Abstract
Intensive agricultural activities in the Hetao irrigation district have severely degraded local aquatic ecosystems and water quality, and Ulansuhai Lake is now the most rapidly degrading eutrophic lake in China. A better understanding of the hydro-agronomic and pollutant transport processes in the area is thus urgently needed. This study simulated monthly streamflow, total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP) for the Hetao irrigation district using the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) to evaluate the nutrient load, source areas, and hydrological pathways. The Nash-Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE) values obtained for the streamflow simulations were 0.75 and 0.78 for the calibration and evaluation periods, respectively. The SWAT model captured the temporal variation in streamflow (R2 > 0.8) for two periods; the NSE values for the TN and TP loads were 0.63 and 0.64 for the calibration period and 0.48 and 0.42 for the evaluation period, respectively. The predicted monthly TN load was correlated with irrigation (r = 0.61) and the monthly TP load with precipitation (r = 0.89), indicating that nitrogen transport is primarily associated with soil leaching and groundwater flow, and phosphorus is primarily transported by sediments caused by rainfall erosion. A case study of split nitrogen fertilizer applications demonstrated reduced annual TN load by as much as 13% in one year. Fertilization timing also affects the load in different pathways especially in lateral subsurface flow and shallow groundwater. Better agricultural management could thus reduce nitrogen losses, and buffer strips could minimize phosphorus transport.
1. Introduction
Agriculture is a basic economic factor for every country and this is especially the case for China, which is a developing agricultural country. Irrigation districts provide the foundation for much of the country’s food crop production, which is largely conducted in six very large irrigation districts with areas greater than 335,000 ha each. In recent years, excessive fertilization has been common, and there has been serious deterioration of water quality in these areas due to agricultural non-point source (ANPS) pollution. The intensification of agricultural activities in recent years has been clearly identified as the major contributor to ANPS pollution of water resources [1].
Many studies on water balance and ANPS management in agricultural areas have been carried out worldwide [2]. The impacts of climate change, uncertainties in agricultural land management by different between farmers, soil properties and complex topography affect water quantity and quality. Water is particularly sensitive to agricultural land management and soil type properties under intensive human actives in the plain area [3,4]. Laurent and coworkers [5] indicated nitrate leaching is highly sensitive to agricultural practices such as crop sequence. Different combinations of soil types and crop management caused different ratios of nitrogen (N) leaching in the plains area, and designing water protection zones according to individual soil type is suggested minimize N [4]. In addition, the quantity and quality of freshwater flows are closely related to the land use and management of agroecosystems. The changes of land use and fertilizer management are primary factors influencing runoff and non-point source pollution transport [1,6].
The Hetao irrigation district, which is part of a large watershed, combines distinct topographic conditions with an arid climate, experiencing very low precipitation, high potential evaporation and rainfall that is both temporally and spatially variable. Irrigation water plays an essential role in agriculture; the annual irrigation water volume extracted from the Yellow River is approximately 4.5 billion m3. In the Bayenaoer region, irrigated agriculture uses approximately 90% of the total surface water resources [7,8]. Salinization of the soil in the area has been aggravated for a considerable time by flood irrigation and increased soil erosion. Irrigation canals and drainage channels extend throughout the entire farming area, and pumping stations have been installed to control the quantity of irrigation water applied and improve the cultivation conditions. Meanwhile, these facilities can cause obvious changes in the water balance and pollutant transport. This catchment is comprised of approximately equal areas of floodplain arable land and mountainous territory, and the main drainage channel has been strongly influenced by the streamflow from these two land types [9], making the Hetao watershed a key example of a human-nature composite ecosystem. It is therefore necessary to build a more detailed picture of the hydrological processes involved in the surface runoff and groundwater discharge affecting ANPS pollution, especially in the Hetao irrigation district where the irrigation scheme controls the groundwater flow and the transport of nutrients.
The Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) has been used broadly to simulate non-point source pollution at various watershed scales for nearly 30 years [10,11,12] and has been used to investigate water quantity and quality issues from watersheds at various scales [13]. However, most of these studies have focused on natural watersheds where precipitation and runoff are the main controlling factors and surface runoff is the major hydrologic process, with the major pollutants transported in the surface runoff. In recent years, intensive human activities such as irrigation have begun to be considered, and several studies have applied SWAT to model lowland and irrigation areas. For example, Volk and coworkers [14,15] identified land use and land management scenarios that would reduce the total nitrogen concentration in Upper Ems River basin, which is a predominantly flat landscape with sandy soils. Schmalz and coworkers [16] assessed the nutrient transport and dominant hydrologic processes in lowland catchments, concluding that surface runoff and shallow groundwater strongly influence the hydrology and nutrient dynamics, especially at the adjacent floodplains. A few years later, Lam and coworkers [17] used the SWAT model to simulate pollutant transport and point out that the groundwater was the main pathway for point and non-point source pollution of nitrate in a rural lowland area. Two other groups [18,19] modified the SWAT model to evaluate the water balance and nutrient loads in the flooded irrigation of paddy areas, demonstrating the utility of the SWAT model for flood irrigation. These studies confirmed the applicability of the SWAT model in lowland and irrigation district areas with special hydrological characteristics, such as flat topography and a shallow groundwater table.
The objectives of this paper were to: (1) assess the SWAT model parameters that affect streamflow processes and nutrient transport, and evaluate the model performance regarding simulation of flow and nutrient load in a topographically complex watershed; (2) evaluate the flowpaths and transport of nutrients for the entire watershed and determine the precise relationships between the generation factors and ANPS pollutants in the Hetao irrigation district watershed; and (3) explore alternative nutrient management scenarios to analyze changes of annual nitrogen load and the effects on different pathways. This research aims to provide a reference and experience for quantifying ANPS pollution from different pathways, which can guide water and nutrient management practices in areas with similar environmental conditions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Model Description
SWAT is a semi-distributed hydrological model that can simulate the long-term hydrologic processes, sediment transport and pollutant loads for different soil and land-use conditions at various scales of watersheds [20]. It is a popular tool to simulate water quantity and quality for watershed scale studies. Major components of the model are hydrologic process components, a weather generator, nutrient transport, and management practices.
There are two major parts in SWAT for simulation of watershed hydrology. One is the land phase of the hydrologic cycle, which simulates the amount of water, sediment, and nutrient loading from each subbasin to the main channel, and the other is the hydraulic routing phase, which describes the water, sediment, nutrients and other material movement through the channel network of the whole watershed to the outlet. A modification of the Soil Conservation Service (SCS) curve number method [21] is used in SWAT for calculating surface runoff. It is an empirical function used to represent the soil’s permeability, land use and antecedent soil water conditions.
The nitrogen cycle through plants, soil and shallow aquifers was simulated with SWAT [20]. In the soil part, there are two inorganic pools of nitrogen and three organic pools. Of these, the inorganic forms of nitrogen are NH4+ and NO3−, and organic forms are fresh organic N, active organic N and stable organic N. Applications of fertilizer, manure or residue management, bacteriological fixation, and rain add N to the soil in different forms. Nitrates in soil water are decreased through plant uptake, leaching, denitrification, volatilization, and soil erosion. Similar to nitrogen, phosphorus pools are estimated using a supply and demand approach. The different phosphorus processes are modeled by SWAT in each hydrologic response unit (HRU) using three major forms: organic P, various insoluble forms of mineral P, and the plant-available P in soil-water solution. The Enhanced Stream Water Quality Model (QUAL2E) model was developed to conduct dynamic simulations of in-stream water quality [22], taking into account nutrient cycling, including algal production in the water column and benthic oxygen demand.
2.2. Study Area
The Hetao irrigation district is the third largest flood irrigation district in China, and is located in the Bayenaoer region of Inner Mongolia. The mean annual precipitation is 180 mm, of which 80% occurs from June–August. The annual potential evaporation is about 2200–2400 mm, the mean annual temperature in the region is about 6–8 °C and the freeze-up period typically lasts for 5 to 6 months of each year [23]. Soil freezes from late November to early May, and the maximum frost depth is typically 1–2 m. The soil parent material of the area is predominantly alluvium deposited by the Yellow River. The average soil thickness is greater than 1.2 m. Due to the high groundwater recharge from irrigation, the mean water table depth fluctuates significantly, ranging from 1.5 m in March to about 0.6 m in October.
The area of the Hetao irrigation district watershed is about 11,195 km2, of which irrigation is applied to about 5740 km2. Farmland occupies about 5247 km2 (Figure 1). The main crops are sunflower, spring wheat and corn. Approximately 600,000 tons of fertilizers are used annually for agricultural production in the Hetao irrigation district [24]. The biggest lake in the Yellow River watershed, Ulansuhai Lake, receives the bulk of the runoff from the Hetao irrigated farmland and thus performs an important ecological function for both storage capacity and ecosystem protection [25]. There are two major irrigation events, one each in May and October for all crops. The total volume of water extracted from the Yellow River is about 4 to 6 billion m3 each year. The summer irrigation event is prescribed to meet the demands of the growing period, while the fall event is to leach the salt out of the soil and recharge the soil moisture to support the following year’s spring wheat crop [26]. The lake’s average annual inflow of about 400 million m3 of water from agricultural return flow contains high nutrient concentrations, giving it the unwelcome distinction of being the lake with the fastest rate of eutrophication in China [27]. The mitigation of ANPS pollution is of great importance for the restoration of water quality in this and other lakes in the region.
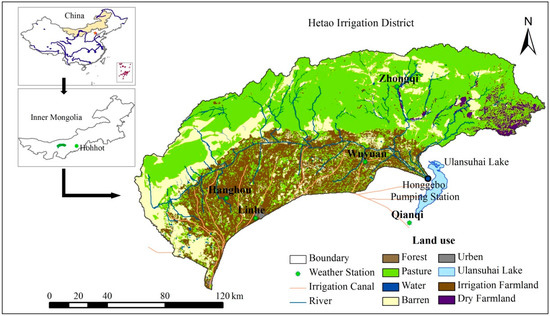
Figure 1.
Location of the Hetao Irrigation District and its land use classifications.
There are eight irrigation canals, with a total length of 181 km, and thirteen drainage channels across the irrigation district. Flood irrigation is the only irrigation method in this area. Water flows from the Yellow River into the farming area; the outlet is at the entrance of Ulansuhai Lake, which is downstream of the main drainage channel, as a drainage recipient from the farmland (Figure 1). The outflow from the lake returns to the Yellow River further downstream.
2.3. Data Preparation
The ArcSWAT interface for SWAT version 2009 [28] was used to compile the SWAT input files. A digital elevation model (DEM) raster dataset for the Hetao watershed (90 m × 90 m), and daily weather data (maximum and minimum temperature, precipitation, relative humidity, wind speed, and sunshine hours as a surrogate for solar radiation) were obtained from the China Meteorological Data website for the period 2000 to 2013 [29]. In this study, five meteorological stations were selected, as shown in Figure 1. The land-use database (1:100,000) for the year 2000 and the soil property database (1:1,000,000) were obtained from the Scientific Data Center of the Cold and Arid Regions website [30] and imported into ArcSWAT.
The Honggebo pumping station is located at the outlet of the Hetao irrigation district (Figure 1), pumping water from the lower drainage channel up into the lake. The monthly average flow data (2003–2013) were recorded at this station. Water quality data are limited by the climate, which drops below freezing in early November each year, so monthly average total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP) load data was only available for May to October, 2007 to 2013.
2.4. Nutrient Management
In this study, the initial fertilizer management scenario for each crop was based upon feedback from local farmers and irrigation district agents. However, most research has focused on optimal nitrogen fertilization for two main crops, which are corn and spring wheat in this study area [31,32]. Based on this information, we selected two scenarios to analyze how fertilization of the two main crops affects nutrient load and transport.
Scenario 1 was the historical fertilizer management with one application of nitrogen and phosphorus per year based on historical rates of fertilizer for corn (240 kg·N·ha−1 and 140 kg·P·ha−1) and spring wheat (240 kg·N·ha−1 and 120 kg·P·ha−1) each applied once per year. Scenario 2 applied split applications of 25% on 2 May and 75% on 5 August of the total amount of nitrogen fertilizer for corn. Meanwhile for spring wheat, we applied 75% on 25 March and 25% on 20 May of total nitrogen fertilizer. There was no change for phosphorus fertilizer management, and the total amounts over the season were the same. Water management (irrigation) was also unchanged in Scenario 2.
2.5. Model Calibration and Evaluation
Improving the reliability of the model is determined by the accuracy of the parameter selection in the model calibration process. Many parameters can affect the SWAT simulation results, and it is often difficult to determine accurate values during the calibration procedure, so a sensitivity analysis is a necessary step before calibration and evaluation. In this study, Latin Hypercube Sampling (LHS) and one factor at a time (OAT) were combined in the parameter sensitivity method [33]. SWAT-CUP (SWAT Calibration and Uncertainty Programs) is a recently developed calibration package for SWAT; SUFI-2 was the main algorithm implemented here [34]. SUFI-2 determines the most sensitive parameters for calibration through Latin Hypercube Sampling and applying OAT and global sensitivity methods.
Model performance was evaluated using qualitative graphical comparisons and quantitative statistical techniques. Based on existing model evaluation guidelines [35,36,37,38], the statistical measures were used to evaluate the hydrology model performance. The Nash-Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE) [39], coefficient of determination (R2), and percent bias (PBIAS) were selected as goodness-of-fit indices to evaluate the SWAT model performance. The following equations are used to calculate these statistical measures:
where n is the number of data points in the whole observation and simulation period. NSE describes the explained variance for the observed values over time that is accounted for by the SWAT model. Similarly, R2 is used as a guideline to evaluate whether the model tracks the general temporal variations in the observed values. The difference between NSE and R2 is that NSE can interpret model performance for replicating individually observed values, while R2 only quantifies the fraction of observed variance explained by the model.
PBIAS measures the average tendency of a model to estimate the observed data. Based on the recommendations of Moriasi and coworkers [36], a satisfactory PBIAS value is ±25% for streamflow, ±70% for nutrients.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Model Sensitivity Analysis
The catchment was divided into 55 subbasins, representing 364 hydrologic response units (HRUs) in the ArcSWAT 2009. There are many parameters to calibrate for each HRU. Thus, a sensitivity analysis of parameters was carried out to calibrate the SWAT model for the Hetao irrigation district watershed. As the mountainous area hydrology is characterized as precipitation-runoff-evaporation, while the plains area hydrology is predominantly irrigation-drainage-evaporation, the values of some parameters are different in these two areas. A sensitivity analysis was performed for stream flow, TN, and TP at the outlet of the Hetao irrigation district watershed (Figure 1). Table 1 presents an overview of the calibrated parameter values for the 20 most sensitive SWAT2009 parameters. For example, the threshold depth of the water in the shallow aquifer required for return flow to occur (GWQMN) may be 207 mm in the mountainous area in the northern portion of the watershed but only 96 mm in the plains area in the southern portion of the watershed. The unique characteristics of the Hetao watershed are reflected by the fitted parameter values. Among these parameters (see Table 1 for descriptions), the most identifiable parameters were ALPHA_BF, SOL_AWC, ESCO and GWQMN for stream flow, and CDN and NPERCO for TN load, and PSP and SLOPE for TP load.

Table 1.
Main variables used for sensitivity analysis and calibration in SWAT and the final calibrated values.
3.2. Flow Calibration and Evaluation
The monthly stream flow data for 2003 to 2013 as the observed data that were obtained from the Honggebo pumping station were selected for model calibration and evaluation. The data for the first 6 years, from 2003 to 2008, were used in the calibration phase and that for the remaining 5 years, from 2009 to 2013, were employed for the model evaluation. The results for the flow calibration and evaluation are shown in Figure 2. The statistical values obtained for NSE and R2 were 0.75 and 0.81, respectively, for the calibration period and 0.78 and 0.82, respectively, for the evaluation period (Table 2). Values of NSE < R2 are expected, because regression takes into account any linear relationship, even if the simulated values deviate from the 1:1 line of simulated versus observed values. Based on standards recommended in the literature [36], these results indicate that the model simulated runoff in the watershed satisfactorily (NSE > 0.5; |PBIAS| < 25%); the bias was particularly low (|PBIAS| < 2%) for streamflow.
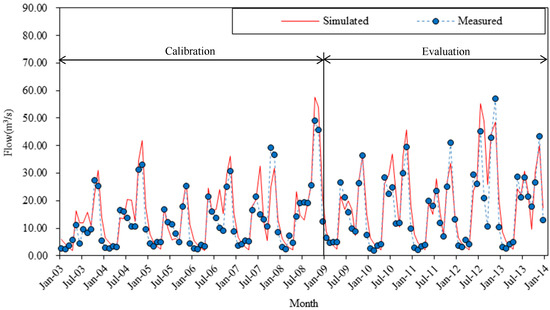
Figure 2.
Simulated and measured streamflow at the outlet of the Honggebu Pumping Station.

Table 2.
Model performance statistics of the simulated and measured monthly streamflow, total nitrogen and total phosphorus at Honggebo pumping station.
The data presented in Figure 2 show flow peaks in May and October every year. The latter peak is clearly due to the autumn irrigation scheme utilized throughout the Hetao district to flush salts from the soil profile. This differs from flows normally observed in cold and arid regions, where the peaks are typically caused by surface runoff from snow melting in spring and precipitation in summer. However, the first peak each year appears to be affected by both irrigation and snowmelt. Snowmelt peak dates over all simulation years (2003–2014) range from 3 February to 13 March. The first peak flow each year (noting that some years had two peaks before the autumn peak flow) occurs during the period of 7–15 May. Thus snowmelt affects the antecedent soil moisture, such that the runoff response to spring irrigation is faster than otherwise expected.
Irrigation water that is not consumed by evapotranspiration in croplands mostly recharges the groundwater, which subsequently flows into drainage channels and becomes the main contributor to streamflow. Lam and coworkers [17] also found evidence that groundwater represents a dominant pathway in lowland areas. When calibrating the SWAT model for the Hetao watershed, the groundwater parameters were calibrated first. Flow processes significantly controlled by the main parameters (see Table 1) in the plains arable area, where groundwater is the primary contributor, were GWQMN, ALPHA_BF, GW_DELAY, REVAPMN, and ESCO. Of these, the most sensitive parameter was GWQMN, which represents the threshold depth of the water in the watershed’s shallow aquifer. The value of ALPHA_BF ranged from 0.04 to 0.31 and GW_DELAY ranged from 22 to 27, which indicates that the groundwater recharge is slightly slower. The irrigation water does not run off via overland flow from fields because of the ridges formed around field boundaries, so the irrigation water is consumed exclusively by interception and evaporation before the remainder percolates into the groundwater. However, the Hetao irrigation area has complex hydrologic characteristics that depend not only on natural factors like evapotranspiration and precipitation but also on human activities such as irrigation and drainage operations. In the resulting human–nature composite ecosystem [40], a clear relationship between surface water and groundwater is evident. Wu and coworkers [10] indicated that approximately 30% of streamflow at the outlet comes from mountainous areas through subbasin runoff (“lateral flow” in SWAT). Also, two parameters (Table 1), CN2 and SOL_AWC, control the discharge in mountainous area, especially during the summer when most runoff from the mountains occurs as rainfall-runoff.
The water routing phase of the hydrologic cycle controls a part of water, sediment and nutrients movement through the channel network of the watershed to the outlet, and also has a significant influence on streamflow processes. As the groundwater table is only 0.6 m deep during the growing season due to the high rates of irrigation, streams in the area receive groundwater flow all the time. The effective hydraulic conductivity in the main channel alluvium (CH_K2) therefore significantly affects the flow process in the study area. The simulation results for the summer months do not always fit the measured data as well as they do at other times of the year, however. Descriptions and values of these parameters are presented in Table 1.
3.3. Water Quality Calibration and Evaluation
Considering the availability of water quality monitoring data and the goal of this study, total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP) were selected as appropriate water quality indicators for calibration and evaluation. All nutrient data were obtained from Honggebo pumping station at the outlet of the Hetao catchment. The comparisons between the simulated and measured results for the monthly TN and TP loads are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4, respectively; as noted earlier, data are only available for May to October 2007–2013. The NSE values for monthly total nitrogen and phosphorus are 0.63 and 0.64, respectively, for the calibration period from 2007 to 2010; and 0.48 and 0.42, respectively, for the evaluation period from 2011 to 2013. The bias is also very low (|PBIAS| < 10%) for TN; the bias of TP is much higher (|PBIAS| < 37%) (Table 2). These modeling results are considered acceptable even though some individual observations may show considerable differences [41].
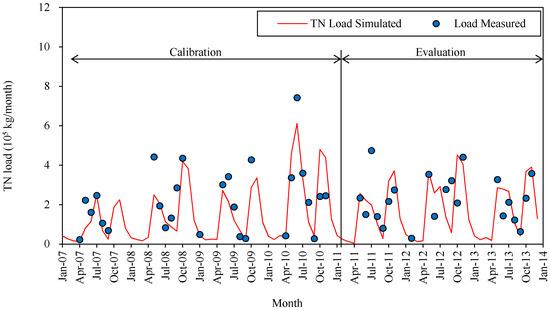
Figure 3.
Simulated and measured monthly total nitrogen (TN) load at the outlet.
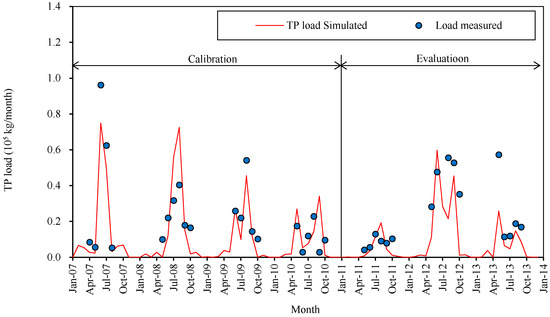
Figure 4.
Simulated and measured monthly total phosphorus (TP) load at the outlet.
Nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) concentrations are primarily governed by three mechanisms, namely loss, transformation, and plant uptake. Based on previous studies, for N the plant uptake is approximately 21%–36%, with most of the nitrogen (64%–74%) staying in the soil to be consumed by ammonia volatilization and denitrification [18]. Therefore, the most sensitive parameter for N is the denitrification exponential rate coefficient (CDN), closely followed by the nitrate percolation coefficient (NPERCO). Phosphorus is generally transported along with the suspended sediment, so the two parameters that control the phosphorus processes and load are the phosphorus availability index (PSP) and the average slope steepness (SLOPE).
3.4. Mechanisms of N and P Transport in Hetao Irrigation District
Agricultural activities such as tillage, fertilization, and irrigation scheduling have significant effects on the generation of ANSP pollution. Figure 5 is a diagram of spatial distributions of source areas of the TN and TP loads for Scenario 1. It clearly indicates that the cropped area is the main contributor of TN and TP loads in this watershed. Each subbasin has a different value which depends on the dominant crops. Traditional agricultural practices such as flood irrigation through irrigation canals and drainage channels across the Hetao irrigation district aggravate the nutrient losses. Although farmers now till fertilizer into the top 10–15 cm of soil to reduce nutrients losses based on past experiments and experience, excess fertilization is a common condition in this area, which leads to serious nutrient losses.
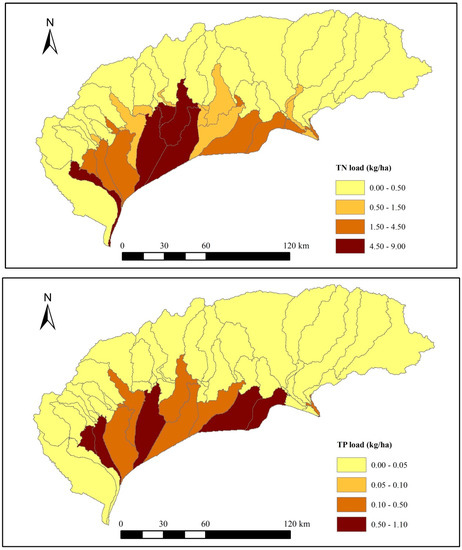
Figure 5.
Map of the spatial partitioning of the TN and TP loads.
Nitrate anion exclusion is a contributor to nitrogen leaching in the study area. This is because the solubility of NO3− is over 1 kg·L−1 and it is repelled by the soil’s negative charge. Irrigation water interception removes a significant amount of nitrate from the soil. As the data presented in Figure 3 indicates, TN has similar temporal characteristics to those exhibited by the stream flow in the region, with two peaks caused by irrigation schemes and the subsequent percolation focused on the two irrigation periods. Figure 6 compares the nitrate loads in the surface runoff, lateral saturated flow and groundwater discharge; the groundwater contributes about 82% of the total load.
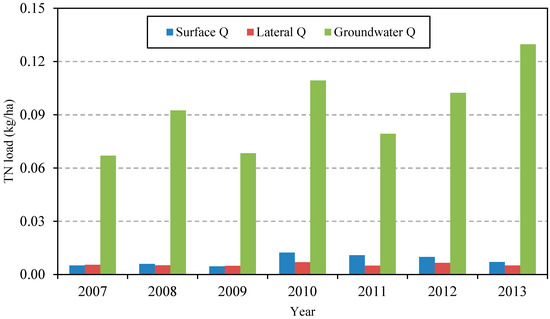
Figure 6.
Total nitrogen in surface water runoff, lateral saturated water and groundwater.
The temporal characteristics of P (Figure 4) differ markedly from the streamflow and N transport patterns. Although there are many irrigation canals and drainage channels in the irrigated area and many diversion terraces in farm lands, the irrigation water is diverted into each field and detained without any measurable surface runoff. This means that P is not lost with surface runoff and lateral runoff, even though for the adsorbed state of P these represent major transportation mechanisms. The practice of flood irrigation and the high potential evaporation both increase the groundwater evaporation, however, creating large areas of saline and alkaline lands where it is hard to grow crops in the Hetao irrigation district [42]. Consequently, soil erosion in these saline and alkaline lands exacerbates the P loss and a heavy rainfall event can easily lead to large amounts of sediment and the associated P being washed away, despite human efforts to prevent surface runoff and soil loss.
To determine the relationship between nutrient loss and natural/agricultural factors, statistically significant Pearson’s correlation coefficients (p < 0.05) were identified between all output variables as monthly averages (Table 3) [33,43]. As expected, streamflow was more closely correlated with irrigation (r = 0.42) than with precipitation (r = 0.17), total nitrogen load was highly correlated with streamflow (r = 0.82), and total phosphorus load was highly correlated with precipitation (r = 0.89). This indicates that nitrogen is transported via the groundwater discharge generated by the irrigation scheme, so the timing of the irrigation may play an important role for nitrogen. In contrast, phosphorus is generated by precipitation when rainfall events generate sediment losses, so improved irrigation methods, such as drip or spray irrigation, could reduce nitrogen losses and planting buffer strips could reduce phosphorus losses.

Table 3.
Relationships between simulated monthly model outputs (significant correlations, p < 0.05).
It has been predicted that both the N and P concentrations will accumulate and become very high in the winter due to ice cover increasing the soil erodibility of drainage channels [44]. Considering the present study results, this model was unable to capture these characteristics during freezing conditions. As accurate data were not available for the winter period, the SWAT model requires modification to simulate pollutant transport during the freezing period, for example by incorporating an ice cover factor into the sediment routing calculation for the stream channels.
3.5. Scenario Analysis for the TN Load and Transportation
In the large irrigation district, the fertilization practices (Scenario 1 versus Scenario 2) affected the nutrient transport and load. Table 4 shows the results from two scenarios; where the annual TN load could be decreased, the difference ranges from 10,605 kg·year−1 to 419,693 kg·year−1. The maximum annual decrease exceeded 13%. Table 5 shows the changes of nitrogen load in different pathways where the nitrogen in lateral flow and shallow groundwater were the most sensitive to the timing of fertilizer application. There was almost no change for nitrogen in surface flow. Comparing these two scenarios, it is indicated that the use of fertilizer in cropland had no effects on surface flow quality but affected lateral flow and shallow groundwater quality. This result is similar to Lam’s study in a lowland area [17]. Effects of other irrigation regimes and fertilization scenarios on nutrient load changes will be studied in future work.

Table 4.
Annual TN load (kg-N) for scenario analysis.

Table 5.
The results of nitrogen changes in different pathways for scenario analysis (kg·year−1).
4. Conclusions
The SWAT model was used to simulate stream flow, TN, and TP loads in the Hetao irrigation district watershed in northern China. Generally, the performance of simulation for the monthly flows and nutrient loads at the catchment outlet is successful. Because observed nutrient data were not available during the winters (November–March) due to freezing conditions, we could not verify simulated changes for the whole years. This constitutes a limitation and source of uncertainty in the simulated results. At the same time, this is an argument for using a calibrated watershed model to estimate nutrient loads in the winter without measured data. Even so, Figure 3 shows one winter load very well. This gives very limited, anecdotal evidence that the model is capturing nutrient transport even during winter months. Hence, this study serves as a useful example for interactions between topographic areas that include both plains arable land and mountainous arid grassland.
The unique watershed topology and relationship with the Yellow River has important hydrological and water quality impacts on the watershed, lake and river system. Hydrological processes in this watershed are affected significantly by human activities. The present irrigation scheme has a significant effect on the timing of hydrology processes in the large Hetao irrigation district, with irrigation water being the major contributor to the groundwater that discharges into the streams and drainage channels in this catchment. The temporal characteristics of streamflow closely match the irrigation scheme. Thus, altering the amounts, frequency and timing of irrigation could reduce both the peaks and average TN loads.
Nitrate loads were assessed and defined the critical pathways from subbasins into the local streams for the Hetao irrigation area. The results indicate that the major source of nitrate in the streams comes from shallow groundwater flow, accounting for about 82% of the total nitrate load, with the remainder of about 18% associated with either lateral saturated flow or surface runoff. The TN load is highly correlated with irrigation (r = 0.82), which clearly indicates that reducing nitrate leaching is a good way to mitigate movement to the outlet. However, phosphorus transport is highly correlated with precipitation (r = 0.89). Following the simple fertilization scenario analysis presented here, a more comprehensive optimization of fertilizer and irrigation management can reduce the nutrient loads to Ulansuhai Lake via the identified pathways. Improved strategies for agricultural management, such as drip or spray irrigation, combined with more optimal irrigation timing and amounts, combined with optimal fertilization, could decrease nitrate leaching to groundwater, while phosphorus transport via surface runoff could be reduced by planting buffer strips. These findings may help decision makers select appropriate measures to further improve water quality in the Hetao irrigation district, Ulansuhai Lake, and the downstream reaches of the Yellow River. Likewise the lessons learned here could be extended to other irrigation districts around the world.
Acknowledgments
The research was funded by IRT13069, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51339002, 51669022, 51569019, 51509133, 51269017, 51269016, 51069007), and the Inner Mongolia Natural Science Foundation (2016MS0406). We are also grateful for assistance with data requirements of Honggebo Pumping Station in Wulateqianqi Banner.
Author Contributions
Yong Wu and Xiaohong Shi conceived and designed the study, then refined it with Timothy R. Green; Fang Peng, Xiaohong Shi, Changyou Li and Shengnan Zhao collected the data, and Yong Wu analyzed the data; Yong Wu and Xiaohong Shi performed the simulations; Yong Wu wrote the paper with assistance from Timothy R. Green.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, R.M.; Zhang, P.P.; Wang, X.J.; Chen, Y.X.; Shen, Z.Y. Assessment of effects of best management practices on agricultural non-point source pollution in Xiangxi River watershed. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 117, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, M.; Bosch, D.; Nangia, V.; Narasimhan, B. SWAT: Agricultural water and nonpoint source pollution management at a watershed scale. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 175, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavan, M.; Ceglar, A.; Pintar, M. Assessing the impacts of climate change on water quantity and quality modelling in small Slovenian Mediterranean catchment—Lesson for policy and decision makers. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 3123–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavan, M.; Pintar, M.; Urbanc, J. Spatial variation of crop rotations and their impacts on provisioning ecosystem services on the river Drava alluvial plain. Sustain. Water Qual. Ecol. 2015, 5, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, F.; Ruelland, D. Assessing impacts of alternative land use and agricultural practices on nitrate pollution at the catchment scale. J. Hydrol. 2011, 409, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willaarts, B.A.; Volk, M.; Aguilera, P.A. Assessing the ecosystem services supplied by freshwater flows in Mediterranean agroecosystems. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 105, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.X.; Takeuchi, K.; Ishidaira, H.; Zhang, X.W. Sustainability analysis for Yellow River water resources using the system dynamics approach. Water Resour. Manag. 2002, 16, 239–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Yang, Z.F.; Wang, X. Trends of annual natural runoff in the Yellow River basin. Water Int. 2004, 29, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, C.Y.; Zhang, C.F.; Shi, X.H.; Bourque, C.P.A.; Zhao, S.N. Evaluation of the applicability of the SWAT model in an arid piedmont-plain oasis. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S. Large area hydrologic modelling and assessment Part I: Model development. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, D.K.; Bera, M. Watershed-scale hydrologic and non-point source pollution models: Review of mathematical bases. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2003, 46, 1553–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holvoet, K.; Van Griensven, A.; Seuntjens, P.; Vanrolleghem, P.A. Sensitivity analysis for hydrology and pesticide supply towards the river in SWAT. Phys. Chem. Earth 2005, 30, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassman, P.; Reyes, M.; Green, C.; Arnold, J. The soil and water assessment tool: Historical development, applications and future research direction. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2007, 50, 1211–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, M.; Liersch, S.; Schmidt, G. Towards the implementation of the European Water Framework Directive? Lessons learned from water quality simulations in an agricultural watershed. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Bernard-Jannin, L.; Garneau, C.; Volk, M.; Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Sauvage, S.; Sanchez-Perez, J.M. Improved simulation of river water and groundwater exchange in an alluvial plain using the SWAT model. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmalz, B.; Tavares, F.; Fohrer, N. Assessment of nutrient entry pathways and dominating hydrological processes in lowland catchments. Adv. Geosci. 2007, 11, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, Q.D.; Schmalz, B.; Fohrer, N. Assessing the spatial and temporal variations of water quality in lowland areas, Northern Germany. J. Hydrol. 2012, 438–439, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.F.; Cui, Y.L. Distributed hydrological model for irrigation area based on SWAT: I. Principle and method. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2009, 40, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Li, G.Y.; Han, Z.Z.; Meng, G.X. Hydrological cycle simulation of an irrigation district based on a SWAT model. Math. Comput. Model. 2010, 51, 1312–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neitsch, S.L.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Williams, J.R. Soil and Water Assessment Tool, Theoretical Documentation, Version 2005; Blackland Research Center, Grassland, Soil and Water Research Laboratory, Agricultural Research Service: Temple, TX, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Soil Conservation Service (SCS). SCS National Engineering Handbook, Section 4: Hydrology, Part 18; The United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1972; pp. 1–30.
- Brown, L.C.; Barnwell, T.O., Jr. The Enhanced Water Quality Models QUAL2E and QUAL2E-UNCAS: Documentation and User Manual; EPA/600/3-87/007; United States Environmental Protect Agency: Athens, GA, USA, 1987.
- Qi, Z.J.; Zhang, T.B.; Zhou, L.F.; Feng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Si, B.C. Combined effects of mulch and tillage on soil hydrothermal conditions under drip irrigation in Hetao Irrigation District, China. Water 2016, 8, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Yang, P.L.; Li, Y.K.; Ren, S.M.; Wang, Y.Z.; Lin, Y. Nitrogen balance in the farmland system based on water balance in Hetao irrigation district, Inner Mongolia. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 4549–4559. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.N.; Ryan, M.C.; Sun, B.; Li, C.Y. The influence of irrigation and Wuliangsuhai Lake on groundwater quality in eastern Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2014, 22, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, A.Y.; Hao, F.H.; Zhang, J.X.; Ouyang, W.; Zhang, M.X.; Tian, W.J. Nitrogen and phosphorus losses caused by the summer and fall irrigation runoff in the agricultural irrigation area in Inner Mongolia. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2008, 28, 838–844. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, B.; Li, C.Y.; Claudia, M.D.S.; Jia, K.L.; Zhang, S.; Varennes, A.D.; Pereira, L.S. Variability of water quality in Wulingsuhai lake receiving drainage water from Hetao irrigation system in Yellow River Basin, China. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2013, 22, 1666–1676. [Google Scholar]
- Winchell, M.; Srinivasan, R.; Diluzio, M.; Arnold, J. ArcSWAT Interface for SWAT2009; Blackland Research Center, Grassland, Soil and Water Research Laboratory, Agricultural Research Service: Temple, TX, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- China Meteorological Data Website. Available online: http://data.cma.cn (accessed on 12 August 2014).
- Scientific Data Center of the Cold and Arid Regions Website. Available online: http://westdc.westgis.ac.cn (accessed on 28 September 2012 ).
- Li, W.B.; Zheng, H.C.; Gao, F.S.; Li, S.T.; Liu, J.P.; Liu, R.L. Study on index of fertilizer recommendation for spring wheat in Hetao irrigated area. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci. 2011, 6, 1327–1334. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.B.; Liu, R.L.; Zheng, H.C.; Li, S.T.; Gao, F.S.; Liu, J.P. Study on index of fertilizer recommendation for spring corn in hetao irrigation area of inner Mongolia. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2012, 45, 93–101. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Van Griensven, A.; Meixner, T.; Bishop, T.; Diluzio, A.; Srinivasan, R. A global sensitivity analysis tool for the parameters of multi-variable catchment models. J. Hydrol. 2006, 324, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Johnson, A.; van Genuchten, M.T. Estimating uncertain flow and transport parameters using a sequential uncertainty fitting procedure. Vadose Zone J. 2004, 3, 1340–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhi, C.; Arnold, J.; Williams, J.; Dugas, W.; Srinivasan, R.; Hauck, L. Validation of the SWAT model on a large river basin with point and nonpoint sources. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2001, 37, 1169–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.; Arnold, J.; Van Liew, M.; Bingner, R.; Harmel, R.; Veith, T. Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar]
- Malone, R.W.; Yagow, G.; Baffaut, C.; Gitau, M.W.; Qi, Z.; Amatya, D.M.; Parajuli, P.B.; Bonta, J.V.; Green, T.R. Parameterization guidelines and considerations for hydrologic models. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 1681–1703. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, M.K. Evaluating hydrologic response of an agricultural watershed for watershed analysis. Water 2011, 3, 604–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models, Part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.H.; Cui, Y.L. Development and test of SWAT for modeling hydrological processed in irrigation districts with paddy rice. J. Hydrol. 2011, 396, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhi, C.; Srinivasan, R.; Arnold, J.; Williams, J. A modeling approach to evaluate the impacts of water quality management plans implemented in a watershed in Texas. Environ. Model. Softw. 2006, 21, 1141–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Huang, G.H.; Qu, Z.Y.; Pereira, L.S. Assessing the groundwater dynamics and impacts of water saving in the Hetao Irrigation District, Yellow River basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 98, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.H.; Li, G.Y.; Meng, G.X.; Xing, L.M. Evaluation of non-point source pollution load in Fenhe Irrigation District based on SWAT model. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2013, 44, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Kӓmӓri, M.; Alho, P.; Veijalainen, N.; Aaltonen, J.; Huokuna, M.; Lotsari, E. River ice cover influence on sediment transportation at present and under projected hydroclimatic conditions. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 4738–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).