Spatial Heterogeneity of Soil Moisture and the Scale Variability of Its Influencing Factors: A Case Study in the Loess Plateau of China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
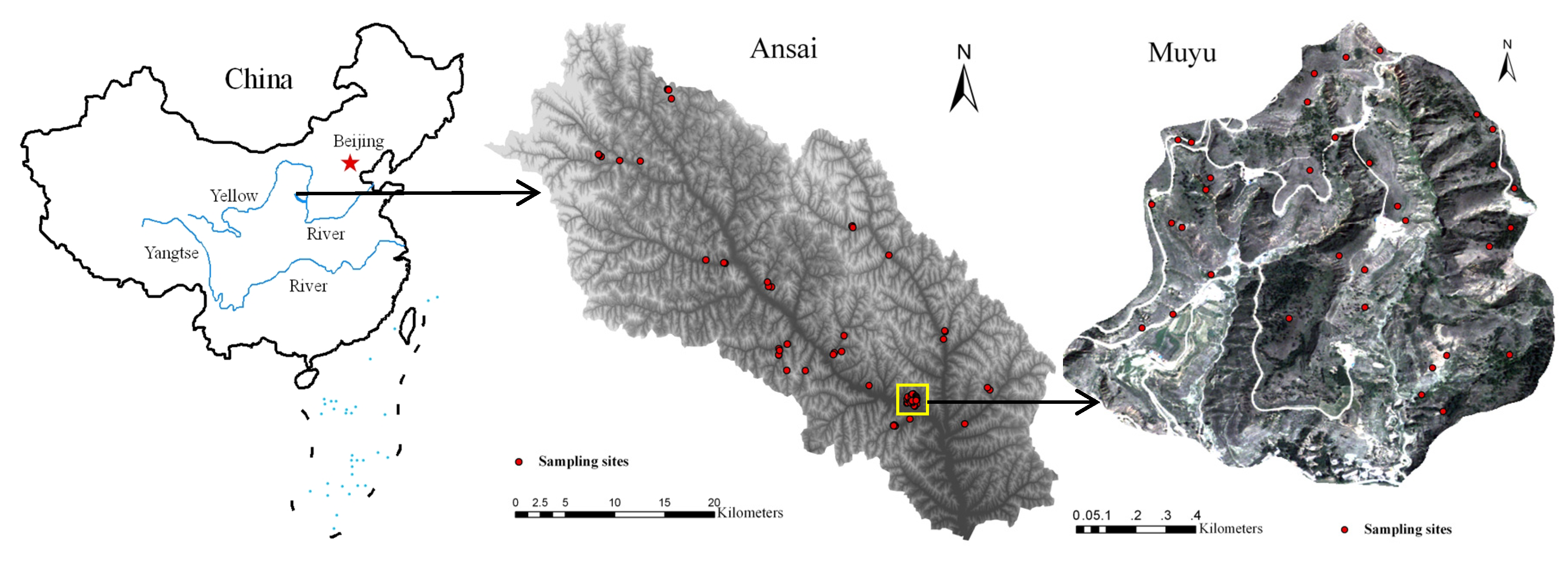
2.2. Experimental Design and Research Methods
| Small watershed scale | Watershed scale | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Land use type | Shrubland | 4 | 10 |
| Woodland | 13 | 24 | |
| Garden plot | 1 | 5 | |
| Wild grassland | 13 | 22 | |
| Cultivated land | 3 | 15 | |
| Location on the hill slope | Slope top | 2 | 4 |
| Upper slope | 7 | 19 | |
| Middle-upper slope | 8 | 11 | |
| Middle slope | 7 | 14 | |
| Middle-lower slope | 4 | 12 | |
| Lower slope | 6 | 16 |
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Relationship between Quantitative Environmental Factors and Soil Moisture Value at Different Scales
| Scale of research | Depth of soil layer | Cosine of aspect | Sine of aspect | Relative elevation | Slope | Vegetation cover |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small watershed scale | 0–20 cm | 0.22 | 0.14 | −0.53 ** | −0.06 | 0.14 |
| 20–40 cm | 0.27 | 0.16 | −0.48 ** | −0.14 | −0.27 | |
| 40–60 cm | 0.27 | 0.11 | −0.62 ** | −0.14 | −0.31 | |
| 60–80 cm | 0.32 | 0.14 | −0.63 ** | −0.29 | −0.37 * | |
| 80–100 cm | 0.32 | 0.16 | −0.52 ** | −0.38 * | −0.47 ** | |
| Depth-averaged | 0.32 | 0.17 | −0.64 ** | −0.24 | −0.3 | |
| Watershedscale | 0–20 cm | 0.09 | 0.08 | −0.35 ** | −0.04 | 0.02 |
| 20–40 cm | 0.19 | −0.01 | −0.27 * | −0.04 | −0.2 | |
| 40–60 cm | 0.14 | −0.08 | −0.21 | −0.22 | −0.29 * | |
| 60–80 cm | 0.17 | −0.11 | −0.25 * | −0.36 ** | −0.38 ** | |
| 80–100 cm | 0.21 | −0.06 | −0.25 * | −0.37 ** | −0.42 ** | |
| Depth-averaged | 0.19 | −0.09 | −0.33 ** | −0.26 * | −0.31 ** |
3.2. Relationship between Qualitative Environmental Factors and Soil Moisture Valuesat Different Scales
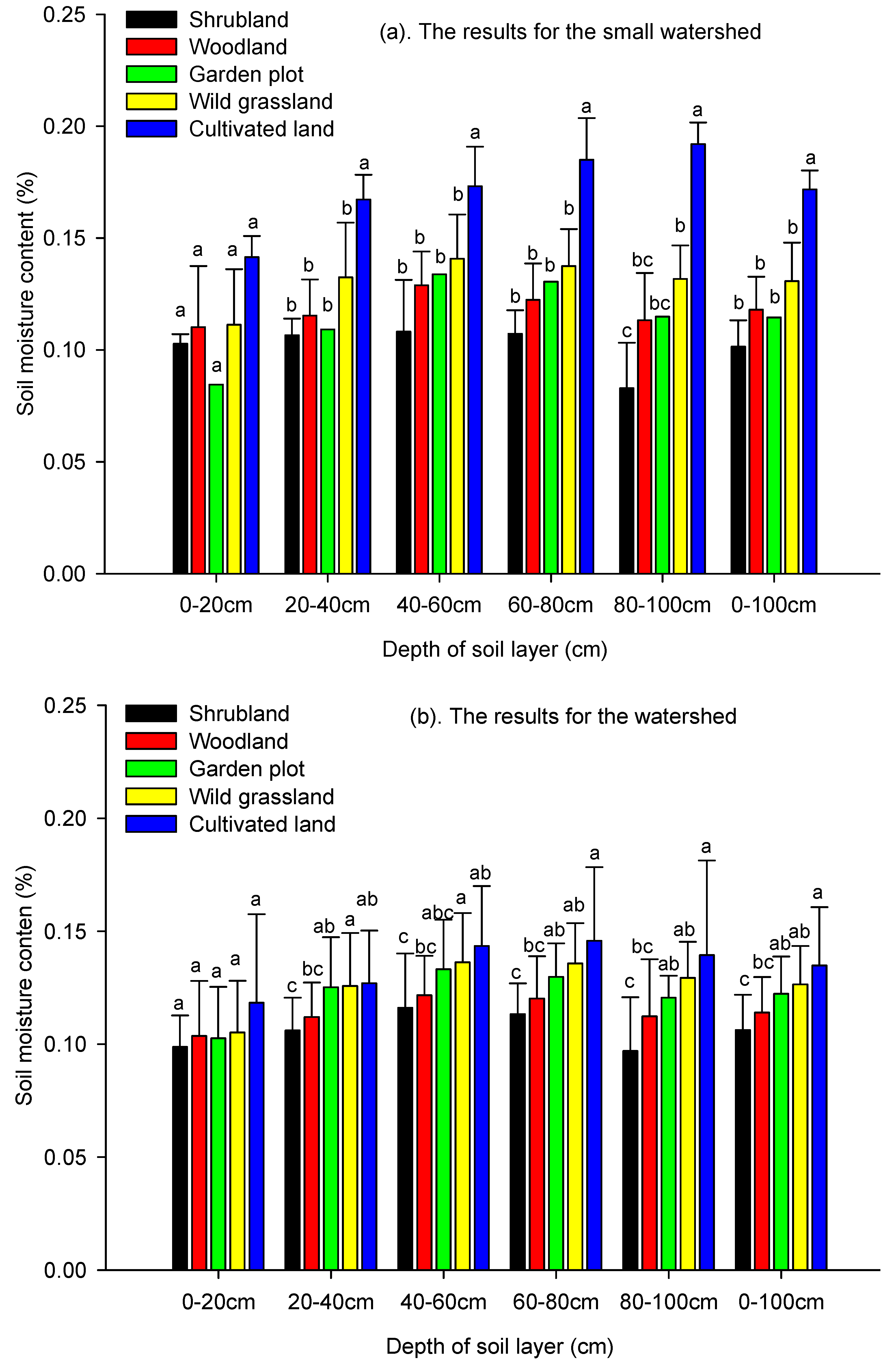
3.2.1. Influence of Land Use on Soil Moisture Value
| Scale of research | Source of variation | Depth of Soil layer | d.f. | F-ratio | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small watershed scale | Land use type | 0–20 cm | 4 | 1.64 | ns |
| 20–40 cm | 4 | 6.05 | ** | ||
| 40–60 cm | 4 | 6.16 | ** | ||
| 60–80 cm | 4 | 12.18 | ** | ||
| 80–100 cm | 4 | 17.75 | ** | ||
| Depth-averaged | 4 | 10.85 | ** | ||
| Watershed scale | Land use type | 0–20 cm | 4 | 0.93 | ns |
| 20–40 cm | 4 | 3.15 | * | ||
| 40–60 cm | 4 | 3.41 | * | ||
| 60–80 cm | 4 | 5.24 | ** | ||
| 80–100 cm | 4 | 5.06 | ** | ||
| Depth-averaged | 4 | 5.03 | ** |
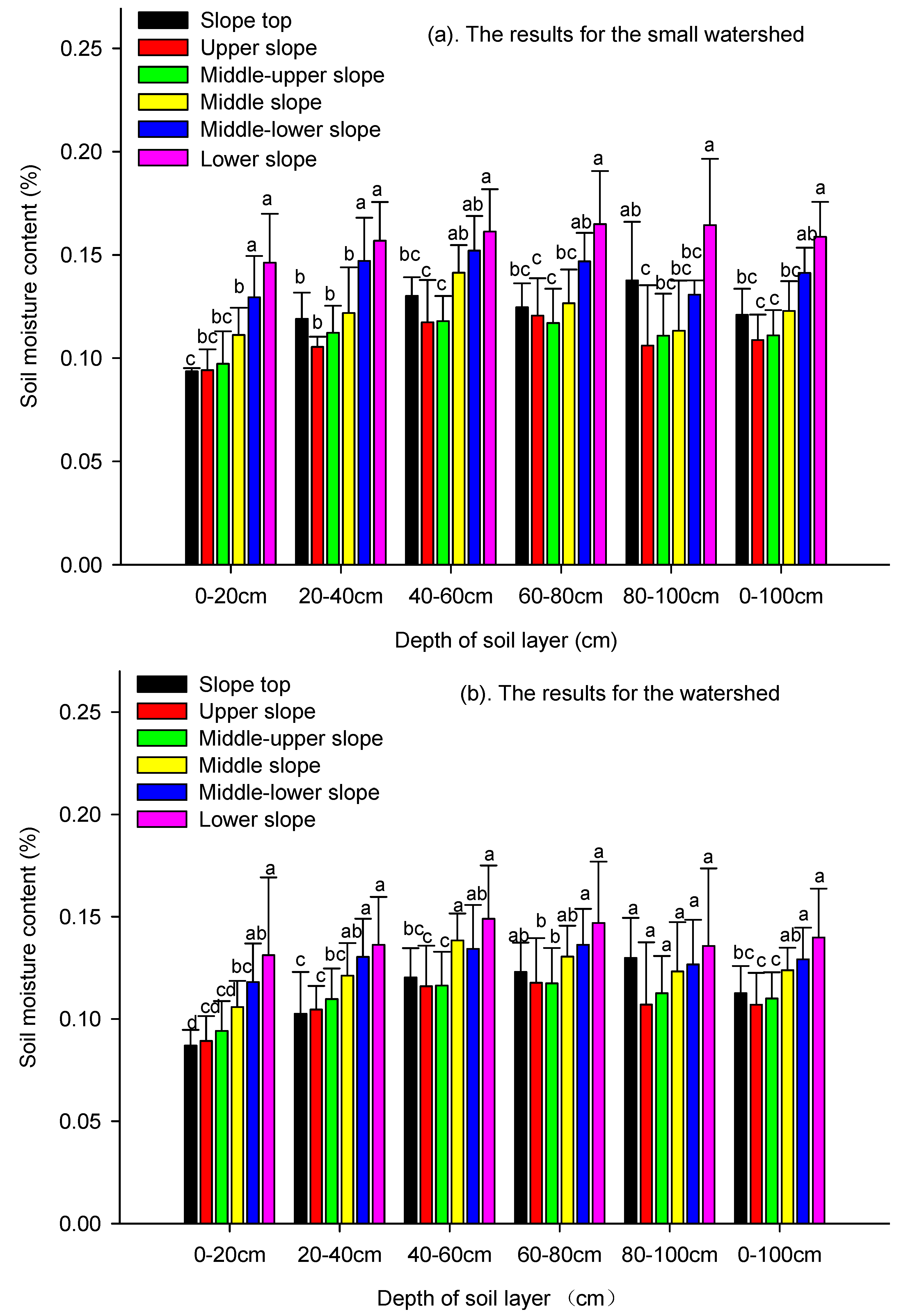
3.2.2. Influence of Location on the Hill Slope on Soil Moisture Value
| Scale of research | source of variation | Depth of Soil layer | d.f. | F-ratio | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small watershed scale | Location on the hill slope | 0–20 cm | 5 | 9.80 | ** |
| 20–40 cm | 5 | 9.06 | ** | ||
| 40–60 cm | 5 | 7.47 | ** | ||
| 60–80 cm | 5 | 6.13 | ** | ||
| 80–100 cm | 5 | 4.69 | ** | ||
| Depth-averaged | 5 | 12.11 | ** | ||
| Watershed scale | Location on the hill slope | 0–20 cm | 5 | 8.72 | ** |
| 20–40 cm | 5 | 8.11 | ** | ||
| 40–60 cm | 5 | 6.59 | ** | ||
| 60–80 cm | 5 | 4.27 | ** | ||
| 80–100 cm | 5 | 2.21 | ns | ||
| Depth-averaged | 5 | 8.66 | ** |
3.3. Statistical Model for Soil Moisture Value Forecasting at Different Scales
| Scale of research | Depth of soil layer | Source of variation | d.f. | F-ratio | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small watershed scale | 0–20 cm | B | 5 | 13.39 | ** |
| X5 | 1 | 7.87 | ** | ||
| 20–40 cm | B | 5 | 9.06 | ** | |
| 40–60 cm | A | 4 | 3.89 | * | |
| B | 5 | 4.25 | ** | ||
| X4 | 1 | 3.70 | ns | ||
| 60–80 cm | A | 4 | 5.46 | ** | |
| X1 | 1 | 3.07 | ns | ||
| 80–100 cm | A | 4 | 17.75 | ** | |
| Depth-averaged | A | 4 | 4.19 | * | |
| B | 5 | 4.74 | ** | ||
| X4 | 1 | 3.29 | * | ||
| Watershed scale | 0–20 cm | B | 5 | 8.72 | ** |
| 20–40 cm | B | 5 | 9.11 | ** | |
| X3 | 1 | 3.50 | ns | ||
| X5 | 1 | 5.57 | * | ||
| 40–60 cm | B | 5 | 6.49 | ** | |
| X5 | 1 | 6.33 | * | ||
| 60–80 cm | B | 5 | 3.94 | ** | |
| X4 | 1 | 2.95 | ns | ||
| X5 | 1 | 8.70 | ** | ||
| 80–100 cm | X1 | 1 | 4.11 | * | |
| X4 | 1 | 5.33 | * | ||
| X5 | 1 | 8.95 | ** | ||
| Depth-averaged | B | 5 | 9.04 | ** | |
| X5 | 1 | 9.02 | ** |
| Scale of research | Depth of soil layer | Forecast model | Regression effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small watershed scale | 0-20 cm | y = 0.114 − 0.04B1 + 0.014B2 − 0.034B3 − 0.023B4 − 0.039B5 + 0.0002X5 | R2 = 0.72 ** |
| 20–40 cm | y = 0.147 − 0.041B1 + 0.01B2 − 0.028B3 − 0.025B4 − 0.035B5 | R2 = 0.62 ** | |
| 40–60 cm | y = 0.110 + 0.039A1 + 0.02A2 + 0.062A3 + 0.018A4 − 0.022B1 + 0.0006B2 + 0.001B3 − 0.007B4 − 0.036B5 + 0.0008X4 | R2 = 0.74 ** | |
| 60–80 cm | y = 0.136 + 0.010A1 + 0.011A2 + 0.062A3 + 0.024A4 − 0.0001X1 | R2 = 0.66 ** | |
| 80–100 cm | y = 0.083 + 0.032A1 + 0.030A2 + 0.109A3 + 0.049A4 | R2 = 0.71 ** | |
| Average on all layers | y = 0.108 + 0.022A1 + 0.013A2 + 0.057A3 + 0.016A4 − 0.020B1 + 0.007B2 − 0.004B3 − 0.0150B4 − 0.028B5 + 0.0006X4 | R2 = 0.82 ** | |
| Watershed scale | 0–20 cm | y = 0.118 − 0.029B1 + 0.013B2 − 0.031B3 − 0.012B4 − 0.024B5 | R2 = 0.38 ** |
| 20–40 cm | y = 0.145 − 0.027B1 + 0.004B2 − 0.034B3 − 0.012B4 − 0.022B5 + 0.005X3−0.0001X5 | R2 = 0.43 ** | |
| 40–60 cm | y = 0.149 − 0.018B1 + 0.013B2 − 0.018B3 + 0.002B4 − 0.018B5 − 0.0001X5 | R2 = 0.38 ** | |
| 60–80 cm | y = 0.162 − 0.019B1 + 0.005B2 − 0.026B3 − 0.009B4 − 0.017B5 − 0.0004X4 − 0.0002X5 | R2 = 0.38 ** | |
| 80–100 cm | y = 0.170 − 0.00007X1 − 0.0005X4 − 0.0002X5 | R2 = 0.27 ** | |
| Average on all layers | y = 0.144 − 0.022B1 + 0.009B2 − 0.020B3 − 0.007B4 − 0.019B5 − 0.0001X5 | R2 = 0.45 ** |
3.4. Scale Effects of the Spatial Distribution of Soil Moisture Values
4. Conclusions
5. Practical Implications of the Study
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, H.S.; Kogelmann, W.; Walker, C.; Bruns, M.A. Soil moisture patterns in a forested catchment: A hydropedological perspective. Geoderma 2006, 131, 345–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. Characterization of annual soil moisture response pattern on a hillslope in Bongsunsa Watershed, South Korea Sanghyun. J. Hydrol. 2012, 448–449, 100–111. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.; Fu, B.J.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.D. Soil moisture variation in relation to topography and land use in a hillslope catchment of the Loess Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2001, 240, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.Z.; Li, B.G.; Hu, K.L.; Xu, Y. Spatial variability of soil water under different landform in Erdos Plateau at beginning of summer. [in Chinese]. J. China Agric. Univ. 2002, 7, 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Western, A.W.; Blöschl, G. On the spatial scaling of soil moisture. J. Hydrol. 1999, 217, 203–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroni, G.; Ortuani, B.; Facchi, A.; Gandolfi, C. The role of vegetation and soil properties on the spatio-temporal variability of the surface soil moisture in a maize-cropped field. J. Hydrol. 2013, 489, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawson, S.D.; Niemann, J.D. Spatial patterns from EOF analysis of soil moisture at a large scale and their dependence on soil, land-use, and topographic properties. Adv. Water Resour. 2007, 30, 366–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.J.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.D.; Qiu, Y. The effects of land use on soil moisture variation in the Danangou catchment of the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2003, 54, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, B.; Lakshman, N.; Purandara, B.K.; Reddy, V.B. Analysis of observed soil moisture patterns under different land coversin Western Ghats, India. J. Hydrol. 2011, 397, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, A.P.; Niemann, J.D. Analysis and estimation of soil moisture at the catchment scale using EOFs. J. Hydrol. 2007, 334, 388–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famiglietti, J.S.; Ryu, D.; Berg, A.A.; Rodell, M.; Jackson, T.J. Field observations of soil moisture variability across scales. Water. Resour. Res. 2008, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Lin, H.S. Influences of soil, terrain, and crop growth on soil moisture variation from transect to farm scales. Geoderma 2011, 163, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosnay, P.D.; Gruhier, C.; Timouk, F.; Baup, F.; Mougin, E.; Hiernaux, P.; Kergoat, L.; LeDantec, V. Multi-scale soil moisture measurements at the Gourma meso-scale site in Mali. J. Hydrol. 2009, 375, 241–252. [Google Scholar]
- Miralles, D.G.; Crow, W.T.; Cosh, M.H. Estimating spatial sampling errors in coarse-scale soil moisture estimates derived from point-scale observations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 1423–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Tullo, T.; Melone, F.; Moramarco, T.; Morbidelli, R. Catchment scale soil moisture spatial-temporal variability. J. Hydrol. 2012, 422–423, 63–75. [Google Scholar]
- Heathman, G.C.; Cosh, M.H.; Merwade, V.; Han, E. Multi-scale temporal stability analysis of surface and subsurface soil moisture within the Upper Cedar Creek Watershed, Indiana. Catena 2012, 95, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; Shao, M.A. Soil hydraulic properties and their influences on soil water content under different land uses in Liudaogou watershed of Loess Plateau. [in Chinese]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 19, 2400–2407. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Jiang, D.S.; Huang, G.J.; Fan, X.K.; Chang, C.E. An analysis to the differences of soil water in varied places of hillslopes. [in Chinese]. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 1990, 10, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Shao, M.A.; Wang, Q.J. Study on spatial variability of soil moisture on the recultivated slope-land on the Loess Plateau. [in Chinese]. Adv. Water Sci. 2006, 17, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, X.L.; Fu, B.J.; Lü, Y.H. Spatial patterns of soil moisture at transect scale in the Loess Plateau of China. [in Chinese]. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 4961–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Fu, B.J.; Wang, J. Spatial heterogeneity of soil moisture content on the Loess Plateau, China and its relation to influencing factors. [in Chinese]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2001, 12, 715–720. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.L.; Chen, L.D.; Fu, B.J.; Wang, Y.L. Spatial pattern of soil water and its influencing factors in a gully catchment of the Loess Plateau. [in Chinese]. J. Nat. Resour. 2005, 20, 483–492. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Shao, M.A.; Wang, Q.J. Scale-dependency of spatial variability of soil moisture on a degraded slope-land on the Loess Plateau. [in Chinese]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2005, 21, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.L.; Ma, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.H. Multifractal study on spatial variability of soil water and salt and its scale effect. [in Chinese]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2010, 26, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.S.; Han, S.F.; Wang, Z.H. Soil water properties and its zonation in the Loess Plateau. [in Chinese]. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 1985, 2, 2–17. [Google Scholar]
- Grayson, R.B.; Blöschl, G.; Western, A.W.; McMahon, T.A. Advances in the use of observed spatial patterns of catchment hydrological response. Adv. Water Resour. 2002, 25, 1313–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famiglietti, J.S.; Rudnicki, J.W.; Rodell, M. Variability in surface moisture content along a hillslope transect:Rattlesnake Hill, Texas. J. Hydrol. 1998, 210, 259–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fu, B.J.; Gao, G.Y.; Yao, X.L.; Zhou, J. Soil moisture and evapotranspiration of different land cover types in the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 2883–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Liu, G.B.; Dang, X.H. Effects of land use on soil moisture in loess hilly and gully region of China. [in Chinese]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2009, 25, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Penna, D.; Borga, M.; Norbiato, D.; Fontana, G.D. Hillslope scale soil moisture variability in a steep alpine terrain. J. Hydrol. 2009, 364, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.H.; Huang, M.B.; Dang, T.H. Soil water distribution characteristics in Wangdonggou watershed in gully region of Loess Plateau. [in Chinese]. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2002, 22, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.P.; Chen, L.H.; Chen, J.H. Study on the distribution of root density of Robinia pseudoacacia L. and Pinus tabulae form is Carr. [in Chinese]. Arid Zone Res. 2007, 24, 647–651. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.X.; Wang, D.H.; Liu, G.Q. Distribution characteristics of effective root density in the planted Robinia Pseudoacacia and Platycladus Orientalis forest site. [in Chinese]. Acta Bot. Boreal. Occident. Sin. 2004, 24, 2208–2214. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Qu, M.; Cheng, X.R.; Wang, D.H. Effects of Robinia Pseudoacacia roots on deep soil moisture status. [in Chinese]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2006, 17, 765–768. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, H.Y. A study on correlation between vegetation division and construction of forest and grasslands in Loess Plateau of northern Shannxi. [in Chinese]. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2000, 7, 96–101. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, T.T.; Fu, B.J.; Liu, G.H.; Wang, Z. Hydrologic feasibility of artificial forestation in the semi-arid LoessPlateau of China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2519–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Q.; Zhao, W.; Qiu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhong, L. Spatial Heterogeneity of Soil Moisture and the Scale Variability of Its Influencing Factors: A Case Study in the Loess Plateau of China. Water 2013, 5, 1226-1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5031226
Feng Q, Zhao W, Qiu Y, Zhao M, Zhong L. Spatial Heterogeneity of Soil Moisture and the Scale Variability of Its Influencing Factors: A Case Study in the Loess Plateau of China. Water. 2013; 5(3):1226-1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5031226
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Qiang, Wenwu Zhao, Yang Qiu, Mingyue Zhao, and Lina Zhong. 2013. "Spatial Heterogeneity of Soil Moisture and the Scale Variability of Its Influencing Factors: A Case Study in the Loess Plateau of China" Water 5, no. 3: 1226-1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5031226
APA StyleFeng, Q., Zhao, W., Qiu, Y., Zhao, M., & Zhong, L. (2013). Spatial Heterogeneity of Soil Moisture and the Scale Variability of Its Influencing Factors: A Case Study in the Loess Plateau of China. Water, 5(3), 1226-1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5031226





