MicroRNA-31 and MicroRNA-155 Are Overexpressed in Ulcerative Colitis and Regulate IL-13 Signaling by Targeting Interleukin 13 Receptor α-1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characteristics of Patients
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Epithelial Cell Isolation
2.4. Reverse Transcription and Real-Time PCR
2.5. Cloning and Dual Luciferase Experiments
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Pre-miR Transfections
2.8. Biopsy Explants Culture and Pre-miR Transfection
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
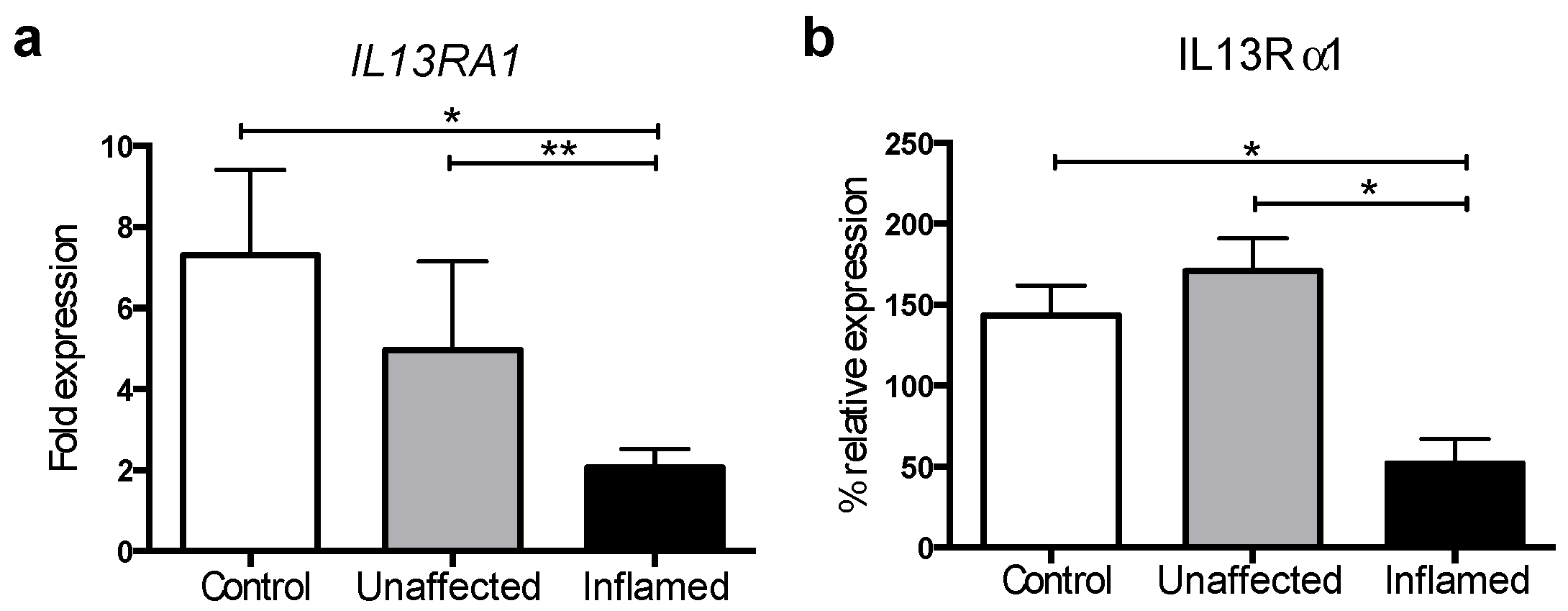
3.1. IL13Rα1 Expression Is Downregulated in Actively Inflamed Ulcerative Colitis
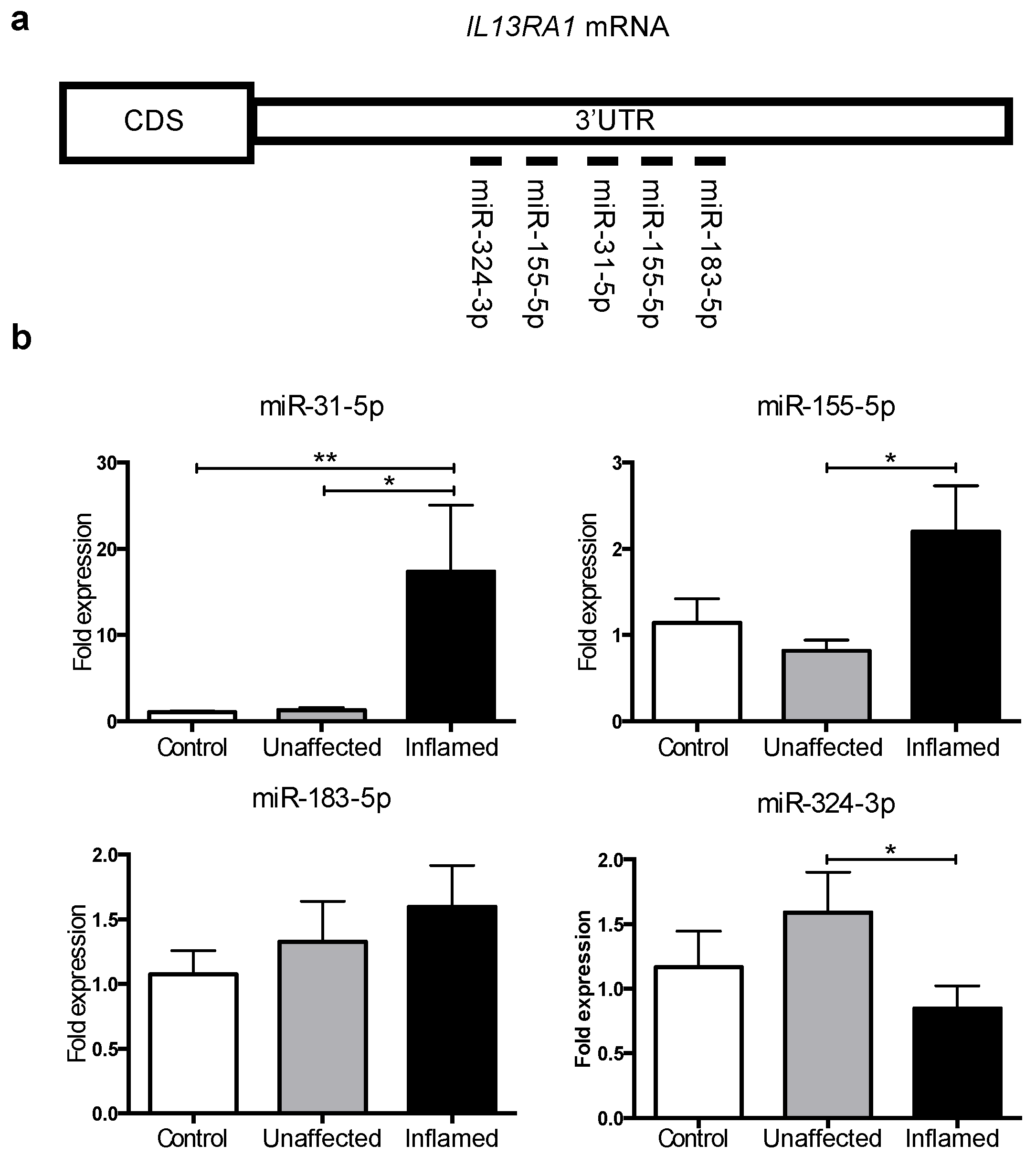
3.2. MicroRNAs -31 and -155 Are Upregulated in Inflamed Tissue from Active UC Patients
3.3. miR-31 Directly Targets IL13RA1 mRNA
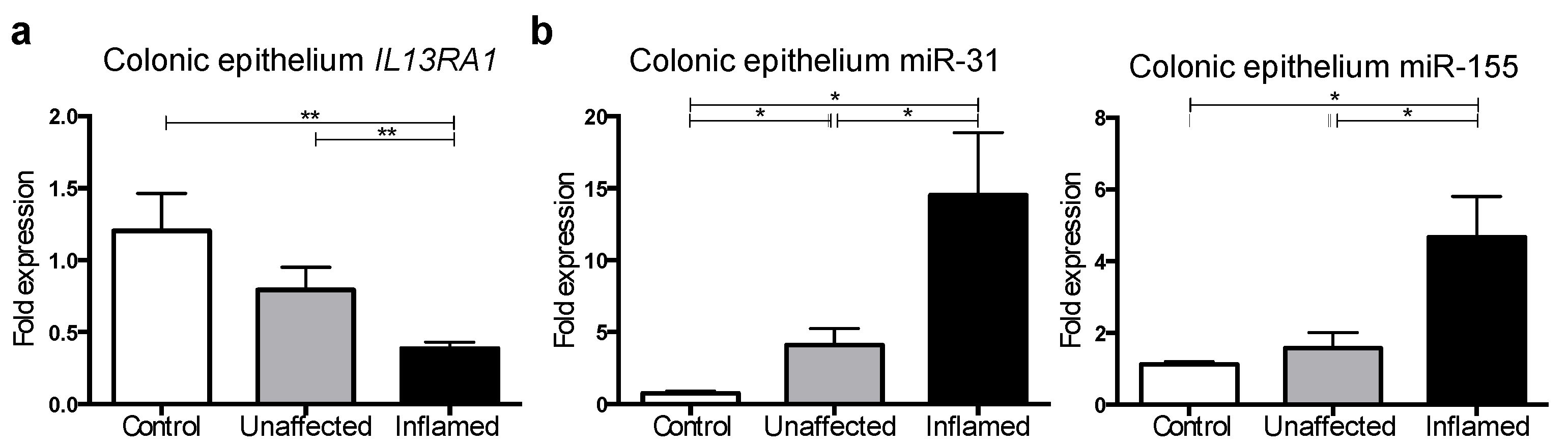
3.4. IL13RA1 Expression Is Reduced in Primary Inflamed Ulcerative Colitis Gut Epithelium with Increased miR-31 and miR-155 Levels
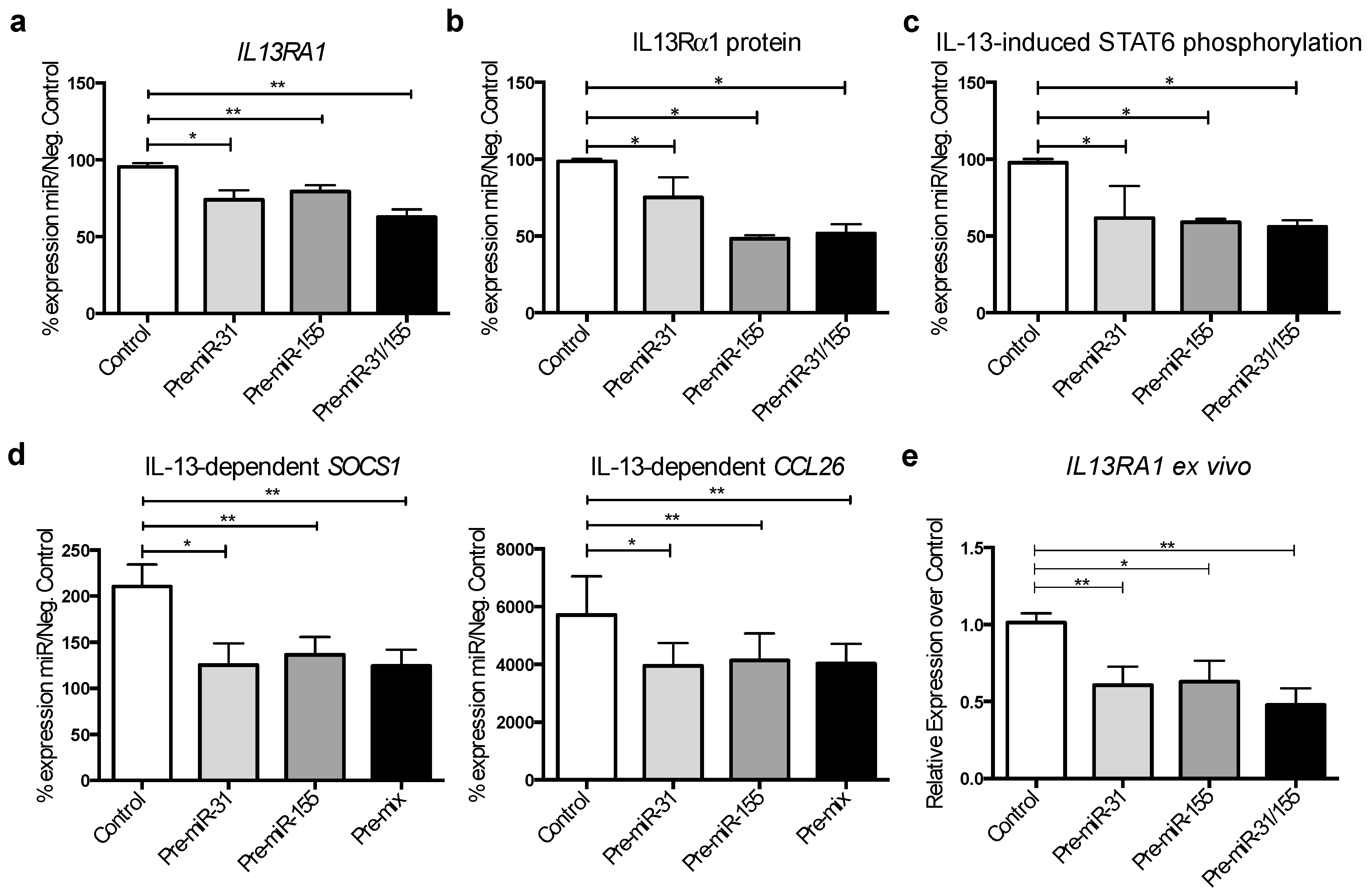
3.5. MicroRNA-31 and miR-155 Reduce IL-13 Signalling by Downregulating IL13Rα1 Expression in Gut Epithelial Cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mannon, P.; Reinisch, W. Interleukin 13 and its role in gut defence and inflammation. Gut 2012, 61, 1765–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, T.A. IL-13 effector functions. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 21, 425–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgart, D.C.; Carding, S.R. Inflammatory bowel disease: Cause and immunobiology. Lancet 2007, 369, 1627–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesen, L.C.; Walsh, A.J.; Protic, M.N.; Heap, G.; Cummings, F.; Warren, B.F.; George, B.; Mortensen, N.J.M.; Travis, S.P.L. The pattern and outcome of acute severe colitis. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2010, 4, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungaro, R.; Mehandru, S.; Allen, P.B.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Colombel, J. Ulcerative colitis. Lancet 2017, 389, 1756–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, C.; Cho, J.H. Inflammatory bowel disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2066–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ueno, A.; Gasia, M.F.; Luider, J.; Wang, T.; Hirota, C.; Jijon, H.B.; Deane, M.; Tom, M.; Chan, R.; et al. Profiles of lamina propria T helper cell subsets discriminate between ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 1779–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vainer, B.; Nielsen, O.H.; Hendel, J.; Horn, T.; Kirman, I. Colonic expression and synthesis of interleukin 13 and interleukin 15 in inflammatory bowel disease. Cytokine 2000, 12, 1531–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, F.; Fromm, A.; Gitter, A.H.; Mankertz, J.; Schulzke, J.-D. Epithelial apoptosis is a prominent feature of the epithelial barrier disturbance in intestinal inflammation: Effect of pro-inflammatory interleukin-13 on epithelial cell function. Mucosal Immunol. 2008, 1, S58–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuss, I.J.; Heller, F.; Boirivant, M.; Leon, F.; Yoshida, M.; Fichtner-Feigl, S.; Yang, Z.; Exley, M.; Kitani, A.; Blumberg, R.S.; et al. Nonclassical CD1d-restricted NK T cells that produce IL-13 characterize an atypical Th2 response in ulcerative colitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 1490–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, F.; Florian, P.; Bojarski, C.; Richter, J.; Christ, M.; Hillenbrand, B.; Mankertz, J.; Gitter, A.H.; Bürgel, N.; Fromm, M.; et al. Interleukin-13 is the key effector Th2 cytokine in ulcerative colitis that affects epithelial tight junctions, apoptosis, and cell restitution. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 550–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, S.; Mingrino, R.; Kaukinen, K.; Hayes, K.L.; Powell, R.M.; MacDonald, T.T.; Collins, J.E. Inflammatory processes have differential effects on claudins 2, 3 and 4 in colonic epithelial cells. Lab. Investig. 2005, 85, 1139–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hershey, G.K. IL-13 receptors and signaling pathways: An evolving web. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 677–690; quiz 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Nunez, R.T.; Louafi, F.; Sanchez-Elsner, T. The interleukin 13 (IL-13) pathway in human macrophages is modulated by microRNA-155 via direct targeting of interleukin 13 receptor α1 (IL13Rα1). J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 1786–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Garcia, I.; Miska, E.A. MicroRNA functions in animal development and human disease. Development 2005, 132, 4653–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, C.G.; Pekow, J. The emerging role of miRNAs in inflammatory bowel disease: A review. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2015, 8, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coskun, M.; Bjerrum, J.T.; Seidelin, J.B.; Nielsen, O.H. MicroRNAs in inflammatory bowel disease—pathogenesis, diagnostics and therapeutics. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 4629–4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, K.; Lin, J. MicroRNA in inflammatory bowel disease: Translational research and clinical implication. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 12274–12282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, J.S.; Attumi, T.; Opekun, A.R.; Abraham, B.; Hou, J.; Shelby, H.; Graham, D.Y.; Streckfus, C.; Klein, J.R. MicroRNA signatures differentiate Crohn’s disease from ulcerative colitis. BMC Immunol. 2015, 16, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteoak, S.R.; Felwick, R.; Sanchez-Elsner, T.; Cummings, J.R.F. MicroRNAs in inflammatory bowel diseases: Paradoxes and possibilities. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Zhang, S.; Dassopoulos, T.; Harris, M.L.; Bayless, T.M.; Meltzer, S.J.; Brant, S.R.; Kwon, J.H. Identification of microRNAs associated with Ileal and colonic Crohn’s disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2010, 16, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Zikusoka, M.; Trindade, A.; Dassopoulos, T.; Harris, M.L.; Bayless, T.M.; Brant, S.R.; Chakravarti, S.; Kwon, J.H. MicroRNAs are differentially expressed in ulcerative colitis and alter expression of macrophage inflammatory peptide-2α. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 1624–1635.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, V.; Varum, F.; Bravo, R.; Furrer, E.; Bojic, D.; Basit, A.W. Inflammatory bowel disease: Exploring gut pathophysiology for novel therapeutic targets. Transl. Res. 2016, 176, 38–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Cheng, J.; Fan, X.M. MicroRNAs: New therapeutic targets for intestinal barrier dysfunction. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 5818–5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Fan, X.M. The pathological role of microRNAs and inflammation in colon carcinogenesis. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2015, 39, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, V.; Bell, G.W.; Nam, J.; Bartel, D.P. Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. Elife 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olaru, A.V.; Selaru, F.M.; Mori, Y.; Vazquez, C.; David, S.; Paun, B.; Cheng, Y.; Jin, Z.; Yang, J.; Agarwal, R.; et al. Dynamic changes in the expression of microRNA-31 during inflammatory bowel disease-associated neoplastic transformation. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, T.; Naito, Y.; Mizushima, K.; Hirata, I.; Yagi, N.; Tomatsuri, N.; Ando, T.; Oyamada, Y.; Isozaki, Y.; Hongo, H.; et al. Increased expression of microRNA in the inflamed colonic mucosa of patients with active ulcerative colitis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 25, S129–S133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasseu, M.; Tréton, X.; Guichard, C.; Pedruzzi, E.; Cazals-Hatem, D.; Richard, C.; Aparicio, T.; Daniel, F.; Soulé, J.; Moreau, R.; et al. Identification of restricted subsets of mature microRNA abnormally expressed in inactive colonic mucosa of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, L.W.; Artis, D. Intestinal epithelial cells: Regulators of barrier function and immune homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biton, M.; Levin, A.; Slyper, M.; Alkalay, I.; Horwitz, E.; Mor, H.; Kredo-Russo, S.; Avnit-Sagi, T.; Cojocaru, G.; Zreik, F.; et al. Epithelial microRNAs regulate gut mucosal immunity via epithelium-T cell crosstalk. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Thai, T.; Calado, D.P.; Chaudhry, A.; Kubo, M.; Tanaka, K.; Loeb, G.B.; Lee, H.; Yoshimura, A.; Rajewsky, K.; et al. Foxp3-dependent microRNA155 confers competitive fitness to regulatory T cells by targeting SOCS1 protein. Immunity 2009, 30, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liu, C.; Zhou, L.; Wang, H.; Zhuang, W.; Huang, Y.; Hong, Z. miR-143 inhibits interleukin-13-induced inflammatory cytokine and mucus production in nasal epithelial cells from allergic rhinitis patients by targeting IL13Rα1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 457, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karo-Atar, D.; Bordowitz, A.; Wand, O.; Pasmanik-Chor, M.; Fernandez, I.E.; Itan, M.; Frenkel, R.; Herbert, D.R.; Finkelman, F.D.; Eickelberg, O.; et al. A protective role for IL-13 receptor α 1 in bleomycin-induced pulmonary injury and repair. Mucosal Immunol. 2016, 9, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christophi, G.P.; Rong, R.; Holtzapple, P.G.; Massa, P.T.; Landas, S.K. Immune markers and differential signaling networks in ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2012, 18, 2342–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manousou, P.; Kolios, G.; Valatas, V.; Drygiannakis, I.; Bourikas, L.; Pyrovolaki, K.; Koutroubakis, I.; Papadaki, H.A.; Kouroumalis, E. Increased expression of chemokine receptor CCR3 and its ligands in ulcerative colitis: The role of colonic epithelial cells in in vitro studies. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2010, 162, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danese, S.; Rudziński, J.; Brandt, W.; Dupas, J.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Bouhnik, Y.; Kleczkowski, D.; Uebel, P.; Lukas, M.; Knutsson, M.; et al. Tralokinumab for moderate-to-severe UC: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase IIa study. Gut 2015, 64, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinisch, W.; Panés, J.; Khurana, S.; Toth, G.; Hua, F.; Comer, G.M.; Hinz, M.; Page, K.; O’Toole, M.; Moorehead, T.M.; et al. Anrukinzumab, an anti-interleukin 13 monoclonal antibody, in active UC: Efficacy and safety from a phase IIa randomised multicentre study. Gut 2015, 64, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Kaser, A. Failure of interleukin 13 blockade in ulcerative colitis. Gut 2015, 64, 857–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoving, J.C.; Cutler, A.J.; Leeto, M.; Horsnell, W.G.C.; Dewals, B.G.; Nieuwenhuizen, N.E.; Brombacher, F. Interleukin 13-mediated colitis in the absence of IL-4Rα signalling. Gut 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, T.; Noguchi, P.D.; Puri, R.K. IL-13 induces phosphorylation and activation of JAK2 Janus kinase in human colon carcinoma cell lines: Similarities between IL-4 and IL-13 signaling. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 2972–2978. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sandborn, W.J.; Su, C.; Sands, B.E.; D’Haens, G.R.; Vermeire, S.; Schreiber, S.; Danese, S.; Feagan, B.G.; Reinisch, W.; Niezychowski, W.; et al. Tofacitinib as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1723–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Active ulcerative Colitis (UC) (n = 11) | Normal Colon (n = 11) | |
|---|---|---|
| Average age (years) | 47.3 (range 22–85) | 56.1 (range 46–78) |
| Sex | Male 6; Female 5 | Male 6; Female 5 |
| Duration of disease; Mean (range) | 10.0 years (1–34) | n/a |
| Extent of disease | Left sided colitis 6; Distal colitis 5 | n/a |
| Mayo score; Mean (St. dev.) | Clinical 7.55 (2.12); Endoscopic 2.73 (0.47) | 0 |
| 5-ASA | 6 | n/a |
| Thiopurines | 3 (2 also on 5-ASA) | n/a |
| Infliximab/Adilumimab | 1 (also on 5-ASA) | n/a |
| No medication | 3 | n/a |
| UC Inactive (n = 6) | UC Active (n = 6) | |
|---|---|---|
| Average age (years) | 42.3 (range 23–69) | 40.1 (range 20–72) |
| Sex | Male: 3/Female: 3 | Male: 3/Female: 3 |
| Duration of disease; Mean (range) | 12.6 years (1–36) | 14.4 years (1–31) |
| Extent of disease | Left sided colitis 5; Distal colitis 1 | Pan-colitis 3; Left sided colitis 3 |
| Mayo score; Mean (St. dev.) | 0.5 | 2.5 |
| 5-ASA | 2 | 2(6) |
| Thiopurines | 2 (2 also on 5-ASA) | 2 (2 also on 5-ASA) |
| No medication | 3 | 3 |
| UC Inactive (n = 5) | UC Active (n = 5) | |
|---|---|---|
| Average age (years) | 39.3 (range 23–71) | 42.1 (range 21–67) |
| Sex | Male: 3/Female: 2 | Male: 2/Female: 3 |
| Duration of disease; Mean (range) | 10.6 years (1–34) | 12.2 years (1–41) |
| Extent of disease | Left sided colitis 4; Distal colitis 1 | Pan-colitis 3; Left sided colitis 2 |
| Mayo score; Mean (St. dev.) | 0.4 (0.5) | 2.6 (0.5) |
| 5-ASA | 2 | 2 |
| Thiopurines | 1 (1 also on 5-ASA) | 1 (1 also on 5-ASA) |
| No medication | 2 | 2 |
| Active UC (n = 7) | |
|---|---|
| Average age (years) | 47.3 (range 20.2) |
| Sex | Male: 4/Female: 3 |
| Duration of disease; Mean (range) | Years 11.6 (range 10.6) |
| Extent of disease | Left sided colitis 3/Pancolitis 4 |
| Mayo score; Mean (St. dev.) | Clinical 7.88 (2.12); Endoscopic 2.64 (0.47) |
| 5-ASA | 3 (7) |
| Azathioprine/6-Mercapropurin | 2 (7) (2 also on 5-ASA) |
| Infliximab/Adilumimab | 0 (7) |
| No medication | 2 (7) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gwiggner, M.; Martinez-Nunez, R.T.; Whiteoak, S.R.; Bondanese, V.P.; Claridge, A.; Collins, J.E.; Cummings, J.R.F.; Sanchez-Elsner, T. MicroRNA-31 and MicroRNA-155 Are Overexpressed in Ulcerative Colitis and Regulate IL-13 Signaling by Targeting Interleukin 13 Receptor α-1. Genes 2018, 9, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9020085
Gwiggner M, Martinez-Nunez RT, Whiteoak SR, Bondanese VP, Claridge A, Collins JE, Cummings JRF, Sanchez-Elsner T. MicroRNA-31 and MicroRNA-155 Are Overexpressed in Ulcerative Colitis and Regulate IL-13 Signaling by Targeting Interleukin 13 Receptor α-1. Genes. 2018; 9(2):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9020085
Chicago/Turabian StyleGwiggner, Markus, Rocio T. Martinez-Nunez, Simon R. Whiteoak, Victor P. Bondanese, Andy Claridge, Jane E. Collins, J. R. Fraser Cummings, and Tilman Sanchez-Elsner. 2018. "MicroRNA-31 and MicroRNA-155 Are Overexpressed in Ulcerative Colitis and Regulate IL-13 Signaling by Targeting Interleukin 13 Receptor α-1" Genes 9, no. 2: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9020085
APA StyleGwiggner, M., Martinez-Nunez, R. T., Whiteoak, S. R., Bondanese, V. P., Claridge, A., Collins, J. E., Cummings, J. R. F., & Sanchez-Elsner, T. (2018). MicroRNA-31 and MicroRNA-155 Are Overexpressed in Ulcerative Colitis and Regulate IL-13 Signaling by Targeting Interleukin 13 Receptor α-1. Genes, 9(2), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9020085






