Validation of TRMM 3B42V7 Rainfall Product under Complex Topographic and Climatic Conditions over Hexi Region in the Northwest Arid Region of China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. TRMM Satellite Precipitation Data
2.2.2. Meteorological Stations Based Precipitation Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Assessment Methods
2.3.2. BIAS Correction Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Assessment Results
3.1.1. Overall Assessment
3.1.2. Seasonal Assessment
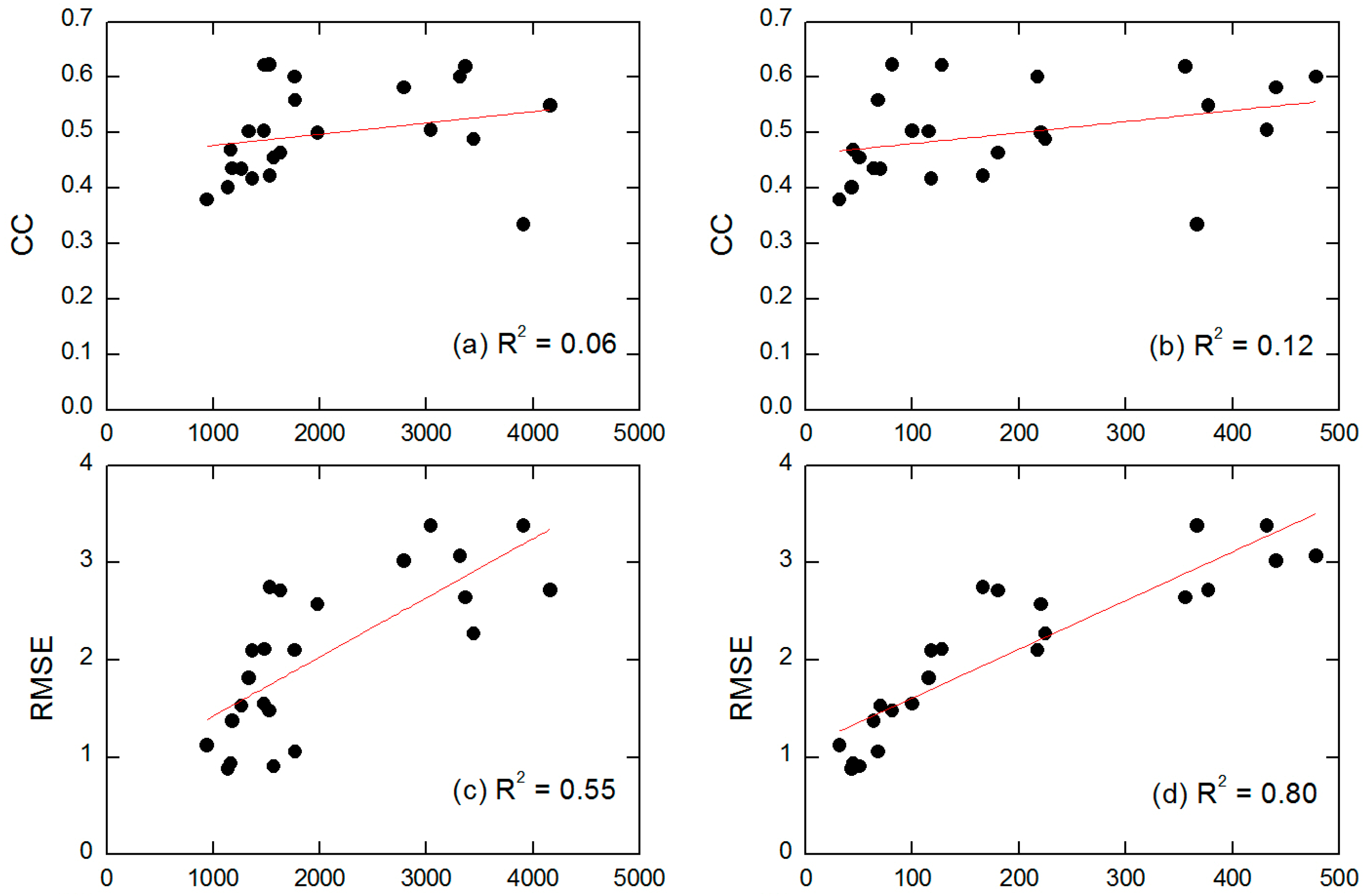
3.1.3. Spatial Distribution of the Error Statistics at Different Time Scales
3.1.4. Analysis of the Detection Capability on Rainfall Events
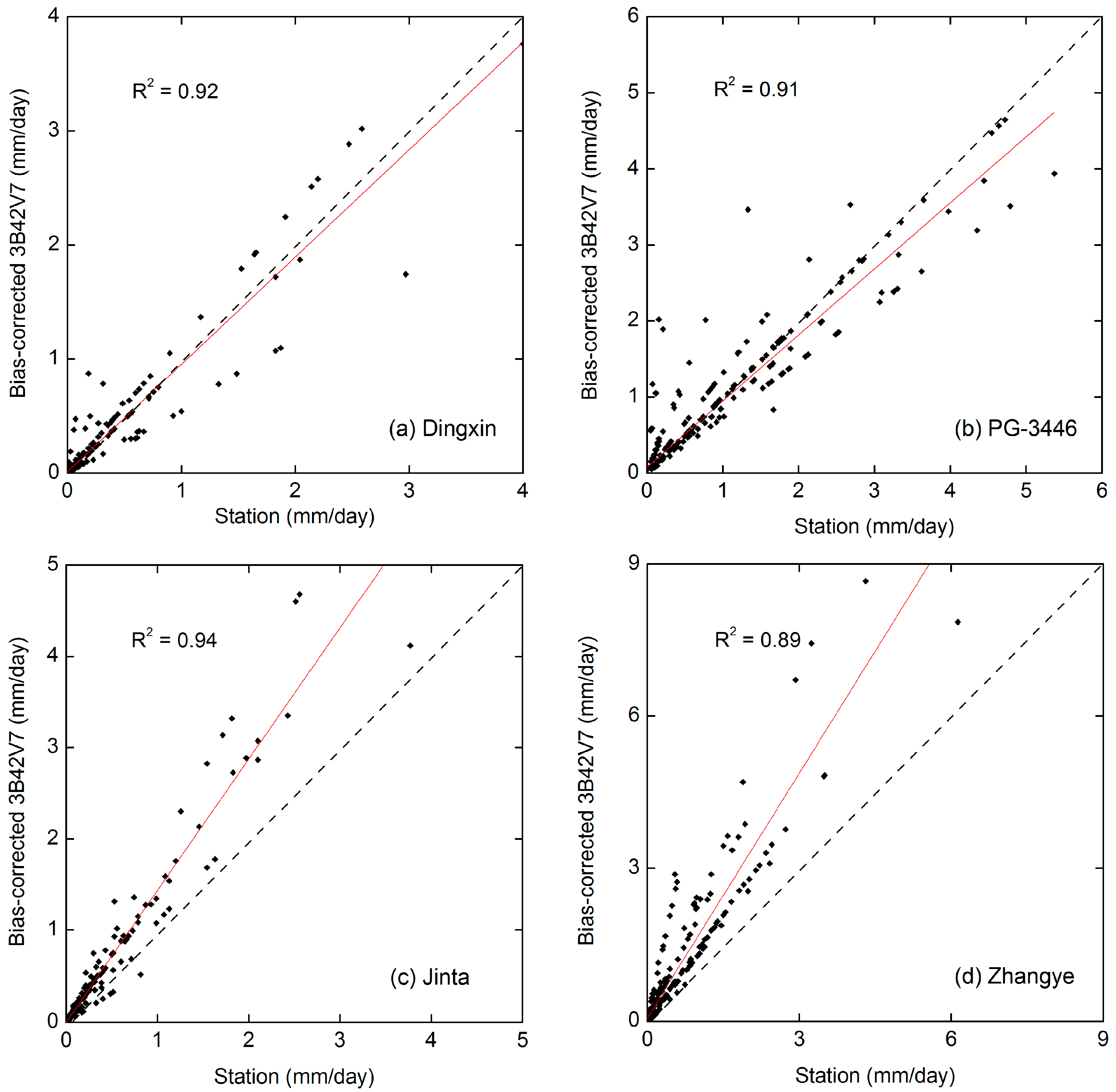
3.2. BIAS Correction Results
4. Conclusions
- The 3B42V7 rainfall product can effectively capture the spatiotemporal variations of precipitation in the Hexi region and overestimate the precipitation with Bias of 11.16%, and ABias of 121.99%, 43.80%, 25.87% at daily, monthly and annual respectively. Compared with ground observations, 3B42V7 shows relatively low correlation at daily time series than at monthly and annual time series. Precipitation in the Hexi region has an obvious seasonal distribution characteristic. The 3B42V7 performs much better during warm seasons (summer and autumn) than in cold seasons (spring and winter).
- Similar spatial distribution characteristics of evaluation metrics are found at daily, monthly and annual time scales. The 3B42V7 is more likely to underestimate the precipitation in high-altitude mountainous areas and overestimate the precipitation in low-elevation areas. The 3B42V7 shows better correlation with rain gauges located in the southern mountainous and central oasis areas than in the northern extreme arid region. The error magnitude measured by RMSE (MAE) exhibited a significant decreasing trend from south to north, east to west.
- Altitude and rainfall are important factors for the different distribution of the evaluation indexes. Absolute error distribution characteristics (MAE, ABias and RMSE) of 3B42V7 have better correlation with altitude and rainfall than the relative error indexes (CC, ME and Bias). The distribution of the error on the daily scale is more related to the elevation and rainfall than in monthly and annual scale.
- The ability of 3B42V7 to detect precipitation events increases with the increasing of precipitation intensity. The 3B42V7 significantly overestimates the precipitation events in the Hexi region with an average POD of 0.59, FAR of 0.60, FBI of 1.46, and CSI of 0.32. The overestimation is mainly concentrated in tiny rain (0–1 mm/d). Better detection capabilities can be found at high-altitude areas.
- The bias-corrected 3B42V7 has been significantly improved in both the monthly and daily time series. The method of correcting 3B42V7 product using the monthly mean deviation is considered to be feasible and can be used for bias correction of 3B42V7 rainfall product across the whole Hexi region.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013.
- Son, K.; Bae, D. Drought analysis according to shifting of climate zones to arid climate zone over Asia monsoon region. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, C.; Yin, F. Impacts of land use and land cover changes on surface energy and water balance in the Heihe River Basin of China, 2000–2010. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2015, 79–82, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, R.P.; Soden, B.J. Atmospheric warming and the amplification of precipitation extremes. Science 2008, 321, 1481–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Chen, Y.; Shi, P.; Zhang, L.; Pan, J.; Zhao, H. Land use and land cover change and driving mechanism in the arid inland river basin: A case study of Tarim River, Xinjiang, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Kang, E.; Chen, R.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, B. The impact of the development of water resources on environment in arid inland river basins of Hexi region, Northwestern China. Environ. Geol. 2006, 50, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.S.; Cheng, G.D.; Lan, Y.C.; Jin, H.J. A model for simulating the response of runoff from the mountainous watersheds of inland river basins in the arid area of northwest China to climatic changes. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 1999, 42, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, H.; Zou, S.; Yang, D.; Wang, Y.; Yin, Z.; Lu, Z.; Li, F.; Xu, B. Runoff Simulation by SWAT Model Using High-Resolution Gridded Precipitation in the Upper Heihe River Basin, Northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Water 2017, 9, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhou, M.; Ren, L.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, P. Evaluation of latest TMPA and CMORPH satellite precipitation products over Yellow River Basin. Water Sci. Eng. 2016, 9, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, G. Temporal Distribution Characteristics of Alpine Precipitation and Their Vertical Differentiation: A Case Study from the Upper Shule River. Water 2017, 9, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Yuan, H.; Liu, X.; Jiang, X. Evaluation of the latest satellite-gauge precipitation products and their hydrologic applications over the Huaihe River basin. J. Hydrol. 2016, 536, 302–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.; Mitra, A.K.; AghaKouchak, A.; Pai, D.S. Error characterization of TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA-3B42) products over India for different seasons. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 1302–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Li, L.; Hao, Z.; Wang, J.; Shao, Q. Suitability of TRMM satellite rainfall in driving a distributed hydrological model in the source region of Yellow River. J. Hydrol. 2014, 509, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.L.; Tan, K.C.; Chua, V.P.; Chan, N.W. Evaluation of TRMM Product for Monitoring Drought in the Kelantan River Basin, Malaysia. Water 2017, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Zad, S.; Zulkafli, Z.; Muharram, F. Satellite Rainfall (TRMM 3B42-V7) Performance Assessment and Adjustment over Pahang River Basin, Malaysia. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Li, W.; Wen, J.; Qiu, C.; Sun, W.; Fang, Q.; Xu, M.; Tan, J. Accuracy Evaluation of Two High-Resolution Satellite-Based Rainfall Products: TRMM 3B42V7 and CMORPH in Shanghai. Water 2018, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Tian, F.; Yang, L.; Hu, H.; Lu, H.; Hou, A. Ground validation of GPM IMERG and TRMM 3B42V7 rainfall products over southern Tibetan Plateau based on a high-density rain gauge network. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 910–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Ren, L.; Yong, B.; Hong, Y.; Yang, X.; Yuan, F. Evaluation of latest TMPA and CMORPH precipitation products with independent rain gauge observation networks over high-latitude and low-latitude basins in China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Jin, C.; Wang, A.; Guan, D.; Wu, J.; Yuan, F.; Xu, L. Comprehensive precipitation evaluation of TRMM 3B42 with dense rain gauge networks in a mid-latitude basin, northeast, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 126, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebere, S.; Alamirew, T.; Merkel, B.; Melesse, A. Performance of High Resolution Satellite Rainfall Products over Data Scarce Parts of Eastern Ethiopia. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 11639–11663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, K.; Su, F.; Yang, D.; Hao, Z. Evaluation of satellite precipitation retrievals and their potential utilities in hydrologic modeling over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C. Suitability of the TRMM satellite rainfalls in driving a distributed hydrological model for water balance computations in Xinjiang catchment, Poyang lake basin. J. Hydrol. 2012, 426–427, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Zhang, K.; Hong, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Xue, X.; Chen, S. Evaluation of the TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis and its applicability in supporting reservoir operation and water resources management in Hanjiang basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2017, 549, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiraie-Boroujerdy, P.; Akbari Asanjan, A.; Hsu, K.; Sorooshian, S. Intercomparison of PERSIANN-CDR and TRMM-3B42V7 precipitation estimates at monthly and daily time scales. Atmos. Res. 2017, 193, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Hong, Y.; Chen, S.; Zou, C.B.; Gourley, J.J.; Yong, B. Performance assessment of the successive Version 6 and Version 7 TMPA products over the climate-transitional zone in the southern Great Plains, USA. J. Hydrol. 2014, 513, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, D.; Hong, Y. Multi-scale evaluation of high-resolution multi-sensor blended global precipitation products over the Yangtze River. J. Hydrol. 2013, 500, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worqlul, A.W.; Ayana, E.K.; Maathuis, B.H.P.; MacAlister, C.; Philpot, W.D.; Osorio Leyton, J.M.; Steenhuis, T.S. Performance of bias corrected MPEG rainfall estimate for rainfall-runoff simulation in the upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. 2018, 556, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrat-Capdevila, A.; Valdes, J.B.; Stakhiv, E.Z. Water Management Applications for Satellite Precipitation Products: Synthesis and Recommendations. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2014, 50, 509–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggioni, V.; Massari, C. On the performance of satellite precipitation products in riverine flood modeling: A review. J. Hydrol. 2018, 558, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stisen, S.; Sandholt, I. Evaluation of remote-sensing-based rainfall products through predictive capability in hydrological runoff modelling. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, E.; Haile, A.; Sazib, N.; Zhang, Y.; Rientjes, T. Effect of Bias Correction of Satellite-Rainfall Estimates on Runoff Simulations at the Source of the Upper Blue Nile. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 6688–6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teutschbein, C.; Seibert, J. Bias correction of regional climate model simulations for hydrological climate-change impact studies: Review and evaluation of different methods. J. Hydrol. 2012, 456–457, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.N.; Li, Z.; Fan, Y.T.; Wang, H.J.; Fang, G.H. Research progress on the impact of climate change on water resources in the arid region of Northwest China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 69, 1295–1304. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Ding, Y.; Iqbal, M. Defining Runoff Indices and Analyzing Their Relationships with Associated Precipitation and Temperature Indices for Upper River Basins in the Northwest Arid Region of China. Water 2017, 9, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Fan, Y.; Wang, H.; Deng, H. Progress and prospects of climate change impacts on hydrology in the arid region of northwest China. Environ. Res. 2015, 139, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C. Groundwater recharge and hydrogeochemical evolution in the Ejina Basin, northwest China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 476, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Deng, H.; Li, B.; Li, Z.; Xu, C. Abrupt change of temperature and precipitation extremes in the arid region of Northwest China. Quat. Int. 2014, 336, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.Z.; Zhao, W.Z.; Su, P.X.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, T.; Ram, R. Ecological effects of desertification control and desertified land reclamation in an oasis–desert ecotone in an arid region: A case study in Hexi Corridor, northwest China. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 29, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapiano, M.R.P.; Arkin, P.A. An Intercomparison and Validation of High-Resolution Satellite Precipitation Estimates with 3-Hourly Gauge Data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2009, 10, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.C.; Liu, M.F. Evaluation of high-resolution satellite precipitation products using rain gauge observations over the Tibetan Plateau. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, N.A.; Zhang, J.M.; Cheng, H.Y.; Guo, J.Y.; Zhao, Q. The age of formation of the mirabilite and sand wedges in the Hexi Corridor and their paleoclimatic interpretation. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2003, 48, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Guo, X.; Wang, T. Relationship between large scale atmospheric circulation, temperature and precipitation in the Extensive Hexi region, China, 1960–2011. Quat. Int. 2016, 392, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhang, J. Relationships between sustainable development and water resources in arid oases area—An example of HEXI corridor. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2004, 18, 50–55. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kang, E. Review and Prospect of Hydrological Studies in Cold and Arid Regions of China. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2000, 22, 178–188. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Ibrahim, A.; Duan, Z.; Cracknell, A.; Chaplot, V. Evaluation of Six High-Resolution Satellite and Ground-Based Precipitation Products over Malaysia. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1504–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E.F. The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): Quasi-Global, Multiyear, Combined-Sensor Precipitation Estimates at Fine Scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, E.E.; Janowiak, J.E.; Kidd, C. Comparison of Near-Real-Time Precipitation Estimates from Satellite Observations and Numerical Models. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arias-Hidalgo, M.; Bhattacharya, B.; Mynett, A.E.; van Griensven, A. Experiences in using the TMPA-3B42R satellite data to complement rain gauge measurements in the Ecuadorian coastal foothills. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 2905–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vernimmen, R.R.E.; Hooijer, A.; Mamenun; Aldrian, E.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M. Evaluation and bias correction of satellite rainfall data for drought monitoring in Indonesia. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anjum, M.N.; Ding, Y.; Shangguan, D.; Tahir, A.A.; Iqbal, M.; Adnan, M. Comparison of two successive versions 6 and 7 of TMPA satellite precipitation products with rain gauge data over Swat Watershed, Hindukush Mountains, Pakistan. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2016, 17, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, F.; Zhang, L.; Win, K.; Ren, L.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y. Assessment of GPM and TRMM Multi-Satellite Precipitation Products in Streamflow Simulations in a Data-Sparse Mountainous Watershed in Myanmar. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Christakos, G.; Ding, X.; Wu, J. Adequacy of TRMM satellite rainfall data in driving the SWAT modeling of Tiaoxi catchment (Taihu lake basin, China). J. Hydrol. 2018, 556, 1139–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.; Arkin, P.A. Improved Estimates of Tropical and Subtropical Precipitation Using the GOES Precipitation Index. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1997, 14, 997–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, R.R.; Smith, E.A.; Berg, W.; Huffman, G.J. A Screening Methodology for Passive Microwave Precipitation Retrieval Algorithms. J. Atmos. Sci. 1998, 55, 1583–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheel, M.L.M.; Rohrer, M.; Huggel, C.; Santos Villar, D.; Silvestre, E.; Huffman, G.J. Evaluation of TRMM Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) performance in the Central Andes region and its dependency on spatial and temporal resolution. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2649–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Hong, Y.; Gourley, J.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Tian, Y.; Cao, Q.; Yong, B.; Kirstetter, P.; Hu, J.; Hardy, J.; et al. Evaluation of the successive V6 and V7 TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis over the Continental United States. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 8174–8186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yong, B.; Hong, Y.; Ren, L.; Gourley, J.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Khan, S.I. Assessment of evolving TRMM-based multisatellite real-time precipitation estimation methods and their impacts on hydrologic prediction in a high latitude basin. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D09108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Duan, Z. Assessment of GPM and TRMM Precipitation Products over Singapore. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Xiao, C.; Anjum, M.; Adnan, M.; Nawaz, Z.; Ijaz, M.; Sajid, M.; Farid, H. Evaluation and Comparison of TRMM Multi-Satellite Precipitation Products with Reference to Rain Gauge Observations in Hunza River Basin, Karakoram Range, Northern Pakistan. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hong, Y.; Cao, Q.; Gourley, J.J.; Kirstetter, P.; Yong, B.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Hu, J.; et al. Similarity and difference of the two successive V6 and V7 TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis performance over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 13060–13074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Yatagai, A. Evaluation of TRMM 3B42 product using a new gauge-based analysis of daily precipitation over China. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 2749–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, D.B.; Marks, D.A.; Amitai, E.; Silberstein, D.S.; Fisher, B.L.; Tokay, A.; Wang, J.; Pippitt, J.L. Ground Validation for the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM). J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2005, 22, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipunic, R.C.; Ryu, D.; Costelloe, J.F.; Su, C. An evaluation and regional error modeling methodology for near-real-time satellite rainfall data over Australia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 10767–10783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Hong, Y.; Limaye, A.S.; Gourley, J.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Khan, S.I.; Dorji, C.; Chen, S. Statistical and hydrological evaluation of TRMM-based Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis over the Wangchu Basin of Bhutan: Are the latest satellite precipitation products 3B42V7 ready for use in ungauged basins? J. Hydrol. 2013, 499, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Duan, Z.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, A. Evaluation of Three Satellite Precipitation Products TRMM 3B42, CMORPH, and PERSIANN over a Subtropical Watershed in China. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 151239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Station | Longitude (°E) | Latitude (°N) | Altitude (m) | Annual Precipitation (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ejina | 101.07 | 41.95 | 940.5 | 31.63 |
| Hongliuhe | 94.67 | 41.53 | 1573.8 | 50.39 |
| Mazongshan | 97.03 | 41.80 | 1770.4 | 68.06 |
| Dunhuang | 94.68 | 40.15 | 1139 | 43.10 |
| Anxi | 95.77 | 40.53 | 1170.9 | 44.63 |
| Yumenzhen | 97.03 | 40.27 | 1526 | 80.87 |
| Dingxin | 99.52 | 40.30 | 1177.4 | 63.37 |
| Jinta | 98.90 | 40.00 | 1270.5 | 69.74 |
| Jiuquan | 98.48 | 39.77 | 1477.2 | 99.54 |
| Gaotai | 99.83 | 39.37 | 1332.2 | 115.17 |
| Tuole | 98.42 | 38.80 | 3367 | 355.90 |
| Yeniugou | 99.58 | 38.42 | 3320 | 478.59 |
| Zhangye | 100.43 | 38.93 | 1482.7 | 128.07 |
| Qilian | 100.25 | 38.18 | 2787.4 | 440.83 |
| Shandan | 101.08 | 38.80 | 1764.6 | 217.40 |
| Yongchang | 101.97 | 38.23 | 1976.9 | 220.30 |
| Wuwei | 102.67 | 37.92 | 1531.5 | 165.87 |
| Minqin | 103.08 | 38.63 | 1367.5 | 117.51 |
| Wushaoling | 102.87 | 37.20 | 3045.1 | 432.07 |
| Jingtai | 104.05 | 37.18 | 1630.9 | 180.37 |
| PG-3446 | 97.72 | 38.84 | 3446 | 224.91 |
| PG-3915 | 98.31 | 38.42 | 3915 | 367.01 |
| PG-4164 | 98.36 | 38.56 | 4164 | 377.52 |
| Statistical Indicators | Daily | Monthly | Annual |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (Station, 3B42V7) | (0.52, 0.58) | (15.84, 17.61) | (190.12, 211.34) |
| CC | 0.53 | 0.89 | 0.91 |
| ME | 0.06 | 1.77 | 21.22 |
| MAE | 0.64 | 6.94 | 49.18 |
| RMSE | 2.21 | 12.37 | 65.47 |
| Bias | 11.16 | 11.16 | 11.16 |
| ABias | 121.99 | 43.80 | 25.87 |
| Statistical Indicators | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (Station, 3B42V7) | (5.07, 8.26) | (66.13, 73.61) | (107.59, 114.06) | (11.33, 15.41) |
| CC | 0.51 | 0.84 | 0.91 | 0.57 |
| ME | 3.19 | 7.48 | 6.46 | 4.09 |
| MAE | 4.66 | 23.29 | 28.90 | 7.21 |
| RMSE | 5.73 | 31.12 | 38.56 | 9.77 |
| Bias | 62.79 | 11.32 | 6.01 | 36.08 |
| ABias | 91.77 | 35.22 | 26.86 | 63.67 |
| Experimental Station | Ground Data, Annual Rainfall (mm/year) | Original 3B42V7 | Monthly Bias Corrector | Corrected 3B42V7 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual Rainfall (mm/year) | Bias (%) | RMSE (mm/year) | Annual Rainfall (mm/year) | Bias (%) | RMSE (mm/year) | |||
| Ejina | 31.63 | 66.61 | 110.60 | 40.67 | 0.47 | 42.39 | 34.04 | 18.56 |
| Hongliuhe | 50.39 | 49.09 | −2.58 1 | 20.83 | 1.03 | 56.68 | 12.49 | 21.01 |
| Mazongshan | 68.06 | 69.85 | 2.63 | 11.93 | 0.97 | 68.59 | 0.78 | 11.57 |
| Dunhuang | 43.10 | 48.41 | 12.33 | 11.23 | 0.89 | 45.65 | 5.92 | 9.27 |
| Yumenzhen | 80.87 | 86.16 | 6.54 | 17.34 | 0.94 | 88.46 | 9.38 | 17.25 |
| Dingxin | 63.37 | 101.98 | 60.92 | 47.41 | 0.62 | 69.93 | 10.36 | 22.39 |
| Jiuquan | 99.54 | 129.56 | 30.15 | 32.08 | 0.77 | 100.83 | 1.29 | 10.47 |
| Gaotai | 115.17 | 161.01 | 39.80 | 54.37 | 0.72 | 121.33 | 5.34 | 28.72 |
| Yeniugou | 478.59 | 456.14 | −4.69 | 55.15 | 1.05 | 482.82 | 0.89 | 50.80 |
| Qilian | 440.83 | 448.33 | 1.70 | 82.75 | 0.98 | 453.67 | 2.91 | 82.09 |
| Shandan | 217.40 | 200.90 | −7.59 | 37.14 | 1.08 | 220.45 | 1.40 | 34.56 |
| Yongchang | 220.30 | 300.72 | 36.50 | 93.57 | 0.73 | 228.00 | 3.49 | 45.79 |
| Minqin | 117.51 | 140.14 | 19.26 | 29.77 | 0.84 | 119.72 | 1.88 | 18.00 |
| Wushaoling | 432.07 | 419.22 | −2.97 | 65.84 | 1.03 | 443.24 | 2.59 | 64.45 |
| Jingtai | 180.37 | 226.19 | 25.40 | 79.29 | 0.80 | 196.56 | 8.98 | 61.59 |
| PG-3446 | 224.91 | 270.78 | 20.39 | 62.02 | 0.83 | 229.72 | 2.14 | 39.42 |
| PG-3915 | 367.01 | 313.32 | −14.63 | 66.31 | 1.17 | 368.53 | 0.41 | 43.29 |
| PG-4164 | 377.52 | 331.97 | −12.06 | 59.92 | 1.14 | 378.12 | 0.16 | 43.21 |
| Verification Station | Ground Data, Annual Rainfall (mm/year) | Original 3B42V7 | Monthly Bias Corrector | Corrected 3B42V7 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual Rainfall (mm/year) | Bias (%) | RMSE (mm/year) | Annual Rainfall (mm/year) | Bias (%) | RMSE (mm/year) | |||
| Anxi | 44.63 | 57.48 | 28.81 | 20.79 | 0.93 | 53.56 | 20.02 | 18.21 |
| Jinta | 69.74 | 125.95 | 80.59 | 61.90 | 0.79 | 99.83 | 43.14 | 37.64 |
| Tuole | 355.90 | 313.26 | −11.98 | 76.72 | 1.04 | 325.80 | −8.46 | 72.20 |
| Zhangye | 128.07 | 277.72 | 116.85 | 157.40 | 0.82 | 226.46 | 76.82 | 106.30 |
| Wuwei | 165.87 | 266.13 | 60.44 | 106.79 | 0.88 | 233.43 | 40.73 | 76.98 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, J. Validation of TRMM 3B42V7 Rainfall Product under Complex Topographic and Climatic Conditions over Hexi Region in the Northwest Arid Region of China. Water 2018, 10, 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10081006
Wang X, Ding Y, Zhao C, Wang J. Validation of TRMM 3B42V7 Rainfall Product under Complex Topographic and Climatic Conditions over Hexi Region in the Northwest Arid Region of China. Water. 2018; 10(8):1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10081006
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiuna, Yongjian Ding, Chuancheng Zhao, and Jian Wang. 2018. "Validation of TRMM 3B42V7 Rainfall Product under Complex Topographic and Climatic Conditions over Hexi Region in the Northwest Arid Region of China" Water 10, no. 8: 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10081006
APA StyleWang, X., Ding, Y., Zhao, C., & Wang, J. (2018). Validation of TRMM 3B42V7 Rainfall Product under Complex Topographic and Climatic Conditions over Hexi Region in the Northwest Arid Region of China. Water, 10(8), 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10081006





