Evaluation of Hyperspectral Multi-Band Indices to Estimate Chlorophyll-A Concentration Using Field Spectral Measurements and Satellite Data in Dianshan Lake, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Datasets
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Field Spectral Measurements Data
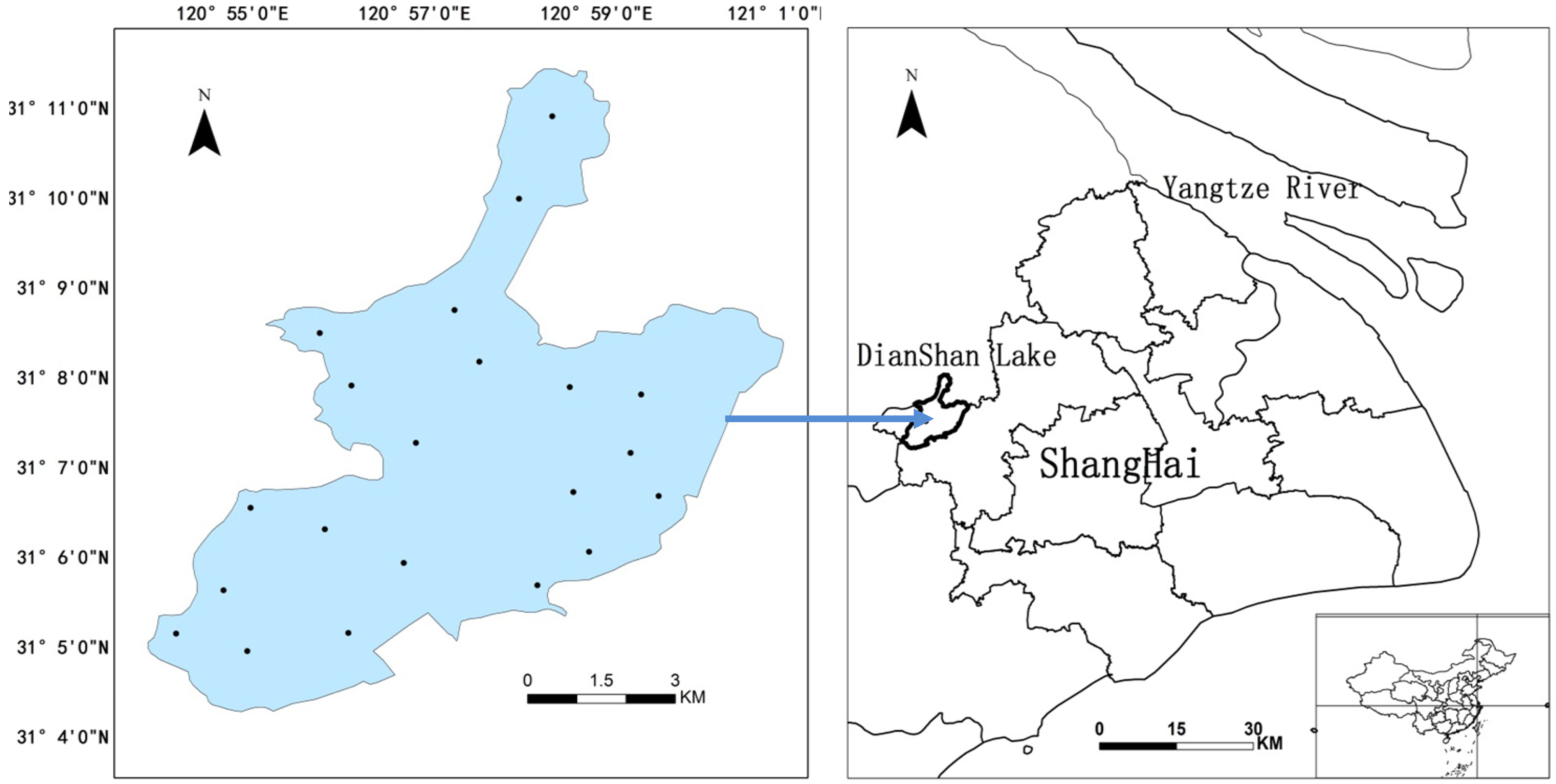
2.3. In-situ Chl-a Data
3. Analyses
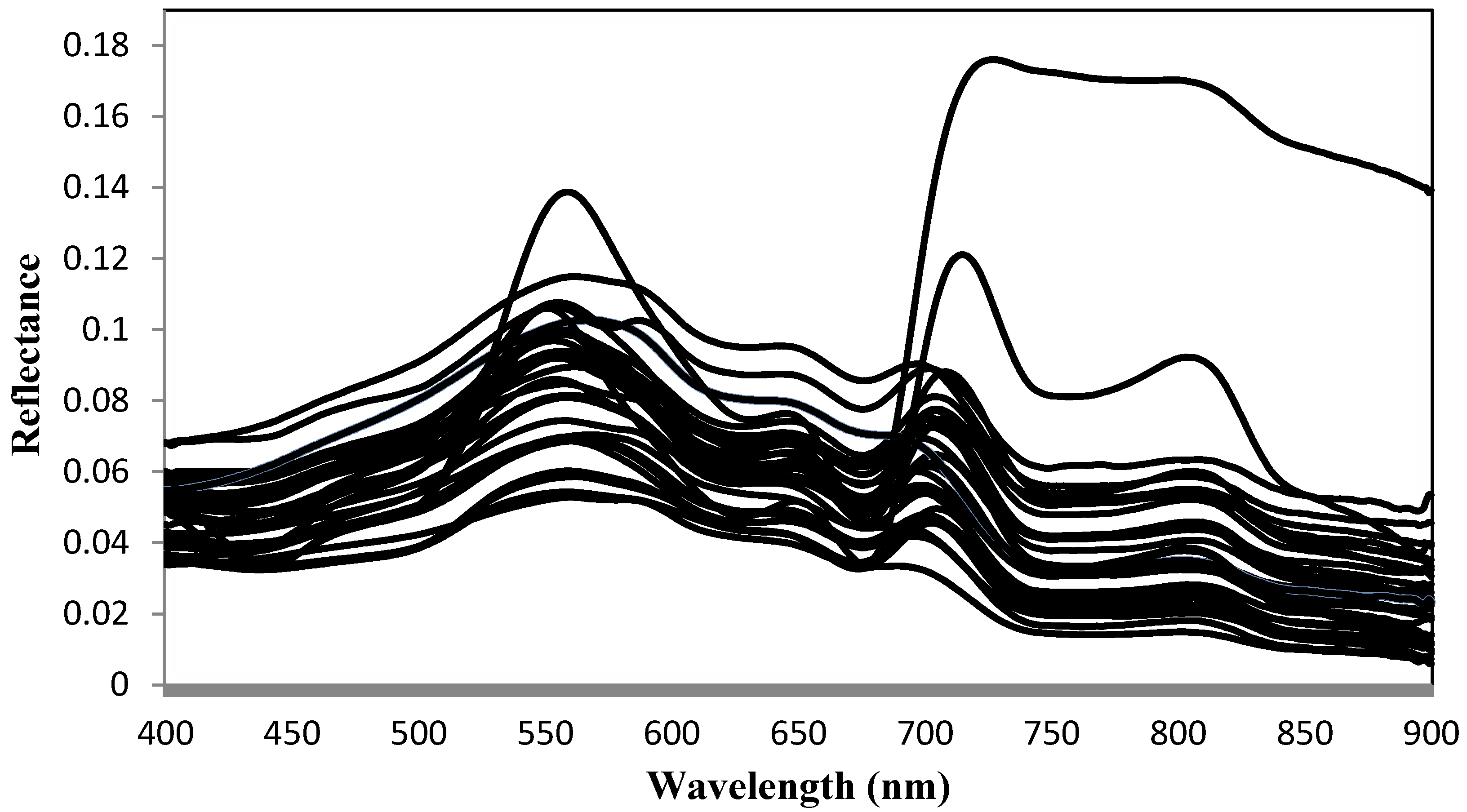
3.1. Spectral Reflectance Properties
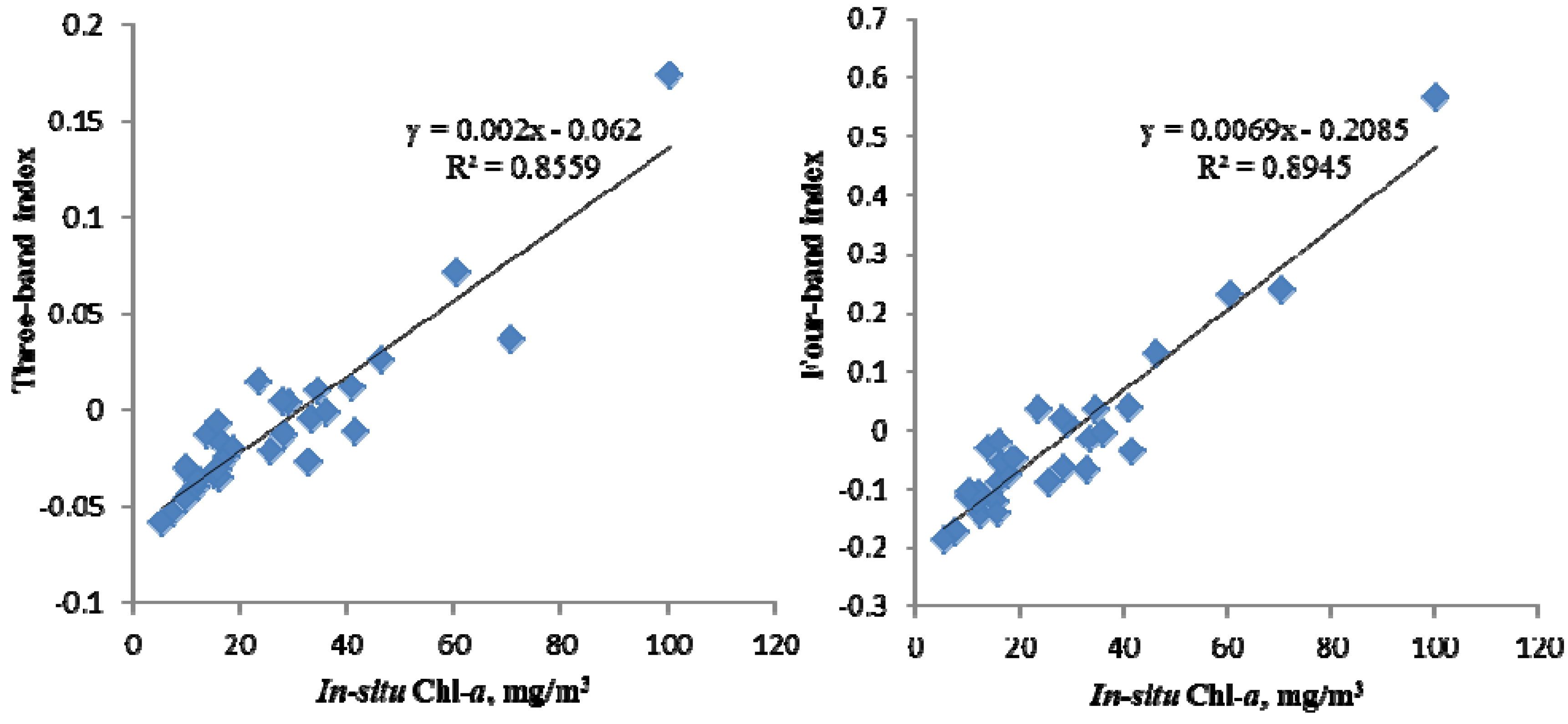
3.2. Multi-Band Indices Tuning
3.2.1. Three-Band Index

 letting vary λ1, (b)
letting vary λ1, (b)  letting vary λ2 varying, (c)
letting vary λ2 varying, (c)  letting vary λ3.
letting vary λ3.
 letting vary λ1, (b)
letting vary λ1, (b)  letting vary λ2 varying, (c)
letting vary λ2 varying, (c)  letting vary λ3.
letting vary λ3.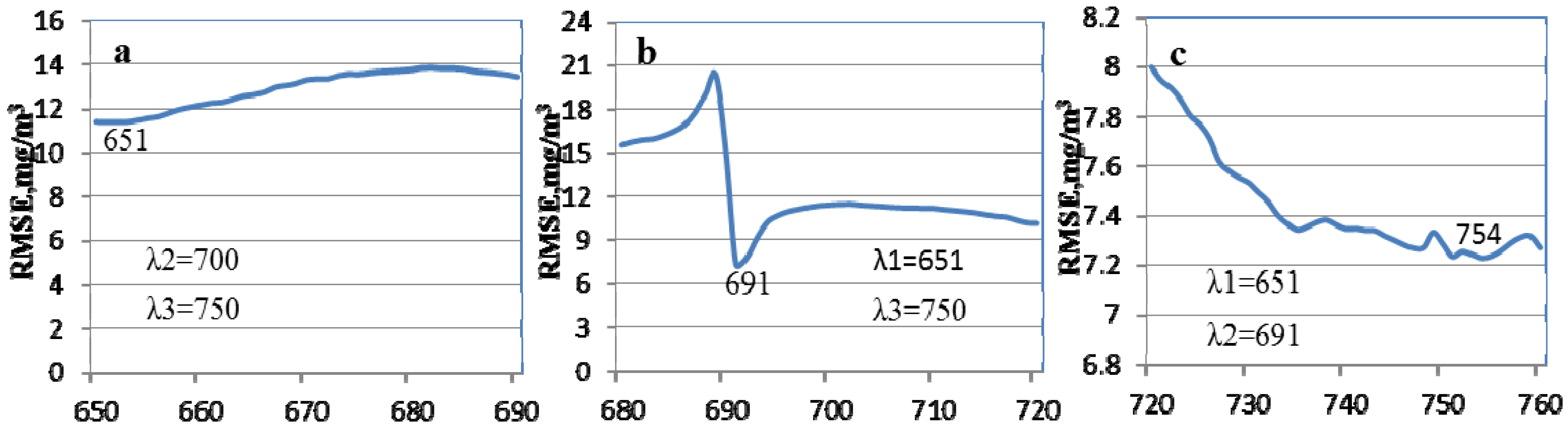
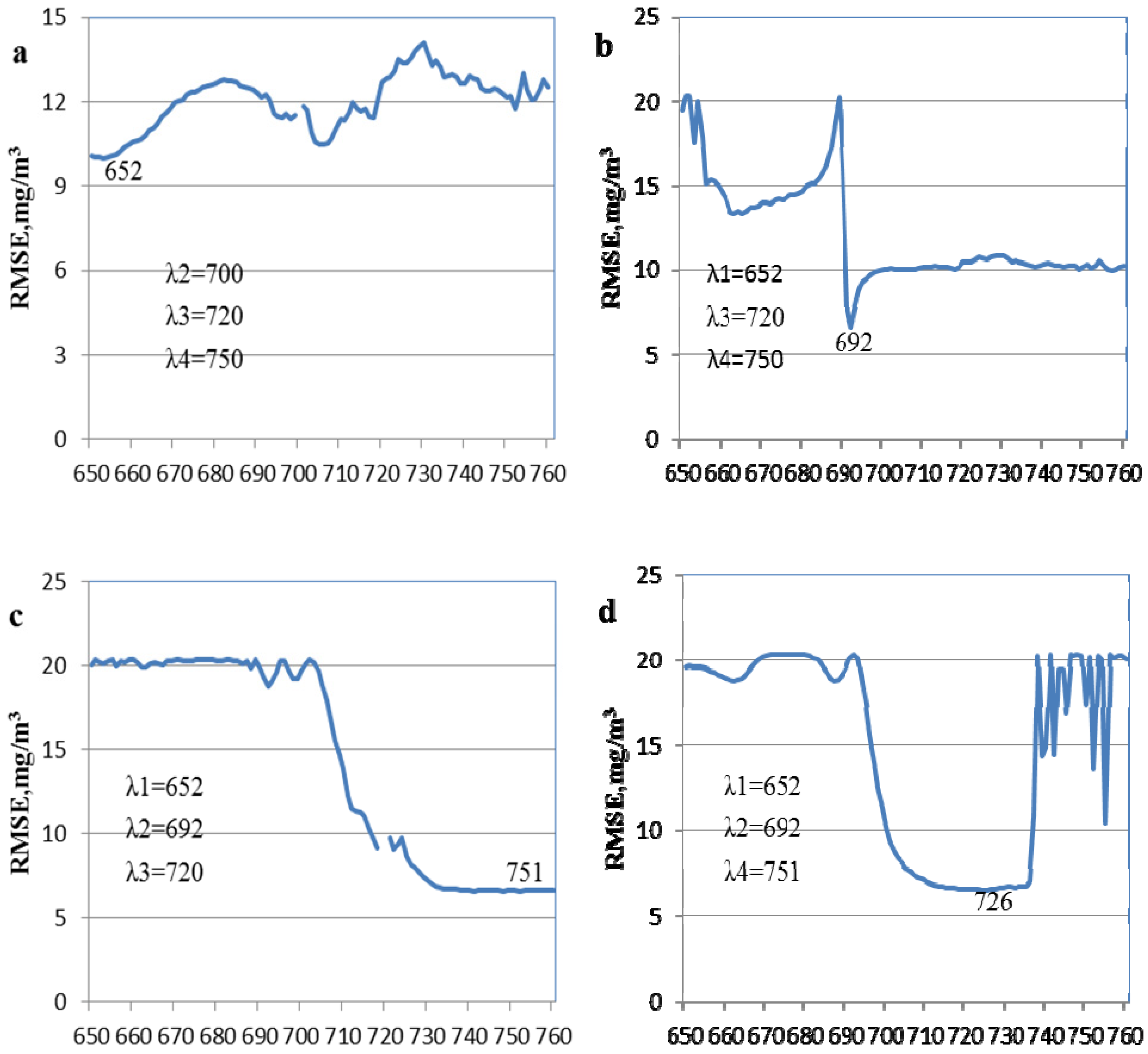
3.2.2. Four-Band Index
 with
with  , which could subtract the effect of suspended solids and minimize the absorption by pure water as well as backscattering in NIR region [18]. The four-band index is shown as Equation (2).
, which could subtract the effect of suspended solids and minimize the absorption by pure water as well as backscattering in NIR region [18]. The four-band index is shown as Equation (2).

 ; (b)
; (b)  ; (c)
; (c)  ; (d)
; (d)  .
.
 ; (b)
; (b)  ; (c)
; (c)  ; (d)
; (d)  .
.
4. Results
4.1. Estimation of Chl-a Concentration with Field Spectral Multi-Band Indices



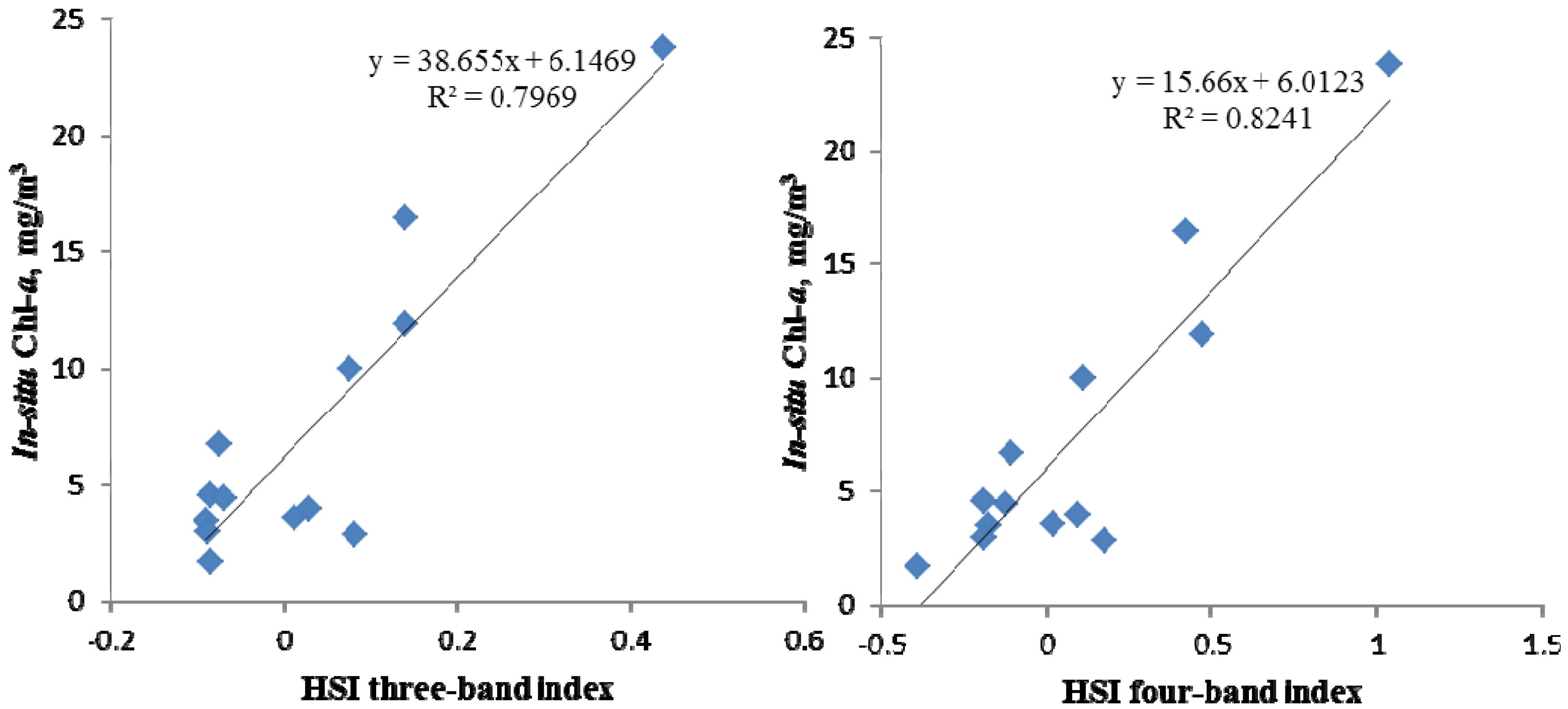
4.2. Estimation of Chl-a Concentration with Satellite Hyperspectral Multi-Band Indices
| Band number | Spectral range (nm) | Center wavelength (nm) | Band number | Spectral range (nm) | Center wavelength (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 66 | 650–654.18 | 652.09 | 79 | 709–713.99 | 711.495 |
| 67 | 654.18–658.43 | 656.305 | 80 | 713.99–719.04 | 716.515 |
| 68 | 658.43–662.72 | 660.575 | 81 | 719.04–724.17 | 721.605 |
| 69 | 662.72–667.08 | 664.9 | 82 | 724.17–729.37 | 726.77 |
| 70 | 667.08–671.49 | 669.285 | 83 | 729.37–734.65 | 732.01 |
| 71 | 671.49–675.96 | 673.725 | 84 | 734.65–740.01 | 737.33 |
| 72 | 675.96–680.49 | 678.225 | 85 | 740.01–745.44 | 742.725 |
| 73 | 680.49–685.08 | 682.785 | 86 | 745.44–750.95 | 748.195 |
| 74 | 685.08–689.74 | 687.41 | 87 | 750.95–756.55 | 753.75 |
| 75 | 689.74–694.45 | 692.095 | 88 | 756.55–762.23 | 759.39 |
| 76 | 694.45–699.24 | 696.845 | 89 | 762.23–767.99 | 765.11 |
| 77 | 699.24–704.08 | 701.66 | 90 | 767.99–773.85 | 770.92 |
| 78 | 704.08–709 | 706.54 | 91 | 773.85–779.79 | 776.82 |



5. Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Cheng, X.; Li, X. Long-term changes in nutrients and phytoplankton response in Lake Dianshan, a shallow temperate lake in China. J. Freshwater Ecol. 2010, 25, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.J.; Gitelson, A.A.; Berdnikov, S. Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in case 2 waters using MODIS and MERIS data-successes and challenges. Environ. Res. Lett. 2009, 6, 845–849. [Google Scholar]
- Giardino, C.; Bresciani, M.; Pilkaitytė, R.; Bartoli, M. In situ measurements and satellite remote sensing of case 2 waters: First results from the Curonian Lagoon. Oceanologia 2010, 52, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutser, T.; Metsamaa, L.; Strombeck, N.; Vahtmäe, E. Monitoring cyanobacteria blooms by satellite remote sensing. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 67, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilham, N.E.; Roberts, D. Amazon River time series of surface sediment concentration from MODIS. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 2659–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darecki, M.; Stramski, D. An evaluation of MODIS and SeaWiFS bio-optical algorithms in the Baltic Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 89, 326–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Olmo, G.; Gitelson, A.A. Effect of bio-optical parameter variability and uncertainties in reflectance measurements on the remote estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in turbid productive waters: Modeling results. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 3577–3592. [Google Scholar]
- Lavender, S.J.; Pinkerton, M.H.; Froidefond, J.M.; Morales, J.; Aiken, J.; Moore, G.F. Sea WIFS validation in European coastal waters using optical and biogeochemical measurements. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A. The peak near 700 nm on radiance spectra of algae and water: Relationships of its magnitude and position with chlorophyll concentration. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1992, 17, 3367–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, C.D.; Sundman, L.K.; Davis, C.O.; Bowles, J.H.; Downes, T.V.; Leathers, R.A.; Montes, M.J.; Bowles, J.H.; Bissett, W.P.; Kohler, D.D.R.; et al. Interpretation of hyperspectral remote-sensing imagery by spectrum matching and look-up tables. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 3576–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Gurlin, D.; Moses, W.; Barrow, T. A bio-optical algorithm for the remote estimation of the chlorophyll-a concentration in case 2 waters. Environ. Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Thiemann, S.; Kaufman, H. Determination of chlorophyll content and tropic state of lakes using field spectrometer and IRS-IC satellite data in the Mecklenburg Lake Distract, Germany. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 73, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, H.; Zha, Y.; Gao, J.; Li, Y.M.; Wei, Y.C.; Huang, J.Z. Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in Lake Tai, China using in-situ hyperspectral data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 4267–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimba, P.V.; Gitelson, A. Remote estimation of chlorophyll concentration in hyper-eutrophic aquatic systems: Model tuning and accuracy optimization. Aquaculture 2006, 256, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Gritz, Y.; Merzlyak, M.N. Relationships between leaf chlorophyll content and spectral reflectance and algorithms for non-destructive chlorophyll assessment in higher plant leaves. J. Plant Physiol. 2003, 160, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Vĭna, A.; Ciganda, V.; Rundquist, D.C.; Arkebauer, T.J. Remote estimation of canopy chlorophyll content in crops. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L08403. [Google Scholar]
- Tzortziou, M.; Herman, J.R.; Gallegos, C.L.; Neale, P.; Subramaniam, A.; Harding, L.; Ahmad, Z. Bio-optics of the Chesapeake Bay from measurements and radiative transfer closure. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 68, 348–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassan, S.; Ferrari, G.M. Variability of light absorption by aquatic particles in the near-infrared spectral region. Appl. Opt. 2003, 42, 4802–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.; Li, Y.; Zha, Y.; Sun, D.; Huang, C.; Lu, H. A four-band semi-analytical model for estimating chlorophyll a in highly turbid lakes: The case of Taihu Lake, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gons, H.J.; Rijkeboer, M.; Ruddick, K.G. Effect of a waveband shift on chlorophyll retrieval from MERIS imagery of inland and coastal waters. J. Plankton Res. 2005, 27, 125–127. [Google Scholar]
- Bresciani, M.; Vascellari, M.; Giardino, C.; Matta, E. Remote sensing supports the definition of the water quality status of Lake Omodeo (Italy). Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 45, 349–360. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.; Liu, Q.; Ma, R.; Tian, G. Inversion of chlorophyll-a concentration in turbid water of Lake Taihu based on optimized multi-spectral combination. J. Lake Sci. 2008, 20, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Brando, V.E.; Dekker, A.G. Satellite hyperspectral remote sensing for estimating estuarine and coastal water quality. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1378–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gons, H.J. Optical teledetection of chlorophyll a in turbid inland waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1127–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, C.; Li, Q.; Li, J.S. Chinese HJ-1A/B satellites and data characteristics. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, C.D. Estimation of the remote-sensing reflectance from above-surface measurements. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 7442–7455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.W.; Tiang, G.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, X.; Song, Q. The methods of water spectra measuring and analysis I: Above-water method. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 8, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Simis, S.G.H.; Peters, S.W.M.; Gons, H.J. Remote sensing of the cyanobacterial pigment phycocyanin in turbid inland water. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO, Determination of photosynthetic pigments in sea-water. In Monographs on Oceanographic Methodology; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1966; pp. 12–14.
- Chen, S.; Fang, L.; Li, H.; Chen, W.; Huang, W. Evaluation of a three-band model for estimating chlorophyll-a concentration in tidal reaches of the Pearl River Estuary, China. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jupp, D.; Kirk, J.; Harris, G. Detection, identification, and mapping of cyanobacteria-using remote sensing to measure the optical quality of turbid inland waters. Aust. J. Mar. Freshwater Res. 1994, 45, 801–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Dai, J.F. Investigation of chlorophyll-a and total suspended matter concentrations using Landsat ETM and field spectral measurement in Taihu Lake, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 2779–2795. [Google Scholar]
- Dall’Olmo, G.; Gitelson, A.A.; Rundquist, D.C.; Leavitt, B.; Barrow, T.; Holz, J.C. Assessing the potential of SeaWiFS and MODIS for estimating chlorophyll concentration in turbid productive waters using red and near-infrared bands. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, L.; Shi, K.; Li, Z.; Song, K. A semi-analytical algorithm for remote estimation of phycocyanin in inland waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 435–436, 141–150. [Google Scholar]
- Du, C.; Wang, S.X.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, F.L. Remote chlorophyll-a retrieval in Taihu Lake by three-band model using hyperion hyperspectral data. Environ Sci. 2009, 30, 2904–2910. [Google Scholar]
- Flink, P.; Lindell, T.; Oslund, C. Statistical analysis of hyperspectral data from two Swedish lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 268, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacobi, Y.Z.; Moses, W.J.; Kaganovsky, S.; Sulimani, B.; Leavitt, B.C.; Gitelson, A.A. NIR-red reflectance-based algorithms for chlorophyll-a estimation in mesotrophic inland and coastal waters: Lake Kinneret case study. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2428–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalles, J.F.; Gitelson, A.; Yacobi, Y.Z.; Kroenke, A.E. Chlorophyll estimation using whole seasonal, remotely sensed high spectral resolution data for an eutrophic lake. J. Phycol. 1998, 34, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, R.P.; Tyler, M.A. Satellite detection of bloom and pigment distributions in estuaries. Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 24, 385–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Ma, R.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B. Comparison of different semi-empirical algorithms to estimate chlorophyll-a concentration in inland lake water. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 170, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, L.; Li, J.; Luo, L.; Yin, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, Y. Seasonal-spatial variation and remote sensing of phytoplankton absorption in Lake Taihu, a large eutrophic and shallow lake in China. J. Plankton Res. 2010, 32, 1023–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, L.; Xu, B.; Ma, W.; Zhao, B.; Li, L.; Huai, H. Evaluation of Hyperspectral Multi-Band Indices to Estimate Chlorophyll-A Concentration Using Field Spectral Measurements and Satellite Data in Dianshan Lake, China. Water 2013, 5, 525-539. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5020525
Zhou L, Xu B, Ma W, Zhao B, Li L, Huai H. Evaluation of Hyperspectral Multi-Band Indices to Estimate Chlorophyll-A Concentration Using Field Spectral Measurements and Satellite Data in Dianshan Lake, China. Water. 2013; 5(2):525-539. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5020525
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Liguo, Bo Xu, Weichun Ma, Bin Zhao, Linna Li, and Hongyan Huai. 2013. "Evaluation of Hyperspectral Multi-Band Indices to Estimate Chlorophyll-A Concentration Using Field Spectral Measurements and Satellite Data in Dianshan Lake, China" Water 5, no. 2: 525-539. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5020525
APA StyleZhou, L., Xu, B., Ma, W., Zhao, B., Li, L., & Huai, H. (2013). Evaluation of Hyperspectral Multi-Band Indices to Estimate Chlorophyll-A Concentration Using Field Spectral Measurements and Satellite Data in Dianshan Lake, China. Water, 5(2), 525-539. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5020525






