Epibenthic Communities on Artificial Reefs in Greece, Mediterranean Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Environmental Factors
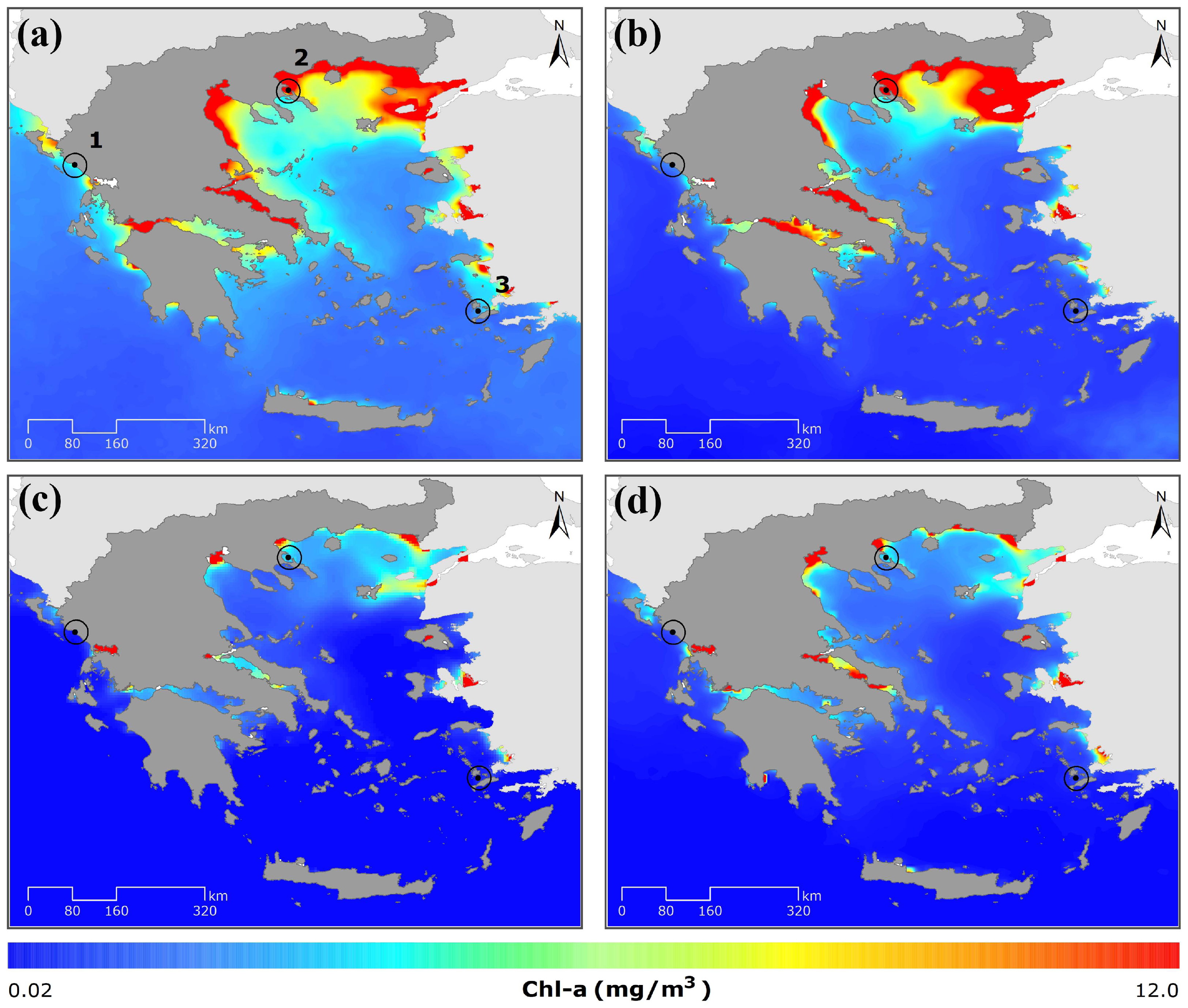
2.2.1. Sea Surface Temperature and Chlorophyll-α
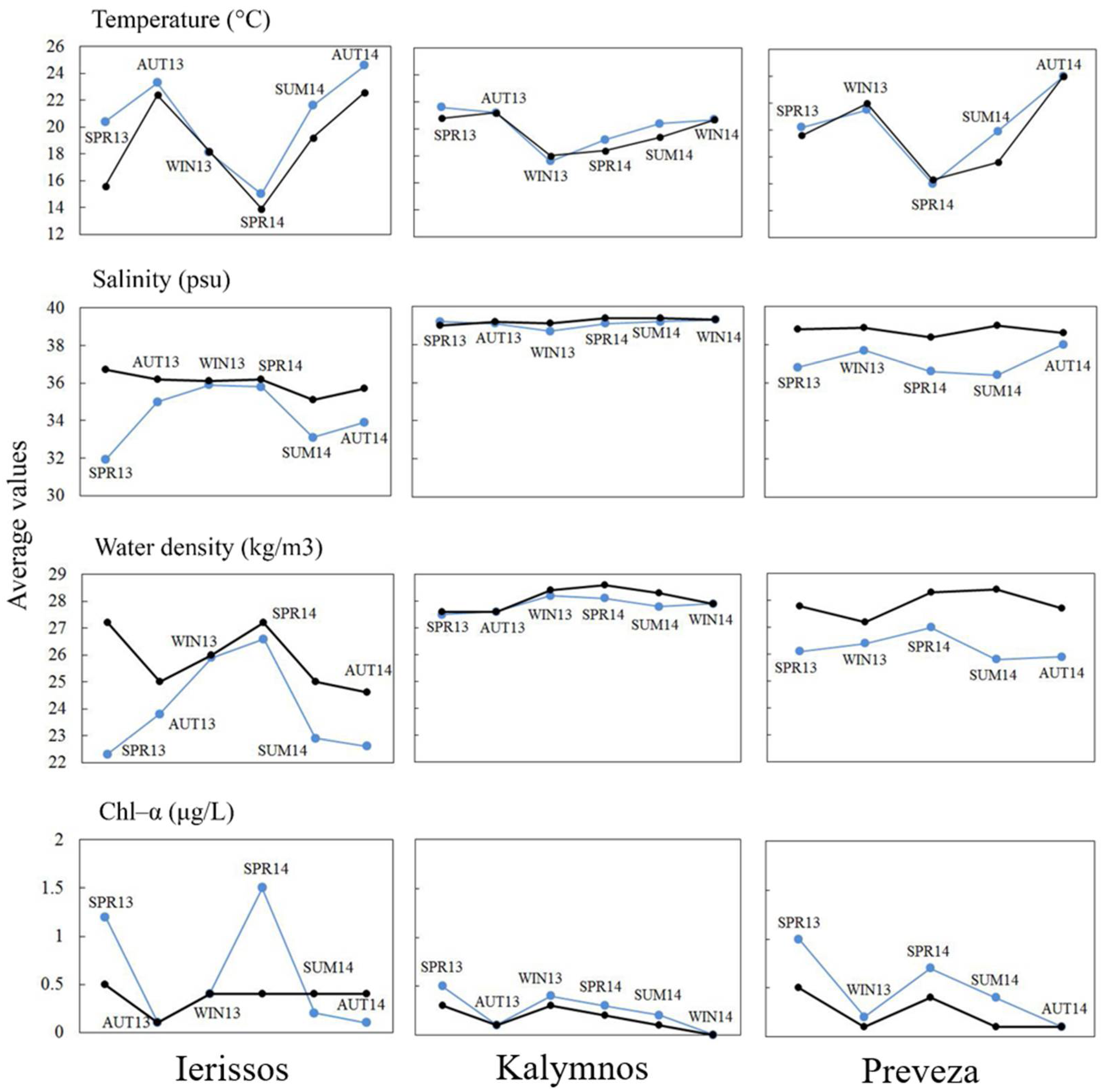
2.2.2. In Situ Environmental Parameters
2.3. Macrofauna Data Analysis
2.3.1. Macrofauna Collection
2.3.2. Community Structure and Diversity
2.3.3. Analysis of Similarity
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Factors
3.1.1. Sea Surface Temperature and Chl-α
3.1.2. In Situ Environmental Parameters
3.2. Macrofauna Data Analysis
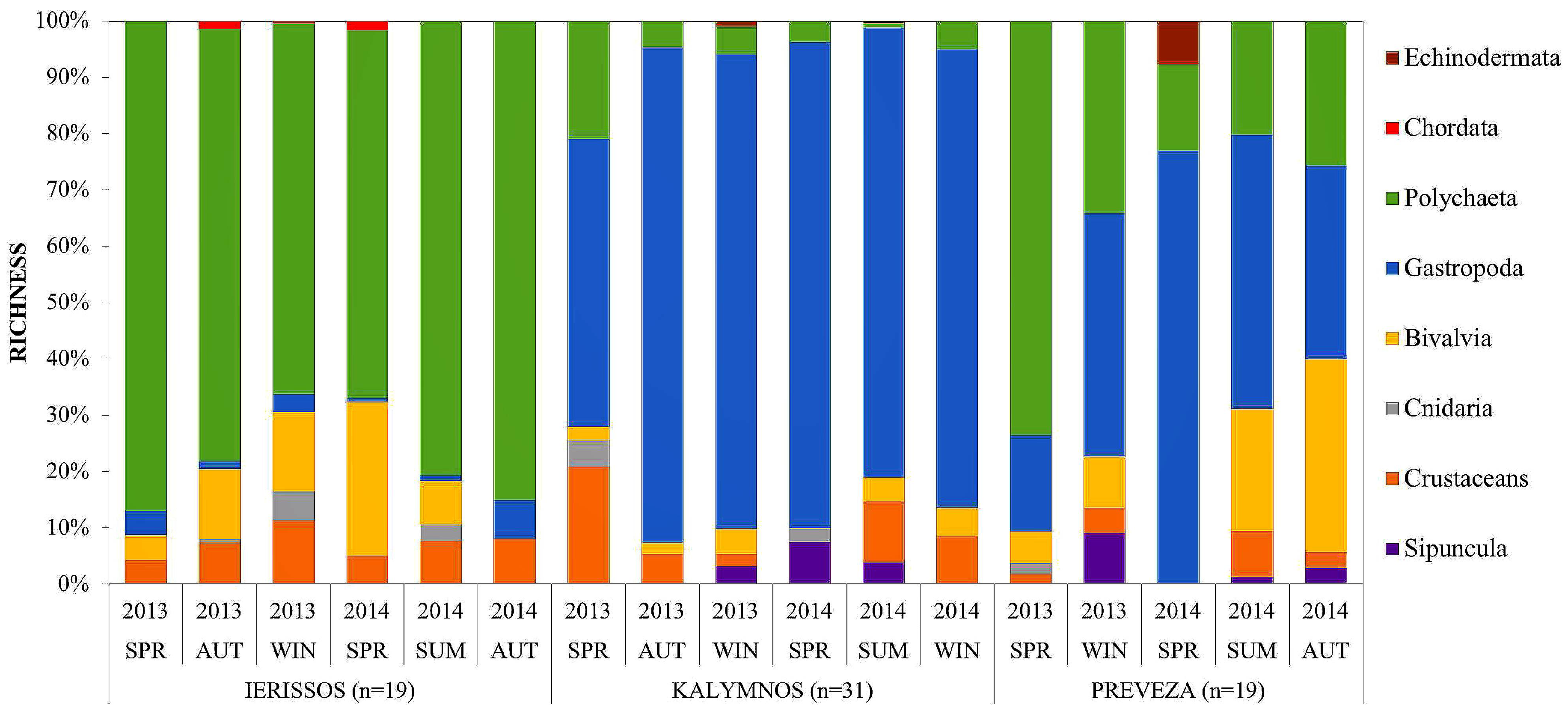
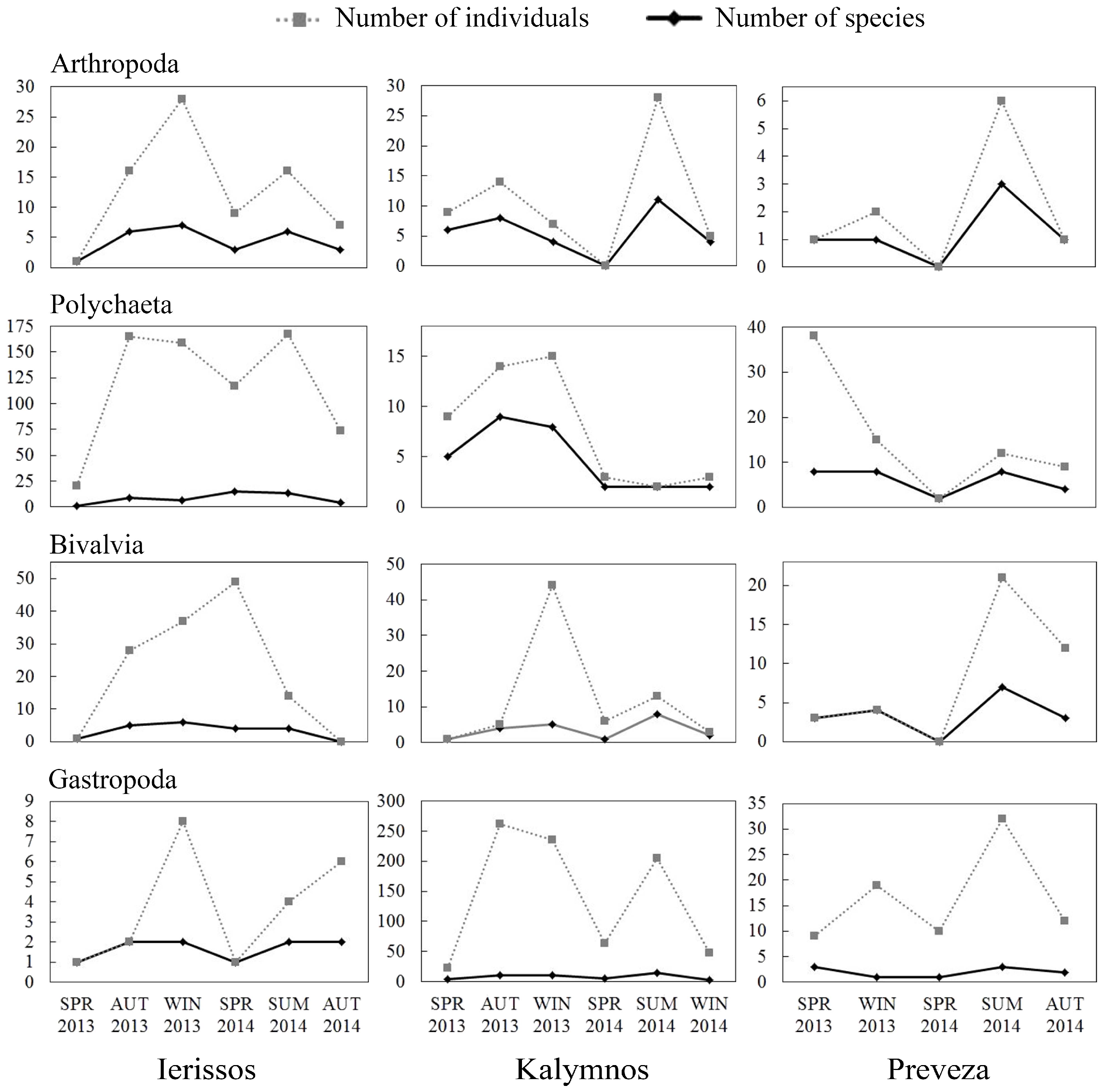
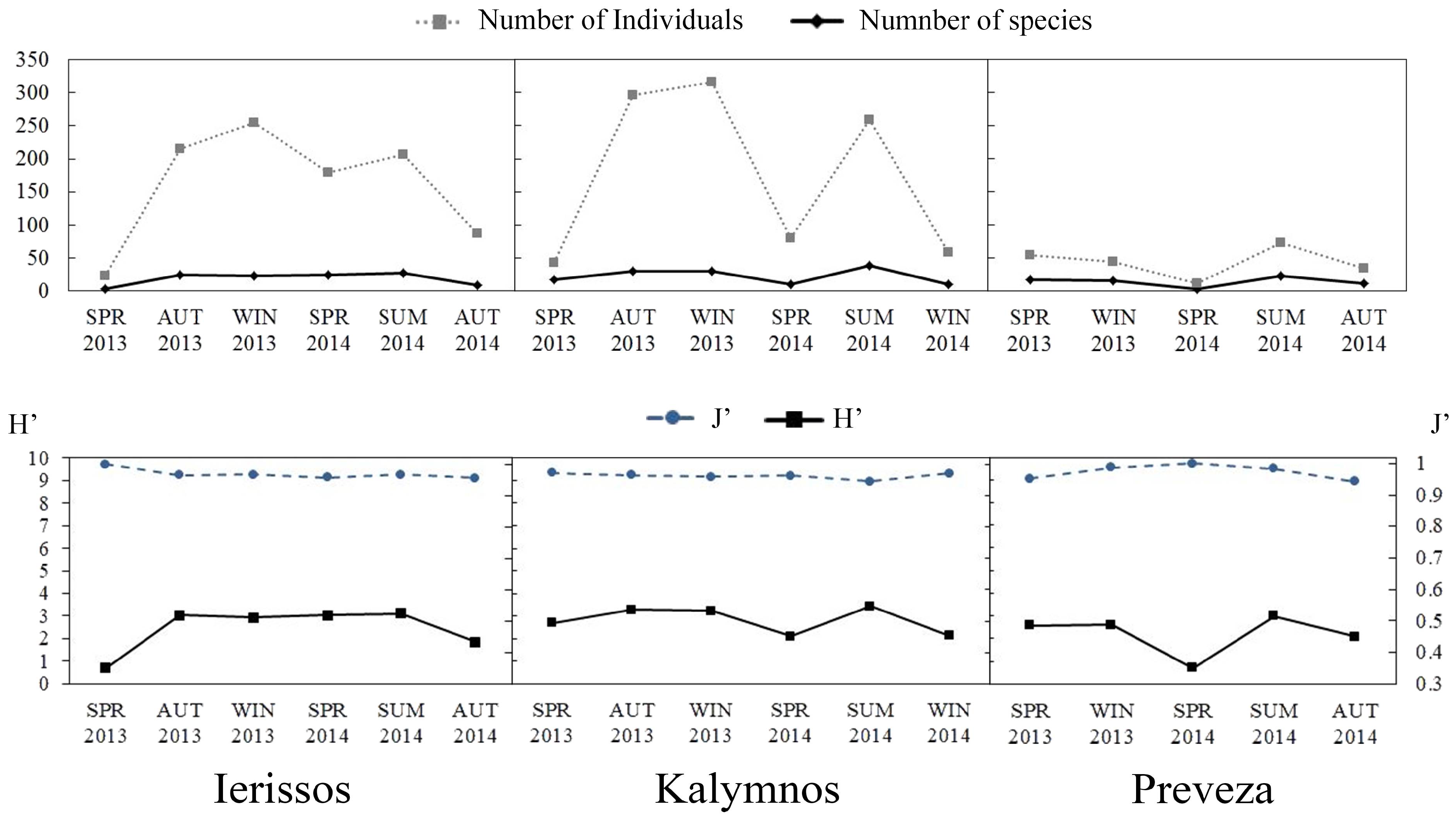
3.2.1. Community Structure
3.2.2. Diversity
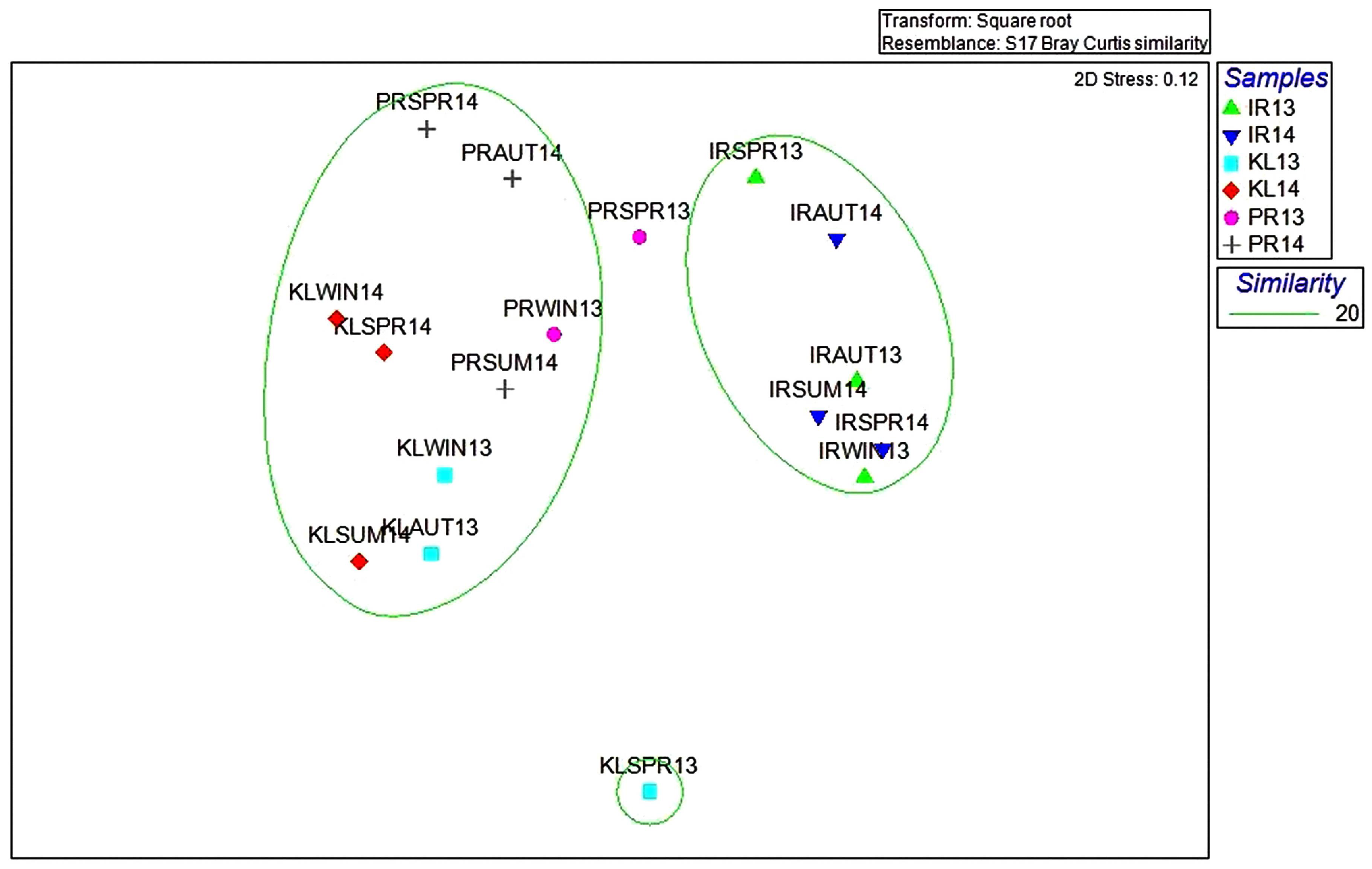
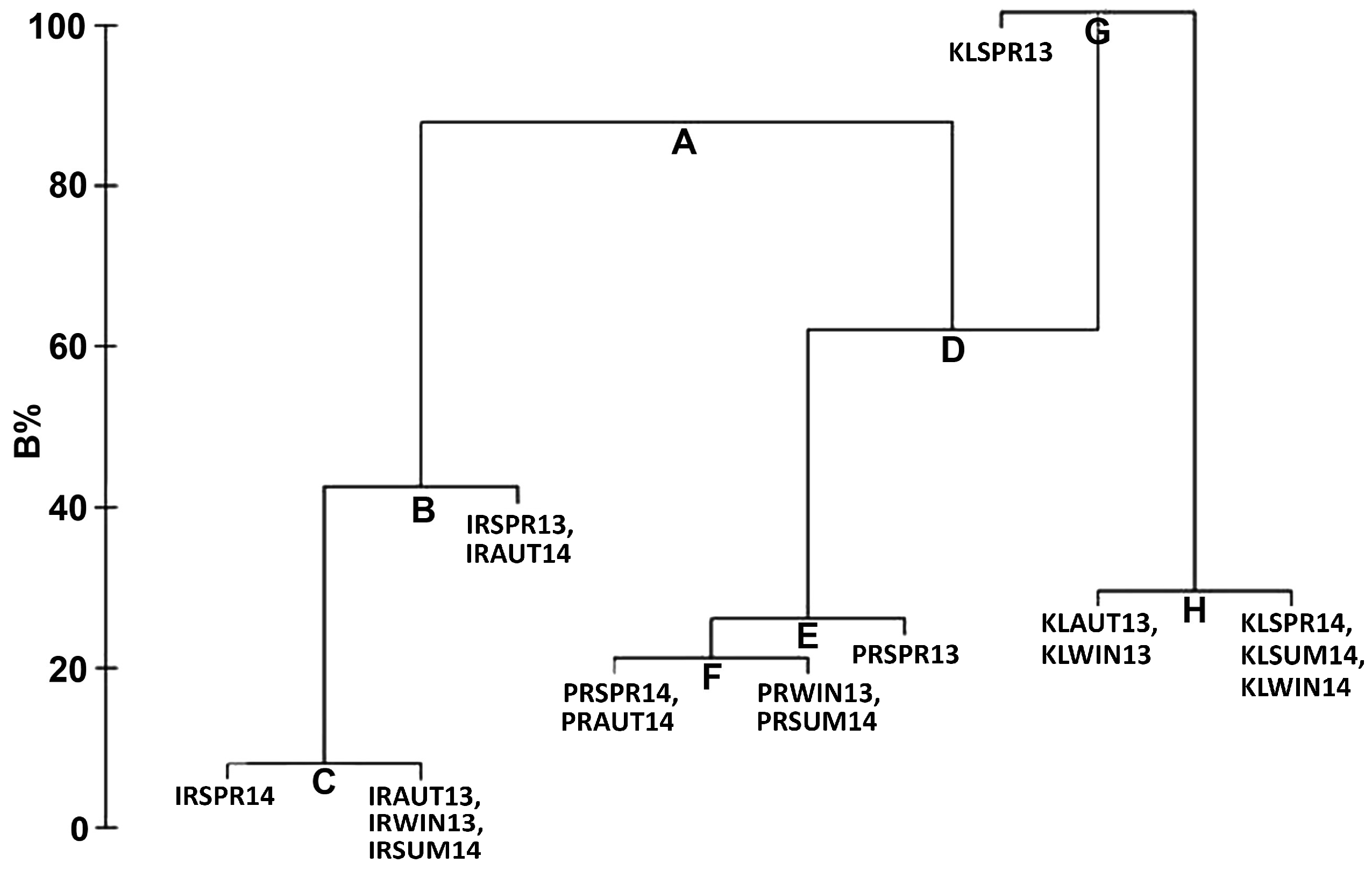
3.2.3. Analysis of Similarity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jensen, A. Artificial reefs of Europe: Perspective and future. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2002, 59, S3–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relini, G. The Loano artificial reef. In Artificial Reefs in European Seas, 1st ed.; Jensen, A.C., Collins, K.J., Lockwood, A.P.M., Eds.; Springer Science & Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 129–149. ISBN 978-0-7923-6144-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ardizzone, G.D.; Gravina, M.F.; Belluscio, A. Temporal development of epibenthic communities on artificial reefs in the Central Mediterranean Sea. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1989, 44, 592–608. [Google Scholar]
- Leitão, F. Artificial reefs: From ecological processes to fishing enhancement tools. Braz. J. Oceanogr. 2013, 61, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, C.; Hadjioannou, L.; Petrou, A.; Andreou, V.; Georgiou, A. Fouling communities of two accidental artificial reefs (modern shipwrecks) in Cyprus (Levantine Sea). Water 2016, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, C.; Andreou, V.; Evriviadou, M.; Munkes, B.; Hadjioannou, L.; Petrou, A.; Abu Alhaija, R. Epibenthic communities associated with unintentional artificial reefs (modern shipwrecks) under contrasting regimes of nutrients in the Levantine Sea (Cyprus and Lebanon). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, S.; Edwards, A.J. An evaluation of artificial reef structures as tools for marine habitat rehabilitation in the Maldives. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 1999, 9, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rilov, G.; Benayahu, Y. Rehabilitation of coral reef-fish communities: The importance of artificial-reef relief to recruitment rates. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2002, 70, 185–197. [Google Scholar]
- Rilov, G.; Benayahu, Y. Fish assemblage on natural versus vertical artificial reefs: The rehabilitation perspective. Mar. Biol. 2000, 136, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkol–Finkel, S.; Benayahu, Y. Recruitment of benthic organisms onto a planned artificial reef: Shifts in community structure one decade post-deployment. Mar. Environ. Res. 2005, 59, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siciliano, A.; Jimenez, C.; Petrou, A. Recreational diving and its effects on the macroalgal communities of the unintentional artificial reef Zenobia shipwreck (Cyprus). J. Oceanogr. Mar. Res. 2016, 4, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Svane, I.B.; Petersen, J.K. On the problems of epibioses, fouling and artificial reefs, a review. Mar. Ecol. 2001, 22, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadou, C.; Chintiroglou, C. Biodiversity of zoobenthic hard-substrate sublittoral communities in the Eastern Mediterranean (North Aegean Sea). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 62, 637–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coma, R.; Ribes, M.; Gili, J.M.; Zabala, M. Seasonality in coastal benthic ecosystems. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2000, 15, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrabou, J.; Ballesteros, E.; Zabala, M. Structure and dynamics of north-western Mediterranean rocky benthic communities along a depth gradient. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2002, 55, 493–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, T. Succession of sessile organisms on experimental plates immersed in Nabeta Bay, Izu Peninsula Japan. II. Succession of invertebrates. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1987, 38, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connell, J.H.; Slatyer, R.O. Mechanisms of succession in natural communities and their role in community stability and organization. Am. Nat. 1977, 111, 1119–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menge, B.A.; Allison, G.W.; Blanchette, C.A.; Farrell, T.M.; Olson, A.M.; Turner, T.A.; van Tamelen, P. Stasis or kinesis? Hidden dynamics of rocky intertidal macrophyte mosaic revealed by a spatially explicit approach. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2005, 314, 3–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadou, C.; Voultsidou, E.; Chintiroglou, C. Seasonal patterns of colonization and early succession on sublittoral rocky cliffs. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2011, 403, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadou, C.; Voultsiadou, E.; Chintiroglou, C. Sublittoral megabenthos along cliffs of different profile (Aegean Sea, Eastern Mediterranean). Belg. J. Zool. 2006, 136, 69–79. [Google Scholar]
- Benedetti–Cecchi, L.; Cinelli, F. Patterns of disturbance and recovery in littoral rock pools: Nonhierarchical competition and spatial variability in secondary succession. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 135, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrabou, J.; Zabala, M. Growth dynamics in four Mediterranean demosponges. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2001, 52, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gili, J.M.; Coma, R. Benthic suspension feeders: Their paramount role in littoral marine food webs. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1998, 13, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, T.; Garrabou, J.; Sartoretto, S.; Harmelin, J.G.; Francour, P.; Vacelet, J. Mass mortality of marine invertebrates: An unprecedented event in the northwestern Mediterranean. C. R. Acad. Sci. Ser. III Life Sci. 2000, 323, 853–865. [Google Scholar]
- Wollgast, S.; Lenz, M.; Wahl, M.; Molis, M. Effects of regular and irregular temporal patterns of disturbance on biomass accrual and species composition of a subtidal hard-bottom assemblage. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2008, 62, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylaios, G.K.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. A budget model to scale nutrient biochemical cycles in two semi enclosed gulfs. Environ. Model. Assess. 2009, 14, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Warwick, R.M. Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation, 2nd ed.; PRIMER-E Ltd.: Plymouth, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- McClanahan, T.R.; Ateweberhan, M.; Sebastian, C.R.; Graham, N.A.J.; Wilson, S.K.; Bruggemann, J.H.; Guillaume, M.M. Predictability of coral bleaching from synoptic satellite and in situ temperature observations. Coral Reefs 2007, 26, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, K.S.; Cornillon, P. A comparison of satellite and in situ-based sea surface temperature climatologies. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 1848–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlizzi, A.; Scuderi, D.; Fraschetti, S.; Guidetti, P.; Boero, F. Molluscs on subtidal cliffs: Patterns of spatial distribution. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2003, 83, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoudis, G.; Antoniadou, C.; Dounas, K.; Chintiroglou, C. Successional stages of experimental artificial reefs deployed in Vistonikos gulf (North Aegean Sea, Greece): Preliminary results. Belg. J. Zool. 2005, 135, 209–215. [Google Scholar]
- Gravina, M.F.; Ardizzone, G.D.; Belluscio, A. Polychaetes of an artificial reef in the Central Mediterranean Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1989, 28, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karalis, P.; Antoniadou, C.; Chintiroglou, C. Structure of the artificial hard substrate assemblages in ports in Thermaikos Gulf (North Aegean Sea). Oceanol. Acta 2003, 26, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukouras, A.; Sinis, A.I.; Bobori, D.; Kazantzidis, S.; Kitsos, M.S. The echinoderm (Deuterostomia) fauna of the Aegean Sea, and comparison with those of the neighbouring seas. J. Biol. Res. 2007, 7, 67–92. [Google Scholar]
- Koukouras, A.; Kallianiotis, A.; Vafidis, D. The decapod crustacean genera Plesionika Bate (Natantia) and Munida Leach (Anomura) in the Aegean Sea. Crustaceana 1998, 71, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukouras, A.; Russo, A.; Voultsiadou-Koukoura, E.; Arvanitidis, C.; Stefanidou, D. Macrofauna associated with sponge species of different morphology. Mar. Ecol. 1996, 17, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukouras, A.; Voultsiadou-Koukoura, E.; Chintiroglou, H.; Dounos, C. Benthic bionomy of the North Aegean Sea III. A comparison of the macrobenthic animal assemblages associated with seven sponge species. Cah. Biol. Mar. 1985, 26, 301–319. [Google Scholar]
- Koukouras, A. The genus Processa Leach (Decapoda, Caridea) in the Aegean Sea. Crustaceana 1998, 71, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanevakis, S.; Lefkaditou, E.; Galinou-Mitsoudi, S.; Koutsoubas, D.; Zenetos, A. Molluscan species of minor commercial interest in Hellenic seas: Distribution, exploitation and conservation status. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2008, 9, 77–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenetos, A.; Vardala-Theodorou, E.; Alexandrakis, C. Update of the marine Bivalvia Mollusca checklist in Greek waters. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2005, 85, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenetos, A.; Christianidis, S.; Pancucci, M.A.; Simboura, N.; Tziavos, C. Oceanologic study of an open coastal area in the Ionian Sea with emphasis on its benthic fauna and some zoogeographical remarks. Oceanol. Acta 1997, 20, 437–451. [Google Scholar]
- Zenetos, A. Diversity of marine Bivalvia in Greek waters: Effects of geography and environment. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 1997, 77, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadou, C.; Koutsoubas, D.; Chintiroglou, C.C. Mollusca fauna from infralittoral hard substrate assemblages in the North Aegean Sea. Belg. J. Zool. 2005, 135, 119. [Google Scholar]
- Dounas, C.G.; Koukouras, A.S. Circalittoral macrobenthic assemblages of Strymonikos Gulf (North Aegean Sea). Mar. Ecol. 1992, 13, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, A.; Boaventura, D.; Cúrdia, J.; Carvalho, S.; Da Fonseca, L.C.; Leitão, F.M.; Santos, M.N.; Monteiro, C.C. Effect of depth and reef structure on early macrobenthic communities of the Algarve artificial reefs (southern Portugal). Hydrobiologia 2007, 580, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olive, P.J.W. Annual breeding cycles in marine invertebrates and environmental temperature: Probing the proximate and ultimate causes of reproductive synchrony. J. Therm. Biol. 1995, 20, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadou, C.; Nicolaidou, A.; Chintiroglou, C. Polychaetes associated with the sciaphilic alga community in the northern Aegean Sea: Spatial and temporal variability. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2004, 58, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzigeorgiou, G.; Keklikoglou, K.; Faulwetter, S.; Badalamenti, F.; Kitsos, M.S.; Arvanitidis, C. Midlittoral polychaete communities in the eastern Mediterranean Sea: New information from the implementation of the Natural Geography in Shore Areas (NaGISA) protocol and comparisons at local and regional scales. Mar. Ecol. 2017, 38, e12339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irlandi, E.; Macia, S.; Serafy, J. Salinity reduction from freshwater canal discharge: Effects on mortality and feeding of an urchin (Lytechinus variegatus) and a gastropod (Lithopoma tectum). Bull. Mar. Sci. 1997, 61, 869–879. [Google Scholar]
- Abbiati, M.; Bianchi, C.N.; Castelli, A.; Giangrande, A.; Lardicci, C. Distribution of polychaetes on hard substrates of the midlittoral–infralittoral transition zone, western Mediterranean. Ophelia 1991, 5, 421–432. [Google Scholar]
- Main, M.B.; Nelson, W.G. Tolerance of the Sabellariid polychaete Phragmatopoma lapidosa Kinberg to burial, turbidity and hydrogen sulfide. Mar. Environ. Res. 1988, 26, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claudet, J.; Pelletier, D. Marine protected areas and artificial reefs: A review of the interactions between management and scientific studies. Aquat. Living Resour. 2004, 17, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francour, P.; Harmelin, J.-G.; Pollard, D.; Sartoretto, S. A review of marine protected areas in the northwestern Mediterranean region: Siting, usage, zonation and management. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2001, 11, 155–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baine, M. Artificial reefs: A review of their design, application, management and performance. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2001, 44, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, H.; Whitmarsh, D.; Jensen, A. Artificial reefs as a tool to aid rehabilitation of coastal ecosystems: Investigating the potential. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1999, 37, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Achilleos, K.; Patsalidou, M.; Jimenez, C.; Kamidis, N.; Georgiou, A.; Petrou, A.; Kallianiotis, A. Epibenthic Communities on Artificial Reefs in Greece, Mediterranean Sea. Water 2018, 10, 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10040347
Achilleos K, Patsalidou M, Jimenez C, Kamidis N, Georgiou A, Petrou A, Kallianiotis A. Epibenthic Communities on Artificial Reefs in Greece, Mediterranean Sea. Water. 2018; 10(4):347. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10040347
Chicago/Turabian StyleAchilleos, Katerina, Maria Patsalidou, Carlos Jimenez, Nikolaos Kamidis, Andreas Georgiou, Antonis Petrou, and Argyris Kallianiotis. 2018. "Epibenthic Communities on Artificial Reefs in Greece, Mediterranean Sea" Water 10, no. 4: 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10040347
APA StyleAchilleos, K., Patsalidou, M., Jimenez, C., Kamidis, N., Georgiou, A., Petrou, A., & Kallianiotis, A. (2018). Epibenthic Communities on Artificial Reefs in Greece, Mediterranean Sea. Water, 10(4), 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10040347





