The Effect of Diluent Mixture with Upper Critical Solution Temperature on Membrane Formation Process, Microstructure, and Performance of PVDF Hollow Fiber Membrane by TIPS Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Methods
2.2. Phase Diagram of PVDF/PC/DOTP System
2.3. Preparation of Hollow Fiber Membrane
2.4. Characterization of Membrane
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Phase Diagram of the Dope
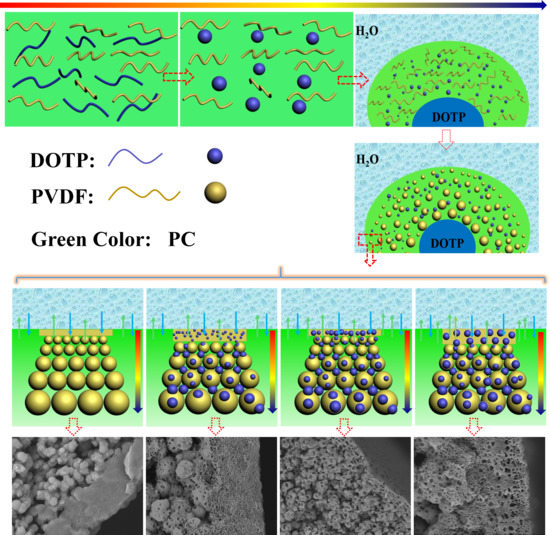
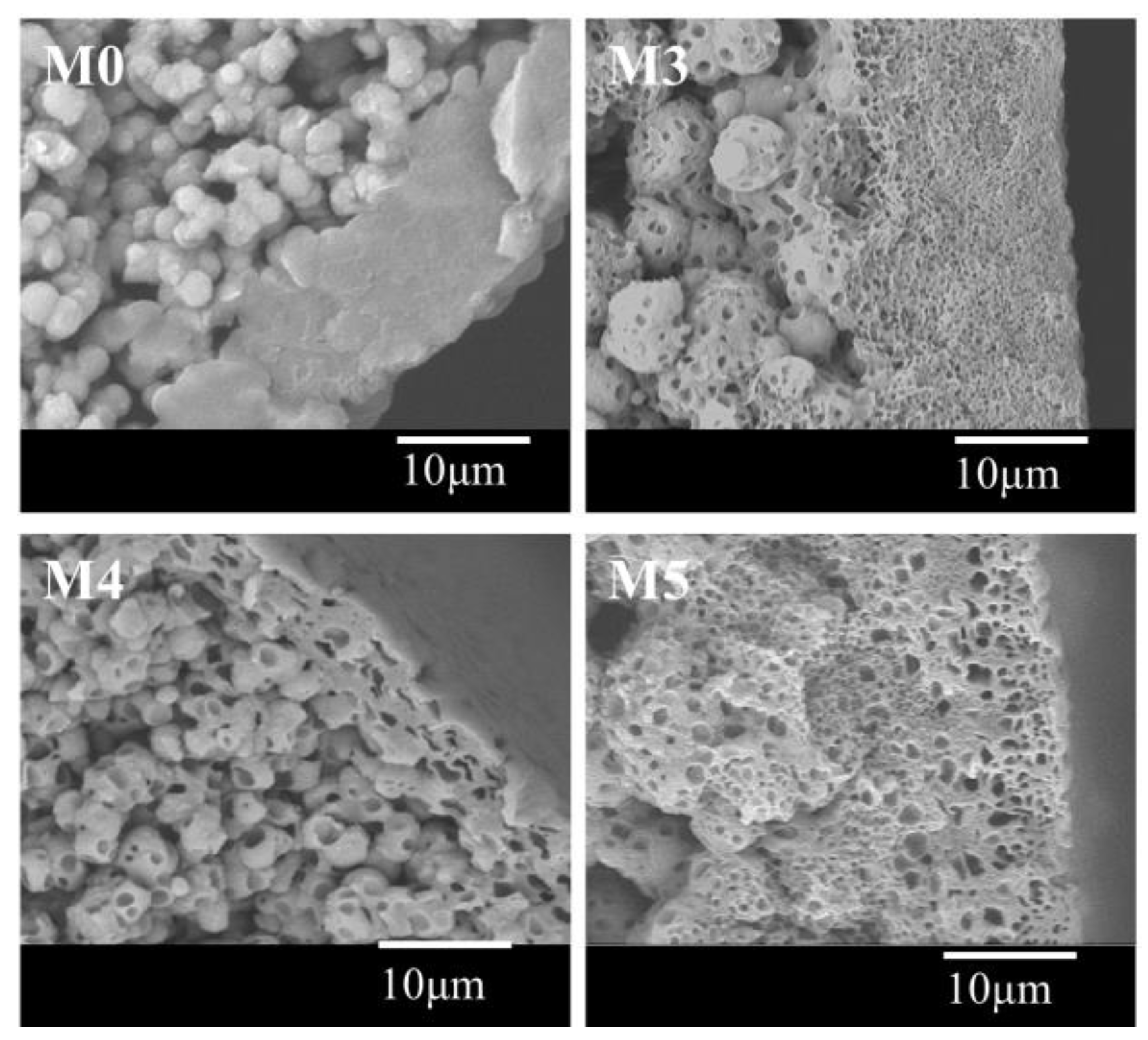
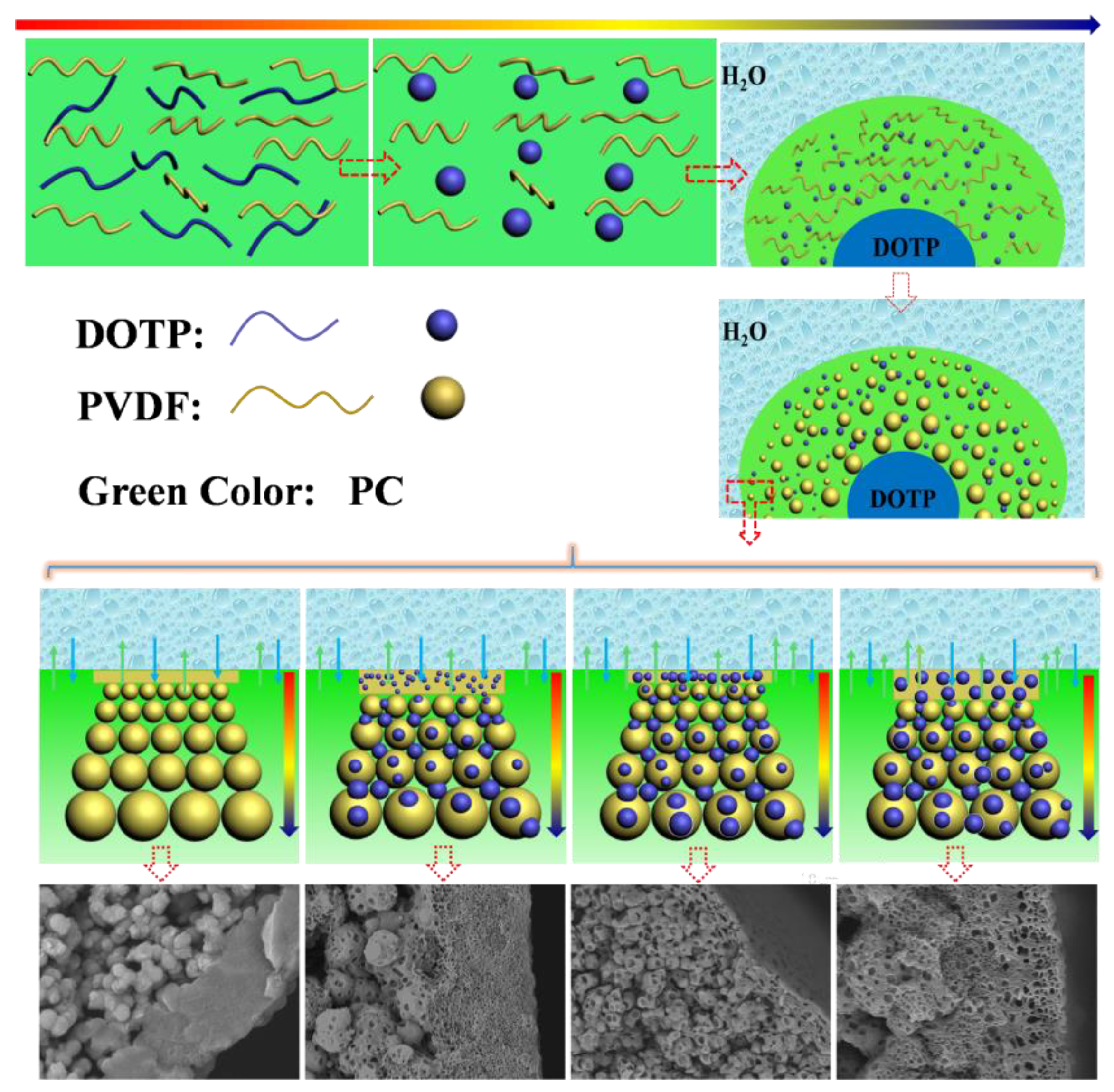
3.2. Morphology of the Membrane
3.3. Crystallization Behaviors of the Membrane
3.4. Permeability Properties of the Membrane
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ji, G.L.; Zhu, B.K.; Cui, Z.Y.; Zhang, C.F.; Xu, Y.Y. PVDF porous matrix with controlled microstructure prepared by TIPS process as polymer electrolyte for lithium ion battery. Polymer 2007, 48, 6415–6425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, D.R.; Kinzer, K.E.; Tseng, H.S. Microporous membrane formation via thermally induced phase separation. I. Solid–liquid phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 1990, 52, 239–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, T.; Hosoda, N.; Uyama, H. Fabrication of Porous Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) Monoliths via Thermally Induced Phase Separation. Polymers 2016, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.L.; Ma, W.Z. Crystallization behavior of PVDF in PVDF–DMP system via thermally induced phase separation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 3714–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.Y.; Du, C.H.; Xu, Y.Y.; Ji, G.L.; Zhu, B.K. Preparation of porous PVDF membrane via thermally induced phase separation using sulfolane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 108, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Zhao, Z.P.; Xi, Z.Y.; Yan, S.Y. Microporous polypropylene membrane prepared via TIPS using environment-friendly binary diluents and its VMD performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 548, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.J.; Kim, C.K. Fabrication of polyethylene microporous membranes using triethylolpropane tris(2-ethylhexanoate) as a novel diluent by a thermally induced phase separation process. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 449, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, H.J.; Li, J.J.; Cao, S. Preparation and morphological characterization of narrow pore size distributed polypropylene hydrophobic membranes for vacuum membrane distillation via thermally induced phase separation. Desalination 2010, 256, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cui, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.W.; Qin, S.H.; Yan, F.; Li, J.X. Fabrication of polysulfone membrane via thermally induced phase separation process. Mater. Lett. 2017, 195, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, H.; Iwatani, T.; Kitamura, Y.; Tearamoto, M.; Sugoh, N. Formation of porous poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) membrane via thermally induced phase separation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 79, 2449–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Karkhanechi, H.; Fang, L.F.; Cheng, L.; Ono, T. Novel preparation and fundamental characterization of polyamide 6 self-supporting hollow fiber membranes via thermally induced phase separation (TIPS). J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 546, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.T.; Li, Z.H.; Cheng, B.W.; Li, J.X. Preparation, characterization of PPS micro-porous membranes and their excellent performance in vacuum membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 556, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Matsuyama, H.; Teramoto, M.; Nagai, H. Preparation of hydrophilic poly(vinyl butyral) hollow fiber membrane via thermally induced phase separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 45, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, F.J.; Torkelson, J.M. Microporous poly(methy methacrylate) membranes: Effect of a low-viscosity solvent on the formation mechanism. Macromolecules 1990, 23, 4983–4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.K.; Tang, Y.H.; Ma, H.Y. Formation of a bicontinuous structure membrane of polyvinylidene fluoride in diphenyl carbonate diluent via thermally induced phase separation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 1523–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.L.; Hassankiadeh, N.T.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J.M. Poly(vinylidene fluoride) membrane preparation with an environmental diluent via thermally induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 444, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Sun, J. An improved process for polyvinylidene fluoride membrane preparation by using a water soluble diluent via thermally induced phase separation technique. Mater. Des. 2015, 86, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Cui, Z.Y.; Wu, Y.; Qin, S.H.; Wang, H.; Yan, F. Preparation of PVDF based blend microporous membranes for lithium ion batteries by thermally induced phase separation: I. Effect of PMMA on the membrane formation process and the properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 444, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Cui, Z.Y.; Li, J.B.; Qin, S.H.; Yan, F. Preparation and performance of polymer electrolyte based on poly(vinylidene fluoride)/polysulfone blend membrane via thermally induced phase separation process for lithium ion battery. J. Power Sources 2014, 266, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.G.; Cui, Z.Y.; Li, T.Y.; Qin, S.H.; He, B.Q. Fabrication of PVDF-based blend membrane with a thin hydrophilic deposition layer and a network structure supporting layer via the thermally induced phase separation followed by non-solvent induced phase separation process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 419, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabzadeh, S.; Maruyama, T.; Ohmukai, Y.; Sotani, T.; Matsuyama, H. Preparation of PVDF/PMMA blend hollow fiber membrane via thermally induced phase separation (TIPS) method. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 66, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, D.R.; Kim, S.S.; Kinzer, K.E. Microporous membrane formation via thermally induced phase separation. II. Liquid–liquid phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 1991, 64, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, S.K.; Yeom, M.O.; Cho, I.S. Thermally-induced phase separation mechanism study for membrane formation, Membrane Formation and Modification. ACS Symp. 1999, 744, 42–64. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Liu, S.H.; Xu, Z.L.; Wei, Y.M.; Yang, H. Formation of microporous polymeric membranes via thermally induced phase separation: A review. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2015, 12, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, H.; Takida, Y.; Maki, T.; Teramoto, M. Preparation of porous membrane by combined use of thermally induced phase separation and immersion precipitation. Polymer 2002, 43, 5243–5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Wang, Y.G.; Lu, X.L.; Xiao, C.F. Morphology changes of polyvinylidene ouoride membrane under different phase separation mechanisms. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 320, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, B.J.; Yang, J.M. Preparation of poly(vinylidene fluoride) hollow ber membranes for microfiltration using modified TIPS process. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 291, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.X.; Meng, G.Z. c-TIPS method for membrane production. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2010, 30, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.P.; Xiaolong, L.; Wu, C.; Jia, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.Y. Preparation of polyvinylidene fluoride hollow fiber porous membrane via a low thermally induced phase separation. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2012, 32, 12–22. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Wei, Y.M.; Xu, Z.L.; Guo, R.Q.; Zhao, L.B. Preparation and characterization of polyethersulfone microporous membrane via thermally induced phase separation with low critical solution tempera; ture system. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 437, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; Xiao, T.H.; Bao, C.H.; Fu, Y.H.; Yang, X. Fabrication of Novel Janus Membrane by Nonsolvent Thermally Induced Phase Separation (NTIPS) for Enhanced Performance in Membrane Distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.F.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, Y.M. Thermally Induced Phase Separation and Electrospinning Methods for Emerging Membrane Applications: A Review. AIChE J. 2016, 62, 461–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.H.; Lin, Y.K.; Zhou, B.; Wang, X.L. PVDF membranes prepared via thermally induced (liquid-liquid) phase separation and theirapplication in municipal sewage and industry wastewater for water recycling. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.L.; Zhu, L.P.; Zhu, B.K.; Zhang, C.F.; Xu, Y.Y. Structure formation and characterization of PVDF hollow fiber membrane prepared via TIPS with diluent mixture. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 319, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Q. Studies on Preparation of iPP Hollow Fiber Microporous Membrane via Thermally Induced Phase Separation. Master Thesis, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Park, B.; Kim, J.; Park, S.B. Effect of PVP, lithium chloride, and glycerol additives on PVDF dual-layer hollow fiber membranes fabricated using simultaneous spinning of TIPS and NIPS. Macromol Res. 2015, 23, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassankiadeh, N.T.; Cui, Z.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, D.W.; Lee, S.Y. Microporous poly(vinylidene fluoride) hollow fiber membranes fabricated with PolarClean as watersoluble green diluent and additives. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 479, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Tao, H.; Ge, L. Formation of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) membranes via thermally induced phase separation. Desalination 2006, 192, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, G.; Lu, X.; Xiao, C. Effects of mixed diluent compositions on poly(vinylidene fluoride) membrane morphology in a thermally induced phase-separation process. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 107, 3630–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.H.; Wang, Z.; Shen, H.J.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Liu, L.P.; Yang, L.B.; Cheng, L.N. Morphology and performance of PVDF TIPS microfiltration hollow fiber membranes prepared from PVDF/DBP/DOP systems for industrial application. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 91, 1697–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, X.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Z.; Wu, S. The unidirectional regulatory role of coagulation bath temperature on cross-section radius of the PVDF hollow-fiber membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 550, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.H.; Zhu, B.K.; Xu, Y.Y. Structure and ionic conductivity of porous polymer electrolytes based on PVDF-HFP copolymer membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorio, R.; Cestari, M. Effect of crysallization Temperature on the cyystalline Phase Content and Morphology of poly(vinylidene fluoride). J. Polym. Sci. Part B 1994, 32, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.D.; Kelvin, A.; Poletto, P.; Meireles, C.S.; Grisa, M.C. Effect of cellulose fibers on morphology and pure water permeation of PSf membranes. Desalin. Water Treat. 2011, 27, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.T.; Kim, J.F.; Wang, H.H.; Nicolo, E.D.; Drioli, E.; Lee, Y.M. Understanding the non-solvent induced phase separation (NIPS) effect during the fabrication of microporous PVDF membranes via thermally induced phase separation (TIPS). J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 514, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorio, R. Determination of the α, β, and γ crystalline phases of poly(vinylidene fluoride) films prepared at different conditions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 100, 3272–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorio, R.; Ueno, E.M. Effect of crystalline phase, orientation and temperature on the dielectric properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF). J. Mater. Sci. 1999, 34, 4489–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Code | PC/DOTP | Spinning temperature | Bore liquid temperature |
|---|---|---|---|
| (wt./wt.) | (°C) | (°C) | |
| M0 | 10/0 | 100 | 70 |
| M1 | 10/1 | 120 | 90 |
| M2 | 10/2 | 130 | 100 |
| M3 | 10/3 | 150 | 120 |
| M4 | 10/4 | 170 | 130 |
| M5 | 10/5 | 180 | 140 |
| Samples | M0 | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aα | 1963.2 | 1398.9 | 1484.6 | 1614.0 | 1753.0 | 1361.4 |
| Aβ | 2537.5 | 2334.2 | 2138.6 | 2064.8 | 2085.2 | 2064.5 |
| F(β) (%) | 51.0 | 57.0 | 53.4 | 50.3 | 48.0 | 54.6 |
| Samples | M0 | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tmp (°C) | 170.0 | 170.5 | 170.6 | 170.8 | 170.6 | 170.2 |
| ΔHf (J g−1) | 71.45 | 72.17 | 72.98 | 75.52 | 69.05 | 63.43 |
| Xc (%) | 68.24 | 68.93 | 69.70 | 72.13 | 65.95 | 60.58 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, Z.; Xu, S.; Ding, J.; Zhang, J.; He, B.; Wang, H.; Li, J. The Effect of Diluent Mixture with Upper Critical Solution Temperature on Membrane Formation Process, Microstructure, and Performance of PVDF Hollow Fiber Membrane by TIPS Process. Polymers 2018, 10, 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070719
Cui Z, Xu S, Ding J, Zhang J, He B, Wang H, Li J. The Effect of Diluent Mixture with Upper Critical Solution Temperature on Membrane Formation Process, Microstructure, and Performance of PVDF Hollow Fiber Membrane by TIPS Process. Polymers. 2018; 10(7):719. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070719
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Zhenyu, Shanshan Xu, Jinyue Ding, Jing Zhang, Benqiao He, Hao Wang, and Jianxin Li. 2018. "The Effect of Diluent Mixture with Upper Critical Solution Temperature on Membrane Formation Process, Microstructure, and Performance of PVDF Hollow Fiber Membrane by TIPS Process" Polymers 10, no. 7: 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070719
APA StyleCui, Z., Xu, S., Ding, J., Zhang, J., He, B., Wang, H., & Li, J. (2018). The Effect of Diluent Mixture with Upper Critical Solution Temperature on Membrane Formation Process, Microstructure, and Performance of PVDF Hollow Fiber Membrane by TIPS Process. Polymers, 10(7), 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070719