Diversity of DNA Replication in the Archaea
Abstract
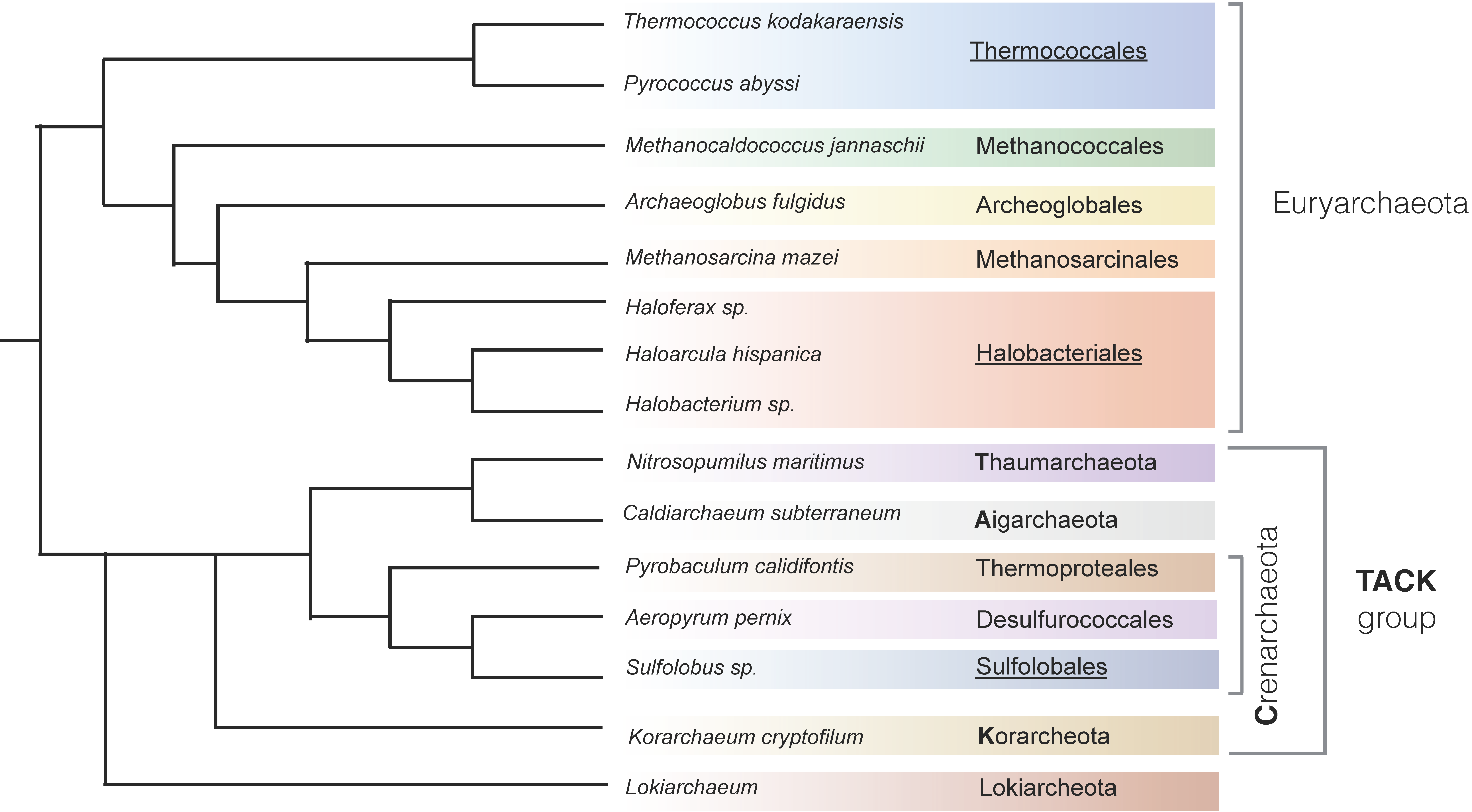
:1. Introduction
2. Machinery for DNA Replication Initiation
2.1. Replication Origins
2.2. Origin Recognition Proteins
2.3. Origin Binding and DNA Unwinding
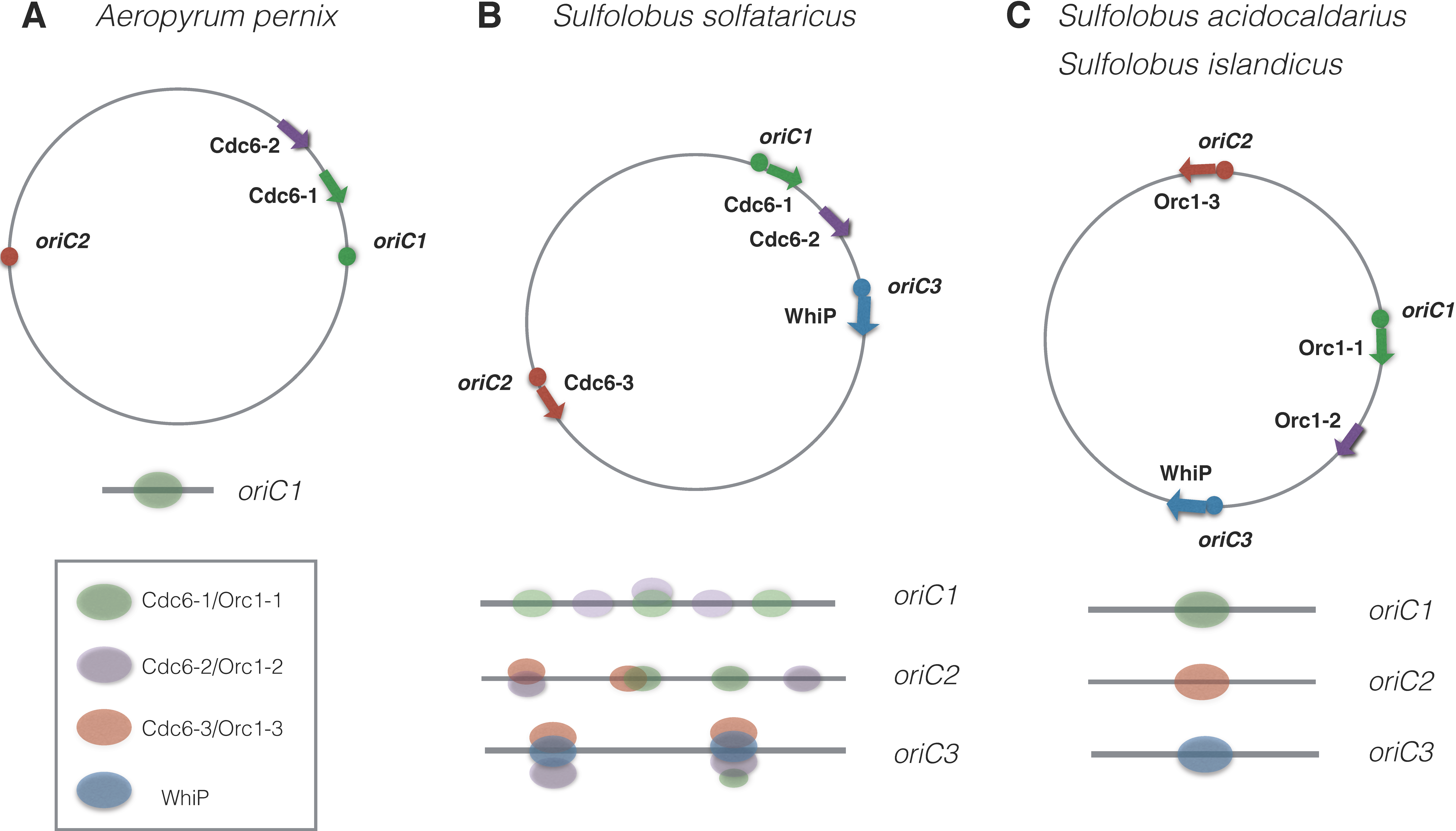
2.4. Multiple Origins on the Chromosome
2.5. Diversity of Functions of Orc1/Cdc6 Proteins in Archaea
2.6. Recruitment of a Helicase
3. Regulation of DNA Replication Initiation
3.1. Cell Cycle Regulation in Haploid Archaea
3.2. Cell Cycle Regulation in Polyploid Archaea
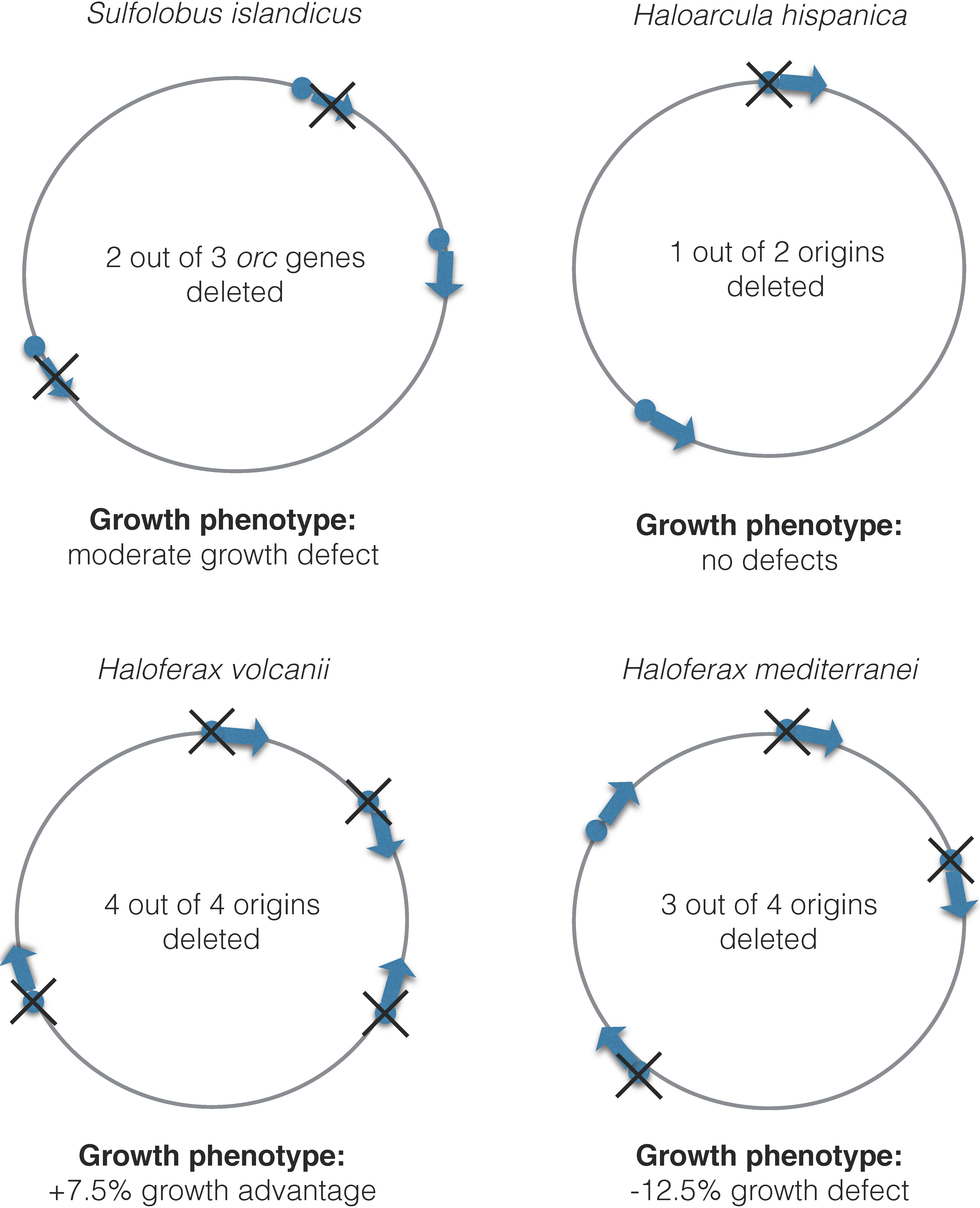
3.3. Regulation of Initiation of Multiple Origins
3.4. Regulation of Replication of Multiple Chromosomal Elements
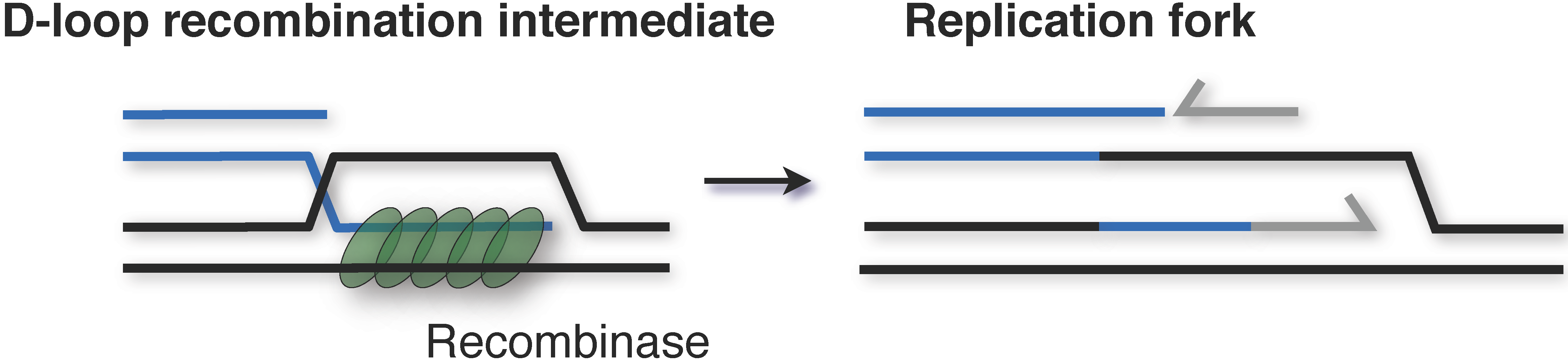
4. Alternative Mechanisms of Replication Initiation
5. Perspectives and Open Questions
5.1. Tools to Control Replication Initiation in Archaeal Cells
5.2. Spatial Organisation of Genome and Replication
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Donnell, M.; Langston, L.; Stillman, B. Principles and concepts of DNA replication in bacteria, archaea, and eukarya. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a010108. [Google Scholar]
- Makarova, K.S.; Koonin, E.V. Archaeology of eukaryotic DNA replication. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a012963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymann, K.; Forterre, P.; Brochier-Armanet, C.; Gribaldo, S. Global phylogenomic analysis disentangles the complex evolutionary history of DNA replication in archaea. Genome Biol. Evol. 2014, 6, 192–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aves, S.J.; Liu, Y.; Richards, T.A. Evolutionary diversification of eukaryotic DNA replication machinery. Subcell. Biochem. 2012, 62, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Woese, C.R.; Kandler, O.; Wheelis, M.L. Towards a natural system of organisms: Proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 4576–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petitjean, C.; Deschamps, P.; Lopez-Garcia, P.; Moreira, D. Rooting the domain archaea by phylogenomic analysis supports the foundation of the new kingdom Proteoarchaeota. Genome Biol. Evol. 2014, 7, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, T.A.; University of Bristol, Bristol, UK. Personal communication, 2016.
- Wu, Z.; Liu, J.; Yang, H.; Xiang, H. DNA replication origins in archaea. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myllykallio, H.; Lopez, P.; Lopez-Garcia, P.; Heilig, R.; Saurin, W.; Zivanovic, Y.; Philippe, H.; Forterre, P. Bacterial mode of replication with eukaryotic-like machinery in a hyperthermophilic archaeon. Science 2000, 288, 2212–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, M.; Malla, S.; Blythe, M.J.; Nieduszynski, C.A.; Allers, T. Accelerated growth in the absence of DNA replication origins. Nature 2013, 503, 544–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundgren, M.; Andersson, A.; Chen, L.; Nilsson, P.; Bernander, R. Three replication origins in Sulfolobus species: Synchronous initiation of chromosome replication and asynchronous termination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 7046–7051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norais, C.; Hawkins, M.; Hartman, A.L.; Eisen, J.A.; Myllykallio, H.; Allers, T. Genetic and physical mapping of DNA replication origins in Haloferax volcanii. PLoS Genet. 2007, 3, e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, N.P.; Dionne, I.; Lundgren, M.; Marsh, V.L.; Bernander, R.; Bell, S.D. Identification of two origins of replication in the single chromosome of the archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus. Cell 2004, 116, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelve, E.A.; Martens-Habbena, W.; Stahl, D.A.; Bernander, R. Mapping of active replication origins in vivo in thaum- and euryarchaeal replicons. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 90, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Wu, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Cai, S.; Xiang, H. Activation of a dormant replication origin is essential for Haloferax mediterranei lacking the primary origins. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, H.; Xiang, H. Multiple replication origins with diverse control mechanisms in Haloarcula hispanica. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 2282–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coker, J.A.; DasSarma, P.; Capes, M.; Wallace, T.; McGarrity, K.; Gessler, R.; Liu, J.; Xiang, H.; Tatusov, R.; Berquist, B.R.; et al. Multiple replication origins of Halobacterium sp. strain NRC-1: Properties of the conserved orc7-dependent oriC1. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 5253–5261. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Samson, R.Y.; Xu, Y.; Gadelha, C.; Stone, T.A.; Faqiri, J.N.; Li, D.; Qin, N.; Pu, F.; Liang, Y.X.; She, Q.; et al. Specificity and function of archaeal DNA replication initiator proteins. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, N.P.; Bell, S.D. Extrachromosomal element capture and the evolution of multiple replication origins in archaeal chromosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5806–5811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelve, E.A.; Lindas, A.C.; Knoppel, A.; Mira, A.; Bernander, R. Four chromosome replication origins in the archaeon Pyrobaculum calidifontis. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 85, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisnier-Patin, S.; Malandrin, L.; Birkeland, N.K.; Bernander, R. Chromosome replication patterns in the hyperthermophilic euryarchaea Archaeoglobus fulgidus and Methanocaldococcus (Methanococcus) jannaschii. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 45, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, C.T. Identification of replication origins in the genome of the methanogenic archaeon, Methanocaldococcus jannaschii. Extremophiles 2004, 8, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, C.T. Single replication origin of the archaeon Methanosarcina mazei revealed by the Z curve method. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 297, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dueber, E.L.; Corn, J.E.; Bell, S.D.; Berger, J.M. Replication origin recognition and deformation by a heterodimeric archaeal Orc1 complex. Science 2007, 317, 1210–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudier, M.; Schuwirth, B.S.; Westcott, S.L.; Wigley, D.B. Structural basis of DNA replication origin recognition by an ORC protein. Science 2007, 317, 1213–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grainge, I.; Gaudier, M.; Schuwirth, B.S.; Westcott, S.L.; Sandall, J.; Atanassova, N.; Wigley, D.B. Biochemical analysis of a DNA replication origin in the archaeon Aeropyrum pernix. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 363, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duggin, I.G.; McCallum, S.A.; Bell, S.D. Chromosome replication dynamics in the archaeon Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16737–16742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capaldi, S.A.; Berger, J.M. Biochemical characterization of Cdc6/Orc1 binding to the replication origin of the euryarchaeon Methanothermobacter thermoautotrophicus. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 4821–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, F.; Takemura, K.; Akita, M.; Adachi, A.; Yamagami, T.; Ishino, Y. Localized melting of duplex DNA by Cdc6/Orc1 at the DNA replication origin in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus. Extremophiles 2010, 14, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dueber, E.C.; Costa, A.; Corn, J.E.; Bell, S.D.; Berger, J.M. Molecular determinants of origin discrimination by Orc1 initiators in archaea. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 3621–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, S.D. Archaeal orc1/cdc6 proteins. Subcell. Biochem. 2012, 62, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Xiang, H. Diversity and evolution of multiple orc/cdc6-adjacent replication origins in haloarchaea. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Xiang, H. Association between the dynamics of multiple replication origins and the evolution of multireplicon genome architecture in haloarchaea. Genome Biol. Evol. 2014, 6, 2799–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartman, A.L.; Norais, C.; Badger, J.H.; Delmas, S.; Haldenby, S.; Madupu, R.; Robinson, J.; Khouri, H.; Ren, Q.; Lowe, T.M.; et al. The complete genome sequence of Haloferax volcanii DS2, a model archaeon. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, F.; Glatigny, A.; Mucchielli-Giorgi, M.H.; Agier, N.; Delacroix, H.; Marisa, L.; Durosay, P.; Ishino, Y.; Aggerbeck, L.; Forterre, P. Genomewide and biochemical analyses of DNA-binding activity of Cdc6/Orc1 and Mcm proteins in Pyrococcus sp. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 3214–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran-Reyna, A.; Coker, J.A. The effects of extremes of pH on the growth and transcriptomic profiles of three haloarchaea. F1000Research 2014, 3, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, J.P.; Hayashi, M.K.; Simon, M.N.; Xu, R.M.; Stillman, B. A double-hexamer archaeal minichromosome maintenance protein is an ATP-dependent DNA helicase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 1530–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grainge, I.; Scaife, S.; Wigley, D.B. Biochemical analysis of components of the pre-replication complex of Archaeoglobus fulgidus. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 4888–4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samson, R.Y.; Abeyrathne, P.D.; Bell, S.D. Mechanism of Archaeal MCM Helicase Recruitment to DNA Replication Origins. Mol. Cell 2016, 61, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akita, M.; Adachi, A.; Takemura, K.; Yamagami, T.; Matsunaga, F.; Ishino, Y. Cdc6/Orc1 from Pyrococcus furiosus may act as the origin recognition protein and Mcm helicase recruiter. Genes Cells 2010, 15, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krupovic, M.; Gribaldo, S.; Bamford, D.H.; Forterre, P. The evolutionary history of archaeal MCM helicases: A case study of vertical evolution combined with hitchhiking of mobile genetic elements. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 2716–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z. Regulation of the cell division cycle in Trypanosoma brucei. Eukaryot. Cell 2012, 11, 1180–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, C.A.; Tiengwe, C.; Lemgruber, L.; Damasceno, J.D.; Scott, A.; Paape, D.; Marcello, L.; McCulloch, R. Diverged composition and regulation of the Trypanosoma brucei origin recognition complex that mediates DNA replication initiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 4763–4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marczynski, G.T.; Rolain, T.; Taylor, J.A. Redefining bacterial origins of replication as centralized information processors. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindas, A.C.; Bernander, R. The cell cycle of archaea. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breuert, S.; Allers, T.; Spohn, G.; Soppa, J. Regulated polyploidy in halophilic archaea. PLoS ONE 2006, 1, e92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildenbrand, C.; Stock, T.; Lange, C.; Rother, M.; Soppa, J. Genome copy numbers and gene conversion in methanogenic archaea. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, S.; Ohbayashi, R.; Kanesaki, Y.; Saito, N.; Chibazakura, T.; Soga, T.; Yoshikawa, H. Intensive DNA Replication and Metabolism during the Lag Phase in Cyanobacteria. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naor, A.; Lapierre, P.; Mevarech, M.; Papke, R.T.; Gophna, U. Low species barriers in halophilic archaea and the formation of recombinant hybrids. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 1444–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, I.J.; Reyes, A. Human mitochondrial DNA replication. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a012971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichler, J.; Maupin-Furlow, J. Post-translation modification in Archaea: Lessons from Haloferax volcanii and other haloarchaea. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 583–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennelly, P.J. Protein Ser/Thr/Tyr phosphorylation in the Archaea. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 9480–9487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkland, P.A.; Gil, M.A.; Karadzic, I.M.; Maupin-Furlow, J.A. Genetic and proteomic analyses of a proteasome-activating nucleotidase A mutant of the haloarchaeon Haloferax volcanii. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Rodriguez, N.; Wong, R.P.; Ulrich, H.D. Functions of Ubiquitin and SUMO in DNA Replication and Replication Stress. Front. Genet. 2016, 7, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humbard, M.A.; Miranda, H.V.; Lim, J.M.; Krause, D.J.; Pritz, J.R.; Zhou, G.; Chen, S.; Wells, L.; Maupin-Furlow, J.A. Ubiquitin-like small archaeal modifier proteins (SAMPs) in Haloferax volcanii. Nature 2010, 463, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gras, S.; Chaumont, V.; Fernandez, B.; Carpentier, P.; Charrier-Savournin, F.; Schmitt, S.; Pineau, C.; Flament, D.; Hecker, A.; Forterre, P.; et al. Structural insights into a new homodimeric self-activated GTPase family. EMBO Rep. 2007, 8, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, E.; Driessen, R.P.; Werner, F.; Dame, R.T. The interplay between nucleoid organization and transcription in archaeal genomes. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, S.D.; Botting, C.H.; Wardleworth, B.N.; Jackson, S.P.; White, M.F. The interaction of Alba, a conserved archaeal chromatin protein, with Sir2 and its regulation by acetylation. Science 2002, 296, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, V.L.; McGeoch, A.T.; Bell, S.D. Influence of chromatin and single strand binding proteins on the activity of an archaeal MCM. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 357, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gristwood, T.; Duggin, I.G.; Wagner, M.; Albers, S.V.; Bell, S.D. The sub-cellular localization of Sulfolobus DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 5487–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Chromosome Size, kb | Number of Origins per Chromosome | |
|---|---|---|
| Haloferax mediterranei | 2949 * | 3 [15] |
| Haloferax volcanii | 2848 * | 3 [10] |
| Haloarcula hispanica | 2995 * | 2 [16] |
| Halobacterium sp. strain NRC-1 | 2014 * | 2 [17] |
| Nitrosopumilus maritimus | 1645 | 1 [14] |
| Sulfolobus islandicus | 2500 | 3 [18] |
| Sulfolobus solfataricus | 2992 | 3 [11,13] |
| Sulfolobus acidocaldarius | 2226 | 3 [11] |
| Aeropyrum pernix | 1670 | 2 [19] |
| Pyrobaculum calidifontis | 2010 | 4 [20] |
| Pyrococcus abyssi | 1770 | 1 [9] |
| Archaeoglobus fulgidus | 2178 | 1 [21] |
| Methanococcus jannaschii | 1660 | 1 ** [22] |
| Methanosarcina mazei | 4096 | 1 ** [23] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ausiannikava, D.; Allers, T. Diversity of DNA Replication in the Archaea. Genes 2017, 8, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8020056
Ausiannikava D, Allers T. Diversity of DNA Replication in the Archaea. Genes. 2017; 8(2):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8020056
Chicago/Turabian StyleAusiannikava, Darya, and Thorsten Allers. 2017. "Diversity of DNA Replication in the Archaea" Genes 8, no. 2: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8020056
APA StyleAusiannikava, D., & Allers, T. (2017). Diversity of DNA Replication in the Archaea. Genes, 8(2), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8020056






