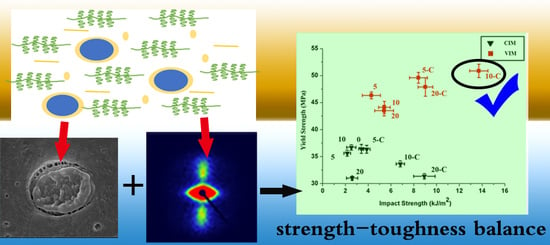
New Approach to Optimize Mechanical Properties of the Immiscible Polypropylene/Poly (Ethylene Terephthalate) Blend: Effect of Shish-Kebab and Core-Shell Structure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Polarized Light Microscopy (PLM)
2.4. Two-Dimensional Small Angle X-ray Scattering (2D-SAXS)
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.6. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.7. Dynamic Rheology Measurement
2.8. Mechanical Testing
3. Results and Discussion
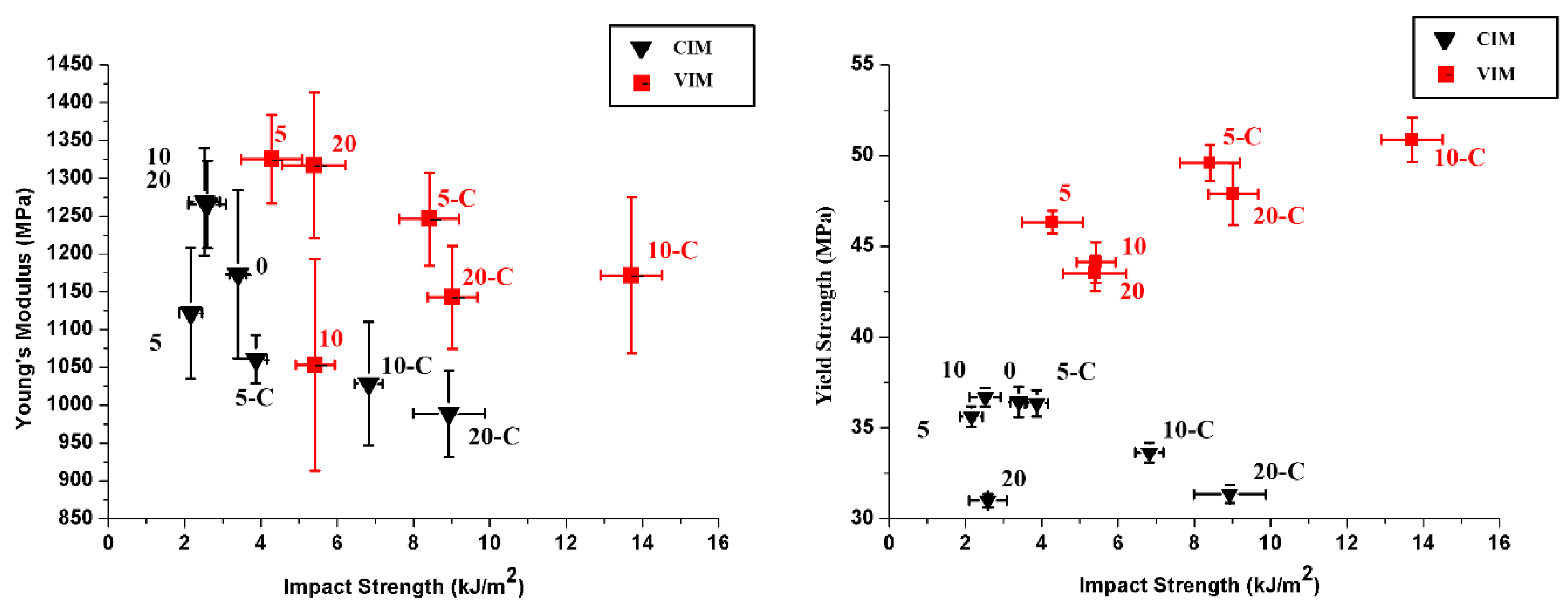
3.1. Mechanical Properties
3.2. Crystallization of PP Matrix
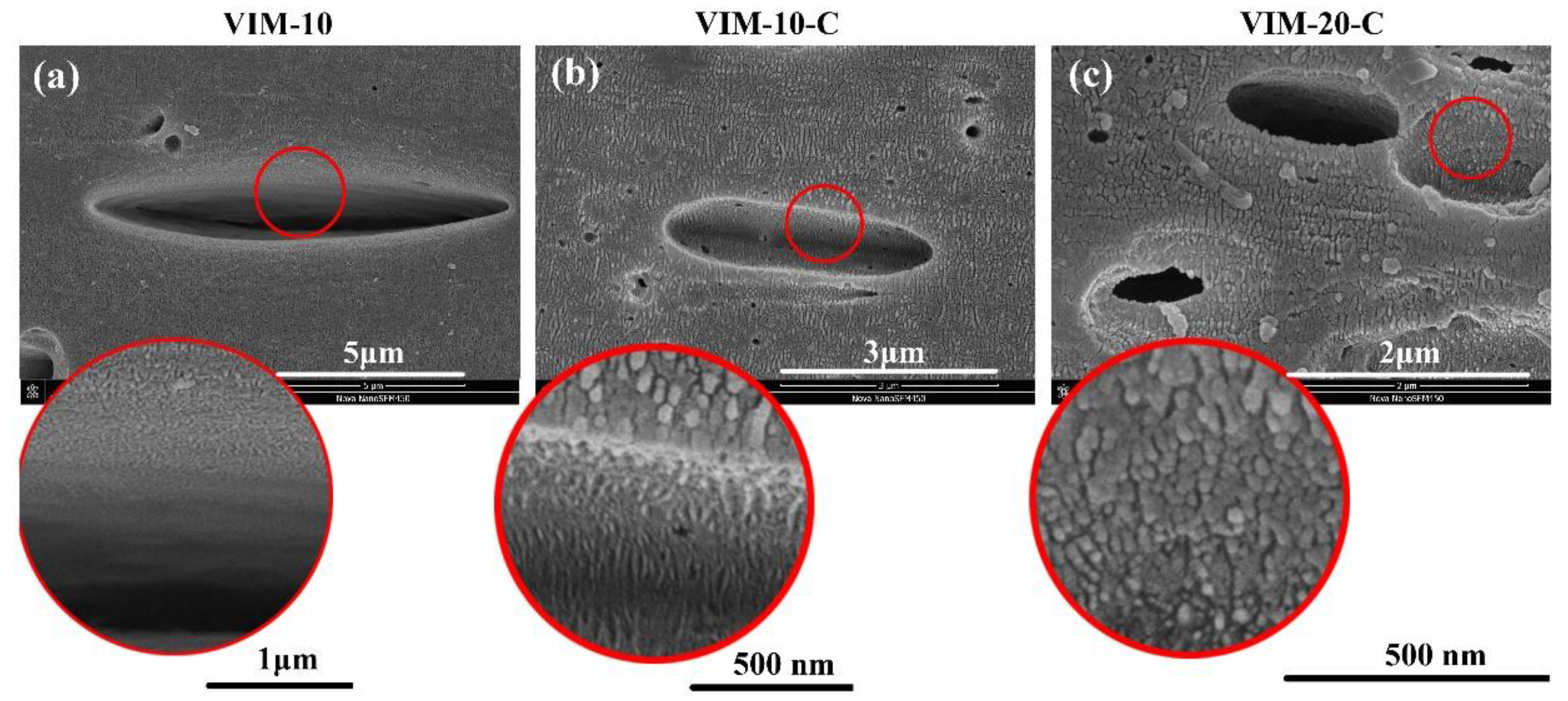
3.3. Phase Morphology and Core-Shell Structure
3.4. Toughening Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ragaert, K.; Delva, L.; Van, G.K. Mechanical and chemical recycling of solid plastic waste. Waste Manag. 2017, 69, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Salem, S.M.; Lettieri, P.; Baeyens, J. Recycling and recovery routes of plastic solid waste (PSW): A review. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2625–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnini, M.S.; Maria, Z. Recyclability of PET from virgin resin. Mater. Res. 1999, 2, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Bruggen, E.P.A.V.; Koster, R.P.; Picken, S.J.; Ragaert, K. Influence of Processing Parameters and Composition on the Effective Compatibilization of Polypropylene–Poly(ethylene terephthalate) Blends. Int. Polym. Process. J. Polym. Process. Soc. 2016, 31, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evstatiev, M.; Fakirov, S.; Krasteva, B.; Friedrich, K.; Covas, J.A.; Cunha, A.M. Recycling of poly(ethylene terephthalate) as polymer-polymer composites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2002, 42, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakirov, S.; Evstatiev, M. Microfibrillar reinforced composites—New materials from polymer blends. Adv. Mater. 2010, 6, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonato, R.C.; Bonse, B.C. A study of PP/PET composites: Factorial design, mechanical and thermal properties. Polym. Test. 2016, 56, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.T.; Hsiao, Y.K. Compatibilization of Poly(ethylene terephthalate)/Polypropylene Blends with Maleic Anhydride Grafted Polyethylene-Octene Elastomer. J. Polym. Res. 2006, 13, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmanović, M.; Delva, L.; Mi, D.; Martins, C.; Cardon, L.; Ragaert, K. Development of Crystalline Morphology and Its Relationship with Mechanical Properties of PP/PET Microfibrillar Composites Containing POE and POE-g-MA. Polymers 2018, 10, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, K. Microfibrillar reinforced composites from PET/PP blends: Processing, morphology and mechanical properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utracki, L.A. Thermodynamics of Polymer Blends. In Polymer Blends Handbook; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 195, pp. 123–202. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S. Formation of dispersed phase in incompatible polymer blends: Interfacial and rheological effects. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1987, 27, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordjazi, Z.; Ebrahimi, N.G. Rheological behavior of noncompatibilized and compatibilized PP/PET blends with SEBS-g-MA. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penco, M.; Pastorino, M.A.; Occhiello, E.; Garbassi, F.; Braglia, R.; Giannotta, G. High-impact poly(ethylene terephthalate) blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 57, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shentu, B.; Weng, Z. In Situ Formation of the Core–Shell Particles and Their Function in Toughening PA6/SEBS-g-MA/PP Blends. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 11657–11663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzano, L.; Ma, Z.; Cavallo, D.; van Erp, T.B.; Fernandez-Ballester, L.; Peters, G.W.M. Molecular Aspects of the Formation of Shish-Kebab in Isotactic Polypropylene. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 3799–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimata, S.; Sakurai, T.; Nozue, Y.; Kasahara, T.; Yamaguchi, N.; Karino, T.; Shibayama, M.; Kornfield, J.A. Molecular basis of the shish-kebab morphology in polymer crystallization. Science 2007, 316, 1014–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, B.S.; Yang, L.; Somani, R.H.; Avila-Orta, C.A.; Zhu, L. Unexpected shish-kebab structure in a sheared polyethylene melt. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 117802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kmetty, Á.; Bárány, T.; Karger-Kocsis, J. Self-reinforced polymeric materials: A review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 1288–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, D.; Xia, C.; Jin, M.; Wang, F.; Shen, K.; Zhang, J. Quantification of the Effect of Shish-Kebab Structure on the Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene Samples by Controlling Shear Layer Thickness. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 4571–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lian, M.; Pan, Y.; Wang, X.; Zheng, G.; Liu, C.; Schubert, D.W.; Shen, C. An Alternating Skin–Core Structure in Melt Multi-Injection-Molded Polyethylene. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 303, 1700465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.J.; Li, L.; Mendes, E.; Byelov, D.; Fu, Q.; Li, Z.M. Suppression of Skin−Core Structure in Injection-Molded Polymer Parts by in Situ Incorporation of a Microfibrillar Network. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 6771–6775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, P.S.; Bevis, M.J. Development and application of multiple live-feed moulding for the management of fibres in moulded parts. Compos. Manuf. 1990, 1, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, P.S.; Bevis, M.J. Multiple live-feed injection moulding. Plast. Rubber Process. Appl. 1987, 7, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Li, X.P.; Jin, M.; Xia, C.; Shen, K.Z.; Zhang, J. Simultaneously improving the tensile and impact properties of isotactic polypropylene with the cooperation of co-PP and β-nucleating agent through pressure vibration injection molding. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 34, 1001–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hou, F.; Mi, D.; Zhou, M.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, J. Self-Reinforcement of Polypropylene Lid-Shaped Samples Induced by Increasing Shish-Kebab Content: Practical Application of Vibration Injection Technology. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 8620–8629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, D.-S.; Hou, F.-Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, J. Distribution of α-, β-, and γ-Phases in a Multi-flow Injection-molded Hierarchical Structure. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 36, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, K.; Jin, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, J. Influence of phase morphology and crystalline structure on the toughness of rubber-toughened isotatic polypropylene blends. Polymer 2014, 55, 5001–5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odent, M.; Colson, S.; De, R.P. Structure development and properties of PET fibre filled PP composites. Polymer 2001, 42, 4537–4548. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, D.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J. The Changes of Microstructure and Physical Properties of Isotactic Polypropylene/β Nucleation Agent/Polyolefin Elastomer Induced by Annealing Following Processing. J. Macromol. Sci., Part B. 2015, 54, 1376–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, S.; Lin, Z.; Yan, X.; Xu, Y.; Xu, X. Effect of blend composition on the rheology property of polypropylene/poly (ethylene-1-octene) blends. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 3218–3222. [Google Scholar]
- Mcnally, T.; Mcshane, P.; Nally, G.M.; Murphy, W.R.; Cook, M.; Miller, A. Rheology, phase morphology, mechanical, impact and thermal properties of polypropylene/metallocene catalysed ethylene 1-octene copolymer blends. Polymer 2002, 43, 3785–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, S.Y.; Dekkers, M.E.J.; Watkins, V.H. Effect of interfacial forces on polymer blend morphologies. Polymer 1988, 29, 1598–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzinov, I.; Pagnoulle, C.; Jérôme, R. Ternary polymer blend with core–shell dispersed phases: Effect of the core-forming polymer on phase morphology and mechanical properties. Polymer 2000, 41, 7099–7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.P.; Yin, B.; Zhou, Y.; Gong, L.; Yang, M.B.; Xie, B.H.; Chen, C. Characterization of PA6/EPDM-g-MA/HDPE ternary blends: The role of core-shell structure. Polymer 2012, 53, 3043–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Na, B.; Du, R.; Fu, Q.; Shen, K. Dependence of impact strength on the fracture propagation direction in dynamic packing injection molded PP/EPDM blends. Polymer 2003, 44, 4261–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, C.; Su, J.; Han, S.; Wang, K.; Fu, Q. Hierarchical structure and unique impact behavior of polypropylene/ethylene-octene copolymer blends as obtained via dynamic packing injection molding. Polymer 2013, 54, 3392–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Li, L.P.; Zhou, Y.; Gong, L.; Yang, M.B.; Xie, B.H. Largely improved impact toughness of PA6/EPDM-g-MA/HDPE ternary blends: The role of core–shell particles formed in melt processing on preventing micro-crack propagation. Polymer 2013, 54, 1938–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, F.; Mi, D.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, J. The influences of a novel shear layer-spherulites layer alternated structure on the mechanical properties of injection-molded isotactic polypropylene. Polymer 2017, 122, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G'Sell, C.; Bai, S.L.; Hiver, J.M. Polypropylene/polyamide 6/polyethylene–octene elastomer blends. Part 2: Volume dilatation during plastic deformation under uniaxial tension. Polymer 2004, 45, 5785–5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Material | PP/PET wt % | POE–g–MA wt % |
|---|---|---|
| Pure PP | 100/0 | 0 |
| 5 | 95/5 | 0 |
| 5-C | 93.5/4.9 | 2 |
| 10 | 90/10 | 0 |
| 10-C | 86.4/9.6 | 4 |
| 20 | 80/20 | 0 |
| 20-C | 75.2/18.8 | 6 |
| Samples | 0 | 5 | 5-C | 10 | 10-C | 20 | 20-C | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CIM | VIM | CIM | VIM | CIM | VIM | CIM | VIM | CIM | VIM | CIM | VIM | CIM | VIM | |
| Yield strength/MPa | 36.42 ± 0.84 | 58.46 ± 0.87 | 35.61 ± 0.56 | 46.33 ± 0.64 | 36.35 ± 0.73 | 49.6 ± 1.00 | 36.69 ± 0.51 | 44.12 ± 1.11 | 33.63 ± 0.55 | 50.87 ± 1.23 | 30.99 ± 0.37 | 43.51 ± 0.99 | 31.34 ± 0.48 | 47.89 ± 1.70 |
| Young’s modulus/MPa | 1173 ± 112 | 1421 ± 120 | 1122 ± 87 | 1326 ± 58 | 1061 ± 32 | 1247 ± 62 | 1269 ± 71 | 1181 ± 96 | 1029 ± 82 | 1172 ± 103 | 1265 ± 58 | 1318 ± 96 | 989 ± 57 | 1143 ± 68 |
| Impact strength/kJ.m-2 | 3.40 ± 0.22 | 18.20 ± 1.00 | 2.16 ± 0.29 | 4.28 ± 0.79 | 3.87 ± 0.3 | 8.41 ± 0.78 | 2.52 ± 0.41 | 5.43 ± 0.51 | 6.82 ± 0.37 | 13.71 ± 0.80 | 2.59 ± 0.50 | 5.4 ± 0.83 | 8.93 ± 0.94 | 9.02 ± 0.65 |
| Samples | Thermal properties | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tm/°C | Tc/°C | ΔH/J·g−1 | Xc/% | |
| CIM-0 | 166.70 | - | 76.39 | 36.5 |
| VIM-0 | 165.66 | 119.36 | 75.83 | 36.3 |
| CIM-10 | 165.57 | - | 70.02 | 37.2 |
| VIM-10 | 167.38 | 125.25 | 73.05 | 38.8 |
| CIM-10-C | 165.32 | - | 66.32 | 36.7 |
| VIM-10-C | 166.43 | 120.40 | 68.95 | 38.2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Mi, D.; Delva, L.; Cardon, L.; Zhang, J.; Ragaert, K. New Approach to Optimize Mechanical Properties of the Immiscible Polypropylene/Poly (Ethylene Terephthalate) Blend: Effect of Shish-Kebab and Core-Shell Structure. Polymers 2018, 10, 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101094
Wang Y, Mi D, Delva L, Cardon L, Zhang J, Ragaert K. New Approach to Optimize Mechanical Properties of the Immiscible Polypropylene/Poly (Ethylene Terephthalate) Blend: Effect of Shish-Kebab and Core-Shell Structure. Polymers. 2018; 10(10):1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101094
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yingxiong, Dashan Mi, Laurens Delva, Ludwig Cardon, Jie Zhang, and Kim Ragaert. 2018. "New Approach to Optimize Mechanical Properties of the Immiscible Polypropylene/Poly (Ethylene Terephthalate) Blend: Effect of Shish-Kebab and Core-Shell Structure" Polymers 10, no. 10: 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101094
APA StyleWang, Y., Mi, D., Delva, L., Cardon, L., Zhang, J., & Ragaert, K. (2018). New Approach to Optimize Mechanical Properties of the Immiscible Polypropylene/Poly (Ethylene Terephthalate) Blend: Effect of Shish-Kebab and Core-Shell Structure. Polymers, 10(10), 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101094