Fouling Communities of Two Accidental Artificial Reefs (Modern Shipwrecks) in Cyprus (Levantine Sea)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites
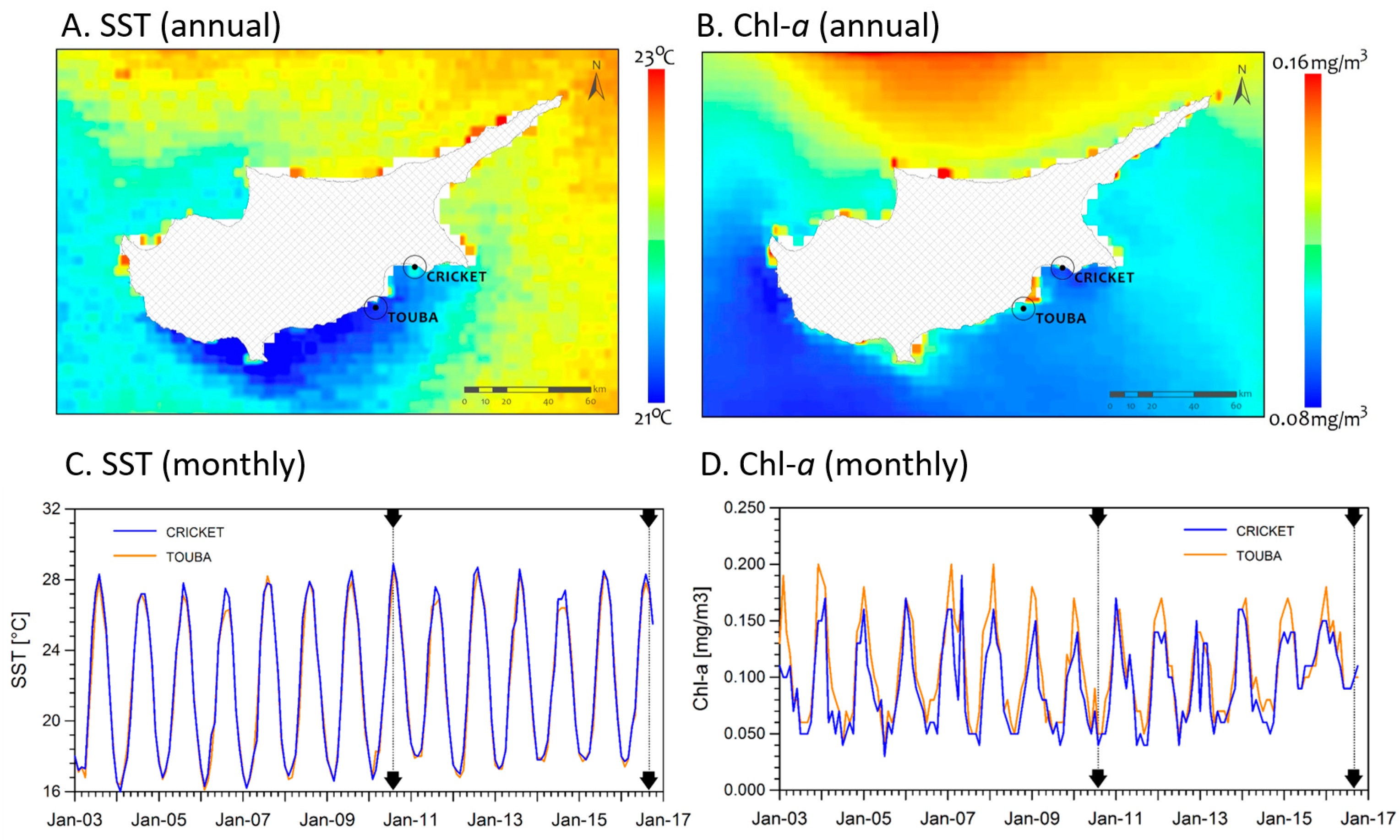
2.2. Environmental Conditions
2.3. Coral Species and Benthic Cover
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Conditions and Study Sites
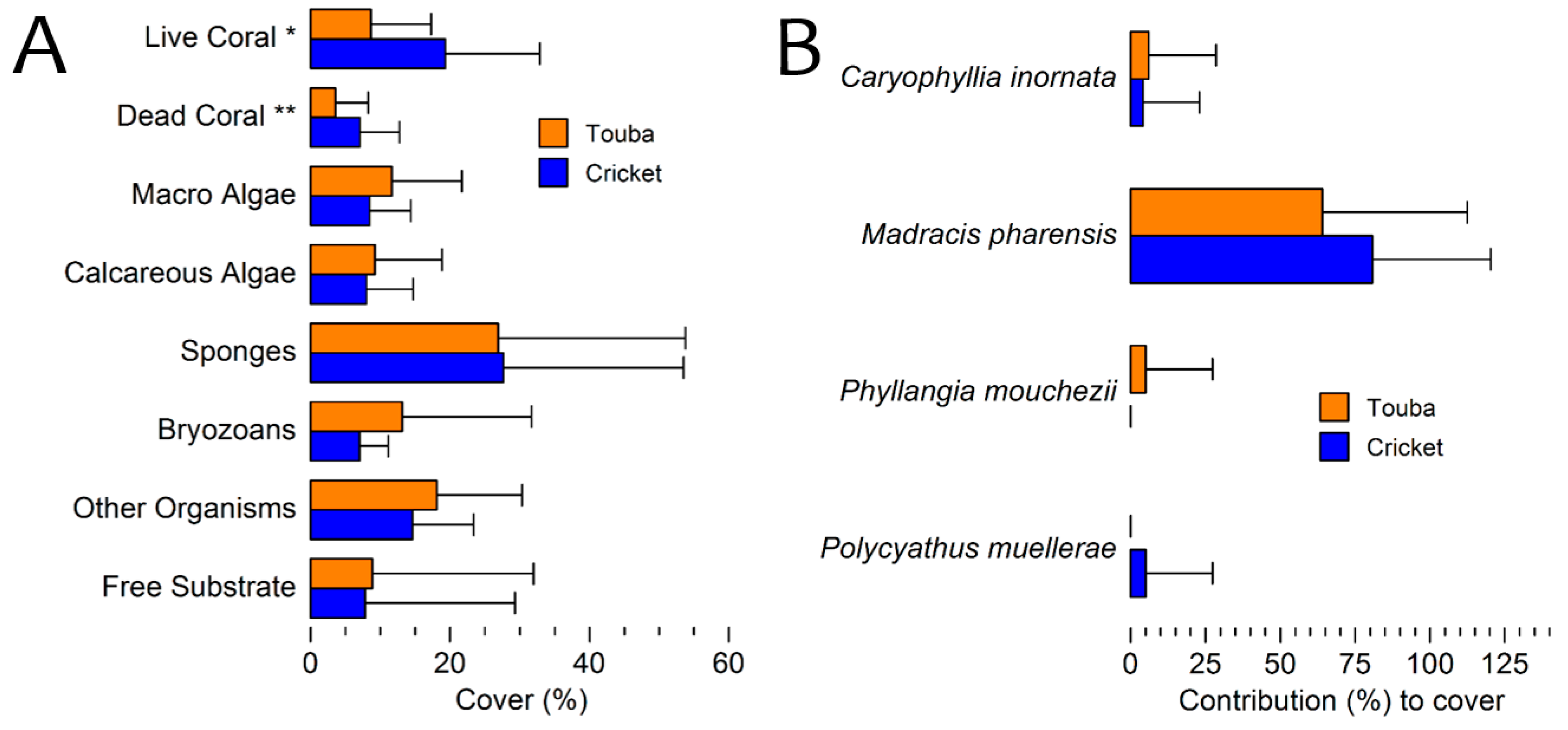
3.2. General Description of the Coral Communities
3.3. Benthic Cover 2010 Surveys
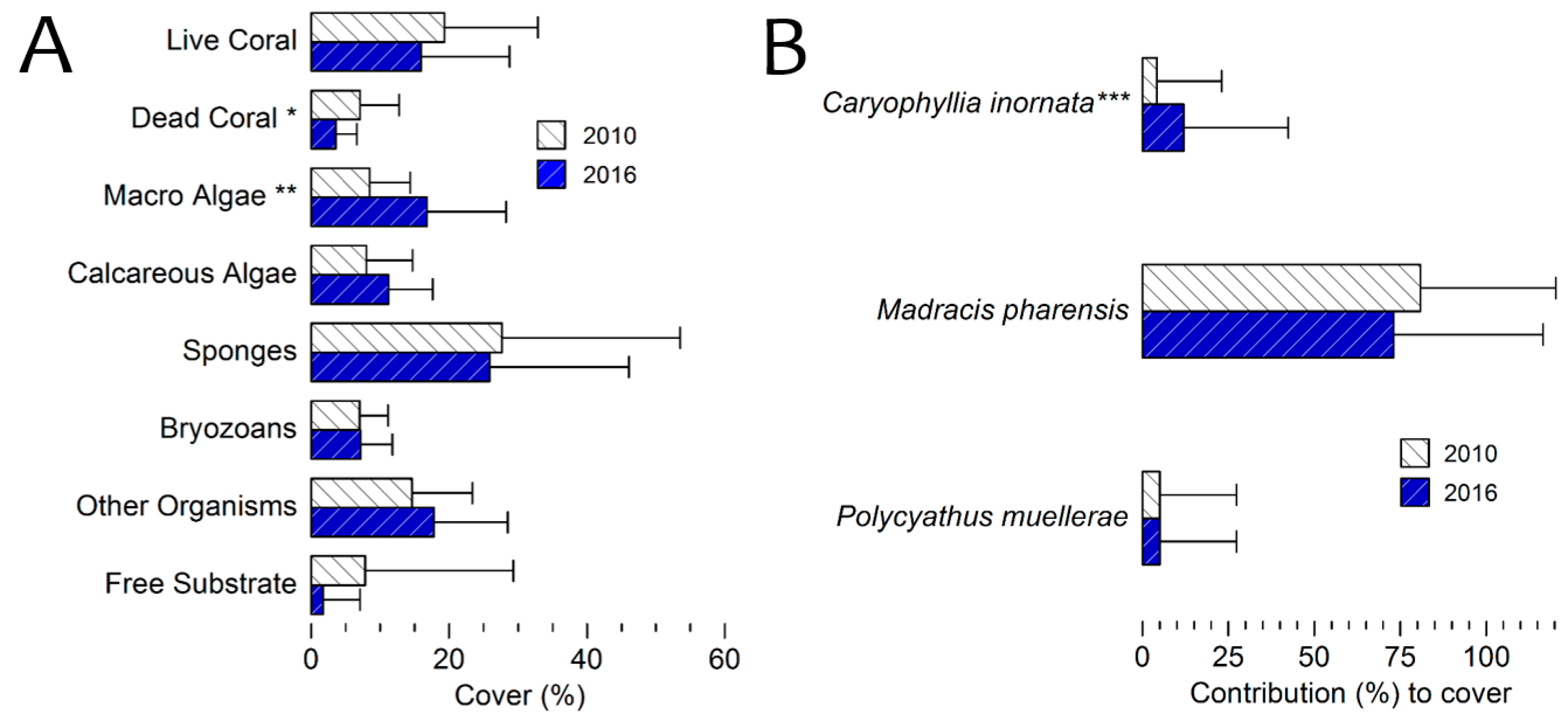
3.4. Benthic Cover 2016 Survey
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zenetos, A.; Siokou-Frangou, I.; Gotsis-Skretas, O.; Groom, S. Europe’s Biodiversity—Biogeographical Regions and Seas: The Mediterranean Sea—Blue Oxygen-Rich, Nutrient-Poor Waters; Technical Report; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, T.; Townsend, D.W.; El-Sayed, S.Z.; Trees, G.C.; Azov, Y. Optical transparency, chlorophyll and primary productivity in the Eastern Mediterranean near the Israeli coast. Oceanol. Acta 1984, 7, 367–372. [Google Scholar]
- Krom, M.D.; Kress, N.; Brenner, S.; Gordon, L.I. Phosphorus limitation of primary productivity in the Eastern Mediterranean. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1991, 36, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannides, C.C.S.; Siokou, I.; Zervoudaki, S.; Frangoulis, C.; Lange, M.A. Mesozooplankton biomass and abundance in Cyprus coastal waters and comparison with the Aegean Sea (Eastern Mediterranean). Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2015, 16/2, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, S.; Reñones, O.; Morales-Nin, B.; Polunin, N.V.C.; Moranta, J.; Coll, J. Spatial variation in the 15N and 13C stable isotope composition of plants, invertebrates and fishes on Mediterranean reefs: Implications for the study of trophic pathways. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 146, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardizzone, G.; Somaschini, A.; Belluscio, A. Artificial Reefs in European Seas, 1st ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 113–128. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrose, R.F.; Anderson, T.W. Influence of an artificial reef on the surrounding infaunal community. Mar. Biol. 1990, 107, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, F. Artificial reefs: From ecological processes to fishing enhancement tools. Braz. J. Oceanogr. 2013, 61, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, H.; Whitmarsh, D. Artificial reefs and fisheries exploitation: A review of the “Attraction versus production” debate, the influence of design and its significance for policy. Fish. Res. 1997, 31, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulloch, D.K. The development of the wreck Pinta as a marine habitat. Underw. Nat. Bull. Am. Littoral Soc. 1965, 31, 17–32. [Google Scholar]
- Hiscock, K. Marine life on the wreck of the M.V. ‘Robert’. Rep. Lundy Field Soc. 1981, 32, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Wendt, P.H.; Knott, D.M.; van Dolah, R.F. Community structure of the sessile biota on five artificial reefs of different ages. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1989, 44, 1106–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Gabriele, M.; Bellot, A.; Gallotti, D.; Brunetti, R. Sublittoral hard substrate communities of the Northern Adriatic Sea. Cah. Biol. Mar. 1999, 40, 65–76. [Google Scholar]
- Amaral, F.M.D.; Farrapeira, C.M.R.; Lira, S.M.A.; Ramos, C.A.C.; Dom, R. Benthic macrofauna inventory of two shipwrecks from Pernambuco coast, northeastern of Brazil. Rev. Nordeste Zool. 2010, 4, 24–41. [Google Scholar]
- Airoldi, L.; Turon, X.; Perkol-Finkel, S.; Rius, M. Corridors for aliens but not for natives: Effects of marine urban sprawl at a regional scale. Divers. Distrib. 2015, 21, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitar, G.; Zibrowius, H. Scleractinian corals from Lebanon, Eastern Mediterranean, including a non-lessepsian invading species (Cnidaria: Scleractinia). Sci. Mar. 1997, 61, 227–231. [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez, C.; Petrou, A.; Ivan, C.; Marija, D.; Evriviadou, M.; Hadjioanou, L.; Lange, M.A. Coral mass mortality associated to seawater temperature anomalies in the Levantine (Cyprus) and Adriatic (Croatia) Seas. Rapp Commun. Int. Mer. Médit. 2013, 40, 655. [Google Scholar]
- Orejas, C.; Gori, A.; Jimenez, C.; Rivera, J.; Lo Iacono, C.; Hadjioannou, L.; Andreou, V.; Petrou, A. First in situ documentation of a live deep population of the coral Dendrophyllia ramea off Cyprus (Levantine Basin, Mediterranean Sea) and evidence of human activities in the area. 2016; in preparation. [Google Scholar]
- Georgiou, A.; Akcit, N. Investigation of Sea Surface Temperature (SST) anomalies over Cyprus Area. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Remote Sensing and Geoinformation of the Environment (RSCy2016), Paphos, Cyprus, 4–8 April 2016.
- Giovanni. The Bridge between Data and Science v 4.21.6. Available online: http://giovanni.sci.gsfc.nasa.gov/giovanni/ (accessed on 27 November 2016).
- Kohler, K.E.; Gill, S.M. Coral Point Count with Excel extensions (CPCe): A Visual Basic program for the determination of coral and substrate coverage using random point count methodology. Comput. Geosci. 2006, 32, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, C.; Hadjioannou, L.; Petrou, A.; Nikolaidis, A.; Evriviadou, M.; Lange, M.A. Mortality of the scleractinian coral Cladocora caespitosa during a warming event in the Levantine Sea (Cyprus). Reg. Environ. Chang. 2014, 16, 1963–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.W.; Micheli, F. Decreased solar radiation and increased temperature combine to facilitate fouling by marine non-indigenous species. Biofouling 2013, 29, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fariñas-Franco, J.M.; Roberts, D. Early faunal successional patterns in artificial reefs used for restoration of impacted biogenic habitats. Hydrobiologia 2014, 727, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, C.; Vasilis, A.; Evriviadou, M.; Hadjioanou, L.; Petrou, A.; Munkes, B.; Abu Alhaija, R. Sessile marine communities associated to artificial reefs (modern shipwrecks) under contrasting regimes of nutrients and pollution in the Levantine Sea (Cyprus and Lebanon). PLoS ONE 2016. in review. [Google Scholar]
- Perkol-Finkel, S.; Shashar, N.; Barneah, O.; Ben-David-Zaslow, R.; Oren, U.; Reichart, T.; Yacobovich, T.; Yahel, G.; Yahel, R.; Benayahu, Y. Fouling reefal communities on artificial reefs: Does age matter? Biofouling 2005, 21, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkol-Finkel, S.; Shashar, N.; Benayahu, Y. Can artificial reefs mimic natural reef communities? The roles of structural features and age. Mar. Environ. Res. 2006, 61, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, A.; Boaventura, D.; Cúrdia, J.; Carvalho, S.; Cancelada Fonseca, L.; Leitão, F.M.; Santos, M.N.; Monteiro, C.C. Effect of depth and reef structure on early macrobenthic communities of the Algarve artificial reefs (southern Portugal). Hydrobiologia 2007, 580, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, J.; Bartholomew, A.; Bauman, A.; Saif, A.; Sale, P.F. Coral recruitment and early benthic community development on several materials used in the construction of artificial reefs and breakwaters. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2009, 373, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjioannou, L.; Jimenez, C. Gradual mortality of Cladocora caespitosa colonies due to prolonged increased SST in Cyprus. 2016; in preparation. [Google Scholar]
- Hadjioannou, L.; Jimenez, C.; Papageorgiou, M.; Petrou, A.; Hall-Spencer, J. Corallivory in the Levantine Sea (Cyprus, Eastern Mediterranean). 2016; in preparation. [Google Scholar]
- Fabi, G.; Spagnolo, A.; Bortone, S.A.; Charbonnel, E.; Goutayer, J.J.; Haddad, N.; Lök, A.; Trommelen, M. Practical Guidelines for the Use of Artificial Reefs in the Mediterranean and the Black Sea; General Fisheries Commission for the Mediterranean: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Consoli, P.; Martino, A.; Romeo, T.; Sinopoli, M.; Perzia, P.; Canese, S.; Vivona, P.; Andaloro, F. The effect of shipwrecks on associated fish assemblages in the central Mediterranean Sea. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2015, 95, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, P.T.; Jordan, L.K.B.; Spieler, R.E. Fish assemblages on sunken vessels and natural reefs in southeast Florida, USA. Hydrobiologia 2007, 580, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megina, C.; González-Duarte, M.M.; López-González, P.J. Benthic assemblages, biodiversity and invasiveness in marinas and commercial harbours: An investigation using a bioindicator group. Biofouling 2016, 32, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jimenez, C.; Hadjioannou, L.; Petrou, A.; Andreou, V.; Georgiou, A. Fouling Communities of Two Accidental Artificial Reefs (Modern Shipwrecks) in Cyprus (Levantine Sea). Water 2017, 9, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010011
Jimenez C, Hadjioannou L, Petrou A, Andreou V, Georgiou A. Fouling Communities of Two Accidental Artificial Reefs (Modern Shipwrecks) in Cyprus (Levantine Sea). Water. 2017; 9(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleJimenez, Carlos, Louis Hadjioannou, Antonis Petrou, Vasilis Andreou, and Andreas Georgiou. 2017. "Fouling Communities of Two Accidental Artificial Reefs (Modern Shipwrecks) in Cyprus (Levantine Sea)" Water 9, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010011
APA StyleJimenez, C., Hadjioannou, L., Petrou, A., Andreou, V., & Georgiou, A. (2017). Fouling Communities of Two Accidental Artificial Reefs (Modern Shipwrecks) in Cyprus (Levantine Sea). Water, 9(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010011






