A Time-Domain Green’s Function for Interaction between Water Waves and Floating Bodies with Viscous Dissipation Effects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Models of
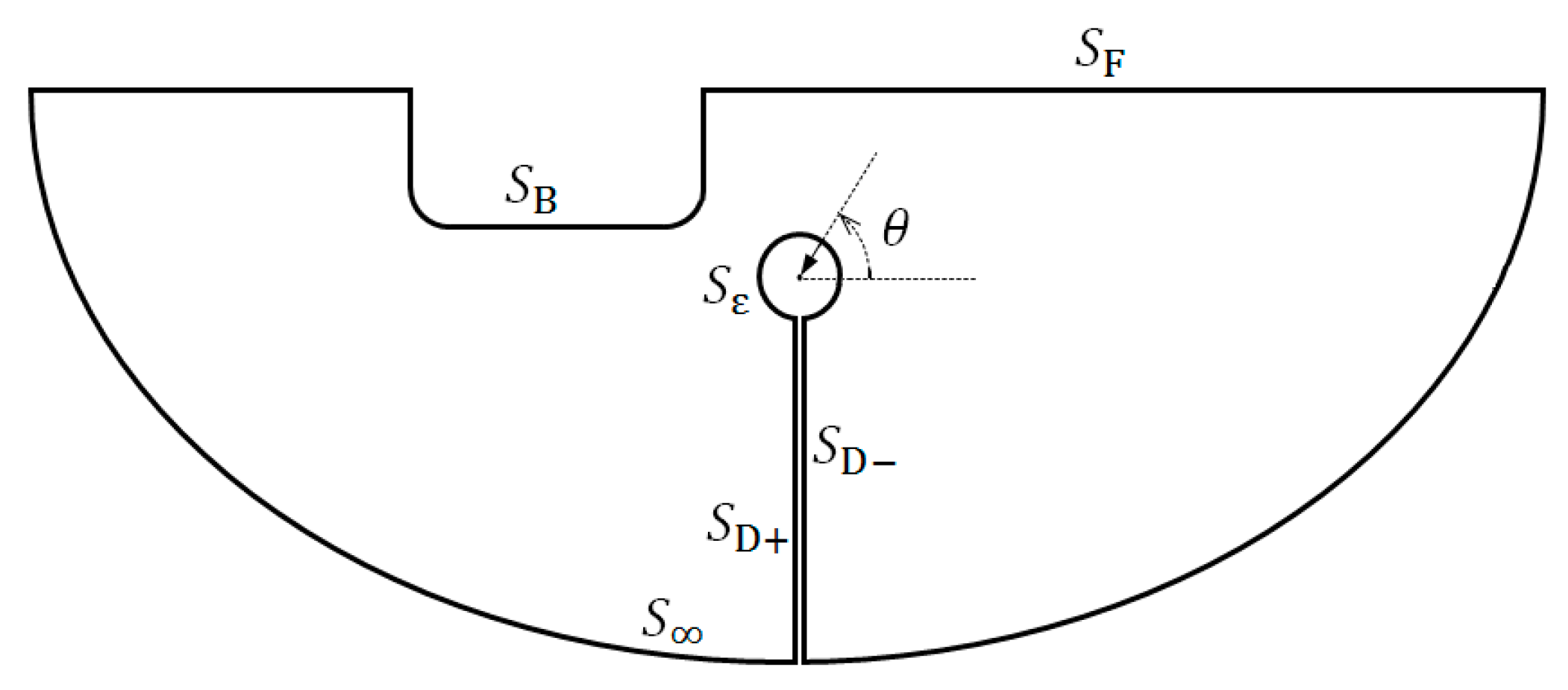
2.1. Definite Problem for
2.2. Free-Surface Memory Term of
2.3. Instantaneous Term of
2.3.1. Definite Conditions for the Instantaneous Term of
2.3.2. Instantaneous Term of
2.3.3. Instantaneous Term of
2.3.4. Characteristics of the Instantaneous Term of
2.4. Boundary Integral Equation Using
3. Application of for Solving Interaction between Water Waves and Floating Bodies with Considering Viscous Dissipation Effects
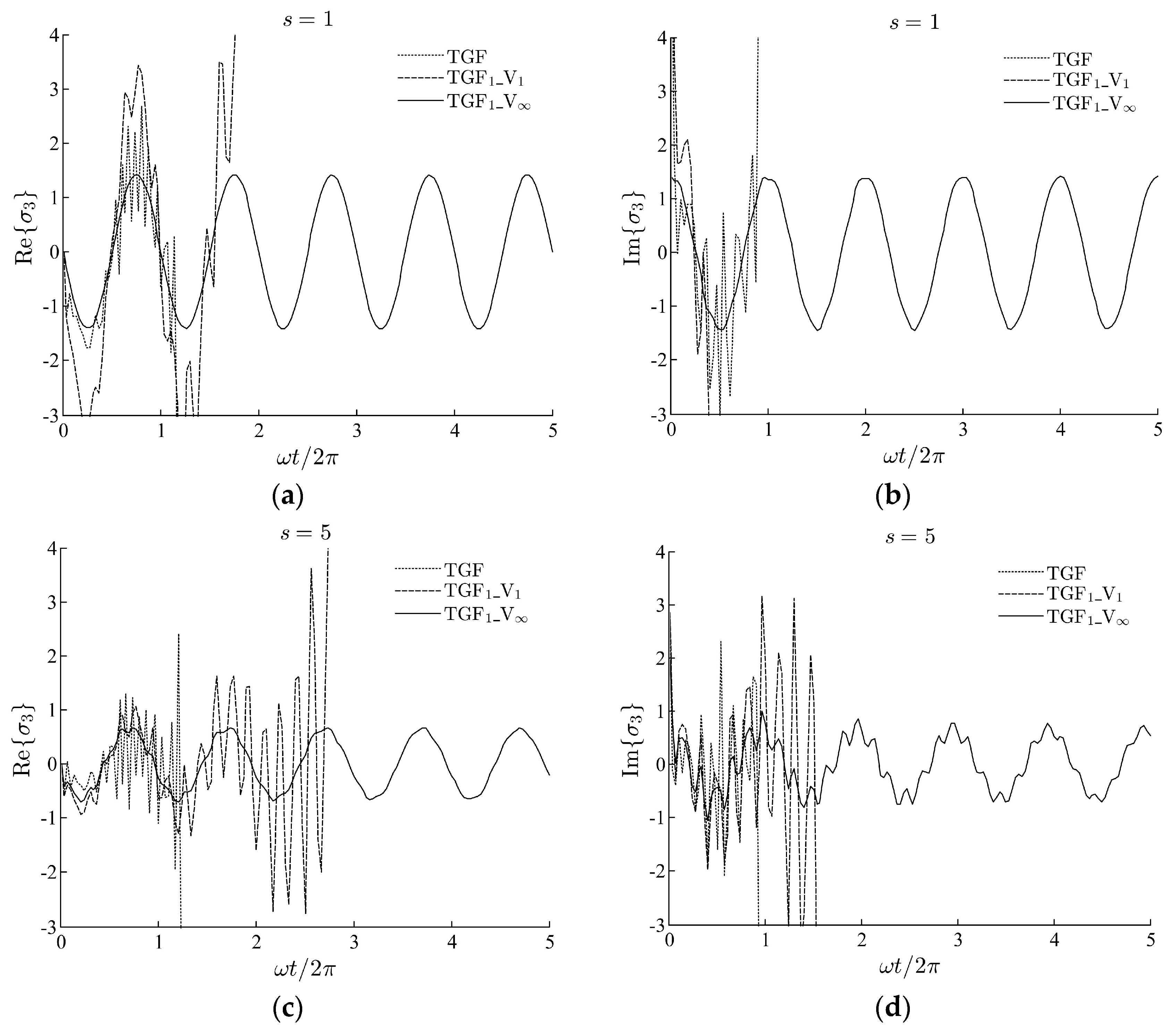
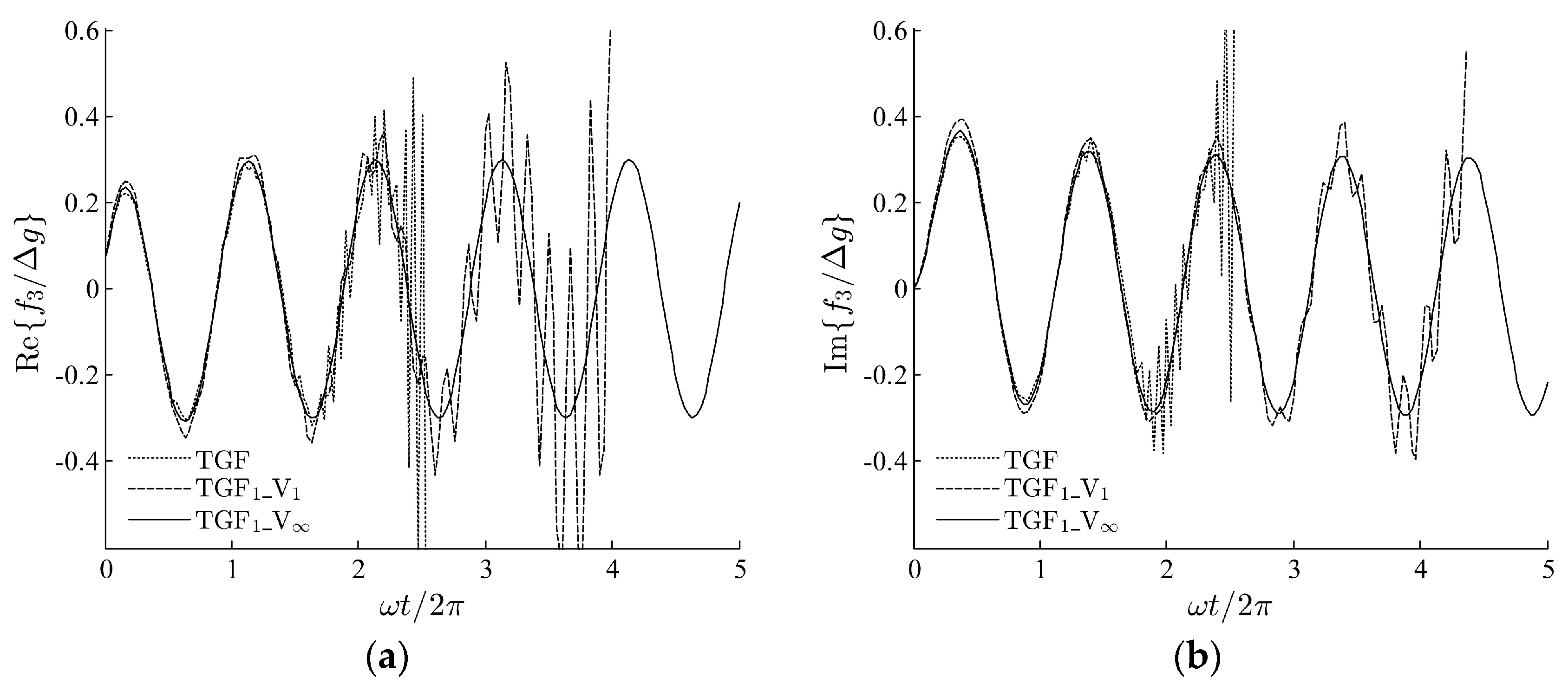
3.1. Wedge Heaving on the Water Surface
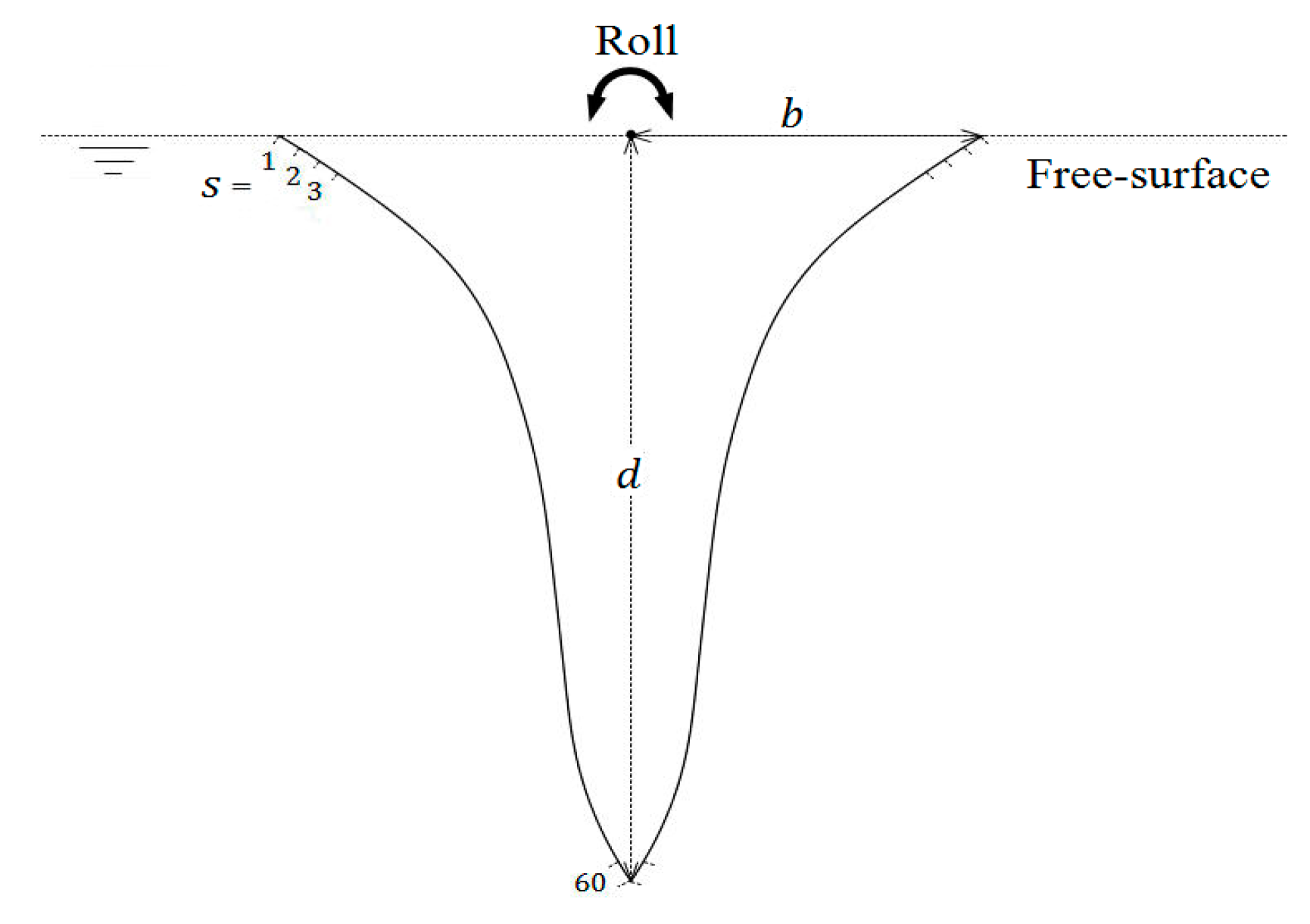
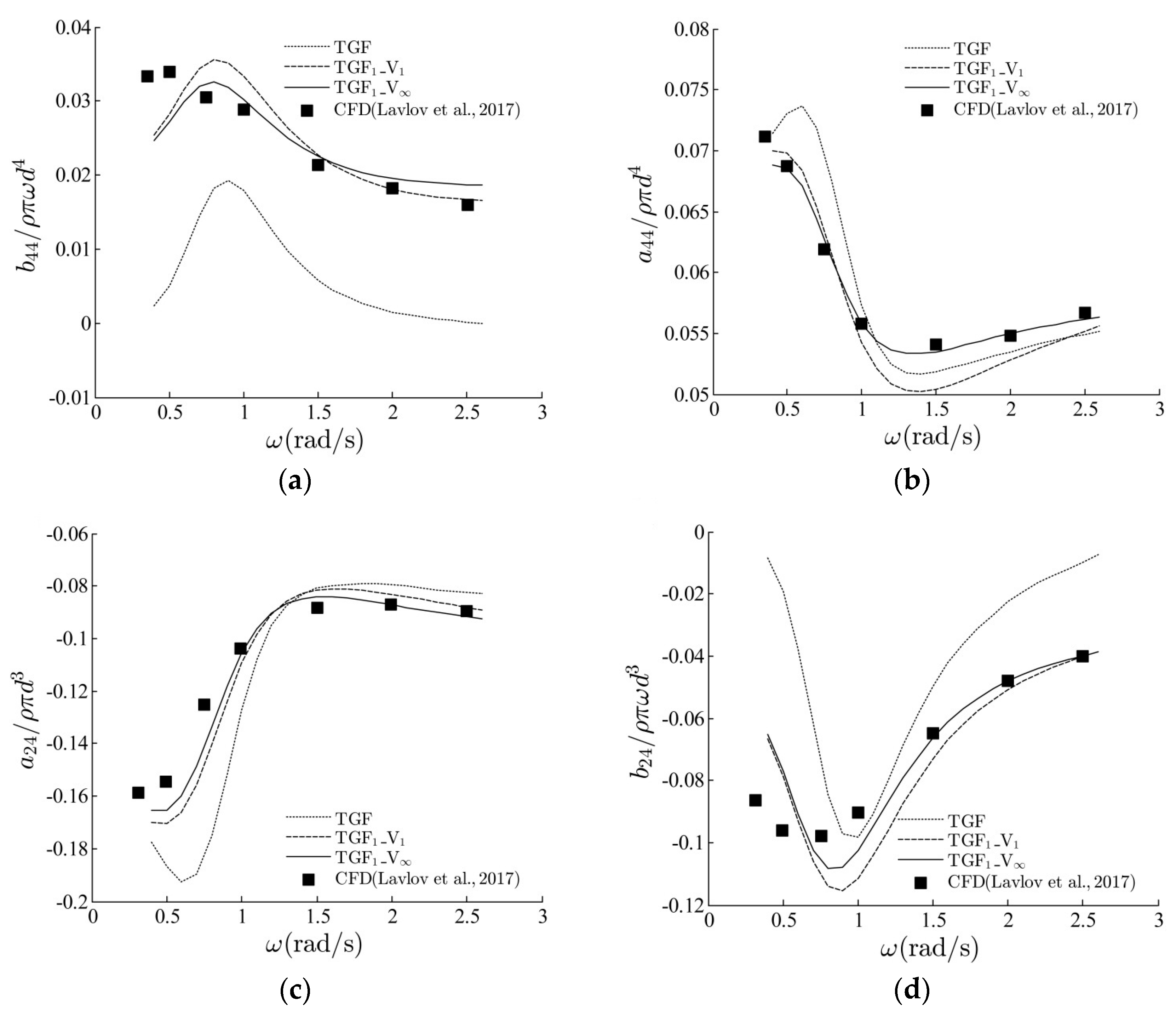
3.2. Hull Section with Sharp Keel Rolling on the Water Surface
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Guével, P. Le Problème de Diffraction-Radiation—Première Partie: Théorèmes Fondamentaux; ENSM, Univ. Nantes: Nantes, France, 1982. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.B. Hydrodynamics in offshore and naval applications-Part. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Hydrodynamics, Perth, Australia, 24–26 November 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, F.; Dyachenko, A.I.; Zakharov, V.E. Theory of weakly damped free-surface flows: A new formulation based on potential flow solutions. Phys. Lett. A 2007, 372, 1297–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.B.; Dias, F. Visco-potential flow and time-harmonic ship waves. In Proceedings of the 25th International Workshop on Water Waves and Floating Bodies (IWWWFB), Harbin, China, 9–12 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, C.B.; Dong, W.C. Modeling of fluid resonance in-between two floating structures in close proximity. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A (Appl. Phys. Eng.) 2015, 16, 987–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.D.; Shen, J.; Chen, X.B. A free surface frequency domain Green function with viscous dissipation and partial reflections from side walls. J. Mar. Sci. Appl. 2011, 10, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.B.; Dias, F.; Duan, W.Y. Introduction of dissipation in potential flows. In Proceedings of the 7th International Workshop on Ship Hydrodynamics, Shanghai, China, 16–19 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cummins, C.P.; Dias, F. A new model of viscous dissipation for an oscillating wave surge converter. J. Eng. Math. 2017, 103, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G. The Time-Domain Green Function Method Involving Fluid Viscosity. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.S.; Duan, W.Y. Potential Flow Theory of Ship Motions in Waves, 1st ed.; The National Defense Industries Press: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 253–254. ISBN 9787118053159. [Google Scholar]
- Faltinsen, O.; Zhao, R. Numerical predictions of ship motions at high forward speed. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 1991, 334, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.Y. Nonlinear Hydrodynamic Forces Acting on a Ship Undergoing Large Amplitude Motions. Ph.D. Thesis, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin, China, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Katayama, T.; Yoshioka, Y.; Kakinoki, T.; Ikeda, Y. Some topics for estimation of bilge-keel component of roll damping. In Proceedings of the 11th International Ship Stability Workshop, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 21–23 June 2010; pp. 225–230. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Li, J.D. Improving longitudinal motion prediction of hybrid monohulls with the viscous effect. J. Mar. Sci. Appl. 2007, 6, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasukawa, H. Application of a 3-D time domain panel method to ship seakeeping problems. In Proceedings of the 24th Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics, Fukuoka, Japan, 8–13 July 2002; pp. 376–392. [Google Scholar]
- Downie, M.J.; Dearman, P.W.; Graham, J.M.R. Effect of vortex shedding on the coupled roll response of bodies in waves. J. Fluid Mech. 1988, 189, 243–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrov, A.; Rodrigues, J.M.; Gadelho, J.; Guedes Soares, C. Calculation of hydrodynamic coefficients of ship sections in roll motion using Navier-Stokes equations. Ocean Eng. 2017, 133, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| 2D Time-Domain Green’s Function | TGF | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viscous dissipation effects in free-surface memory term | Temporal effect | - | ||
| Spatial effect | - | - | ||
| Instantaneous term | ||||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Z.; Ma, Q.W.; Qin, H. A Time-Domain Green’s Function for Interaction between Water Waves and Floating Bodies with Viscous Dissipation Effects. Water 2018, 10, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10010072
Guo Z, Ma QW, Qin H. A Time-Domain Green’s Function for Interaction between Water Waves and Floating Bodies with Viscous Dissipation Effects. Water. 2018; 10(1):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10010072
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Zhiqun, Q. W. Ma, and Hongde Qin. 2018. "A Time-Domain Green’s Function for Interaction between Water Waves and Floating Bodies with Viscous Dissipation Effects" Water 10, no. 1: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10010072
APA StyleGuo, Z., Ma, Q. W., & Qin, H. (2018). A Time-Domain Green’s Function for Interaction between Water Waves and Floating Bodies with Viscous Dissipation Effects. Water, 10(1), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10010072





