UV-LEDs Efficiently Inactivate DNA and RNA Coliphages
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Purification of Coliphages
2.2. Identification of Genetic Material of Coliphages with RNase Spot Test
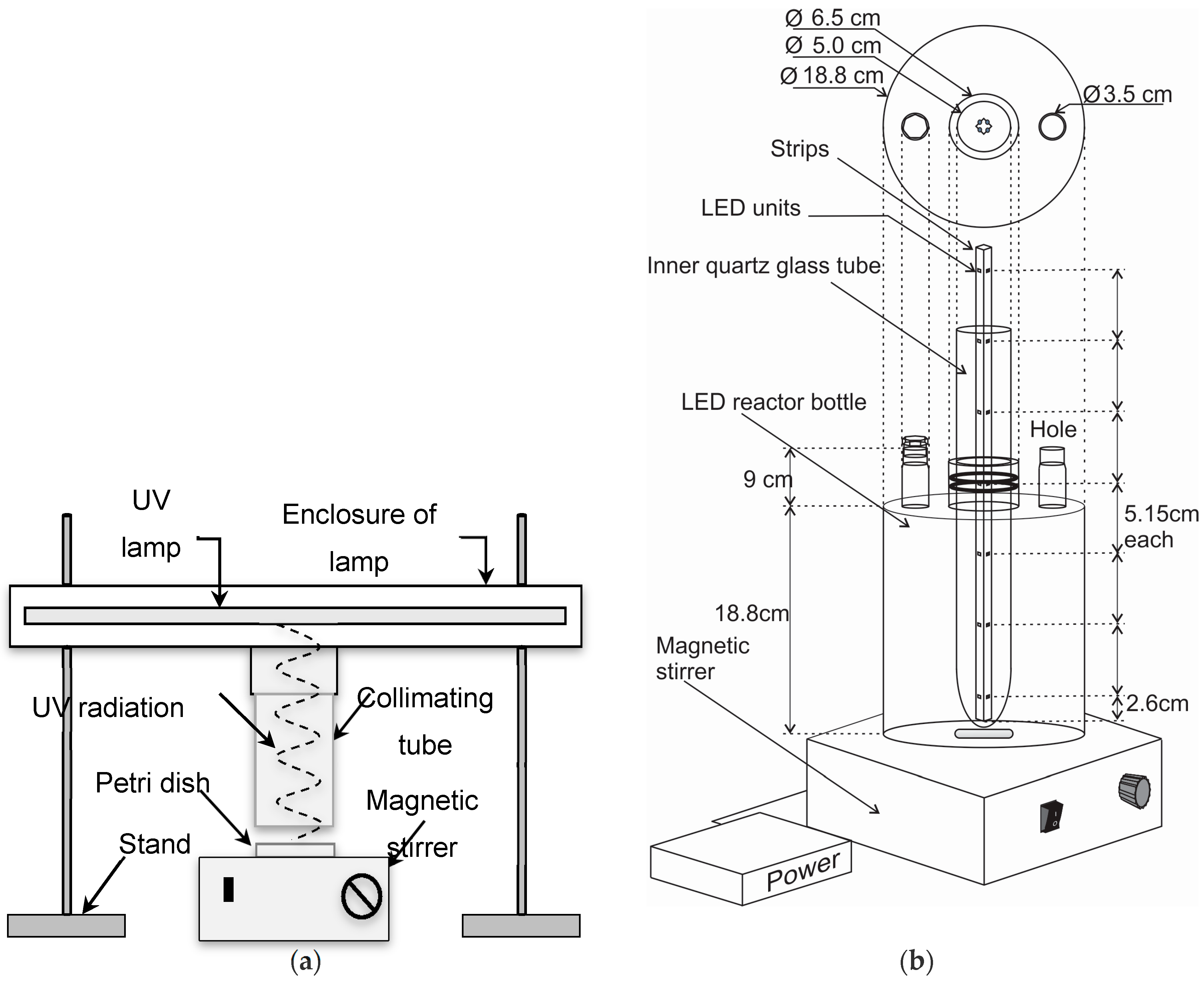
2.3. UV Experiments
2.4. Calculations and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Water Health Organization (WHO). Diarrhoeal Disease; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Love, D.; Vinje, J.; Khalil, S.; Murphy, J.; Lovelace, G.; Sobsey, M. Evaluation of RT-PCR and reverse line blot hybridization for detection and genotyping F+ RNA coliphages from estuarine waters and molluscan shellfish. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, S.C.; El-Khoury, S.S.; Oudejans, S.J.G.; Sobsey, M.D.; Vinjé, J. Assessment of sources and diversity of male-specific coliphage for source tracking. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2005, 22, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijnen, W.A.M.; Beerendonk, E.F.; Medema, G.J. Inactivation credit of UV radiation for viruses, bacteria and protozoan (oo) cysts in water: A review. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, H.B.; Cairns, W.L. Ultraviolet Light. In Proceedings of the Regional Symposium on Water Quality: Effective Disinfection, Lima, Peru, 27–29 October 1998; pp. 1–26.
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Alternative Disinfectants and Oxidants Guidance Manual; EPA Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 1999.
- Tamulaitis, G. Ultraviolet light emitting diodes: Review. LITH J. Phys. 2011, 51, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Mohseni, M.; Taghipour, F. Application of ultraviolet light-emitting diodes (UV-LEDs) for water disinfection: A review. Water Res. 2016, 94, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinonen-Tanski, H.; Juntunen, P.; Rajala, R.; Haume, E.; Niemelä, A. Costs of tertiary treatment of municipal wastewater by rapid sand filter with coagulants and UV. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2003, 3, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Challenge Organisms for Inactivation of Viruses by Ultraviolet Treatment; Water Research Foundation: Denver, CO, USA, 2010.
- Eischeid, A.C.; Linden, K.G. Molecular indications of protein damage in adenovirus after UV disinfection. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 1145–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Water Research Institute (NWRI). Ultraviolet Disinfection Guidelines for Drinking Water and Water Reuse, 3rd ed.; National Water Research Institute in Collaboration with Water Research Foundation: Fountain Valley, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, S.E.; Ryu, H.; Boczek, L.A.; Cashdollar, J.L.; Jeanis, K.M.; Rosenblum, J.S.; Lawal, O.R.; Linden, K.G. Evaluating UV-C LED disinfection performance and investigating potential dual wavelength synergy. Water Res. 2017, 109, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenny, R.M.; Jasper, M.N.; Simmons, O.D., III; Shatalov, M.; Ducoste, J.J. Heuristic optimization of a continuous flow point-of-use UV-LED disinfection reactor using computational fluid dynamics. Water Res. 2015, 83, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilhunen, S.; Särkkä, H.; Sillanpää, M. Ultraviolet light-emitting diodes in water disinfection. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2009, 16, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenny, R.M.; Simmons, O.D., III; Shatalov, M.; Ducoste, J.J. Modeling a continuous flow ultraviolet light emitting diode reactor using computational fluid dynamics. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2014, 116, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterley, C.; Linden, K. Demonstration and evaluation of germicidal UV-LEDs for point-of-use water disinfection. J. Water Health 2010, 8, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowker, C.; Sain, A.; Shatalov, M.; Ducoste, J. Microbial UV fluence-response assessment using a novel UV-LED collimated beam system. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2011–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, K.Y.; McMartin, D.W.; Yost, C.K.; Runtz, K.J.; Ono, T. Point-of-use water disinfection using UV light-emitting diodes to reduce bacterial contamination. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5441–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oguma, K.; Kita, R.; Sakai, H.; Murakami, M.; Takizawa, S. Application of UV light emitting diodes to batch and flow-through water disinfection system. Desalination 2013, 328, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguma, K.; Rattanakul, S.; Bolton, J.R. Application of UV light-emitting diodes to adenovirus in water. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 142, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, G.Y.; Roser, D.; Corkish, R.; Ashbolt, N.J.; Stuetz, R. Point-of-use water disinfection using ultraviolet and visible light-emitting diodes. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 553, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sholtes, K.A.; Lowe, K.; Walters, G.W.; Sobsey, M.D.; Linden, K.G.; Casanova, L.M. Comparison of ultraviolet light-emitting diodes and low-pressure mercury-arc lamps for disinfection of water. Environ. Technol. 2016, 37, 2183–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyagi, Y.; Takeuchi, M.; Yoshida, K.; Kurouchi, M.; Yasui, N.; Kamiko, N.; Araki, T.; Nanishi, Y. Inactivation of bacterial viruses in water using deep ultraviolet semiconductor light-emitting diode. J. Environ. Eng. 2011, 137, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyara, A.M.; Torvinen, E.; Veijalainen, A.-M.; Heinonen-Tanski, H. The effect of UV and combined Chlorine/UV treatment on coliphages in drinking water disinfection. Water 2016, 8, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, F.-C.; Shieh, Y.S.; Duin, J.V.; Beekwilder, M.J.; Sobsey, M.D. Genotyping male-specific RNA coliphages by hybridization with oligonucleotide probes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 3960–3966. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bolton, J.R.; Linden, K.G. Standardization of methods for fluence (UV Dose) determination in Bench-Scale UV experiments. J. Environ. Eng. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuopion Vesi. Drinking Water Quality in Kuopio. Available online: http//www.kuopionvesi.fi/c/document_library/get_file?uuid=e6c27e13-472e-4496-8f99-9fb7933e89b4&groupId=518539 (accessed on 27 January 2016).
- American Public Health Association (APHA); American Water Works Association (AWWA); Water Environment Federation (WEF). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; APHA, AWWA and WEF: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, M.H. Bacteriophages; Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Rajala-Mustonen, R.L.; Heinonen-Tanski, H. Sensitivity of host strains and host range of coliphages isolated from Finnish and Nicaraguan wastewater. Water Res. 1994, 28, 1811–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyara, A.M.; Torvinen, E.; Veijalainen, A.-M.; Heinonen-Tanski, H. The effect of chlorine and combined chlorine/UV treatment on coliphages in drinking water disinfection. J. Water Health 2016, 14, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, S.E.; Wright, H.B.; Hargy, T.M.; Larason, T.C.; Linden, K.G. Action spectra for validation of pathogen disinfection in medium-pressure ultraviolet (UV) systems. Water Res. 2015, 70, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, S.E.; Rodriguez, R.A.; Hawkins, M.A.; Hargy, T.M.; Larason, T.C.; Linden, K.G. Comparison of UV-Induced Inactivation and RNA Damage in MS2 Phage across the Germicidal UV Spectrum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 1468–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oguma, K.; Kita, R.; Takizawa, S. Effects of arrangement of UV light-emitting diodes on the inactivation efficiency of microorganisms in water. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 2016, 92, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Ultraviolet Disinfection Guidance Manual for the Final Long Term 2 Enhanced Surface Water Treatment Rule; EPA Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2006.
- Kalisvaart, B.F. Re-use of wastewater: Preventing the recovery of pathogens by using medium-pressure UV lamp technology. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 50, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oppezzo, O.J.; Pizarro, R.A. Sublethal effects of ultraviolet A radiation on Enterobacter cloacae. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2001, 62, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamamoto, A.; Mori, M.; Takahashi, A.; Nakano, M.; Wakikawa, N.; Akutagawa, M.; Ikehara, T.; Nakaya, Y.; Kinouchi, Y. New water disinfection system using UVA light-emitting diodes. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 2291–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevremont, A.C.; Farnet, A.M.; Coulomb, B.; Boudenne, J.L. Effect of coupled UV-A and UV-C LEDs on both microbiological and chemical pollution of urban wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 426, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevremont, A.C.; Farnet, A.M.; Sergent, M.; Coulomb, B.; Boudenne, J.L. Multivariate optimization of fecal bioindicator inactivation by coupling UV-A and UV-C LEDs. Desalination 2012, 285, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahashi, M.; Mawatari, K.; Hirata, A.; Maetani, M.; Shimohata, T.; Uebanso, T.; Hamada, Y.; Akutagawa, M.; Kinouchi, Y.; Takahashi, A. Simultaneous irradiation with different wavelengths of ultraviolet light has synergistic bactericidal effect on Vibrio Parahaemolyticus. Photochem. Photobiol. 2014, 90, 1397–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattanakul, S.; Oguma, K.; Sakai, H.; Takizawa, S. Inactivation of viruses by combination processes of UV and chlorine. J. Water Environ. Technol. 2014, 12, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanakul, S.; Oguma, K.; Sakai, H.; Takizawa, S. Sequential and simultaneous applications of UV and chlorine for adenovirus inactivation. Food Environ. Virol. 2015, 7, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
 Hg-UV and for
Hg-UV and for  UV-LEDs.
UV-LEDs.
 Hg-UV and for
Hg-UV and for  UV-LEDs.
UV-LEDs.
| Coliphage Strains According to [22] | Host ATCC Strain | Genetic Material | Resistant (R), Intermediate Resistant (I) or Sensitive (S) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hg-UV [25] | Cl [32] | |||
| MS2 | 15597 | RNA | R | I |
| 1 | 15597 | RNA | R | R |
| 5 | 15597 | RNA | R | R |
| 7 | 13706 | DNA | S | R |
| 17 | 13706 | DNA | R | R |
| Coliphage Strains | Linear Regression Equations of UV-LEDs | Linear Regression Equations of Hg-UV | |
|---|---|---|---|
| y = Log10-Reduction x = Time (0–15 min) | y = Log10-Reduction x = Time (0–10 min) | y = Log10-Reduction x = Time (0–10 min) | |
| MS2 | y = −(0.09 ± 0.030)x (R2 = 0.82) | y = −(0.11 ± 0.047)x (R2 = 0.91) | y = −(0.32 ± 0.003)x (R2 = 0.95) |
| 1 | y = −(0.25 ± 0.057)x (R2 = 0.68) | y = −(0.53 ± 0.081)x (R2 = 0.60) | y = −(0.69 ± 0.016)x (R2 = 0.96) |
| 5 | y = −(0.42 ± 0.057)x (R2 = 0.93) | y = −(0.54 ± 0,094)x (R2 = 0.99) | y = −(0.51 ± 0.012)x (R2 = 0.97) |
| 7 | y = −(0.33 ± 0.046)x (R2 = 0.79) | y = −(0.59 ± 0.044)x (R2 = 0.71) | y = −(0.93 ± 0.013)x (R2 = 0.85) |
| 17 | y = −(0.30 ± 0.049)x (R2 = 0.82) | y = −(0.49 ± 0.079)x (R2 = 0.94) | y = −(0.56 ± 0.019)x (R2 = 0.91) |
© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zyara, A.M.; Heinonen-Tanski, H.; Veijalainen, A.-M.; Torvinen, E. UV-LEDs Efficiently Inactivate DNA and RNA Coliphages. Water 2017, 9, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010046
Zyara AM, Heinonen-Tanski H, Veijalainen A-M, Torvinen E. UV-LEDs Efficiently Inactivate DNA and RNA Coliphages. Water. 2017; 9(1):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010046
Chicago/Turabian StyleZyara, Alyaa M., Helvi Heinonen-Tanski, Anna-Maria Veijalainen, and Eila Torvinen. 2017. "UV-LEDs Efficiently Inactivate DNA and RNA Coliphages" Water 9, no. 1: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010046
APA StyleZyara, A. M., Heinonen-Tanski, H., Veijalainen, A.-M., & Torvinen, E. (2017). UV-LEDs Efficiently Inactivate DNA and RNA Coliphages. Water, 9(1), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010046






