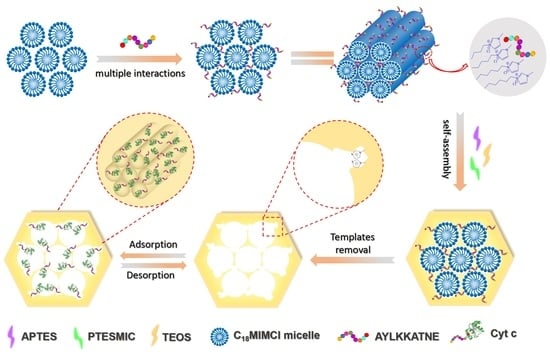
Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Mesoporous Materials for Highly Enhancing Adsorption Performance of Cytochrome C
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
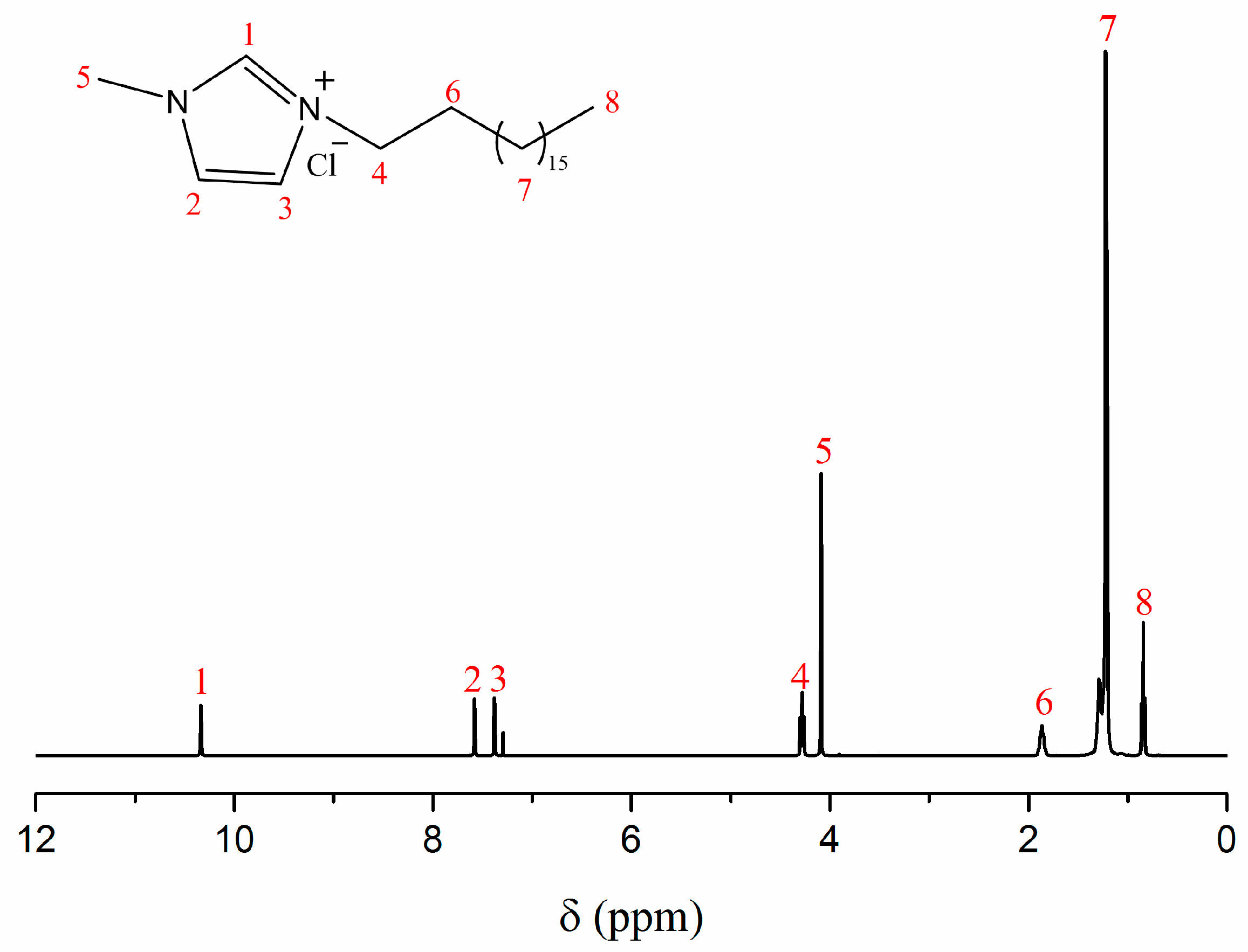
2.2. Synthesis of Amphiphilic Ionic Liquid C18MIMCl
2.3. Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Mesoporous Materials (MIMs)
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Isothermal Rebinding and Dynamic Adsorption
2.6. Selectivity and Competitive Adsorption Experiments
2.7. Reusability Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Effect of Alkyl Chain Length of ILs on Mesoporous Diameter
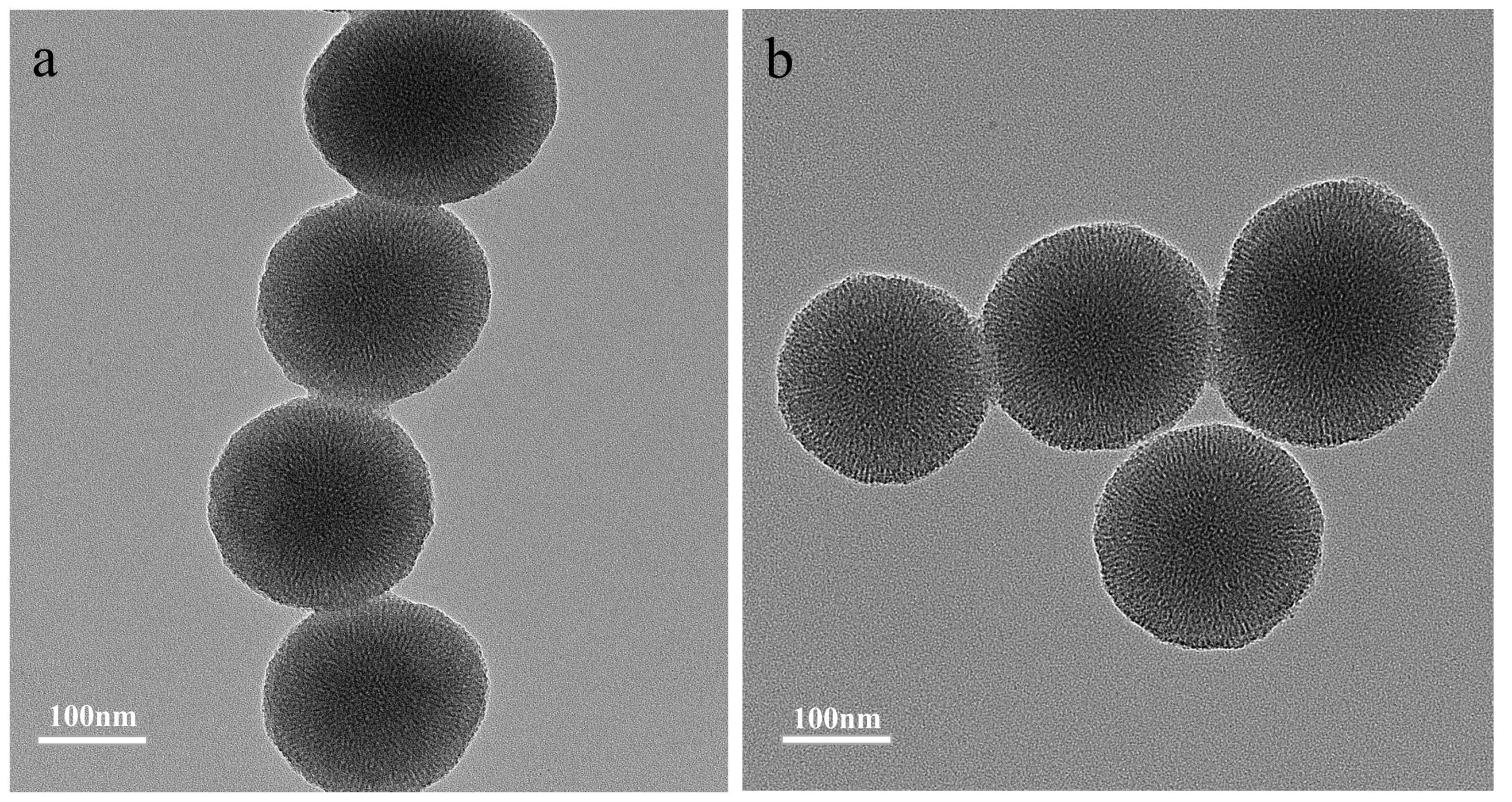
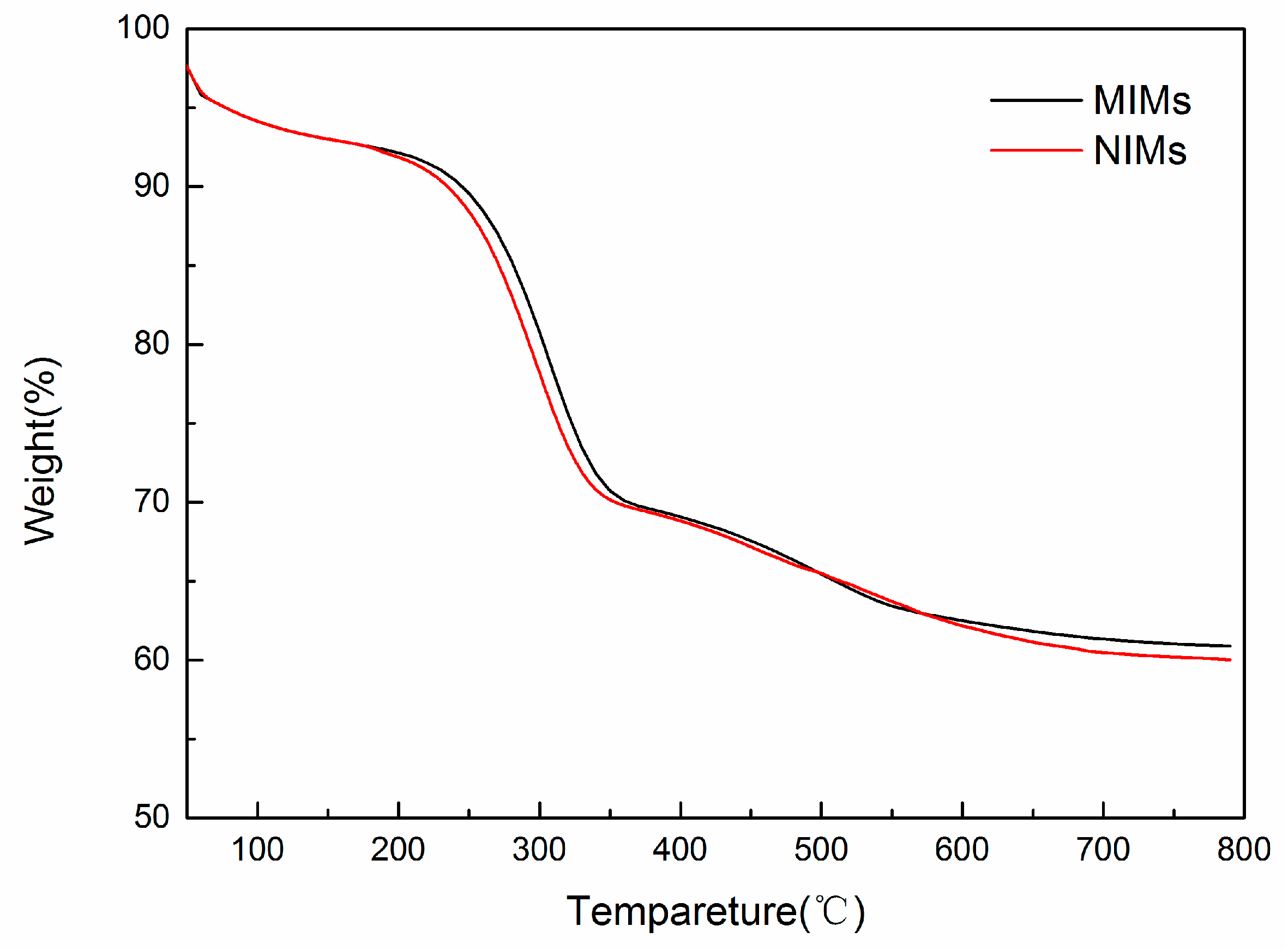
3.2. Preparation and Characterization of MIMs and NIMs
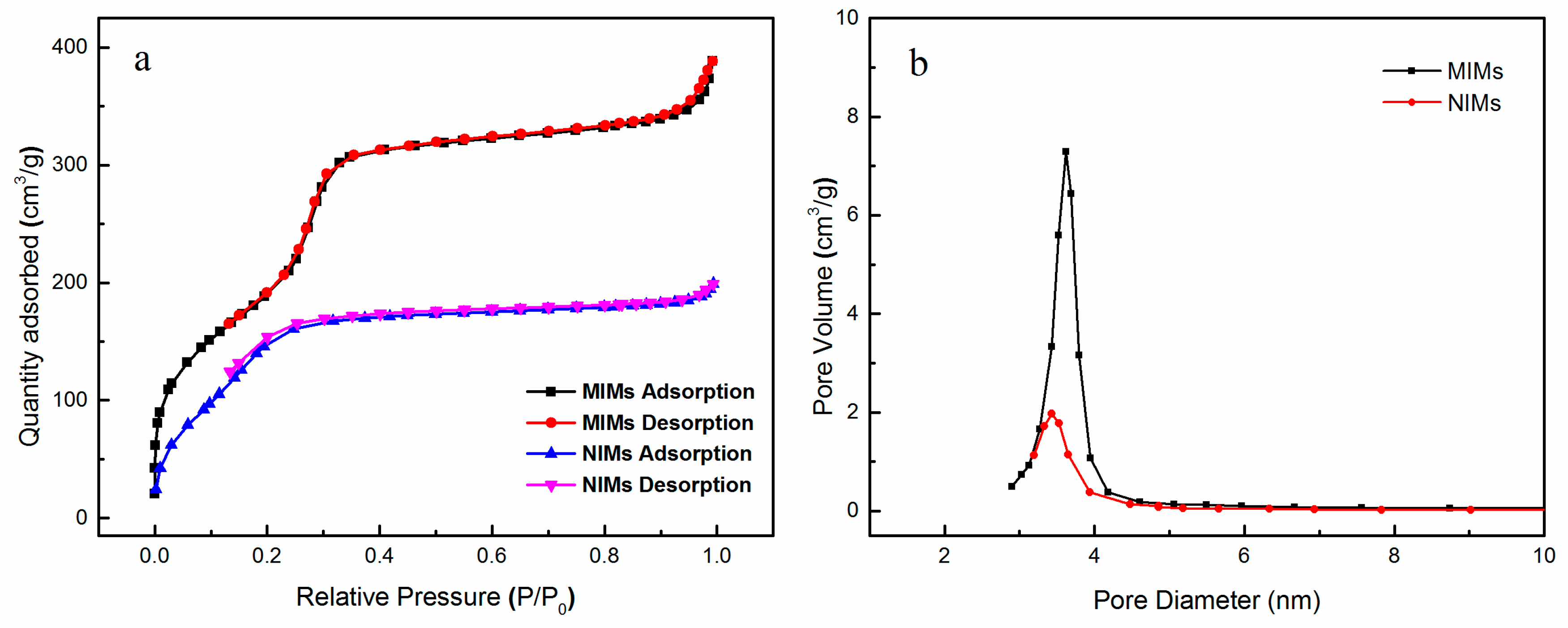
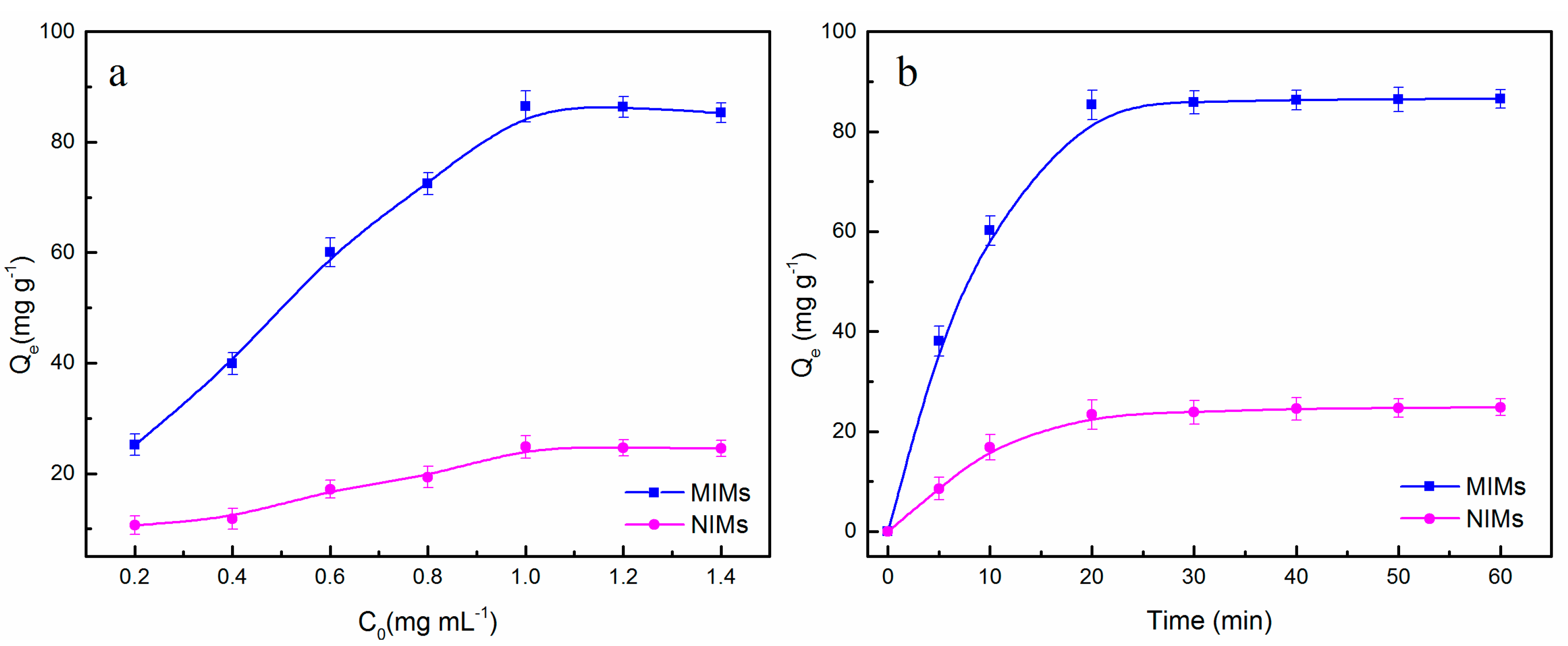
3.3. Adsorption Properties of MIMs and NIMs
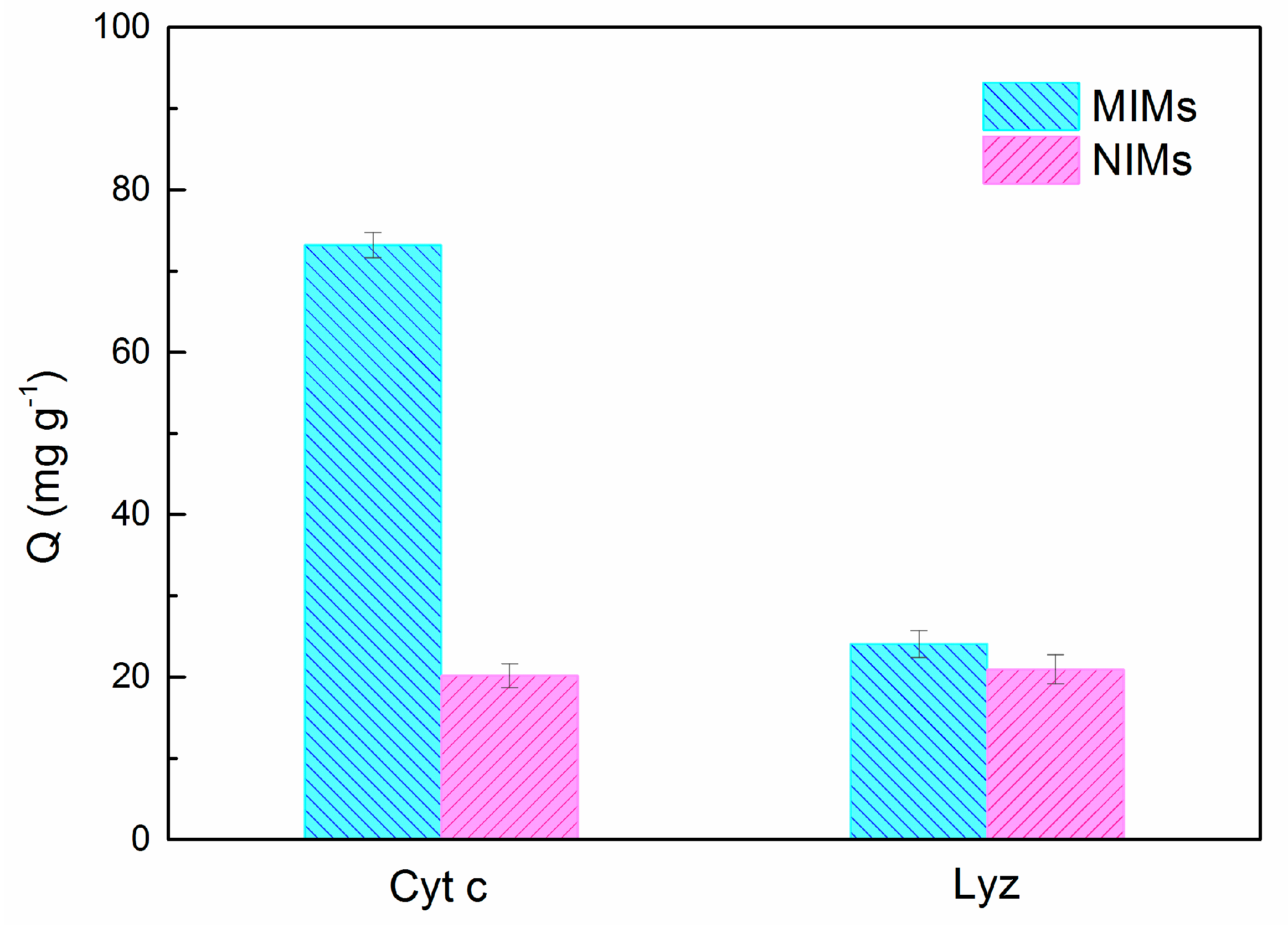
3.4. Selectivity Study
3.5. Competitive Batch Rebinding Tests
3.6. Comparison of Imprinting Methods for Cyt C
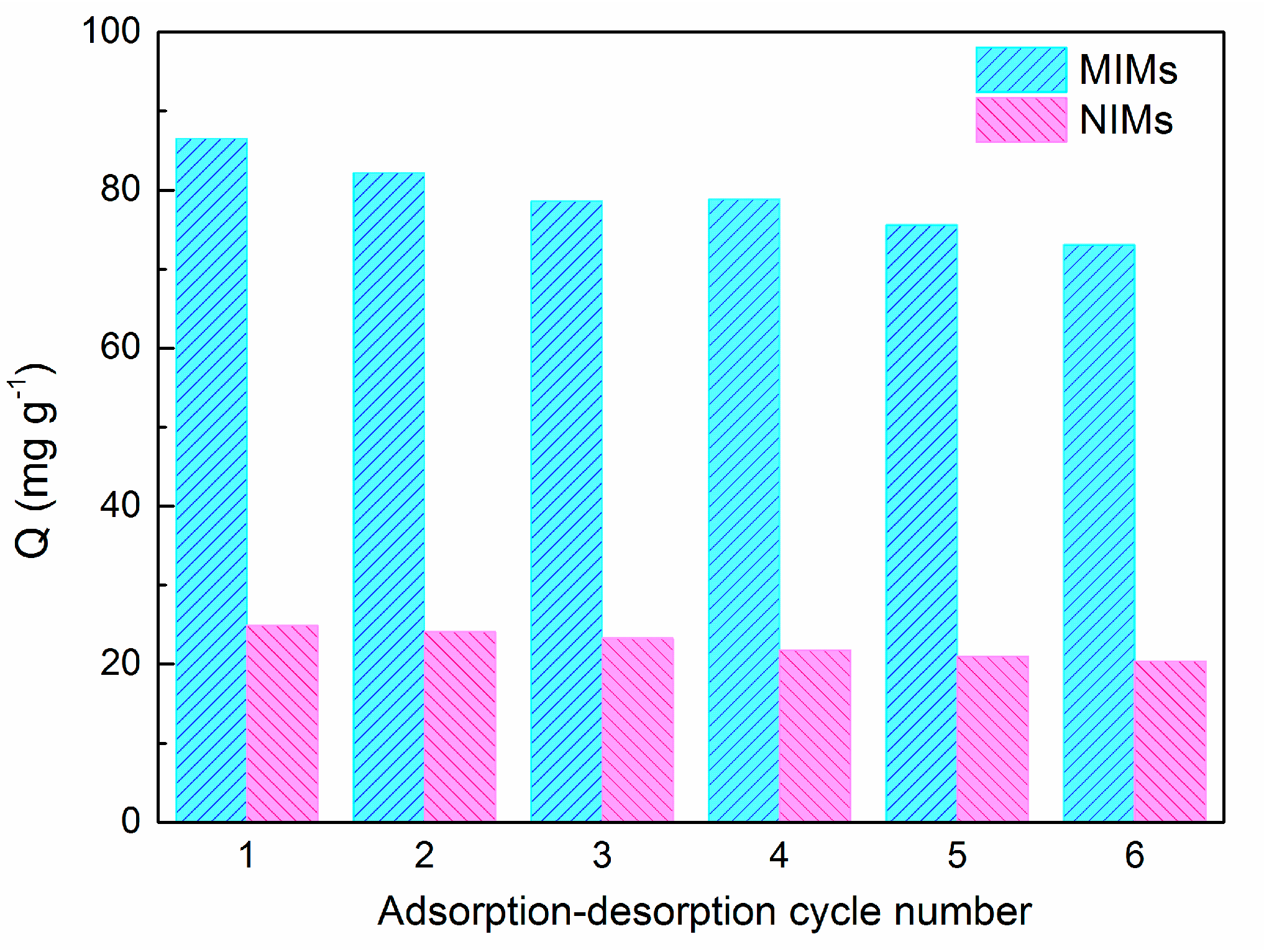
3.7. Reusability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, K.; Wu, P.; Gong, P.; Huo, H. Selective separation of proteins with pH-dependent magnetic nanoadsorbents. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 365604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCallum, R.M.; Martin, A.C.R.; Thornton, J.M. Antibody-antigen interactions: Contact analysis and binding site topography. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 262, 732–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, W.J.; Ali, F.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, J.O.; Sung, K.Y. Recent applications of molecular imprinted polymers for enantio-selective recognition. Talanta 2013, 106, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Esteban, A. Molecularly-imprinted polymers as a versatile, highly selective tool in sample preparation. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 45, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Hu, X.; Guan, P.; Wang, D.; Li, J.; Du, C.; Song, R.; Wang, C.; Song, W. The effectively specific recognition of bovine serum albumin imprinted silica nanoparticles by utilizing a macromolecularly functional monomer to stabilize and imprint template. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 884, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Cao, S.; Whitcombe, M.J.; Piletsky, S.A. Size matters: Challenges in imprinting macromolecules. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, H.; Huang, C.S.; Shea, K.J. Selective protein capture by epitope imprinting. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 2392–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, D.F.; Lin, C.Y.; Wu, T.Z.; Chen, L.K. Recognition of dengue virus protein using epitope-mediated molecularly imprinted film. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 5140–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.Q.; He, X.W.; Wang, Y.Z.; Li, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.K. Epitope imprinted polymer coating CdTe quantum dots for specific recognition and direct fluorescent quantification of the target protein bovine serum albumin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachkov, A.; Minoura, N. Recognition of oxytocin and oxytocin-related peptides in aqueous media using a molecularly imprinted polymer synthesized by the epitope approach. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 889, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wan, Y.; Zhao, D. Ordered mesoporous non-oxide materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3854–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, A.; Schüth, F. Ordered mesoporous materials in catalysis. Microporous Microporous Mater. 2005, 77, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhao, D. An overview of the synthesis of ordered mesoporous materials. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 943–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.M.; Yang, X.Q.; Wu, N.N.; Wang, L.J.; Wang, J.M.; Guo, J.; Yin, S.W. Protein-based pickering emulsion and oil gel prepared by complexes of zein colloidal particles and stearate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2672–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Yin, D.; Li, D.; Bie, Z.; Liu, Z. Dual-template docking oriented molecular imprinting: A facile strategy for highly efficient imprinting within mesoporous materials. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 10929–10932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Lei, S.; Xie, Y.; Wang, M.; Yang, J.; Ge, X. Fabrication of high-performance magnetic lysozyme-imprinted microsphere and its NIR-responsive controlled release property. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 28606–28615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Q.; Li, J.; Luo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Elzatahry, A.A.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Li, W.; Cheng, X.; Alghamdi, A.; et al. An interface coassembly in biliquid phase: Toward core–shell magnetic mesoporous silica microspheres with tunable pore size. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 13282–13289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, S.; Cooney, J.; Magner, E. Proteins in mesoporous silicates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 8582–8594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Antonietti, M. A novel tailored bimodal porous silica with well-defined inverse opal microstructure and super-microporous lamellar nanostructure. Chem. Commun. 2003, 20, 2564–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žilková, N.; Zukal, A.; Čejka, J. Synthesis of organized mesoporous alumina templated with ionic liquids. Microporous Microporous Mater. 2006, 95, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, D.; Brezesinski, T.; Smarsly, B. Hierarchical porous silica materials with a trimodal pore system using surfactant templates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 10534–10535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, Y.; Shi, F.; Liu, L.; Deng, Y. Room temperature ionic liquids as templates in the synthesis of mesoporous silica via a sol-gel method. Microporous Microporous Mater. 2009, 119, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofgreen, J.E.; Ozin, G.A. Controlling morphology and porosity to improve performance of molecularly imprinted sol-gel silica. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 911–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprynskyy, M.; Kowalkowski, T.; Tutu, H.; Cukrowska, E.M.; Buszewski, B. Ionic liquid modified diatomite as a new effective adsorbent for uranium ions removal from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 465, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Fang, L. One-step immobilization of antibodies for α-1-fetoprotein immunosensor based on dialdehyde cellulose/ionic liquid composite. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 471, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Hu, X.; Guan, P.; Du, C.; Li, J.; Qian, L.; Zhang, X.; Ding, S.; Li, B. Preparation of protein imprinted microspheres using amphiphilic ionic liquid as stabilizer and emulsifier via miniemulsion polymerization. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trewyn, B.G.; Whitman, C.M.; Lin, V.S.Y. Morphological control of room-temperature ionic liquid templated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for controlled release of antibacterial agents. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 2139–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.; Jung, D. Biocatalysis with enzymes immobilized on mesoporous hosts: The status quo and future trends. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 844–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Hou, M.; Ge, J. Metal-organic frameworks and inorganic nanoflowers: A type of emerging inorganic crystal nanocarrier for enzyme immobilization. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 5077–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Hu, X.; Guan, P.; Zhang, N.; Li, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, X.; Ding, X.; Du, C. Preparation of surface-imprinted microspheres using ionic liquids as novel cross-linker for recognizing an immunostimulating peptide. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 8027–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Hu, X.; Guan, P.; Gao, X.; Song, R.; Li, J.; Qian, L.; Zhang, N.; Guo, L. Preparation of surface-imprinted microspheres effectively controlled by orientated template immobilization using highly cross-linked raspberry-like microspheres for the selective recognition of an immunostimulating peptide. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 1510–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, Y.; Kubo, T.; Kaya, K.; Hosoya, K. Effective Recognition on the surface of a polymer prepared by molecular imprinting using ionic complex. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 2911–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, E.K.; Pranowo, R.; Sunarso, J.; Indraswati, N.; Ismadji, S. Performance of activated carbon and bentonite for adsorption of amoxicillin from wastewater: Mechanisms, isotherms and kinetics. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2419–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, L.; Sun, J.; Hou, C.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Lei, D.; Yang, M.; Zhang, S. Immobilization of BSA on ionic liquid functionalized magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles for use in surface imprinting strategy. Talanta 2017, 168, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Hu, X.; Guan, P.; Du, C.; Ding, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Wei, X.; Song, R. Synthesis of core–shell imprinting polymers with uniform thin imprinting layer via iniferter-induced radical polymerization for the selective recognition of thymopentin in aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 110019–110031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamahkar, E.; Kutsal, T.; Denizli, A. Surface imprinted bacterial cellulose nanofibers for cytochrome c purification. Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 2289–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, N.; Du, C.; Guan, P.; Gao, X.; Wang, C.; Du, Y.; Ding, S.; Hu, X. Preparation of magnetic epitope imprinted polymer microspheres using cyclodextrin-based ionic liquids as functional monomer for highly selective and effective enrichment of cytochrome c. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Deng, Q.; Fang, G.; Liu, C.; Huang, X.; Wang, S. Molecularly imprinted upconversion nanoparticles for highly selective and sensitive sensing of cytochrome c. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Ionic Liquids | BET Surface Areas | Pore Volume | BJH Average Pore |
|---|---|---|---|
| (ILs) | (m2/g) | (cm3/g) | Diameter (nm) |
| C8MIMCl | 1031 | 0.673 | 1.85 |
| C14MIMCl | 692 | 0.662 | 2.23 |
| C18MIMCl | 795 | 0.810 | 3.58 |
| Isotherm Model | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | Qmax (mg·g−1) | KL (mg·mL−1) | R2 | KF (mg·g−1) | n | R2 |
| MIMs | 156.05 | 1.0192 | 0.9632 | 77.29 | 1.6931 | 0.9340 |
| NIMs | 38.61 | 1.3998 | 0.9256 | 22.12 | 1.9729 | 0.9291 |
| Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | Qe,e a (mg·g−1) | Qe,c b (mg·g−1) | K1 (min−1) | R2 | Qe,c b (mg·g−1) | K1 (g mg−1·min−1) | R2 |
| MIMs | 86.47 | 87.86 | 0.1209 | 0.9784 | 101.10 | 0.0015 | 0.9948 |
| NIMs | 24.85 | 25.11 | 0.1048 | 0.9753 | 29.71 | 0.0040 | 0.9919 |
| Carrier | Imprinting Strategies | Recongation Interactions | Adsorption Equilibrium | Q (mg·g−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC nanofibers | Protein imprinting | metal ion coordination | 10 min | 36.4 | [36] |
| Fe3O4@SiO2 | Epitope imprinting | Multiple | 2 h | 67.6 | [37] |
| Organic polymers | Protein imprinting | Hydrogen bond | 4 h | 67.4 | [38] |
| Mesoporous silica | Epitope imprinting | Multiple | 20 min | 86.47 | This method |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Guan, P.; Hu, X.; Ding, S.; Tian, Y.; Xu, Y.; Qian, L. Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Mesoporous Materials for Highly Enhancing Adsorption Performance of Cytochrome C. Polymers 2018, 10, 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030298
Li Z, Guan P, Hu X, Ding S, Tian Y, Xu Y, Qian L. Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Mesoporous Materials for Highly Enhancing Adsorption Performance of Cytochrome C. Polymers. 2018; 10(3):298. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030298
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhiling, Ping Guan, Xiaoling Hu, Shichao Ding, Yuan Tian, Yarong Xu, and Liwei Qian. 2018. "Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Mesoporous Materials for Highly Enhancing Adsorption Performance of Cytochrome C" Polymers 10, no. 3: 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030298
APA StyleLi, Z., Guan, P., Hu, X., Ding, S., Tian, Y., Xu, Y., & Qian, L. (2018). Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Mesoporous Materials for Highly Enhancing Adsorption Performance of Cytochrome C. Polymers, 10(3), 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030298