Process, Design and Materials for Unidirectionally Tilted Polymeric Micro/Nanohairs and Their Adhesion Characteristics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Effect of the Tilted Hairy Nanostructure of Gecko Feet
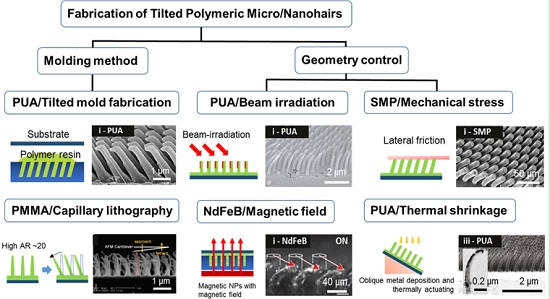
3. Various Fabrication Methods for the Tilted Nanohairs
3.1. Molding Method
3.2. Control of the Geometry of Polymeric Nanohairs
3.2.1. Beam Irradiation
3.2.2. Magnetic Field
3.2.3. Mechanical Stress
3.2.4. Thermal Shrinkage
4. Limitations of Tilted Nanohairs and New Strategies to Overcome These Limitations
4.1. Geometric Effects of the Nanohairs
4.1.1. Tip Shape Effect
4.1.2. Hierarchical Structure for High AR Nanostructures
4.2. Enhanced Durability of Nanohairs
5. Applications of Tilted Dry Adhesive
5.1. Transfer Printing Tool
5.2. Climbing Robots
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PS | polystyrene |
| HDPE | high-density polyethylene |
| SU-8 | ultraviolet curable epoxy |
| PUA | polyurethane acrylate |
| PC | polycarbonate |
| PDMS | polydimethyl siloxane |
| PP | polypropylene |
| PSA | pressure sensitive adhesive |
| PI | polyimide |
| CNT | carbon nanotube |
| PE | polyethylene |
| Pt | platinum |
| Al | aluminum |
| DPS | Directional Polymer Stalks |
References
- Mahdavi, A.; Ferreira, L.; Sundback, C.; Langer, R.; Karp, J.M. A biodegradable and biocompatible gecko-inspired tissue adhesive. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2307–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, M.K.; Jeong, H.-E.; Suh, K.Y. Rational design and enhanced biocompatibility of a dry adhesive medical skin patch. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3949–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.; Kim, J.; Song, K.; Autumn, K.; Lee, J. Geckoprinting: Assembly of microelectronic devices on unconventional surfaces by transfer printing with isolated gecko setal arrays. J. R. Soc. Interface 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.Y.; Carlson, A.; Cheng, H.; Yu, Q.; Ahmed, N.; Wu, J.; Kim, S.; Sitti, M.; Ferreira, P.M.; Huang, Y.; et al. Elastomer surfaces with directionally dependent adhesion strength and their use in transfer printing with continuous roll-to-roll applications. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2117–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, B.; Cho, S.; Seo, S.; Lee, J. Elastomeric angled microflaps with reversible adhesion for transfer-printing semiconductor membranes onto dry surfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 19247–19253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Spenko, M.; Trujillo, S.; Heyneman, B.; Santos, D.; Cutkoskly, M.R. Smooth vertical surface climbing with directional adhesion. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2008, 24, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Sitti, M. Biologically inspired polymer microfibers with spatulate tips as repeatable fibrillar adhesives. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzt, E.; Gorb, S.; Spolenak, R. From micro to nano contacts in biological attachment devices. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10603–10606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autumn, K.; Liang, Y.A.; Hsleh, S.T.; Zesch, W.; Chan, W.P.; Kenny, T.W.; Fearing, R.; Full, R.J. Adhesive force of a single gecko foot-hair. Nature 2000, 405, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Pesika, N.; Zeng, H.; Rosenberg, K.; Zhao, B.; McGuiggan, P.; Autumn, K.; Israelachvili, J. Adhesion and friction in gecko toe attachment and detachment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 19320–19325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autumn, K.; Niewiarowski, P.H.; Puthoff, J.B. Gecko adhesion as a model system for integrative biology, interdisciplinary science, and bioinspired engineering. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2014, 45, 445–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Wang, X.; Yao, H.; Gorb, S.; Arzt, E. Mechanics of hierarchical adhesion structures of geckos. Mech. Mater. 2005, 37, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C. Purity of scared lotus, or escape from contaminaton in biological surfaces. Planta 1997, 202, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhai, J.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. Super-hydrophobic surfaces; from natural to artificial. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1857–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autumn, K.; Sitti, M.; Liang, Y.A.; Peattie, A.M.; Hansen, W.R.; Sponberg, S.; Kenny, T.W.; Fearing, R.; Israelachvili, J.; Full, R.J. Evidence for van der Waals adhesion in gecko setae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12252–12256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.-E.; Lee, J.-K.; Kwak, M.K.; Moon, S.H.; Suh, K.Y. Effect of leaning angle of gecko-inspired slanted polymer nanohairs on dry adhesion. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autumn, K.; Majidi, C.; Groff, R.E.; Dittmore, A.; Fearing, R. Effective elastic modulus of isolated gecko setal arrays. J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 3558–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Pesika, N.; Zeng, H.; Wei, Z.; Chen, Y.; Atumn, K.; Turner, K.; Israelachvili, J. Role of tilted adhesion fibirils (setae) in the adhesion and locomotion of gecko-like systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 3615–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, A.M.; Puthoff, J.; Cohen, M.J.; Autumn, K.; Fearing, R. Dry self-cleaning properties of hard and soft fibrillar Structures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 6081–6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Fearing, R. Contact self-cleaning of synthetic gecko adhesive from polymer microfibers. Langmuir 2008, 24, 10587–10591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Fearing, R. Wet self-cleaning of superhydrophobic microfiber adhesives formed from high density polyethylene. Langmuir 2012, 28, 15372–15377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Cheung, E.; Sitti, M. Wet self-cleaning of biologically inspired elastomer mushroom shaped microfibrillar adhesives. Langmuir 2009, 25, 7196–7199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.-E.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, P.; Suh, K.Y. Stretched polymer nanohairs by nanodrawing. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 1508–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Majidi, C.; Schubert, B.; Fearing, R. Sliding-induced adhesion of stiff polymer microfibre arrays: І. Microscale behaviour. J. R. Soc. Interface 2008, 5, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, A.G.; Fearing, R. Shear adhesion strength of thermoplastic gecko-inspired synthetic adhesive exceeds material limits. Langmuir 2011, 27, 11278–11281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.-I.; Jeong, H.-E.; Suh, K.Y.; Lee, H.H. Stooped nanohairs: Geometry-controllable, unidirectional, reversible, and robust gecko-like dry adhesive. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2276–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurdumakan, B.; Raravikar, N.R.; Ajayan, P.M.; Dhinojwala, A. Synthetic gecko foot-hairs from multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Chem. Commun. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, L.; Sethi, S.; Ci, L.; Ajayan, P.M.; Dhinojwala, A. Carbon nanotube-based synthetic gecko tapes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10792–10795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Shaw, D.T.; Guo, L. Field emission of different oriented carbon nanotubes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Ju, Y.; Xu, B.; Wang, P.; Kojima, N.; Ichioka, K.; Hosoi, A. Mimicking a gecko’s foot with strong adhesive strength based on a spinnable vertically aligned carbon nanotube array. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 9056–9060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geim, A.K.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Novoselov, K.S.; Zhukov, A.A.; Shapoval, S.Y. Microfabricated adhesive mimicking gecko foot-hair. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 461–463. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, H.; Hwang, I.S.; Lee, J.; Lee, D.E.; Lim, H.; Tahk, D.H.; Sung, M.H.; Bae, W.-G.; Kwak, M.K.; Jeong, H.-E. Continuous and scaleable fabrication of bioinspired dry adhesives via a roll-to-roll process with modulated ultraviolet-curable resin. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 14590–14599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamperman, M.; Kroner, E.; del Campo, A.; Mcmeeking, R.M.; Arzt, E. Functional adhesive surfaces with “gecko” effect: The concepot of contact splitting. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattantyus-Abraham, A.; Krahn, J.; Menon, C. Recent advances in nanostructured biomimetic dry adhesives. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sameoto, D.; Menon, C. Recent advances in the fabrication and adhesion testing of biomimetic dry adhesives. Smart Mater. Struct. 2010, 19, 103001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, M.K.; Pang, C.; Jeong, H.-E.; Kim, H.N.; Yoon, H.; Jung, H.S.; Suh, K.Y. Towards the next level of bioinspired dry adhesives: New designs and applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 3606–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federle, W.; Barnes, W.J.P.; Baumgartner, W.; Drechsler, P.; Smith, J.M. Wet but not slippery: Boundary friction in tree frog adhesive toe pads. J. R. Soc. Interface 2006, 3, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Tian, H.; Hu, H.; Tian, Y.; Shao, J.; Ding, Y. Rectangle-capped and tilted micropillar array for enhanced anisotropic anti-shearing in biomimetic adhesion. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sameoto, D.; Menon, C. Deep UV patterning of acrylic masters for molding biomimetic dry adhesives. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2010, 20, 115037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Chary, S.; Das, S.; Tamelier, J.; Pesika, N.S.; Turner, K.L.; Israelachvili, J. Gecko-inspired dry adhesive for robotic applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 3010–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.-E.; Lee, J.-K.; Kim, H.N.; Moon, S.H.; Suh, K.Y. A nontransferring dry adhesive with hierarchical polymer nanohairs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5639–5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksak, B.; Murphy, M.P.; Sitti, M. Adhesion of biologically inspired vertical and angled polymer microfiber arrays. Langmuir 2007, 23, 3322–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parness, A.; Soto, D.; Esparza, N.; Gravish, N.; Wilkinson, M.; Autumn, K.; Cutkosky, M. A microfabricated wedge-shaped adhesive array displaying gecko-like dynamic adhesion, directionality and long lifetime. J. R. Soc. Interface 2009, 6, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Bush, B.; Maboudian, R.; Fearing, R. Gecko-inspired combined lamellar and nanofibrillar array for adhesion on nonplanar surface. Langmuir 2009, 25, 12449–12453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, K.; Tian, Y.; Erickson, J.S.; Puthoff, J.; Autumn, K.; Pesika, N.S. Design and fabrication of gecko-inspired adhesives. Langmuir 2012, 28, 5737–5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, K.; Cremaldi, J.; Erickson, J.S.; Tian, Y.; Israelachvili, J.; Pesika, N.S. Biomimetic bidirectional switchable adhesive inspired by the gecko. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, B.E.; Gillies, A.G.; Fearing, R. Angled microfiber arrays as low-modulus low poisson’s ratio compliant substrates. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2014, 24, 065016–065023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, D.; Tak, H.; Choi, S.-J.; Kim, T.-I. Permeability- and surface-energy-tunable polyurethane acrylate molds for capillary force lithography. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 23824–23830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.U.; Lee, S.; Kim, T.-I. Recent advances in unconventional lithography for challenging 3D hierarchical nanostructures and their applications. J. Nanomater. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-I.; Pang, C.; Suh, K.Y. Shape-tunable polymer nanofibrillar structures by oblique electron beam irradiation. Langmuir 2009, 25, 8879–8882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmawan, Y.; Kim, T.-I.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, K.-R.; Moon, M.-W.; Suh, K.Y. Surface energy tunable nanohairy dry adhesive by broad ion beam irradiation. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, M.-W.; Cha, T.-G.; Lee, K.-R.; Vaziri, A.; Kim, H.-Y. Tilted Janus polymer pillars. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 3924–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drotlef, D.-M.; Blümler, P.; del Campo, A. Magnetically actuated patterns for bioinspired reversible adhesion (dry and wet). Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, A.G.; Kwak, J.; Fearing, R. Controllable particle adhesion with a magnetically actuated synthetic gecko adhesive. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 3256–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.; Arzt, E.; del Campo, A. Bioinspired surfaces with switchable adhesion. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3833–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Fearing, R.; Komvopoulos, K. Directional adhesion of gecko-inspired angled microfiber arrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Woo, H.; Choi, M.K.; Suh, K.Y.; Char, K. Face selection in one-step bending of Janus nanopillars. Langmuir 2010, 26, 9198–9201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.; Jeong, H.-E.; Kim, T.-I.; Kang, T.J.; Tahk, D.; Char, K.; Suh, K.Y. Adhesion hysteresis of Janus nanopillars fabricated by nanomolding and oblique metal deposition. Nano Today 2009, 4, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Campo, A.; Greiner, C.; Arzt, E. Contact shape controls adhesion of bioinspired fibrillar surfaces. Langmuir 2007, 23, 10235–10243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greiner, C.; Spolenak, R.; Arzt, E. Adhesion design maps for fibrillary adhesives: The effect of shape. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, S.W.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.-S.; Ko, K.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J. Anistropic adhesion of micropillars with spatula pads. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menguc, Y.; Yang, S.Y.; Kim, S.; Rogers, J.A.; Sitti, M. Gecko-inspired controllable adhesive structures applied to micromanipulation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Sitti, M.; Xie, T.; Xiao, X. Reversible dry micro-fibrillar adhesives with thermally controllable adhesion. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 3689–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varenberg, M.; Pugno, N.M.; Gorb, S. Spatulate structures in biological fibrillar adhesion. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 3269–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Campo, A.; Greiner, C.; Alvarez, I.; Arzt, E. Patterned surfaces with pillars with controlled 3D tip geometry mimicking bioattachment devices. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 1973–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Kovalev, A.; Thole, F.; Rengarajan, G.T.; Steinhar, M.; Gorb, S. Tailoring normal adhesion of arrays of thermoplastic, spring-like polymer nanorods by shaping nanorod tips. Laungmuir 2012, 28, 10781–10788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.-E.; Suh, K.Y. Precise tip shape transformation of nanopillars for enhanced dry adhesion strength. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 5375–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.P.; Aksa, B.; Sitti, M. Gecko-inspired directional and controllable adhesion. Small 2009, 5, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, M.; Kim, S.; Sitti, M. Enhanced adhesion by gecko-Inspired hierarchical fibrillar adhesives. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, G.; Gorb, S.; Hosoda, N.; Spolenak, R.; Arzt, E. Influence of surface roughness on gecko adhesion. Acta Biomater. 2007, 3, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippov, A.E.; Gorb, S. Spatial model of the gecko foot hair; functional significance of highly specialized non-uniform geometry. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, H.S.; Kwon, K.Y.; Kim, J.U.; Kim, K.S.; Yi, H.; Yoo, P.J.; Pang, C.; Jeong, H.-E.; Kim, T.-I. Highly durable and unidirectionally stooped polymeric nanohairs for gecko-like dry adhesive. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 415301–415306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chary, S.; Tamelier, J.; Turner, K. A microfabricated gecko-inspired controllable and reusable dry adhesive. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 025013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Ahn, J.-H.; Ahn, J.-H.; Choi, W.M.; Rogers, J.A. Stretchable and foldable silicon integrated circuits. Science 2008, 320, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Lu, N.; Ma, R.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, R.-H.; Rogers, J.A. Epidermal electronics. Science 2011, 333, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Lu, N.; Ghaffari, R.; Kim, Y.-S.; Rogers, J.A. Materials for multifunctional ballon catheters with capabilities in cardiac electrophysiological mapping and ablation therapy. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Viventi, J. Dissolvable films of silk fibroin for ultrathin conformal bio-integrated electronics. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arns, R.G. The other transisotr: early history of the metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transisotr. Eng. Sci. Educ. J. 1998, 7, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meitl, M.A.; Zhu, Z.T.; Kumar, V.; Lee, K.J.; Feng, X.; Rogers, J.A. Transfer printing by kinetic control of adhesion to an elastomeric stamp. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-I.; Kim, M.J.; Jung, Y.H.; Jang, H.; Dagdeviren, C.; Rogers, J.A. Thin film receiver materials for deterministic assembly of transfer printing. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 3502–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-I.; Lee, S.H.; Li, Y.; Shi, Y.; Shin, G.; Lee, S.D.; Huang, Y.; Rogers, J.A.; Yu, J.S. Temperature- and size-dependent characteristics in ultrathin inorganic light-emitting diodes assembled by transfer printing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-I.; Jung, Y.H.; Chung, H.-J.; Yu, K.J.; Rogers, J.A. Deterministic assembly of releasable single crystal silicon-metal oxide field-effect devices formed from bulk wafers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-I.; McCall, J.G.; Jung, Y.H.; Huang, X.; Siuda, E.R.; Song, J.; Song, Y.M.; Pao, H.A.; Kim, R.-H.; Song, I.-S.; et al. Injectable cellular scale optoelectronics with applications for wireless optogenetics. Science 2013, 340, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkes, E.W.; Eason, E.V.; Asbeck, A.T.; Cutkosky, M.R. The Gecko’s toe: Scaling directional adhesives for climbing applications. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2013, 18, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, E.W.; Eason, E.V.; Christensen, D.L.; Cutkosky, M.R. Human climbing with efficiently scaled gecko-inspired dry adhesives. J. R. Soc. Interface 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Sun, D.; Tso, S.-K. Development of a tracked climbing robot. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2002, 35, 427–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Ma, P. A wall-climbing robot for labelling scale of oil tank’s volume. Robotica 2002, 20, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daltorio, K.A.; Horchler, A.D.; Gorb, S.; Ritzmann, R.E.; Quinn, R.D. A small wall-walking robot with compliant, ahdesive feet. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2002, 35, 427–444. [Google Scholar]







© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Im, H.S.; Kim, J.U.; Han, S.; Kim, T.-i. Process, Design and Materials for Unidirectionally Tilted Polymeric Micro/Nanohairs and Their Adhesion Characteristics. Polymers 2016, 8, 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8090326
Im HS, Kim JU, Han S, Kim T-i. Process, Design and Materials for Unidirectionally Tilted Polymeric Micro/Nanohairs and Their Adhesion Characteristics. Polymers. 2016; 8(9):326. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8090326
Chicago/Turabian StyleIm, Hyeon Seong, Jong Uk Kim, Sungwon Han, and Tae-il Kim. 2016. "Process, Design and Materials for Unidirectionally Tilted Polymeric Micro/Nanohairs and Their Adhesion Characteristics" Polymers 8, no. 9: 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8090326
APA StyleIm, H. S., Kim, J. U., Han, S., & Kim, T.-i. (2016). Process, Design and Materials for Unidirectionally Tilted Polymeric Micro/Nanohairs and Their Adhesion Characteristics. Polymers, 8(9), 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8090326