Tissue Specificity and Dynamics of Sex-Biased Gene Expression in a Common Frog Population with Differentiated, Yet Homomorphic, Sex Chromosomes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Sampling and Rearing Conditions
2.2. Genotyping
2.3. Phenotypic Sex
2.4. RNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.5. De Novo Transcriptome Assembly and Assigning Transcripts to Chromosomes
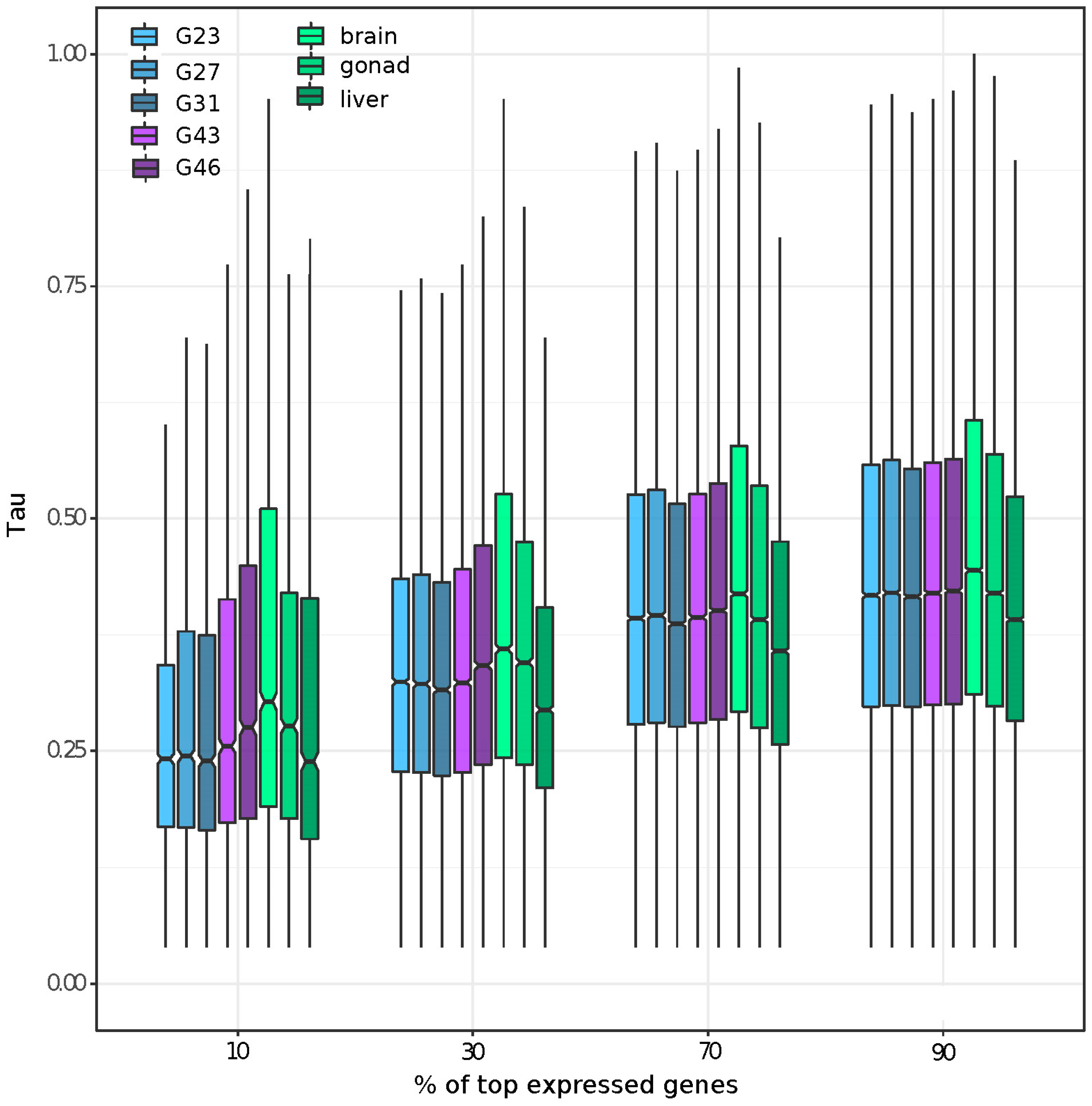
2.6. Tissue Specificity and Tissue-Specific Gene Expression
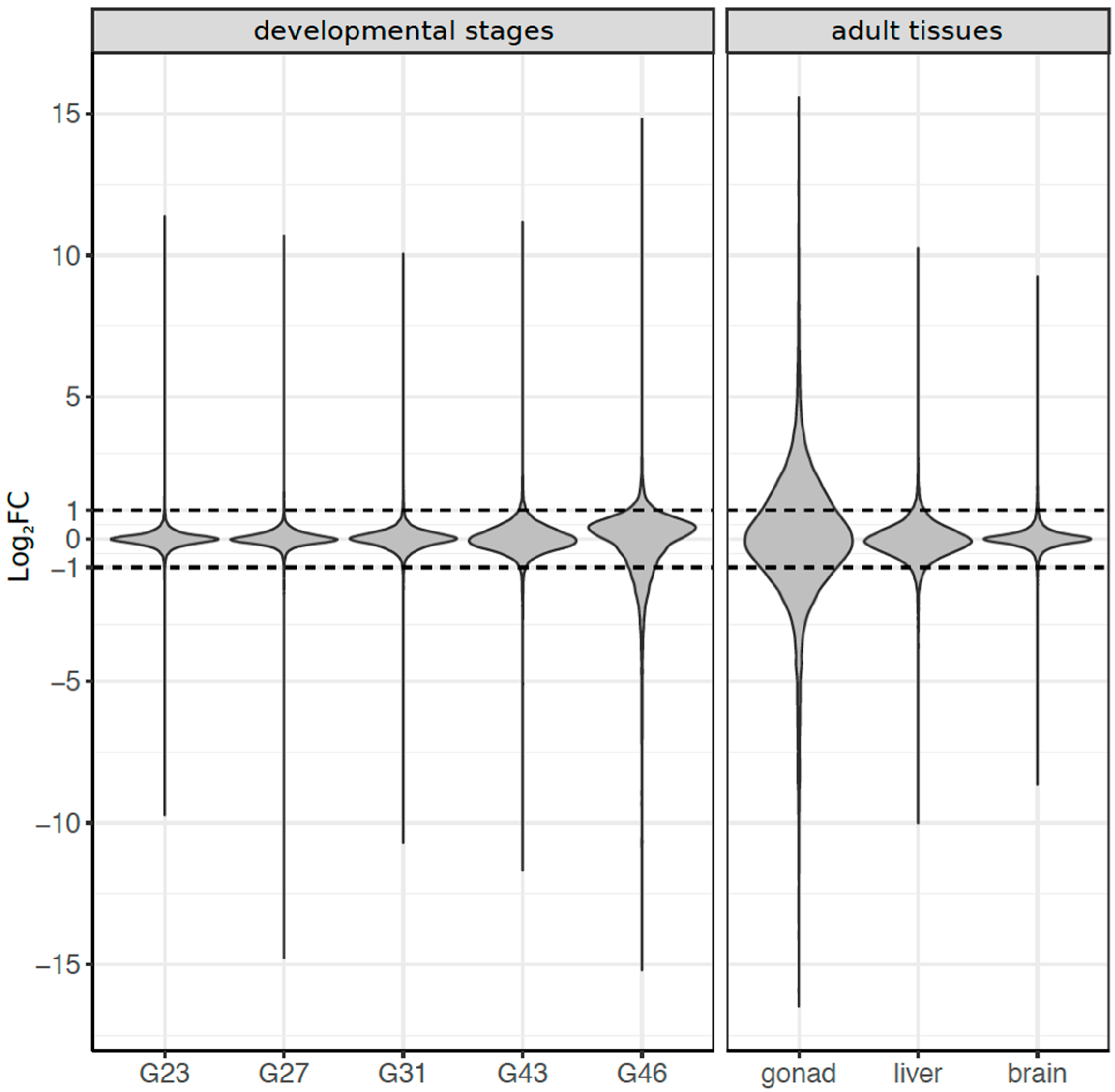
2.7. Sex-Biased Gene Expression Analysis
2.8. Tests for Enrichment of Sex Chromosomes in Sex-Biased Expression
2.9. Faster-XY Evolution
3. Results
3.1. De Novo Transcriptome Assembly
3.2. Gene Expression and Tissue-Specific Expression among Eight Stages/Tissues
3.3. Dynamics of Sex-Biased Gene Expression across Stages/Tissues and Chromosomes
3.4. Coding Sequence Evolution of Sex-Biased Genes
3.5. Tissue or Stage Specificity Is Highly Correlated with Sex-Biased Gene Expression and Rate of Evolution
4. Discussion
4.1. Gene Expression across Multiple Tissues and Tissue Specific Expression
4.2. Dynamics of Sex-Biased Gene Expression across Tissues and Chromosomes
4.3. Signature of Selection on Sex-Biased Genes and Sex Linked Genes
4.4. Rate of Evolution, Tissue Specificity, and Sex Bias
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Founding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Availability of Data and Materials
References
- Perry, J.C.; Harrison, P.W.; Mank, J. The ontogeny and evolution of sex-biased gene expression in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 1206–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellegren, H.; Parsch, J. The evolution of sex-biased genes and sex-biased gene expression. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mank, J.E.; Nam, K.; Brunström, B.; Ellegren, H. Ontogenetic complexity of sexual dimorphism and sex-specific selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 1570–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pointer, M.A.; Harrison, P.W.; Wright, A.E.; Mank, J.E. Masculinization of gene expression is associated with exaggeration of male sexual dimorphism. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutter, A.D.; Ward, S. Sexual and temporal dynamics of molecular evolution in C. elegans development. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mank, J.E.; Hultin-Rosenberg, L.; Axelsson, E.; Ellegren, H. Rapid evolution of female-biased, but not male-biased, genes expressed in the avian brain. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 2698–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranz, J.M.; Castillo-Davis, C.I.; Meiklejohn, C.D.; Hartl, D.L. Sex-dependent gene expression and evolution of the Drosophila transcriptome. Science 2003, 300, 1742–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graveley, B.R.; Brooks, A.N.; Carlson, J.W.; Duff, M.O.; Landolin, J.M.; Yang, L.; Artieri, C.G.; van Baren, M.J.; Boley, N.; Booth, B.W.; et al. The developmental transcriptome of Drosophila melanogaster. Nature 2011, 471, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leder, E.H.; Cano, J.M.; Leinonen, T.; O’Hara, R.B.; Nikinmaa, M.; Primmer, C.R.; Merilä, J. Female-biased expression on the X chromosome as a key step in sex chromosome evolution in threespine sticklebacks. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 1495–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khil, P.P.; Smirnova, N.A.; Romanienko, P.J.; Camerini-Otero, R.D. The mouse X chromosome is enriched for sex-biased genes not subject to selection by meiotic sex chromosome inactivation. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnusson, K.; Mendes, A.M.; Windbichler, N.; Papathanos, P.A.; Nolan, T.; Dottorini, T.; Rizzi, E.; Christophides, G.K.; Crisanti, A. Transcription regulation of sex-biased genes during ontogeny in the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Schadt, E.E.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Arnold, A.P.; Ingram-Drake, L.; Drake, T.A.; Lusis, A.J. Tissue-specific expression and regulation of sexually dimorphic genes in mice. Genome Res. 2006, 16, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harrison, P.W.; Wright, A.E.; Zimmer, F.; Dean, R.; Montgomery, S.H.; Pointer, M.A.; Mank, J.E. Sexual selection drives evolution and rapid turnover of male gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4393–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meisel, R.P. Towards a more nuanced understanding of the relationship between sex-biased gene expression and rates of protein-coding sequence evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 1893–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachtrog, D.; Hom, E.; Wong, K.M.; Maside, X.; de Jong, P. Genomic degradation of a young Y chromosome in Drosophila miranda. Genome Biol. 2008, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, M.; Nuttall, R.; Edwards, P.; Minor, J.; Naiman, D.; Lü, J.; Doctolero, M.; Vainer, M.; Chan, C.; Malley, J.; et al. A survey of ovary-, testis-, and soma-biased gene expression in Drosophila melanogaster adults. Genome Biol. 2004, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Assis, R.; Zhou, Q.; Bachtrog, D. Sex-biased transcriptome evolution in Drosophila. Genome Biol. Evol. 2012, 4, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grath, S.; Parsch, J. Sex-biased gene expression. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2016, 50, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaitovich, P.; Enard, W.; Lachmann, M.; Pääbo, S. Evolution of primate gene expression. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 7, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mank, J.E.; Hultin-Rosenberg, L.; Zwahlen, M.; Ellegren, H. Pleiotropic constraint hampers the resolution of sexual antagonism in vertebrate gene expression. Am. Nat. 2008, 171, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingleby, F.C.; Flis, I.; Morrow, E.H. Sex-biased gene expression and sexual conflict throughout development. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.-J.; Veltsos, P.; Sermier, R.; Parker, D.J.; Perrin, N. Sex-biased gene expression and sexual conflict throughout development in a common frog population with proto-Y chromosome. Genome Biol. under review.
- Meiklejohn, C.D.; Parsch, J.; Ranz, J.M.; Hartl, D.L. Rapid evolution of male-biased gene expression in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9894–9899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pröschel, M.; Zhang, Z.; Parsch, J. Widespread adaptive evolution of Drosophila genes with sex-biased expression. Genetics 2006, 174, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Sturgill, D.; Parisi, M.; Kumar, S.; Oliver, B. Constraint and turnover in sex-biased gene expression in the genus Drosophila. Nature 2007, 450, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baines, J.F.; Sawyer, S.A.; Hartl, D.L.; Parsch, J. Effects of X-linkage and sex-biased gene expression on the rate of adaptive protein evolution in Drosophila. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1639–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Hambuch, T.M.; Parsch, J. Molecular evolution of sex-biased genes in Drosophila. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 21, 2130–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittle, C.A.; Johannesson, H. Evolutionary dynamics of sex-biased genes in a hermaphrodite fungus. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2435–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, F.; Windbichler, N.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Cagnetti, A.; D’Amato, R.; Persampieri, T.; Lawniczak, M.K.N.; Nolan, T.; Papathanos, P.A. Rapid evolution of female-biased genes among four species of Anopheles malaria mosquitoes. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 1536–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittle, C.A.; Extavour, C.G. Rapid evolution of ovarian-biased genes in the yellow fever mosquito (Aedes aegypti). Genetics 2017, 206, 2119–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, M.; Villalta, J.E.; Eisen, M.B.; Lott, S.E. Sex bias and maternal contribution to gene expression divergence in Drosophila blastoderm embryos. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgkin, J. Seven types of pleiotropy. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 1998, 42, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stern, D.L.; Orgogozo, V. The loci of evolution: How predictable is genetic evolution? Evolution 2008, 62, 2155–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, I.; Benjamin, H.; Shmoish, M.; Chalifa-Caspi, V.; Shklar, M.; Ophir, R.; Bar-Even, A.; Horn-Saban, S.; Safran, M.; Domany, E.; et al. Genome-wide midrange transcription profiles reveal expression level relationships in human tissue specification. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kryuchkova-Mostacci, N.; Robinson-Rechavi, M. A benchmark of gene expression tissue-specificity metrics. Brief. Bioinform. 2017, 18, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mank, J.E.; Hultin-Rosenberg, L.; Webster, M.T.; Ellegren, H. The unique genomic properties of sex-biased genes: Insights from avian microarray data. BMC Genom. 2008, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlesworth, B. The evolution of sex chromosomes. Science 1991, 251, 1030–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicoso, B.; Charlesworth, B. Effective population size and the faster-X effect: An extended model. Evolution 2009, 63, 2413–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connallon, T.; Clark, A.G. Sex linkage, sex-specific selection, and the role of recombination in the evolution of sexually dimorphic gene expression. Evolution 2010, 64, 3417–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mank, J.E. The W, X, Y and Z of sex-chromosome dosage compensation. Trends Genet. 2009, 25, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pollack, J.R.; Sørlie, T.; Perou, C.M.; Rees, C.A.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Lonning, P.E.; Tibshirani, R.; Botstein, D.; Børresen-Dale, A.L.; Brown, P.O. Microarray analysis reveals a major direct role of DNA copy number alteration in the transcriptional program of human breast tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12963–12968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Birchler, J.A.; Riddle, N.C.; Auger, D.L.; Veitia, R.A. Dosage balance in gene regulation: Biological implications. Trends Genet. 2005, 21, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, E.M.; Sokolsky, T.; Tucker, C.M.; Chan, L.Y.; Boselli, M.; Dunham, M.J.; Amon, A. Effects of aneuploidy on cellular physiology and cell division in haploid yeast. Science 2007, 317, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mank, J.E. Sex chromosome dosage compensation: Definitely not for everyone. Trends Genet. 2013, 29, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K.; Makino, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Shigenobu, S.; Hasebe, M.; Kawata, M.; Kume, M.; Mori, S.; Peichel, C.L.; Toyoda, A.; et al. Sex chromosome turnover contributes to genomic divergence between incipient stickleback species. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturgill, D.; Zhang, Y.; Parisi, M.; Oliver, B. Demasculinization of X chromosomes in the Drosophila genus. Nature 2007, 450, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, N.; Vuille, Y.; Loman, J.; Perrin, N. Sex-chromosome differentiation and ‘sex races’ in the common frog (Rana temporaria). Proc. Biol. Sci. 2015, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, M.; Steinlein, C. Sex chromosomes, sex-linked genes, and sex determination in the vertebrate class amphibia. EXS 2001, 91, 143–176. [Google Scholar]
- Spasić-Bošković, O.; Tanić, N.; Blagojević, J.; Vujošević, M. Comparative cytogenetic analysis of European brown frogs: Rana temporaria, R. dalmatina and R. graeca. Caryologia 1997, 50, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teacher, A.G.; Garner, T.W.; Nichols, R.A. European phylogeography of the common frog (Rana temporaria): Routes of postglacial colonization into the British Isles, and evidence for an Irish glacial refugium. Heredity 2009, 102, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brelsford, A.; Rodrigues, N.; Perrin, N. High-density linkage maps fail to detect any genetic component to sex determination in a Rana temporaria family. J. Evol. Biol. 2016, 29, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.J.; Rodrigues, N.; Sermier, R.; Brelsford, A.; Perrin, N. Dmrt1 polymorphism covaries with sex-determination patterns in Rana temporaria. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 5107–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toups, M.; Rodrigues, N.; Perrin, N.; Kirkpatrick, M. A chromosome translocation radically reshapes sex-linked inheritance in the common frog. Curr. Biol. under review.
- Gosner, K.L. A simplified table for staging anuran embryos and larvae with notes on identification. Herpetologica 1960, 16, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Ogielska, M.; Kotusz, A. Pattern and rate of ovary differentiation with reference to somatic development in anuran amphibians. J. Morphol. 2004, 259, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haczkiewicz, K.; Ogielska, M. Gonadal sex differentiation in frogs: How testes become shorter than ovaries. Zool. Sci. 2013, 30, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, B.J.; Papanicolaou, A.; Yassour, M.; Grabherr, M.; Blood, P.D.; Bowden, J.; Couger, M.B.; Eccles, D.; Li, B.; Lieber, M.; et al. De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1494–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smit, A.F.A.; Hubley, R.; Green, P. RepeatMasker Open-4.0. 2013–2015. Available online: http://www.repeatmasker.org (accessed on 24 April 2018).
- Brelsford, A.; Stöck, M.; Betto-Colliard, C.; Dubey, S.; Dufresnes, C.; Jourdan-Pineau, H.; Rodrigues, N.; Savary, R.; Sermier, R.; Perrin, N. Homologous sex chromosomes in three deeply divergent anuran species. Evolution 2013, 67, 2434–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brelsford, A.; Dufresnes, C.; Perrin, N. High-density sex-specific linkage maps of a European tree frog (Hyla arborea) identify the sex chromosome without information on offspring sex. Heredity 2016, 116, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.B.; Xiong, Z.J.; Xiang, X.Y.; Liu, S.P.; Zhou, W.W.; Tu, X.L.; Zhong, L.; Wang, L.; Wu, D.D.; Zhang, B.L.; et al. Whole-genome sequence of the tibetan frog Nanorana parkeri and the comparative evolution of tetrapod genomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1257–E1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellsten, U.; Harland, R.M.; Gilchrist, M.J.; Hendrix, D.; Jurka, J.; Kapitonov, V.; Ovcharenko, I.; Putnam, N.H.; Shu, S.; Taher, L.; et al. The genome of the Western clawed frog Xenopus tropicalis. Science 2010, 328, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Horikoshi, M.; Li, W. ggfortify: Unified interface to visualize statistical result of popular R packages. R J. 2016, 8, 474–485. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, N.L.; Pimentel, H.; Melsted, P.; Pachter, L. Near-optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; Oshlack, A. A scaling normalization method for differential expression analysis of RNA-seq data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montgomery, S.H.; Mank, J.E. Inferring regulatory change from gene expression: The confounding effects of tissue scaling. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 5114–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 18 April 2018).
- Zeileis, A.; Grothendieck, G. Zoo: S3 Infrastructure for regular and irregular time series. J. Stat. Softw. 2005, 14, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. PAML 4: Phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simão, F.A.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Ioannidis, P.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO: Assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3210–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Li, J.; Yu, L.; Wei, Y.; Miao, Z.; Chen, M.; Huang, R. De novo transcriptome assembly of the new marine fish model of goby, Mugilogobius chulae. Mar. Genom. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Zhang, L.; Han, Y.; Ren, X.; Huang, J.; Chen, H. De novo transcriptome sequencing and analysis of Coccinella septempunctata L. in non-diapause, diapause and diapause-terminated states to identify diapause-associated genes. BMC Genom. 2015, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, E.; Künstner, A.; Fraser, B.A.; Zipprich, G.; Kottler, V.A.; Henz, S.R.; Weigel, D.; Dreyer, C. Transcriptome assemblies for studying sex-biased gene expression in the guppy, Poecilia reticulata. BMC Genom. 2014, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, Q.; Luo, J.Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, C.F. De novo transcriptome of the mayfly Cloeon viridulum and transcriptional signatures of Prometabola. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, S.J.; Garner, T.W.; Balloux, F.; Ruis, C.; Paszkiewicz, K.H.; Moore, K.; Griffiths, A.G. A de novo assembly of the common frog (Rana temporaria) transcriptome and comparison of transcription following exposure to Ranavirus and Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brawand, D.; Soumillon, M.; Necsulea, A.; Julien, P.; Csárdi, G.; Harrigan, P.; Weier, M.; Liechti, A.; Aximu-Petri, A.; Kircher, M.; et al. The evolution of gene expression levels in mammalian organs. Nature 2011, 478, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White-Cooper, H. Molecular mechanisms of gene regulation during Drosophila spermatogenesis. Reproduction 2010, 139, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Modrek, B.; Lee, C. Genome-wide detection of tissue-specific alternative splicing in the human transcriptome. Nucl. Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3754–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yeo, G.; Holste, D.; Kreiman, G.; Burge, C.B. Variation in alternative splicing across human tissues. Genome Biol. 2004, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perrin, N. Sex reversal: A fountain of youth for sex chromosomes? Evolution 2009, 63, 3043–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, N.; Studer, T.; Dufresnes, C.; Perrin, N. Sex-chromosome recombination in common frogs brings water to the fountain-of-youth. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, M.C.; Xu, P.; Scardina, J.; Wheeler, P.A.; Thorgaard, G.H.; Nichols, K.M. Differential gene expression in male and female rainbow trout embryos prior to the onset of gross morphological differentiation of the gonads. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iturra, P.; Lam, N.; de la Fuente, M.; Vergara, N.; Medrano, J.F. Characterization of sex chromosomes in rainbow trout and coho salmon using fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Genetica 2001, 111, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haselman, J.T.; Olmstead, A.W.; Degitz, S.J. Global gene expression during early differentiation of Xenopus (Silurana) tropicalis gonad tissues. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2015, 214, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Small, C.M.; Carney, G.E.; Mo, Q.; Vannucci, M.; Jones, A.G. A microarray analysis of sex- and gonad-biased gene expression in the zebrafish: evidence for masculinization of the transcriptome. BMC Genomics 2009, 10, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darolti, I.; Wright, A.E.; Pucholt, P.; Berlin, S.; Mank, J.E. Slow evolution of sex-biased genes in the reproductive tissue of the dioecious plant Salix viminalis. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 27, 694–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, P.W.; Mank, J.E.; Wedell, N. Incomplete sex chromosome dosage compensation in the Indian meal moth, Plodia interpunctella, based on de novo transcriptome assembly. Genome Biol. Evol. 2012, 4, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, N.; Studer, T.; Dufresnes, C.; Ma, W.J.; Veltsos, P.; Perrin, N. Dmrt1 polymorphism and sex-chromosome differentiation in Rana temporaria. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 4897–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumida, M.; Nishioka, M. Sex-linked genes and linkage maps in amphibians. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 2000, 126, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, I. Sex determination and sex chromosomes in amphibia. Sex Dev. 2017, 11, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffries, D.N.; Lavanchy, G.; Sermier, R.; Sredl, M.J.; Miura, I.; Borzée, A.; Barrow, L.N.; Canestrelli, D.; Crochet, P.-A.; Dufresnes, C.; et al. An unprecedented rate of sex-chromosome turnover and non-random transitions in true frogs. Nat. Commun. under review.
- Malone, J.H.; Michalak, P. Gene expression analysis of the ovary of hybrid females of Xenopus laevis and X. muelleri. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malone, J.H.; Michalak, P. Physiological sex predicts hybrid sterility regardless of genotype. Science 2008, 319, 8231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, W.R. The accumulation of sexually antagonistic genes as a selective agent promoting the evolution of reduced recombination between primitive sex chromosomes. Evolution 1987, 41, 911–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlesworth, D.; Charlesworth, B.; Marais, G.A. Steps in the evolution of heteromorphic sex chromosomes. Heredity 2005, 95, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grossen, C.; Neuenschwander, S.; Perrin, N. The evolution of XY recombination: Sexually antagonistic selection versus deleterious mutation load. Evolution 2012, 66, 3155–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Developmental Stage/ Adult Tissue | Cut-Off Threshold (Fold Change) | Female-Biased | Male-Biased | Sex-Biased (p Value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gosner stage 23 | 5% FDR | 4 | 16 | 0.09 |
| ≥2 | 4 | 16 | 0.09 | |
| ≥4 | 3 | 16 | 0.01 | |
| ≥8 | 3 | 12 | 0.05 | |
| Gosner stage 27 | 5% FDR | 9 | 2 | 0.066 |
| ≥2 | 9 | 2 | 0.066 | |
| ≥4 | 9 | 2 | 0.066 | |
| ≥8 | 9 | 1 | 0.14 | |
| Gosner stage 31 | 5% FDR | 11 | 18 | 0.43 |
| ≥2 | 11 | 18 | 0.43 | |
| ≥4 | 4 | 14 | 0.16 | |
| ≥8 | 3 | 12 | 0.047 | |
| Gosner stage 43 | 5% FDR | 156 | 30 | <0.0001 |
| ≥2 | 156 | 30 | <0.0001 | |
| ≥4 | 156 | 30 | <0.0001 | |
| ≥8 | 136 | 21 | <0.0001 | |
| Gosner stage 46 | 5% FDR | 4403 | 810 | <0.0001 |
| ≥2 | 3964 | 714 | <0.0001 | |
| ≥4 | 1708 | 143 | <0.0001 | |
| ≥8 | 802 | 54 | <0.0001 | |
| Brain | 5% FDR | 77 | 83 | 0.82 |
| ≥2 | 73 | 75 | 1 | |
| ≥4 | 59 | 44 | 0.36 | |
| ≥8 | 54 | 28 | 0.058 | |
| Liver | 5% FDR | 139 | 100 | 0.06 |
| ≥2 | 139 | 100 | 0.06 | |
| ≥4 | 106 | 37 | <0.0001 | |
| ≥8 | 68 | 17 | <0.0001 | |
| Gonad | 5% FDR | 6059 | 6262 | 0.2 |
| ≥2 | 5227 | 5687 | <0.001 | |
| ≥4 | 2538 | 2901 | <0.0001 | |
| ≥8 | 1317 | 1260 | 0.44 |
| Stage | Tissue | Nr. Shared Sex-Biased Genes | Turnover in Sex Bias Direction | Proportion of Turnover in Total Sex Bias | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female to Male | Male to Female | ||||
| Juvenile | G43 vs. G46 | 156 | 0 | 0 | 0% |
| Adult | Gonad vs. Liver | 92 | 15 | 28 | 47% |
| Gonad vs. Brain | 62 | 7 | 1 | 13% | |
| Juvenile and Adult | G46 vs. Gonad | 2661 | 134 | 29 | 6% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, W.-J.; Veltsos, P.; Toups, M.A.; Rodrigues, N.; Sermier, R.; Jeffries, D.L.; Perrin, N. Tissue Specificity and Dynamics of Sex-Biased Gene Expression in a Common Frog Population with Differentiated, Yet Homomorphic, Sex Chromosomes. Genes 2018, 9, 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9060294
Ma W-J, Veltsos P, Toups MA, Rodrigues N, Sermier R, Jeffries DL, Perrin N. Tissue Specificity and Dynamics of Sex-Biased Gene Expression in a Common Frog Population with Differentiated, Yet Homomorphic, Sex Chromosomes. Genes. 2018; 9(6):294. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9060294
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Wen-Juan, Paris Veltsos, Melissa A. Toups, Nicolas Rodrigues, Roberto Sermier, Daniel L. Jeffries, and Nicolas Perrin. 2018. "Tissue Specificity and Dynamics of Sex-Biased Gene Expression in a Common Frog Population with Differentiated, Yet Homomorphic, Sex Chromosomes" Genes 9, no. 6: 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9060294
APA StyleMa, W.-J., Veltsos, P., Toups, M. A., Rodrigues, N., Sermier, R., Jeffries, D. L., & Perrin, N. (2018). Tissue Specificity and Dynamics of Sex-Biased Gene Expression in a Common Frog Population with Differentiated, Yet Homomorphic, Sex Chromosomes. Genes, 9(6), 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9060294





