Differential Binding of Three Major Human ADAR Isoforms to Coding and Long Non-Coding Transcripts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmid Construction
- ADAR1-p150-F: 5’-AAAGGGaagcttATGAATCCGCGGCAGGGGTATTCC-3’ (HindIII),
- ADAR1-p110-F: 5’-AAAGGGaagcttATGGCCGAGATCAAGGAGAAAATC-3’ (HindIII),
- ADAR1-R: 5’-AAAGGGtctagaCTATACTGGGCAGAGATAAAAGTTC-3’ (XbaI),
- ADAR2-F: 5’-AAAGGGgaattcATGGATATAGAAGATGAAGAAAACATG-3’ (EcoRI),
- ADAR2-R: 5’-AAAAGGAAAAgcggccgcTCAGGGCGTGAGTGAGAACTGGTC-3’ (NotI).
2.2. Cell Culture and Transfection
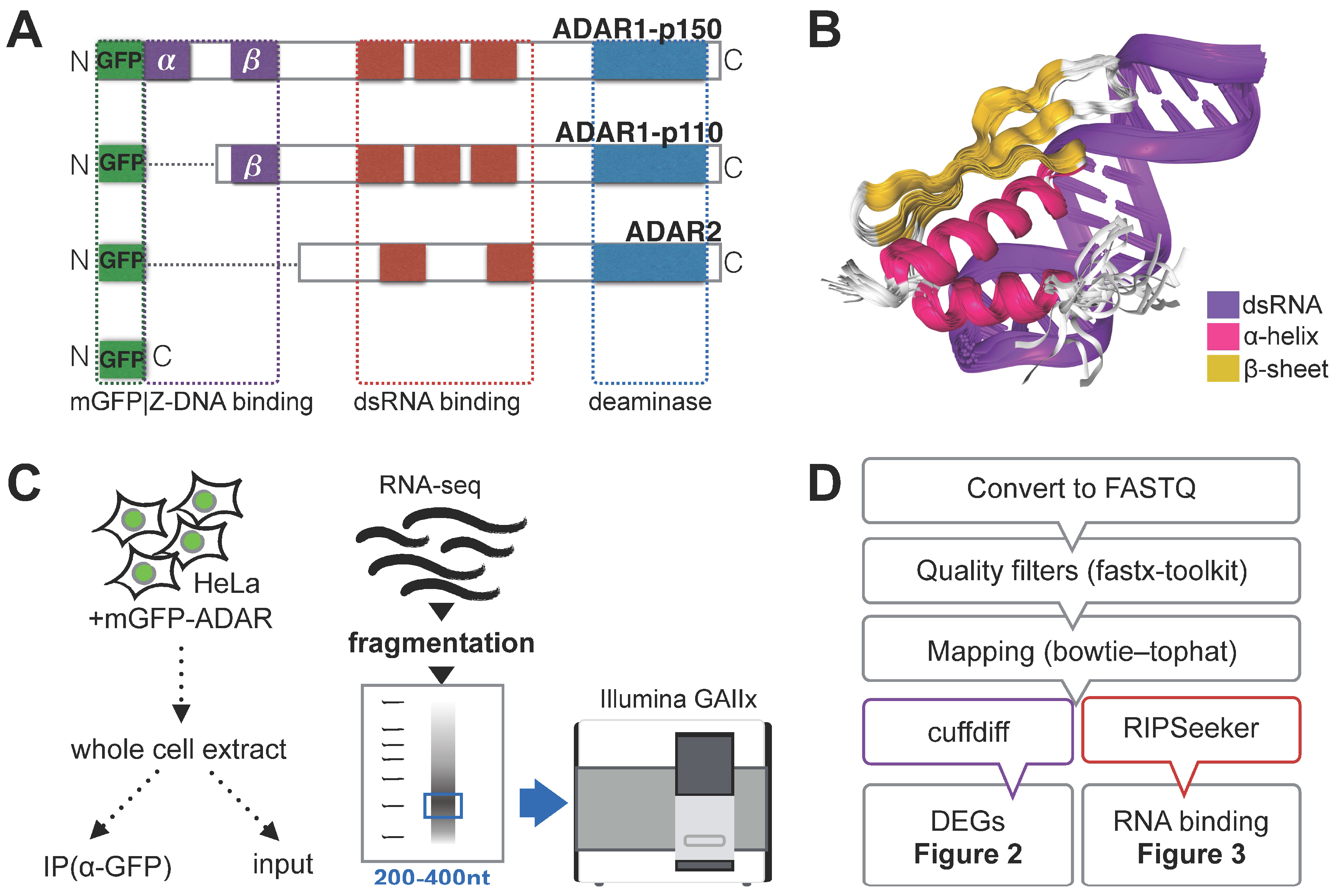
2.3. RNA Immunoprecipitation and Illumina Library Preparation
2.4. DEG Analysis (Tuxedo Pipeline)
tophat -G annotation.gtf --no-novel-juncs --no-novel-indels -N 1 --read-gap-length 0 --read-edit-dist 1 --read-realign-edit-distance 0 --bowtie1 -o ./tophat_output_samplename/ --coverage-search bowtie_index input.fastq
cuffdiff -p 8 -o ./cuffdiff_output_folder -b genome_bowtie.fa -L C2,C4,C6,C7 -u annotation.gtf ./tophat_output_C2/accepted_hits.bam ./tophat_output_C4/accepted_hits.bam ./tophat_output_C6/accepted_hits.bam ./tophat_output_C7/accepted_hits.bam
2.5. Identification of Binding Targets (RIPSeeker)
# read path to BAM fileshg38<-getBSgenome("hg38",masked=F) #load human genome version 38extdata.dir<-system.file("tophat_out", package="RIPSeeker") #set location of tophat outputbamFiles<-list.files(extdata.dir, "\\.bam$", recursive=T, full.names=T) #read filenamesoutDir<-file.path("~/path/to/ripseeker_output") #set location of RIPSeeker outputfile<-bamFiles[1] #set BAM file (replace 1 by number corresponding to desired file)seqOut.file<-ripSeek(bamPath=file, genomeBuild="hg38", uniqueHit=T, assignMultihits=T, rerunWithDisambiguatedMultihits=T, binSize=200, biomart="ensembl", biomaRt_dataset="hsapiens_gene_ensembl", goAnno="org.Hs.eg.db", multicore=F, outDir=outDir) #multicore should always be set to FALSE
2.6. Downstream Functional Analysis of Results
3. Results
3.1. RNA Immunoprecipitation (RIP)-Sequencing Experimental Setup
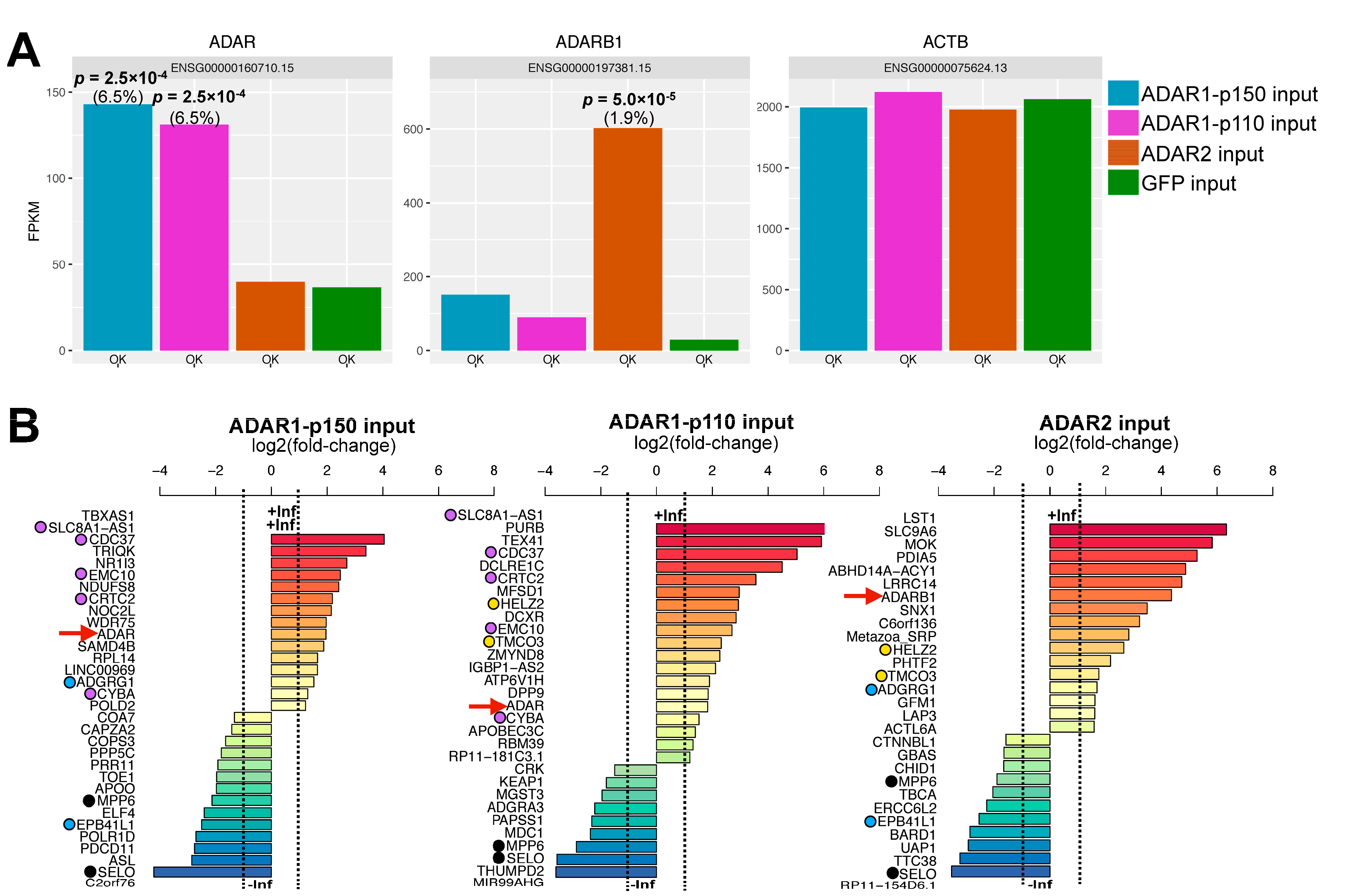
3.2. Effect of ADAR Isoform Overexpression on Global Gene Expression
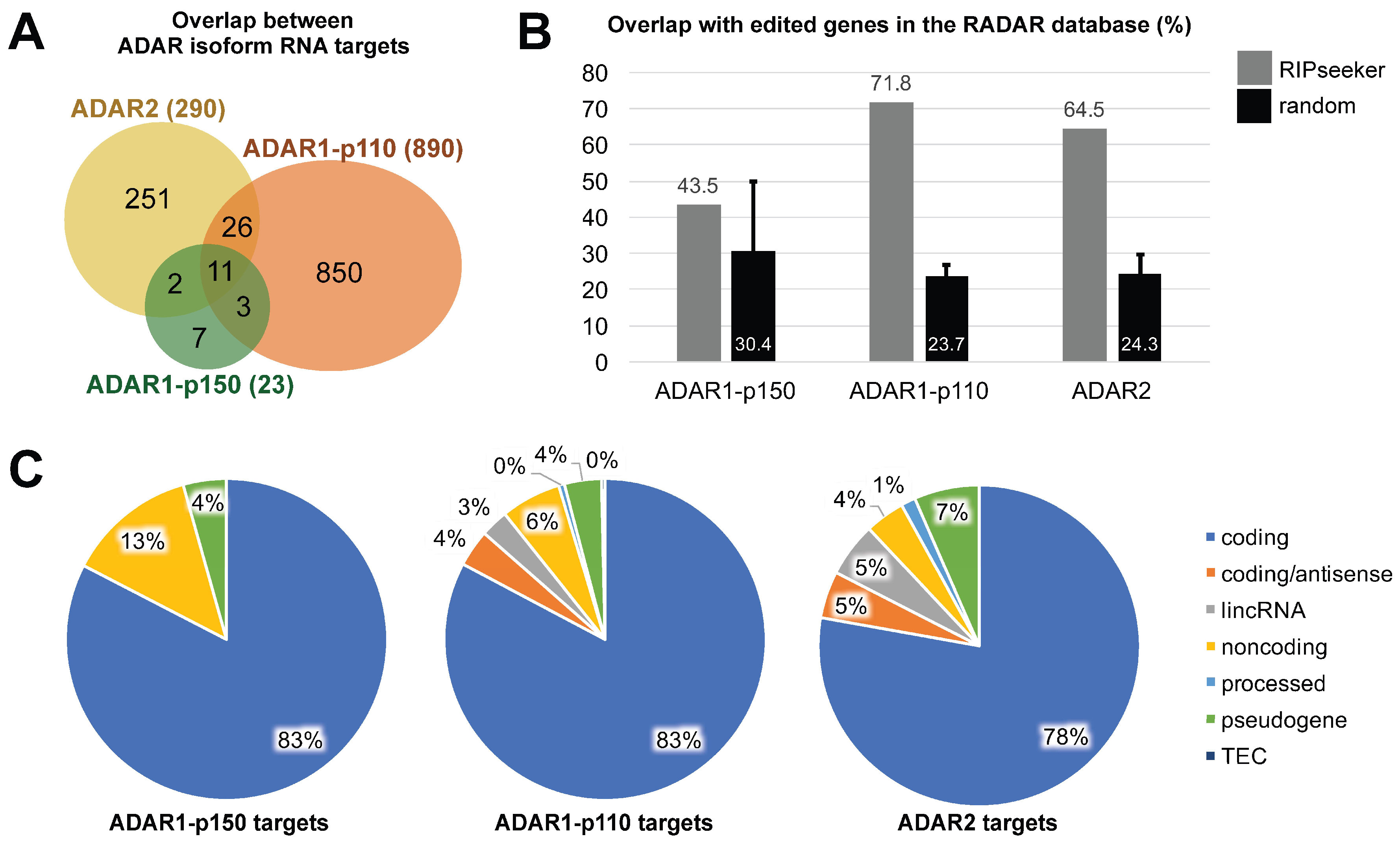
3.3. ADAR Isoforms Bind to Distinct Targets Genome-Wide
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Higuchi, M.; Single, F.N.; Köhler, M.; Sommer, B.; Sprengel, R.; Seeburg, P.H. RNA editing of AMPA receptor subunit GluR-B: A base-paired intron-exon structure determines position and efficiency. Cell 1993, 31, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.X.; Cho, D.S.; Wang, Q.; Lai, F.; Carter, K.C.; Nishikura, K. A third member of the RNA-specific adenosine deaminase gene family, ADAR3, contains both single- and double-stranded RNA binding domains. RNA 2000, 6, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Miyakoda, M.; Yang, W.; Khillan, J.; Stachura, D.L.; Weiss, M.J.; Nishikura, K. Stress-induced apoptosis associated with null mutation of ADAR1 RNA editing deaminase gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 6, 4952–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, M.; Maas, S.; Single, F.N.; Hartner, J.; Rozov, A.; Burnashev, N.; Feldmeyer, D.; Sprengel, R.; Seeburg, P.H. Point mutation in an AMPA receptor gene rescues lethality in mice deficient in the RNA-editing enzyme ADAR2. Nature 2000, 406, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patterson, J.B.; Thomis, D.C.; Hans, S.L.; Samuel, C.E. Mechanism of interferon action: double-stranded RNA-specific adenosine deaminase from human cells is inducible by alpha and gamma interferons. Virology 1995, 210, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crick, F.H. Codon-anticodon pairing: The wobble hypothesis. J. Mol. Biol. 1966, 19, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.B.; Levanon, E.Y.; Yoon, J.-K.; Aach, J.; Xie, B.; Leproust, E.; Zhang, K.; Gao, Y.; Church, G.M. Genome-wide identification of human RNA editing sites by parallel DNA capturing and sequencing. Science 2009, 324, 1210–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikura, K. Functions and regulation of RNA editing by ADAR deaminases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010, 79, 321–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, C.X.; Samuel, C.E. Human RNA-specific adenosine deaminase ADAR1 transcripts possess alternative exon 1 structures that initiate from different promoters, one constitutively active and the other interferon inducible. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 4621–4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.R.; Wilkie, A.M.; Clemens, M.J.; Smith, C.W. Detection of double-stranded RNA-protein interactions by methylene blue-mediated photo-crosslinking. RNA 1996, 2, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nishi, K.; Nishi, A.; Nagasawa, T.; Ui-Tei, K. Human TNRC6A is an Argonaute-navigator protein for microRNA-mediated gene silencing in the nucleus. RNA 2013, 19, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popendorf, K. qseq2fastq. Available online: www.dna.bio.keio.ac.jp/~krisp/qseq2fastq/ (accessed on 6 February 2017).
- Hannon laboratory. Available online: http://hannonlab.cshl.edu/fastx_toolkit/ (accessed on 6 February 2017).
- Trapnell, C.; Roberts, A.; Goff, L.; Pertea, G.; Kim, D.; Kelly, D.R.; Pimentel, H.; Salzberg, S.L.; Rinn, J.L.; Pachter, L. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 562–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Pertea, G.; Trapnell, C.; Pimentel, H.; Kelley, R.; Salzberg, S. TopHat2: Accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2008. Available online: http://www.R-project.org (accessed on 6 February 2017).
- Huber, W.; Carey, V.J.; Gentleman, R.; Anders, S.; Carlson, M.; Carvalho, B.S.; Bravo, H.C.; Davis, S.; Gatto, L.; Girke, T.; et al. Orchestrating high-throughput genomic analysis with Bioconductor. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, D.Y.; Greenblatt, J.F.; Zhang, Z. RIPSeeker: A statistical package for identifying protein-associated transcripts for RIP-seq experiments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D457–D462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, P.D.; Campbell, M.J.; Kejariwal, A.; Mi, H.; Karlak, B.; Daverman, R.; Diemer, K.; Muruganujan, A.; Narechania, A. PANTHER: A library of protein families and subfamilies indexed by function. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2129–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, H.; Dong, Q.; Muruganujan, A.; Gaudet, P.; Lewis, S.; Thomas, P.D. PANTHER version 7: Improved phylogenetic trees, orthologs and collaboration with the Gene Ontology Consortium. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, D204–D210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desterro, J.M.P.; Keegan, L.P.; Lafarga, M.; Berciano, M.T.; O’Connell, M.; Carmo-Fonseca, M. Dynamic association of RNA-editing enzymes with the nucleolus. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 1805–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barraud, P.; Allain, F.H.-T. ADAR proteins: Double-stranded RNA and Z-DNA binding domains. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 353, 35–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.K.; Weissbach, R.; Ronson, G.E.; Schadden, A.D. Proteins that contain a functional Z-DNA-binding domain localize to cytoplasmic stress granules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 9786–9899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, T.; Behike, J.; Lowenhaupt, K.; Heinemann, U.; Rich, A. Structure of the DLM-1-Z-DNA complex reveals a conserved family of Z-DNA-binding proteins. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2001, 8, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cufflinks Manual. Available online: http://cole-trapnell-lab.github.io/cufflinks/cuffdiff/#cross-replicate-dispersion-estimation-methods (accessed on 6 February 2017).
- Samuel, C.E. Adenosine deaminases acting on RNA (ADARs) are both antiviral and proviral dependent upon the virus. Virology 2011, 411, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, D.; Yeomanson, D.; Bryant, H.E. PI3King the Lock: Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy in Neuroblastoma. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 37, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.-Y.; Ye, H.; Han, B.-W.; Wang, W.-T.; Wei, P.-P.; He, B.; Li, X.-J.; Chen, Y.-Q. Genome-wide screen identified let-7c/miR-99a/miR-125b regulating tumor progression and stem-like properties in cholangiocarcinoma. Oncogene 2016, 35, 3376–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anadón, C.; Guil, S.; Simó-Riudalbas, L.; Moutinho, C.; Setien, F.; Martínez-Cardús, A.; Moran, S.; Villanueva, A.; Calaf, M.; Vidal, A.; et al. Gene amplification-associated overexpression of the RNA editing enzyme ADAR1 enhances human lung tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2016, 35, 4407–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarmuz, A.; Chester, A.; Bayliss, J.; Gisbourne, J.; Dunham, I.; Scott, J.; Navaratnam, N. An anthropoid-specific locus of orphan C to U RNA-editing enzymes on chromosome 22. Genomics 2002, 79, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licht, K.; Kapoor, U.; Mayrhofer, E.; Jantsch, M.F. Adenosine to inosine editing frequency controlled by splicing efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6398–6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaswami, G.; Li, J.B. RADAR: A rigorously annotated database of A-to-I editing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D109–D113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.D.Y.; Kim, T.T.Y.; Walsh, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Matise, T.C.; Byske, S.; Gabriel, A. Widespread RNA editing of embedded alu elements in the human transcriptome. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1719–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahn, J.H.; Ahn, J.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Q.; Lee, J.H.; Civelek, M.; Xiao, X. Genomic analysis of ADAR1 binding and its involvement in multiple RNA processing pathways. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germanguz, I.; Shtrichman, R.; Osenberg, S.; Ziskind, A.; Novak, A.; Domev, H.; Laevsky, I.; Jacob-Hirsch, J.; Feiler, Y.; Rechavi, G.; et al. ADAR1 is involved in the regulation of reprogramming human fibroblasts to induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2014, 23, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shtrichman, R.; Germanguz, I.; Mandel, R.; Ziskind, A.; Nahor, I.; Safran, M.; Osenberg, S.; Sherf, O.; Rechavi, G.; Itskovitz-Eldor, J. Altered A-to-I RNA editing in human embryogenesis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Diao, L.; Yu, S.; Xu, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, R.; Yang, Y.; Werner, H.M.; Eterovic, A.K.; Yuan, Y.; et al. The Genomic Landscape and Clinical Relevance of A-to-I RNA Editing in Human Cancers. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene ID | KEGG Name | KEGG ID | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| APPL1 | APPL | K08733 | DCC-interacting protein 13 alpha |
| CTNNB1 | β-catenin | K02105 | Catenin beta 1 |
| RHOA | Rho, Rac/Rho | K04513 | Ras homolog gene family, member A |
| GSK3B | GSK-3β | K03083 | Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta |
| ITGB1 | ITGB | K05719 | integrin beta 1 |
| GNB1 | βγ | K04536 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(T) subunit beta-1 |
| VHL | VHL | K03871 | von Hippel-Lindau disease tumor suppressor |
| MLH1 | hMLH1 | K08734 | DNA mismatch repair protein MutL homolog 1 |
| TGFBR2 | TGFβRII | K04388 | Transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta receptor type 2 |
| MITF | MITF | K09455 | Melanogenesis associated transcription factor |
| RAF1 | Raf | K04366 | RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase |
| TFG | TRK | K09292 | Tyrosine kinase receptor (TRK)-fused gene |
| NCOA4 | RET/PTC | K09289 | Nuclear receptor coactivator 4 |
| NFKB1 | NFκB | K02580 | Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit |
| Bound Isoform | GO Biological Process | Hits | Expected | Fold-Enrichment | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADAR1-p150 | SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane | 4 | 0.09 | 45.99 | 1.34 × 10−2 |
| Viral transcription | 4 | 0.1 | 38.39 | 2.73 × 10−2 | |
| Nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, nonsense-mediated decay | 4 | 0.11 | 36.79 | 3.23 × 10−2 | |
| rRNA processing | 5 | 0.24 | 20.91 | 2.64 × 10−2 | |
| ADAR1-p110 | Nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process | 25 | 6.95 | 3.6 | 6.34 × 10−2 |
| SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane | 15 | 3.39 | 4.43 | 2.21 × 10−2 | |
| Viral life cycle | 33 | 10.59 | 3.12 | 1.63 × 10−4 | |
| Translation | 37 | 16.09 | 2.3 | 3.47 × 10−2 | |
| ADAR2 | No significantly enriched GO biological process | ||||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galipon, J.; Ishii, R.; Suzuki, Y.; Tomita, M.; Ui-Tei, K. Differential Binding of Three Major Human ADAR Isoforms to Coding and Long Non-Coding Transcripts. Genes 2017, 8, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8020068
Galipon J, Ishii R, Suzuki Y, Tomita M, Ui-Tei K. Differential Binding of Three Major Human ADAR Isoforms to Coding and Long Non-Coding Transcripts. Genes. 2017; 8(2):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8020068
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalipon, Josephine, Rintaro Ishii, Yutaka Suzuki, Masaru Tomita, and Kumiko Ui-Tei. 2017. "Differential Binding of Three Major Human ADAR Isoforms to Coding and Long Non-Coding Transcripts" Genes 8, no. 2: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8020068
APA StyleGalipon, J., Ishii, R., Suzuki, Y., Tomita, M., & Ui-Tei, K. (2017). Differential Binding of Three Major Human ADAR Isoforms to Coding and Long Non-Coding Transcripts. Genes, 8(2), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8020068







