Characterization and Performance of Soy-Based Adhesives Cured with Epoxy Resin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
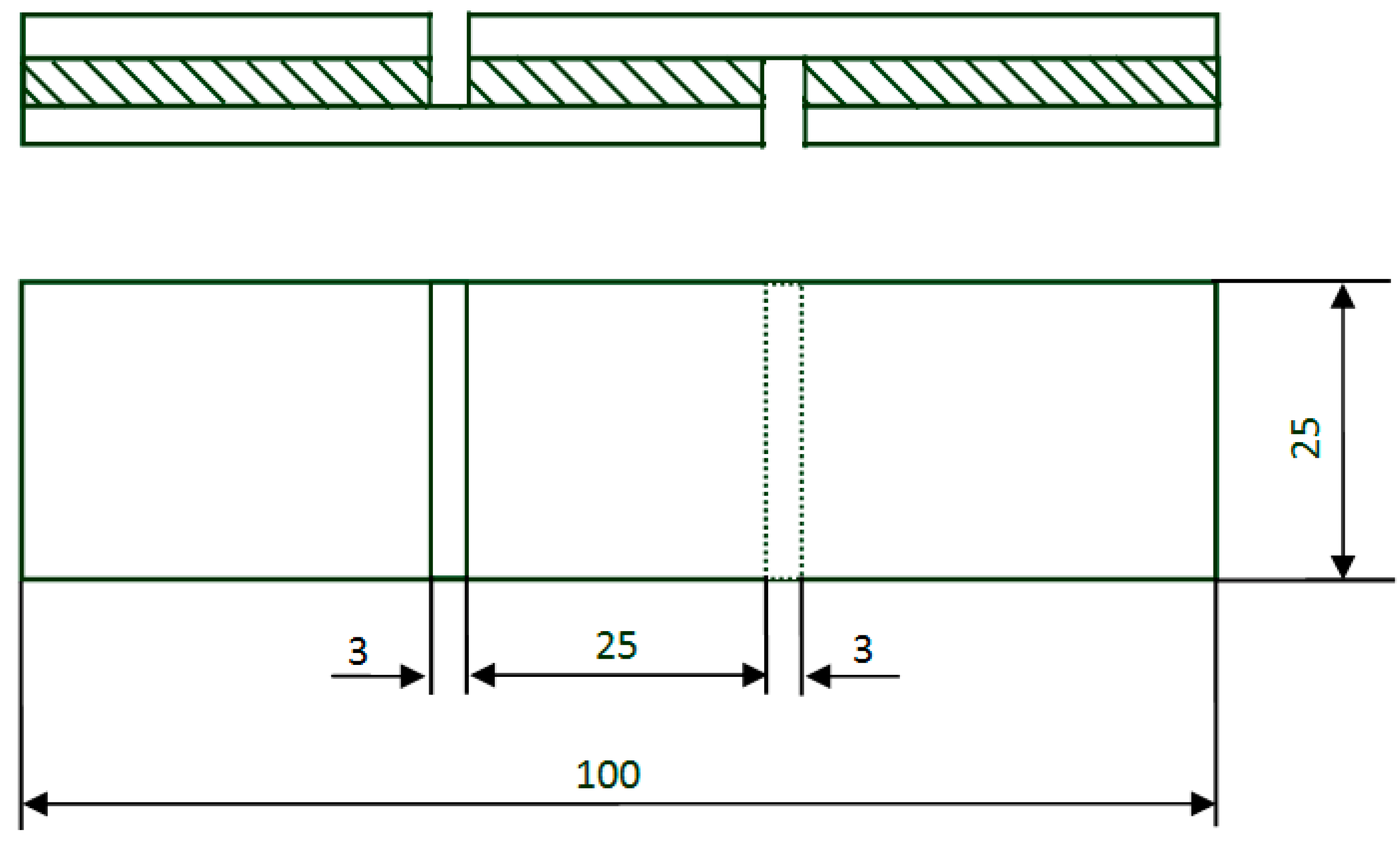
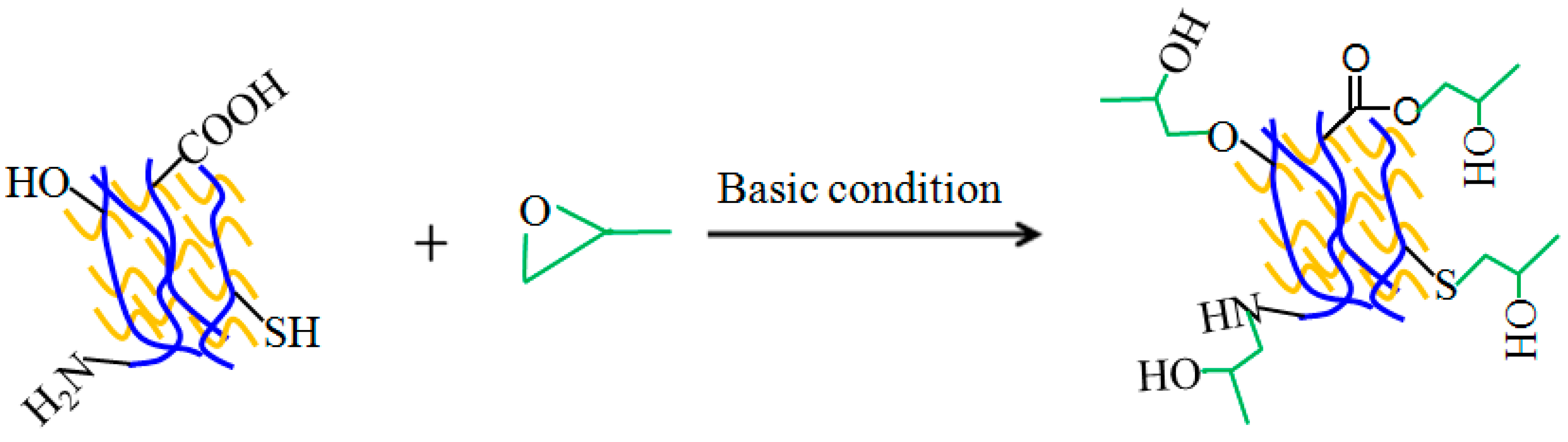
2.2. Preparation of Soy-Based Adhesive
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
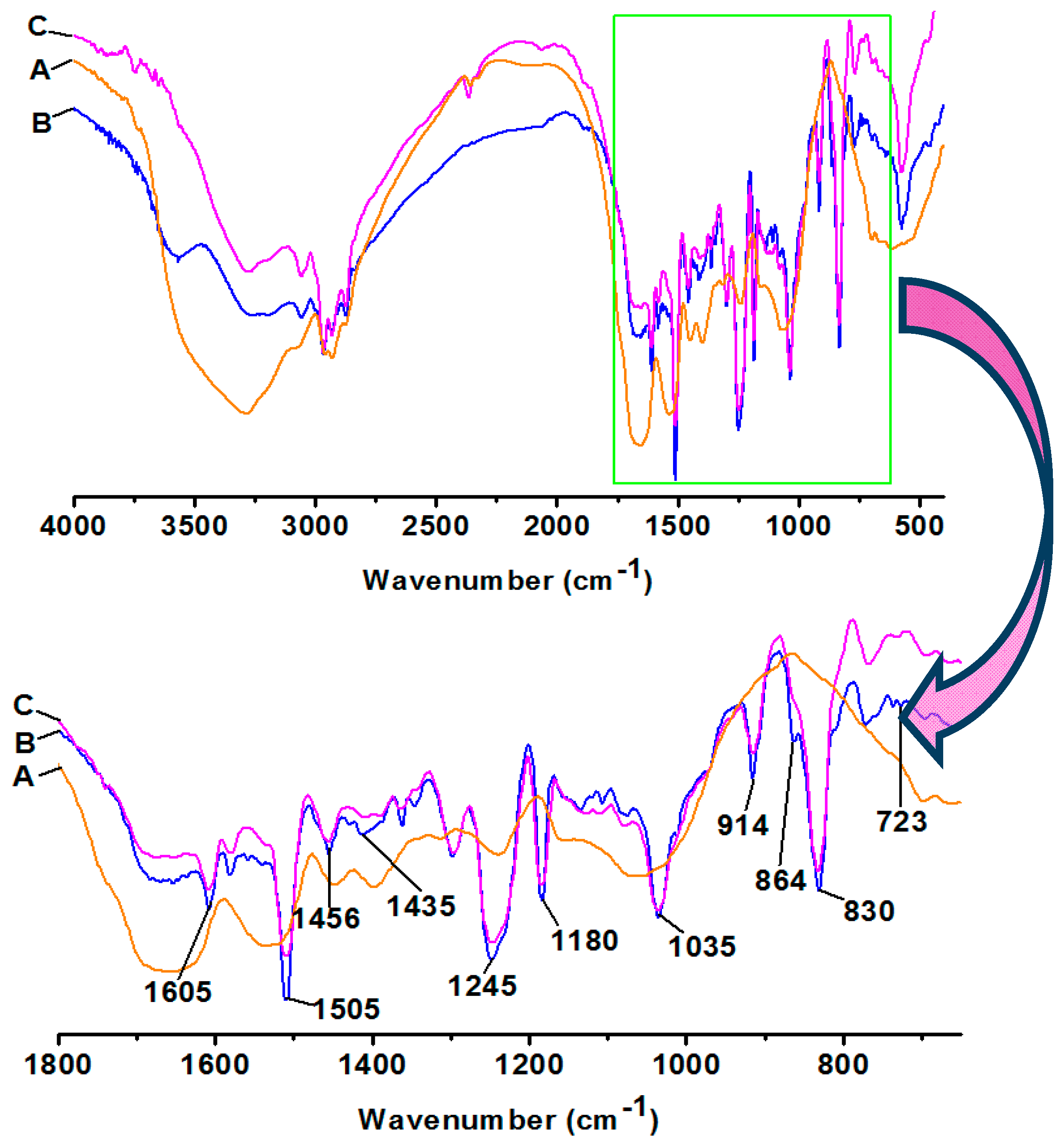
3.1. FTIR Analysis
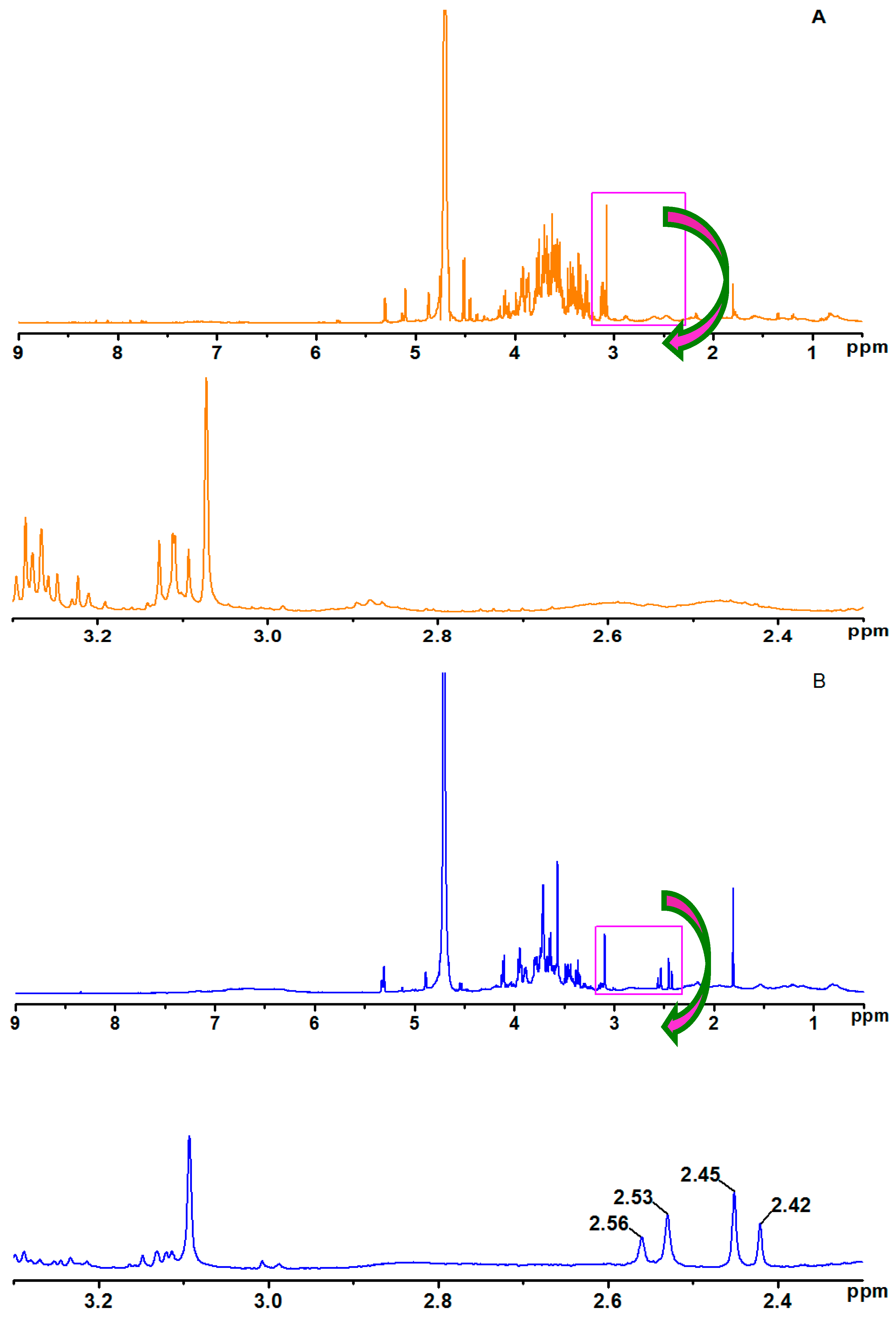
3.2. 1H-NMR Analysis
3.3. Viscosity and Solid Content
3.4. Hydrophilicity and Gluability
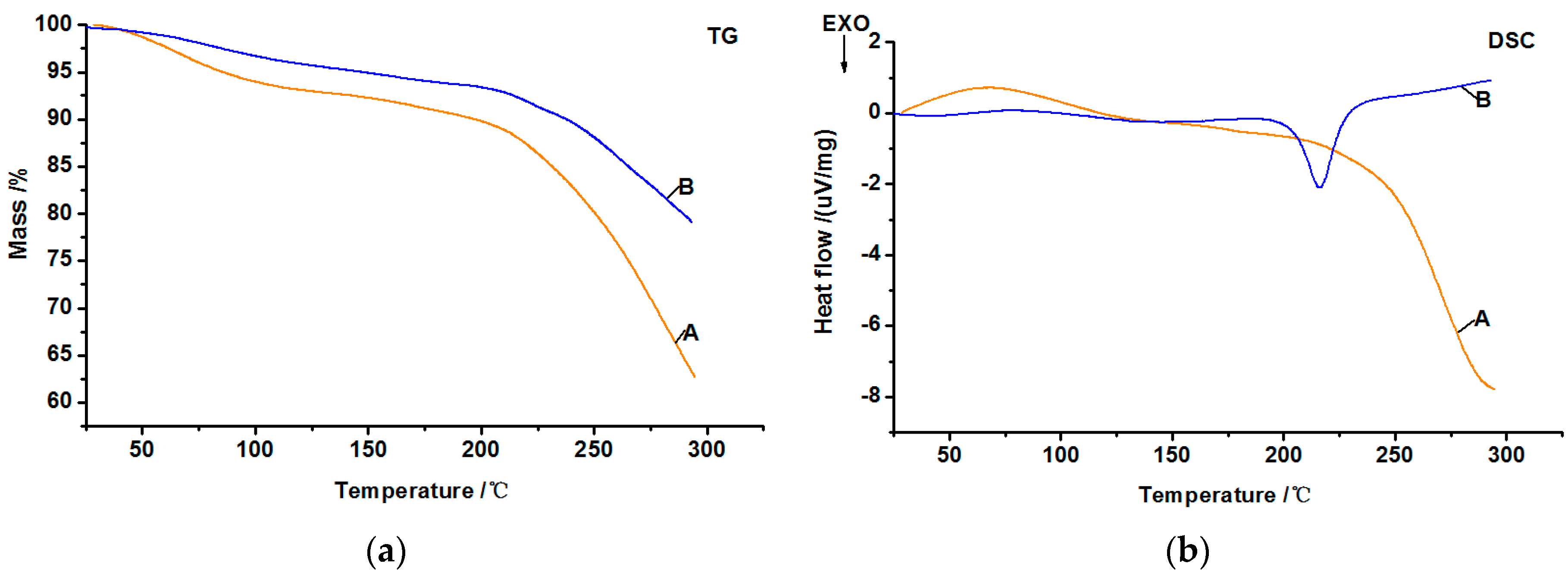
3.5. DSC and TG Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meier, M.A.; Metzger, J.O.; Schubert, U.S. Plant oil renewable resources as green alternatives in polymer science. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 1788–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z. Bio-Based Wood Adhesives: Preparation, Characterization, and Testing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; p. 356. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, N.; Lin, Q.; Zeng, Q.; Rao, J. Optimization of preparation conditions of soy flour adhesive for plywood by response surface methodology. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 51, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frihart, C.R.; Birkeland, M.J. Soy properties and soy wood adhesives. In Soy-Based Chemicals and Materials; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; pp. 167–192. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Cheng, H. Preparation and utilization of water washed cottonseed meal as wood adhesives. In Bio-Based Wood Adhesives: Preparation, Characterization, and Testing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 156–178. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Chapital, D.C.; Cheng, H.N.; Klasson, K.T.; Olanya, O.M.; Uknalis, J. Application of tung oil to improve adhesion strength and water resistance of cottonseed meal and protein adhesives on maple veneer. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2014, 61, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Qi, G.; Sun, X.S.; Wang, D. Canola protein and oil-based wood adhesives. In Bio-Based Wood Adhesives: Preparation, Characterization, and Testing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 111–139. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, N.; Zeng, Q.; Lin, Q.; Rao, J. Development of defatted soy flour based bio-adhesives using Viscozyme L. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 76, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frihart, C.R.; Coolidge, T.; Mock, C.; Valle, E. High bonding temperatures greatly improve soy adhesive wet strength. Polymers 2016, 8, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahri, S.; Pizzi, A.; Mohebby, B.; Mirshokraie, A.; Mansouri, H.R. Soy-based, tannin-modified plywood adhesives. J. Adhes. 2016, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral-Labat, G.; Pizzi, A.; Goncalves, A.; Celzard, A.; Rigolet, S.; Rocha, G. Environment-friendly soy flour-based resins without formaldehyde. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 108, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Peshkova, S.; Geng, X. Investigation of soy protein-kymene® adhesive systems for wood composites. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2004, 81, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzi, A. Recent developments in eco-efficient bio-based adhesives for wood bonding: Opportunities and issues. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2006, 20, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vnučec, D.; Kutnar, A.; Goršek, A. Soy-based adhesives for wood-bonding–a review. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2017, 31, 910–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Lu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Gu, J. Nano-scale blocking mechanism of mmt and its effects on the properties of polyisocyanate-modified soybean protein adhesive. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2014, 57, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenorio-Alfonso, A.; Sánchez, M.C.; Franco, J.M. Preparation, characterization and mechanical properties of bio-based polyurethane adhesives from isocyanate-functionalized cellulose acetate and castor oil for bonding wood. Polymers 2017, 9, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Du, G.; Wu, Z.; Xi, X.; Dong, Z. Cross-linked soy-based wood adhesives for plywood. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2014, 50, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslah, F.; Jonoobi, M.; Faezipour, M.; Afsharpour, M.; Enayati, A.A. Preparation and development of a chemically modified bio-adhesive derived from soybean flour protein. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2016, 71, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Sun, X.S. Soy protein adhesive blends with synthetic latex on wood veneer. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2011, 88, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Q.; Li, J. Properties of a soybean meal-based plywood adhesive modified by a commercial epoxy resin. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2016, 71, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Luo, J.; Bai, Y.; Gao, Q.; Li, J. A high performance soy protein-based bio-adhesive enhanced with a melamine/epichlorohydrin prepolymer and its application on plywood. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 67669–67676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciriminna, R.; Pagliaro, M. Sustainable production of glycerol. In Encyclopedia of Inorganic and Bioinorganic Chemistry; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, K.; Huang, J.; Li, K. Preparation and evaluation of particleboard bonded with a soy flour-based adhesive with a new curing agent. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2013, 27, 2053–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.L.; Luo, J.; Li, X.N.; Li, K.; Gao, Q.; Li, J.Z. Toughening improvement to a soybean meal-based bioadhesive using an interpenetrating acrylic emulsion network. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 9330–9341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szolnoki, B.; Bocz, K.; Sóti, P.L.; Bodzay, B.; Zimonyi, E.; Toldy, A.; Morlin, B.; Bujnowicz, K.; Wladyka-Przybylak, M.; Marosi, G. Development of natural fibre reinforced flame retarded epoxy resin composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 119, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Tian, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, K.; Wang, J. Research on starch-g-polyvinyl acetate and epoxy resin-modified corn starch adhesive. Polym. Compos. 2013, 34, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croccolo, D.; De Agostinis, M.; Fini, S.; Liverani, A.; Marinelli, N.; Nisini, E.; Olmi, G. Mechanical characteristics of two environmentally friendly resins reinforced with flax fibers. J. Mech. Eng. 2015, 61, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zeng, Q.; Rao, J.; Lin, Q. Effect of preparation conditions on bonding strength of soy-based adhesives via viscozyme l action on soy flour slurry. BioResources 2014, 9, 7444–7453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, M.J.; Jia, X.R.; Yang, S.; Chen, X.F.; Wei, Y. Reversible tuning luminescent color and emission intensity: A dipeptide-based light-emitting material. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Berridi, M.J.; González, N.; Mugica, A.; Bernicot, C. Pyrolysis-ftir and tga techniques as tools in the characterization of blends of natural rubber and sbr. Thermochim. Acta 2006, 444, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, T.; Mussone, P.; El-Thaher, N.; Choi, P.Y.; Bressler, D.C. Thermosetting proteinaceous plastics from hydrolyzed specified risk material. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Lin, Q.; Rao, J.; Zeng, Q. Water resistances and bonding strengths of soy-based adhesives containing different carbohydrates. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 50, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fache, M.; Montérémal, C.; Boutevin, B.; Caillol, S. Amine hardeners and epoxy cross-linker from aromatic renewable resources. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 73, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, B.H. Infrared Spectroscopy: Fundamentals and Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez, C.; Rico, M.; Torres, A.; Barral, L.; López, J.; Montero, B. Epoxy/poss organic–inorganic hybrids: Atr-ftir and dsc studies. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 3035–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, H.; Agag, T. Handbook of Benzoxazine Resins; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 524–526. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, P.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Ou, Y.; Lin, Q.; Chen, N. Development of defatted soy flour-based adhesives by acid hydrolysis of carbohydrates. Polymers 2017, 9, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.F.; Shi, L.Y.; Yuan, S.; Zhong, Q.D.; Zhang, D.S.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J. Morphology, toughness mechanism, and thermal properties of hyperbranched epoxy modified diglycidyl ether of bisphenol a (dgeba) interpenetrating polymer networks. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2008, 19, 1597–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Gupta, A.; Sharmin, E.; Alam, M.; Pandey, S. Synthesis, characterization and development of high performance siloxane-modified epoxy paints. Prog. Org. Coat. 2005, 54, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frihart, C.R.; Satori, H. Soy flour dispersibility and performance as wood adhesive. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2013, 27, 2043–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacigalupe, A.; He, Z.; Escobar, M.M. Effects of rheology and viscosity of biobased adhesives on bonding performance. In Bio-Based Wood Adhesives: Preparation, Characterization, and Testing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 293–309. [Google Scholar]
- Auvergne, R.; Caillol, S.; David, G.; Boutevin, B.; Pascault, J.-P. Biobased thermosetting epoxy: Present and future. Chem. Rev. 2013, 114, 1082–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Lin, Q.; Bian, L. Curing mechanism of modified soy-based adhesive and optimized plywood hot-pressing technology. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2012, 28, 248–253. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Lei, H.; Cao, M.; Xi, X.; Liang, J.; Du, G. Soy-based adhesive cross-linked by melamine–glyoxal and epoxy resin. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2016, 30, 2120–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Choi, H.; Shim, M.; Kim, S. Kinetic studies of an epoxy cure reaction by isothermal dsc analysis. Thermochim. Acta 2000, 343, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| The Amounts of Epoxy Resin (%) | Viscosity ± SD (Pa·s) | Solid Contents ± SD (%) | Water Absorption ± SD (%) | Wet Shear Strength ± SD (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.816 (± 0.021) a | 19.4 (± 0.21) a | 6.52 (± 0.11) a | 0.60 (± 0.15) a |
| 10 | 2.533 (± 0.011) b | 21.1 (± 0.13) ab | 3.91 (± 0.08) b | 0.64 (± 0.12) a |
| 20 | 2.576 (± 0.017) b | 22.3 (± 0.18) ac | 3.65 (± 0.10) b | 0.83 (± 0.21) ab |
| 30 | 2.668 (± 0.014) b | 23.6 (± 0.24) ac | 3.64 (± 0.04) b | 0.95 (± 0.17) ac |
| 40 | 2.719 (± 0.013) b | 24.7 (± 0.16) bc | 3.56 (± 0.05) b | 1.15 (± 0.07) bc |
| 50 | 2.851 (± 0.009) b | 26.1 (± 0.19) c | 3.54 (± 0.07) b | 1.31 (± 0.13) c |
| Entry | Mass Loss at 100 °C (%) | Mass Loss at 160 °C (%) | Endothermic Peak Temperature (°C) | Endothermic Peak Area (uV·s/mg) | Endothermic End-Point Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 6.04 | 8.13 | 68.1 | 162.6 | 117.1 |
| B | 3.33 | 5.46 | 70.9 | 30.3 | 97.8 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, N.; Zheng, P.; Zeng, Q.; Lin, Q.; Rao, J. Characterization and Performance of Soy-Based Adhesives Cured with Epoxy Resin. Polymers 2017, 9, 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9100514
Chen N, Zheng P, Zeng Q, Lin Q, Rao J. Characterization and Performance of Soy-Based Adhesives Cured with Epoxy Resin. Polymers. 2017; 9(10):514. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9100514
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Nairong, Peitao Zheng, Qinzhi Zeng, Qiaojia Lin, and Jiuping Rao. 2017. "Characterization and Performance of Soy-Based Adhesives Cured with Epoxy Resin" Polymers 9, no. 10: 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9100514
APA StyleChen, N., Zheng, P., Zeng, Q., Lin, Q., & Rao, J. (2017). Characterization and Performance of Soy-Based Adhesives Cured with Epoxy Resin. Polymers, 9(10), 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9100514






