Performance Evaluations of Three Silt Fence Practices Using a Full-Scale Testing Apparatus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Literature Review
1.1.1. Design Criteria for Silt Fence
1.1.2. Relevant Research Studies
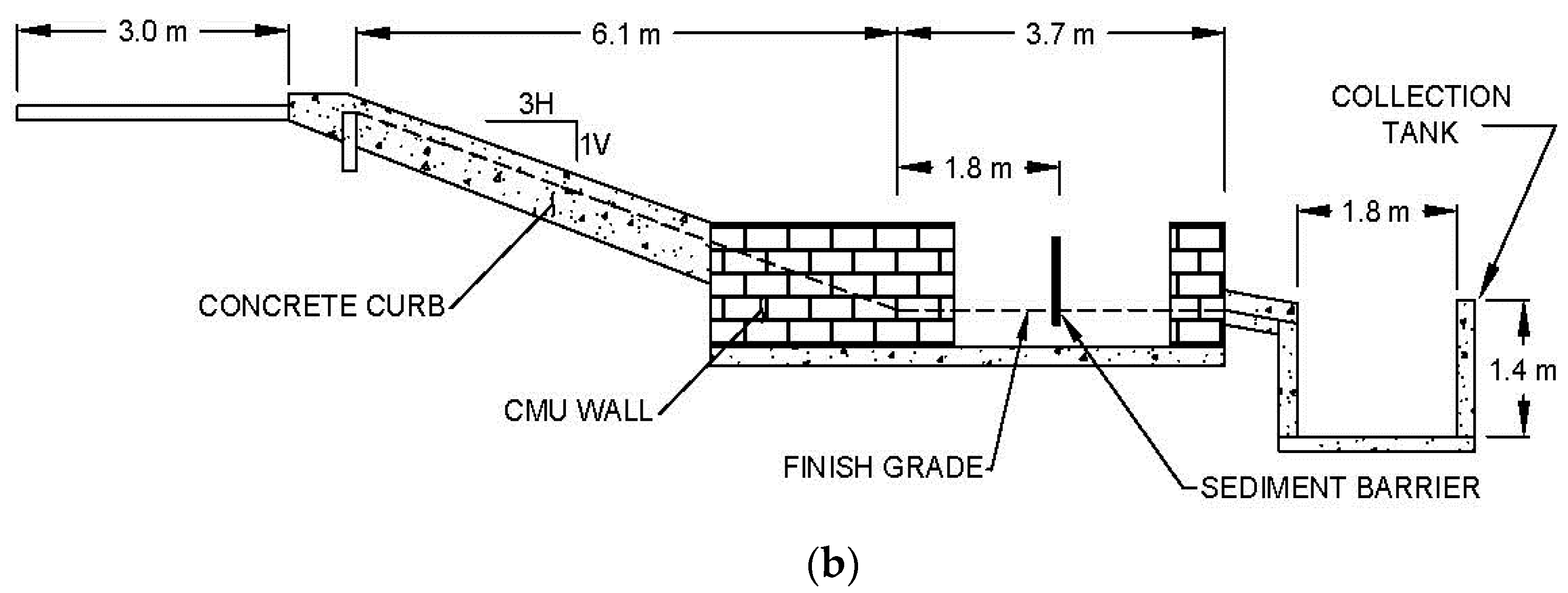
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Calculation of Test Flow Rate and Sediment Quantity
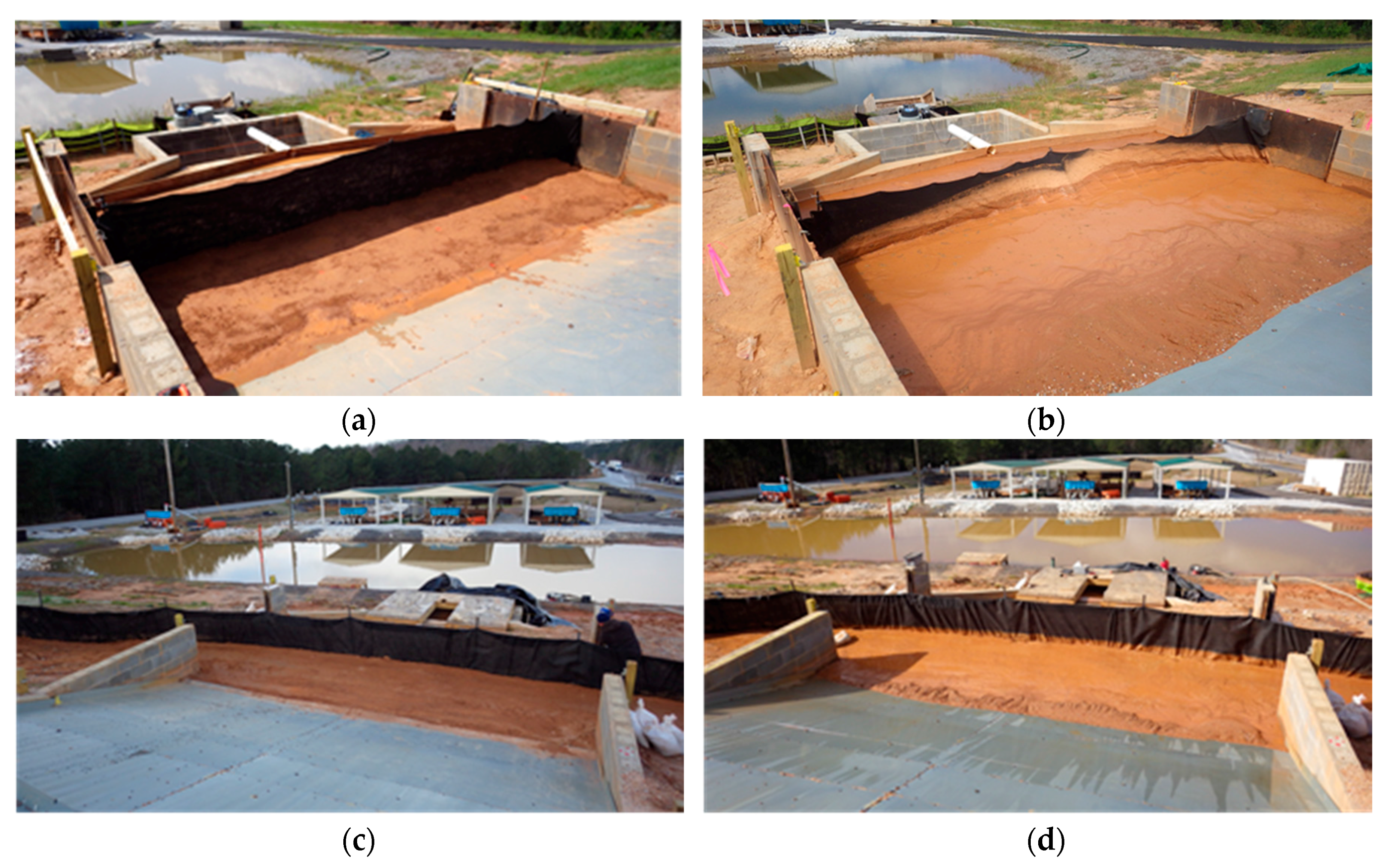
2.2. Testing Regime
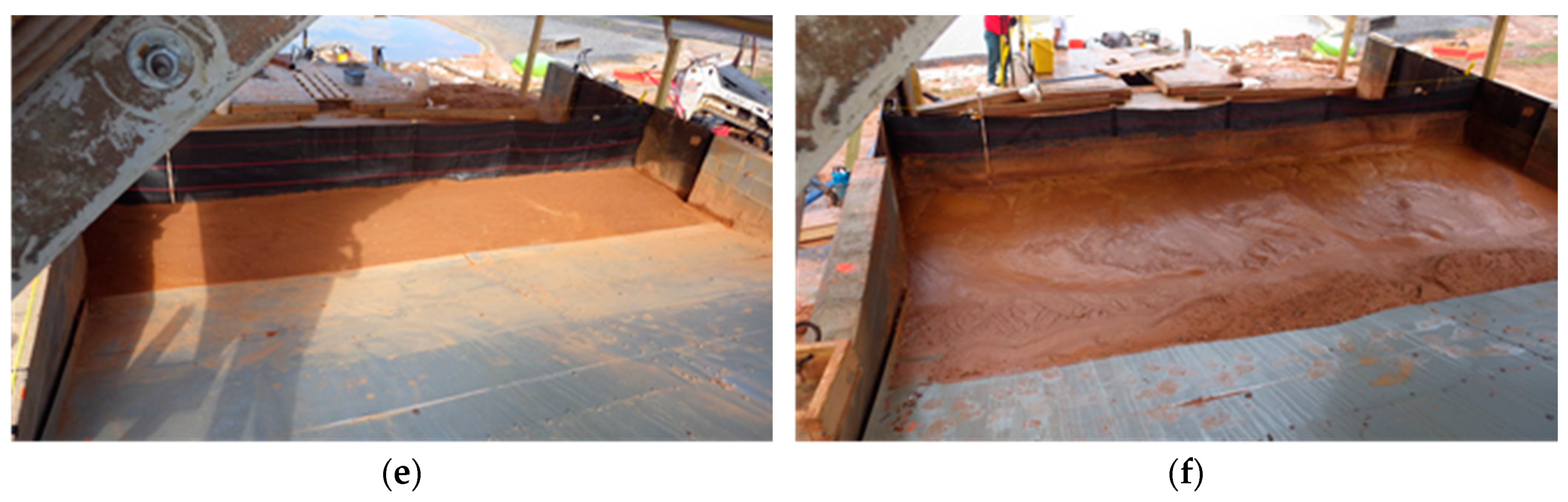
Evaluated Silt Fences
- configuration: ALDOT Standard Drawing ESC 200 (Sheet 4 of 5) [18];
- silt fence fabric: nonwoven, 135 gm/m2 (4 oz/yd2) geotextile fabric;
- reinforcement: 1.41 mm (17 ga.) steel woven wire reinforcement; and
- posts: 1.53 m (5 ft) long, steel t-post, 1.4 kg/m (0.95 lbs/ft), spaced at 3.05 m (10 ft) on-center.
- configuration: Alabama Handbook for Erosion and Sediment Control on Construction Sites, Volume 1 [8];
- silt fence fabric: woven, 194 gr/m2 (5.72 oz/yd2), polypropylene geotextile fabric;
- reinforcement: gridded polypropylene reinforcement, 25.4 mm × 15.9 mm (1.0 in. × 0.6 in.) grid; and
- posts: 5.1 cm × 5.1 cm (2 in. × 2 in.) hardwood stakes, spaced 1.2 m (4 ft) on-center.
3. Results and Discussion
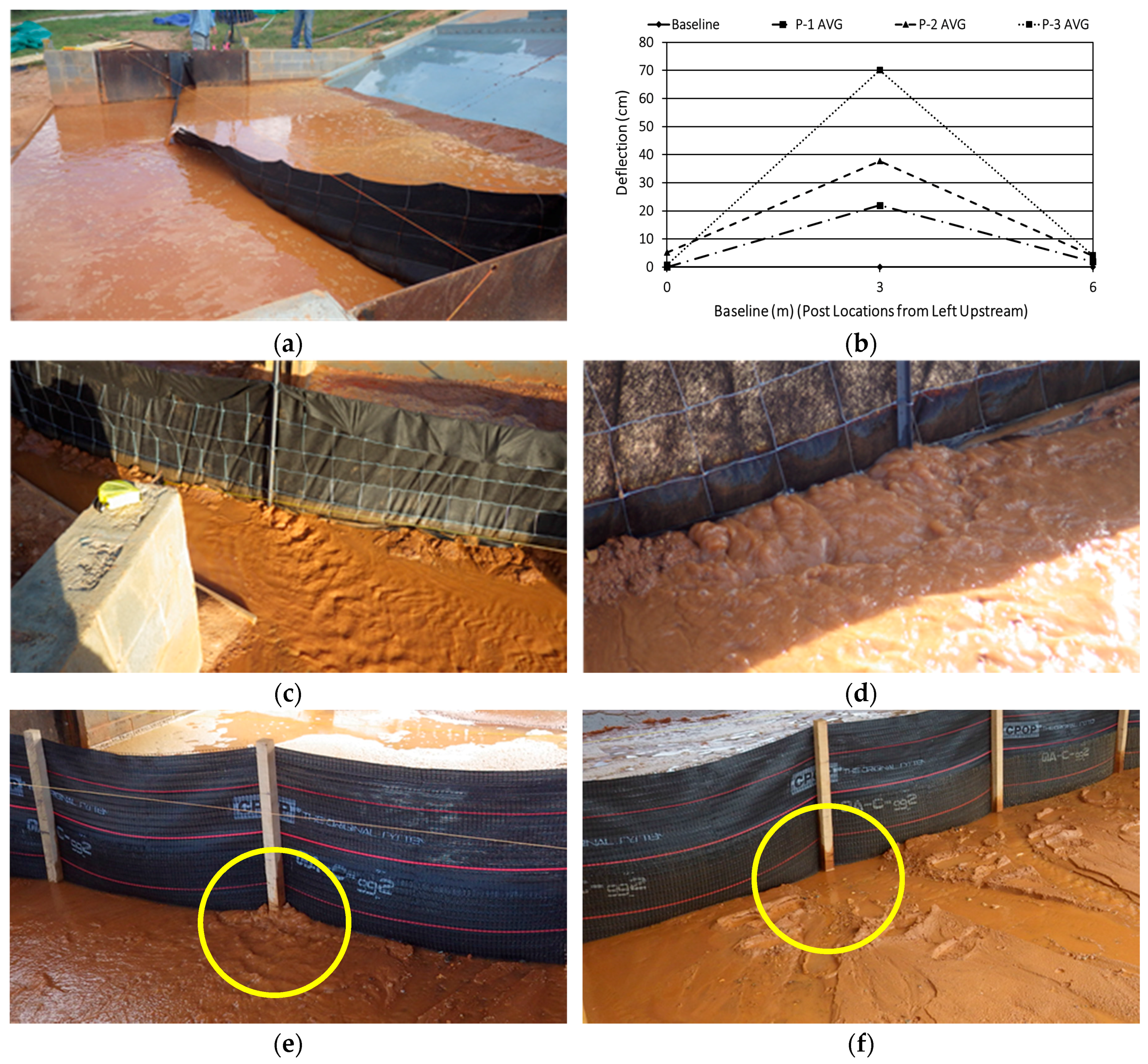
3.1. Structural Performance
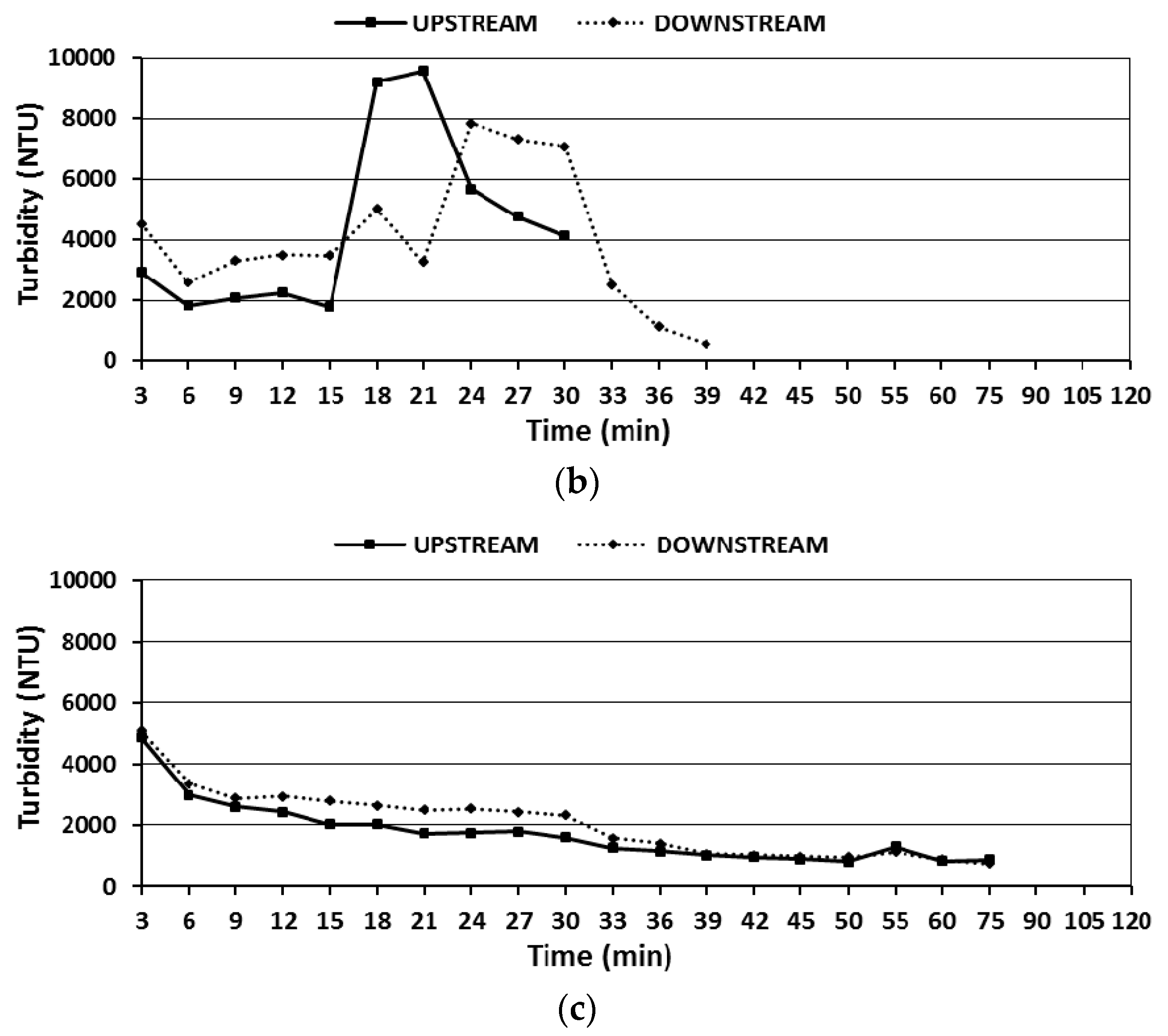
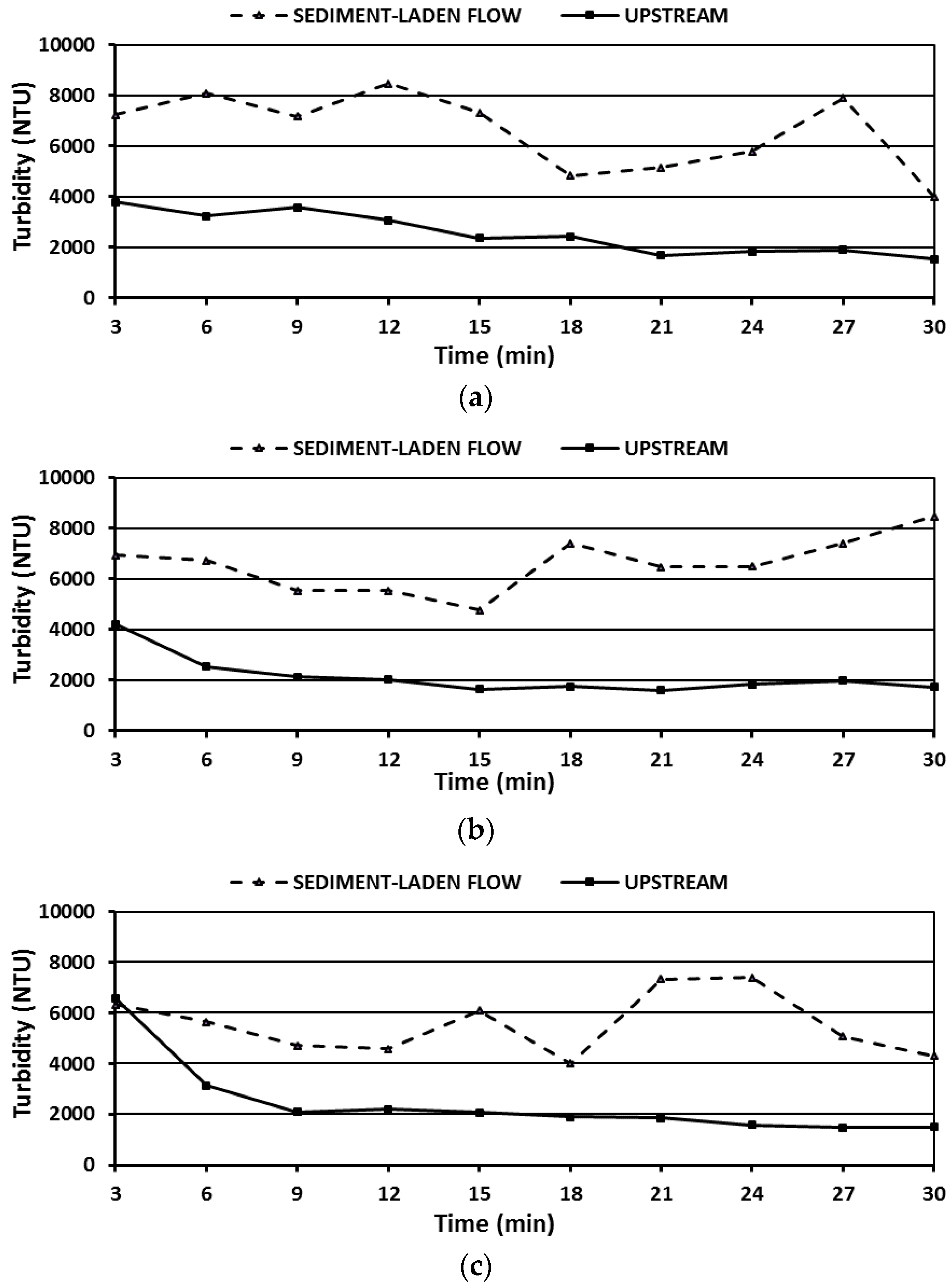
3.2. Sediment Retention
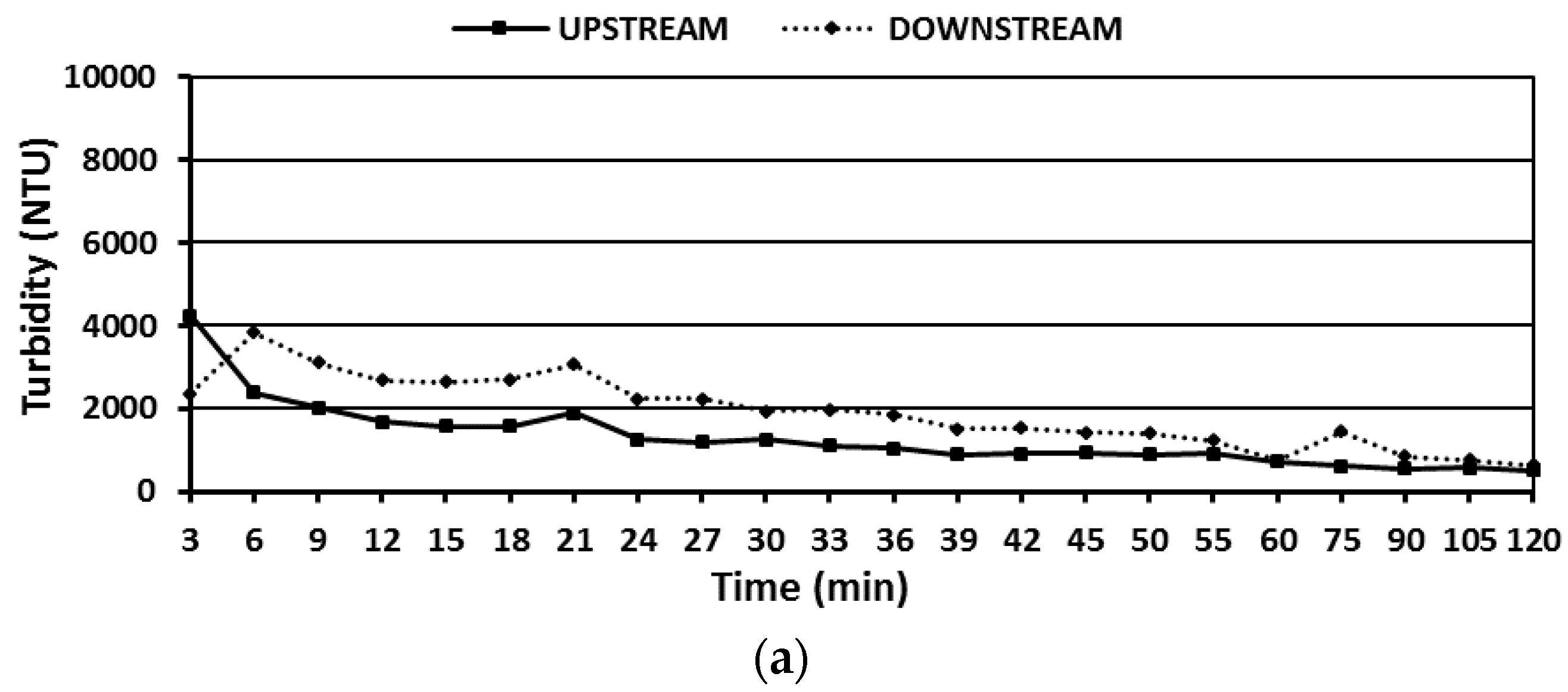
3.3. Water Quality
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). Soil Quality—Urban Technical Note No.1, Erosion and Sedimentation on Construction Sites; Natural Resources Conservation Service: Auburn, AL, USA, 2006.
- U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). Urban Soil Erosion and Sediment Control; Natural Resources Conservation Service: Champaign, IL, USA, 2008.
- U.S. Congress. Clean Water Act. In Federal Water Pollution Control Act, 33 U.S.C. §1251 et seq.; U.S. Congress: Washington, DC, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Congress. Water Quality Act of 1987. In Public Law 100-4; U.S. Congress: Washington, DC, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, M.; Malina, J.F., Jr.; Charbeneau, R. An evaluation of the performance of geotextiles for temporary sediment control. Water Environ. Res. 1998, 70, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.; Sattar, A.; Gharabaghi, B.; Warner, R. Event-Based Total Suspended Sediment Particle Size Distribution Model. J. Hydrol. 2016, 536, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugg, R.A.; Zech, W.C.; Donald, W.N.; Perez, M.A. Improvements in Standardized Testing for Evaluating Sediment Barrier Performance: Design of a Full-Scale Testing Apparatus. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2017, 143, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabama Soil and Water Conservation Committee (AL-SWCC). Alabama Handbook for Erosion Control, Sediment Control and Stormwater Management on Construction Sites and Urban Areas; Alabama Soil and Water Conservation Committee: Montgomery, AL, USA, 2014; Volume 1.
- ASTM International. Standard Test Method for Determination of Sediment Retention Device Effectiveness in Sheet Flow Applications; ASTM D7351-13; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. Standard Test Method for Determining Filtering Efficiency and Flow Rate of the Filtration Component for a Sediment Retention Device; ASTM D5141-11; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sprague, C.; Sprague, J. BMP Testing for Erosion and Sediment Control; Unpublished Report; Georgia Soil and Water Conservation Commission: Athens, GA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Risse, L.M.; Thompson, S.A.; Governo, J.; Harris, K. Testing of new silt fence materials: A case study of a belted strand retention fence. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2008, 63, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troxel, C.F. Life Cycle Analysis of Sediment Control Devices. Master’s Thesis, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Donald, W.; Zech, W.; Perez, M.; Fang, X. Evaluation and modification of wire-backed nonwoven geotextile silt fence for use as a ditch check. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2016, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabama Department of Environmental Management (ADEM). National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Permit, General Permit; Alabama Department of Environmental Management: Montgomery, AL, USA, 2016.
- Perez, M.A.; Zech, W.C.; Donald, W.N.; Fang, X. Methodology for evaluating inlet protection practices using large-scale testing techniques. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2015, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.R.; Berndt, H.D. Sediment Yield Prediction Based on Watershed Hydrology. Trans. ASAE 1977, 20, 1100–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabama Department of Transportation (ALDOT). Standard Drawing ESC-200 (Sheet 4 of 5); Alabama Department of Transportation: Montgomery, AL, USA, 2016.



| Description | Installation | Test | Failure Time (min:sec) | Failure Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALDOT Trenched Silt Fence 1 | I-1 | P-1, 2 | -- | No structural failure |
| P-3 | 15:15 | Center post deflected; overtopped | ||
| I-2 | P-1, 2 | -- | No structural failure | |
| P-3 | 14:30 | Center post deflected; overtopped | ||
| I-3 | P-1 | -- | No structural failure | |
| P-2 | 15:30 | End post guy-wire failed; center post deflected; overtopped | ||
| ALDOT Sliced Silt Fence 2 | I-1 | P-1 | 8:15 | Undermined at 5+ locations |
| I-2 | P-1 | 9:00 | Undermined at 7+ locations | |
| I-3 | P-1 | 12:00 | Undermined at 4+ locations | |
| AL-SWCC Trenched Silt Fence | I-1 | P-1, 2, 3 | -- | No structural failure |
| I-2 | P-1 | 28:00 | Undermined at Post #5, “sealed itself” during P-2 and P-3 | |
| P-2, 3 | -- | No structural failure | ||
| I-3 | P-1, 2, 3 | -- | No structural failure |
| Silt Fence Practice | Description | Installation | % Sediment Retained by Installation | Avg. % Retained |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ALDOT Trenched Silt Fence | I-1 | 86.6% | 82.7% |
| I-2 | 86.7% | |||
| I-3 | 74.8% | |||
| 2 | ALDOT Sliced Silt Fence | I-1 | 59.5% | 66.9% |
| I-2 | 68.2% | |||
| I-3 | 73.1% | |||
| 3 | AL-SWCC Trenched Silt Fence | I-1 | 90.5% | 90.5% |
| I-2 | 91.0% | |||
| I-3 | 90.0% |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bugg, R.A.; Donald, W.; Zech, W.; Perez, M. Performance Evaluations of Three Silt Fence Practices Using a Full-Scale Testing Apparatus. Water 2017, 9, 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9070502
Bugg RA, Donald W, Zech W, Perez M. Performance Evaluations of Three Silt Fence Practices Using a Full-Scale Testing Apparatus. Water. 2017; 9(7):502. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9070502
Chicago/Turabian StyleBugg, R. Alan, Wesley Donald, Wesley Zech, and Michael Perez. 2017. "Performance Evaluations of Three Silt Fence Practices Using a Full-Scale Testing Apparatus" Water 9, no. 7: 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9070502
APA StyleBugg, R. A., Donald, W., Zech, W., & Perez, M. (2017). Performance Evaluations of Three Silt Fence Practices Using a Full-Scale Testing Apparatus. Water, 9(7), 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9070502






