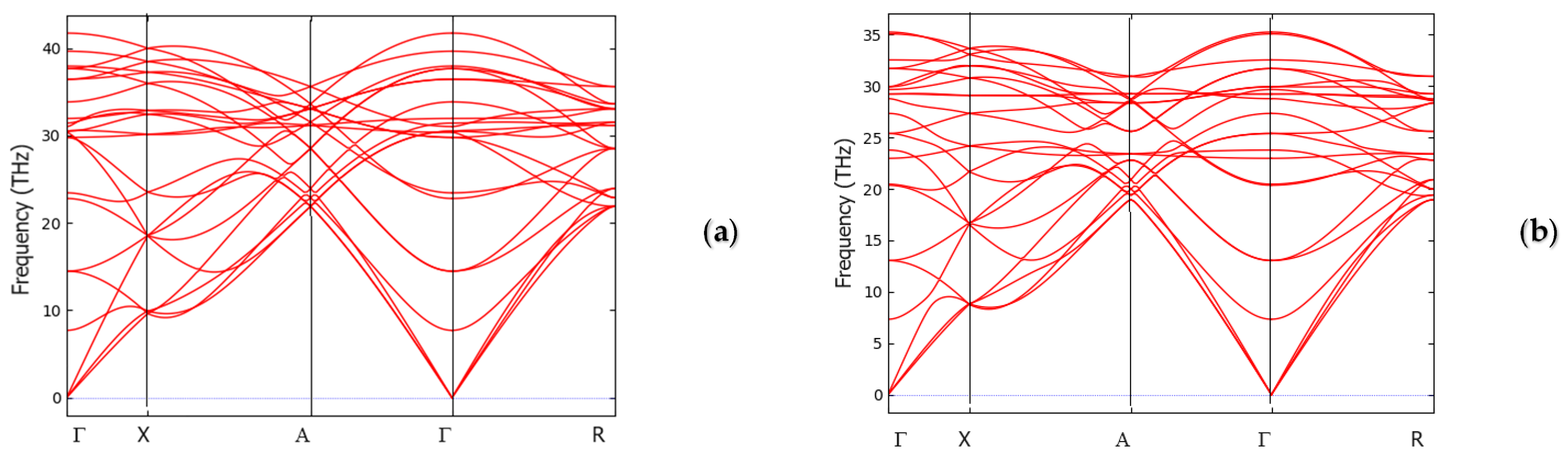
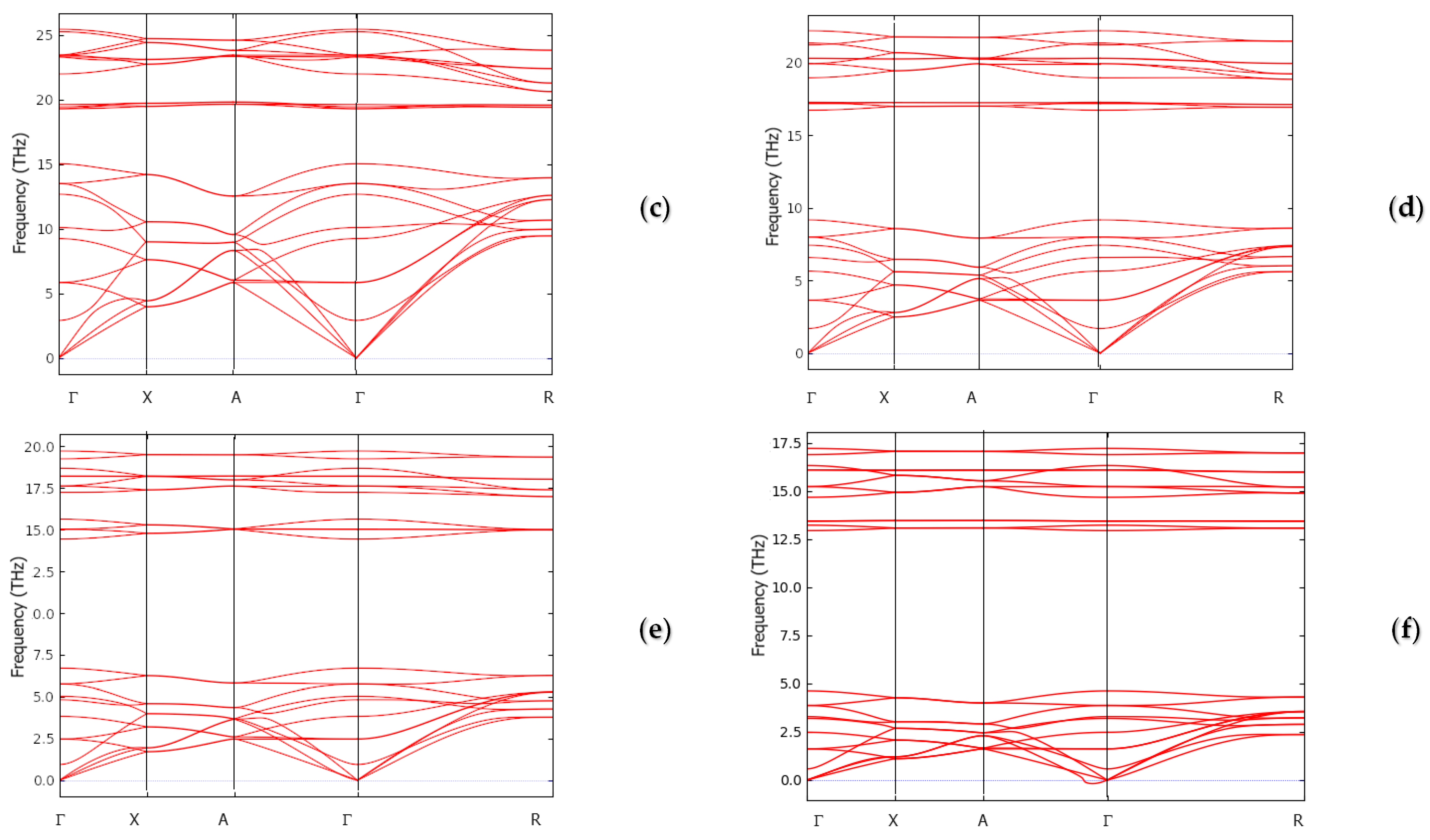
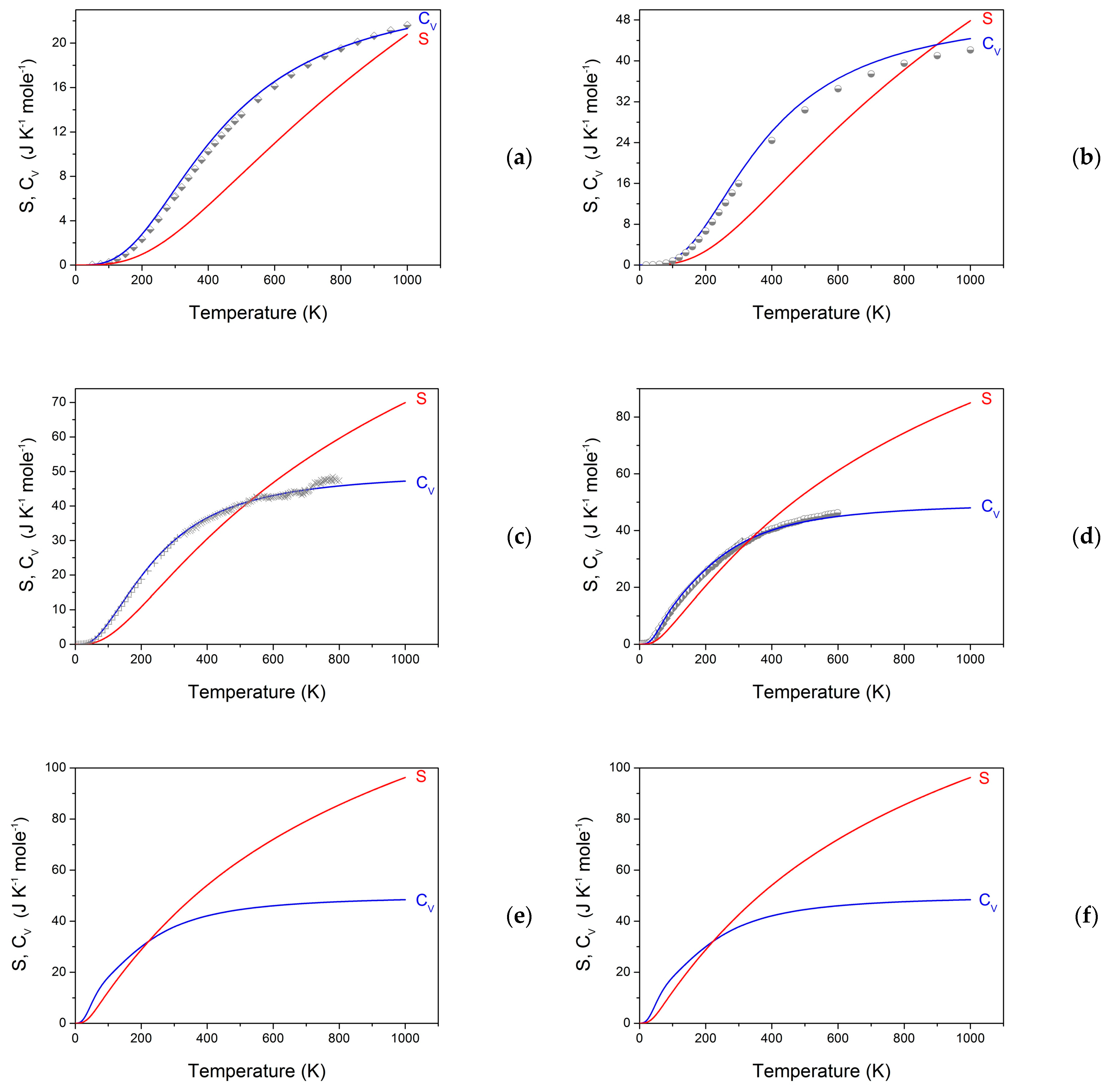
4.3. Dynamic and Thermodynamic Properties from the Phonons
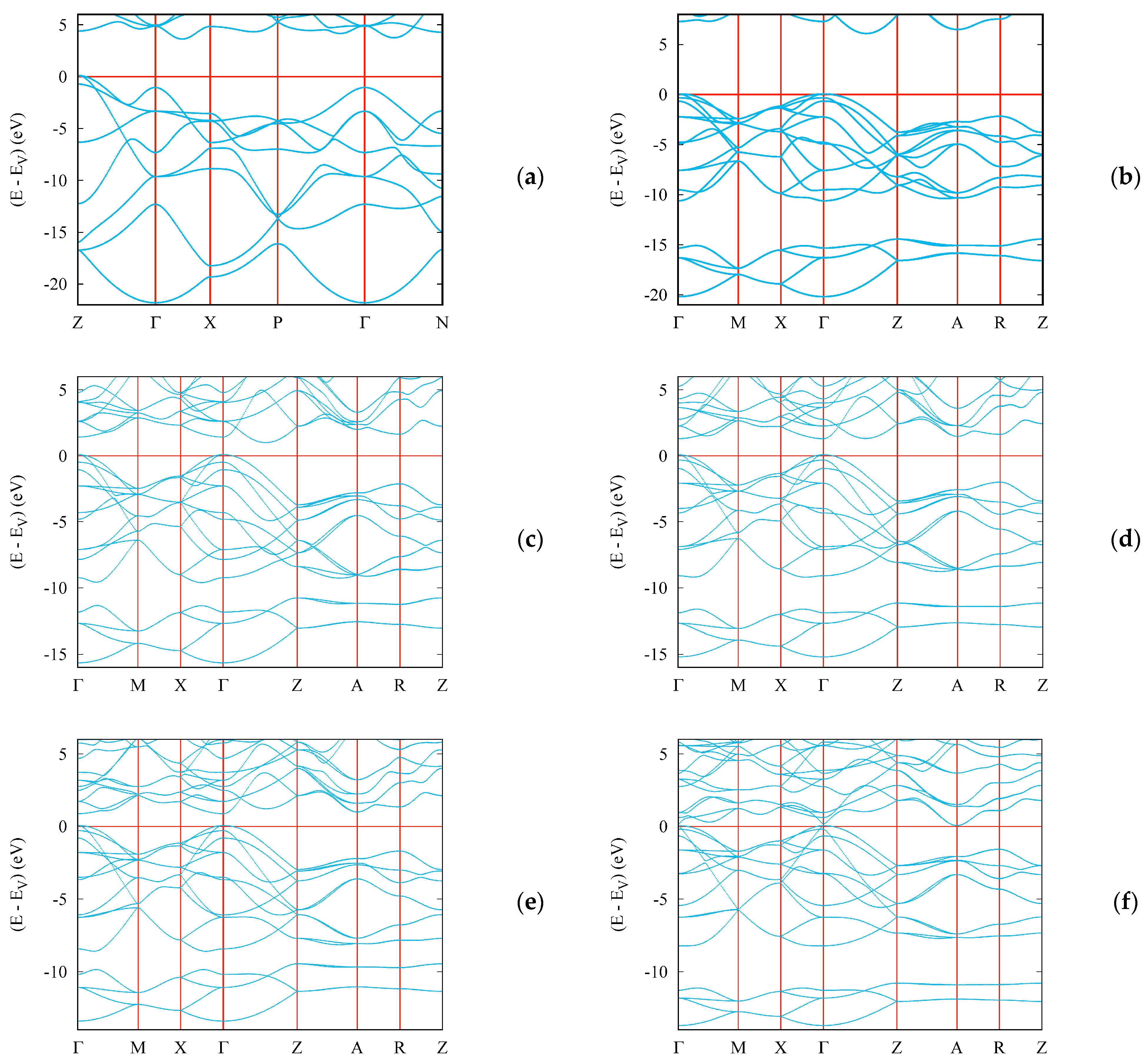
4.4. Electronic Band Structures
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oganov, A.R.; Glass, C.W. Crystal structure prediction using ab initio evolutionary techniques: Principles and applications. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 124, 244704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, A.; Batzner, S.; Schoenholz, S.S.; Aykol, M.; Cheon, G.; Cubuk, E.D. Scaling deep learning for materials discovery. Nature 2023, 624, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, C.W.; Oganov, A.R.; Hansen, N. USPEX—Evolutionary crystal structure prediction. Comput. Phys. Comm. 2006, 175, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenberg, P.; Kohn, W. Inhomogeneous electron gas. Phys. Rev. B 1964, 136, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, W.; Sham, L.J. Self-consistent equations including exchange and correlation effects. Phys. Rev. A 1965, 140, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchenko, A.P.; Shabalin, A.A.; Karpukhin, I.Y.; Blatov, V.A. Topological representations of crystal structures: Generation, analysis and implementation in the TopCryst system. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mat. 2022, 2, 250–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, D.L.V.K.; Gerovac, N.M.; Bucknum, M.J.; Hoffmann, R. Squaroglitter: A 3,4-connected carbon net. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 3855–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucknum, M.J.; Hoffmann, R. A hypothetical dense 3,4-connected carbon net and related B2C and CN2 nets built from 1,4-cyclohexadienoid units. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 11456–11464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, R.; Kabanov, A.A.; Golov, A.A.; Proserpio, D.M. Homo Citans and carbon allotropes: For an ethics of citation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 10962–10976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matar, S.F.; Solozhenko, V.L. Ultrahigh-density superhard hexagonal BN and SiC with quartz topology from crystal chemistry and first principles. Crystals 2023, 13, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solozhenko, V.L.; Matar, S.F. Superdense hexagonal BP and AlP with quartz topology: Crystal chemistry and DFT study. Crystals 2023, 13, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solozhenko, V.L.; Matar, S.F. High-pressure phases of boron pnictides BX (X = As, Sb, Bi) with quartz topology from first principles. Crystals 2024, 14, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 11169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Joubert, J. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented wave. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 1758–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöchl, P.E. Projector augmented wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 50, 17953–17979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. The Generalized Gradient Approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Press, W.H.; Flannery, B.P.; Teukolsky, S.A.; Vetterling, W.T. Numerical Recipes, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Blöchl, P.; Jepsen, O.; Anderson, O. Improved tetrahedron method for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 49, 16223–16233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methfessel, M.; Paxton, A.T. High-precision sampling for Brillouin-zone integration in metals. Phys. Rev. B 1989, 40, 3616–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special k-points for Brillouin Zone integration. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyert, V. Basic notions and applications of the augmented spherical wave method. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2000, 77, 1007–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillac, R.; Pullumbi, P.; Coudert, F.X. ELATE: An open-source online application for analysis and visualization of elastic tensors. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2016, 28, 275201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigt, W. Über die Beziehung zwischen den beiden Elasticitätsconstanten isotroper Körper. Annal. Phys. 1889, 274, 573–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhnik, E.; Oganov, A.R. A model of hardness and fracture toughness of solids. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 126, 125109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Q.; Niu, H.; Li, D.; Li, Y. Modeling hardness of polycrystalline materials and bulk metallic glasses. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhanov, V.A.; Kurakevych, O.O.; Solozhenko, V.L. The interrelation between hardness and compressibility of substances and their structure and thermodynamic properties. J. Superhard Mater. 2008, 30, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhanov, V.A.; Kurakevych, O.O.; Solozhenko, V.L. Hardness of materials at high temperature and high pressure. Phil. Mag. 2009, 89, 2117–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyakhov, A.O.; Oganov, A.R. Evolutionary search for superhard materials: Methodology and applications to forms of carbon and TiO2. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 092103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhanov, V.A.; Kurakevych, O.O.; Solozhenko, V.L. Thermodynamic model of hardness: Particular case of boron-rich solids. J. Superhard Mater. 2010, 32, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solozhenko, V.L.; Matar, S.F. Prediction of novel ultrahard phases in the B–C–N system from first principles: Progress and problems. Materials 2023, 16, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solozhenko, V.L.; Bushlya, V. Mechanical properties of boron phosphides. J. Superhard Mater. 2019, 41, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solozhenko, V.L. Hardness of new boron-rich chalcogenides B12S and B12Se. J. Superhard Mater. 2021, 43, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solozhenko, V.L. On hardness of boron subarsenide B12As2. J. Superhard Mater. 2022, 44, 377–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, C.A. The mechanical properties of cubic boron nitride. In Science of Hard Materials. Proceedings of the International Conference; Adam Hilger Ltd.: Accord, MA, USA, 1986; pp. 207–220. [Google Scholar]
- Birch, F. Finite strain isotherm and velocities for single-crystal and polycrystalline NaCl at high pressures and 300 K. J. Geophys. Res. 1978, 83, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togo, A.; Tanaka, I. First principles phonon calculations in materials science. Scr. Mater. 2015, 108, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, R.S. Raman spectrum of diamond. Nature 1945, 155, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dove, M.T. Introduction to Lattice Dynamics; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- DeSorbo, W. Specific heat of diamond at low temperatures. J. Chem. Phys. 1953, 21, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, A.C. Heat capacity of diamond at high temperatures. J. Chem. Phys. 1962, 36, 1903–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solozhenko, V.L.; Gavrichev, K.S. Thermodynamic properties of boron nitride. In Wide Band Gap Electronic Materials; Prelas, M.A., Gielisse, P., Popovici, G., Spitsyn, B.V., Stacy, T., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 377–392. [Google Scholar]
- Ohsawa, J.; Nishinaga, T.; Uchiyama, S. Measurement of specific heat of boron monophosphide by AC calorimetry. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1978, 17, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshchenko, V.I.; Grinberg, Y.K.; Demidenko, A.F. Thermodynamic properties of AlN (5–2700 K), GaP (5–1500 K) and BP (5–800 K). Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR Neorg. Mater. 1984, 20, 1787–1790. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.S.; Li, M.; Wu, H.; Nguyen, H.; Hua, Y. Basic physical properties of cubic boron arsenide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 115, 122103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshchenko, V.I.; Demidenko, A.F.; Grinberg, Y.K.; Yachmenev, V.E. Specific-heats and thermodynamic functions of BP, BAs and B6As at 5–310 K. Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR Neorg. Mater. 1981, 17, 1965–1968. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]

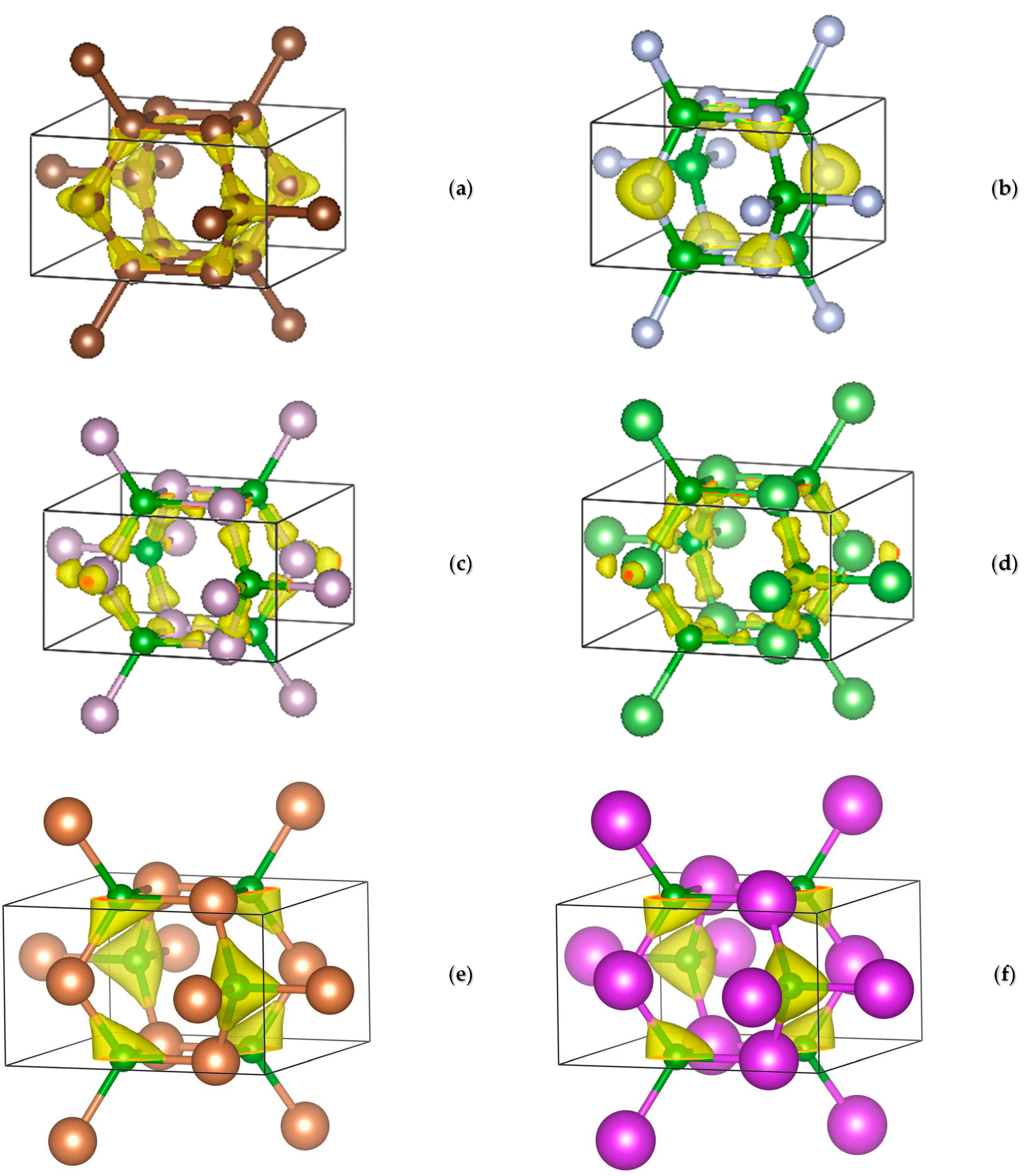

| crb C8 I4/mmm (No. 139) | crb (C1)4(C2)4 P42/mnm (No. 136) | |
|---|---|---|
| a, Å | 4.3665 | 4.3662 |
| c, Å | 2.5045 | 2.5048 |
| Vcell, Å3 | 47.75 | 47.75 |
| Density, g/cm3 | 3.34 | 3.34 |
| Atomic positions | C (8h) 0.6803, x, 0.0 | C1 (4g) 0.3197, −x, 0.0 C2 (4f) 0.6803, x, 0.0 |
| Bond lengths, Å | 1.519 and 1.574 Å | 1.519 and 1.574 Å |
| Angles (deg.) | ∠C-C-C = 90° (within the square) ∠C-C-C = 110.96° (along z direction) | ∠C-C-C = 90° (within the square) ∠C-C-C = 110.96° (along z direction) |
| Etotal, eV | −71.33 | −71.33 |
| Etotal/atom, eV | −2.32 | −2.32 |
| BN | BP | BAs | BSb | BBi | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P42/mnm (No. 136) | |||||
| a, Å | 4.398 | 5.558 | 5.894 | 6.453 | 6.764 |
| c, Å | 2.538 | 3.199 | 3.392 | 3.723 | 3.900 |
| Vcell, Å3 | 49.11 | 98.88 | 117.83 | 155.01 | 178.43 |
| Shortest bond length, Å | d(B-N) = 1.53 | d(B-P) = 1.95 | d(B-As) = 2.06 | d(B-Sb) = 2.31 | d(B-Bi) = 2.38 |
| Angles (deg.) | ∠BNB = 85.76 ∠NBN = 112.44 | ∠BPB = 90.73 ∠PBP = 113.59 | ∠BAsB = 91. 23 ∠AsBAs = 113.50 | ∠BSbB = 91.36 ∠SbBSb = 110.49 | ∠BBiB = 91. 79 ∠BiBBi = 110.28 |
| Atomic positions | B(4g) 0.3258, −x, 0 N(4i) 0.6875, x, 0 | B(4g) 0.3217, −x, 0 P(4i) 0.6806, x, 0 | B(4g) 0.323, −x, 0 As(4i) 0.681, x, 0 | B(4g) 0.3229, −x, 0 Sb(4i) 0.6814, x, 0 | B(4g) 0.3238, −x, 0 Bi(4i) 0.6818, x, 0 |
| Etotal, eV | −68.86 | −50.51 | −45.293 | −39.45 | −35.05 |
| Ecoh/FU, eV | −5.12 | −2.13 | −1.52 | −0.60 | −0.053 |
| (zinc-blende) | −5.32 | −2.39 | −1.57 | −0.70 | −0.60 |
| C11 | C12 | C13 | C33 | C44 | C66 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C8 | 949 | 234 | 59 | 1202 | 323 | 450 |
| BN | 757 | 174 | 114 | 988 | 239 | 336 |
| BP | 215 | 165 | 48 | 403 | 83 | 135 |
| BAs | 242 | 71 | 40 | 317 | 77 | 104 |
| BSb | 171 | 60 | 38 | 228 | 58 | 69 |
| BBi | 117 | 48 | 31 | 155 | 40 | 45 |
| HV | B | GV | EV | ν | KIc * | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MO * | CN † | T ‡ | LO § | B0 ‡ | BV | |||||
| GPa | MPa·m½ | |||||||||
| C8 | 67 | 60 | 93 | 85 | 423 | 423 | 402 | 916 | 0.139 | 7.1 |
| BN | 43 | 42 | 53 | 48 | 363 | 367 | 303 | 713 | 0.177 | 6.0 |
| BP | 10 | 15 | 28 | 24 | 173 | 151 | 98 | 242 | 0.232 | 1.4 |
| BAs | 12 | 18 | 22 | 20 | 135 | 123 | 95 | 226 | 0.192 | 1.3 |
| BSb | 8 | 12 | 17 | 3 | 101 | 94 | 66 | 160 | 0.215 | 0.8 |
| BBi | 5 | 8 | 13 | 2 | 82 | 68 | 44 | 108 | 0.235 | 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matar, S.F.; Solozhenko, V.L. Novel Tetragonal Boron Pnictides BX (X = N, P, As, Sb, Bi) with Square B2X2 Motifs from Crystal Chemistry and First Principles. Crystals 2024, 14, 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14040359
Matar SF, Solozhenko VL. Novel Tetragonal Boron Pnictides BX (X = N, P, As, Sb, Bi) with Square B2X2 Motifs from Crystal Chemistry and First Principles. Crystals. 2024; 14(4):359. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14040359
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatar, Samir F., and Vladimir L. Solozhenko. 2024. "Novel Tetragonal Boron Pnictides BX (X = N, P, As, Sb, Bi) with Square B2X2 Motifs from Crystal Chemistry and First Principles" Crystals 14, no. 4: 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14040359
APA StyleMatar, S. F., & Solozhenko, V. L. (2024). Novel Tetragonal Boron Pnictides BX (X = N, P, As, Sb, Bi) with Square B2X2 Motifs from Crystal Chemistry and First Principles. Crystals, 14(4), 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14040359






