Biodegradation of Halloysite Nanotubes-Polyester Nanocomposites Exposed to Short Term Seawater Immersion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
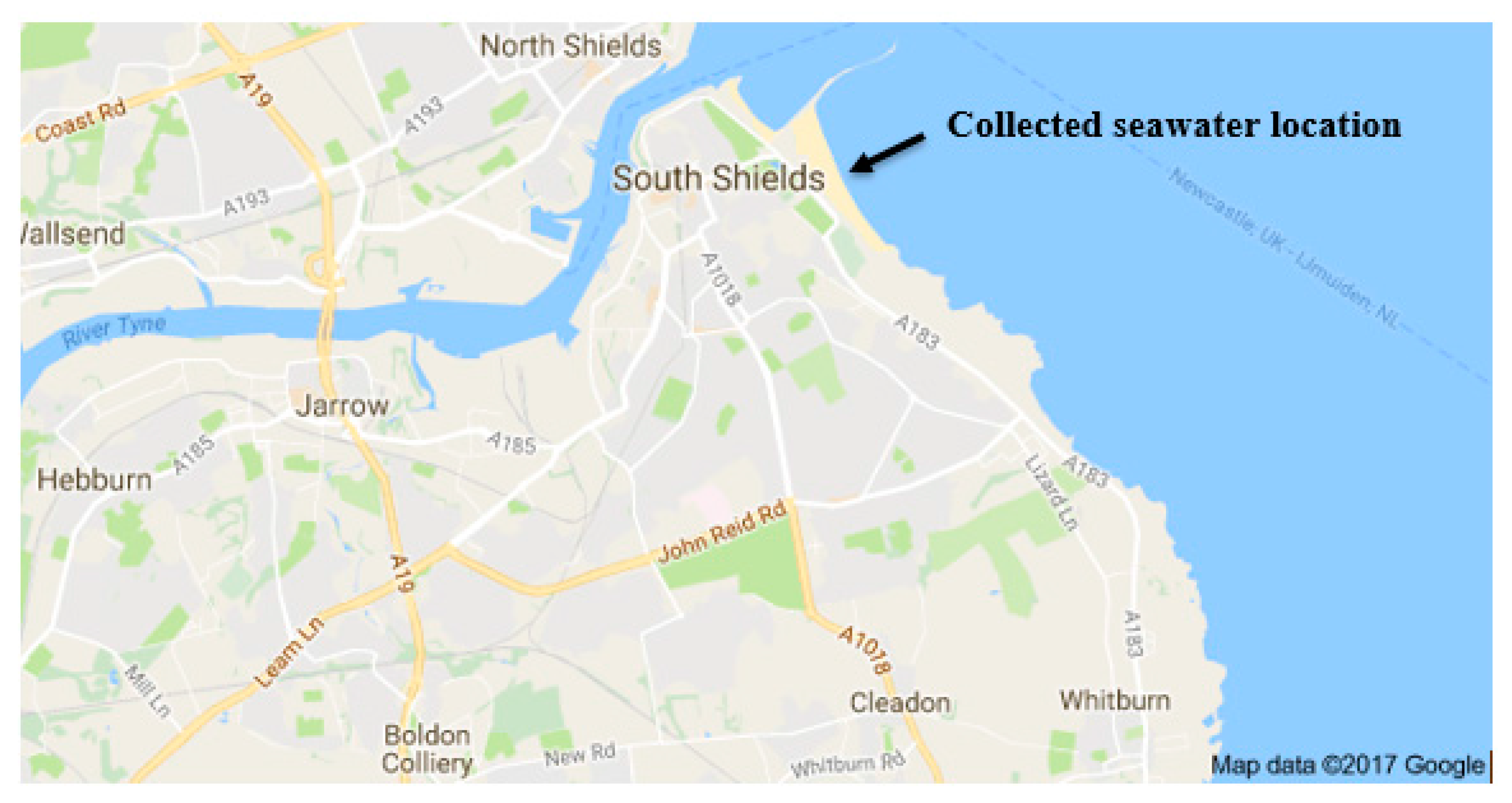
2. Materials and Methods
Characterization
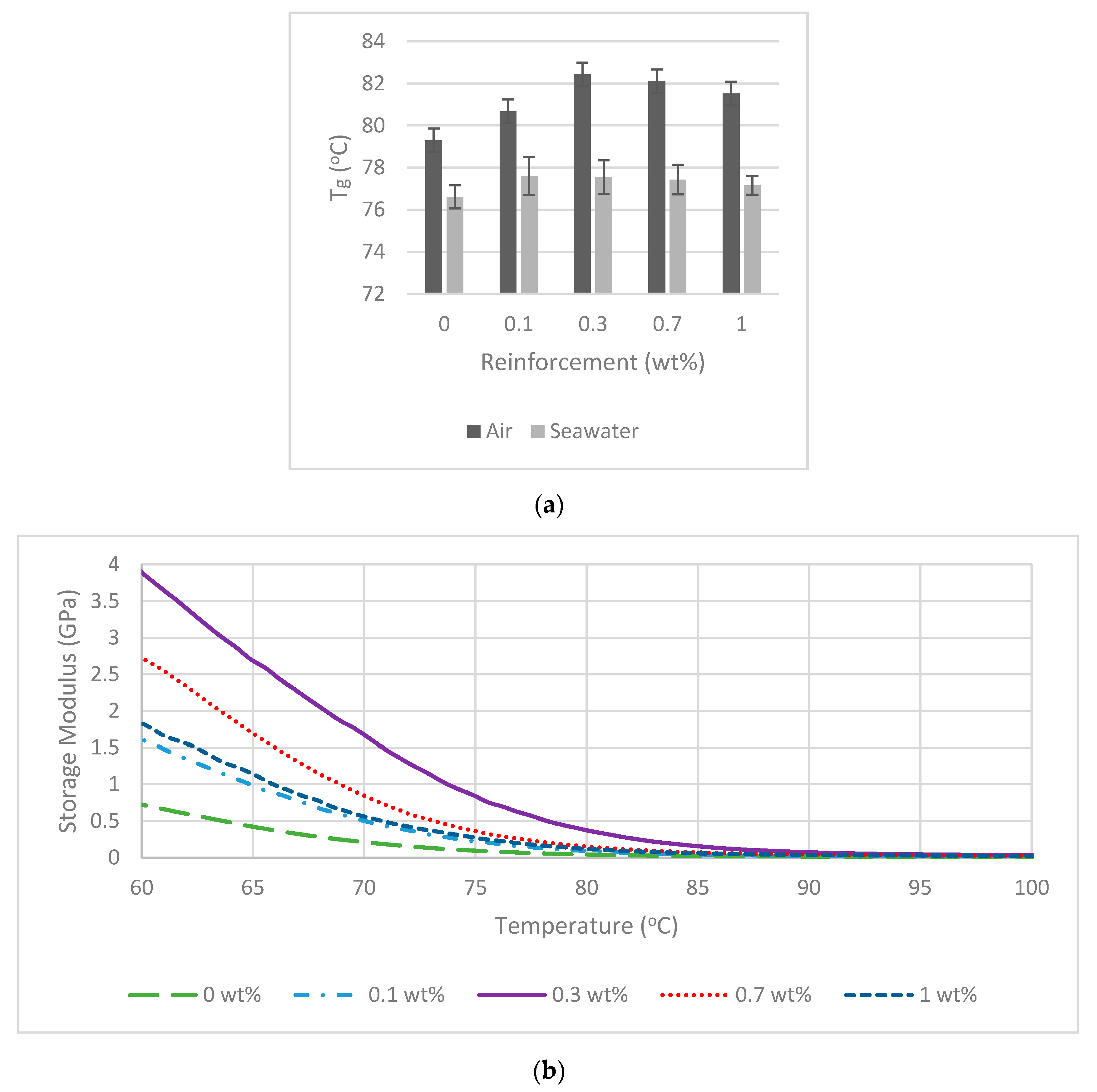
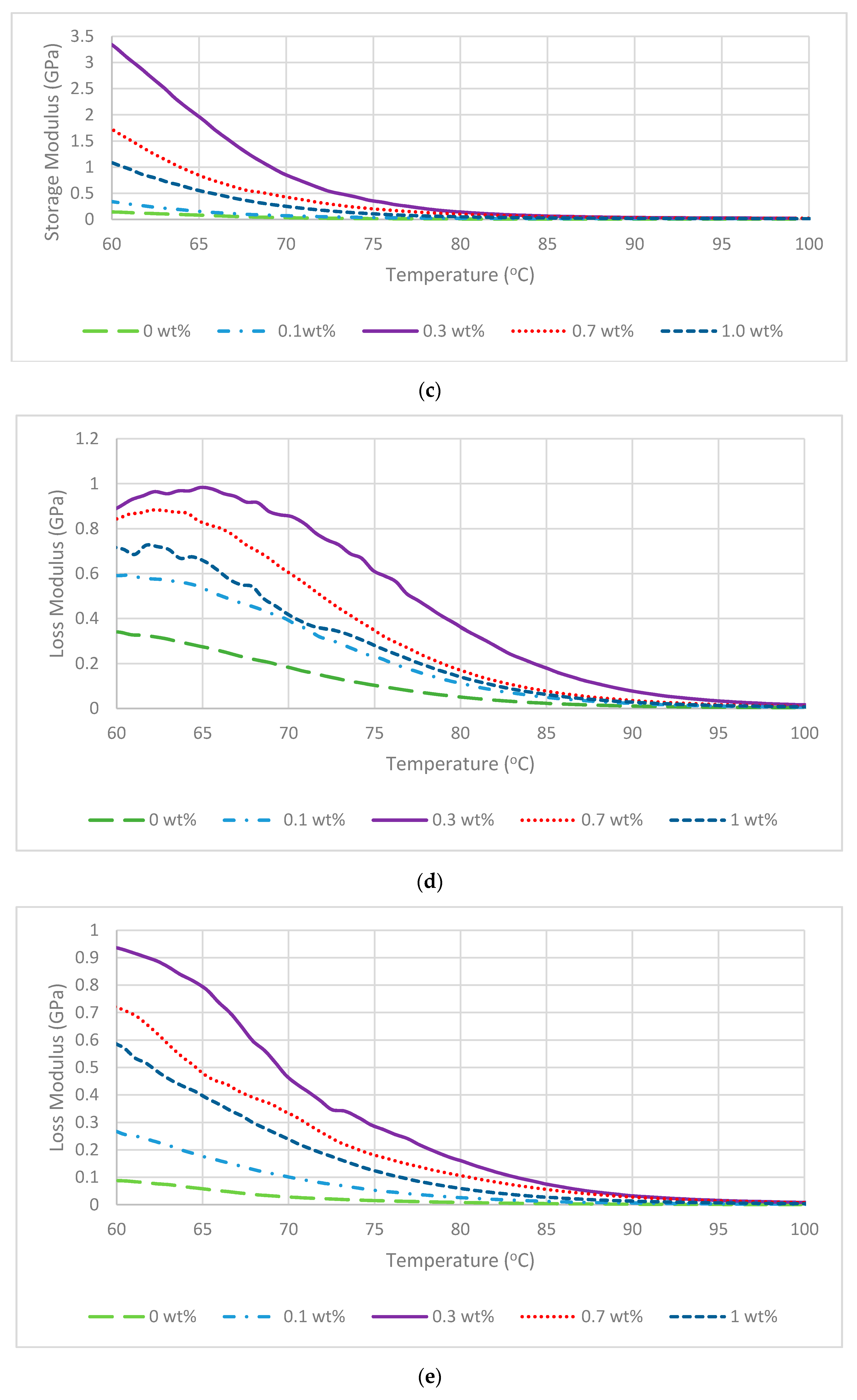
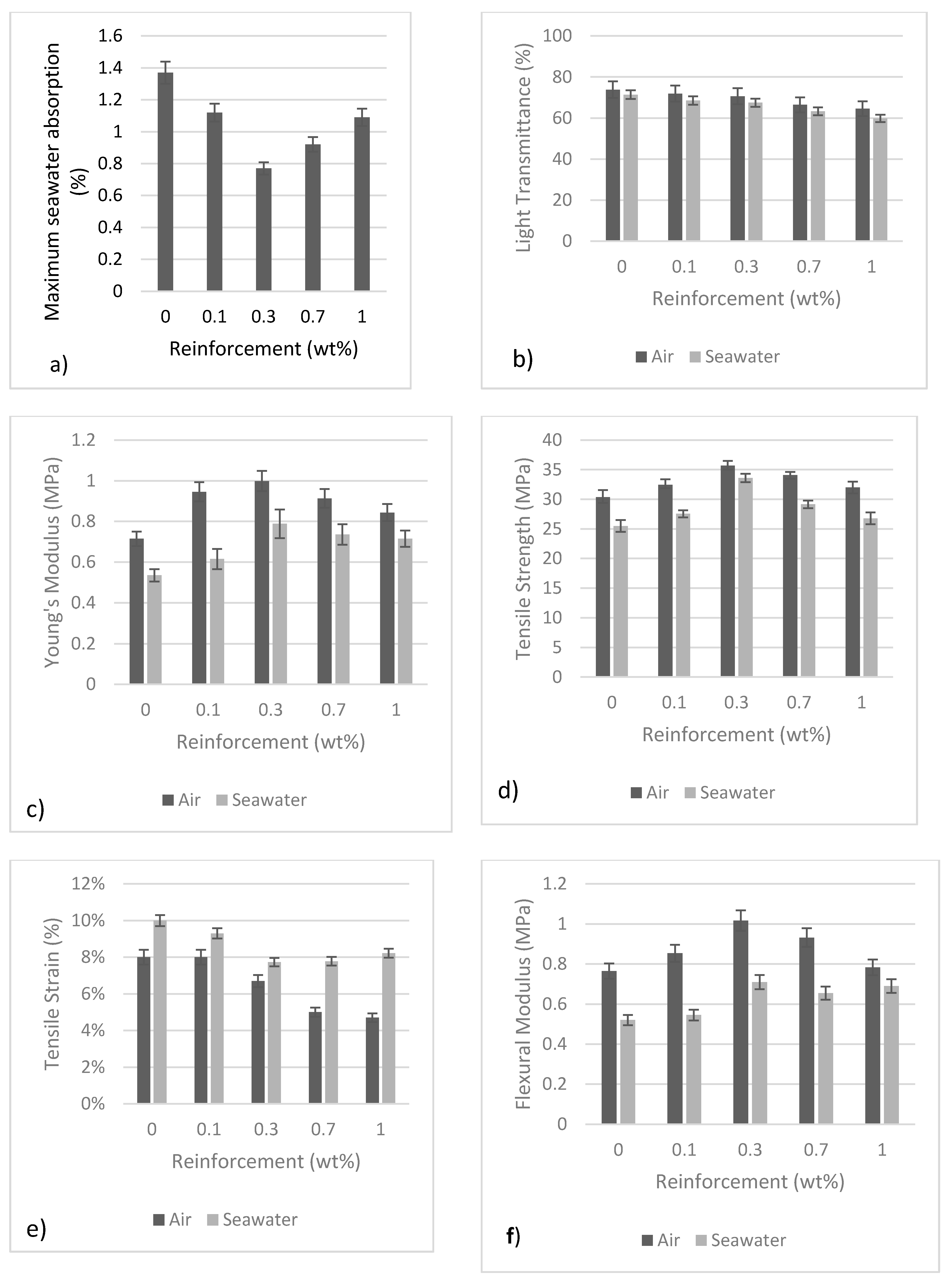
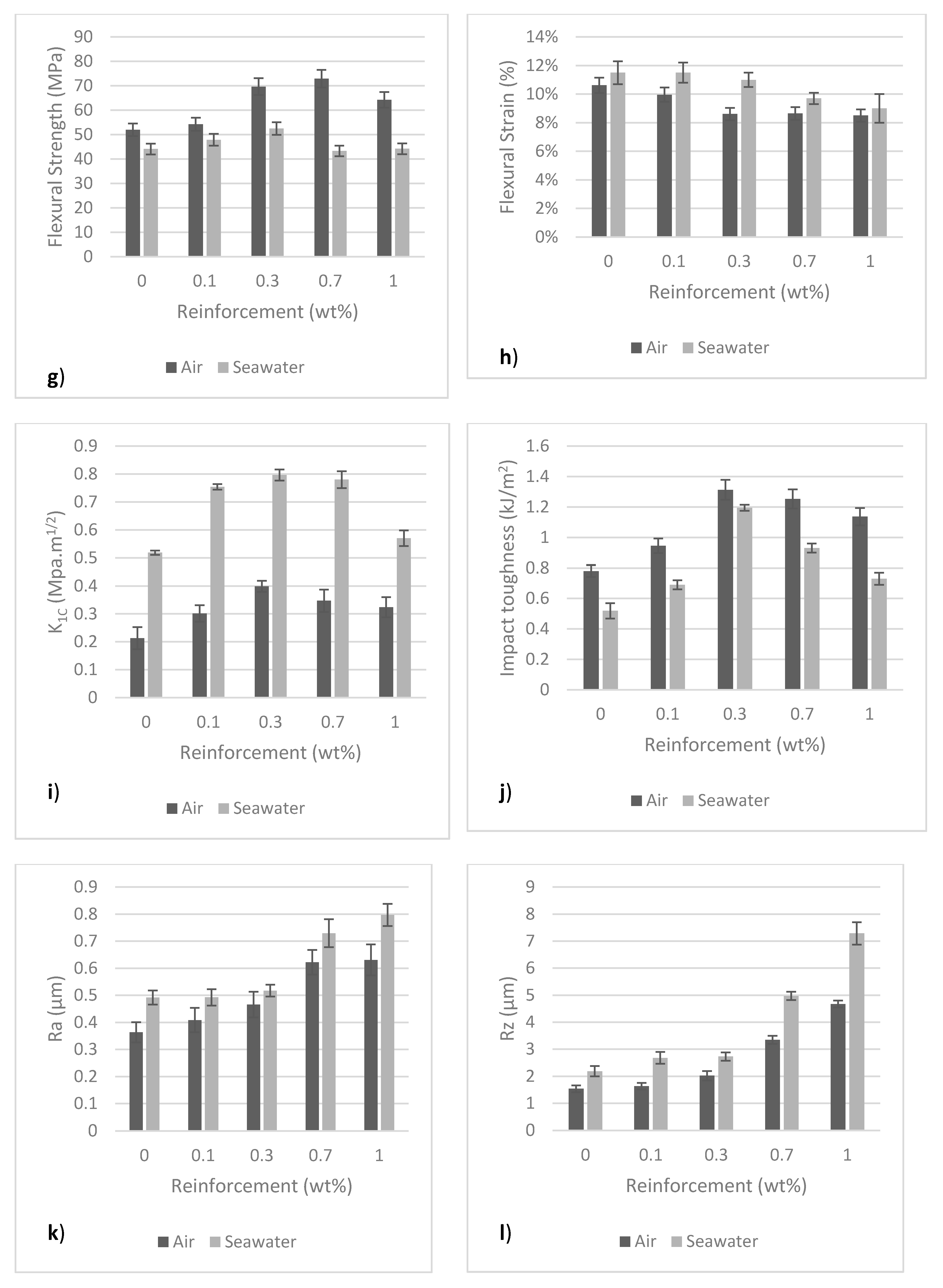
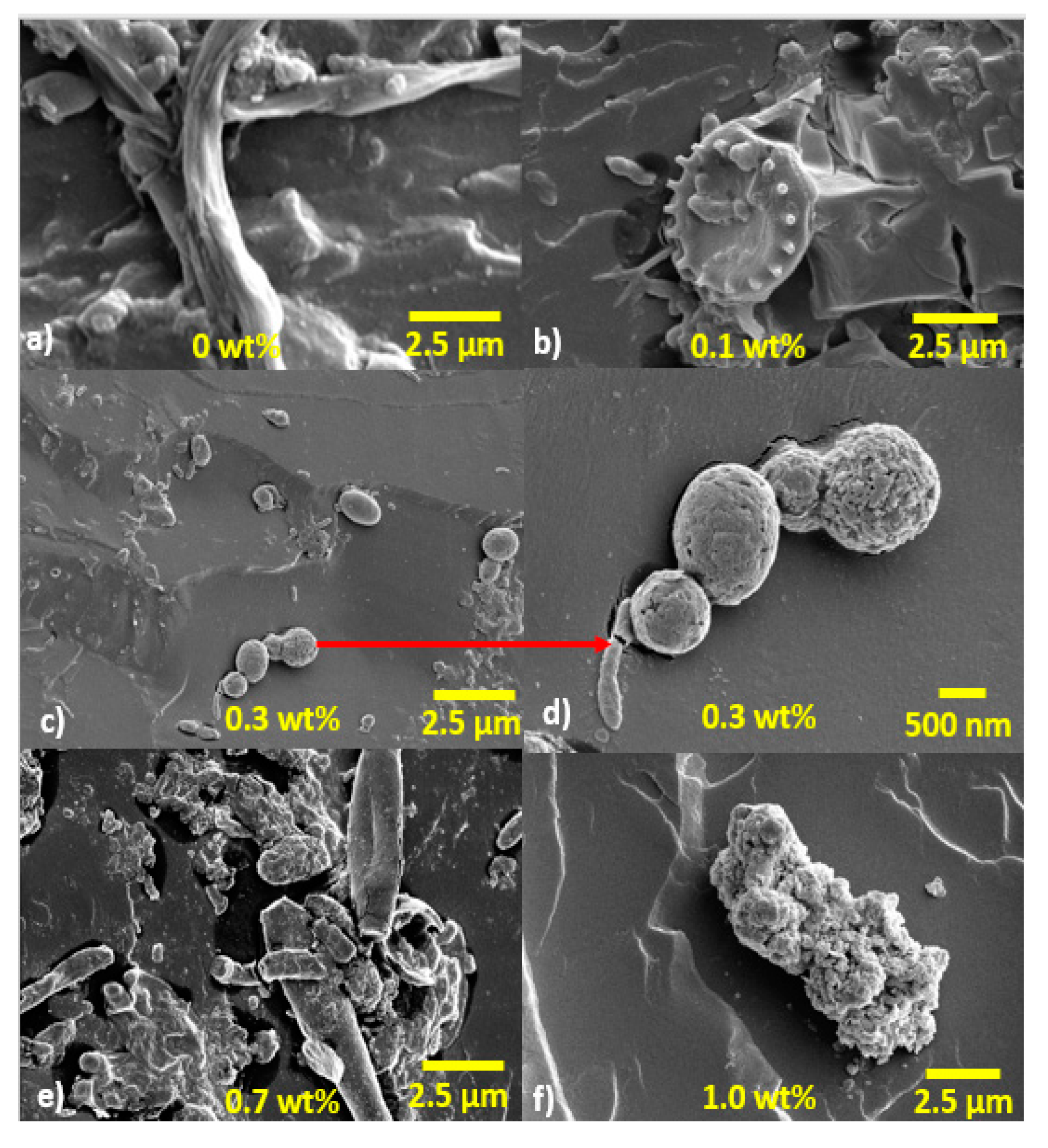
3. Results and Discussion
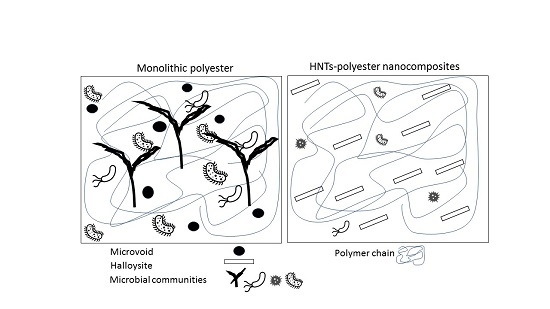
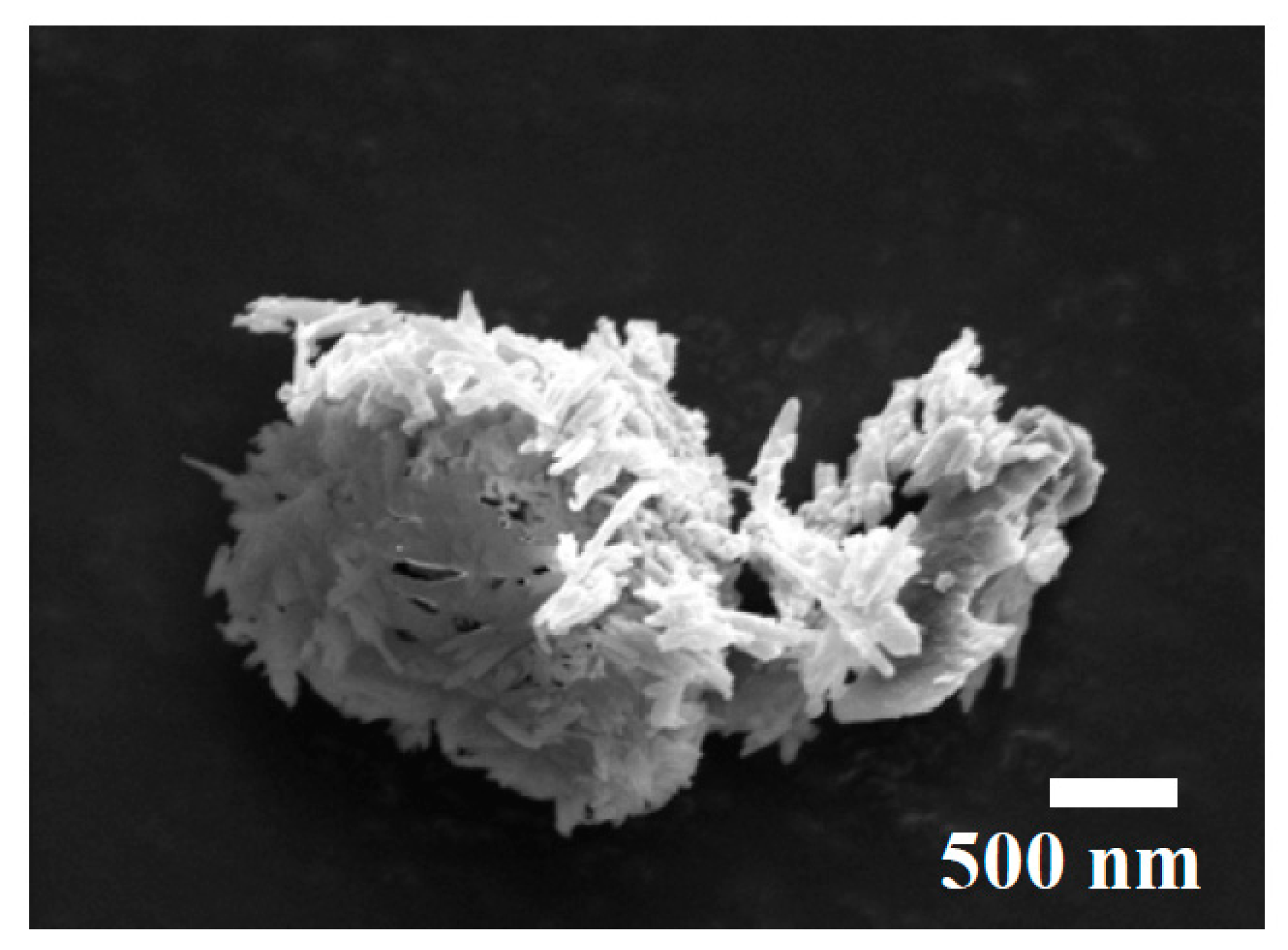
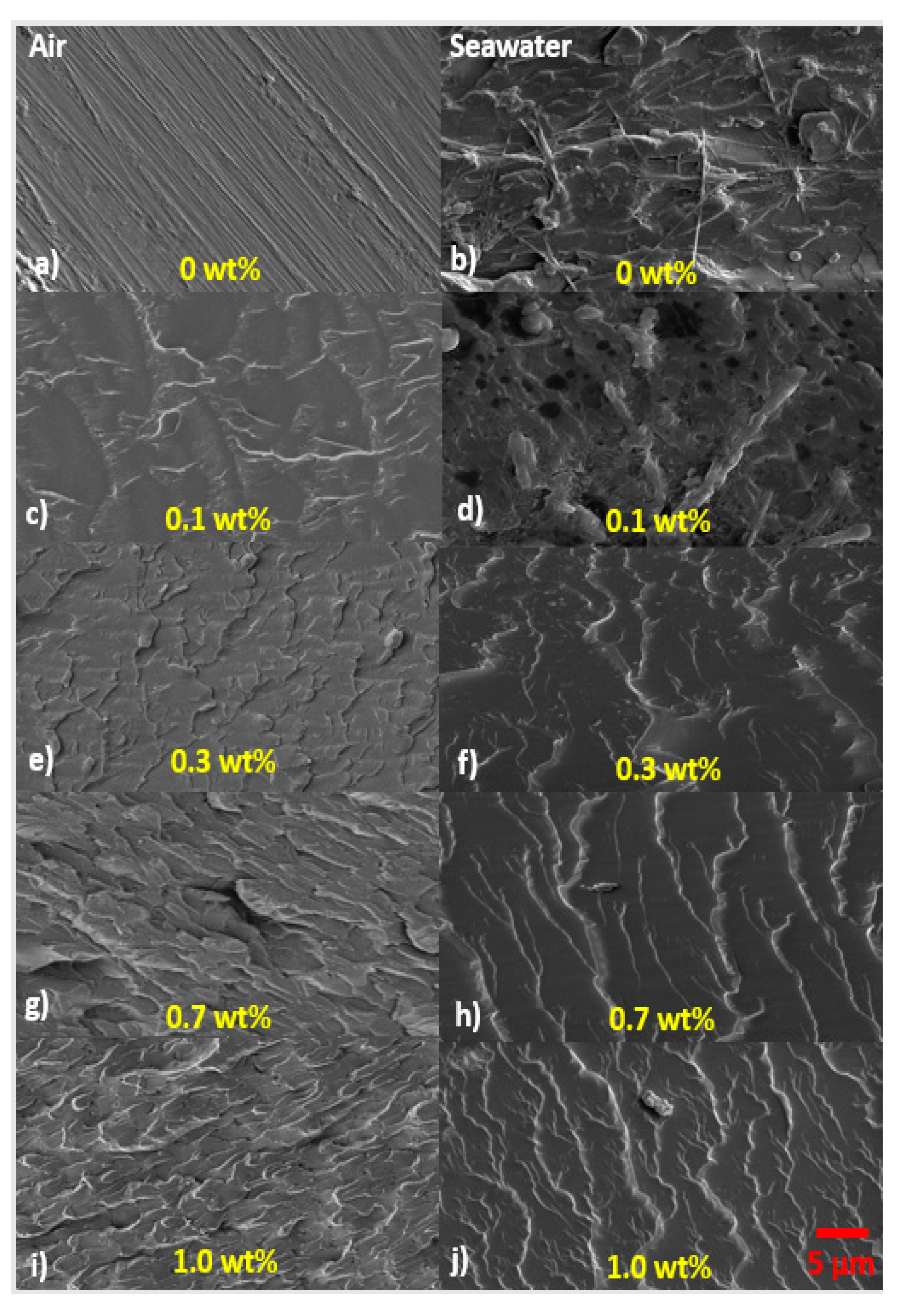
SEM Images
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saharudin, M.S.; Shyha, I.; Inam, F. The effect of methanol exposure on the flexural and tensile properties of halloysite nanoclay polyester. In Proceedings of the IRES-17th International Conference on Innovative Engineering Technologies, London, UK, 21 November 2015; pp. 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.; Chen, S.; Campbell, J.; Zhang, X.; Tang, Y. Fracture toughness and wear properties of nanosilica/epoxy composites under marine environment. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 177, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima Sobrinho, L.; Ferreira, M.; Bastian, F.L. The effects of water absorption on an ester vinyl resin system. Mater. Res. 2009, 12, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharudin, M.S.; Wei, J.; Shyha, I.; Inam, F. Environmental Stress Cracking Resistance of Halloysite Nanoclay-Polyester Nanocomposites. World J. Eng. Technol. 2017, 5, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharudin, M.; Wei, J.; Shyha, I.; Inam, F. The degradation of mechanical properties in halloysite nanoclay-polyester nanocomposites exposed in seawater environment. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, C.; Gogoi, P.; Baglari, S.; Dolui, S.K. Preparation of polyester resin/graphene oxide nanocomposite with improved mechanical strength. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 3432–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Saharudin, M.S.; Vo, T.; Inam, F. N,N-Dimethylformamide (DMF) Usage in Epoxy/Graphene Nanocomposites: Problems Associated with Reaggregation. Polymers 2017, 9, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharudin, M.S.; Atif, R.; Shyha, I.; Inam, F. The degradation of mechanical properties in polymer nano-composites exposed to liquid media—A review. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 1076–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharudin, M.S.; Shyha, I.; Inam, F. Viscoelastic and mechanical properties of multi-layered-graphene polyester composites. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Advances in Mechanical Engineering, Istanbul, Turkey, 10–13 May 2016; pp. 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Saharudin, M.S.; Jumahat, A.; Kahar, A.Z.; Ahmad, S. The Influence of Alumina Filler on Impact Properties of Short Glass Fiber Reinforced Epoxy. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 393, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F. Clay/polymer composites: The story. Mater. Today 2004, 7, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, H.; Low, I.M. Effect of water absorption on the mechanical properties of nano-filler reinforced epoxy nanocomposites. Mater. Des. 2012, 42, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albdiry, M.T.; Yousif, B.F.; Ku, H. Fracture toughness and toughening mechanisms of unsaturated polyester-based clay nanocomposites. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Fracture, Beijing, China, 16–21 June 2013; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zainuddin, S.; Hosur, M.V.; Zhou, Y.; Kumar, A.; Jeelani, S. Durability studies of montmorillonite clay filled epoxy composites under different environmental conditions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 507, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhrullina, G.I.; Akhatova, F.S.; Lvov, M.; Fakhrullin, R.F. Environmental Science Nano Toxicity of halloysite clay nanotubes in vivo: A Caenorhabditis elegans study. Environ. Sci. Nano 2015, 2, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvov, Y.; Abdullayev, E. Functional polymer-clay nanotube composites with sustained release of chemical agents. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1690–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, R.; Ghag, M.; Gaikawad, S.; Panda, B.K. Review article halloysite nanotubes and applications: A review. J. Adv. Sci. Res. 2012, 3, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Bhuvana, S.; Prabakaran, M. Synthesis and Characterisation of Polyamide/Halloysite Nanocomposites Prepared by Solution Intercalation Method. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 4, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabr, M.H.; Phong, N.T.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Okubo, K.; Uzawa, K.; Kimpara, I.; Fujii, T. Mechanical, thermal, and moisture absorption properties of nano-clay reinforced nano-cellulose biocomposites. Cellulose 2013, 20, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albdiry, M.; Yousif, B.; Ku, H.; Lau, K. A critical review on the manufacturing processes in relation to the properties of nanoclay/polymer composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2012, 47, 1093–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hoa, S.V.; Pugh, M. Fracture toughness and water uptake of high-performance epoxy/nanoclay nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 2364–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, L.N.; Crespo, J.S.; Mauler, R.S. PHBV nanocomposites based on organomodified montmorillonite and halloysite: The effect of clay type on the morphology and thermal and mechanical properties. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2011, 42, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidou, S.; Papaspyrides, C.D. A review on polymer-layered silicate nanocomposites. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 1119–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobelle, D.; Cunliffe, M. Early microbial biofilm formation on marine plastic debris. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Zeferino, J.C.; Beltrán-Villavicencio, M.; Vázquez-Morillas, A. Degradation of Plastics in Seawater in Laboratory. Open J. Polym. Chem. 2015, 5, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimowska, A.; Krasowska, K.; Rutkowska, M. Degradability of Different Packaging Polymeric Materials in Seawater. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual General Assembly IAMU, St. Johns, NL, Canada, 15–17 October 2012; pp. 153–163. [Google Scholar]
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gewert, B.; Plassmann, M.M.; MacLeod, M. Pathways for degradation of plastic polymers floating in the marine environment. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albdiry, M.T.; Ku, H.; Yousif, B.F. Impact fracture behaviour of silane-treated halloysite nanotubes-reinforced unsaturated polyester. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2013, 35, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Ng, K.M.; Chan, C.-M.; Sun, G.; Wu, J. High-impact polystyrene/halloysite nanocomposites prepared by emulsion polymerization using sodium dodecyl sulfate as surfactant. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 358, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chozhan, C.K.; Rajasekaran, R.; Alagar, M.; Gnanasundaram, P. Thermomechanical Behavior of Vinyl Ester Oligomer-Toughened Epoxy-Clay Hybrid Nanocomposites. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 2008, 57, 319–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, J.; Ye, L. High impact strength epoxy nanocomposites with natural nanotubes. Polymer 2007, 48, 6426–6433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancaktar, E.; Kuznicki, J. Nanocomposite adhesives: Mechanical behavior with nanoclay. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2011, 31, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, Q.; Berglund, L.A.; Fan, J.; Qi, Z. Polyamide 6-clay nanocomposites/polypropylene-grafted-maleic anhydride alloys. Polymer 2001, 42, 8235–8239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepoittevin, B.; Devalckenaere, M.; Pantoustier, N.; Alexandre, M.; Kubies, D.; Calberg, C.; Jérôme, R.; Dubois, P. Poly(ε-caprolactone)/clay nanocomposites prepared by melt intercalation: Mechanical, thermal and rheological properties. Polymer 2002, 43, 4017–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, H.; Low, I.M. Microstructural, mechanical, and thermal characteristics of recycled cellulose fiber-halloysite-epoxy hybrid nanocomposites. Polym. Compos. 2012, 33, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, L.B.; De Santis, H.; Vázquez, A. Influence of the addition of montmorillonite to the matrix of unidirectional glass fibre/epoxy composites on their mechanical and water absorption properties. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 1726–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Wetzel, B.; Friedrich, K.; Al, N. Tribological properties of surface modified nano-alumina/epoxy composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 9, 6487–6493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahedi, V.; Pasbakhsh, P. Instrumented impact properties and fracture behaviour of epoxy/modified halloysite nanocomposites. Polym. Test. 2014, 39, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atif, R.; Inam, F. Influence of macro-topography on damage tolerance and fracture toughness of 0.1 wt % multi-layer graphene/clay-epoxy nanocomposites. Polymers 2016, 8, 335–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, B.; Nair, C.P.R.; Ninan, K.N. Effect of nanoclay on the mechanical, dynamic mechanical and thermal properties of cyanate ester syntactic foams. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 5435–5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourad, A.H.I.; Beckry Mohamed, A.M.; El-Maaddawy, T. Effect of seawater and warm environment on glass/epoxy and glass/polyurethane composites. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2010, 17, 557–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharudin, M.S.; Wei, J.; Shyha, I.; Inam, F. Flexural Properties of Halloysite Nanotubes-Polyester Nanocomposites Exposed to Aggressive Environment. Int. J. Chem. Mol. Nucl. Mater. Metall. Eng. 2017, 11, 292–296. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, B.; Thomas, N.L. A review of the water barrier properties of polymer/clay and polymer/graphene nanocomposites. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 514, 595–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Picard, E.; Gérard, J.-F.; Espuche, E. Water transport properties of polyamide 6 based nanocomposites prepared by melt blending: On the importance of the clay dispersion state on the water transport properties at high water activity. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 313, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, R.K.; Mehrabi, A.R.; Hamilton, C.; Trujillo, C.; Murga, M. Structure property relationships in cross-linked polyester clay nanocomposites. Polymer 2002, 43, 3699–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Atif, R.; Vo, T.; Inam, F. Graphene Nanoplatelets in Epoxy System: Dispersion, Reaggregation, and Mechanical Properties of Nanocomposites. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurin, R.; Perrot, Y.; Bourmaud, A.; Davies, P.; Baley, C. Seawater ageing of low styrene emission resins for marine composites: Mechanical behaviour and nano-indentation studies. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2009, 40, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraverty, A.P.; Mohanty, U.K.; Mishra, S.C.; Satapathy, A. Sea Water Ageing of GFRP Composites and the Dissolved salts. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 75, 12029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Zhang, J.; Ye, L.; Wu, J. Toughening epoxies with halloysite nanotubes. Polymer 2008, 49, 5119–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsaroop, A.; Kanny, K.; Mohan, T.P. Fracture Toughness Studies of Polypropylene-Clay Nanocomposites and Glass Fibre Reinfoerced Polypropylene Composites. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2010, 1, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saidi, L.F.; Mortensen, K.; Almdal, K. Environmental stress cracking resistance. Behaviour of polycarbonate in different chemicals by determination of the time-dependence of stress at constant strains. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2003, 82, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buehler, F.U.; Seferis, J.C. Effect of reinforcement and solvent content on moisture absorption in epoxy composite materials. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2000, 31, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharudin, M.S.; Atif, R.; Inam, F. Effect of Short-Term Water Exposure on the Mechanical Properties of Halloysite Nanotube-Multi Layer Graphene Reinforced Polyester Nanocomposites. Polymers 2017, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffaro, R.; Morreale, M.; Lo Re, G.; La Mantia, F.P. Degradation of Mater-Bi/wood flour biocomposites in active sewage sludge. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2009, 94, 1220–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukumar, T.; Aravinthan, A.; Lakshmi, K.; Venkatesan, R.; Vedaprakash, L.; Doble, M. Fouling and stability of polymers and composites in marine environment. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2011, 65, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharudin, M.S.; Atif, R.; Shyha, I.; Inam, F. The degradation of mechanical properties in halloysite nanoclay-polyester nanocomposites exposed to diluted methanol. J. Compos. Mater. 2016, 51, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Kumar, S.; Rao Kona, B.; van Houcke, D. Gas barrier properties of polymer/clay nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 63669–63690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zettler, E.R.; Mincer, T.J.; Amaral-Zettler, L.A. Life in the “plastisphere”: Microbial communities on plastic marine debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7137–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Espinel, J.D.; Castro-Fresno, D.; Parbole Gayo, P.; Ballester-Muñoz, F. Effects of sea water environment on glass fiber reinforced plastic materials used for marine civil engineering constructions. Mater. Des. 2015, 66, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzah, E.; Hussain, M.F.; Ibrahim, Z.; Abdolahi, A. Corrosion Behaviour of Carbon Steel in Sea Water Medium in Presence of P. aeruginosa Bacteria. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2014, 39, 6863–6870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Nr | Authors | Year | Reinforcement/(wt %) | Polymer | Mechanical Properties | Max Increase (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Albdiry et al. | 2013 | Halloysite nanotubes/3 | Unsaturated polyester | Impact strength | 16 | [29] |
| 2 | Lin et al. | 2011 | Halloysite nanotubes/5 | Epoxy | Impact strength | 300 | [30] |
| 3 | Chozhan et al. | 2008 | Clay/3 | Epoxy | Impact strength | 19.2 | [31] |
| 4 | Ye et al. | 2007 | Halloysite nanotubes/2.3 | Epoxy | Impact strength | 413 | [32] |
| 5 | Sancaktar | 2011 | Nanoclay/1 | Epoxy | Young’s modulus | 11 | [33] |
| 6 | Carli et al. | 2011 | Halloysite nanotubes/5 | PHBV | Young’s modulus | 63 | [22] |
| 7 | Liu et al. | 2001 | Nanoclay/5 | Epoxy | Young’s modulus | 40 | [34] |
| 8 | Lepoittevin | 2002 | MMT/10 | PCL(Poly(ε-caprolactone) | Young’s modulus | 54 | [35] |
| 9 | Alamri and Low | 2012 | Halloysite/5 | Epoxy | Flexural Modulus | 88 | [36] |
| 10 | Pavlidou et al. | 2008 | MMT/5 | Epoxy | Flexural modulus | 224 | [23] |
| 11 | Manfredi et al. | 2008 | Cloisite/5 | Epoxy | Flexural modulus | 29 | [37] |
| 12 | Wetzel et al. | 2006 | MMT/10 | Epoxy | Flexural modulus | 40 | [38] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saharudin, M.S.; Wei, J.; Shyha, I.; Inam, F. Biodegradation of Halloysite Nanotubes-Polyester Nanocomposites Exposed to Short Term Seawater Immersion. Polymers 2017, 9, 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9080314
Saharudin MS, Wei J, Shyha I, Inam F. Biodegradation of Halloysite Nanotubes-Polyester Nanocomposites Exposed to Short Term Seawater Immersion. Polymers. 2017; 9(8):314. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9080314
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaharudin, Mohd Shahneel, Jiacheng Wei, Islam Shyha, and Fawad Inam. 2017. "Biodegradation of Halloysite Nanotubes-Polyester Nanocomposites Exposed to Short Term Seawater Immersion" Polymers 9, no. 8: 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9080314
APA StyleSaharudin, M. S., Wei, J., Shyha, I., & Inam, F. (2017). Biodegradation of Halloysite Nanotubes-Polyester Nanocomposites Exposed to Short Term Seawater Immersion. Polymers, 9(8), 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9080314