An Assessment of the Coupled Weather Research and Forecasting Hydrological Model on Streamflow Simulations over the Source Region of the Yellow River
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
3. Methodology
3.1. The Numerical Model
3.1.1. WRF Model
3.1.2. Noah-MP Model
3.1.3. WRF-Hydro Model
3.2. Experimental Designs
3.2.1. The Parameterization Schemes in the WRF and Coupled WRF-Hydro Model
3.2.2. The Calibration of Sensitivity Parameters in the Offline WRF-Hydro Model
3.2.3. The Interpolation Method
3.2.4. Evaluation Index
3.2.5. The Applicability of the WRF-Hydro Model
4. Results
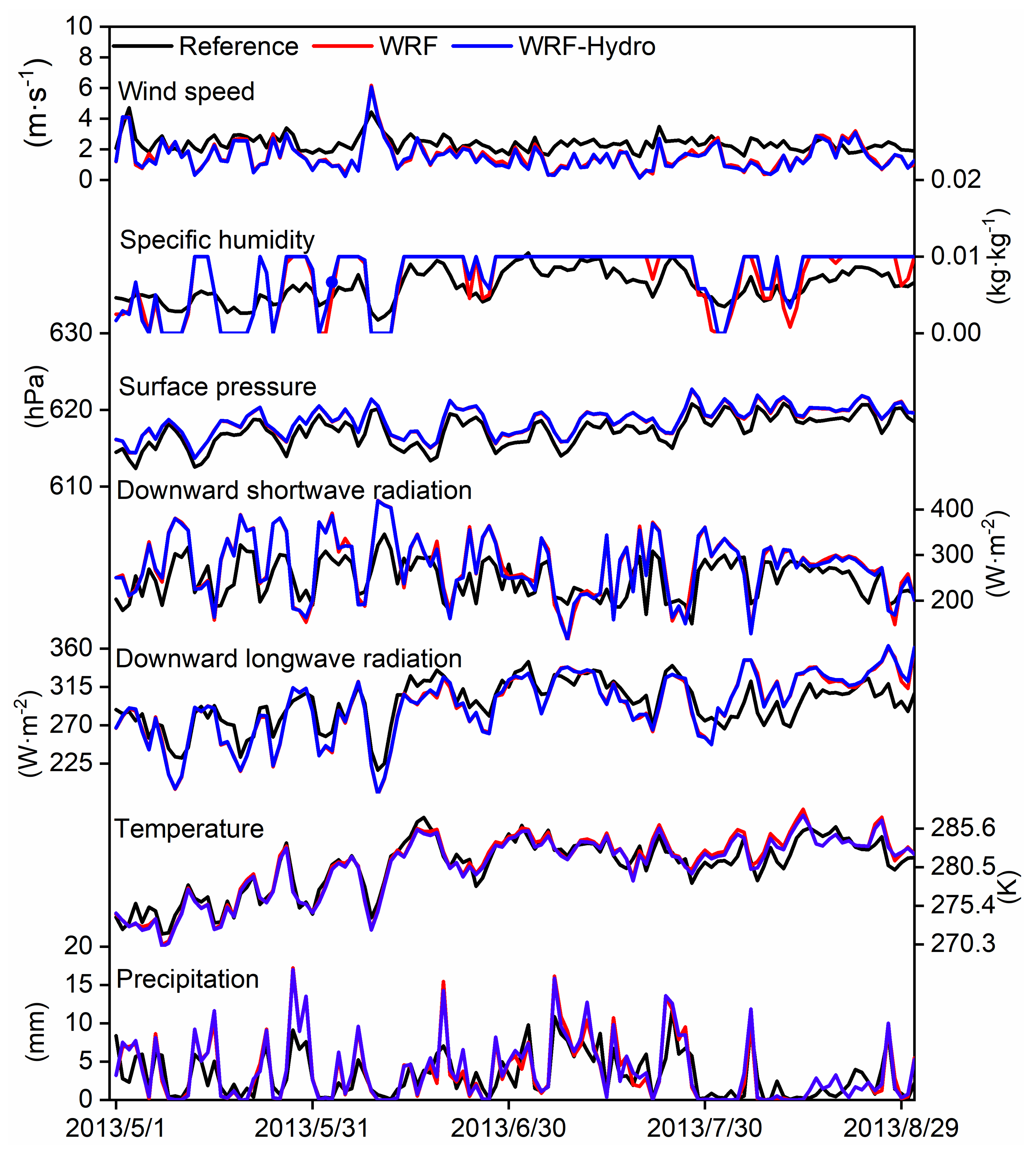
4.1. The Temporal Variation in Hydrometeorological Elements
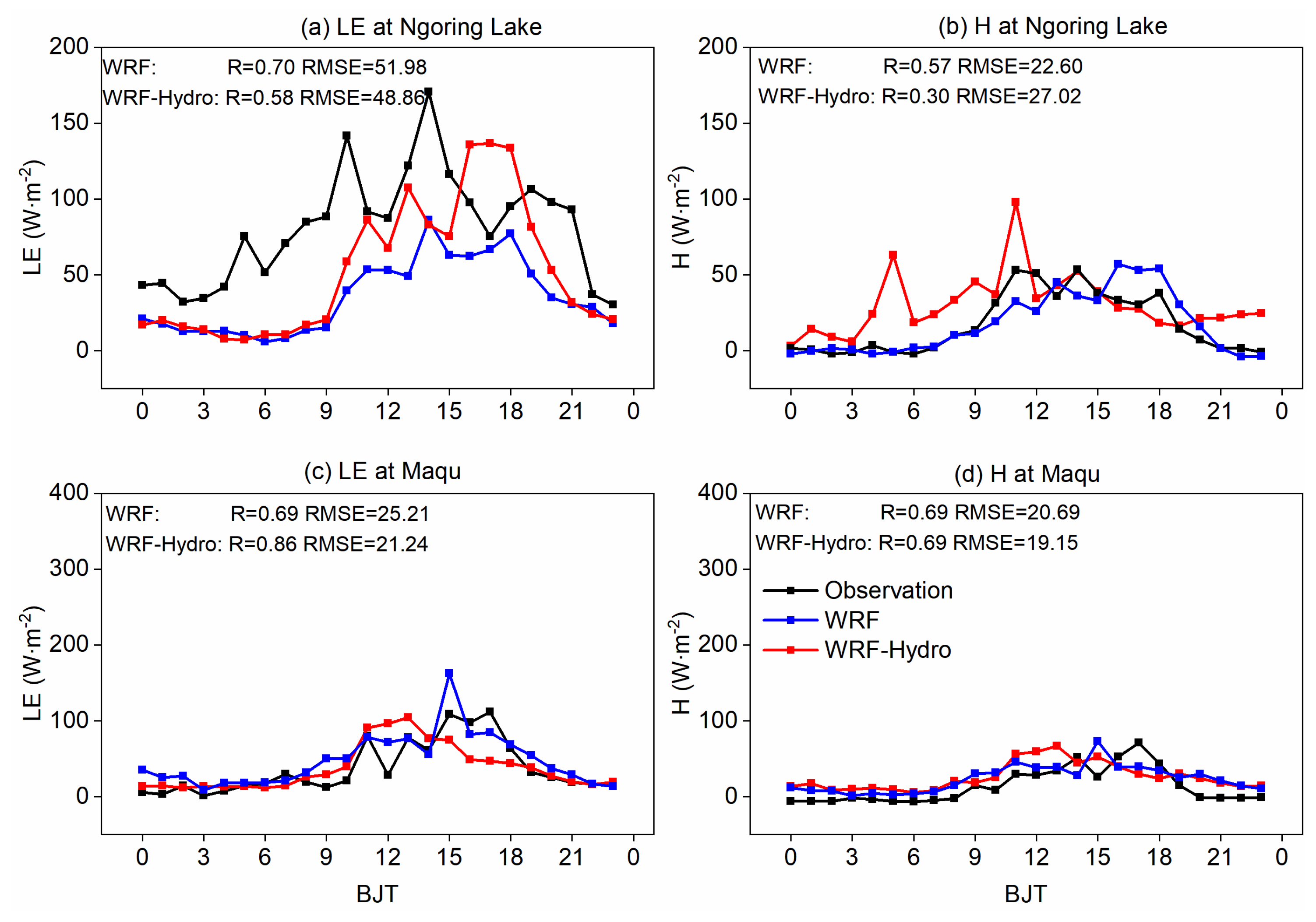
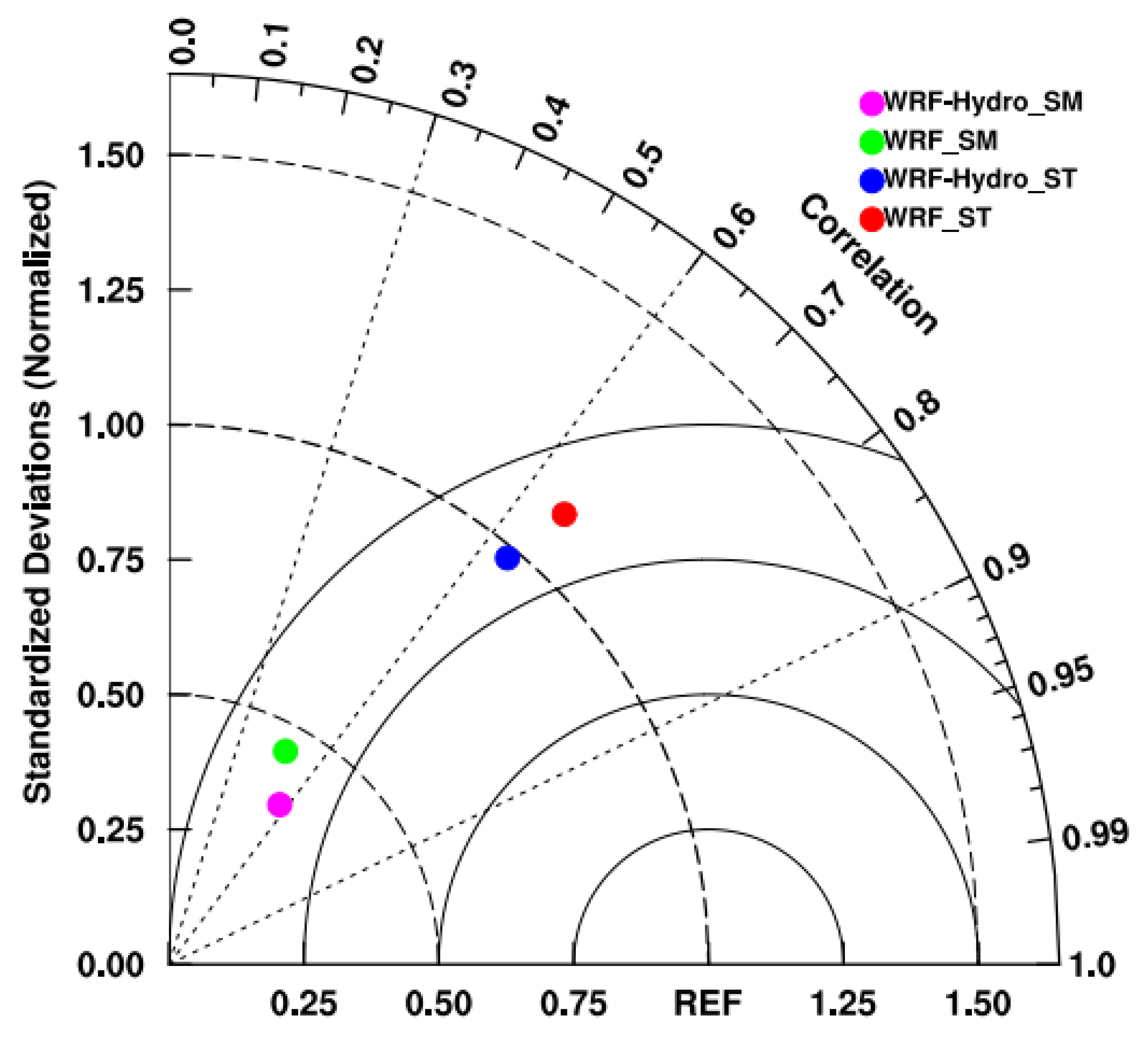
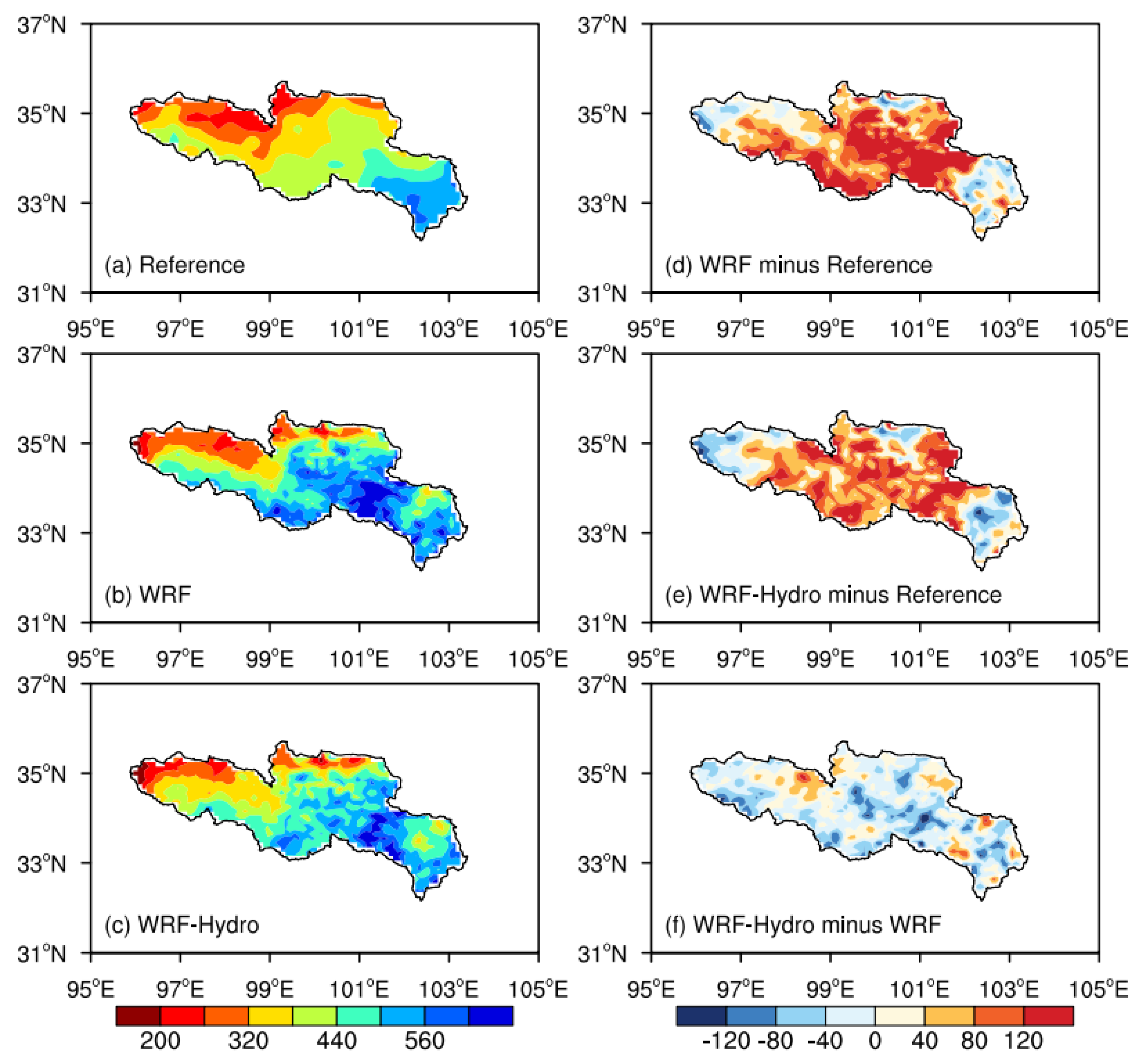
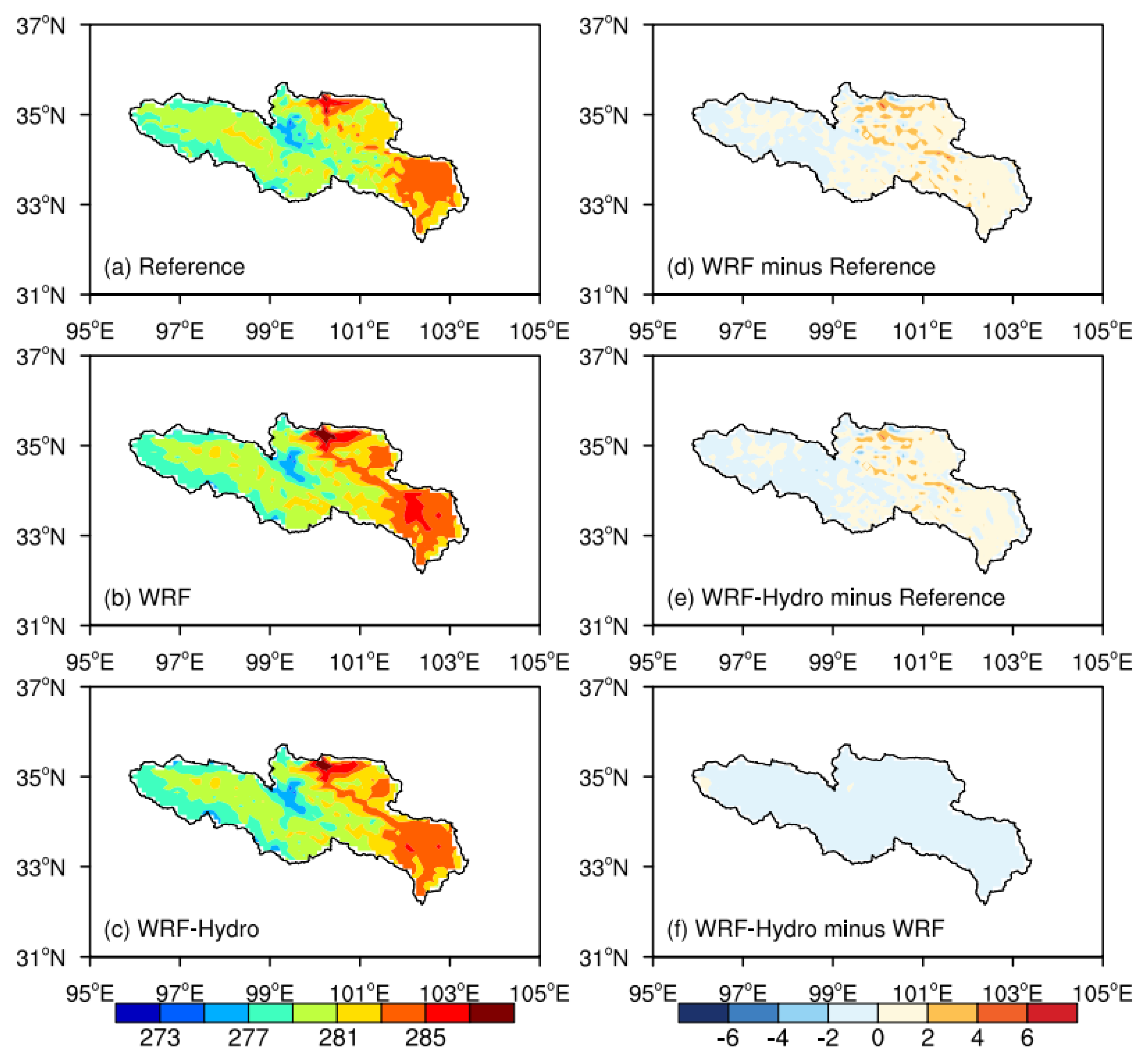
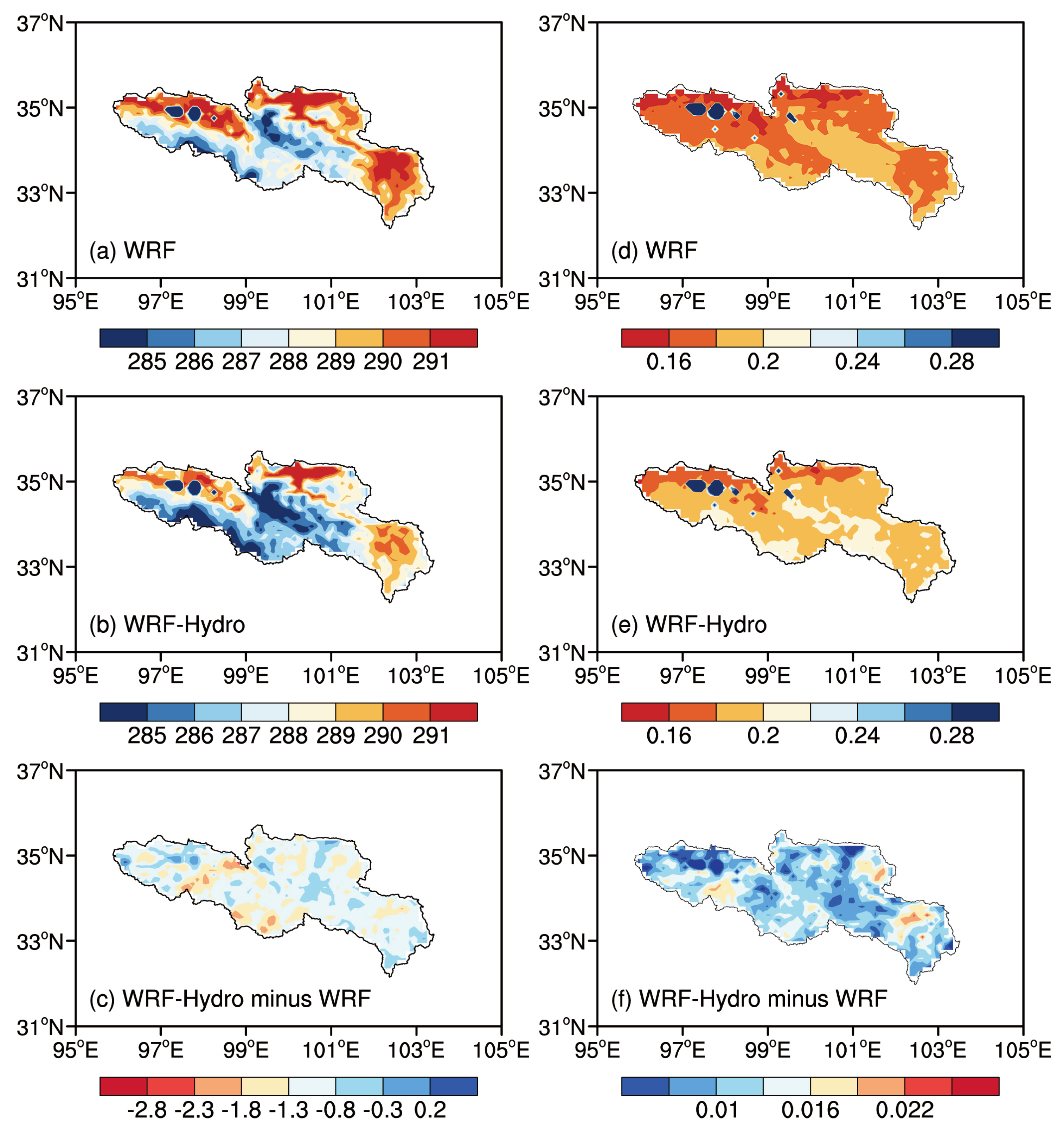
4.2. The Spatial Distribution of Hydrometeorological Elements
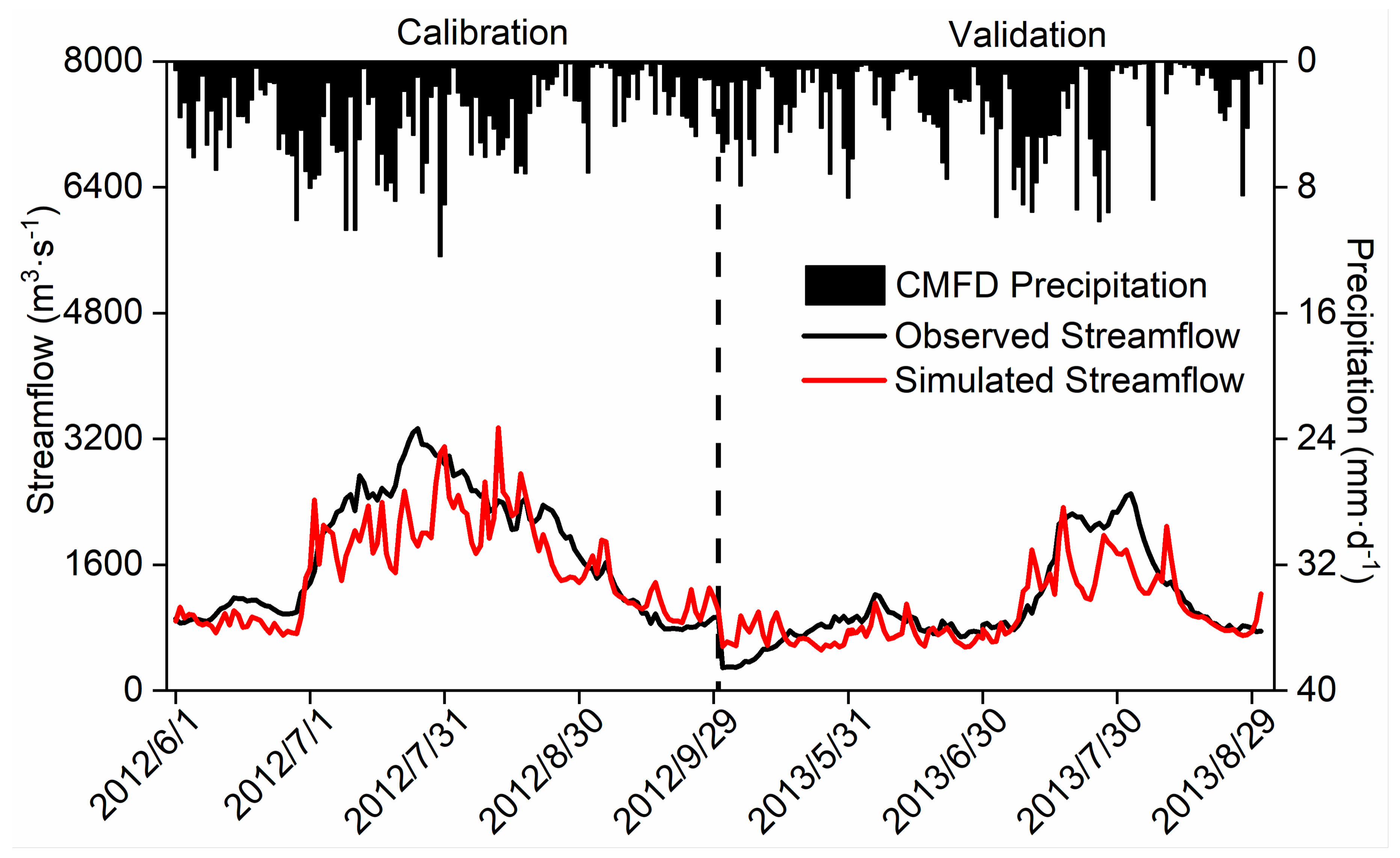
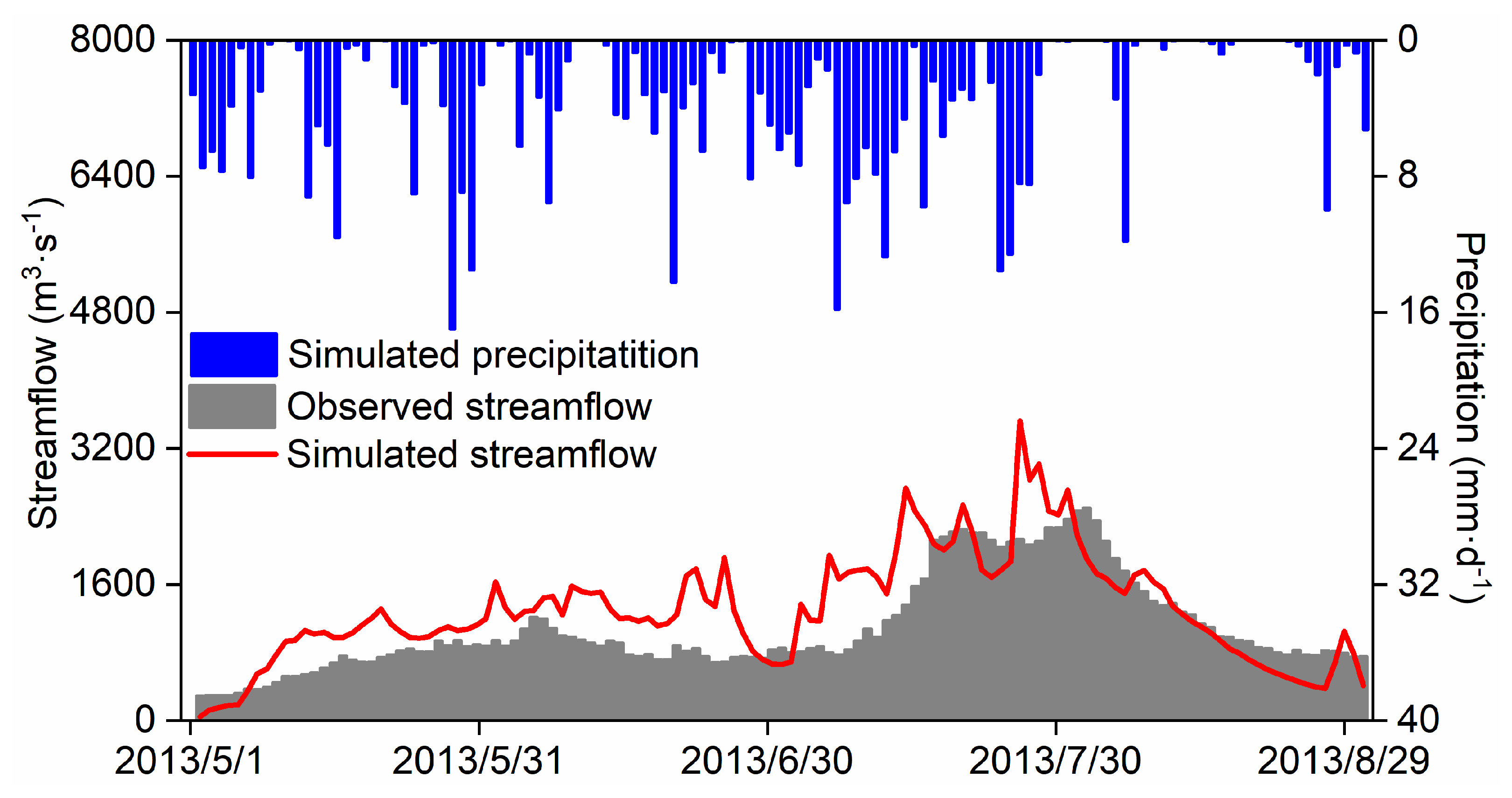
4.3. The Time Series of the Streamflow Simulated by the Coupled Model
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The uncoupled WRF-Hydro model effectively characterizes the variability of streamflow over the SRYR basin, demonstrating an R of 0.84 and an NSE of 0.44 during the calibration period and an R of 0.81 and an NSE of 0.61 during the validation period.
- (2)
- Both the standalone WRF and coupled WRF-Hydro models indicate reasonable performance in reproducing variables associated with atmosphere–land–hydrology processes over the SRYR. The consideration of soil water lateral flow in the coupling process significantly reduces biases in water–heat exchange fluxes, soil temperature, and soil moisture simulations, with mean RMSE values of 32.27 W·m−2, 24.91 W·m−2, 4.22 K, and 0.06 m3/m3, respectively.
- (3)
- The coupled model success captures the streamflow variation. Nevertheless, reproducing daily streamflow with the coupled model remains a challenge, yielding an NSE of 0.33 and an RMSE of 458.85 m3·s−1.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnault, J.; Wagner, S.; Rummler, T.; Fersch, B.; Bliefernicht, J.; Andresen, S.; Kunstmann, H. Role of Runoff-Infiltration Partitioning and Resolved Overland Flow on Land-Atmosphere Feedbacks: A Case Study with the WRF-Hydro Coupled Modeling System for West Africa. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 1489–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fersch, B.; Senatore, A.; Adler, B.; Arnault, J.; Mauder, M.; Schneider, K.; Völksch, I.; Kunstmann, H. High-resolution fully-coupled atmospheric-hydrological modeling: A cross-compartment regional water and energy cycle evaluation. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 2457–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milly, P.C.D.; Dunne, K.A.; Vecchia, A.V. Global pattern of trends in streamflow and water availability in a changing climate. Nature 2005, 438, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.H.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.G.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, B.R.; Lvy, S.H.; Deng, M.S.; Liu, Y.M.; Li, G.W. Review of Climate Change and Its Environmental Influence on the Three-River Regions. Plateau Meteor. 2020, 39, 1113–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.X.; Mao, J.Y.; Duan, A.M.; Zhang, Q. Recent progressing in the study on the impacts of Tibetan Plateau on Asian summer climate. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2004, 62, 528–549. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, D.X.; Tian, S.M.; Jiang, S.Q.; Dong, X.N.; Li, Z.W.; Zhang, L. Research process of the evolition of runoff in the Source Area of the Yellow River. Yellow River 2020, 42, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.; Li, T.J.; Fu, W.; Wang, Y.T. Model simulation of flood season runoff in the headwaters of the Yellow River Basin using satellite-ground merged precipitation data. J. Abbr. 2017, 25, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Milly, P.C.D.; Wetherald, R.T.; Dunne, K.A.; Delworth, T.L. Increasing risk of great floods in a changing climate. Nature 2002, 415, 514–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, P.; Yuan, X. High-resolution land surface modeling of hydrological changes over the Sanjiangyuan Region in the eastern Tibetan Plateau: 2. Impact of climate and land cover change. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2018, 10, 2829–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.P.; Fan, Y.; Lawrence, D.M.; Adam, J.C.; Bolster, D.; Gochis, D.J.; Hooper, R.P.; Kumar, M.; Leung, L.R.; Mackay, D.S.; et al. Improving the representation of hydrologic processes in Earth System Models. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 5929–5956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.H.; Liu, X.C.; Li, Z.; Yun, X.B.; Zhang, X.J.; Yu, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Cui, H.J.; Sun, S.A.; et al. Integrated water systems model for terrestrial water cycle simulation. Adv. Earth Sci. 2019, 34, 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Kruk, N.S.; Vendrame, I.F.; Chou, S.C. Coupling a Mesoscale Atmospheric Model with a Distributed Hydrological Model Applied to a Watershed in Southeast Brazil. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2012, 18, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuo, L.; Zhang, Y.X.; Gao, Y.H.; Hao, Z.C.; Cairang, L.S. The impacts of climate change and land cover/use transition on the hydrology in the upper Yellow River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 502, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, M.Y.; Lei, H.M.; Jiao, Y.; Yang, D.W. Evaluation of the runoff and river routing schemes in the Community Land Model of the Yellow River Basin. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2017, 9, 2993–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergant, K.; Belda, M.; Halenka, T. Systematic errors in the simulation of european climate (1961–2000) with RegCM3 driven by NCEP/NCAR reanalysis. Int. J. Climatol. 2007, 27, 455–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flocas, H.A.; Hatzaki, M.; Yolika, K.; Anagnostopoulou, C.; Kostopoulou, E.; Giannakopoulos, C.; Kolokytha, C.; Tegoulias, K. Ability of RCM/GCM couples to represent the relationship of large scale circulation to climate extremes over the Mediterranean region. J. Clim. Res. 2011, 46, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Lan, Y.C.; Su, Z.B.; Tian, H.; Shi, X.K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, R.; Zhang, T.T.; Kang, Y.; et al. Advances in observation and modeling of land surface process over the Source Region of the Yellow River. Adv. Earth Sci. 2011, 26, 575–585. [Google Scholar]
- Gochis, D.J.; Chen, F. Hydrological Enhancements to the Community Noah Land Surface Model (No. NCAR/TN-454+STR); University Corporation for Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gharamti, M.E.; McCreight, J.L.; Noh, S.J.; Hoar, T.J.; RafieeiNasab, A.; Johnson, B.K. Ensemble streamflow data assimilation using WRF-Hydro and DART: Novel localization and inflation techniques applied to Hurricane Florence flooding. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 5315–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.W.; Chen, Y.D.; Gao, Y.F.; Qin, L.Y.; Wu, Y.Q.; Wu, Y.Z. Improved streamflow forecast in a small-medium sized river basin with coupled WRF and WRF-Hydro: Effects of radar data assimilation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Arnault, J.; Wagner, S.; Laux, P.; Kunstmann, H. Impact of lateral terrestrial water flow on land-atmosphere interactions in the Heihe River Basin in China: Fully coupled modeling and precipitation recycling analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 8401–8423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senatore, A.; Mendicino, G.; Dochis, D.J.; Yu, W.; Yates, D.N.; Kunstmann, H. Fully coupled atmosphere-hydrology simulations for the central Mediterranean: Impact of enhanced hydrological parameterization for short and long time scales. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2015, 7, 1693–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.W.; Meng, X.H.; Blyth, E.; Chen, H.; Shu, L.L.; Li, Z.G.; Zhao, L.; Ma, Y.S. Impact of Fully Coupled Hydrology-Atmosphere Processes on Atmosphere Conditions: Investigating the Performance of the WRF-Hydro Model in the Three River Source Region on the Tibetan Plateau, China. Water 2021, 13, 3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.; Yuan, X.; Ma, F.; Pan, M. Accelerated hydrological cycle over the Sanjiangyuan region induces more streamflow extremes at different global warming levels. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 5439–5451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.M.; Shao, Q.X.; Fukushima, Y. Changes in stream flow regime in headwater catchments of the Yellow River basin since the 1950s. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 21, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.H.; Lyu, S.H. Observation Data of Turbulent Flow at Lakeside Observation Points in Erling Lake Basin. 2013. Available online: http://www.ncdc.ac.cn (accessed on 17 December 2022).
- Meng, X.H.; Lyu, S.H.; Li, Z.G.; Ao, Y.H.; Wen, L.J.; Shang, L.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Deng, M.S.; Zhang, S.B.; Zhao, L.; et al. Dataset of comparative observations for land surface processes over the semi-arid alpine grassland against alpine lakes in the Source Region of the Yellow River. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2023, 40, 1142–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.Y.; Meng, X.H.; Zhao, L.; Li, Z.G.; Lyu, S.H.; Ma, Y.T. Evaluation the applicability of albedo products of GLASS, MODIS and GlobAlbedo under the alpine meadow over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Plateau Meteor. 2019, 38, 88–100. [Google Scholar]
- An, Y.Y.; Meng, X.H.; Zhao, L.; Li, Z.G.; Wang, S.Y.; Shang, L.Y.; Chen, H.; Lyu, S.H.; Li, G.W.; Ma, Y.S. Performance of GLASS and MODIS Satellite Albedo products in diagnosing Albedo variations during different time scales and special weather conditions in the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2008, 12, 2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, Y.H.; Wang, W.Z.; Lan, Y.C.; Xu, J.W.; Li, K. Climate changes and applicability of GLDAS in the headwater of the Yellow River Basin. Adv. Earth Sci. 2014, 29, 531–540. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Yang, K.; Tang, W.J.; Lyu, H.; Qin, J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Li, X. The first high-resolution meteorological forcing dataset for land process studies over China. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitriev, V.; Ovchinnikov, V. Interpolation in real method spaces. Geoderma 1979, 246, 794–797. [Google Scholar]
- Shangguan, W.; Dai, Y.J.; Liu, B.Y.; Ye, A.Z.; Yuan, H. A soil particle-size distribution dataset for regional land and climate modelling in China. Geoderma 2012, 171–172, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B. A time-split nonhydrostatic atmospheric model for weather research and forecasting applications. J. Comput. Phys. 2008, 227, 3465–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.-Y.; Yang, Z.-L.; Mitchell, K.E.; Chen, F.; Ek, M.B.; Barlage, M.; Kumar, A.; Manning, K.; Niyogi, D.; Rosero, E.; et al. The community Noah land surface model with multiparameterization options (Noah-MP): 1. Model description and evaluation with local-scale measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D12109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Z.; Yuan, H.L.; Yu, W. Uncertainties of 3D soil hydraulic parameters in streamflow simulations using a distributed hydrological model system. J. Hydrol. 2011, 567, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.Y.; Yang, Z.L. Effects of frozen soil on snowmelt runoff and soil water storage at a continental scale. J. Hydrometeorol. 2006, 7, 937–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G.; Field, P.R.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Hall, W.D. Explicit forecasts of winter precipitation using an improved bulk microphysics scheme. Part II: Implementation of a new snow parameterization. Mon. Weather Rev. 2008, 136, 5095–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, G.A.; Devenyi, D. A generalized approach to parameterizing convection combining ensemble and data assimilation techniques. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 38-1–38-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, M.; Niino, H. An improved mellor-yamada level-3 model: Its numerical stability and application to a regional prediction of advection fog. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2006, 119, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacono, M.J.; Delamere, J.S.; Mlawer, E.J.; Shephard, M.W.; Clough, S.A.; Collins, W.D. Radiative forcing by long-lived greenhouse gases: Calculations with the AER radiative transfer models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yucel, I.; Onen, A.; Yilmaz, K.K.; Gochis, D.J. Calibration and evaluation of a flood forecasting system: Utility of numerical weather prediction model, data assimilation and satellite-based rainfall. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, D.W.; Tian, S.N.; Hu, Y.H.; Ma, J.L.; Wang, L.X. Coupling analysis of short-term weather and runoff in an arid lake basin of China. Reg. Sustain. 2021, 2, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Zhang, S.W.; Wang, F.Y.; Mao, F.P.; Yang, X.X. The applicability of different parameterization schemes in semi-arid region based on Noah-MP land surface model. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 41, 189–201. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.L.; Wen, J.; Yang, C.G.; Long, Y.P.; Li, G.W.; Jia, H.J.; Liu, Z. Analysis on the applicability of different precipitation products and WRF-Hydro model over the Source Region of the Yellow River. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. Available online: http://www.dqkxqk.ac.cn/dqkx/dqkx/article/abstract/2022057B (accessed on 17 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.Y.; Wen, J.; Zhang, T.T.; Xi, J.J. Response of soil water content and soil thermal conductivity on precipitation in Loess Plateau. Plateau Meteor. 2014, 33, 712–720. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Wen, J.; Zhang, T.T.; Yang, Y.T.; Wu, Y.Y.; Zhang, G.; Liu, W.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Yan, Z.T. The impacts of roughness length on the simulation of land-atmosphere water and heat exchanges over the Yarlung Zangbo Grand canyon region. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 10, 2296–6463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.E. Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 7183–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.X.; Yuan, N.M.; Ma, Z.G.; Huang, Y. Understanding the soil temperature variability at different depths: Effects of surface air temperature, snow cover, and the soil memory. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.F.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, S.F. Discussion on evaluation of natural runoff in the Yellow River Basin. Water Resour. Prot. 2022, 38, 33–38+55. [Google Scholar]


| Category | Data Type | Temporal and Spatial Resolutions | Variables |
|---|---|---|---|
| Climate | CMFD | 3 h; 0.10° × 0.10° | Precipitation |
| GLDAS | 3 h; 0.25° × 0.25° | Temperature, wind speed, solar radiation, downward longwave radiation, pressure, specific humidity | |
| FNL | 6 h; 1.00° × 1.00° | Initial and boundary conditions | |
| Hydrology | Site | 1 d | Streamflow |
| Eddy covariance | Site | 30 min | Water/heat flux, soil temperature and moisture |
| Topography | HydroSHEDS | 90.0 m × 90.0 m | Digital Elevation Model |
| Physics Process | Parameterization | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Microphysics | Thompson | [38] |
| Cumulus parameterization | G-D | [39] |
| Planetary boundary layer | MYNN2 | [40] |
| Land surface | Noah-MP | [34] |
| Longwave radiation | RRTMG | [41] |
| Shortwave radiation | RRTMG | [41] |
| Variables | Model | R | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation | WRF | 0.80 | 2.50 |
| WRF-Hydro | 0.81 | 2.51 | |
| Temperature | WRF | 0.96 | 1.45 |
| WRF-Hydro | 0.96 | 1.2 | |
| Downward longwave radiation | WRF | 0.90 | 20.43 |
| WRF-Hydro | 0.90 | 20.01 | |
| Downward shortwave radiation | WRF | 0.76 | 63.14 |
| WRF-Hydro | 0.77 | 61.27 | |
| Surface pressure | WRF | 0.98 | 1.04 |
| WRF-Hydro | 0.98 | 1.08 | |
| Specific humidity | WRF | 0.93 | 0.002 |
| WRF-Hydro | 0.91 | 0.002 | |
| Wind speed | WRF | 0.72 | 0.01 |
| WRF-Hydro | 0.75 | 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Wen, J.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Chen, R. An Assessment of the Coupled Weather Research and Forecasting Hydrological Model on Streamflow Simulations over the Source Region of the Yellow River. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040468
Chen Y, Wen J, Meng X, Zhang Q, Li X, Zhang G, Chen R. An Assessment of the Coupled Weather Research and Forecasting Hydrological Model on Streamflow Simulations over the Source Region of the Yellow River. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(4):468. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040468
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yaling, Jun Wen, Xianhong Meng, Qiang Zhang, Xiaoyue Li, Ge Zhang, and Run Chen. 2024. "An Assessment of the Coupled Weather Research and Forecasting Hydrological Model on Streamflow Simulations over the Source Region of the Yellow River" Atmosphere 15, no. 4: 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040468
APA StyleChen, Y., Wen, J., Meng, X., Zhang, Q., Li, X., Zhang, G., & Chen, R. (2024). An Assessment of the Coupled Weather Research and Forecasting Hydrological Model on Streamflow Simulations over the Source Region of the Yellow River. Atmosphere, 15(4), 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040468







